The Tigray Region, officially the Tigray National Regional State, is the northernmost
regional state
A regional state, or a regionalised unitary state, is a term used to denote a type of state that is formally unitary but where a high degree of political power has been highly decentralised to regional governments. This contrasts with a state org ...
in
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
. The Tigray Region is the homeland of the
Tigrayan,
Irob, and
Kunama people. Its capital and largest city is
Mekelle
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a List of zones of Ethiopia, special zone and capital city, capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta province, Enderta Awrajj ...
. Tigray is the fifth-largest by area, the fifth-most populous, and the fifth-most densely populated of the 11 regional states.
Tigray's official language is
Tigrinya, similar to that
spoken in Eritrea just to the North. The estimated population as of 2019 is 5,443,000. The majority of the population (c. 80%) are farmers, contributing 46% to the regional gross domestic product (2009). The highlands have the highest population density, especially in
eastern and
central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
Tigray. The much less densely populated lowlands comprise 48% of Tigray's area. Like many parts of Africa, Tigray is far from a religious monolith. Despite the historical identification of Ethiopia with Orthodox Christianity, the presence of Islam in Ethiopia is as old as the religion itself. The most recent Ethiopian census, collected in 2007, estimates that Muslims make up 34% of the rapidly growing national population. Although the percentage of Muslims in Tigray is only 5 to 10%, it has historically been Islam’s doorway to the region and to Africa at large. 96% of
Tigrayans are
Orthodox Christian
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Churche ...
.
Tigray is bordered by
Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
to the north,
Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
to the west, the
Amhara Region to the south and the
Afar Region to the east and southeast.
Towns in Tigray include:
Mekelle
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a List of zones of Ethiopia, special zone and capital city, capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta province, Enderta Awrajj ...
,
Adigrat,
Axum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
,
Shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the beginn ...
,
Humera,
Adwa
Adwa ( ti, ዓድዋ; amh, ዐድዋ; also spelled Aduwa) is a town and separate woreda in Tigray Region, Ethiopia. It is best known as the community closest to the site of the 1896 Battle of Adwa, in which Ethiopian soldiers defeated Italian ...
,
Addi Remets
Adi Remets (Tigrinya: ዓዲ ረመፅ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Located in the West Tigray of tigray region, this town has a latitude and longitude of with an elevation of 1870 meters above sea level. It is the administrative ...
,
Alamata
Alamata (Tigrinya: ኣላማጣ ) is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Located in the Debubawi (Southern) zone of Tigray it has a latitude and longitude of and an elevation of above sea level and is located along Ethiopian Highway 2. ...
,
Wukro
Wukro (Tigrigna: ውቕሮ) (also known as Wukro Kilte Awulaelo; Tigrigna: ውቕሮ ክልተ ኣውላዕሎ) (also transliterated Wuqro; is a town and separate woreda in Tigray, Ethiopia. Wukro is located along Genfel River, in the Misraqaw ...
,
Maychew
Maychew, also Maichew ( ti, ማይጨው, "salt water"), is a town and woreda in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. It is located at 665 km north of Addis Ababa along Ethiopian Highway 2. According to Ethiopia’s agro-ecological setting, Maychew ...
,
Sheraro
Sheraro (), also spelt Shiraro, is a town and separate woreda in Tigray, Ethiopia. It is located in the North Western Zone of the Tigray Region, at an elevation of 1246 meters above sea level. It is the administrative center of Tahtay Adiyabo. ...
,
Abiy Addi
Abiy Addi (also spelled Abi Addi; Tigrigna ዓብዪ ዓዲ "Big town") is a town in central Tigray Region, Tigray, Ethiopia. Abiy Addi is at the southeastern edge of the Kola Tembien woreda, of which it is the capital.
Overview
The town is di ...
,
Korem
Korem (Agewugna: ኮረ/ Sun) (alternative forms include Quoram, Kworam) is a town and separate woreda in Tigray, Ethiopia. Located on the eastern edge of the Ethiopian highlands in the Debubawi (Southern) Zone of the Tigray Region, this town ...
,
Qwiha
Qwiha (also Kuha or Kwiha) is a town located in Tigray, Ethiopia. The name comes from the local word for willows, which are abundant in the area.Nathaniel Pearce, (J.J. Halls, editor), ''The Life and Adventures of Nathaniel Pearce'' (London, 18 ...
,
Atsbi
Atsbi (Ge'ez: ኣጽቢ) (officially known as Atsbi Endaselase Ge'ez: ኣጽቢ እንዳስላሴ ) is a town in Tigray Region, Tigray, Ethiopia. Located in the Misraqawi Zone, Misraqawi (Eastern) Zone of the Tigray Region, about 50 kilometers nor ...
,
Hawzen
Hawzen ( Ge'ez: ሓውዜን) is a town in northern Ethiopia. Located in the Misraqawi (Eastern) Zone of the Tigray Region (or ''kilil''), this town has a latitude and longitude of with an elevation of 2105 meters above sea level. Its market da ...
,
Mekoni
Mekoni, also Mehoni ( Ge'ez: መኾኒ or መሆኒ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. "Mekoni" (pronounced as 'Me-koni') is located at 657 km north of Addis Ababa along Ethiopian Highway 2 which runs to Mekelle (the capital city of ...
,
Dansha
Dansha is a town in Tigray, Ethiopia, located in the northwestern part of the country.
History
On July 7, 1988, during the Ethiopian Civil War, the Ethiopia government's Third Revolutionary Army's 604 Army Corps was ambushed by the Tigray P ...
,
Adi Gudom
Adi Gudem (Tigrigna: ዓዲጉደም) is a town in Tigray, Ethiopia. Located in the Debub Misraqawi (Southeastern) Zone of the Tigray Region (or ''kilil''), this town has a latitude and longitude of {{coord, 13, 15, N, 39, 31, E with an elevati ...
,
Sheraro
Sheraro (), also spelt Shiraro, is a town and separate woreda in Tigray, Ethiopia. It is located in the North Western Zone of the Tigray Region, at an elevation of 1246 meters above sea level. It is the administrative center of Tahtay Adiyabo. ...
, Indabaguna, Mai Tsebri, and
Zalambessa
Zalambessa (Tigrigna: ዛላምበሳ) is a town located in Tigray, Ethiopia. Zalambessa is part of the Misraqawi (Eastern) Zone of the Tigray Region. It is about 42 kilometers north of Adigrat. The Serha-Zalambesa border crossing is located in ...
.
The government of Tigray consists of the
executive branch
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a State (polity), state.
In poli ...
, led by the president,
Debretsion Gebremichael
Debretsion Gebremichael ( ti, ደብረጽዮን ገብረሚካኤል, pronunciation: ) is an Ethiopian politician and current president of the Tigray Region and chairman of Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF). His position as titular head ...
; the
legislative branch
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as ...
, which comprises the state council; and the
judicial branch
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
, which is led by the state supreme court. In early November 2020, a
conflict
Conflict may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton
* ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne
* ''Conflict'' (1937 film) ...
between the Tigray Region, involving the
Tigray People's Liberation Front
The Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF; ti, ህዝባዊ ወያነ ሓርነት ትግራይ, lit=Popular Struggle for the Freedom of Tigray), also called the Tigrayan People's Liberation Front, is a left-wing ethnic nationalist paramilitar ...
(TPLF) and the Ethiopian federal government began, in which Eritrea took part on the side of the federal government, rapidly escalating into the
Tigray War and destabilizing the region.
History
3rd millennium to 1st century BC
Tigray is often regarded as the cradle of Ethiopian civilization. Its landscape has many historic monuments. Three major monotheistic religions,
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
,
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
and
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
arrived in Ethiopia through the
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
and then Tigray.
Given the presence of a large temple complex and fertile surroundings, the capital of the 3,000-year-old kingdom of
Dʿmt
D mt ( Ge'ez: ደዐመተ, ''DʿMT'' theoretically vocalized as ዳዓማት, ''Daʿamat'' or ዳዕማት, Daʿəmat) was a kingdom located in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia that existed between the 10th and 5th centuries BC. Few inscriptions ...
may have been near present-day
Yeha.
Dʿmt developed irrigation schemes, used the
plough
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
, grew
millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
, and made
iron tools and weapons. Some modern historians, including Stuart Munro-Hay, Rodolfo Fattovich, Ayele Bekerie,
Cain Felder
Cain Hope Felder (June 9, 1943 – October 1, 2019) was an American biblical scholar, serving as professor of New Testament language and literature and editor of ''The Journal of Religious Thought'' at the Howard University School of Divinity. He ...
, and
Ephraim Isaac
Ephraim Isaac (born 29 May 1936) is an Ethiopian scholar of ancient Ethiopian Semitic languages and of Classical African civilization, African and History of Ethiopia, Ethiopian civilizations. He is the director of the Institute of Semitic Studi ...
consider this civilization to be indigenous, although
Sabaean Sabean or Sabaean may refer to:
*Sabaeans, ancient people in South Arabia
**Sabaean language, Old South Arabian language
*Sabians, name of a religious group mentioned in the Quran, historically adopted by:
**Mandaeans, Gnostic sect from the marshl ...
-influenced due to the latter's dominance of the
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
. Others, including Joseph Michels, Henri de Contenson, Tekletsadik Mekuria, and Stanley Burstein, have viewed Dʿmt as the result of a mixture of Sabaean and indigenous peoples.
[Nadia Durrani, ''The Tihamah Coastal Plain of South-West Arabia in its Regional context c. 6000 BC-AD 600 (Society for Arabian Studies Monographs No. 4)'', Oxford: Archaeopress, 2005, p. 121 ] The most recent research, however, shows that
Ge'ez, the ancient Semitic language spoken in Tigray, Eritrea and northern Ethiopia in ancient times, is not likely to have been derived from
Sabaean Sabean or Sabaean may refer to:
*Sabaeans, ancient people in South Arabia
**Sabaean language, Old South Arabian language
*Sabians, name of a religious group mentioned in the Quran, historically adopted by:
**Mandaeans, Gnostic sect from the marshl ...
. There is evidence of a Semitic-speaking presence in Tigray, Eritrea and northern Ethiopia at least as early as 2000 BC.
It is now believed that Sabaean influence was minor, limited to a few localities and disappearing after a few decades or a century, It may have represented a trading or military colony, in some sort of symbiosis or military alliance with the civilization of Dʿmt or some other proto-
Aksumite
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in wha ...
state.
After the fall of Dʿmt in the 5th century BC, the plateau came to be dominated by smaller, unknown successor kingdoms. This lasted until the rise of one of these polities during the first century BC, the
Aksumite Kingdom, which succeeded in reunifying the area and is, in effect, the ancestor of medieval and modern states in Eritrea and Ethiopia using the name "Ethiopia" as early as the 4th century.
