Tiger Z100 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living
 Following Linnaeus's first descriptions of the species, several tiger specimens were described and proposed as
Following Linnaeus's first descriptions of the species, several tiger specimens were described and proposed as
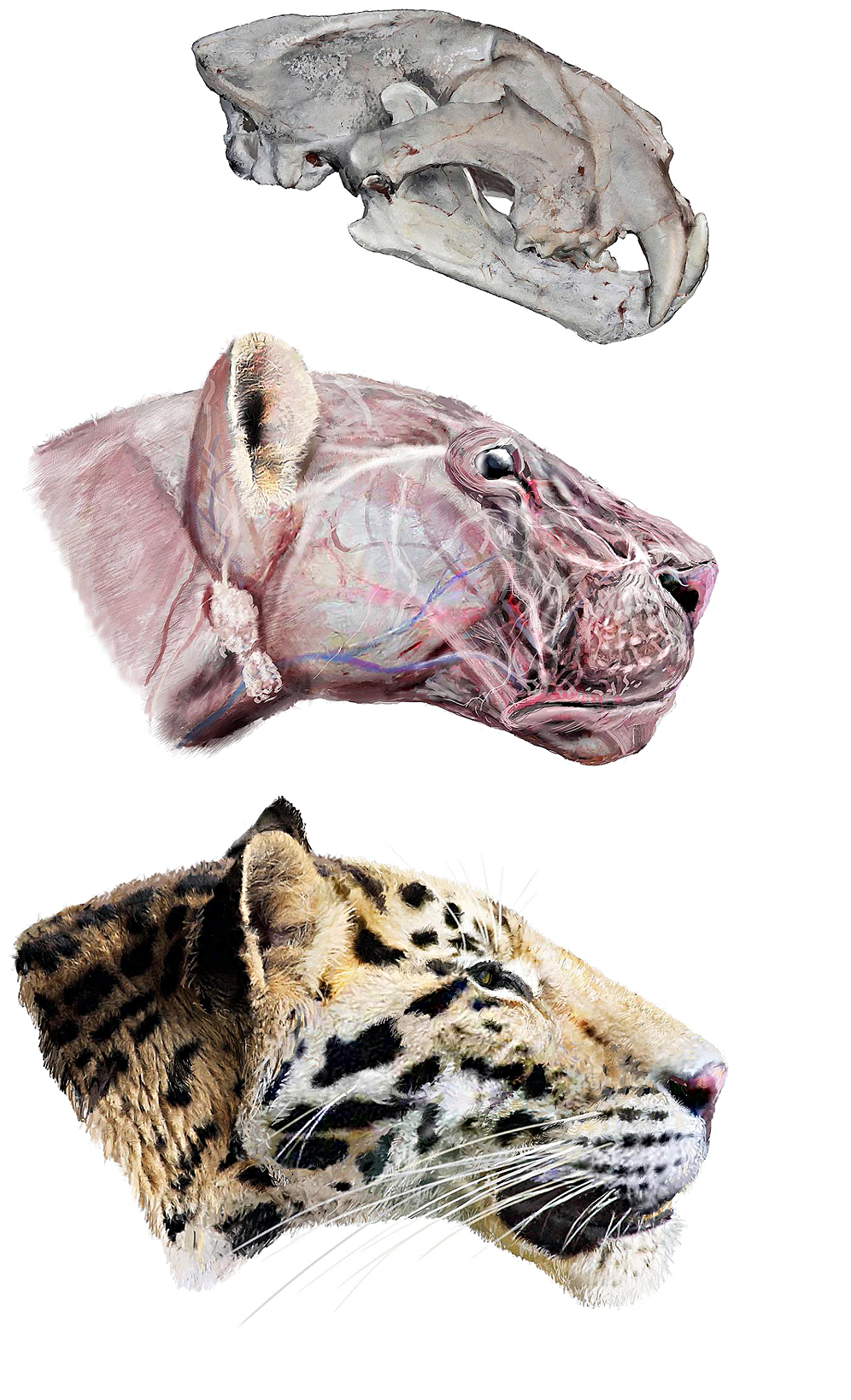 The tiger's closest living relatives were previously thought to be the ''Panthera'' species
The tiger's closest living relatives were previously thought to be the ''Panthera'' species
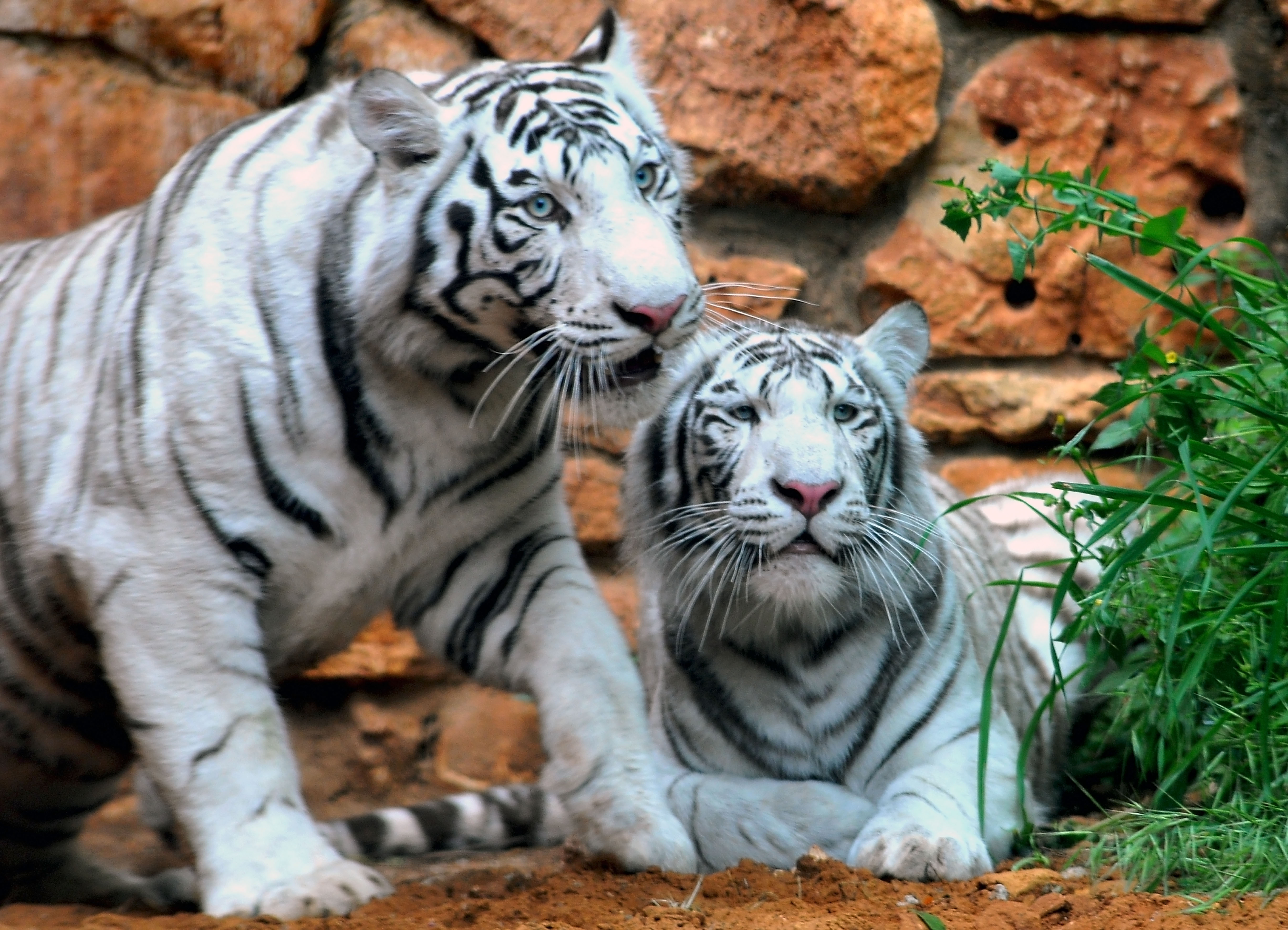 There are three other Polymorphism (biology), colour variants – white, golden and nearly stripeless snow white – that are now virtually non-existent in the wild due to the reduction of wild tiger populations, but continue in captive populations. The white tiger has white fur and Sepia (color), sepia-brown stripes. The golden tiger has a pale golden pelage with a blond tone and reddish-brown stripes. The snow white tiger is a morph with extremely faint stripes and a pale reddish-brown ringed tail. Both snow white and golden tigers are homozygous for CORIN gene mutations.
The white tiger lacks pheomelanin (which creates the orange colour), and has dark sepia-brown stripes and blue eyes. This altered pigmentation is caused by a mutant gene that is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, which is determined by a white Locus (genetics), locus. It is not an albinism, albino, as the eumelanin, dark pigments are scarcely affected. The mutation changes a single amino acid in the transporter protein SLC45A2. Both parents need to have the allele for whiteness to have white cubs.
Between the early and mid 20th century, white tigers were recorded and shot in the Indian states of Odisha, Bihar, Assam and in the area of Rewa, Madhya Pradesh. The local maharaja started breeding tigers in the early 1950s and kept a white male tiger together with its normal-coloured daughter; they had white cubs.
To preserve this recessive trait, only a few white individuals were used in captive breeding, which led to a high degree of inbreeding. Inbreeding depression is the main reason for many health problems of captive white tigers, including strabismus, stillbirth, cripple, deformities and premature death.
Other physical defects include cleft palate and scoliosis.
The Tiger Species Survival Plan has condemned the breeding of white tigers, alleging they are of mixed ancestry and of unknown lineage. The genes responsible for white colouration are represented by 0.001% of the population. The disproportionate growth in numbers of white tigers points to inbreeding among homozygous recessive individuals. This would lead to inbreeding depression and loss of genetic variability.
There are also records of pseudomelanic or black tigers which have thick stripes that merge. In Simlipal National Park, 37% of the tiger population has this condition, which has been linked to isolation and inbreeding.
There are three other Polymorphism (biology), colour variants – white, golden and nearly stripeless snow white – that are now virtually non-existent in the wild due to the reduction of wild tiger populations, but continue in captive populations. The white tiger has white fur and Sepia (color), sepia-brown stripes. The golden tiger has a pale golden pelage with a blond tone and reddish-brown stripes. The snow white tiger is a morph with extremely faint stripes and a pale reddish-brown ringed tail. Both snow white and golden tigers are homozygous for CORIN gene mutations.
The white tiger lacks pheomelanin (which creates the orange colour), and has dark sepia-brown stripes and blue eyes. This altered pigmentation is caused by a mutant gene that is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, which is determined by a white Locus (genetics), locus. It is not an albinism, albino, as the eumelanin, dark pigments are scarcely affected. The mutation changes a single amino acid in the transporter protein SLC45A2. Both parents need to have the allele for whiteness to have white cubs.
Between the early and mid 20th century, white tigers were recorded and shot in the Indian states of Odisha, Bihar, Assam and in the area of Rewa, Madhya Pradesh. The local maharaja started breeding tigers in the early 1950s and kept a white male tiger together with its normal-coloured daughter; they had white cubs.
To preserve this recessive trait, only a few white individuals were used in captive breeding, which led to a high degree of inbreeding. Inbreeding depression is the main reason for many health problems of captive white tigers, including strabismus, stillbirth, cripple, deformities and premature death.
Other physical defects include cleft palate and scoliosis.
The Tiger Species Survival Plan has condemned the breeding of white tigers, alleging they are of mixed ancestry and of unknown lineage. The genes responsible for white colouration are represented by 0.001% of the population. The disproportionate growth in numbers of white tigers points to inbreeding among homozygous recessive individuals. This would lead to inbreeding depression and loss of genetic variability.
There are also records of pseudomelanic or black tigers which have thick stripes that merge. In Simlipal National Park, 37% of the tiger population has this condition, which has been linked to isolation and inbreeding.
