tomogram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
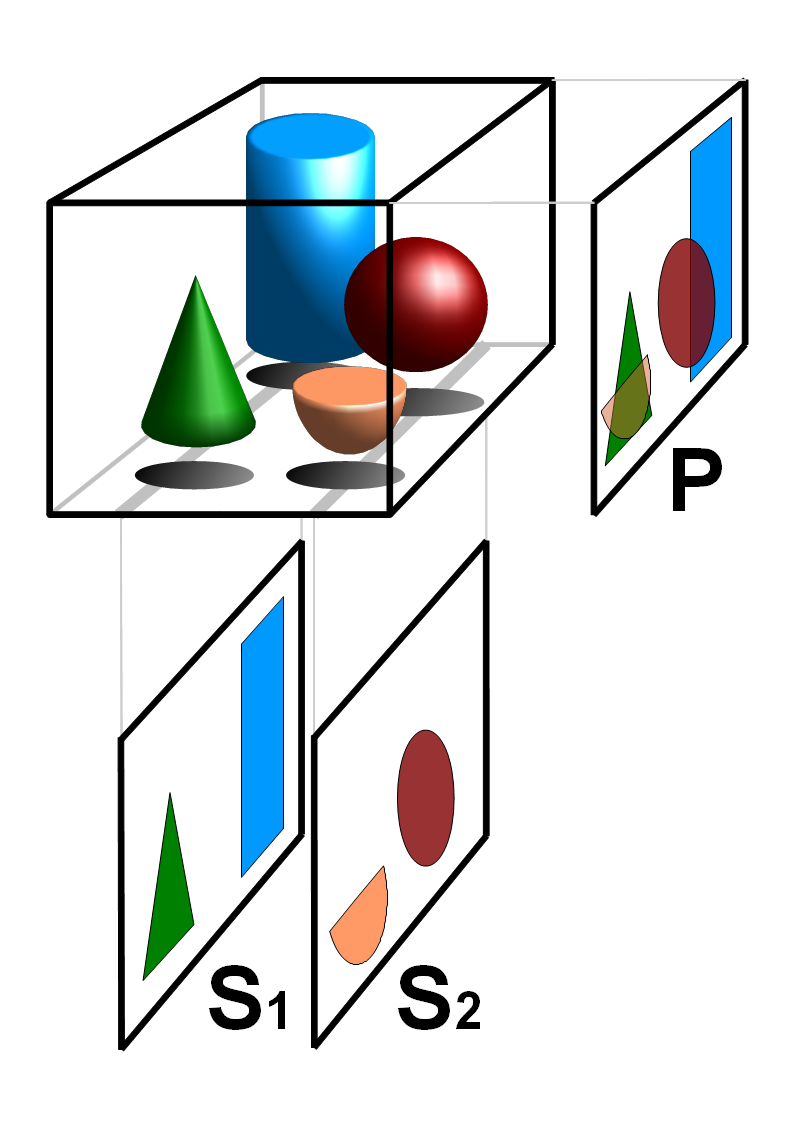 Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology,
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology,
 Volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D
Volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D
Image reconstruction algorithms for microtomography
{{Authority control Medical imaging
 Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology,
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science
Atmospheric science is the study of the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climat ...
, geophysics, oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
, plasma physics, materials science, cosmochemistry, astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the h ...
, quantum information, and other areas of science. The word ''tomography'' is derived from Ancient Greek τόμος ''tomos'', "slice, section" and γράφω ''graphō'', "to write" or, in this context as well, "to describe." A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram.
In many cases, the production of these images is based on the mathematical procedure tomographic reconstruction
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann ...
, such as X-ray computed tomography technically being produced from multiple projectional radiographs. Many different reconstruction algorithm
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann ...
s exist. Most algorithms fall into one of two categories: filtered back projection
In mathematics, the Radon transform is the integral transform which takes a function ''f'' defined on the plane to a function ''Rf'' defined on the (two-dimensional) space of lines in the plane, whose value at a particular line is equal to the ...
(FBP) and iterative reconstruction (IR). These procedures give inexact results: they represent a compromise between accuracy and computation time required. FBP demands fewer computational resources, while IR generally produces fewer artifacts (errors in the reconstruction) at a higher computing cost.
Although MRI (magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
), optical coherence tomography and ultrasound are transmission methods, they typically do not require movement of the transmitter to acquire data from different directions. In MRI, both projections and higher spatial harmonics are sampled by applying spatially varying magnetic fields; no moving parts are necessary to generate an image. On the other hand, since ultrasound and optical coherence tomography uses time-of-flight to spatially encode the received signal, it is not strictly a tomographic method and does not require multiple image acquisitions.
Types of tomography
Some recent advances rely on using simultaneously integrated physical phenomena, e.g. X-rays for both CT and angiography, combined CT/ MRI and combined CT/ PET. Discrete tomography andGeometric tomography Geometric tomography is a mathematical field that focuses on problems of reconstructing homogeneous (often convex) objects from tomographic data (this might be X-rays, projections, sections, brightness functions, or covariograms). More precisely, ac ...