[Henze, Paul B. (2005) ''Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia'', ]
1st to 10th century AD


The Kingdom of Aksum was a trading empire rooted in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia. It existed from approximately 100–940 AD, growing from the proto-Aksumite
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
period c. 4th century BC to achieve prominence by the 1st century AD.
According to the ''
Book of Axum
The ''Book of Axum'' ( Ge'ez መጽሐፈ ፡ አክሱም ''maṣḥafa aksūm'', am, meṣhafe aksūm, ti, meṣḥafe aksūm, la, Liber Axumae) is the name accepted since the time of James Bruce in the latter part of the 18th century CE for a ...
'', Axum's first capital, Mazaber, was built by Itiyopis, son of Cush. The capital was later moved to
Aksum in northern Ethiopia.
The Empire of Aksum, at its height, at times extended across most of present-day
Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
, Ethiopia,
Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, Sudan, Yemen and Saudi Arabia. The capital city of the empire was
Axum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
, now in northern Ethiopia. Today a smaller community, the city of Axum was once a bustling metropolis and a cultural and economic hub. Two hills and two streams lie on the east and west expanses of the city; perhaps providing the initial impetus for settling this area. Along the hills and plain outside the city, the Aksumites had cemeteries with elaborate grave stones, which are called
stelae, or
obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by Anc ...
s. Other important cities included
Yeha,
Hawulti-Melazo
Hawulti-Melazo (''Hawelti-Melazo'') is a pre-Aksumite and Aksumite archaeological site located in Eritrea. It contains various old funerary monuments, as well as ancient inscriptions.
See also
*Ezana Stone
*Qohaito
*Hawulti (monument)
Hawulti ...
,
Matara,
Adulis, and
Qohaito, the last three of which are now in Eritrea. By the reign of
Endubis
Endubis or Endybis was a late-3rd-century sovereign of the Kingdom of Aksum in East Africa (modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea). He was among the earliest rulers in the Horn of Africa to mint his own coins; the Aksumite currency of his reign was issu ...
in the late 3rd century, Aksum had begun minting its own currency and was named by
Mani
Mani may refer to:
Geography
* Maní, Casanare, a town and municipality in Casanare Department, Colombia
* Mani, Chad, a town and sub-prefecture in Chad
* Mani, Evros, a village in northeastern Greece
* Mani, Karnataka, a village in Dakshi ...
as one of the four great powers of his time, along with
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and the
Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
and
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
empires. It converted to
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
in 325 or 328 under
King Ezana and was the first state to use the image of
the cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars.
Cross or The Cross may also refer to:
Religion
* Christian cross, the basic symbol of Christianity
* Cross necklace, a necklace worn by adherents of the Christian r ...
on its coins.

11th to 19th century AD
In the 14th century the Tigrinya-speaking lands (Tigray-
Mareb Melash) were divided into two provinces, separated by the Mereb River, by the newly enthroned Amhara emperors. The governor of the northern province received the title Bahre Negash (Ruler of the sea), whereas the governor of the southern province was given the title of Tigray Mekonen (Lord of Tigray). The Portuguese Jesuit Emanuele Baradas's work titled "Do reino de Tigr", written in 1633–34, states that the "Reino de Tigr" (Kingdom of Tigray) extended from
Hamasien to
Temben, from the borders of
Dankel to the
Adwa
Adwa ( ti, ዓድዋ; amh, ዐድዋ; also spelled Aduwa) is a town and separate woreda in Tigray Region, Ethiopia. It is best known as the community closest to the site of the 1896 Battle of Adwa, in which Ethiopian soldiers defeated Italian ...
mountain. He also stated that Tigray-Mereb Melash was divided into 24 smaller political units (principalities), twelve of which were located south of the Mereb and governed by the Tigray Mekonen, based in
Enderta. The other twelve were located north of the Mereb, under the authority of the
Bahre Negash, based in the district of
Serae
The Provinces of Eritrea existed between Eritrea's incorporation as a colony of Italy until the conversion of the provinces into administrative regions.
Overview
In Italian Eritrea, the Italian colonial administration had divided the colony into e ...
.
The ''Book of Aksum'', likely written and compiled before the 15th century, shows a traditional schematic map of Tigray with the city of
Aksum at its center, surrounded by the 13 principal provinces: "Tembien, Shire, Serae, Hamasien,
Bur
A bur (also spelled burr) is a seed or dry fruit or infructescence that has hooks or teeth. The main function of the bur is to spread the seeds of the bur plant, often through epizoochory. The hooks of the bur are used to catch on to for exam ...
, Sam’a,
Agame, Amba Senayt,
Garalta,
Enderta, Sahart and Abergele."
During the Middle Ages, the position of Tigray Mekonnen ("Governor of Tigray") was established to rule over the area. Other districts included
Akele Guzay
The Provinces of Eritrea existed between Eritrea's incorporation as a colony of Italy until the conversion of the provinces into administrative regions.
Overview
In Italian Eritrea, the Italian colonial administration had divided the colony into e ...
(now part of
Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
), and the kingdom of the
Bahr negus
Medri Bahri ( ti, ምድሪ ባሕሪ, English: Land of the Sea Kingdom), also known as Mereb Melash, was an Eritrean kingdom emerged in 1137 until conquest by the Ethiopian Empire in 1879. It was situated in modern-day Eritrea, and was ruled by ...
, who ruled much of what is now Eritrea and
Shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the beginn ...
district and town in Western Tigray. At the time when Tigray Mekonnen existed simultaneously with that of Bahr negus, their frontier seems to have been the
Mareb River
The Mareb River, or Gash River ( ar, القاش) is a river flowing out of central Eritrea. Its chief importance is defining part of the boundary between Eritrea and Ethiopia, between the point where the Mai Ambassa enters the river at to the co ...
, which is currently constitutes the border between the Ethiopian province of Tigray and Eritrea.
After the loss of power of the Bahr negus in the aftermath of
Bahr negus Yeshaq
Yeshaq (died 1578) was the Bahr Negus, or ruler of the Medri Bahri, during the mid to late 16th century A subordinate of Ethiopian Emperor Dawit II, he was noted for supporting Gelawdewos during the Ethiopian-Adal war, and rebelling against his su ...
's rebellions, By the unsettled
Zemene Mesafint period ("Era of the Princes"), both designations had declined to little more than empty titles, and the lord who succeeded them used (and received from the Emperor) the title of either
Ras
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio stati ...
or
Dejazmach, beginning with Ras
Mikael Sehul. Rulers of Tigray such as Ras
Wolde Selassie
Wolde Selassie (; c.1736 - 28 May 1816) was Ras of the Tigray province between 1788-1816, and Regent of the Ethiopian Empire between 1797-1800. John J. Halls, in his ''Life and Correspondence of Henry Salt'', preserves a description of this power ...
alternated with others, chiefly those of
Begemder or
Yejju
Yejju Oromo people are a sub clan of the Barento branch of Oromo people. They are one of the northernmost communities of Oromo people residing in Ethiopia.
During the 17th century, the Yejju dynasty, more specifically, the Warra Sheik, or sons ...
, as warlords to maintain the Ethiopian monarchy during the Zemene Mesafint.
In the mid-19th century, the lords of Tembien and Enderta managed to establish an overlordship of Tigray. One of its members, Dejazmach Kahsay Mercha, ascended the imperial throne in 1872 under the name
Yohannes IV
''girmāwī''His Imperial Majesty, spoken= am , ጃንሆይ ''djānhoi''Your Imperial Majesty(lit. "O steemedroyal"), alternative= am , ጌቶቹ ''getochu''Our Lord (familiar)(lit. "Our master" (pl.)) yohanes
Yohannes IV (Tigrinya: ዮሓ� ...
. Following his 1889 death in the
Battle of Metemma, the Ethiopian throne came under the control of the king of
Shewa
Shewa ( am, ሸዋ; , om, Shawaa), formerly romanized as Shua, Shoa, Showa, Shuwa (''Scioà'' in Italian language, Italian), is a historical region of Ethiopia which was formerly an autonomous monarchy, kingdom within the Ethiopian Empire. The ...
, and the center of power shifted south and away from Tigray.
20th century
In 1943, open resistance
broke out all over southern and eastern Tigray under the slogan, "there is no government; let's organize and govern ourselves". Throughout Enderta Awraja, including
Mekelle
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a List of zones of Ethiopia, special zone and capital city, capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta province, Enderta Awrajj ...
, Didibadergiajen,
Hintalo
Hintalo ( ti, ሕንጣሎ), also called Antalo, was Administrative Center of Enderta’s historical wereda of Gabat Melash, is a small town located in the Debub Misraqawi (Southeastern) Zone of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. It lies on a platea ...
, Saharti,
Samre and Wajirat, Raya Awraja, Kilte-Awlaelo Awraja and Tembien Awraja, local assemblies, called gerreb, were formed. The gerreb sent representatives to a central congress, called the shengo, which elected leaders and established a military command system. Although the first
Woyane rebellion
The Woyane rebellion () was an uprising in Tigray Province, Ethiopia against the centralization process from the government of Emperor Haile Selassie which took place in May–November 1943. The rebels called themselves
the ''Woyane'', a name bo ...
of 1943 had shortcomings as a prototype revolution, historians agree that it involved a fairly high level of spontaneity and peasant initiative. It demonstrated considerable popular participation and reflected widely shared grievances. The uprising was specifically directed against the central Shoan Amhara regime of
Haile Selassie I, rather than the Tigrayan imperial elite.
Ethiopian Civil War

After the February 1974 popular revolution, the first signal of any mass uprising was the actions of the soldiers of the 4th Brigade of the 4th Army Division in Nagelle in southern Ethiopia. The Coordinating Committee of the Armed Forces, Police, and Territorial Army, or the
Derg
The Derg (also spelled Dergue; , ), officially the Provisional Military Administrative Council (PMAC), was the military junta that ruled Ethiopia, then including present-day Eritrea, from 1974 to 1987, when the military leadership formally " c ...