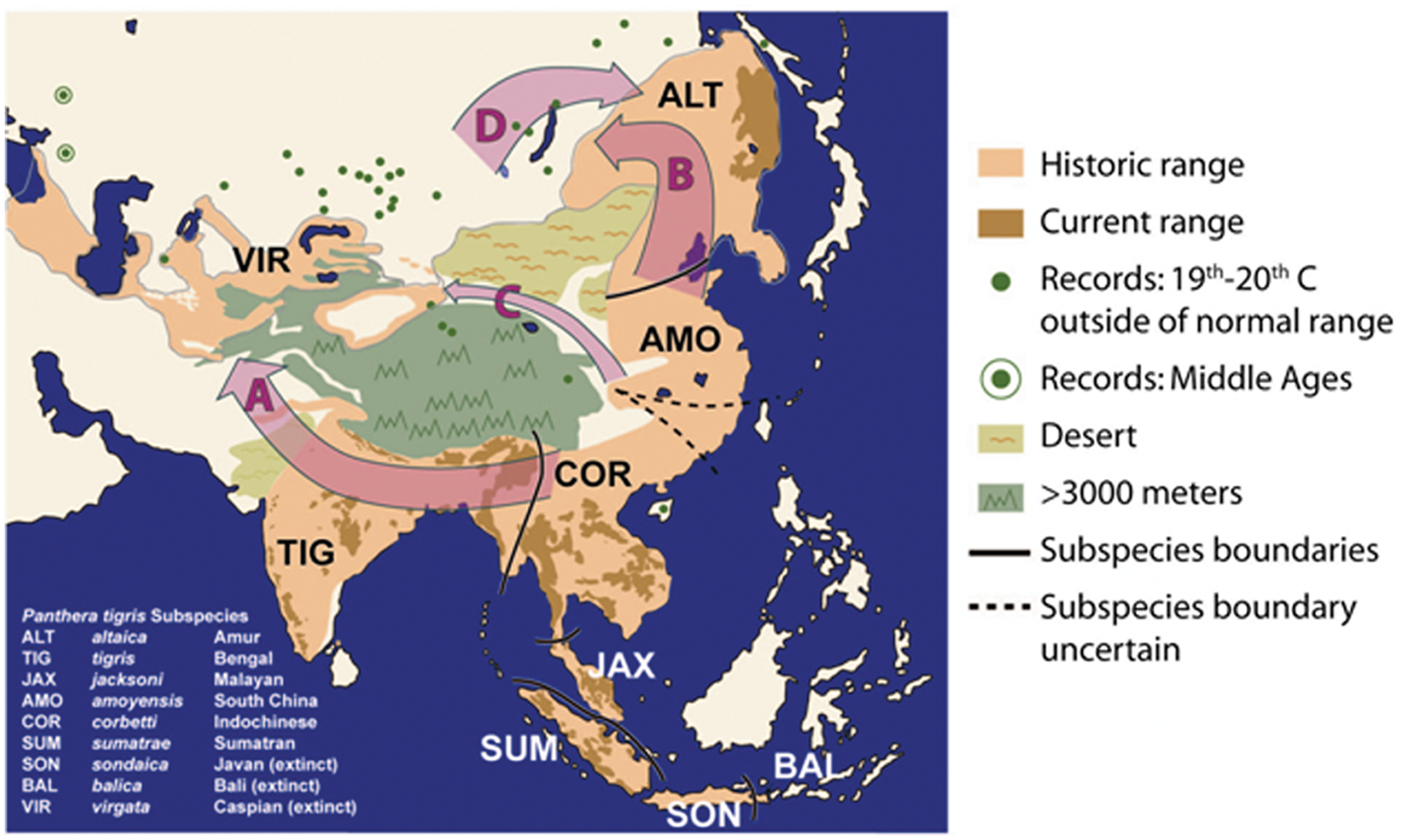 The tiger historically ranged from eastern Turkey and Transcaucasia to the coast of the Sea of Japan, and from South Asia across Southeast Asia to the Indonesian islands of
The tiger historically ranged from eastern Turkey and Transcaucasia to the coast of the Sea of Japan, and from South Asia across Southeast Asia to the Indonesian islands of
 To identify his territory, the male marks trees by urine spraying, spraying urine, anal gland secretions, marking trails with feces and marking trees or the ground with their claws. Females also use these "scrapes", urine and fecal markings. Scent markings of this type allow an individual to pick up information on another's identity, sex and reproductive status. Females in Estrous cycle, oestrus will signal their availability by scent marking more frequently and increasing their vocalisations.
Although for the most part avoiding each other, tigers are not always territorial and relationships between individuals can be complex. An adult of either sex will sometimes share its kill with others, even with unrelated tigers. George Schaller observed a male share a kill with two females and four cubs. Unlike male lions, male tigers allow females and cubs to feed on the kill before the male is finished with it; all involved generally seem to behave amicably, in contrast to the competitive behaviour shown by a lion pride. Stephen Mills described a social feeding event in Ranthambore National Park:
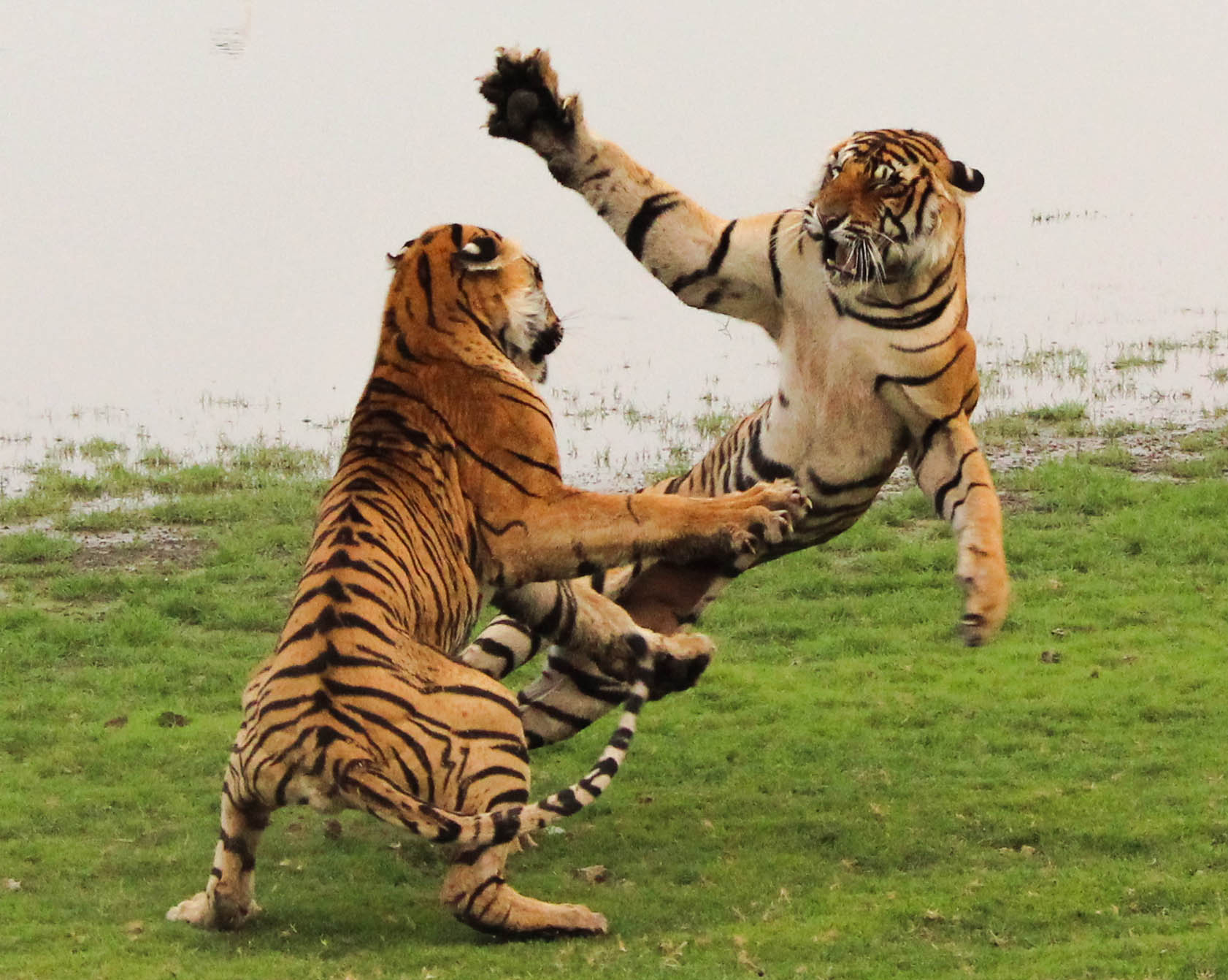
Male tigers are generally less tolerant of other males within their territories than females are of other females. Territory disputes are usually solved by intimidation rather than outright violence. Several such incidents have been observed in which the subordinate tiger yielded by rolling onto its back and showing its belly in a submissive posture. Once dominance (ethology), dominance has been established, a male may tolerate a subordinate within his range, as long as they do not live in too close quarters. The most serious disputes tend to occur between two males competing for a female in oestrus, sometimes fighting to the death.
To identify his territory, the male marks trees by urine spraying, spraying urine, anal gland secretions, marking trails with feces and marking trees or the ground with their claws. Females also use these "scrapes", urine and fecal markings. Scent markings of this type allow an individual to pick up information on another's identity, sex and reproductive status. Females in Estrous cycle, oestrus will signal their availability by scent marking more frequently and increasing their vocalisations.
Although for the most part avoiding each other, tigers are not always territorial and relationships between individuals can be complex. An adult of either sex will sometimes share its kill with others, even with unrelated tigers. George Schaller observed a male share a kill with two females and four cubs. Unlike male lions, male tigers allow females and cubs to feed on the kill before the male is finished with it; all involved generally seem to behave amicably, in contrast to the competitive behaviour shown by a lion pride. Stephen Mills described a social feeding event in Ranthambore National Park:
Male tigers are generally less tolerant of other males within their territories than females are of other females. Territory disputes are usually solved by intimidation rather than outright violence. Several such incidents have been observed in which the subordinate tiger yielded by rolling onto its back and showing its belly in a submissive posture. Once dominance (ethology), dominance has been established, a male may tolerate a subordinate within his range, as long as they do not live in too close quarters. The most serious disputes tend to occur between two males competing for a female in oestrus, sometimes fighting to the death.
 Facial expressions include the "defense threat", where an individual bares its teeth, flattens its ears and its pupils enlarge. Both males and females show a flehmen response, a characteristic grimace, when sniffing urine markings, but flehmen is more often associated with males detecting the markings made by tigresses in oestrus.
Tigers Roar (vocalization), roar to signal their presence to other individuals over long distances. This vocalization is forced through an open mouth as it closes and can be heard away. They may roar three or four times in a row, and other tigers may respond in kind. When tense, tigers will moan, a sound similar to a roar but softer and made when the mouth is at least partially closed. Moaning can be heard away. For aggressive encounters, tigers growling, growl, snarling, snarl and hiss. During an attack, an explosive "coughing roar" or "coughing snarl" is emitted though an open mouth and exposed teeth. Prusten, Chuffing—soft, low-frequency snorting similar to purring in smaller cats—is heard in more friendly situations. Other vocalizations include grunts, woofs and miaows.
Facial expressions include the "defense threat", where an individual bares its teeth, flattens its ears and its pupils enlarge. Both males and females show a flehmen response, a characteristic grimace, when sniffing urine markings, but flehmen is more often associated with males detecting the markings made by tigresses in oestrus.
Tigers Roar (vocalization), roar to signal their presence to other individuals over long distances. This vocalization is forced through an open mouth as it closes and can be heard away. They may roar three or four times in a row, and other tigers may respond in kind. When tense, tigers will moan, a sound similar to a roar but softer and made when the mouth is at least partially closed. Moaning can be heard away. For aggressive encounters, tigers growling, growl, snarling, snarl and hiss. During an attack, an explosive "coughing roar" or "coughing snarl" is emitted though an open mouth and exposed teeth. Prusten, Chuffing—soft, low-frequency snorting similar to purring in smaller cats—is heard in more friendly situations. Other vocalizations include grunts, woofs and miaows.
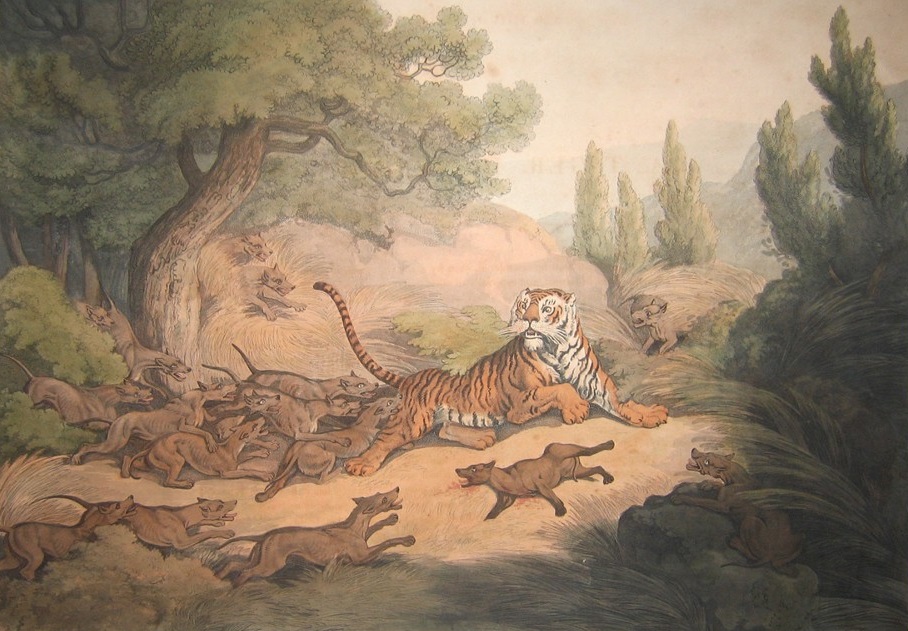 Tigers usually prefer to eat self-killed prey, but eat carrion in times of scarcity and also Kleptoparasitism, steal prey from other large carnivores. Although predators typically avoid one another, if a prize is under dispute or a serious competitor is encountered, displays of aggression are common. If these fail, the conflicts may turn violent; tigers may kill or even prey on competitors such as leopards, dholes, striped hyenas, wolves, bears, Pythonidae, pythons, and mugger crocodiles on occasion. Crocodiles, bears, and large packs of dholes may win conflicts with tigers, and crocodiles and bears can even kill them.
