Tigranes II of Armenia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of
11.14.15
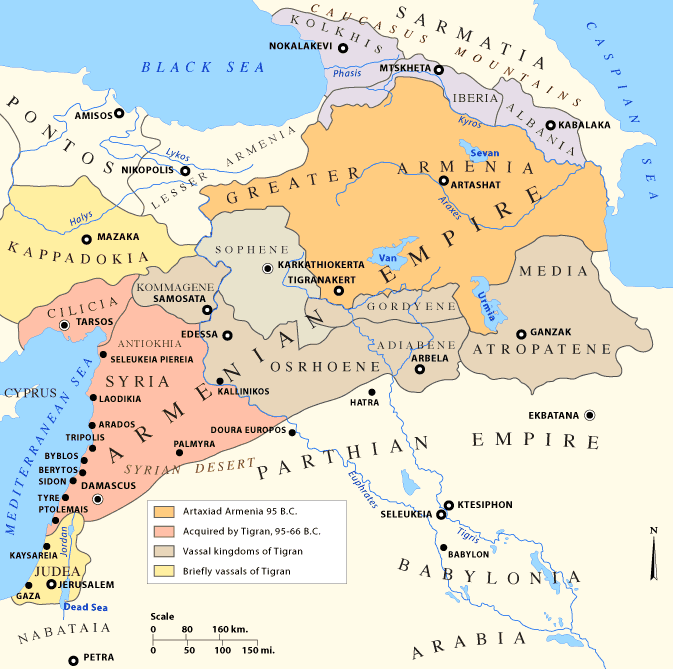
 After the death of
After the death of
 Over the course of his conquests, Tigranes founded four cities that bore his name, including the capital of Tigranocerta (Tigranakert).
Over the course of his conquests, Tigranes founded four cities that bore his name, including the capital of Tigranocerta (Tigranakert).
 Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
under whom the country became, for a short time, the strongest state to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
's east. He was a member of the Artaxiad Royal House. Under his reign, the Armenian kingdom expanded beyond its traditional boundaries, allowing Tigranes to claim the title Great King
Great king, and the equivalent in many languages, refers to historical titles of certain monarchs, suggesting an elevated status among the host of kings and princes. This title is most usually associated with the ''shahanshah'' (shah of shahs, ...
, and involving Armenia in many battles against opponents such as the Parthian Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
and Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
empires, and the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
.
Early years
In approximately 120 BC, theParthian Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
king Mithridates II () invaded Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
and made its king Artavasdes I acknowledge Parthian suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
. Artavasdes I was forced to give the Parthians Tigranes, who was either his son or nephew, as a hostage. Tigranes lived in the Parthian court at Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
, where he was schooled in Parthian culture. Tigranes remained a hostage at the Parthian court until , when Mithridates II released him and appointed him as the king of Armenia. Tigranes ceded an area called "seventy valleys" in the Caspiane to Mithridates II, either as a pledge or because Mithridates II demanded it. Tigranes' daughter Ariazate Ariazate (also spelled Aryzate or Aryazate, meaning "Child of an Iranian peoples, Iranian"), also known as Automa, was a Parthian queen consort as the wife of the Parthian Empire, Parthian monarch Gotarzes I ().
She was an Artaxiad dynasty, Artaxi ...
had also married a son of Mithridates II, which has been suggested by the modern historian Edward Dąbrowa to have taken place shortly before he ascended the Armenian throne as a guarantee of his loyalty. Tigranes would remain a Parthian vassal until the end of the 80's BC.
When he came to power, the foundation upon which Tigranes was to build his Empire was already in place, a legacy of the founder of the Artaxiad Dynasty, Artaxias I
Artaxias I (from gr, Άρταξίας; in hy, Արտաշէս, translit=Artašēs) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling d ...
, and subsequent kings. The mountains of Armenia, however, formed natural borders between the different regions of the country and as a result, the feudalistic ''nakharar
''Nakharar'' ( hy, նախարար ''naxarar'', from Parthian ''naxvadār'' "holder of the primacy""նախարար" in H. Ačaṙean (1926–35), ''Hayerēn Armatakan Baṙaran'' (Yerevan: Yerevan State University), 2nd ed., 1971–79) was a heredi ...
s'' had significant influence over the regions or provinces in which they were based. This did not suit Tigranes, who wanted to create a centralist empire. He thus proceeded by consolidating his power within Armenia before embarking on his campaign.