(
Ge'ez "Committee"), was officially announced 28 June 1974 by a group of military officers. The committee elected Major
Mengistu Haile Mariam as its chairman and Major
Atnafu Abate
Lieutenant Colonel Atnafu Abate ( gez, አጥናፉ አባተ; 31 January 1931 – 12 November 1977) was an Ethiopian military officer and a leading member of the Derg, the military junta which deposed Emperor Haile Selassie and ruled the co ...
as its vice-chairman. In July 1974, the Derg obtained key concessions from the emperor, Haile Selassie, which included the power to arrest not only military officers but government officials at every level. Soon both former Prime Ministers
Tsehafi Taezaz Aklilu Habte-Wold
''Ethiopian aristocratic and religious titles#Important offices of the Imperial Court, Tsehafi Taezaz'' Aklilu Habte-Wold ( am, አክሊሉ ሀብተ ወልድ; 12 March 1912 – 23 November 1974) was an Ethiopian politician under Emperor Haile ...
and
Endalkachew Makonnen, along with most of their cabinets, most regional governors, many senior military officers and officials of the Imperial court were imprisoned. In August 1974, after a proposed constitution creating a constitutional monarchy was presented to the emperor, the Derg began a program of dismantling the imperial government in order to forestall further developments in that direction. The Derg deposed and imprisoned the emperor on 12 September 1974.

In addition, the Derg in 1975 nationalized most industries and private and somewhat secure urban real-estate holdings. But mismanagement, corruption, and general hostility to the Derg's violent rule, coupled with the draining effects of constant warfare with the separatist guerrilla movements in Tigray, led to a drastic fall in general productivity of food and cash crops. In October 1978, the Derg announced the National Revolutionary Development Campaign to mobilize human and material resources to transform the economy, which led to a Ten-Year Plan (1984/1985-1993/1994) to expand agricultural and industrial output, forecasting a 6.5% growth in GDP and a 3.6% rise in per capita income. Instead per capita income declined 0.8% over this period. Famine scholar
Alex de Waal
Alexander William Lowndes de Waal (born 22 February 1963), a British researcher on African elite politics, is the executive director of the World Peace Foundation at the Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy at Tufts University. Previously, he wa ...
observes that while the
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
that struck the country in the mid-1980s is usually ascribed to drought, "closer investigation shows that widespread drought occurred only some months after the famine was already under way". Hundreds of thousands fled economic misery, conscription, and political repression, and went to live in neighboring countries and all over the
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania. , creating an Ethiopian
diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
.
Toward the end of January 1991, a coalition of rebel forces, the
(EPRDF) captured
Gondar, the ancient capital city,
Bahar Dar
Bahir Dar ( amh, ባሕር ዳር, 3=sea shore) is the capital city of Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Bahir Dar is one of the leading tourist destinations in Ethiopia, with a variety of attractions in the nearby Lake Tana and Blue Nile river. The ...
, and
Dessie
Dessiè City which is politically oppressed by the past Ethiopian government systems due to the fact that most of the population follow Islamic religion.
Dessie ( am, ደሴ, Däse; also spelled Dese or Dessye) is a town in north-central Ethiopia ...
.
Postwar
John Young, who visited the area several times in the early 1990s, attributes this delay in part to "central budget restraint, structural readjustment, and lack of awareness by government bureaucrats in
Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; am, አዲስ አበባ, , new flower ; also known as , lit. "natural spring" in Oromo), is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. It is also served as major administrative center of the Oromia Region. In the 2007 census, t ...
of conditions in the province", but notes "an equally significant obstacle was posed by an entrenched, and largely Amhara-dominated, central bureaucracy which used its power to block government-authorised funds from reaching Tigray". At the same time, a growing urban middle class of traders, businessmen and government officials emerged that was suspicious of and distant from the victorious EPRDF.
From 1991 to 2001, the president of Tigray was
Gebru Asrat
Gebru Asrat is an Ethiopian politician, former president of Tigray Region (1991–2001), and one of the top leaders of the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) and the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) until around 2000, ...
.
In 1998,
war erupted between Eritrea and Ethiopia over a portion of territory that had been administered as part of Tigray, which included the town of
Badme. A 2002
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
decision awarded much of this land to Eritrea, but Ethiopia did not accept the ruling until 2018, when a
bilateral agreement ended the
border conflict
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders ca ...
. The text of this agreement has not been publicly availed.
21st century
From 2001 to 2010 the president was
Tsegay Berhe.
2020 administrative reorganisation
Between 2018 and 2020, as part of a reform aimed to deepen and strengthen decentralisation, woredas were reorganised, and new boundaries established. As smaller towns had been growing, they had started providing a larger range of services, such as markets and even banks, that encouraged locals to travel there rather than to their formal woreda centre. However, these locals still had to travel to their local woreda centre for most local government services - often in a different direction. In 2018 and 2019, after multiple village discussions that were often vigorous in the more remote areas, 21 independent urban administrations were added and other boundaries re-drawn, resulting in an increase from 35 to 88 woredas in January 2020.
Tigray War
Following the
2020 Tigray regional election
On 9 September 2020, the Ethiopian region of Tigray held an election for its state council. The election was considered illegal by the federal government of Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed, who postponed the 2020 general election earlier in the year ...
, after months of preparation with the Eritrean army, as demonstrated by the Eritrean president visiting the Ethiopian air force on October 14 2020,
the Ethiopian military launched attacks on the government of Tigray headquarters in
Mekelle
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a List of zones of Ethiopia, special zone and capital city, capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta province, Enderta Awrajj ...
on 4 November, marking the beginning of the Tigray War. Ethiopian troops as well as Amhara militia advanced through southern Tigray, while Eritrean troops occupied border towns in northern Tigray. Amhara militias took over parts of western Tigray.
Warfare, the
COVID-19 pandemic in Ethiopia
The COVID-19 pandemic in Ethiopia is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 () caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (). The virus was confirmed to have reached Ethiopia on 13 March 2020. The ...
, and a
locust outbreak all contributed to an
emergency food situation in the region in January
2021
File:2021 collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: the James Webb Space Telescope was launched in 2021; Protesters in Yangon, Myanmar following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état, coup d'état; A civil demonstration against the October–November 2021 ...
. Two million people faced food shortages; the situation was particularly dire in
Shire Inda Selassie, where there are 100,000 refugees. The
Famine Early Warning Systems Network
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
said parts of central and eastern Tigray are likely in emergency phase 4, a step below famine.
Geography
Location and size
Tigray is situated between 12° – 15°N and 36° 30' – 40° 30'E.
A 2006 national statistics report stated the land area as .
The 2011 National Statistics gave an area of , but the sum of the figures it gave for the Tigray zones was substantially different,
rendering the 2011 report internally inconsistent. The figure of 50,079 km
2 is supported by the
Google Maps
Google Maps is a web mapping platform and consumer application offered by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360° interactive panoramic views of streets ( Street View), real-time traffic conditions, and rou ...
area calculator.
Geology
Overview
The
East African Orogeny led to the growth of a mountain chain in the
Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
(up to 800 Ma
illion years ago
, is a Japanese singer, songwriter, musician, record producer and actor. Noda is the lead vocalist, songwriter and guitarist of the Japanese rock band Radwimps and also began a solo project, Illion, in 2012.
Life and career
Early life, Radwi ...
, which was largely eroded afterwards. Around 600 Ma, the
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
break-up led to the presence of
tectonic structures and a Palaeozoic planation surface, that extents to the north and west of the Dogu'a Tembien massif.
Subsequently, there was the deposition of sedimentary and volcanic formations, from older (at the foot of the massif) to younger, near the summits. From Palaeozoic to Triassic, Tigray was located near the South Pole. The (reactivate) Precambrian extensional faults guided the deposition of Till, glacial sediments (Edaga Arbi Glacials and Enticho Sandstone). Later alluvial plain sediments were deposited (Adigrat Sandstone). The break-up of Gondwana (Late Palaeozoic to Early Triassic) led to an extensional tectonic phase, what caused the lowering of large parts of the Horn of Africa. As a consequence a marine transgression occurred, leading to the deposition of marine sediments (Antalo Limestone and Agula Shale). The region has an estimated 3.89 billion tons of mostly "excellent" quality oil shale.

At the end of the Mesozoic tectonic phase, a new (Cretaceous) planation took place. After that, the deposition of continental sediments (Amba Aradam Formation) indicates the presence of less shallow seas, probably caused by a regional uplift. At the beginning of the Caenozoic, there was a relative tectonic quiescence, during which the Amba Aradam Sandstones were partially eroded, which led to the formation of a new planation surface.
In the Eocene, the Afar Mantle plume, plume, a broad regional uplift, deformed the lithosphere, leading to the eruption of flood basalts. Three major formations may be distinguished: Ashangi Basalts, lower basalts, Intra-volcanic sedimentary rock in North Ethiopia, interbedded lacustrine deposits and Alaji Basalts, upper basalts.
Almost at the same time, the Mekelle Dolerite intruded into the Mesozoic sediments, following joints and Fault (geology), faults.
A new magma intrusion occurred in the Early Miocene, which gave rise to Phonolite series in North Ethiopia, phonolite plugs, mainly in the Adwa area and also in Dogu’a Tembien.
The present geomorphology is marked by deep valleys, eroded as a result of the regional uplift. Throughout the Quaternary, deposition of alluvium and freshwater tufa occurred in the valley bottoms.
Fossils
In Tigray, there are two main fossil-bearing geological units. The Antalo Limestone (upper Jurassic) is the largest. Its marine deposits comprise mainly benthic marine invertebrates. Also, the Tertiary lacustrine deposits, interbedded in the basalt formations, contain a range of silicified mollusc fossils.
In the Antalo Limestone: large ''Paracenoceratidae'' cephalopods (nautilus); ''Nerineidae'' indet.; sea urchins; Rhynchonellid brachiopod; crustaceans; coral colonies; crinoid stems.
In the Tertiary Intra-volcanic sedimentary rock in North Ethiopia, silicified lacustrine deposits: ''Pila (gastropod)''; ''Lanistes'' sp.; ''Pirenella conica''; and land snails (''Achatinidae'' indet.).
All snail shells, both fossil and recent, are called ''t’uyo'' in Tigrinya language, which means ‘helicoidal’.
Traditional uses of rock
As Tigray holds a wide variety of rock types, there is expectedly a varied use of rock.
:* Natural stone masonry. Preferentially, the easier shaped limestone and sandstone are used to build homesteads and churches, but particularly in the upland areas, basalt is also used. Traditionally, fermented mud will be used as mortar
:* Fencing of homesteads, generally in dry stones
:* Church bells, generally three elongated plates in phonolite or clinkstone, with different tonalities
:* Milling stone: for this purpose plucked-bedrock pits, small rock-cut basins that naturally occur in rivers with Kolk (vortex), kolks, are excavated from the river bed and further shaped. Mill (grinding), Milling is done at home using an elongated small boulder
:* Door and window lintels, prepared from rock types that frequently have an elongated shape (sandstone, phonolite, limestone), or that are easily shaped (tufa)
:* Troughs for livestock watering and feeding, generally hewn from tufa
:* Footpath Sidewalk, paving, generally done as community service, community work. Some very ancient paved footpaths occur on major communication lines dating back to the period before the introduction of the automobile
:* foot travellers stop, pray and put an additional stone
:* Stones collected from farmlands in order to free space for the crop, and heaped in typical rounded metres-high heaps, called ''zala''
:* Contour bunding or ''gedeba'': Terrace (agriculture), terrace walls in dry stone, typically laid out along the contour for sake of soil conservation
:* Check dams or ''qetri'' in gullies for sake of gully erosion control
:* Cobble stones, used for paving secondary streets in the towns. Generally limestone is used.