The considerably smaller leopard avoids competition from tigers by hunting at different times of the day and hunting different prey. Ecology.info In India's Nagarhole National Park, most prey selected by leopards were from against a preference for heavier prey by tigers. The average prey weight in the two respective big cats in India was against . With relatively abundant prey, tigers and leopards were seen to successfully coexist without competitive exclusion or interspecies dominance (ethology), dominance hierarchies that may be more common to the African savanna, where the leopard lives beside the lion. Golden jackals may scavenge on tiger kills. Tigers appear to inhabit the deep parts of a forest while smaller predators like leopards and dholes are pushed closer to the fringes.
Tigers usually prefer to eat self-killed prey, but eat carrion in times of scarcity and also Kleptoparasitism, steal prey from other large carnivores. Although predators typically avoid one another, if a prize is under dispute or a serious competitor is encountered, displays of aggression are common. If these fail, the conflicts may turn violent; tigers may kill or even prey on competitors such as leopards, dholes, striped hyenas, wolves, bears, Pythonidae, pythons, and mugger crocodiles on occasion. Crocodiles, bears, and large packs of dholes may win conflicts with tigers, and crocodiles and bears can even kill them.
The considerably smaller leopard avoids competition from tigers by hunting at different times of the day and hunting different prey. Ecology.info In India's Nagarhole National Park, most prey selected by leopards were from against a preference for heavier prey by tigers. The average prey weight in the two respective big cats in India was against . With relatively abundant prey, tigers and leopards were seen to successfully coexist without competitive exclusion or interspecies dominance (ethology), dominance hierarchies that may be more common to the African savanna, where the leopard lives beside the lion. Golden jackals may scavenge on tiger kills. Tigers appear to inhabit the deep parts of a forest while smaller predators like leopards and dholes are pushed closer to the fringes.
 In 1994, the Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Conservation Strategy addressed the potential crisis that tigers faced in Sumatra. The Sumatran Tiger Project (STP) was initiated in June 1995 in and around the Way Kambas National Park to ensure the long-term viability of wild Sumatran tigers and to accumulate data on tiger life-history characteristics vital for the management of wild populations. By August 1999, the teams of the STP had evaluated 52 sites of potential tiger habitat in Lampung Province, of which only 15 these were intact enough to contain tigers.Tilson, R. (1999). ''Sumatran Tiger Project Report No. 17 & 18: July − December 1999''. Grant number 1998-0093-059. Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Steering Committee, Jakarta. In the framework of the STP a community-based conservation programme was initiated to document the tiger-human dimension in the park to enable conservation authorities to resolve tiger-human conflicts based on a comprehensive database rather than anecdotes and opinions.Nyhus, P., Sumianto and R. Tilson (1999). ''The tiger-human dimension in southeast Sumatra'', pp. 144–145 in: Seidensticker, J., Christie, S. and Jackson, P. (eds). ''Riding the tiger: tiger conservation in human-dominated landscapes''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, .
The Wildlife Conservation Society and Panthera Corporation formed the collaboration ''Tigers Forever'', with field sites including the world's largest tiger reserve, the Hukaung Valley in Myanmar. Other reserves were in the Western Ghats in India, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, the Russian Far East covering in total about .
Tigers have been studied in the wild using a variety of techniques. Tiger population have been estimated using plaster casts of their pugmarks, although this method was criticized as being inaccurate. More recent techniques include the use of camera traps and studies of DNA from tiger scat, while radio telemetry, radio-collaring has been used to track tigers in the wild. Tiger spray has been found to be just as good, or better, as a source of DNA than scat.
In 1994, the Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Conservation Strategy addressed the potential crisis that tigers faced in Sumatra. The Sumatran Tiger Project (STP) was initiated in June 1995 in and around the Way Kambas National Park to ensure the long-term viability of wild Sumatran tigers and to accumulate data on tiger life-history characteristics vital for the management of wild populations. By August 1999, the teams of the STP had evaluated 52 sites of potential tiger habitat in Lampung Province, of which only 15 these were intact enough to contain tigers.Tilson, R. (1999). ''Sumatran Tiger Project Report No. 17 & 18: July − December 1999''. Grant number 1998-0093-059. Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Steering Committee, Jakarta. In the framework of the STP a community-based conservation programme was initiated to document the tiger-human dimension in the park to enable conservation authorities to resolve tiger-human conflicts based on a comprehensive database rather than anecdotes and opinions.Nyhus, P., Sumianto and R. Tilson (1999). ''The tiger-human dimension in southeast Sumatra'', pp. 144–145 in: Seidensticker, J., Christie, S. and Jackson, P. (eds). ''Riding the tiger: tiger conservation in human-dominated landscapes''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, .
The Wildlife Conservation Society and Panthera Corporation formed the collaboration ''Tigers Forever'', with field sites including the world's largest tiger reserve, the Hukaung Valley in Myanmar. Other reserves were in the Western Ghats in India, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, the Russian Far East covering in total about .
Tigers have been studied in the wild using a variety of techniques. Tiger population have been estimated using plaster casts of their pugmarks, although this method was criticized as being inaccurate. More recent techniques include the use of camera traps and studies of DNA from tiger scat, while radio telemetry, radio-collaring has been used to track tigers in the wild. Tiger spray has been found to be just as good, or better, as a source of DNA than scat.
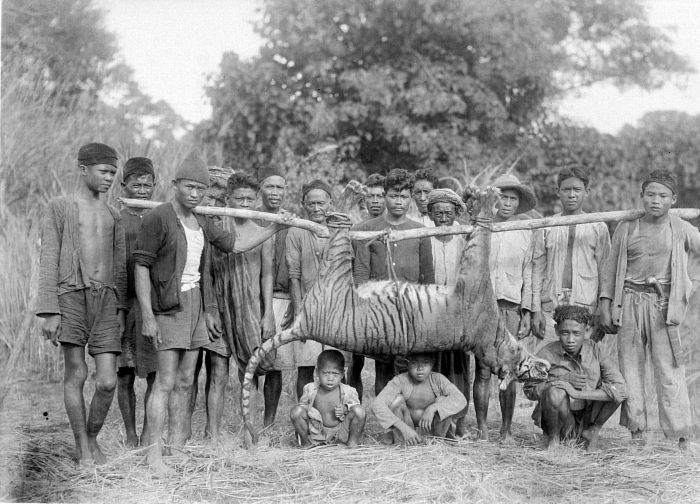
 The tiger has been one of the most sought after game animals of Asia. Tiger hunting took place on a large scale in the early 19th and 20th centuries, being a recognised and admired sport by the British in Presidencies and provinces of British India, colonial India, the maharajas and aristocratic class of the erstwhile princely states of pre-independence India. A single maharaja or English hunter could claim to kill over a hundred tigers in their hunting career. Over 80,000 tigers were slaughtered in just 50 years spanning from 1875 to 1925 in British-ruled India. Tiger hunting was done by some hunters on foot; others sat up on ''Hunting blind, machans'' with a goat or buffalo tied out as bait; yet others on elephant-back. King George V on his visit to Colonial India in 1911 killed 39 tigers in a matter of 10 days One of these is on display at the Royal Albert Memorial Museum.
Historically, tigers have been hunted at a large scale so their famous striped skins could be collected. The trade in tiger skins peaked in the 1960s, just before international conservation efforts took effect. By 1977, a tiger skin in an English market was considered to be worth US$4,250.
The tiger has been one of the most sought after game animals of Asia. Tiger hunting took place on a large scale in the early 19th and 20th centuries, being a recognised and admired sport by the British in Presidencies and provinces of British India, colonial India, the maharajas and aristocratic class of the erstwhile princely states of pre-independence India. A single maharaja or English hunter could claim to kill over a hundred tigers in their hunting career. Over 80,000 tigers were slaughtered in just 50 years spanning from 1875 to 1925 in British-ruled India. Tiger hunting was done by some hunters on foot; others sat up on ''Hunting blind, machans'' with a goat or buffalo tied out as bait; yet others on elephant-back. King George V on his visit to Colonial India in 1911 killed 39 tigers in a matter of 10 days One of these is on display at the Royal Albert Memorial Museum.
Historically, tigers have been hunted at a large scale so their famous striped skins could be collected. The trade in tiger skins peaked in the 1960s, just before international conservation efforts took effect. By 1977, a tiger skin in an English market was considered to be worth US$4,250.
 Many people in China and other parts of Asia have a belief that various tiger parts have Traditional Chinese medicine, medicinal properties, including as pain killers and aphrodisiacs. There is no scientific evidence to support these beliefs. The use of tiger parts in pharmaceutical drugs in China is already banned, and the government has made some offences in connection with tiger poaching punishable by death. Furthermore, all trade in tiger parts is illegal under the CITES, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora and a domestic trade ban has been in place in China since 1993.
However, the trading of tiger parts in Asia has become a major black market industry and governmental and conservation attempts to stop it have been ineffective to date. Almost all black marketers engaged in the trade are based in China and have either been shipped and sold within in their own country or into Taiwan,
Many people in China and other parts of Asia have a belief that various tiger parts have Traditional Chinese medicine, medicinal properties, including as pain killers and aphrodisiacs. There is no scientific evidence to support these beliefs. The use of tiger parts in pharmaceutical drugs in China is already banned, and the government has made some offences in connection with tiger poaching punishable by death. Furthermore, all trade in tiger parts is illegal under the CITES, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora and a domestic trade ban has been in place in China since 1993.
However, the trading of tiger parts in Asia has become a major black market industry and governmental and conservation attempts to stop it have been ineffective to date. Almost all black marketers engaged in the trade are based in China and have either been shipped and sold within in their own country or into Taiwan,
 Wild tigers that have had no prior contact with humans actively avoid interactions with them. However, tigers cause more human deaths through direct attack than any other wild mammal. Attacks are occasionally provoked, as tigers lash out after being injured while they themselves are hunted. Attacks can be provoked accidentally, as when a human surprises a tiger or inadvertently comes between a mother and her young, or as in a case in rural India when a postman startled a tiger, used to seeing him on foot, by riding a bicycle. Occasionally tigers come to view people as prey. Such attacks are most common in areas where population growth, logging, and farming have put pressure on tiger habitats and reduced their wild prey. Most man-eating tigers are old, missing teeth, and unable to capture their preferred prey. For example, the Champawat Tiger, a tigress found in Nepal and then India, had two broken canines. She was responsible for an estimated 430 human deaths, the most attacks known to be perpetrated by a single wild animal, by the time she was shot in 1907 by Jim Corbett. According to Corbett, tiger attacks on humans are normally in daytime, when people are working outdoors and are not keeping watch. Early writings tend to describe man-eating tigers as cowardly because of their ambush tactics.Tiger of Segur, The Man-Eater of Segur", from ''Nine Man-Eaters and One Rogue'', Kenneth Anderson, Allen & Unwin, 1954
Man-eaters have been a particular problem in recent decades in India and Bangladesh, especially in Kumaon division, Kumaon, Garhwal division, Garhwal and the Sundarbans mangrove swamps of Bengal, where some healthy tigers have hunted humans. Because of rapid habitat loss attributed to climate change, tiger attacks have increased in the Sundarbans. The Sundarbans area had 129 human deaths from tigers from 1969 to 1971. In the 10 years prior to that period, about 100 attacks per year in the Sundarbans, with a high of around 430 in some years of the 1960s. Unusually, in some years in the Sundarbans, more humans are killed by tigers than vice versa. In 1972, India's production of honey and beeswax dropped by 50% when at least 29 people who gathered these materials were devoured. In 1986 in the Sundarbans, since tigers almost always attack from the rear, masks with human faces were worn on the back of the head, on the theory that tigers usually do not attack if seen by their prey. This decreased the number of attacks only temporarily. All other means to prevent attacks, such as providing more prey or using electrified human dummies, did not work as well.
Wild tigers that have had no prior contact with humans actively avoid interactions with them. However, tigers cause more human deaths through direct attack than any other wild mammal. Attacks are occasionally provoked, as tigers lash out after being injured while they themselves are hunted. Attacks can be provoked accidentally, as when a human surprises a tiger or inadvertently comes between a mother and her young, or as in a case in rural India when a postman startled a tiger, used to seeing him on foot, by riding a bicycle. Occasionally tigers come to view people as prey. Such attacks are most common in areas where population growth, logging, and farming have put pressure on tiger habitats and reduced their wild prey. Most man-eating tigers are old, missing teeth, and unable to capture their preferred prey. For example, the Champawat Tiger, a tigress found in Nepal and then India, had two broken canines. She was responsible for an estimated 430 human deaths, the most attacks known to be perpetrated by a single wild animal, by the time she was shot in 1907 by Jim Corbett. According to Corbett, tiger attacks on humans are normally in daytime, when people are working outdoors and are not keeping watch. Early writings tend to describe man-eating tigers as cowardly because of their ambush tactics.Tiger of Segur, The Man-Eater of Segur", from ''Nine Man-Eaters and One Rogue'', Kenneth Anderson, Allen & Unwin, 1954
Man-eaters have been a particular problem in recent decades in India and Bangladesh, especially in Kumaon division, Kumaon, Garhwal division, Garhwal and the Sundarbans mangrove swamps of Bengal, where some healthy tigers have hunted humans. Because of rapid habitat loss attributed to climate change, tiger attacks have increased in the Sundarbans. The Sundarbans area had 129 human deaths from tigers from 1969 to 1971. In the 10 years prior to that period, about 100 attacks per year in the Sundarbans, with a high of around 430 in some years of the 1960s. Unusually, in some years in the Sundarbans, more humans are killed by tigers than vice versa. In 1972, India's production of honey and beeswax dropped by 50% when at least 29 people who gathered these materials were devoured. In 1986 in the Sundarbans, since tigers almost always attack from the rear, masks with human faces were worn on the back of the head, on the theory that tigers usually do not attack if seen by their prey. This decreased the number of attacks only temporarily. All other means to prevent attacks, such as providing more prey or using electrified human dummies, did not work as well.