He deposed Artanes, the last king of the Kingdom of Sophene
The Kingdom of Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopʻkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnḗ), was a Hellenistic-era political entity situated between ancient Armenia and Syria. Ruled by the Orontid dynasty, the kingdom was culturally mixed ...
and a descendant of Zariadres
Zariadres was an Orontid ruler of Sophene.
Name
''Zariadres'' () is the Greek transliteration of an Iranian name, attested as ZRYTR (ZRYHR) in the Aramaic engravings in Sevan and Siwnik, and as ''Zareh'' in Armenian sources. The name is derived ...
.Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
. ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (Ancient Greek: Γεωγραφικά ''Geōgraphiká''), or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Ancient Greek, Greek and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen ...
''11.14.15
Alliance with Pontus
During theFirst Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridates ...
(89–85 BC), Tigranes supported Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
, but was careful not to become directly involved in the war.
He rapidly built up his power and established an alliance with Mithridates VI, marrying his daughter Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
. Tigranes agreed to extend his influence in the East, while Mithridates set to conquer Roman land in Asia Minor and in Europe. By creating a stronger Hellenistic state, Mithridates was to contend with the well-established Roman foothold in Europe. Mithridates executed a planned general attack on Romans and Italians in Asia Minor, tapping into local discontent with the Romans and their taxes and urging the peoples of Asia Minor to raise against foreign influence. The slaughter of 80,000 people in the province of Asia Minor was known as the Asiatic Vespers
The Asiatic Vespers (also known as the Asian Vespers, Ephesian Vespers, or the Vespers of 88 BC) refers to the massacres of Roman and other Latin-speaking peoples living in parts of western Anatolia in 88 BC by forces loyal to Mithridates VI Eupat ...
. The two kings' attempts to control Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
and then the massacres resulted in guaranteed Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
intervention. The senate decided that Lucius Cornelius Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had t ...
, who was then one of the consuls, would command the army against Mithridates.
The renowned French historian René Grousset
Biography
Grousset was born in Aubais, Gard in 1885. Having graduated from the University of Montpellier with a degree in history, he began his distinguished career soon afterward. He served in the French army during World War I. In 1925, ...
remarked that in their alliance Mithridates was somewhat subservient to Tigranes.
Wars against the Parthians and Seleucids

Mithridates II of Parthia
Mithridates II (also spelled Mithradates II or Mihrdad II; xpr, 𐭌𐭄𐭓𐭃𐭕 ''Mihrdāt'') was king of the Parthian Empire from 124 to 91 BC. Considered one of the most magnificent of his dynasty to ever rule Iran, he was known as Mithrida ...
his son Gotarzes I
Gotarzes I ( xpr, 𐭂𐭅𐭕𐭓𐭆 ''Gōdarz'') was king of the Parthian Empire from 91 BC to 87 or 80 BC. He was the son and successor of Mithridates II (), and was succeeded by his son Orodes I.
Name
"Gotarzes" is from Middle Iranian ''G� ...
succeeded him. He reigned during a period coined in scholarship as the "Parthian Dark Age The so-called "Parthian Dark Age" refers to a period of three decades in the history of Parthian Empire between the death (or last years) of Mithridates II in 91 BC, and the accession to the throne of Orodes II in 57 BC, with various date ranges be ...
," due to the lack of clear information on the events of this period in the empire, except a series of, apparently overlapping, reigns. This system of split monarchy weakened Parthia, allowing Tigranes II of Armenia to annex Parthian territory in western Mesopotamia. This land would not be restored to Parthia until the reign of Sinatruces (''r''. c. 78–69 BC).