Major mountains
:* Ferrah Imba, 3954 metres, summit of the Tsibet massif in Endamekoni ''woreda'' (), and highest peak of Tigray
:* Amba Alagi, Imba Alaje, 3438 metres, in Alaje ''woreda'' ()
:* Mugulat, 3263 metres, in Ganta Afeshum ''woreda'' (); one of its spurs is crossed by the Siqurto foot tunnel
:* Asimba, 3199 metres, in Irob (Ethiopian District), Irob ''woreda'' ()
:* Upper plateaus of the Atsbi Horst at 3057 metres in Atsbi Wenberta ''woreda'' ()
:* Maebino, 3031 metres, in Irob (Ethiopian District), Irob ''woreda'' ()
:* Imba Tsion, 2917 metres, in
Hawzen
Hawzen ( Ge'ez: ሓውዜን) is a town in northern Ethiopia. Located in the Misraqawi (Eastern) Zone of the Tigray Region (or ''kilil''), this town has a latitude and longitude of with an elevation of 2105 meters above sea level. Its market da ...
''woreda'' ()
:* Ekli Imba, 2799 metres, summit of the Arebay massif in Degua Tembien ''woreda'' ()
:* Amba Aradam, Imba Aradom – sometimes transliterated as Amba Aradam, 2756 metres, in Hintalo Wajirat ''woreda'' ()
:* Soloda, 2436 metres, part of the Adwa plugs in
Adwa
Adwa ( ti, ዓድዋ; amh, ዐድዋ; also spelled Aduwa) is a town and separate woreda in Tigray Region, Ethiopia. It is best known as the community closest to the site of the 1896 Battle of Adwa, in which Ethiopian soldiers defeated Italian ...
''woreda'' ()
:* Imba Neway, 2388 metres, in Abergele (woreda)()
Water challenge

Overall, the region is semi-arid. The wet season lasts only for a couple of months. The farmers are adapted to this, but the problem arises when rains are less than normal. Another major challenge is providing water to urban areas. Smaller towns, but particularly Mekelle, face endemic water shortages. Reservoirs have been built, but their management is sub-optimal.
Wildlife
Large mammals

Besides elephants in Western Tigray and the endemic gelada baboon on the highest mountains, large mammals in the region, with scientific (italics), English and Tigrinya language names, are:
* ''Cercopithecus aethiops''; grivet monkey, ወዓግ ()
* ''Crocuta crocuta'', spotted hyena, ዝብኢ ()
* ''Caracal caracal'', caracal, ጭክ ኣንበሳ ()
* ''Panthera pardus'', leopard, ነብሪ ()
* ''Xerus rutilus'', unstriped ground squirrel, ምጹጽላይ or ጨጨራ (, )
* ''Canis mesomelas'', black-backed jackal, ቡኳርያ ()
* ''Canis anthus'', golden jackal, ቡኳርያ ()
* ''Papio hamadryas'', hamadryas baboon, ጋውና ()
* ''Procavia capensis'', rock hyrax, ጊሐ ()
* ''Felis silvestris'', African wildcat, ሓክሊ ድሙ ()
* ''Civettictis civetta'', African civet, ዝባድ ()
* ''Papio anubis'', olive baboon, ህበይ ()
* ''Ichneumia albicauda'', white-tailed mongoose, ፂሒራ ()
* ''Herpestes ichneumon'', large grey mongoose, ፂሒራ ()
* ''Hystrix cristata'', crested porcupine, ቅንፈዝ ()
* ''Oreotragus oreotragus''; klipspringer, ሰስሓ ()
* ''Orycteropus afer'', aardvark, ፍሒራ ()
* ''Genetta genetta'', common genet, ስልሕልሖት ()
* ''Lepus capensis'', cape hare, ማንቲለ ()
* ''Mellivora capensis'', honey badger, ትትጊ ()
Small rodents
The most common pest rodents with widespread distribution in agricultural fields and storage areas are three Ethiopian endemic species: the Dembea grass rat (''Arvicanthis dembeensis'', sometimes considered a subspecies of ''Arvicanthis niloticus''), Ethiopian white-footed rat (''Stenocephalemys albipes''), and Awash multimammate mouse (''Mastomys awashensis'').
Bats
Bats occur in natural caves, church buildings and abandoned homesteads. The large colony of bats that roosts in Zeyi cave comprises ''Hipposideros megalotis'' (Ethiopian large-eared roundleaf bat), ''Hipposideridae, Hipposideros tephrus'', and ''Rhinolophus blasii'' (Blasius's horseshoe bat).
[The Zeyi Cave Geosite in Northern Ethiopia](_blank)
/ref>
Birds
With its numerous exclosures, forest fragments and church forests, Tigray is a birdwatcher's paradise. Detailed inventories
Administrative zones and districts
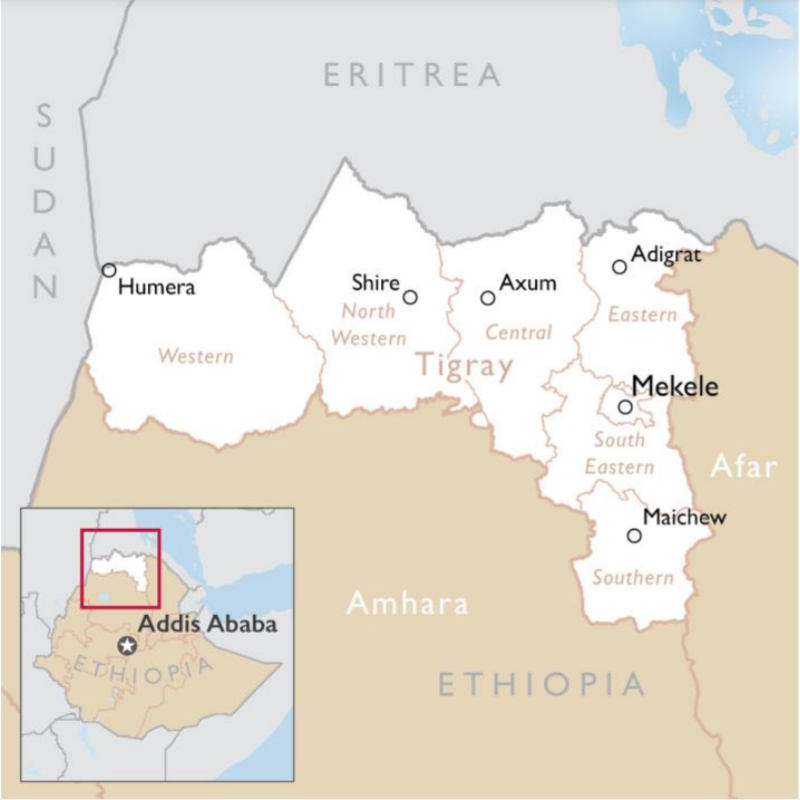
 Like other Regions in Ethiopia, Tigray is subdivided into administrative zones, and further into ''woredas'' or districts. Up to January 2020, these were the ''woredas'' of Tigray:
* Mehakelegnaw Zone, Central Tigray
** Abergele (woreda), Abergele
** Abiy Addi, Abiy Addi Town
** Adwa (woreda), Adwa
** Adwa, Adwa Town
** Axum, Aksum Town
** Degua Tembien, Dogu'a Tembien
** Enticho (woreda), Enticho
** Kola Tembien
** La'ilay Maychew
** Mereb Lehe
** Naeder Adet
** Tahtay Maychew
** Werie Lehe
* Misraqawi Zone, East Tigray
** Adigrat, Adigrat Town
** Atsbi Wenberta
** Ganta Afeshum
** Gulomahda
** Hawzen (woreda), Hawzen
** Irob (woreda), Irob
** Kilte Awulaelo
** Saesi Tsaedaemba
** Wukro, Wukro Town
* Semien Mi'irabawi Zone, North West Tigray
** Asigede Tsimbela
** La'ilay Adiyabo
** Medebay Zana
** Tahtay Adiyabo
** Tahtay Koraro
** Tselemti
** Shiraro, Ethiopia, Shiraro Town
** Shire, Ethiopia, Shire Town
* Debubawi Zone, South Tigray (Disputed)
** Alaje
** Alamata (woreda), Alamata
** Alamata, Alamata Town
** Endamehoni
** Korem, Korem Town
** Maychew, Maychew Town
** Ofla
** Raya Azebo
* Debub Misraqawi Zone, South East Tigray
** Enderta (woreda), Enderta
** Hintalo Wajirat
** Samre (woreda), Samre
* Mi'irabawi Zone, West Tigray (Disputed)
** Kafta Humera
** Humera, Humera Town
** Wolqayt
** Tsegede
*
Like other Regions in Ethiopia, Tigray is subdivided into administrative zones, and further into ''woredas'' or districts. Up to January 2020, these were the ''woredas'' of Tigray:
* Mehakelegnaw Zone, Central Tigray
** Abergele (woreda), Abergele
** Abiy Addi, Abiy Addi Town
** Adwa (woreda), Adwa
** Adwa, Adwa Town
** Axum, Aksum Town
** Degua Tembien, Dogu'a Tembien
** Enticho (woreda), Enticho
** Kola Tembien
** La'ilay Maychew
** Mereb Lehe
** Naeder Adet
** Tahtay Maychew
** Werie Lehe
* Misraqawi Zone, East Tigray
** Adigrat, Adigrat Town
** Atsbi Wenberta
** Ganta Afeshum
** Gulomahda
** Hawzen (woreda), Hawzen
** Irob (woreda), Irob
** Kilte Awulaelo
** Saesi Tsaedaemba
** Wukro, Wukro Town
* Semien Mi'irabawi Zone, North West Tigray
** Asigede Tsimbela
** La'ilay Adiyabo
** Medebay Zana
** Tahtay Adiyabo
** Tahtay Koraro
** Tselemti
** Shiraro, Ethiopia, Shiraro Town
** Shire, Ethiopia, Shire Town
* Debubawi Zone, South Tigray (Disputed)
** Alaje
** Alamata (woreda), Alamata
** Alamata, Alamata Town
** Endamehoni
** Korem, Korem Town
** Maychew, Maychew Town
** Ofla
** Raya Azebo
* Debub Misraqawi Zone, South East Tigray
** Enderta (woreda), Enderta
** Hintalo Wajirat
** Samre (woreda), Samre
* Mi'irabawi Zone, West Tigray (Disputed)
** Kafta Humera
** Humera, Humera Town
** Wolqayt
** Tsegede
* Mekelle
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a List of zones of Ethiopia, special zone and capital city, capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta province, Enderta Awrajj ...