 In Ancient Rome, Ancient Roman times, tigers were kept in menageries and amphitheatres to be exhibited, trained and paraded, and were often provoked to fight gladiators and other exotic beasts. Since the 17th century, tigers, being rare and ferocious, were sought after to keep at European castles as symbols of their owners' power. Tigers became central zoo and circus exhibits in the 18th century: a tiger could cost up to 4,000 French franc, francs in France (for comparison, a professor of the Beaux-Arts at Lyons earned only 3,000 francs a year), or up to $3,500 in the United States, where a lion cost no more than $1,000.
In 2007, over 4,000 captive tigers lived in China, of which 3,000 were held by about 20 larger facilities, with the rest held by some 200 smaller facilities. In 2011, 468 facilities in the USA kept 2,884 tigers. Nineteen US states banned private ownership of tigers, fifteen require a license, and sixteen states have no regulation. Genetic ancestry of 105 captive tigers from fourteen countries and regions showed that forty-nine animals belonged distinctly to five subspecies; fifty-two animals had mixed subspecies origins. Many Siberian tigers in zoos today are actually the result of crosses with Bengal tigers.
In Ancient Rome, Ancient Roman times, tigers were kept in menageries and amphitheatres to be exhibited, trained and paraded, and were often provoked to fight gladiators and other exotic beasts. Since the 17th century, tigers, being rare and ferocious, were sought after to keep at European castles as symbols of their owners' power. Tigers became central zoo and circus exhibits in the 18th century: a tiger could cost up to 4,000 French franc, francs in France (for comparison, a professor of the Beaux-Arts at Lyons earned only 3,000 francs a year), or up to $3,500 in the United States, where a lion cost no more than $1,000.
In 2007, over 4,000 captive tigers lived in China, of which 3,000 were held by about 20 larger facilities, with the rest held by some 200 smaller facilities. In 2011, 468 facilities in the USA kept 2,884 tigers. Nineteen US states banned private ownership of tigers, fifteen require a license, and sixteen states have no regulation. Genetic ancestry of 105 captive tigers from fourteen countries and regions showed that forty-nine animals belonged distinctly to five subspecies; fifty-two animals had mixed subspecies origins. Many Siberian tigers in zoos today are actually the result of crosses with Bengal tigers.
 Tigers and their superlative qualities have been a source of fascination for mankind since ancient times, and they are routinely visible as important cultural and media motifs. They are also considered one of the
Tigers and their superlative qualities have been a source of fascination for mankind since ancient times, and they are routinely visible as important cultural and media motifs. They are also considered one of the
 In Chinese mythology and Chinese culture, culture, the Tiger (zodiac), tiger is one of the 12 animals of the Chinese astrology, Chinese zodiac. In Chinese art, the tiger is depicted as an earth symbol and equal rival of the Chinese dragon – the two representing matter and spirit respectively. The Southern Chinese martial art Hung Ga is based on the movements of the tiger and the crane. In History of China, Imperial China, a tiger was the personification of war and often represented the highest army General Officer, general (or present day United States Secretary of Defense, defense secretary), while the emperor and empress were represented by a dragon and Fenghuang, phoenix, respectively. The White Tiger (Chinese constellation), White Tiger () is one of the Four Symbols (Chinese constellation), Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (), and it represents the west and the autumn season.
The tiger's tail appears in stories from countries including China and Korea, it being generally inadvisable to grasp a tiger by the tail. In Korean mythology, Korean myth and Korean culture, culture, the tiger is regarded as a guardian that drives away evil spirits and a sacred creature that brings good luck – the symbol of courage and absolute power. For the people who live in and around the forests of Korea, the tiger considered the symbol of the Mountain Spirit or King of mountain animals. So, Koreans also called the tigers "San Gun" (산군) means Mountain Lord.
In Buddhism, the tiger is one of the Three Senseless Creatures, symbolising anger, with the monkey representing greed and the deer lovesickness. The Tungusic peoples considered the Siberian tiger a near-deity and often referred to it as "Grandfather" or "Old man". The Udege people, Udege and Nani people, Nanai called it "Amba". The Manchu people, Manchu considered the Siberian tiger as "Hu Lin," the king. In Hinduism, the god Shiva wears and sits on tiger skin. The ten-armed warrior goddess Durga rides the tigress (or lioness) Damon into battle. In southern India the god Ayyappan was associated with a tiger. Dingu-Aneni is the god in North-East India is also associated with tiger. The Werecat, weretiger replaces the werewolf in shapeshifting folklore in Asia; in India they were evil sorcerers, while in Indonesia and Malaysia they were somewhat more benign. In Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman tradition, the tiger was depicted being ridden by the god Dionysus.
In Chinese mythology and Chinese culture, culture, the Tiger (zodiac), tiger is one of the 12 animals of the Chinese astrology, Chinese zodiac. In Chinese art, the tiger is depicted as an earth symbol and equal rival of the Chinese dragon – the two representing matter and spirit respectively. The Southern Chinese martial art Hung Ga is based on the movements of the tiger and the crane. In History of China, Imperial China, a tiger was the personification of war and often represented the highest army General Officer, general (or present day United States Secretary of Defense, defense secretary), while the emperor and empress were represented by a dragon and Fenghuang, phoenix, respectively. The White Tiger (Chinese constellation), White Tiger () is one of the Four Symbols (Chinese constellation), Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (), and it represents the west and the autumn season.
The tiger's tail appears in stories from countries including China and Korea, it being generally inadvisable to grasp a tiger by the tail. In Korean mythology, Korean myth and Korean culture, culture, the tiger is regarded as a guardian that drives away evil spirits and a sacred creature that brings good luck – the symbol of courage and absolute power. For the people who live in and around the forests of Korea, the tiger considered the symbol of the Mountain Spirit or King of mountain animals. So, Koreans also called the tigers "San Gun" (산군) means Mountain Lord.
In Buddhism, the tiger is one of the Three Senseless Creatures, symbolising anger, with the monkey representing greed and the deer lovesickness. The Tungusic peoples considered the Siberian tiger a near-deity and often referred to it as "Grandfather" or "Old man". The Udege people, Udege and Nani people, Nanai called it "Amba". The Manchu people, Manchu considered the Siberian tiger as "Hu Lin," the king. In Hinduism, the god Shiva wears and sits on tiger skin. The ten-armed warrior goddess Durga rides the tigress (or lioness) Damon into battle. In southern India the god Ayyappan was associated with a tiger. Dingu-Aneni is the god in North-East India is also associated with tiger. The Werecat, weretiger replaces the werewolf in shapeshifting folklore in Asia; in India they were evil sorcerers, while in Indonesia and Malaysia they were somewhat more benign. In Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman tradition, the tiger was depicted being ridden by the god Dionysus.

 The tiger is one of the animals displayed on the Pashupati seal of the Indus Valley civilisation. The tiger was the emblem of the Chola Dynasty and was depicted on coins, seals and banners. The seals of several Chola copper coins show the tiger, the Pandyan emblem fish and the Chera dynasty, Chera emblem bow, indicating that the Cholas had achieved political supremacy over the latter two dynasties. Gold coins found in Kavilayadavalli in the Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh have motifs of the tiger, bow and some indistinct marks. The tiger symbol of Chola Empire was later adopted by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam and the tiger became a symbol of the unrecognised state of Tamil Eelam and Tamil independence movement. The Bengal tiger is the
The tiger is one of the animals displayed on the Pashupati seal of the Indus Valley civilisation. The tiger was the emblem of the Chola Dynasty and was depicted on coins, seals and banners. The seals of several Chola copper coins show the tiger, the Pandyan emblem fish and the Chera dynasty, Chera emblem bow, indicating that the Cholas had achieved political supremacy over the latter two dynasties. Gold coins found in Kavilayadavalli in the Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh have motifs of the tiger, bow and some indistinct marks. The tiger symbol of Chola Empire was later adopted by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam and the tiger became a symbol of the unrecognised state of Tamil Eelam and Tamil independence movement. The Bengal tiger is the
cat
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
and a member of the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
''Panthera
''Panthera'' is a genus within the family (biology), family Felidae that was named and described by Lorenz Oken in 1816 who placed all the spotted cats in this group. Reginald Innes Pocock revised the classification of this genus in 1916 as co ...
''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
, it primarily preys on ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, cam ...
s, such as deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
and wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
. It is territorial and generally a solitary but social
Sociality is the degree to which individuals in an animal population tend to associate in social groups (gregariousness) and form cooperative societies.
Sociality is a survival response to evolutionary pressures. For example, when a mother wasp ...
predator, requiring large contiguous areas of habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
to support its requirements for prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
and rearing of its offspring. Tiger cubs stay with their mother for about two years and then become independent, leaving their mother's home range
A home range is the area in which an animal lives and moves on a periodic basis. It is related to the concept of an animal's territory which is the area that is actively defended. The concept of a home range was introduced by W. H. Burt in 1943. He ...
to establish their own.
The tiger was first scientifically described
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have be ...
in 1758. It once ranged widely from the Eastern Anatolia Region
The Eastern Anatolia Region ('' tr, Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi'') is a geographical region of Turkey. The most populous province in the region is Van Province. Other populous provinces are Malatya, Erzurum and Elazığ.
It is bordered by the Black ...
in the west to the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
basin in the east, and in the south from the foothills of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
to Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
in the Sunda Islands
The Sunda Islands ( id, Kepulauan Sunda) are a group of islands in the Malay Archipelago.Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Sunda Islands" . ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 26 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. They consist of the Greater Sunda ...
. Since the early 20th century, tiger populations have lost at least 93% of their historic range and have been extirpated
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
from Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, the islands of Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
and Bali, and in large areas of Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. What remains of the range where tigers still roam free is fragmented, stretching in spots from Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
n temperate forest
A temperate forest is a forest found between the tropical and boreal regions, located in the temperate zone. It is the second largest biome on our planet, covering 25% of the world's forest area, only behind the boreal forest, which covers abou ...
s to subtropical and tropical forest
Tropical forests (a.k.a. jungle) are forested landscapes in tropical regions: ''i.e.'' land areas approximately bounded by the tropic of Cancer and Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing winds.
Some tropical fores ...
s on the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
and a single Indonesian island, Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
.
The tiger is listed as Endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inva ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
. As of 2015, the global wild tiger population was estimated to number between 3,062 and 3,948 mature individuals, with most populations living in small isolated pockets. India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
currently hosts the largest tiger population. Major reasons for population decline are habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, habitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological processes ...
and poaching
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
. Tigers are also victims of human–wildlife conflict
Human–wildlife conflict (HWC) refers to the negative interactions between human and wild animals, with undesirable consequences both for people and their resources, on the one hand, and wildlife and their habitats on the other (IUCN 2020). HWC ...
, due to encroachment in countries with a high human population density.
The tiger is among the most recognisable and popular of the world's charismatic megafauna
Charismatic megafauna are animal species that are large—in the relevant category that they represent—with symbolic value or widespread popular appeal, and are often used by environmental activists to gain public support for environmentalist g ...
. It featured prominently in the ancient mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
and folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
of cultures throughout its historic range and continues to be depicted in modern films and literature, appearing on many flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design empl ...
s, coats of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its wh ...
and as mascot
A mascot is any human, animal, or object thought to bring luck, or anything used to represent a group with a common public identity, such as a school, professional sports team, society, military unit, or brand name. Mascots are also used as fi ...
s for sporting teams. The tiger is the national animal
This is a list of countries that have officially designated one or more animals as their national animals.
National animal
{, class="wikitable sortable"
! Country
! Name of animal
! Scientific name (Latin name)
! class="unsortable", Picture
...
of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
.
Etymology
TheMiddle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
''tigre'' and Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
''tigras'' derive from Old French ''tigre'', from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''tigris''.
This was a borrowing of Classical Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
τίγρις 'tigris', a foreign borrowing of unknown origin meaning 'tiger' and the river Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
.
The origin may have been the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
word ''tigra'' ('pointed or sharp') and the Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
word ''tigrhi'' ('arrow'), perhaps referring to the speed of the tiger's leap, although these words are not known to have any meanings associated with tigers.
The generic name ''Panthera'' is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word ''panthera'' and the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
word πάνθηρ ('panther').
Taxonomy
In 1758,Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
described the tiger in his work ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
'' and gave it the scientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
''Felis tigris''. In 1929, the British taxonomist Reginald Innes Pocock
Reginald Innes Pocock F.R.S. (4 March 1863 – 9 August 1947) was a British zoologist.
Pocock was born in Clifton, Bristol, the fourth son of Rev. Nicholas Pocock and Edith Prichard. He began showing interest in natural history at St. Edward ...
subordinated the species under the genus ''Panthera
''Panthera'' is a genus within the family (biology), family Felidae that was named and described by Lorenz Oken in 1816 who placed all the spotted cats in this group. Reginald Innes Pocock revised the classification of this genus in 1916 as co ...
'' using the scientific name ''Panthera tigris''.