In 83 BC, after bloody strife for the throne of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, governed by the Seleucids, the Syrians decided to choose Tigranes as the protector of their kingdom and offered him the crown of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. Magadates was appointed as his governor in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
. He then conquered Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
and Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
, effectively putting an end to the last remnants of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, though a few holdout cities appear to have recognized the shadowy boy-king Seleucus VII Philometor
Seleucus VII Philometor ( grc-gre, Φιλομήτωρ) or Kybiosactes ( grc-gre, Κυβιοσάκτης), was a ruler of the Seleucid kingdom based in Syria. But his existence is disputed.
Biography King of Syria
The last members of the once mig ...
as the legitimate king during his reign. The southern border of his domain reached as far as Ptolemais (modern Akko
Acre ( ), known locally as Akko ( he, עַכּוֹ, ''ʻAkō'') or Akka ( ar, عكّا, ''ʻAkkā''), is a city in the coastal plain region of the Northern District of Israel.
The city occupies an important location, sitting in a natural harb ...
). Many of the inhabitants of conquered cities were sent to his new metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big c ...
of Tigranocerta __NOTOC__
Tigranocerta ( el, Τιγρανόκερτα, ''Tigranόkerta''; Tigranakert; hy, Տիգրանակերտ), also called Cholimma or Chlomaron in antiquity, was a city and the capital of the Armenian Kingdom between 77 and 69 BCE. It bore ...
.
At its height, his empire extended from the Pontic Alps
The Pontic Mountains or Pontic Alps ( Turkish: ''Kuzey Anadolu Dağları'', meaning North Anatolian Mountains) form a mountain range in northern Anatolia, Turkey. They are also known as the ''Parhar Mountains'' in the local Turkish and Pontic Gr ...
(in modern north-eastern Turkey) to Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, and from the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
to the Mediterranean. A series of victories led him to assume the Achaemenid title of King of Kings, which even the Parthian kings did not assume, appearing on coins struck after 85 BC. He was called "Tigranes the Great" by many Western historians and writers, such as Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''P ...
. The "King of Kings" never appeared in public without having four kings attending him. Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the estab ...
, referring to his success in the east, said that he "made the Republic of Rome tremble before the prowess of his arms."
Tigranes' coins consist of tetradrachm
The tetradrachm ( grc-gre, τετράδραχμον, tetrádrachmon) was a large silver coin that originated in Ancient Greece. It was nominally equivalent to four Greek drachma, drachmae. Over time the tetradrachm effectively became the standard ...
s and copper coins having on the obverse his portrait wearing a decorated Armenian tiara with ear-flaps. The reverse has a completely original design. There are the seated Tyche of Antioch
Tyche (; Ancient Greek: Τύχη ''Túkhē'', 'Luck', , ; Roman equivalent: Fortuna) was the presiding tutelary deity who governed the fortune and prosperity of a city, its destiny. In Classical Greek mythology, she is the daughter of Aphrodite a ...
and the river god Orontes at her feet.
Wars against Rome
Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
had found refuge in Armenian land after confronting Rome, considering the fact that Tigranes was his ally and relative. The King of Kings eventually came into direct contact with Rome. The Roman commander, Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingdom ...
, demanded the expulsion of Mithridates from Armenia – to comply with such a demand would be, in effect, to accept the status of vassal to Rome and this Tigranes refused. Charles Rollin
Charles Rollin (January 30, 1661 in Paris - December 14, 1741 in Paris) was a French historian and educator, whose popularity in his time combined with becoming forgotten by later generations makes him an epithet, applied to historians such as J ...
, in his ''Ancient History'', says:
Lucullus' reaction was an attack that was so precipitate that he took Tigranes by surprise. According to Roman historians Mithrobazanes, one of Tigranes' generals, told Tigranes of the Roman approach. Tigranes was, according to Keaveney, so impressed by Mithrobazanes' courage that he appointed Mithrobazanes to command an army against Lucullus – Tigranes sent Mithrobarzanes with 2,000 to 3,000 cavalry to expel the invader. Mithrobarzanes charged the Romans while they were setting up their camp, but was met by a 3,500-strong sentry force and his horsemen were routed. He perished in the attempt. After this defeat, Tigranes withdrew north to Armenia to regroup, leaving Lucullus free to besiege Tigranocerta.