, on the other hand, are research areas that deal with the reconstruction of objects that are discrete (such as crystals) or homogeneous. They are concerned with reconstruction methods, and as such they are not restricted to any of the particular (experimental) tomography methods listed above.
Synchrotron X-ray tomographic microscopy
A new technique called synchrotron X-ray tomographic microscopy ( SRXTM) allows for detailed three-dimensional scanning of fossils. The construction of third-generation synchrotron sources combined with the tremendous improvement of detector technology, data storage and processing capabilities since the 1990s has led to a boost of high-end synchrotron tomography in materials research with a wide range of different applications, e.g. the visualization and quantitative analysis of differently absorbing phases, microporosities, cracks, precipitates or grains in a specimen. Synchrotron radiation is created by accelerating free particles in high vacuum. By the laws of electrodynamics this acceleration leads to the emission of electromagnetic radiation (Jackson, 1975). Linear particle acceleration is one possibility, but apart from the very high electric fields one would need it is more practical to hold the charged particles on a closed trajectory in order to obtain a source of continuous radiation. Magnetic fields are used to force the particles onto the desired orbit and prevent them from flying in a straight line. The radial acceleration associated with the change of direction then generates radiation.Volume rendering
 Volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D
Volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D scalar field
In mathematics and physics, a scalar field is a function (mathematics), function associating a single number to every point (geometry), point in a space (mathematics), space – possibly physical space. The scalar may either be a pure Scalar ( ...
. A typical 3D data set is a group of 2D slice images acquired, for example, by a CT, MRI, or MicroCT
X-ray microtomography, like tomography and X-ray computed tomography, uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model ( 3D model) without destroying the original object. The prefix ''micro- ...
scanner. These are usually acquired in a regular pattern (e.g., one slice every millimeter) and usually have a regular number of image pixels in a regular pattern.
This is an example of a regular volumetric grid, with each volume element, or voxel represented by a single value that is obtained by sampling the immediate area surrounding the voxel.
To render a 2D projection of the 3D data set, one first needs to define a camera in space relative to the volume. Also, one needs to define the opacity
Opacity or opaque may refer to:
* Impediments to (especially, visible) light:
** Opacities, absorption coefficients
** Opacity (optics), property or degree of blocking the transmission of light
* Metaphors derived from literal optics:
** In lingu ...
and color of every voxel.
This is usually defined using an RGBA (for red, green, blue, alpha) transfer function that defines the RGBA value for every possible voxel value.
For example, a volume may be viewed by extracting isosurfaces (surfaces of equal values) from the volume and rendering them as polygonal meshes or by rendering the volume directly as a block of data. The marching cubes algorithm is a common technique for extracting an isosurface from volume data. Direct volume rendering is a computationally intensive task that may be performed in several ways.
History
Focal plane tomography
In radiography, focal plane tomography is tomography (imaging a single plane, or slice, of an object) by simultaneously moving the X-ray generator and X-ray detector so as to keep a consistent exposure of only the plane of interest during image ac ...
was developed in the 1930s by the radiologist Alessandro Vallebona, and proved useful in reducing the problem of superimposition of structures in projectional radiography.
In a 1953 article in the medical journal ''Chest'', B. Pollak of the Fort William Sanatorium Fort William Sanatorium was a tuberculosis hospital or sanatorium in Fort William, Ontario, today part of the city of Thunder Bay. It opened in 1935 as a tuberculosis treatment centre for settlers, adding 20 government-funded beds for Indigenous pat ...
described the use of planography, another term for tomography.
Focal plane tomography remained the conventional form of tomography until being largely replaced by mainly computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
in the late 1970s. Focal plane tomography uses the fact that the focal plane appears sharper, while structures in other planes appear blurred. By moving an X-ray source and the film in opposite directions during the exposure, and modifying the direction and extent of the movement, operators can select different focal planes which contain the structures of interest.
See also
* Chemical imaging *3D reconstruction
In computer vision and computer graphics, 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance of real objects.
This process can be accomplished either by active or passive methods. If the model is allowed to change its shape i ...
* Discrete tomography
* Geometric tomography Geometric tomography is a mathematical field that focuses on problems of reconstructing homogeneous (often convex) objects from tomographic data (this might be X-rays, projections, sections, brightness functions, or covariograms). More precisely, ac ...
* Geophysical imaging
Geophysical imaging (also known as geophysical tomography) is a minimally destructive geophysical technique that investigates the subsurface of a terrestrial planet. Geophysical imaging is a noninvasive imaging technique with a high parametrical a ...
* Industrial computed tomography
* Johann Radon
* Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
* Network tomography
* Nonogram – a type of puzzle based on a discrete model of tomography
* Radon transform
In mathematics, the Radon transform is the integral transform which takes a function ''f'' defined on the plane to a function ''Rf'' defined on the (two-dimensional) space of lines in the plane, whose value at a particular line is equal to the l ...
* Tomographic reconstruction
Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann ...
* Multiscale tomography
* Voxel
References
External links
*Image reconstruction algorithms for microtomography
{{Authority control Medical imaging