Subspecies
 Following Linnaeus's first descriptions of the species, several tiger specimens were described and proposed as
Following Linnaeus's first descriptions of the species, several tiger specimens were described and proposed as subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
. The validity
Validity or Valid may refer to:
Science/mathematics/statistics:
* Validity (logic), a property of a logical argument
* Scientific:
** Internal validity, the validity of causal inferences within scientific studies, usually based on experiments
** ...
of several tiger subspecies was questioned in 1999. Most putative subspecies described in the 19th and 20th centuries were distinguished on basis of fur length and colouration, striping patterns and body size, hence characteristics that vary widely within populations. Morphologically, tigers from different regions vary little, and gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent a ...
between populations in those regions is considered to have been possible during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
. Therefore, it was proposed to recognize only two tiger subspecies as valid, namely '' P. t. tigris'' in mainland Asia, and '' P. t. sondaica'' in the Greater Sunda Islands
The Greater Sunda Islands (Indonesian and Malay: ''Kepulauan Sunda Besar'') are four tropical islands situated within Indonesian Archipelago, in the Pacific Ocean. The islands, Borneo, Java, Sulawesi and Sumatra, are internationally recognised fo ...
.
Results of craniological analysis of 111 tiger skulls from Southeast Asian range countries indicate that Sumatran tiger skulls differ from Indochinese and Javan tiger skulls, whereas Bali tiger skulls are similar in size to Javan tiger skulls. The authors proposed to classify the Sumatran and Javan tigers as distinct species, ''P. sumatrae'' and ''P. sondaica'', with the Bali tiger as subspecies ''P. sondaica balica''.
In 2015, morphological, ecological, and molecular traits of all putative tiger subspecies were analysed in a combined approach. Results support distinction of the two evolutionary groups continental and Sunda tigers. The authors proposed recognition of only two subspecies, namely ''P. t. tigris'' comprising the Bengal, Malayan, Indochinese, South Chinese, Siberian and Caspian tiger populations, and ''P. t. sondaica'' comprising the Javan, Bali and Sumatran tiger populations. The authors also noted that this reclassification will affect tiger conservation management. The nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
''P. t. tigris'' constitutes two clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
s:
* a northern clade composed of the Siberian and Caspian tiger populations
* a southern clade composed of all other mainland populations.
One conservation specialist welcomed this proposal as it would make captive breeding programmes and future rewilding of zoo-born tigers easier. One geneticist
A geneticist is a biologist or physician who studies genetics, the science of genes, heredity, and variation of organisms. A geneticist can be employed as a scientist or a lecturer. Geneticists may perform general research on genetic processe ...
was sceptical of this study and maintained that the currently recognised nine subspecies can be distinguished genetically.
In 2017, the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN Cat Specialist Group revised felid taxonomy and recognized the tiger populations in continental Asia as ''P. t. tigris'', and those in the Sunda Islands as ''P. t. sondaica''. This two-subspecies view has been largely rejected by researchers. Results of a 2018 whole-genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a ...
of 32 specimens support six monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
tiger clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
s corresponding with the living subspecies and indicate that the most recent common ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
lived about 110,000 years ago.
The following tables are based on the classification Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes.
It may also refer to:
Business, organizat ...
of the species ''Panthera tigris'' provided in ''Mammal Species of the World
''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference'' is a standard reference work in mammalogy giving descriptions and bibliographic data for the known species of mammals. It is now in its third edition, published in late 2005, ...
''. It also reflects the classification used by the Cat Classification Task Force in 2017:
Evolution
 The tiger's closest living relatives were previously thought to be the ''Panthera'' species
The tiger's closest living relatives were previously thought to be the ''Panthera'' species lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
, leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
and jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus '' Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
. Results of genetic analysis
Genetic analysis is the overall process of studying and researching in fields of science that involve genetics and molecular biology. There are a number of applications that are developed from this research, and these are also considered parts of ...
indicate that about 2.88 million years ago, the tiger and the snow leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia''), also known as the ounce, is a Felidae, felid in the genus ''Panthera'' native to the mountain ranges of Central Asia, Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable species, Vulnerable on the IUCN Red ...
lineages diverged from the other ''Panthera'' species, and that both may be more closely related to each other than to the lion, leopard and jaguar.
The geographic origin of the ''Panthera'' is most likely northern Central Asia. The tiger–snow leopard lineage dispersed in Southeast Asia during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
.
''Panthera zdanskyi
''Panthera zdanskyi'', also known as the Longdan tiger, is an extinct pantherine species that is seen as a close relative of the modern tiger. Fossils were excavated in northwestern China's Gansu province.
Etymology
''Panthera zdanskyi'' was fi ...
'' is considered to be a sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
of the modern tiger. It lived at the beginning of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
about two million years ago, its fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
remains were excavated in Gansu of northwestern China. It was smaller and more " primitive", but functionally and ecologically similar to the modern tiger. It is disputed as to whether it had the striping pattern. Northwestern China is thought to be the origin of the tiger lineage. Tigers grew in size, possibly in response to adaptive radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic int ...
s of prey species like deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
and bovid
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species, the ...
s, which may have occurred in Southeast Asia during the Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
.
''Panthera tigris trinilensis
''Panthera tigris trinilensis'', known as the Trinil tiger, is an extinct tiger subspecies dating from about 1.2 million years ago that was found at the locality of Trinil, Java, Indonesia. The fossil remains are now stored in the Dubois Collec ...
'' lived about and is known from fossils excavated near Trinil
Trinil is a palaeoanthropological site on the banks of the Bengawan Solo River in Ngawi Regency, East Java Province, Indonesia. It was at this site in 1891 that the Dutch anatomist Eugène Dubois discovered the first early hominin remains to be ...
in Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
. The Wanhsien, Ngandong
Solo Man (''Homo erectus soloensis'') is a subspecies of ''H. erectus'' that lived along the Solo River in Java, Indonesia, about 117,000 to 108,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. This population is the last known record of the species. I ...
, Trinil, and Japanese tigers became extinct in prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
times. Tigers reached India and northern Asia in the late Pleistocene, reaching eastern Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
, Japan, and Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: ...
. Some fossil skulls are morphologically distinct from lion skulls, which could indicate tiger presence in Alaska during the last glacial period, about 100,000 years ago.
Fossil teeth and bones found in Borneo were attributed to the Bornean tiger
The Bornean tiger or Borneo tiger is possibly an extinct tiger population that lived on the island of Borneo in prehistoric times.
A live Bornean tiger has not been conclusively recorded, but the indigenous Dayak people believe in its existence, ...
and date to about 13,745 to 3,000 years ago. It may have accessed Borneo, when the sea level was low during a glaciation period, and may have survived until about 200 years ago.
In the Ille Cave Dewil Valley, located in the northernmost part of Palawan, an island province of the Philippines that is located in the Mimaropa region, is an archaeological site composed of thousands of artifacts and features. According to the University of the ...
on the island of Palawan, two articulated phalanx bone
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones.
...
s were found amidst an assemblage of other animal bones and stone tools. They were smaller than mainland tiger fossils, possibly due to insular dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is disti ...
. It has been speculated that the tiger parts were either imported from elsewhere, or that the tiger colonised Palawan from Borneo before the Holocene. Fossil remains of tigers were also excavated in Sri Lanka, China, Japan and Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the M ...
dating to the Late Pliocene
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
, Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
and Early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
.
Results of a phylogeographic
Phylogeography is the study of the historical processes that may be responsible for the past to present geographic distributions of genealogical lineages. This is accomplished by considering the geographic distribution of individuals in light of ge ...
study indicate that all living tigers had a common ancestor 108,000 to 72,000 years ago. The potential tiger range during the late Pleistocene and Holocene was predicted applying ecological niche modelling
Species distribution modelling (SDM), also known as environmental (or ecological) niche modelling (ENM), habitat modelling, predictive habitat distribution modelling, and range mapping uses computer algorithms to predict the distribution of a spec ...
based on more than 500 tiger locality records combined with bioclimatic
Green building (also known as green construction or sustainable building) refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from plannin ...
data. The resulting model shows a contiguous tiger range at the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
, indicating gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent a ...
between tiger populations in mainland Asia. The Caspian tiger population was likely connected to the Bengal tiger population through corridors below elevations of in the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Provinc ...
. The tiger populations on the Sunda Islands and mainland Asia were possibly separated during interglacial period
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene in ...
s.
The tiger's full genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
sequence was published in 2013. It was found to have similar repeat composition to other cat genomes and an appreciably conserved synteny
In genetics, the term synteny refers to two related concepts:
* In classical genetics, ''synteny'' describes the physical co-localization of genetic loci on the same chromosome within an individual or species.
* In current biology, ''synteny'' mo ...
.
Hybrids
Captive tigers were bred with lions to create hybrids called liger and tigon. They share physical and behavioural qualities of both parent species. Breeding hybrids is now discouraged due to the emphasis on conservation. The liger is a cross between a male lion and a tigress. Ligers are typically between in length, and weigh between or more. Because the lion sire passes on a growth-promoting gene, but the corresponding growth-inhibiting gene from the female tiger is absent, ligers grow far larger than either parent species. The less common tigon is a cross between a lioness and a male tiger. Because the male tiger does not pass on a growth-promoting gene and the lioness passes on a growth inhibiting gene, tigons are around the same size as their parents. Some females are fertile and have occasionally given birth tolitigon
A litigon (/ˌlaɪˈtaɪɡən/) is a rare, second-generation hybrid from a female tigon (a hybrid between a male tiger and a female lion) and a male lion, specifically an Asiatic lion.
Description
Litigons inherit and share characteristics with ...
s when mated to a male Asiatic lion
The Asiatic lion is a population of ''Panthera leo leo'' that today survives in the wild only in India. Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat ...
.
Description
The tiger has a muscular body with strong forelimbs, a large head and a tail that is about half the length of its body. Itspelage
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily #Guard hair, guard hair on top and thick #Down hair, underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as ...
colouration varies between shades of orange with a white underside and distinctive vertical black stripes; the patterns of which are unique in each individual. Stripes are likely advantageous for camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the ...
in vegetation such as long grass with strong vertical patterns of light and shade. The tiger is one of only a few striped cat species; it is not known why spotted patterns and rosettes are the more common camouflage pattern among felids. The orange colour may also aid in camouflage as the tiger's prey are dichromat
Dichromacy (from Greek ''di'', meaning "two" and ''chromo'', meaning "color") is the state of having two types of functioning photoreceptors, called cone cells, in the eyes. Organisms with dichromacy are called dichromats. Dichromats require ...
s, and thus may perceive the cat as green and blended in with the vegetation.
A tiger's coat pattern is still visible when it is shaved. This is not due to skin pigmentation, but to the stubble and hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between h ...
s embedded in the skin. It has a mane-like heavy growth of fur around the neck and jaws and long whiskers, especially in males. The pupils are circular with yellow irises. The small, rounded ears have a prominent white spot on the back, surrounded by black. These spots are thought to play an important role in intraspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species.
Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organ ...
communication.
The tiger's skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
is similar to a lion's skull, with the frontal region usually less depressed or flattened, and a slightly longer postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
region. The lion skull shows broader nasal openings. Due to the variation in skull sizes of the two species, the structure of the lower jaw is a reliable indicator for their identification. The tiger has fairly stout teeth; its somewhat curved canines
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* a dog-like Canid animal in the subfamily Caninae
** ''Canis'', a genus including dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Dog, the domestic dog
* Canine tooth, in mammalian oral anatomy
People with the surn ...
are the longest among living felids with a crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
height of up to .
Size
There is notablesexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
between male and female tigers, with the latter being consistently smaller. The size difference between them is proportionally greater in the large tiger subspecies, with males weighing up to 1.7 times more than females. Males also have wider forepaw pads, enabling sex to be identified from tracks. It has been hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obse ...
ed that body size of different tiger populations may be correlated with climate and be explained by thermoregulation and Bergmann's rule, or by distribution and size of available prey species.
Generally, males vary in total length from and weigh between with skull length ranging from . Females vary in total length from , weigh with skull length ranging from . In either sex, the tail represents about of the total length. The Bengal and Siberian tigers are amongst the tallest cats in shoulder height. They are also ranked among the biggest cats that have ever existed reaching weights of more than . The tigers of the Sunda islands are smaller and less heavy than tigers in mainland Asia, rarely exceeding in weight.
Colour variations
 There are three other Polymorphism (biology), colour variants – white, golden and nearly stripeless snow white – that are now virtually non-existent in the wild due to the reduction of wild tiger populations, but continue in captive populations. The white tiger has white fur and Sepia (color), sepia-brown stripes. The golden tiger has a pale golden pelage with a blond tone and reddish-brown stripes. The snow white tiger is a morph with extremely faint stripes and a pale reddish-brown ringed tail. Both snow white and golden tigers are homozygous for CORIN gene mutations.
The white tiger lacks pheomelanin (which creates the orange colour), and has dark sepia-brown stripes and blue eyes. This altered pigmentation is caused by a mutant gene that is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, which is determined by a white Locus (genetics), locus. It is not an albinism, albino, as the eumelanin, dark pigments are scarcely affected. The mutation changes a single amino acid in the transporter protein SLC45A2. Both parents need to have the allele for whiteness to have white cubs.
