Tinea Versicolour on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tinea versicolor (also pityriasis versicolor) is a condition characterized by a skin eruption on the trunk and proximal extremities. The majority of tinea versicolor is caused by the fungus ''
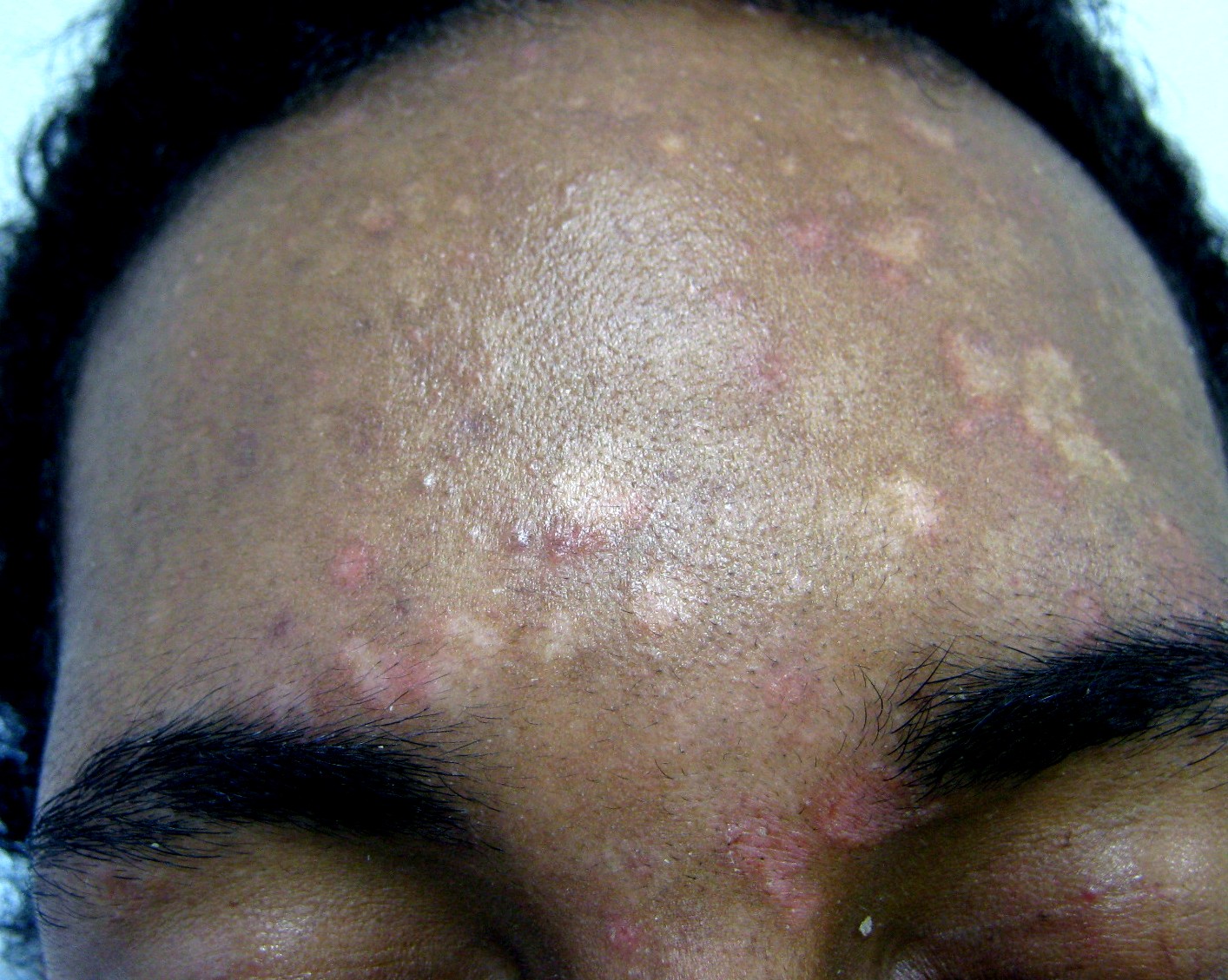
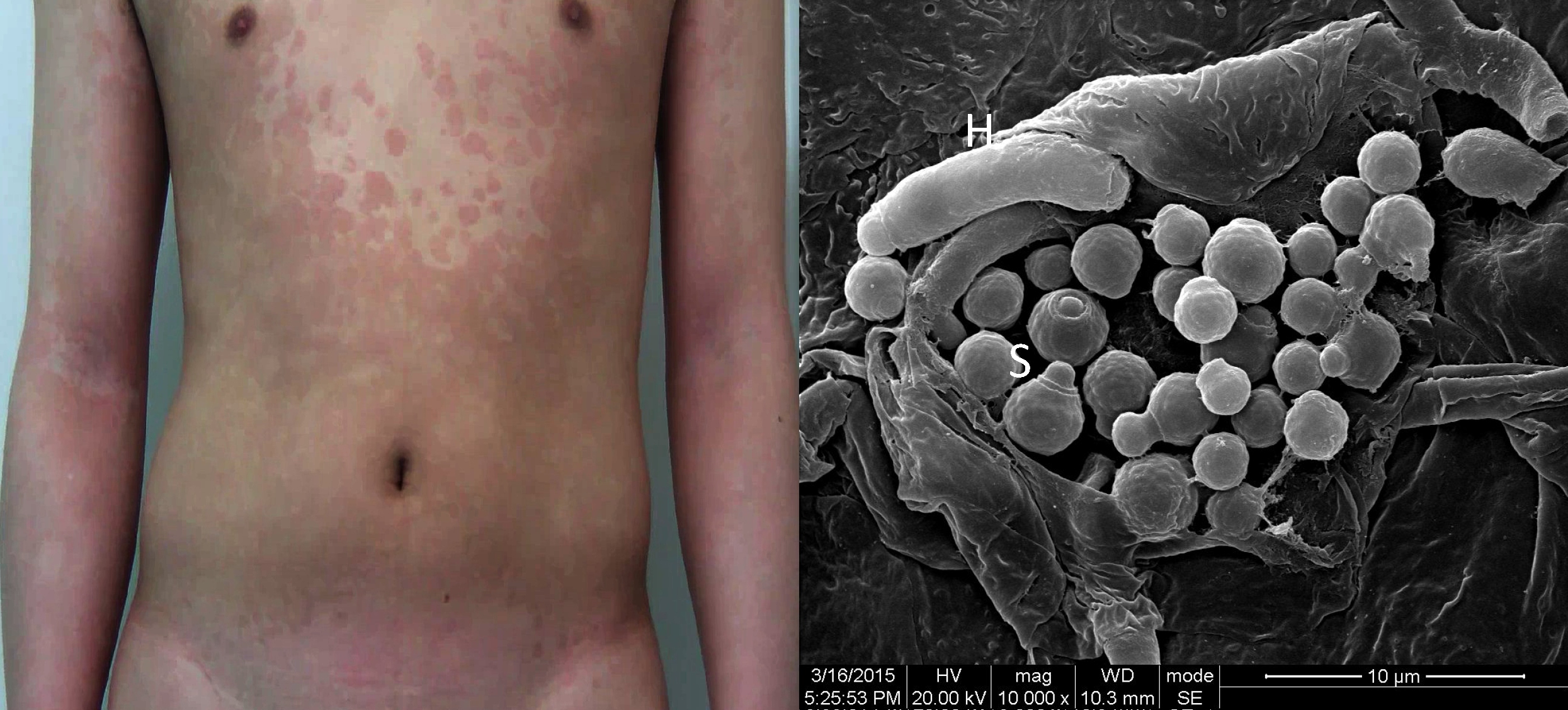 The symptoms of this condition include:
* Occasional fine scaling of the skin producing a very superficial ash-like scale
* Pale, dark tan, or pink in color, with a reddish undertone that can darken when the patient is overheated, such as in a hot shower or during/after exercise. Tanning typically makes the affected areas contrast more starkly with the surrounding skin.
* Sharp borderPityriasis versicolor , DermNet New Zealand
The symptoms of this condition include:
* Occasional fine scaling of the skin producing a very superficial ash-like scale
* Pale, dark tan, or pink in color, with a reddish undertone that can darken when the patient is overheated, such as in a hot shower or during/after exercise. Tanning typically makes the affected areas contrast more starkly with the surrounding skin.
* Sharp borderPityriasis versicolor , DermNet New Zealand
Dermnetnz.org. Retrieved on 2016-10-14. Pityriasis versicolor is more common in hot, humid climates or in those who sweat heavily, so it may recur each summer. The yeasts can often be seen under the microscope within the lesions and typically have a so-called "spaghetti and meatball appearance" as the round yeasts produce filaments. In people with dark skin tones, pigmentary changes such as hypopigmentation (loss of color) are common, while in those with lighter skin color, hyperpigmentation (increase in skin color) is more common. These discolorations have led to the term "sun fungus".