(special zone)
In 2018 and 2019, after multiple village discussions that were often vigorous in the more remote areas, 21 independent urban administrations were added and other boundaries re-drawn, resulting in an increase from 35 to 88 ''woredas'' in January 2020:
* Mehakelegnaw Zone, Central Tigray
** Abergele (woreda), Abergele
** Adet
** Abiy Addi, Abiy Addi Town
** Adwa (woreda), Adwa
** Adwa, Adwa Town
** Ahlerorn
** Ahsea
** Axum, Aksum Town
** Chila, Tigray, Chila
** Egada Arbi
** Egela
** Emba Seneyti
** Endaleiasi
** Enticho Town
** Hahayle
** Kayeh Tekli
** Kola Tembien, Kola Temben
** La'ilay Maychew, Laelay Maychew
** Naeder Adet, Naeder
** Rama, Tigray, Rama
** Tahtay Maychew
** Tanqwa Melash
* Misraqawi Zone, East Tigray
** Adigrat, Adigrat Town
** Agulae
** Atsbi Wenberta, Atsbi
** Atsbi Town
** Bizet, Tigray, Bizet
** Edaga Hamus Town
** Irob (woreda), Erob
** Freweyni Town
** Ganta Afeshum
** Geralta
** Hawzen (woreda), Hawzen
** Hawzen Town
** Irob (woreda), Irob
** Kilte Awulaelo, Kelete Awelallo
** Saesi Tsaedaemba, Saesie
** Tsaeda Emba
** Wukro, Wukro Town
** Zala Anbesa Town
* Semien Mi'irabawi Zone, North West Tigray
** Adi Daero
** Adi Hageray
** Asigede Tsimbela, Asgede
** Dima, Tigray, Dima
** Endabaguna Town
** Indasilassie
** La'ilay Adiyabo, Laelay Adiabo
** May Tsebri Town
** Selekleka
** Seyemti Adyabo
** Shiraro, Ethiopia, Sheraro Town
** Tahtay Adiyabo
** Tahtay Koraro
** Tselemti
** Tsimbia
** Zena, Tigray, Zena
* Debubawi Zone, South Tigray
** Alamata, Alamata Town
** Bora, Tigray, Bora
** Chercher, Tigray, Chercher
** Alaje, Emba Alaje
** Endamehoni
** Korem, Korem Town
** Maychew, Maichew Town
** Mekhoni Town
** Neqsage
** Ofla
** Raya Alamata
** Raya Azebo
** Selewa
** Zata
* Debub Misraqawi Zone, South East Tigray
** Adigudom
** Dogua Temberi
** Enderta (woreda), Enderta
** Hagere Setam Town
** Hintalo Wajirat, Hintalo
** Saharti
** Samre (woreda), Samre
** Wajirat
* Mi'irabawi Zone, West Tigray
** Awora
** Dansha Town
** Kafta Humera
** Korant
** May Gaba
** May Kadra
** Setit Hemera
** Tsegede
** Wolqayt, Welkalt
* Mekelle
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a List of zones of Ethiopia, special zone and capital city, capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta province, Enderta Awrajj ...
(special zone)
Major cities
Mekelle
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a List of zones of Ethiopia, special zone and capital city, capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta province, Enderta Awrajj ...
, home to Mekelle University, Mekelle Institute of Technology, Microlink College, Nile College, and Mekelle College of Teacher Education is the capital of Tigray, near the geographic center of the state.
Other Tigray cities functioning as centers of Ethiopian metropolitan areas include:
:* Adigrat (home of Adigrat University, Debre Damo, Debre Damo monastery and Addis Pharmaceuticals)
:* Adwa
Adwa ( ti, ዓድዋ; amh, ዐድዋ; also spelled Aduwa) is a town and separate woreda in Tigray Region, Ethiopia. It is best known as the community closest to the site of the 1896 Battle of Adwa, in which Ethiopian soldiers defeated Italian ...
(home of Adwa Pan-African University, Adwa Pan African University,)
:* Axum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
(home of Aksum University,)
:* Maychew
Maychew, also Maichew ( ti, ማይጨው, "salt water"), is a town and woreda in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. It is located at 665 km north of Addis Ababa along Ethiopian Highway 2. According to Ethiopia’s agro-ecological setting, Maychew ...
(home of Raya University)
Of the 10 largest cities in Tigray, Maychew
Maychew, also Maichew ( ti, ማይጨው, "salt water"), is a town and woreda in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. It is located at 665 km north of Addis Ababa along Ethiopian Highway 2. According to Ethiopia’s agro-ecological setting, Maychew ...
has the highest elevation at 2479 meter above sea level. Plenty of smaller towns, like Atsbi
Atsbi (Ge'ez: ኣጽቢ) (officially known as Atsbi Endaselase Ge'ez: ኣጽቢ እንዳስላሴ ) is a town in Tigray Region, Tigray, Ethiopia. Located in the Misraqawi Zone, Misraqawi (Eastern) Zone of the Tigray Region, about 50 kilometers nor ...
and Idaga Hamus (Saesi Tsaedaemba), Edaga Hamus are located at even higher elevations. Of the large cities, Humera is located at the lowest altitude (585 m).
Government and politics
Executive branch
The executive branch is headed by the Chief Administrator of Tigray. The current president is Debretsion Gebremichael
Debretsion Gebremichael ( ti, ደብረጽዮን ገብረሚካኤል, pronunciation: ) is an Ethiopian politician and current president of the Tigray Region and chairman of Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF). His position as titular head ...
, a TPLF member, elected in 2018 and again in 2020 Tigray regional election, 2020.
Judicial branch
There are three levels of the Tigray state judiciary. The lowest level is the court of common pleas: each woreda maintains its own constitutionally mandated court of common pleas, which maintain jurisdiction over all justiciable matters. The intermediate-level court system is the district court system. Four courts of appeals exist, each retaining jurisdiction over appeals from common pleas, municipal, and county courts in an administrative zone. A case heard in this system is decided by a three-judge panel, and each judge is elected.
The highest-ranking court, the Tigray Supreme Court, is Tigray's "court of last resort". A seven-justice panel composes the court, which, by its own discretion, hears appeals from the courts of appeals, and retains original jurisdiction over limited matters. The chief judge is called the President of Tigray Supreme Court (''W/ro'' Hirity Miheretab).
Legislative branch
The State Council, which is the highest administrative body of the state, is made up of 152 members.
National politics
Tigray is represented by 38 representatives in the House of Peoples' Representatives, Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia House of Peoples' Representatives. But currently after the illegitimate postponement of the national election of Ethiopia Tigray has pulled it representative from the House of House of Peoples' Representatives and has no representation in the Federal parliamen
Demographics
 Based on the 2007 census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency (Ethiopia), Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), the Tigray Region has a population of 4,316,988, of whom 2,126,465 are men and 2,190,523 women; urban inhabitants number 844,040 or 19.55% of the population. With an estimated area of 84,722 km2, the region had an estimated density of 51 people per km2. In the entire region 992,635 households were counted, for an average of 4.4 people per household, with urban households having on average 3.4 and rural households 4.6.
Based on the 2007 census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency (Ethiopia), Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), the Tigray Region has a population of 4,316,988, of whom 2,126,465 are men and 2,190,523 women; urban inhabitants number 844,040 or 19.55% of the population. With an estimated area of 84,722 km2, the region had an estimated density of 51 people per km2. In the entire region 992,635 households were counted, for an average of 4.4 people per household, with urban households having on average 3.4 and rural households 4.6.["Census 2007"](_blank)
first draft, Tables 1, 4, 5, 6
Ethnicity
 With 96.55% of the local population, the region is predominantly inhabited by the Tigrinya-speaking Tigrayans, Tigrayan people. The Tigrinya language belongs to the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic family of languages. Most other residents hail from other Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic-speaking communities, including the Amhara people, Amhara, Irob, Afar people, Afar, Agaw people, Agaw and Oromo people, Oromo. Partly assimilated Oromo live in remoter villages in Raya Azebo and Alamata (woreda), whereas there are Agaw in Abergele (woreda). There are also Nilo-Saharan languages, Nilo-Saharan-speaking Kunama as well.
With 96.55% of the local population, the region is predominantly inhabited by the Tigrinya-speaking Tigrayans, Tigrayan people. The Tigrinya language belongs to the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic family of languages. Most other residents hail from other Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic-speaking communities, including the Amhara people, Amhara, Irob, Afar people, Afar, Agaw people, Agaw and Oromo people, Oromo. Partly assimilated Oromo live in remoter villages in Raya Azebo and Alamata (woreda), whereas there are Agaw in Abergele (woreda). There are also Nilo-Saharan languages, Nilo-Saharan-speaking Kunama as well.
Languages
The working language is Tigrinya. Saho language, Saho and Kunama language, Kunama are also spoken, and people in urban areas are also able to speak Amharic.
Notable people
*Mehari Taddele Mar, Mehari Taddele Maru, author, professor at European university Institute
*Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director General, World Health Organization WHO
*Meles Zenawi Asres, Prime Minister, Ethiopia 1995–2012
*Zeresenay Alemseged, Anthropologist, known for his discovery of Selam (Australopithecus), Selam, also referred to as "Lucy (Australopithecus), Lucy’s child", the almost-complete Fossil, fossilized remains of a 3.3 million-year-old child of the species ''Australopithecus afarensis''.
Agriculture
Cropping

Terracing and dam construction
 An important aspect of the agricultural work in Tigray after the end of the 1991 civil war was to minimize the problems of drought. In the past, Tigray was covered with forests and had a micro-climate that favoured the rains. Subsequently, the forests were cut down, usually to impoverish the population during the wars. Consequently, Tigray achieved a fair amount of rainfall during the rainy season, from August to September, but quickly lost these waters downstream. In the process the fertile soil of the fields eroded. After a few weeks of rain, the country again dried up.
An important aspect of the agricultural work in Tigray after the end of the 1991 civil war was to minimize the problems of drought. In the past, Tigray was covered with forests and had a micro-climate that favoured the rains. Subsequently, the forests were cut down, usually to impoverish the population during the wars. Consequently, Tigray achieved a fair amount of rainfall during the rainy season, from August to September, but quickly lost these waters downstream. In the process the fertile soil of the fields eroded. After a few weeks of rain, the country again dried up.