When Tigranes had gathered a large army, he returned to confront Lucullus. On October 6, 69 BC, Tigranes' much larger force was decisively defeated by the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
under Lucullus in the Battle of Tigranocerta
The Battle of Tigranocerta (, ''Tigranakerti tchakatamart'') was fought on 6 October 69 BC between the forces of the Roman Republic and the army of the Kingdom of Armenia led by King Tigranes the Great. The Roman force, led by Consul Lucius ...
. Tigranes' treatment of the inhabitants (the majority of the population had been forced to move to the city) led disgruntled city guards to open the gates of the city to the Romans. Learning of this, Tigranes hurriedly sent 6000 cavalrymen to the city in order to rescue his wives and some of his assets. Tigranes escaped capture with a small escort.
On October 6, 68 BC, the Romans approached the old capital of Artaxata
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of t ...
. Tigranes' and Mithridates' combined Armeno-Pontic army of 70,000 men formed up to face them but were resoundingly defeated. Once again, both Mithridates and Tigranes evaded capture by the victorious Romans. However, the Armenian historians claim that the Romans lost the battle of Artaxata and Lucullus' following withdrawal from the Kingdom of Armenia in reality was an escape due to the above-mentioned defeat. The Armenian-Roman wars are depicted in Alexandre Dumas
Alexandre Dumas (, ; ; born Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie (), 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas père (where '' '' is French for 'father', to distinguish him from his son Alexandre Dumas fils), was a French writer ...
' ''Voyage to the Caucasus''.
The long campaigning and hardships that Lucullus' troops had endured for years, combined with a perceived lack of reward in the form of plunder, led to successive mutinies among the legions in 68–67. Frustrated by the rough terrain of Northern Armenia and seeing the worsening morale of his troops, Lucullus moved back south and put Nisibis under siege. Tigranes concluded (wrongly) that Nisibis would hold out and sought to regain those parts of Armenia that the Romans had captured. Despite his continuous success in battle, Lucullus could still not capture either one of the monarchs. With Lucullus' troops now refusing to obey his commands, but agreeing to defend positions from attack, the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
sent Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
to recall Lucullus to Rome and take over his command.
Pompey and submission to Rome
In 67 BCPompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
was given the task of defeating Mithridates and Tigranes. Pompey first concentrated on attacking Mithridates while distracting Tigranes by engineering a Parthian attack on Gordyene
Corduene hy, Կորճայք, translit=Korchayk; ; romanized: ''Kartigini'') was an ancient historical region, located south of Lake Van, present-day eastern Turkey.
Many believe that the Kardouchoi—mentioned in Xenophon’s Anabasis as havin ...
. Phraates III
Phraates III (also spelled Frahad III; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭇𐭕 ''Frahāt''), was King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 69 BC to 57 BC. He was the son and successor of Sinatruces ().
At Phraates III's accession, his empire cou ...
, the Parthian king, was soon persuaded to take things a little further than an annexation of Gordyene when a son of Tigranes (also named Tigranes) went to join the Parthians and persuaded Phraates to invade Armenia in an attempt to replace the elder Tigranes with the Tigranes the Younger
Tigranes the Younger was an Artaxiad prince, who briefly ruled the Kingdom of Sophene in 65 BC.
Biography
Tigranes the Younger was the son and heir of the Artaxiad king of Armenia, Tigranes the Elder (). His mother was Cleopatra of Pontus, ...
. Tigranes decided not to meet the invasion in the field but instead ensured that his capital, Artaxata, was well defended and withdrew to the hill country. Phraates soon realized that Artaxata would not fall without a protracted siege, the time for which he could not spare due to his fear of plots at home. Once Phraates left, Tigranes came back down from the hills and drove his son from Armenia. The son then fled to Pompey.
In 66 BC, Pompey advanced into Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
with Tigranes the Younger, and Tigranes, now almost 75 years old, surrendered. Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
allowed him to retain his kingdom shorn of his conquests as he planned to have Armenia as a buffer state and he took 6,000 talents/180 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of silver. His unfaithful son was sent back to Rome as a prisoner.
Tigranes continued to rule Armenia as a formal ally of Rome until his death in 55/54, at age 85.