Between the early and mid 20th century, white tigers were recorded and shot in the Indian states of Odisha, Bihar, Assam and in the area of Rewa, Madhya Pradesh. The local maharaja started breeding tigers in the early 1950s and kept a white male tiger together with its normal-coloured daughter; they had white cubs.
To preserve this recessive trait, only a few white individuals were used in captive breeding, which led to a high degree of inbreeding. Inbreeding depression is the main reason for many health problems of captive white tigers, including strabismus, stillbirth, cripple, deformities and premature death.
Other physical defects include cleft palate and scoliosis.
The Tiger Species Survival Plan has condemned the breeding of white tigers, alleging they are of mixed ancestry and of unknown lineage. The genes responsible for white colouration are represented by 0.001% of the population. The disproportionate growth in numbers of white tigers points to inbreeding among homozygous recessive individuals. This would lead to inbreeding depression and loss of genetic variability.
There are also records of pseudomelanic or black tigers which have thick stripes that merge. In Simlipal National Park, 37% of the tiger population has this condition, which has been linked to isolation and inbreeding.
There are three other Polymorphism (biology), colour variants – white, golden and nearly stripeless snow white – that are now virtually non-existent in the wild due to the reduction of wild tiger populations, but continue in captive populations. The white tiger has white fur and Sepia (color), sepia-brown stripes. The golden tiger has a pale golden pelage with a blond tone and reddish-brown stripes. The snow white tiger is a morph with extremely faint stripes and a pale reddish-brown ringed tail. Both snow white and golden tigers are homozygous for CORIN gene mutations.
The white tiger lacks pheomelanin (which creates the orange colour), and has dark sepia-brown stripes and blue eyes. This altered pigmentation is caused by a mutant gene that is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, which is determined by a white Locus (genetics), locus. It is not an albinism, albino, as the eumelanin, dark pigments are scarcely affected. The mutation changes a single amino acid in the transporter protein SLC45A2. Both parents need to have the allele for whiteness to have white cubs.
Between the early and mid 20th century, white tigers were recorded and shot in the Indian states of Odisha, Bihar, Assam and in the area of Rewa, Madhya Pradesh. The local maharaja started breeding tigers in the early 1950s and kept a white male tiger together with its normal-coloured daughter; they had white cubs.
To preserve this recessive trait, only a few white individuals were used in captive breeding, which led to a high degree of inbreeding. Inbreeding depression is the main reason for many health problems of captive white tigers, including strabismus, stillbirth, cripple, deformities and premature death.
Other physical defects include cleft palate and scoliosis.
The Tiger Species Survival Plan has condemned the breeding of white tigers, alleging they are of mixed ancestry and of unknown lineage. The genes responsible for white colouration are represented by 0.001% of the population. The disproportionate growth in numbers of white tigers points to inbreeding among homozygous recessive individuals. This would lead to inbreeding depression and loss of genetic variability.
There are also records of pseudomelanic or black tigers which have thick stripes that merge. In Simlipal National Park, 37% of the tiger population has this condition, which has been linked to isolation and inbreeding.
Distribution and habitat
 The tiger historically ranged from eastern Turkey and Transcaucasia to the coast of the Sea of Japan, and from South Asia across Southeast Asia to the Indonesian islands of
The tiger historically ranged from eastern Turkey and Transcaucasia to the coast of the Sea of Japan, and from South Asia across Southeast Asia to the Indonesian islands of Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
and Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
. Since the end of the last glacial period, it was probably restricted by periods of deep snow lasting longer than six months. Currently, it occurs in less than 6% of its historical range, as it has been extirpated from Southwest Asia, Southwest and Central Asia, large parts of Southeast and East Asia. It now mainly occurs in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, the Indochinese Peninsula, Sumatra and the Russian Far East. In China and Myanmar, breeding populations appear to rely on immigration from neighbouring countries while its status in the Korean Peninsula is unknown.
The tiger is essentially associated with forest habitats. Tiger populations thrive where populations of wild cervids, bovid
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species, the ...
s and suids are stable.
Records in Central Asia indicate that it occurred foremost in Tugay riverine forests along the Atrek, Amu Darya, Syr Darya, Hari (Afghanistan), Hari, Chu River, Chu and Ili Rivers and their tributaries. In the Caucasus, it inhabited hilly and lowland forests.
Historical records in Iran are known only from the southern coast of the Caspian Sea and adjacent Alborz Mountains. In the Amur River, Amur-Ussuri River, Ussuri region, it inhabits Korean pine and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, where riparian forests provide food and water, and serve as dispersal corridors for both tiger and ungulates.
On the Indian subcontinent, it inhabits mainly tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist evergreen forests, tropical dry forests and the swamp forests of the Sundarbans. In the Eastern Himalayas, tigers were documented in temperate forest
A temperate forest is a forest found between the tropical and boreal regions, located in the temperate zone. It is the second largest biome on our planet, covering 25% of the world's forest area, only behind the boreal forest, which covers abou ...
up to an elevation of in Bhutan and of in the Mishmi Hills. In Myanmar, tigers are distributed across the country and among every province. The country is home to two tiger populations, Bengal and Indochinese tigers. In 1996, the composition of the two populations was 60% Bengal tigers and 40% Indochinese tigers. The natural ecological divide for these two populations is assumed to be the Irrawaddy River, but there is no scientific evidence for that hypothesis. DNA studies are needed to confirm it. Today, the presence of tigers was confirmed in the Hukawng Valley, Htamanthi Wildlife Sanctuary, and in two small areas in the Tanintharyi Region. The Tenasserim Hills is an important area, but forests are harvested there. In 2015, tigers were recorded by camera traps for the first time in the hill forests of Kayin State. In Thailand, it lives in deciduous and evergreen forests. In Laos, 14 tigers were documented in semi-evergreen and evergreen forest interspersed with grassland in Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area during surveys from 2013 to 2017. In Sumatra, tiger populations range from lowland peat swamp forests to rugged montane forests.
Behaviour and ecology
Social and daily activities
When not subject to human disturbance, the tiger is mainly Diurnality, diurnal. It does not often climb trees but cases have been recorded. It is a strong swimmer and often bathes in ponds, lakes and rivers, thus keeping cool in the heat of the day. Individuals can cross rivers up to wide and can swim up to in a day. During the 1980s, a tiger was observed frequently hunting prey through deep lake water in Ranthambhore National Park. The tiger is a long-ranging species, and individuals disperse over distances of up to to reach tiger populations in other areas. Radio telemetry, Radio-collared tigers in Chitwan National Park started Dispersal (ecology), dispersing from their natal areas earliest at the age of 19 months. Four females dispersed between , and 10 males between . None of them crossed open cultivated areas that were more than wide, but moved through forested habitat. Adult tigers lead largely solitary lives. They establish and maintain Territory (animal), territories but have much wider home ranges within which they roam. Resident adults of either sex generally confine their movements to their home ranges, within which they satisfy their needs and those of their growing cubs. Individuals sharing the same area are aware of each other's movements and activities. The size of the home range mainly depends on prey abundance, geographic area and sex of the individual. In India, home ranges appear to be while in Manchuria, they range from . In Nepal, defended territories are recorded to be for males and for females. Young female tigers establish their first territories close to their mother's. The overlap between the female and her mother's territory reduces with time. Males, however, migrate further than their female counterparts and set out at a younger age to territorial marking, mark out their own area. A young male acquires territory either by seeking out an area devoid of other male tigers, or by living as a transient in another male's territory until he is older and strong enough to challenge the resident male. Young males seeking to establish themselves thereby comprise the highest mortality rate (30–35% per year) amongst adult tigers. To identify his territory, the male marks trees by urine spraying, spraying urine, anal gland secretions, marking trails with feces and marking trees or the ground with their claws. Females also use these "scrapes", urine and fecal markings. Scent markings of this type allow an individual to pick up information on another's identity, sex and reproductive status. Females in Estrous cycle, oestrus will signal their availability by scent marking more frequently and increasing their vocalisations.
Although for the most part avoiding each other, tigers are not always territorial and relationships between individuals can be complex. An adult of either sex will sometimes share its kill with others, even with unrelated tigers. George Schaller observed a male share a kill with two females and four cubs. Unlike male lions, male tigers allow females and cubs to feed on the kill before the male is finished with it; all involved generally seem to behave amicably, in contrast to the competitive behaviour shown by a lion pride. Stephen Mills described a social feeding event in Ranthambore National Park:
Male tigers are generally less tolerant of other males within their territories than females are of other females. Territory disputes are usually solved by intimidation rather than outright violence. Several such incidents have been observed in which the subordinate tiger yielded by rolling onto its back and showing its belly in a submissive posture. Once dominance (ethology), dominance has been established, a male may tolerate a subordinate within his range, as long as they do not live in too close quarters. The most serious disputes tend to occur between two males competing for a female in oestrus, sometimes fighting to the death.
To identify his territory, the male marks trees by urine spraying, spraying urine, anal gland secretions, marking trails with feces and marking trees or the ground with their claws. Females also use these "scrapes", urine and fecal markings. Scent markings of this type allow an individual to pick up information on another's identity, sex and reproductive status. Females in Estrous cycle, oestrus will signal their availability by scent marking more frequently and increasing their vocalisations.
Although for the most part avoiding each other, tigers are not always territorial and relationships between individuals can be complex. An adult of either sex will sometimes share its kill with others, even with unrelated tigers. George Schaller observed a male share a kill with two females and four cubs. Unlike male lions, male tigers allow females and cubs to feed on the kill before the male is finished with it; all involved generally seem to behave amicably, in contrast to the competitive behaviour shown by a lion pride. Stephen Mills described a social feeding event in Ranthambore National Park:
Male tigers are generally less tolerant of other males within their territories than females are of other females. Territory disputes are usually solved by intimidation rather than outright violence. Several such incidents have been observed in which the subordinate tiger yielded by rolling onto its back and showing its belly in a submissive posture. Once dominance (ethology), dominance has been established, a male may tolerate a subordinate within his range, as long as they do not live in too close quarters. The most serious disputes tend to occur between two males competing for a female in oestrus, sometimes fighting to the death.
 Facial expressions include the "defense threat", where an individual bares its teeth, flattens its ears and its pupils enlarge. Both males and females show a flehmen response, a characteristic grimace, when sniffing urine markings, but flehmen is more often associated with males detecting the markings made by tigresses in oestrus.
Tigers Roar (vocalization), roar to signal their presence to other individuals over long distances. This vocalization is forced through an open mouth as it closes and can be heard away. They may roar three or four times in a row, and other tigers may respond in kind. When tense, tigers will moan, a sound similar to a roar but softer and made when the mouth is at least partially closed. Moaning can be heard away. For aggressive encounters, tigers growling, growl, snarling, snarl and hiss. During an attack, an explosive "coughing roar" or "coughing snarl" is emitted though an open mouth and exposed teeth. Prusten, Chuffing—soft, low-frequency snorting similar to purring in smaller cats—is heard in more friendly situations. Other vocalizations include grunts, woofs and miaows.
Facial expressions include the "defense threat", where an individual bares its teeth, flattens its ears and its pupils enlarge. Both males and females show a flehmen response, a characteristic grimace, when sniffing urine markings, but flehmen is more often associated with males detecting the markings made by tigresses in oestrus.
Tigers Roar (vocalization), roar to signal their presence to other individuals over long distances. This vocalization is forced through an open mouth as it closes and can be heard away. They may roar three or four times in a row, and other tigers may respond in kind. When tense, tigers will moan, a sound similar to a roar but softer and made when the mouth is at least partially closed. Moaning can be heard away. For aggressive encounters, tigers growling, growl, snarling, snarl and hiss. During an attack, an explosive "coughing roar" or "coughing snarl" is emitted though an open mouth and exposed teeth. Prusten, Chuffing—soft, low-frequency snorting similar to purring in smaller cats—is heard in more friendly situations. Other vocalizations include grunts, woofs and miaows.
Hunting and diet
In the wild, tigers mostly feed on large and medium-sized mammals, particularlyungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, cam ...
s weighing . Range-wide the most selected prey are sambar deer, Manchurian wapiti, barasingha and wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
. Tigers are capable of taking down larger prey like adult gaur and wild water buffalo but will also opportunistically eat much smaller prey, such as monkeys, peafowl and other ground-based birds, hares, porcupines, and fish. They also prey on other predators, including dogs, leopards, pythons, bears, and crocodiles. Tigers generally do not prey on fully grown adult Asian elephants and Indian rhinoceros but incidents have been reported. More often, it is the more vulnerable small calves that are taken. When in close proximity to humans, tigers will also sometimes prey on such domestic livestock as cattle, horses, and donkeys. Although almost exclusively carnivorous, tigers will occasionally eat vegetation for dietary fibre such as fruit of the Careya arborea, slow match tree.
Tigers are thought to be mainly Nocturnality, nocturnal predators, but in areas where humans are absent, remote-controlled, hidden camera traps recorded them hunting in daylight. They generally hunt alone and ambush their prey as most other cats do, overpowering them from any angle, using their body size and strength to knock the prey off balance. Successful hunts usually require the tiger to almost simultaneously leap onto its quarry, knock it over, and grab the throat or nape with its teeth. Despite their large size, tigers can reach speeds of about but only in short bursts; consequently, tigers must be close to their prey before they break cover. If the prey senses the tiger's presence before this, the tiger usually abandons the hunt rather than give chase or battle pre-alerted prey. Horizontal leaps of up to have been reported, although leaps of around half this distance are more typical. One in 2 to 20 hunts, including stalking near potential prey, ends in a successful kill.