 The government undertook two projects in Tigray. The first was the construction of terraces which, with the agreement and help of local communities, go up to the tops of the mountains at 2,500 metres. The goal was to prevent the rainfall flowing away immediately so that it could be conserved for the agricultural season. On the highest terraces were planted trees, mainly eucalyptus, the dominant tree in Ethiopia and native to Australia. These plants created a new microclimate. The terracing method was very simple but required good organization. Long stretches of the fields were terraced by the villagers using stone walls from stones that erosion had exposed. The rains eroding the still non-terraced ground formed mudslides that were held by the topmost walls, which permitted construction of a new terrace field and another wall with uncovered stones, creating new ground terraced farmland every year.
The government undertook two projects in Tigray. The first was the construction of terraces which, with the agreement and help of local communities, go up to the tops of the mountains at 2,500 metres. The goal was to prevent the rainfall flowing away immediately so that it could be conserved for the agricultural season. On the highest terraces were planted trees, mainly eucalyptus, the dominant tree in Ethiopia and native to Australia. These plants created a new microclimate. The terracing method was very simple but required good organization. Long stretches of the fields were terraced by the villagers using stone walls from stones that erosion had exposed. The rains eroding the still non-terraced ground formed mudslides that were held by the topmost walls, which permitted construction of a new terrace field and another wall with uncovered stones, creating new ground terraced farmland every year.
 Another endeavour involved the construction of small reservoirs for local irrigation. As rains last only for a couple of months per year, reservoirs of different sizes allow harvesting runoff from the rainy season for further use in the dry season. The dams needed to create these basins are typically an embankment of a few hundreds of meters, closing off one part of a valley, with a maximum height of 20 metres. Each took months of work, in which people carried earth on their back, and with assistance of donkeys. Generally 2,000–3,000 people — men, women and children — carried the earth in simple baskets.
The small reservoirs in Tigray include:
* Addi Abagiè
* Addi Akhor
* Addi Amharay
* May Leiba
* Hiza'iti Wedi Cheber
* Addi Asme'e
* Chini
* Addi Gela
* Addi Hilo
* Addi Qenafiz
* Addi Shihu
* Aqushela
* Arato
* Belesat
* Betqua
* Chichat
* Dibdibo
* Dur Anbesa
* Imbagedo
* Inda Zib'i
* Era (reservoir)
* Era Quhila
* Gereb Mihiz
* Filiglig
* Gereb May Zib'i
* Gereb Bi'ati
* Gereb Awso
* Felaga
* Gereb Segen (Hintalo)
* Gereb Segen (May Gabat)
* Gereb Shegal
* Ginda'i
* Godew
Overall, these reservoirs suffer from rapid siltation. Part of the water that could be used for irrigation is lost through seepage; the positive side-effect is that this contributes to groundwater recharge.
Another endeavour involved the construction of small reservoirs for local irrigation. As rains last only for a couple of months per year, reservoirs of different sizes allow harvesting runoff from the rainy season for further use in the dry season. The dams needed to create these basins are typically an embankment of a few hundreds of meters, closing off one part of a valley, with a maximum height of 20 metres. Each took months of work, in which people carried earth on their back, and with assistance of donkeys. Generally 2,000–3,000 people — men, women and children — carried the earth in simple baskets.
The small reservoirs in Tigray include:
* Addi Abagiè
* Addi Akhor
* Addi Amharay
* May Leiba
* Hiza'iti Wedi Cheber
* Addi Asme'e
* Chini
* Addi Gela
* Addi Hilo
* Addi Qenafiz
* Addi Shihu
* Aqushela
* Arato
* Belesat
* Betqua
* Chichat
* Dibdibo
* Dur Anbesa
* Imbagedo
* Inda Zib'i
* Era (reservoir)
* Era Quhila
* Gereb Mihiz
* Filiglig
* Gereb May Zib'i
* Gereb Bi'ati
* Gereb Awso
* Felaga
* Gereb Segen (Hintalo)
* Gereb Segen (May Gabat)
* Gereb Shegal
* Ginda'i
* Godew
Overall, these reservoirs suffer from rapid siltation. Part of the water that could be used for irrigation is lost through seepage; the positive side-effect is that this contributes to groundwater recharge.
Vegetation and enclosures
 Tigray holds numerous exclosures, areas that are set aside for regreening. Logging and livestock grazing are not allowed there. Besides effects on biodiversity,
Tigray holds numerous exclosures, areas that are set aside for regreening. Logging and livestock grazing are not allowed there. Besides effects on biodiversity,[EthioTrees on Plan Vivo website](_blank)
/ref> The revenues are then reinvested in the villages, according to the priorities of the communities;[EthioTrees on Davines website](_blank)
/ref> it may be for an additional class in the village school, a water pond, conservation in the exclosures, or a store for incense.
Livestock
The CSA estimated in 2005 that farmers in Tigray had a total of 2,713,750 cattle (representing 7.0% of Ethiopia's total cattle), 72,640 sheep (0.42%), 208,970 goats (1.61%), 1,200 horses (less than 0.1%), 9,190 mules (6.24%), 386,600 asses (15.43%), 32,650 camels (7.15%), 3,180,240 poultry of all species (10.3%), and 20,480 beehives (0.47%). Cattle are an essential component in the dominant grain-plough agricultural system. In the rainy season, a large part of the cattle herds are in Transhumance in Ethiopia, transhumance.
Landmarks
 A distinctive feature of Tigray are its rock-hewn churches. Similar in design to those of Lalibela in the Amhara Region, these churches are found in four or five clusters – Gheralta, Teka-Tesfay,
A distinctive feature of Tigray are its rock-hewn churches. Similar in design to those of Lalibela in the Amhara Region, these churches are found in four or five clusters – Gheralta, Teka-Tesfay, Atsbi
Atsbi (Ge'ez: ኣጽቢ) (officially known as Atsbi Endaselase Ge'ez: ኣጽቢ እንዳስላሴ ) is a town in Tigray Region, Tigray, Ethiopia. Located in the Misraqawi Zone, Misraqawi (Eastern) Zone of the Tigray Region, about 50 kilometers nor ...
and Tembien Province, Tembien – with Wukro sometimes included. Some of the churches are considered earlier than those of Lalibela, perhaps dating from the eighth century. Mostly monolithic architecture, monolithic, with designs partly inspired by classical architecture, they are often located at the top of cliffs or steep hills, for security. For example, Tigray's ancient Debre Damo monastery is accessible only by climbing a rope 25 metres up a sheer cliff.
Looting has become a major issue in the Tigray Region, as archaeological sites have become sources for construction materials and ancient artifacts used for everyday purposes by local populations.
The area is famous for a single rock sculptured 23 meter long obelisk in Axum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
as well as for other fallen obelisks. The Axum treasure site of ancient Tigrayan history is a major landmark. Yeha is another important local landmark that is little-known outside the region.
Transport
Ground travel
A major north–south road corridor goes through Tigray. This is facilitated by Highway 2 which goes from Adigrat to Addis Ababa and Highway 3 which goes from Shire to Addis Ababa.
Air travel
 Tigray has one international airport and four commercial airports. The international airport is Alula Aba Nega Airport (MQX) near Mekelle. The region's four other commercial airports are Shire Airport (SHC), Humera Airport (HUE), Dansha Airport, and Axum Airport, Emperor Yohannes IV Airport (AXU), which serves Axum.
Tigray has one international airport and four commercial airports. The international airport is Alula Aba Nega Airport (MQX) near Mekelle. The region's four other commercial airports are Shire Airport (SHC), Humera Airport (HUE), Dansha Airport, and Axum Airport, Emperor Yohannes IV Airport (AXU), which serves Axum.
Sports
Mekelle 70 Enderta F.C. (Tigrinya: ጋንታ መቐለ 70 እንደርታ) is an Ethiopian football club based in the capital, Mekelle. They are a member of the Ethiopian Football Federation and currently play in the top division of Ethiopian football, the Ethiopian Premier League. They are known by the nickname the ''Lion of Judah'' (ምዓም ኣንበሳ /ምዓም አናብስት/ኣናብስቶቹ). The club won its first Ethiopian Premier League title in the 2018–2019 Ethiopian Premier League Season.
Shire Endaselassie F.C., Shire Indasillasie F.C. (Tigrinya: ጋንታ ስሑል ሽረ, also known as Sihul Shire FC) is an Ethiopian football club based in Shire Inda Selassie, Shire. They are a member of the Ethiopian Football Federation and play in the Ethiopian Premier League, the first division of football in Ethiopia.
Mekele City, Suhul Shire, and Adigrat University football clubs were Tigray-based clubs among the 14 clubs to participate in the Ethiopian Premier League in 2020/2021. However, due to the war, they were replaced by other clubs from the League one rank below the Ethiopian Premier League.
Education
At the regional level, the Tigray Education Bureau governs primary and secondary educational institutions. At the municipal level, there are approximately 300 school districts region-wide.
Colleges and universities
* Adigrat University
* Axum University
* Adwa Pan-African University
* Ethio-lmage College
* Greenwich College
* Hashenge College
* Mars Engineering College
* Mekelle University
* Mekelle Institute of Technology
* New Millennium College
* Nile College
* Raya University
* Sehba Info Tech & Business College
* Signal College
* St. Mary's University College
* Winner college Axum
Libraries
Tigray is home to Ethiopia's most extensive church libraries that are found in the eastern and central zones of the region. There are several ongoing digitization projects to preserve previous historical texts.
* Axum Heritage Foundation
* Romanat Qeddus Mika'el Church
* Gunda Gunde, Gunda Gunde Monastery
* Agwaza Monastery
* Debre Damo, Debre Damo Monastery
Non-governmental organisations
Major NGOs, involved in development activities are:
*Relief Society of Tigray
*Tigrai Development Association
Tegaru Disaster Relief Fund (TDRF)
Notes
References
External links
Tigray Region Web Portal
Tigray Revenue Development Authority
Map of Tigray Region at DPPA of Ethiopia
Endowment Fund for the Rehabilitation of Tigray website
* [http://www.ethiopiantreasures.co.uk/pages/mekele.htm Ethiopian Treasures – Emperor Yohannes IV Castle – Mekele]
Future Observatory
– Dam Building in Tigray by David Mercer
"Tigrayans want end to border row"
by Elizabeth Blunt, ''BBC News'', 20 December 2007
Tigray: Then and Now
– the son of Mohamed Amin covers sustainable agriculture in Tigray following the Horn of Africa drought in 2011.