Offspring
Tigranes had four sons and three daughters. The eldest son, Zariadres, according toAppian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Hadr ...
and Valerius Maximus
Valerius Maximus () was a 1st-century Latin writer and author of a collection of historical anecdotes: ''Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX'' ("Nine books of memorable deeds and sayings", also known as ''De factis dictisque memorabilibus'' ...
rebelled against Tigranes and was killed during a battle (possibly late 90s BCE). Appian also mentions an unnamed younger son who was executed for conspiring against Tigranes: he disregarded his father's health and wore Tigranes's crown (Tigranes having been injured during a hunting accident). His third son, Tigranes the Younger
Tigranes the Younger was an Artaxiad prince, who briefly ruled the Kingdom of Sophene in 65 BC.
Biography
Tigranes the Younger was the son and heir of the Artaxiad king of Armenia, Tigranes the Elder (). His mother was Cleopatra of Pontus, ...
, who showed great care for his injured father and was rewarded for his loyalty, has already been mentioned. He is also alleged to have led a military campaign in 82 BCE. Tigranes was succeeded by his fourth and youngest son, Artavasdes II
Artavasdes II ( grc, ΑΡΤΑΒΑΖΔΟΥ ''Artabázēs'') was king of Armenia from 55 BC to 34 BC. A member of the Artaxiad Dynasty, he was the son and successor of Tigranes the Great (). His mother was Cleopatra of Pontus, thus making his matern ...
.
One daughter of Tigranes according to Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
married Mithridates I of Atropatene. Another daughter married Parthian prince Pacorus, son of Orodes II
Orodes II (also spelled Urud II; xpr, 𐭅𐭓𐭅𐭃 ''Wērōd''), was King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 57 BC to 37 BC. He was a son of Phraates III, whom he murdered in 57 BC, assisted by his elder brother Mithridates IV. The two br ...
. Parchments of Avroman
The Parchments of Avroman (or Awraman) are three parchment documents, found in 1909 in a cave in the Hawraman region of Iranian Kurdistan. They were found in Tang-i Var, Kuh-e Salan Mountain, near the village of Shahr Hawraman. The documents were f ...
also mention his third daughter, Ariazate "Automa", who married Gotarzes I
Gotarzes I ( xpr, 𐭂𐭅𐭕𐭓𐭆 ''Gōdarz'') was king of the Parthian Empire from 91 BC to 87 or 80 BC. He was the son and successor of Mithridates II (), and was succeeded by his son Orodes I.
Name
"Gotarzes" is from Middle Iranian ''G� ...
of Parthia.
Although Cleopatra of Pontus
Cleopatra of Pontus (110 BC – after 58 BC) was a Pontian princess and a queen consort of Armenia.
She was one of the daughters of King Mithridates VI of Pontus and Queen Laodice. Cleopatra is sometimes known as Cleopatra the Elder, to dist ...
is usually considered to be their mother (Appian writes that she gave birth to three sons), historian Gagik Sargsyan
Gagik Sargsyan ( hy, Գագիկ Խորենի Սարգսյան; 6 April 1926, in Yerevan – 25 August 1998, in Yerevan) was an Armenian historian, who served as the vice president of the Armenian Academy of Sciences.
Biography
He studied at Yer ...
considered only Artavasdes II and one of the unnamed daughters to be her children. According to him, the rest had a different mother and were born before Tigranes became king. The reasoning behind it is that if Tigranes the Younger did indeed lead a campaign in 82 BCE, then he and hence his two older brothers (and possibly two sisters) would be too old to be Cleopatra's children. Another argument supporting this claim would be the situation with Ariazate. As she was probably the mother of Orodes I
Orodes I (also spelled Urud I; xpr, 𐭅𐭓𐭅𐭃 ''Wērōd/Urūd''), was king of the Parthian Empire from 80 to 75 BC. He was the son and heir of Gotarzes I (). His reign is relatively obscure. His throne may have been usurped in 87–80 BC ...
(), then Ariazate could not have been the daughter of Cleopatra who married Tigranes only in 94 BCE at the age of 15 or 16. Sargsyan also proposed a possible candidate as Tigranes's first wife and the children's mother: Artaxiad princess Zaruhi, a daughter of Tigranes's paternal uncle Zariadres and granddaughter of Artaxias I
Artaxias I (from gr, Άρταξίας; in hy, Արտաշէս, translit=Artašēs) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling d ...