When hunting larger animals, tigers prefer to Throat clamp, bite the throat and use their powerful forelimbs to hold onto the prey, often simultaneously wrestling it to the ground. The tiger remains latched onto the neck until its target dies of Strangling, strangulation. By this method, gaurs and water buffaloes weighing over a ton have been killed by tigers weighing about a sixth as much. Although they can kill healthy adults, tigers often select the calves or infirm of very large species. Healthy adult prey of this type can be dangerous to tackle, as long, strong horns, legs and tusks are all potentially fatal to the tiger. No other extant land predator routinely takes on prey this large on its own.
With small prey such as monkeys and hares, the tiger bites the nape, often breaking the spinal cord, piercing the vertebrate trachea, windpipe, or severing the jugular vein or common carotid artery. Rarely, tigers have been observed to kill prey by swiping with their paws, which are powerful enough to smash the skulls of domestic cattle, and break the backs of sloth bears.
After killing their prey, tigers sometimes drag it to conceal it in vegetation, grasping with their mouths at the site of the killing bite. This, too, can require great physical strength. In one case, after it had killed an adult gaur, a tiger was observed to drag the massive carcass over a distance of . When 13 men simultaneously tried to drag the same carcass later, they were unable to move it. An adult tiger can go for up to two weeks without eating, then gorge on of flesh at one time. In captivity, adult tigers are fed of meat a day.
Enemies and competitors
 Tigers usually prefer to eat self-killed prey, but eat carrion in times of scarcity and also Kleptoparasitism, steal prey from other large carnivores. Although predators typically avoid one another, if a prize is under dispute or a serious competitor is encountered, displays of aggression are common. If these fail, the conflicts may turn violent; tigers may kill or even prey on competitors such as leopards, dholes, striped hyenas, wolves, bears, Pythonidae, pythons, and mugger crocodiles on occasion. Crocodiles, bears, and large packs of dholes may win conflicts with tigers, and crocodiles and bears can even kill them.
The considerably smaller leopard avoids competition from tigers by hunting at different times of the day and hunting different prey. Ecology.info In India's Nagarhole National Park, most prey selected by leopards were from against a preference for heavier prey by tigers. The average prey weight in the two respective big cats in India was against . With relatively abundant prey, tigers and leopards were seen to successfully coexist without competitive exclusion or interspecies dominance (ethology), dominance hierarchies that may be more common to the African savanna, where the leopard lives beside the lion. Golden jackals may scavenge on tiger kills. Tigers appear to inhabit the deep parts of a forest while smaller predators like leopards and dholes are pushed closer to the fringes.
Tigers usually prefer to eat self-killed prey, but eat carrion in times of scarcity and also Kleptoparasitism, steal prey from other large carnivores. Although predators typically avoid one another, if a prize is under dispute or a serious competitor is encountered, displays of aggression are common. If these fail, the conflicts may turn violent; tigers may kill or even prey on competitors such as leopards, dholes, striped hyenas, wolves, bears, Pythonidae, pythons, and mugger crocodiles on occasion. Crocodiles, bears, and large packs of dholes may win conflicts with tigers, and crocodiles and bears can even kill them.
The considerably smaller leopard avoids competition from tigers by hunting at different times of the day and hunting different prey. Ecology.info In India's Nagarhole National Park, most prey selected by leopards were from against a preference for heavier prey by tigers. The average prey weight in the two respective big cats in India was against . With relatively abundant prey, tigers and leopards were seen to successfully coexist without competitive exclusion or interspecies dominance (ethology), dominance hierarchies that may be more common to the African savanna, where the leopard lives beside the lion. Golden jackals may scavenge on tiger kills. Tigers appear to inhabit the deep parts of a forest while smaller predators like leopards and dholes are pushed closer to the fringes.
Reproduction and life cycle
The tiger Mating, mates all year round, but most cubs are born between March and June, with a second peak in September. Gestation ranges from 93 to 114 days, with an average of 103 to 105 days. A female is only estrus cycle, receptive for three to six days. Mating is frequent and noisy during that time. The female gives birth in a sheltered location such as in tall grass, in a dense thicket, cave or rocky crevice. The father generally takes no part in rearing. Litters consist of two or three cubs, rarely as many as six. Cubs weigh from each at birth, and are born with eyes closed. They open their eyes when they are six to 14 days old. Their milk teeth break through at the age of about two weeks. They start to eat meat at the age of eight weeks. At around this time, females usually shift them to a new den. They make short ventures with their mother, although they do not travel with her as she roams her territory until they are older. Females lactate for five to six months. Around the time they are weaned, they start to accompany their mother on territorial walks and are taught how to hunt. A dominance (ethology), dominant cub emerges in most litters, usually a male. The dominant cub is more active than its siblings and takes the lead in their play, eventually leaving its mother and becoming independent earlier. The cubs start hunting on their own earliest at the age of 11 months, and become independent around 18 to 20 months of age. They separate from their mother at the age of two to two and a half years, but continue to grow until the age of five years. Young females reach sexual maturity at three to four years, whereas males at four to five years. Unrelated wandering male tigers often kill cubs to make the female receptive, since the tigress may give birth to another litter within five months if the cubs of the previous litter are lost. The mortality rate of tiger cubs is about 50% in the first two years. Few other predators attack tiger cubs due to the diligence and ferocity of the mother. Apart from humans and other tigers, common causes of cub mortality are starvation, freezing, and accidents. Generation time, Generation length of the tiger is about eight years. The oldest recorded captive tiger lived for 26 years. Occasionally, male tigers participate in raising cubs, usually their own, but this is extremely rare and not always well understood. In May 2015, Amur tigers were photographed by camera traps in the Sikhote-Alin Nature Reserve. The photos show a male Amur tiger pass by, followed by a female and three cubs within the span of about two minutes. In Ranthambore, a male Bengal tiger raised and defended two orphaned female cubs after their mother had died of illness. The cubs remained under his care, he supplied them with food, protected them from his rival and sister, and apparently also trained them.Conservation
In the 1990s, a new approach to tiger conservation was developed: Tiger Conservation Units (TCUs), which are blocks of habitat that have the potential to host tiger populations in 15 habitat types within five bioregions. Altogether 143 TCUs were identified and prioritized based on size and integrity of habitat, poaching pressure and population status. They range in size from . In 2016, an estimate of a global wild tiger population of approximately 3,890 individuals was presented during the Third Asia Ministerial Conference on Tiger Conservation. The World Wildlife Fund, WWF subsequently declared that the world's count of wild tigers had risen for the first time in a century. Major threats to the tiger includehabitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, habitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological processes ...
and poaching
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
for fur and body parts, which have simultaneously greatly reduced tiger populations in the wild. In India, only 11% of the historical tiger habitat remains due to habitat fragmentation. Demand for tiger parts for use in traditional Chinese medicine has also been cited as a major threat to tiger populations. Some estimates suggest that there are fewer than 2,500 mature breeding individuals, with no subpopulation containing more than 250 mature breeding individuals.
India is home to the world's largest population of wild tigers. A 2014 census estimated a population of 2,226, a 30% increase since 2011. On International Tiger Day 2019, the 'Tiger Estimation Report 2018' was released by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. The report estimates a population of 2967 tigers in India with 25% increase since 2014. Modi said "India is one of the safest habitats for tigers as it has achieved the target of doubling the tiger population from 1411 in 2011 to 2967 in 2019".
As of 2022, India accounts for 75 percent of global tiger population.
In 1973, India's ''Project Tiger'', started by Indira Gandhi, established numerous tiger reserves. The project was credited with tripling the number of wild Bengal tigers from some 1,200 in 1973 to over 3,500 in the 1990s, but a 2007 census showed that numbers had dropped back to about 1,400 tigers because of poaching. Following the report, the Indian government pledged $153 million to the initiative, set up measures to combat poaching, promised funds to relocate up to 200,000 villagers in order to reduce human-tiger interactions, and set up eight new tiger reserves in India, tiger reserves. India also reintroduced tigers to the Sariska Tiger Reserve and by 2009 it was claimed that poaching had been effectively countered at Ranthambore National Park.
In the 1940s, the Siberian tiger was on the brink of extinction with only about 40 animals remaining in the wild in Russia. As a result, anti-poaching controls were put in place by the Soviet Union and a network of protected zones (zapovedniks) were instituted, leading to a rise in the population to several hundred. Poaching again became a problem in the 1990s, when the economy of Russia collapsed. The major obstacle in preserving the species is the enormous territory individual tigers require, up to needed by a single female and more for a single male. Current conservation efforts are led by local governments and NGO's in concert with international organisations, such as the World Wide Fund for Nature and the Wildlife Conservation Society. The competitive exclusion of wolves by tigers has been used by Russian conservationists to convince hunters to tolerate the big cats. Tigers have less impact on ungulate populations than do wolves, and are effective in controlling the latter's numbers. In 2005, there were thought to be about 360 animals in Russia, though these exhibited little genetic diversity. However, in a decade later, the Siberian tiger census was estimated from 480 to 540 individuals.
In China, tigers became the target of large-scale 'anti-pest' campaigns in the early 1950s, where suitable habitats were fragmented following deforestation and resettlement of people to rural areas, who hunted tigers and prey species. Though tiger hunting was prohibited in 1977, the population continued to decline and is considered extinct in southern China since 2001. Having earlier rejected the Western-led environmentalist movement, China changed its stance in the 1980s and became a party to the CITES treaty. By 1993 it had banned the trade in tiger parts, and this diminished the use of tiger bones in traditional Chinese medicine. The Tibetan people's trade in tiger skins has also been a threat to tigers. The pelts were used in clothing, tiger-skin ''chuba'' being worn as fashion. In 2006 the 14th Dalai Lama was persuaded to take up the issue. Since then there has been a change of attitude, with some Tibetans publicly burning their chubas.
 In 1994, the Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Conservation Strategy addressed the potential crisis that tigers faced in Sumatra. The Sumatran Tiger Project (STP) was initiated in June 1995 in and around the Way Kambas National Park to ensure the long-term viability of wild Sumatran tigers and to accumulate data on tiger life-history characteristics vital for the management of wild populations. By August 1999, the teams of the STP had evaluated 52 sites of potential tiger habitat in Lampung Province, of which only 15 these were intact enough to contain tigers.Tilson, R. (1999). ''Sumatran Tiger Project Report No. 17 & 18: July − December 1999''. Grant number 1998-0093-059. Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Steering Committee, Jakarta. In the framework of the STP a community-based conservation programme was initiated to document the tiger-human dimension in the park to enable conservation authorities to resolve tiger-human conflicts based on a comprehensive database rather than anecdotes and opinions.Nyhus, P., Sumianto and R. Tilson (1999). ''The tiger-human dimension in southeast Sumatra'', pp. 144–145 in: Seidensticker, J., Christie, S. and Jackson, P. (eds). ''Riding the tiger: tiger conservation in human-dominated landscapes''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, .
The Wildlife Conservation Society and Panthera Corporation formed the collaboration ''Tigers Forever'', with field sites including the world's largest tiger reserve, the Hukaung Valley in Myanmar. Other reserves were in the Western Ghats in India, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, the Russian Far East covering in total about .
Tigers have been studied in the wild using a variety of techniques. Tiger population have been estimated using plaster casts of their pugmarks, although this method was criticized as being inaccurate. More recent techniques include the use of camera traps and studies of DNA from tiger scat, while radio telemetry, radio-collaring has been used to track tigers in the wild. Tiger spray has been found to be just as good, or better, as a source of DNA than scat.
In 1994, the Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Conservation Strategy addressed the potential crisis that tigers faced in Sumatra. The Sumatran Tiger Project (STP) was initiated in June 1995 in and around the Way Kambas National Park to ensure the long-term viability of wild Sumatran tigers and to accumulate data on tiger life-history characteristics vital for the management of wild populations. By August 1999, the teams of the STP had evaluated 52 sites of potential tiger habitat in Lampung Province, of which only 15 these were intact enough to contain tigers.Tilson, R. (1999). ''Sumatran Tiger Project Report No. 17 & 18: July − December 1999''. Grant number 1998-0093-059. Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Steering Committee, Jakarta. In the framework of the STP a community-based conservation programme was initiated to document the tiger-human dimension in the park to enable conservation authorities to resolve tiger-human conflicts based on a comprehensive database rather than anecdotes and opinions.Nyhus, P., Sumianto and R. Tilson (1999). ''The tiger-human dimension in southeast Sumatra'', pp. 144–145 in: Seidensticker, J., Christie, S. and Jackson, P. (eds). ''Riding the tiger: tiger conservation in human-dominated landscapes''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, .
The Wildlife Conservation Society and Panthera Corporation formed the collaboration ''Tigers Forever'', with field sites including the world's largest tiger reserve, the Hukaung Valley in Myanmar. Other reserves were in the Western Ghats in India, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, the Russian Far East covering in total about .
Tigers have been studied in the wild using a variety of techniques. Tiger population have been estimated using plaster casts of their pugmarks, although this method was criticized as being inaccurate. More recent techniques include the use of camera traps and studies of DNA from tiger scat, while radio telemetry, radio-collaring has been used to track tigers in the wild. Tiger spray has been found to be just as good, or better, as a source of DNA than scat.