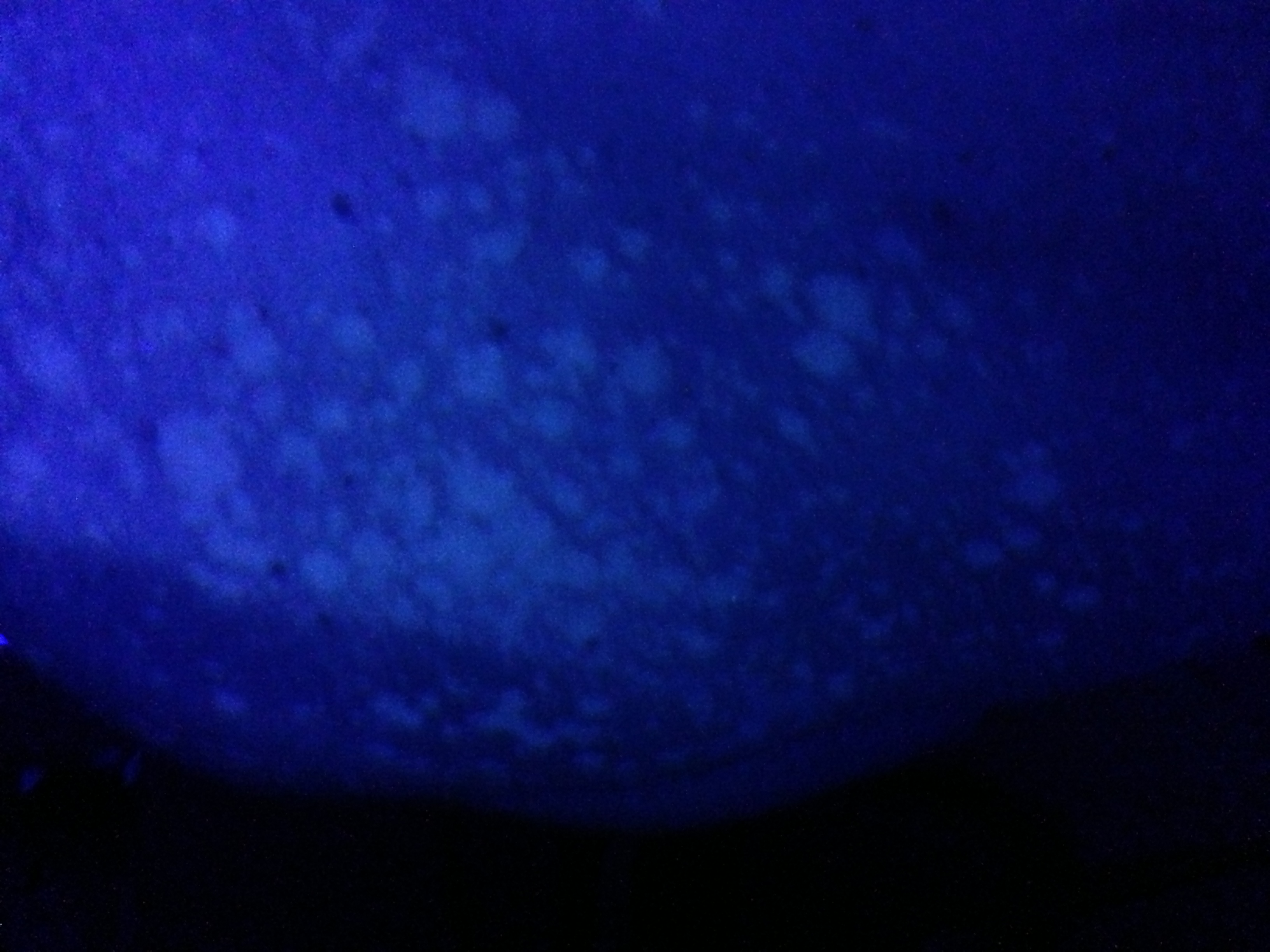 Tinea versicolor may be diagnosed by a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation and lesions may fluoresce copper-orange when exposed to
Tinea versicolor may be diagnosed by a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation and lesions may fluoresce copper-orange when exposed to
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
The single-dose regimens an
pulse therapy
regimens can be made more effective by having the patient exercise 1–2 hours after the dose, to induce sweating. The sweat is allowed to evaporate, and showering is delayed for a day, leaving a film of the medication on the skin.
Fpnotebook.com. Retrieved on 2016-10-14.
Malassezia globosa
''Malassezia globosa'' is a species of yeast-like fungus.
Cause of dandruff and dermatitis
In 2007, it was discovered that the responsible agent is a scalp specific fungus, ''Malassezia globosa'' (previously thought to be '' Malassezia furfur'' ...
'', although ''Malassezia furfur
''Malassezia furfur'' (formerly known as ''Pityrosporum ovale'' in its hyphal form) is a species of yeast (a type of fungus) that is naturally found on the skin surfaces of humans and some other mammals. It is associated with a variety of dermato ...
'' is responsible for a small number of cases. These yeasts are normally found on the human skin and become troublesome only under certain circumstances, such as a warm and humid environment, although the exact conditions that cause initiation of the disease process are poorly understood.
The condition pityriasis versicolor was first identified in 1846. Versicolor comes from the Latin ' 'to turn' + ''color''. It is also commonly referred to as Peter Elam's disease in many parts of South Asia.