. He also considered likely that the reason for the rebellion of Tigranes's son Zariadres was the birth of Artavasdes who was declared the heir by virtue of being born to a king and not a prince.
Imperial ideology
Tigranes is a typical example of the mixed culture of his period. The ceremonial of his court was ofAchaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
origin, and also incorporated Parthian aspects. He had Greek rhetoricians and philosophers in his court, possibly as a result of the influence of his queen, Cleopatra. Greek was also possibly spoken in the court. Following the example of the Parthians, Tigranes adopted the title of ''Philhellene
Philhellenism ("the love of Greek culture") was an intellectual movement prominent mostly at the turn of the 19th century. It contributed to the sentiments that led Europeans such as Lord Byron and Charles Nicolas Fabvier to advocate for Greek i ...
'' ("friend of the Greeks"). The layout of his capital Tigranocerta __NOTOC__
Tigranocerta ( el, Τιγρανόκερτα, ''Tigranόkerta''; Tigranakert; hy, Տիգրանակերտ), also called Cholimma or Chlomaron in antiquity, was a city and the capital of the Armenian Kingdom between 77 and 69 BCE. It bore ...
was a blend of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
architecture.
Like the majority Armenia's inhabitants, Tigranes was a follower of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion and one of the world's History of religion, oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian peoples, Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a Dualism in cosmology, du ...
. On his crown, a star of divinity and two birds of prey
Birds of prey or predatory birds, also known as raptors, are hypercarnivorous bird species that actively hunt and feed on other vertebrates (mainly mammals, reptiles and other smaller birds). In addition to speed and strength, these predators ...
are displayed, both Iranian aspects. The bird of prey was associated with the ''khvarenah
Khvarenah (also spelled khwarenah or xwarra(h): ae, 𐬓𐬀𐬭𐬆𐬥𐬀𐬵 ') is an Avestan word for a Zoroastrian concept literally denoting "glory" or "splendour" but understood as a divine mystical force or power projected upon and aidi ...
'', i.e. kingly glory. It was possibly also a symbol of the bird of the deity Verethragna
Verethragna ( ae, 𐬬𐬆𐬭𐬆𐬚𐬭𐬀𐬖𐬥𐬀 ') is an Indo-Iranian deity.
The neuter noun ''verethragna'' is related to Avestan ''verethra'', 'obstacle' and ''verethragnan'', 'victorious'. Representing this concept is the divin ...
.
Legacy and recognition
 Over the course of his conquests, Tigranes founded four cities that bore his name, including the capital of Tigranocerta (Tigranakert).
Over the course of his conquests, Tigranes founded four cities that bore his name, including the capital of Tigranocerta (Tigranakert).
Historical
Tigranes is mentioned in ''Macrobii'', a Roman essay detailing the famous long livers of the day, which is attributed toLucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
Pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets, unbound (and therefore ...
.
In ''The Art of War
''The Art of War'' () is an ancient Chinese military treatise dating from the Late Spring and Autumn Period (roughly 5th century BC). The work, which is attributed to the ancient Chinese military strategist Sun Tzu ("Master Sun"), is com ...
'' (1521), Italian political philosopher Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli ( , , ; 3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527), occasionally rendered in English as Nicholas Machiavel ( , ; see below), was an Italian diplomat, author, philosopher and historian who lived during the Renaissance. ...
attributes Tigranes' military failure to his excessive reliance on his cavalry.
According to one count, 24 operas have been composed about Tigranes by European composers, including by prominent Italian and German composers, such as Alessandro Scarlatti
Pietro Alessandro Gaspare Scarlatti (2 May 1660 – 22 October 1725) was an Italian Baroque composer, known especially for his operas and chamber cantatas. He is considered the most important representative of the Neapolitan school of opera.
...