{{Authority control
Tigray Region,
Regions of Ethiopia
 The Kingdom of Aksum was a trading empire rooted in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia. It existed from approximately 100–940 AD, growing from the proto-Aksumite
The Kingdom of Aksum was a trading empire rooted in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia. It existed from approximately 100–940 AD, growing from the proto-Aksumite 
 After the February 1974 popular revolution, the first signal of any mass uprising was the actions of the soldiers of the 4th Brigade of the 4th Army Division in Nagelle in southern Ethiopia. The Coordinating Committee of the Armed Forces, Police, and Territorial Army, or the
After the February 1974 popular revolution, the first signal of any mass uprising was the actions of the soldiers of the 4th Brigade of the 4th Army Division in Nagelle in southern Ethiopia. The Coordinating Committee of the Armed Forces, Police, and Territorial Army, or the  In addition, the Derg in 1975 nationalized most industries and private and somewhat secure urban real-estate holdings. But mismanagement, corruption, and general hostility to the Derg's violent rule, coupled with the draining effects of constant warfare with the separatist guerrilla movements in Tigray, led to a drastic fall in general productivity of food and cash crops. In October 1978, the Derg announced the National Revolutionary Development Campaign to mobilize human and material resources to transform the economy, which led to a Ten-Year Plan (1984/1985-1993/1994) to expand agricultural and industrial output, forecasting a 6.5% growth in GDP and a 3.6% rise in per capita income. Instead per capita income declined 0.8% over this period. Famine scholar
In addition, the Derg in 1975 nationalized most industries and private and somewhat secure urban real-estate holdings. But mismanagement, corruption, and general hostility to the Derg's violent rule, coupled with the draining effects of constant warfare with the separatist guerrilla movements in Tigray, led to a drastic fall in general productivity of food and cash crops. In October 1978, the Derg announced the National Revolutionary Development Campaign to mobilize human and material resources to transform the economy, which led to a Ten-Year Plan (1984/1985-1993/1994) to expand agricultural and industrial output, forecasting a 6.5% growth in GDP and a 3.6% rise in per capita income. Instead per capita income declined 0.8% over this period. Famine scholar  At the end of the Mesozoic tectonic phase, a new (Cretaceous) planation took place. After that, the deposition of continental sediments (Amba Aradam Formation) indicates the presence of less shallow seas, probably caused by a regional uplift. At the beginning of the Caenozoic, there was a relative tectonic quiescence, during which the Amba Aradam Sandstones were partially eroded, which led to the formation of a new planation surface.
In the Eocene, the Afar Mantle plume, plume, a broad regional uplift, deformed the lithosphere, leading to the eruption of flood basalts. Three major formations may be distinguished: Ashangi Basalts, lower basalts, Intra-volcanic sedimentary rock in North Ethiopia, interbedded lacustrine deposits and Alaji Basalts, upper basalts. Almost at the same time, the Mekelle Dolerite intruded into the Mesozoic sediments, following joints and Fault (geology), faults.
A new magma intrusion occurred in the Early Miocene, which gave rise to Phonolite series in North Ethiopia, phonolite plugs, mainly in the Adwa area and also in Dogu’a Tembien. The present geomorphology is marked by deep valleys, eroded as a result of the regional uplift. Throughout the Quaternary, deposition of alluvium and freshwater tufa occurred in the valley bottoms.
At the end of the Mesozoic tectonic phase, a new (Cretaceous) planation took place. After that, the deposition of continental sediments (Amba Aradam Formation) indicates the presence of less shallow seas, probably caused by a regional uplift. At the beginning of the Caenozoic, there was a relative tectonic quiescence, during which the Amba Aradam Sandstones were partially eroded, which led to the formation of a new planation surface.
In the Eocene, the Afar Mantle plume, plume, a broad regional uplift, deformed the lithosphere, leading to the eruption of flood basalts. Three major formations may be distinguished: Ashangi Basalts, lower basalts, Intra-volcanic sedimentary rock in North Ethiopia, interbedded lacustrine deposits and Alaji Basalts, upper basalts. Almost at the same time, the Mekelle Dolerite intruded into the Mesozoic sediments, following joints and Fault (geology), faults.
A new magma intrusion occurred in the Early Miocene, which gave rise to Phonolite series in North Ethiopia, phonolite plugs, mainly in the Adwa area and also in Dogu’a Tembien. The present geomorphology is marked by deep valleys, eroded as a result of the regional uplift. Throughout the Quaternary, deposition of alluvium and freshwater tufa occurred in the valley bottoms.
 Overall, the region is semi-arid. The wet season lasts only for a couple of months. The farmers are adapted to this, but the problem arises when rains are less than normal. Another major challenge is providing water to urban areas. Smaller towns, but particularly Mekelle, face endemic water shortages. Reservoirs have been built, but their management is sub-optimal.
Overall, the region is semi-arid. The wet season lasts only for a couple of months. The farmers are adapted to this, but the problem arises when rains are less than normal. Another major challenge is providing water to urban areas. Smaller towns, but particularly Mekelle, face endemic water shortages. Reservoirs have been built, but their management is sub-optimal.
 Besides elephants in Western Tigray and the endemic gelada baboon on the highest mountains, large mammals in the region, with scientific (italics), English and Tigrinya language names, are:
* ''Cercopithecus aethiops''; grivet monkey, ወዓግ ()
* ''Crocuta crocuta'', spotted hyena, ዝብኢ ()
* ''Caracal caracal'', caracal, ጭክ ኣንበሳ ()
* ''Panthera pardus'', leopard, ነብሪ ()
* ''Xerus rutilus'', unstriped ground squirrel, ምጹጽላይ or ጨጨራ (, )
* ''Canis mesomelas'', black-backed jackal, ቡኳርያ ()
* ''Canis anthus'', golden jackal, ቡኳርያ ()
* ''Papio hamadryas'', hamadryas baboon, ጋውና ()
* ''Procavia capensis'', rock hyrax, ጊሐ ()
* ''Felis silvestris'', African wildcat, ሓክሊ ድሙ ()
* ''Civettictis civetta'', African civet, ዝባድ ()
* ''Papio anubis'', olive baboon, ህበይ ()
* ''Ichneumia albicauda'', white-tailed mongoose, ፂሒራ ()
* ''Herpestes ichneumon'', large grey mongoose, ፂሒራ ()
* ''Hystrix cristata'', crested porcupine, ቅንፈዝ ()
* ''Oreotragus oreotragus''; klipspringer, ሰስሓ ()
* ''Orycteropus afer'', aardvark, ፍሒራ ()
* ''Genetta genetta'', common genet, ስልሕልሖት ()
* ''Lepus capensis'', cape hare, ማንቲለ ()
* ''Mellivora capensis'', honey badger, ትትጊ ()
Besides elephants in Western Tigray and the endemic gelada baboon on the highest mountains, large mammals in the region, with scientific (italics), English and Tigrinya language names, are:
* ''Cercopithecus aethiops''; grivet monkey, ወዓግ ()
* ''Crocuta crocuta'', spotted hyena, ዝብኢ ()
* ''Caracal caracal'', caracal, ጭክ ኣንበሳ ()
* ''Panthera pardus'', leopard, ነብሪ ()
* ''Xerus rutilus'', unstriped ground squirrel, ምጹጽላይ or ጨጨራ (, )
* ''Canis mesomelas'', black-backed jackal, ቡኳርያ ()
* ''Canis anthus'', golden jackal, ቡኳርያ ()
* ''Papio hamadryas'', hamadryas baboon, ጋውና ()
* ''Procavia capensis'', rock hyrax, ጊሐ ()
* ''Felis silvestris'', African wildcat, ሓክሊ ድሙ ()
* ''Civettictis civetta'', African civet, ዝባድ ()
* ''Papio anubis'', olive baboon, ህበይ ()
* ''Ichneumia albicauda'', white-tailed mongoose, ፂሒራ ()
* ''Herpestes ichneumon'', large grey mongoose, ፂሒራ ()
* ''Hystrix cristata'', crested porcupine, ቅንፈዝ ()
* ''Oreotragus oreotragus''; klipspringer, ሰስሓ ()
* ''Orycteropus afer'', aardvark, ፍሒራ ()
* ''Genetta genetta'', common genet, ስልሕልሖት ()
* ''Lepus capensis'', cape hare, ማንቲለ ()
* ''Mellivora capensis'', honey badger, ትትጊ ()

 Like other Regions in Ethiopia, Tigray is subdivided into administrative zones, and further into ''woredas'' or districts. Up to January 2020, these were the ''woredas'' of Tigray:
* Mehakelegnaw Zone, Central Tigray
** Abergele (woreda), Abergele
** Abiy Addi, Abiy Addi Town
** Adwa (woreda), Adwa
** Adwa, Adwa Town
** Axum, Aksum Town
** Degua Tembien, Dogu'a Tembien
** Enticho (woreda), Enticho
** Kola Tembien
** La'ilay Maychew
** Mereb Lehe
** Naeder Adet
** Tahtay Maychew
** Werie Lehe
* Misraqawi Zone, East Tigray
** Adigrat, Adigrat Town
** Atsbi Wenberta
** Ganta Afeshum
** Gulomahda
** Hawzen (woreda), Hawzen
** Irob (woreda), Irob
** Kilte Awulaelo
** Saesi Tsaedaemba
** Wukro, Wukro Town
* Semien Mi'irabawi Zone, North West Tigray
** Asigede Tsimbela
** La'ilay Adiyabo
** Medebay Zana
** Tahtay Adiyabo
** Tahtay Koraro
** Tselemti
** Shiraro, Ethiopia, Shiraro Town
** Shire, Ethiopia, Shire Town
* Debubawi Zone, South Tigray (Disputed)
** Alaje
** Alamata (woreda), Alamata
** Alamata, Alamata Town
** Endamehoni
** Korem, Korem Town
** Maychew, Maychew Town
** Ofla
** Raya Azebo
* Debub Misraqawi Zone, South East Tigray
** Enderta (woreda), Enderta
** Hintalo Wajirat
** Samre (woreda), Samre
* Mi'irabawi Zone, West Tigray (Disputed)
** Kafta Humera
** Humera, Humera Town
** Wolqayt
** Tsegede
*
Like other Regions in Ethiopia, Tigray is subdivided into administrative zones, and further into ''woredas'' or districts. Up to January 2020, these were the ''woredas'' of Tigray:
* Mehakelegnaw Zone, Central Tigray
** Abergele (woreda), Abergele
** Abiy Addi, Abiy Addi Town
** Adwa (woreda), Adwa
** Adwa, Adwa Town
** Axum, Aksum Town
** Degua Tembien, Dogu'a Tembien
** Enticho (woreda), Enticho
** Kola Tembien
** La'ilay Maychew
** Mereb Lehe
** Naeder Adet
** Tahtay Maychew
** Werie Lehe
* Misraqawi Zone, East Tigray
** Adigrat, Adigrat Town
** Atsbi Wenberta
** Ganta Afeshum
** Gulomahda
** Hawzen (woreda), Hawzen
** Irob (woreda), Irob
** Kilte Awulaelo
** Saesi Tsaedaemba
** Wukro, Wukro Town
* Semien Mi'irabawi Zone, North West Tigray
** Asigede Tsimbela
** La'ilay Adiyabo
** Medebay Zana
** Tahtay Adiyabo
** Tahtay Koraro
** Tselemti
** Shiraro, Ethiopia, Shiraro Town
** Shire, Ethiopia, Shire Town
* Debubawi Zone, South Tigray (Disputed)
** Alaje
** Alamata (woreda), Alamata
** Alamata, Alamata Town
** Endamehoni
** Korem, Korem Town
** Maychew, Maychew Town
** Ofla
** Raya Azebo
* Debub Misraqawi Zone, South East Tigray
** Enderta (woreda), Enderta
** Hintalo Wajirat
** Samre (woreda), Samre
* Mi'irabawi Zone, West Tigray (Disputed)
** Kafta Humera
** Humera, Humera Town
** Wolqayt
** Tsegede
* 
 Based on the 2007 census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency (Ethiopia), Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), the Tigray Region has a population of 4,316,988, of whom 2,126,465 are men and 2,190,523 women; urban inhabitants number 844,040 or 19.55% of the population. With an estimated area of 84,722 km2, the region had an estimated density of 51 people per km2. In the entire region 992,635 households were counted, for an average of 4.4 people per household, with urban households having on average 3.4 and rural households 4.6.