Signs and symptoms

 The symptoms of this condition include:
* Occasional fine scaling of the skin producing a very superficial ash-like scale
* Pale, dark tan, or pink in color, with a reddish undertone that can darken when the patient is overheated, such as in a hot shower or during/after exercise. Tanning typically makes the affected areas contrast more starkly with the surrounding skin.
* Sharp borderPityriasis versicolor , DermNet New Zealand
The symptoms of this condition include:
* Occasional fine scaling of the skin producing a very superficial ash-like scale
* Pale, dark tan, or pink in color, with a reddish undertone that can darken when the patient is overheated, such as in a hot shower or during/after exercise. Tanning typically makes the affected areas contrast more starkly with the surrounding skin.
* Sharp borderPityriasis versicolor , DermNet New ZealandDermnetnz.org. Retrieved on 2016-10-14. Pityriasis versicolor is more common in hot, humid climates or in those who sweat heavily, so it may recur each summer. The yeasts can often be seen under the microscope within the lesions and typically have a so-called "spaghetti and meatball appearance" as the round yeasts produce filaments. In people with dark skin tones, pigmentary changes such as hypopigmentation (loss of color) are common, while in those with lighter skin color, hyperpigmentation (increase in skin color) is more common. These discolorations have led to the term "sun fungus".
Pathophysiology
In cases of tinea versicolor caused by the fungus ''Malassezia furfur
''Malassezia furfur'' (formerly known as ''Pityrosporum ovale'' in its hyphal form) is a species of yeast (a type of fungus) that is naturally found on the skin surfaces of humans and some other mammals. It is associated with a variety of dermato ...
'', lightening of the skin occurs due to the fungus's production of azelaic acid, which has a slight bleaching effect.
Diagnosis
Wood's lamp
A blacklight, also called a UV-A light, Wood's lamp, or ultraviolet light, is a lamp that emits long-wave ( UV-A) ultraviolet light and very little visible light. One type of lamp has a violet filter material, either on the bulb or in a se ...
.
The differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
for tinea versicolor infection includes:
*Progressive macular hypomelanosis
Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a common skin condition, a disorder, observed more frequently in young women with darkly pigmented skin who originate from or reside in tropical climates.
An interesting property of the skin condition is that i ...
* Pityriasis alba
* Pityriasis rosea
* Seborrheic dermatitis
* Erythrasma
* Vitiligo
* Leprosy
*Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
*Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation
Treatment
Treatments for tinea versicolor include: * Topical antifungal medications containing selenium sulfide are often recommended.Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral among others, is an antiandrogen and antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous candid ...
( Nizoral ointment and shampoo) is another treatment. It is normally applied to dry skin and washed off after 10 minutes, repeated daily for two weeks. Ciclopirox
Ciclopirox (sometimes known by the abbreviation CPX) is a synthetic antifungal agent for topical dermatologic treatment of superficial mycoses. It is most useful against tinea versicolor. It is sold under many brand names worldwide.Drugs.coInt ...
(ciclopirox olamine) is an alternative treatment to ketoconazole, as it suppresses growth of the yeast ''Malassezia furfur''. Initial results show similar efficacy to ketoconazole with a relative increase in subjective symptom relief due to its inherent anti-inflammatory properties. Other topical antifungal agents such as clotrimazole, miconazole, terbinafine, or zinc pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione (or pyrithione zinc) is a coordination complex of zinc. It has fungistatic (inhibiting the division of fungal cells) and bacteriostatic (inhibiting bacterial cell division) properties and is used in the treatment of seborrhoeic de ...
can lessen symptoms in some patients. Additionally, hydrogen peroxide has been known to lessen symptoms and, on certain occasions, remove the problem, although permanent scarring has occurred with this treatment in some people. Clotrimazole is also used combined with selenium sulfide.
* Oral medications are viewed as a second-line of treatment for pityriasis versicolor in the event of widespread, severe, recalcitrant or recurrent cases. Systemic therapies include itraconazole (200 mg daily for seven days) and fluconazole (150 to 300 mg weekly dose for 2 to 4 weeks) that are preferred to oral ketoconazole which is no longer approved due to its potential hepatotoxic sides effects.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
The single-dose regimens an
pulse therapy
regimens can be made more effective by having the patient exercise 1–2 hours after the dose, to induce sweating. The sweat is allowed to evaporate, and showering is delayed for a day, leaving a film of the medication on the skin.
Fpnotebook.com. Retrieved on 2016-10-14.
Epidemiology
This skin disease commonly affects adolescents and young adults, especially in warm and humid climates. The yeast is thought to feed on skin oils ( lipids), as well as dead skin cells. Infections are more common in people who have seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff, and hyperhidrosis.References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Tinea Versicolor Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions Animal fungal diseases Papulosquamous disorders