('' Tigrane'', 1715), Antonio Vivaldi
Antonio Lucio Vivaldi (4 March 1678 – 28 July 1741) was an Italian composer, virtuoso violinist and impresario of Baroque music. Regarded as one of the greatest Baroque composers, Vivaldi's influence during his lifetime was widespread a ...
(''La virtu trionfante dell'amore e dell'odio ovvero il Tigrane'', 1724), Niccolò Piccinni
Niccolò Piccinni (; 16 January 1728 – 7 May 1800) was an Italian composer of symphonies, sacred music, chamber music, and opera. Although he is somewhat obscure today, Piccinni was one of the most popular composers of opera—particularly the ...
(''Tigrane'', 1761), Tomaso Albinoni
Tomaso Giovanni Albinoni (8 June 1671 – 17 January 1751) was an Italian composer of the Baroque era. His output includes operas, concertos, sonatas for one to six instruments, sinfonias, and solo cantatas. While famous in his day as an opera comp ...
, Giovanni Bononcini
Giovanni Bononcini (or Buononcini) (18 July 1670 – 9 July 1747) (sometimes cited also as Giovanni Battista Bononcini) was an Italian Baroque composer, cellist, singer and teacher, one of a family of string players and composers.
Biography
E ...
, Francesco Gasparini
Francesco Gasparini (19 March 1661 – 22 March 1727) was an Italian Baroque composer and teacher whose works were performed throughout Italy, and also on occasion in Germany and England.
Biography
Born in Camaiore, near Lucca, he studied in ...
, Pietro Alessandro Guglielmi
Pietro Alessandro Guglielmi (9 December 1728 – 19 November 1804) was an Italian opera composer of the classical period.
Biography
Guglielmi was born into the Guglielmi family of musicians in Massa. His father, Jacopo Guglielmi, was a comp ...
, Johann Adolph Hasse
Johann Adolph Hasse (baptised 25 March 1699 – 16 December 1783) was an 18th-century German composer, singer and teacher of music. Immensely popular in his time, Hasse was best known for his prolific operatic output, though he also composed a co ...
, Giovanni Battista Lampugnani
Giovanni Battista Lampugnani (c. 1708 – 2 June 1786) was an Italian composer, born in Milan. He studied in Naples where he made his debut as a composer of opera in 1732. In 1743 he went to London to take over the Opera from Baldassare Galuppi at ...
, Vincenzo Righini
Vincenzo Maria Righini (22 January 1756 – 19 August 1812) was an Italian composer, singer and kapellmeister.
Life and career
Righini was born in Bologna and studied singing and composition with Padre Martini in his home town. Initially ...
, Antonio Tozzi
Antonio Tozzi (c. 1736 - after 1812) was an Italian opera composer.
He was born at Bologna, Italy. He studied with Padre Martini and became a member of the Accademia Filarmonica di Bologna in 1761. His first opera ''Tigrane'', was performed ...
, and others.
Modern
According toRazmik Panossian
Razmik Panossian ( hy, Ռազմիկ Փանոսեան, born 1964) is a Canadian-Armenian historian and political scientist.
Career
An ethnic Armenian, Panossian was born in Beirut, Lebanon and raised in Canada in a family "engaged with rmenianco ...
, Tigranes' short-lived empire has been a source of pride for modern Armenian nationalists. Nevertheless, his empire was a multi-ethnic one.
The phrase "sea to sea Armenia" ( hy, ծովից ծով Հայաստան, ''tsovits tsov Hayastan'') is a popular expression used by Armenians to refer to the kingdom of Tigranes which extended from the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
.
See also
*History of Armenia
The history of Armenia covers the topics related to the history of the Armenia, Republic of Armenia, as well as the Armenians, Armenian people, the Armenian language, and the regions historically and Armenian Highlands, geographically consid ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
;English * * . * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * . * * * * * * * * * * * * ;Russian * * * * * * * * * * ;French * * * * ;German * * ;Armenian *Further reading
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tigranes the Great 140 BC births 55 BC deaths 1st-century BC kings of Armenia 1st-century BC rulers 1st-century BC rulers in Europe 1st-century BC rulers in Asia People of the Roman Republic Artaxiad dynasty 1st century BC in Armenia Prisoners and detainees of the Parthian Empire