In the previous census, conducted in 1994, the region's population was 3,136,267, of whom 1,542,165 were men and 1,594,102 women; urban inhabitants numbered 621,210, or 14% of the population.
According to the CSA, , 53.99% of the total population had access to Water supply and sanitation in Ethiopia, safe drinking water, of whom 42.68% were rural inhabitants and 97.28% were urban. Values for other reported common indicators of the standard of living for Tigray include: 31.6% of the inhabitants fall into the lowest wealth quintile; adult literacy for men is 67.5% and for women 33.7%; and the infant mortality rate is 67 infant deaths per 1,000 live births, less than the national average of 77; at least half of these deaths occurred in the infants' first month of life.
The predominant religion in Tigray is Orthodox Christianity"Census 2007"
Based on the 2007 census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency (Ethiopia), Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), the Tigray Region has a population of 4,316,988, of whom 2,126,465 are men and 2,190,523 women; urban inhabitants number 844,040 or 19.55% of the population. With an estimated area of 84,722 km2, the region had an estimated density of 51 people per km2. In the entire region 992,635 households were counted, for an average of 4.4 people per household, with urban households having on average 3.4 and rural households 4.6.
In the previous census, conducted in 1994, the region's population was 3,136,267, of whom 1,542,165 were men and 1,594,102 women; urban inhabitants numbered 621,210, or 14% of the population.
According to the CSA, , 53.99% of the total population had access to Water supply and sanitation in Ethiopia, safe drinking water, of whom 42.68% were rural inhabitants and 97.28% were urban. Values for other reported common indicators of the standard of living for Tigray include: 31.6% of the inhabitants fall into the lowest wealth quintile; adult literacy for men is 67.5% and for women 33.7%; and the infant mortality rate is 67 infant deaths per 1,000 live births, less than the national average of 77; at least half of these deaths occurred in the infants' first month of life.
The predominant religion in Tigray is Orthodox Christianity"Census 2007" With 96.55% of the local population, the region is predominantly inhabited by the Tigrinya-speaking Tigrayans, Tigrayan people. The Tigrinya language belongs to the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic family of languages. Most other residents hail from other Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic-speaking communities, including the Amhara people, Amhara, Irob, Afar people, Afar, Agaw people, Agaw and Oromo people, Oromo. Partly assimilated Oromo live in remoter villages in Raya Azebo and Alamata (woreda), whereas there are Agaw in Abergele (woreda). There are also Nilo-Saharan languages, Nilo-Saharan-speaking Kunama as well.
With 96.55% of the local population, the region is predominantly inhabited by the Tigrinya-speaking Tigrayans, Tigrayan people. The Tigrinya language belongs to the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic family of languages. Most other residents hail from other Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic-speaking communities, including the Amhara people, Amhara, Irob, Afar people, Afar, Agaw people, Agaw and Oromo people, Oromo. Partly assimilated Oromo live in remoter villages in Raya Azebo and Alamata (woreda), whereas there are Agaw in Abergele (woreda). There are also Nilo-Saharan languages, Nilo-Saharan-speaking Kunama as well.

 An important aspect of the agricultural work in Tigray after the end of the 1991 civil war was to minimize the problems of drought. In the past, Tigray was covered with forests and had a micro-climate that favoured the rains. Subsequently, the forests were cut down, usually to impoverish the population during the wars. Consequently, Tigray achieved a fair amount of rainfall during the rainy season, from August to September, but quickly lost these waters downstream. In the process the fertile soil of the fields eroded. After a few weeks of rain, the country again dried up.
An important aspect of the agricultural work in Tigray after the end of the 1991 civil war was to minimize the problems of drought. In the past, Tigray was covered with forests and had a micro-climate that favoured the rains. Subsequently, the forests were cut down, usually to impoverish the population during the wars. Consequently, Tigray achieved a fair amount of rainfall during the rainy season, from August to September, but quickly lost these waters downstream. In the process the fertile soil of the fields eroded. After a few weeks of rain, the country again dried up.
 The government undertook two projects in Tigray. The first was the construction of terraces which, with the agreement and help of local communities, go up to the tops of the mountains at 2,500 metres. The goal was to prevent the rainfall flowing away immediately so that it could be conserved for the agricultural season. On the highest terraces were planted trees, mainly eucalyptus, the dominant tree in Ethiopia and native to Australia. These plants created a new microclimate. The terracing method was very simple but required good organization. Long stretches of the fields were terraced by the villagers using stone walls from stones that erosion had exposed. The rains eroding the still non-terraced ground formed mudslides that were held by the topmost walls, which permitted construction of a new terrace field and another wall with uncovered stones, creating new ground terraced farmland every year.
The government undertook two projects in Tigray. The first was the construction of terraces which, with the agreement and help of local communities, go up to the tops of the mountains at 2,500 metres. The goal was to prevent the rainfall flowing away immediately so that it could be conserved for the agricultural season. On the highest terraces were planted trees, mainly eucalyptus, the dominant tree in Ethiopia and native to Australia. These plants created a new microclimate. The terracing method was very simple but required good organization. Long stretches of the fields were terraced by the villagers using stone walls from stones that erosion had exposed. The rains eroding the still non-terraced ground formed mudslides that were held by the topmost walls, which permitted construction of a new terrace field and another wall with uncovered stones, creating new ground terraced farmland every year.
 Another endeavour involved the construction of small reservoirs for local irrigation. As rains last only for a couple of months per year, reservoirs of different sizes allow harvesting runoff from the rainy season for further use in the dry season. The dams needed to create these basins are typically an embankment of a few hundreds of meters, closing off one part of a valley, with a maximum height of 20 metres. Each took months of work, in which people carried earth on their back, and with assistance of donkeys. Generally 2,000–3,000 people — men, women and children — carried the earth in simple baskets.
The small reservoirs in Tigray include:
* Addi Abagiè
* Addi Akhor
* Addi Amharay
* May Leiba
* Hiza'iti Wedi Cheber
* Addi Asme'e
* Chini
* Addi Gela
* Addi Hilo
* Addi Qenafiz
* Addi Shihu
* Aqushela
* Arato
* Belesat
* Betqua
* Chichat
* Dibdibo
* Dur Anbesa
* Imbagedo
* Inda Zib'i
* Era (reservoir)
* Era Quhila
* Gereb Mihiz
* Filiglig
* Gereb May Zib'i
* Gereb Bi'ati
* Gereb Awso
* Felaga
* Gereb Segen (Hintalo)
* Gereb Segen (May Gabat)
* Gereb Shegal
* Ginda'i
* Godew
Overall, these reservoirs suffer from rapid siltation. Part of the water that could be used for irrigation is lost through seepage; the positive side-effect is that this contributes to groundwater recharge.
Another endeavour involved the construction of small reservoirs for local irrigation. As rains last only for a couple of months per year, reservoirs of different sizes allow harvesting runoff from the rainy season for further use in the dry season. The dams needed to create these basins are typically an embankment of a few hundreds of meters, closing off one part of a valley, with a maximum height of 20 metres. Each took months of work, in which people carried earth on their back, and with assistance of donkeys. Generally 2,000–3,000 people — men, women and children — carried the earth in simple baskets.
The small reservoirs in Tigray include:
* Addi Abagiè
* Addi Akhor
* Addi Amharay
* May Leiba
* Hiza'iti Wedi Cheber
* Addi Asme'e
* Chini
* Addi Gela
* Addi Hilo
* Addi Qenafiz
* Addi Shihu
* Aqushela
* Arato
* Belesat
* Betqua
* Chichat
* Dibdibo
* Dur Anbesa
* Imbagedo
* Inda Zib'i
* Era (reservoir)
* Era Quhila
* Gereb Mihiz
* Filiglig
* Gereb May Zib'i
* Gereb Bi'ati
* Gereb Awso
* Felaga
* Gereb Segen (Hintalo)
* Gereb Segen (May Gabat)
* Gereb Shegal
* Ginda'i
* Godew
Overall, these reservoirs suffer from rapid siltation. Part of the water that could be used for irrigation is lost through seepage; the positive side-effect is that this contributes to groundwater recharge.
 A distinctive feature of Tigray are its rock-hewn churches. Similar in design to those of Lalibela in the Amhara Region, these churches are found in four or five clusters – Gheralta, Teka-Tesfay,
A distinctive feature of Tigray are its rock-hewn churches. Similar in design to those of Lalibela in the Amhara Region, these churches are found in four or five clusters – Gheralta, Teka-Tesfay,  Tigray has one international airport and four commercial airports. The international airport is Alula Aba Nega Airport (MQX) near Mekelle. The region's four other commercial airports are Shire Airport (SHC), Humera Airport (HUE), Dansha Airport, and Axum Airport, Emperor Yohannes IV Airport (AXU), which serves Axum.
Tigray has one international airport and four commercial airports. The international airport is Alula Aba Nega Airport (MQX) near Mekelle. The region's four other commercial airports are Shire Airport (SHC), Humera Airport (HUE), Dansha Airport, and Axum Airport, Emperor Yohannes IV Airport (AXU), which serves Axum.