Relation with humans
Tiger hunting
 The tiger has been one of the most sought after game animals of Asia. Tiger hunting took place on a large scale in the early 19th and 20th centuries, being a recognised and admired sport by the British in Presidencies and provinces of British India, colonial India, the maharajas and aristocratic class of the erstwhile princely states of pre-independence India. A single maharaja or English hunter could claim to kill over a hundred tigers in their hunting career. Over 80,000 tigers were slaughtered in just 50 years spanning from 1875 to 1925 in British-ruled India. Tiger hunting was done by some hunters on foot; others sat up on ''Hunting blind, machans'' with a goat or buffalo tied out as bait; yet others on elephant-back. King George V on his visit to Colonial India in 1911 killed 39 tigers in a matter of 10 days One of these is on display at the Royal Albert Memorial Museum.
Historically, tigers have been hunted at a large scale so their famous striped skins could be collected. The trade in tiger skins peaked in the 1960s, just before international conservation efforts took effect. By 1977, a tiger skin in an English market was considered to be worth US$4,250.
The tiger has been one of the most sought after game animals of Asia. Tiger hunting took place on a large scale in the early 19th and 20th centuries, being a recognised and admired sport by the British in Presidencies and provinces of British India, colonial India, the maharajas and aristocratic class of the erstwhile princely states of pre-independence India. A single maharaja or English hunter could claim to kill over a hundred tigers in their hunting career. Over 80,000 tigers were slaughtered in just 50 years spanning from 1875 to 1925 in British-ruled India. Tiger hunting was done by some hunters on foot; others sat up on ''Hunting blind, machans'' with a goat or buffalo tied out as bait; yet others on elephant-back. King George V on his visit to Colonial India in 1911 killed 39 tigers in a matter of 10 days One of these is on display at the Royal Albert Memorial Museum.
Historically, tigers have been hunted at a large scale so their famous striped skins could be collected. The trade in tiger skins peaked in the 1960s, just before international conservation efforts took effect. By 1977, a tiger skin in an English market was considered to be worth US$4,250.
Body part use
Tiger parts are commonly used as amulets in South Asia, South and Southeast Asia. In the Philippines, the fossils in Palawan were found besides stone tools. This, besides the evidence for cuts on the bones, and the use of fire, suggests that early humans had accumulated the bones, and the condition of the tiger subfossils, dated to approximately 12,000 to 9,000 years ago, differed from other fossils in the assemblage, dated to the Upper Paleolithic. The tiger subfossils showed longitudinal fracture of the cortical bone due to weathering, which suggests that they had post-mortem been exposed to light and air. Tiger canines were found in Ambangan sites dating to the 10th to 12th centuries in Butuan, Mindanao. Many people in China and other parts of Asia have a belief that various tiger parts have Traditional Chinese medicine, medicinal properties, including as pain killers and aphrodisiacs. There is no scientific evidence to support these beliefs. The use of tiger parts in pharmaceutical drugs in China is already banned, and the government has made some offences in connection with tiger poaching punishable by death. Furthermore, all trade in tiger parts is illegal under the CITES, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora and a domestic trade ban has been in place in China since 1993.
However, the trading of tiger parts in Asia has become a major black market industry and governmental and conservation attempts to stop it have been ineffective to date. Almost all black marketers engaged in the trade are based in China and have either been shipped and sold within in their own country or into Taiwan,
Many people in China and other parts of Asia have a belief that various tiger parts have Traditional Chinese medicine, medicinal properties, including as pain killers and aphrodisiacs. There is no scientific evidence to support these beliefs. The use of tiger parts in pharmaceutical drugs in China is already banned, and the government has made some offences in connection with tiger poaching punishable by death. Furthermore, all trade in tiger parts is illegal under the CITES, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora and a domestic trade ban has been in place in China since 1993.
However, the trading of tiger parts in Asia has become a major black market industry and governmental and conservation attempts to stop it have been ineffective to date. Almost all black marketers engaged in the trade are based in China and have either been shipped and sold within in their own country or into Taiwan, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
or Japan. The Chinese subspecies was almost completely decimated by killing for commerce due to both the parts and skin trades in the 1950s through the 1970s. Contributing to the illegal trade, there are a number of tiger farms in the country specialising in breeding them for profit. It is estimated that between 5,000 and 10,000 captive-bred, semi-tame animals live in these farms today. However, many tigers for traditional medicine black market are wild ones shot or snared by poachers and may be caught anywhere in the tiger's remaining range (from Siberia to India to the Malay Peninsula to Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
). In the Asian black market, a tiger penis can be worth the equivalent of around $300 U.S. dollars. In the years of 1990 through 1992, 27 million products with tiger derivatives were found. In July 2014 at an international convention on endangered species in Geneva, Switzerland, a Chinese representative admitted for the first time his government was aware trading in tiger skins was occurring in China.
Man-eating tigers
 Wild tigers that have had no prior contact with humans actively avoid interactions with them. However, tigers cause more human deaths through direct attack than any other wild mammal. Attacks are occasionally provoked, as tigers lash out after being injured while they themselves are hunted. Attacks can be provoked accidentally, as when a human surprises a tiger or inadvertently comes between a mother and her young, or as in a case in rural India when a postman startled a tiger, used to seeing him on foot, by riding a bicycle. Occasionally tigers come to view people as prey. Such attacks are most common in areas where population growth, logging, and farming have put pressure on tiger habitats and reduced their wild prey. Most man-eating tigers are old, missing teeth, and unable to capture their preferred prey. For example, the Champawat Tiger, a tigress found in Nepal and then India, had two broken canines. She was responsible for an estimated 430 human deaths, the most attacks known to be perpetrated by a single wild animal, by the time she was shot in 1907 by Jim Corbett. According to Corbett, tiger attacks on humans are normally in daytime, when people are working outdoors and are not keeping watch. Early writings tend to describe man-eating tigers as cowardly because of their ambush tactics.Tiger of Segur, The Man-Eater of Segur", from ''Nine Man-Eaters and One Rogue'', Kenneth Anderson, Allen & Unwin, 1954
Man-eaters have been a particular problem in recent decades in India and Bangladesh, especially in Kumaon division, Kumaon, Garhwal division, Garhwal and the Sundarbans mangrove swamps of Bengal, where some healthy tigers have hunted humans. Because of rapid habitat loss attributed to climate change, tiger attacks have increased in the Sundarbans. The Sundarbans area had 129 human deaths from tigers from 1969 to 1971. In the 10 years prior to that period, about 100 attacks per year in the Sundarbans, with a high of around 430 in some years of the 1960s. Unusually, in some years in the Sundarbans, more humans are killed by tigers than vice versa. In 1972, India's production of honey and beeswax dropped by 50% when at least 29 people who gathered these materials were devoured. In 1986 in the Sundarbans, since tigers almost always attack from the rear, masks with human faces were worn on the back of the head, on the theory that tigers usually do not attack if seen by their prey. This decreased the number of attacks only temporarily. All other means to prevent attacks, such as providing more prey or using electrified human dummies, did not work as well.
Wild tigers that have had no prior contact with humans actively avoid interactions with them. However, tigers cause more human deaths through direct attack than any other wild mammal. Attacks are occasionally provoked, as tigers lash out after being injured while they themselves are hunted. Attacks can be provoked accidentally, as when a human surprises a tiger or inadvertently comes between a mother and her young, or as in a case in rural India when a postman startled a tiger, used to seeing him on foot, by riding a bicycle. Occasionally tigers come to view people as prey. Such attacks are most common in areas where population growth, logging, and farming have put pressure on tiger habitats and reduced their wild prey. Most man-eating tigers are old, missing teeth, and unable to capture their preferred prey. For example, the Champawat Tiger, a tigress found in Nepal and then India, had two broken canines. She was responsible for an estimated 430 human deaths, the most attacks known to be perpetrated by a single wild animal, by the time she was shot in 1907 by Jim Corbett. According to Corbett, tiger attacks on humans are normally in daytime, when people are working outdoors and are not keeping watch. Early writings tend to describe man-eating tigers as cowardly because of their ambush tactics.Tiger of Segur, The Man-Eater of Segur", from ''Nine Man-Eaters and One Rogue'', Kenneth Anderson, Allen & Unwin, 1954
Man-eaters have been a particular problem in recent decades in India and Bangladesh, especially in Kumaon division, Kumaon, Garhwal division, Garhwal and the Sundarbans mangrove swamps of Bengal, where some healthy tigers have hunted humans. Because of rapid habitat loss attributed to climate change, tiger attacks have increased in the Sundarbans. The Sundarbans area had 129 human deaths from tigers from 1969 to 1971. In the 10 years prior to that period, about 100 attacks per year in the Sundarbans, with a high of around 430 in some years of the 1960s. Unusually, in some years in the Sundarbans, more humans are killed by tigers than vice versa. In 1972, India's production of honey and beeswax dropped by 50% when at least 29 people who gathered these materials were devoured. In 1986 in the Sundarbans, since tigers almost always attack from the rear, masks with human faces were worn on the back of the head, on the theory that tigers usually do not attack if seen by their prey. This decreased the number of attacks only temporarily. All other means to prevent attacks, such as providing more prey or using electrified human dummies, did not work as well.
In captivity
 In Ancient Rome, Ancient Roman times, tigers were kept in menageries and amphitheatres to be exhibited, trained and paraded, and were often provoked to fight gladiators and other exotic beasts. Since the 17th century, tigers, being rare and ferocious, were sought after to keep at European castles as symbols of their owners' power. Tigers became central zoo and circus exhibits in the 18th century: a tiger could cost up to 4,000 French franc, francs in France (for comparison, a professor of the Beaux-Arts at Lyons earned only 3,000 francs a year), or up to $3,500 in the United States, where a lion cost no more than $1,000.
In 2007, over 4,000 captive tigers lived in China, of which 3,000 were held by about 20 larger facilities, with the rest held by some 200 smaller facilities. In 2011, 468 facilities in the USA kept 2,884 tigers. Nineteen US states banned private ownership of tigers, fifteen require a license, and sixteen states have no regulation. Genetic ancestry of 105 captive tigers from fourteen countries and regions showed that forty-nine animals belonged distinctly to five subspecies; fifty-two animals had mixed subspecies origins. Many Siberian tigers in zoos today are actually the result of crosses with Bengal tigers.
In Ancient Rome, Ancient Roman times, tigers were kept in menageries and amphitheatres to be exhibited, trained and paraded, and were often provoked to fight gladiators and other exotic beasts. Since the 17th century, tigers, being rare and ferocious, were sought after to keep at European castles as symbols of their owners' power. Tigers became central zoo and circus exhibits in the 18th century: a tiger could cost up to 4,000 French franc, francs in France (for comparison, a professor of the Beaux-Arts at Lyons earned only 3,000 francs a year), or up to $3,500 in the United States, where a lion cost no more than $1,000.
In 2007, over 4,000 captive tigers lived in China, of which 3,000 were held by about 20 larger facilities, with the rest held by some 200 smaller facilities. In 2011, 468 facilities in the USA kept 2,884 tigers. Nineteen US states banned private ownership of tigers, fifteen require a license, and sixteen states have no regulation. Genetic ancestry of 105 captive tigers from fourteen countries and regions showed that forty-nine animals belonged distinctly to five subspecies; fifty-two animals had mixed subspecies origins. Many Siberian tigers in zoos today are actually the result of crosses with Bengal tigers.
Cultural depictions
 Tigers and their superlative qualities have been a source of fascination for mankind since ancient times, and they are routinely visible as important cultural and media motifs. They are also considered one of the
Tigers and their superlative qualities have been a source of fascination for mankind since ancient times, and they are routinely visible as important cultural and media motifs. They are also considered one of the charismatic megafauna
Charismatic megafauna are animal species that are large—in the relevant category that they represent—with symbolic value or widespread popular appeal, and are often used by environmental activists to gain public support for environmentalist g ...
, and are used as the face of conservation campaigns worldwide. In a 2004 online poll conducted by cable television channel Animal Planet, involving more than 50,000 viewers from 73 countries, the tiger was voted the world's favourite animal with 21% of the vote, narrowly beating the dog.
Mythology and legend
 In Chinese mythology and Chinese culture, culture, the Tiger (zodiac), tiger is one of the 12 animals of the Chinese astrology, Chinese zodiac. In Chinese art, the tiger is depicted as an earth symbol and equal rival of the Chinese dragon – the two representing matter and spirit respectively. The Southern Chinese martial art Hung Ga is based on the movements of the tiger and the crane. In History of China, Imperial China, a tiger was the personification of war and often represented the highest army General Officer, general (or present day United States Secretary of Defense, defense secretary), while the emperor and empress were represented by a dragon and Fenghuang, phoenix, respectively. The White Tiger (Chinese constellation), White Tiger () is one of the Four Symbols (Chinese constellation), Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (), and it represents the west and the autumn season.
The tiger's tail appears in stories from countries including China and Korea, it being generally inadvisable to grasp a tiger by the tail. In Korean mythology, Korean myth and Korean culture, culture, the tiger is regarded as a guardian that drives away evil spirits and a sacred creature that brings good luck – the symbol of courage and absolute power. For the people who live in and around the forests of Korea, the tiger considered the symbol of the Mountain Spirit or King of mountain animals. So, Koreans also called the tigers "San Gun" (산군) means Mountain Lord.
In Buddhism, the tiger is one of the Three Senseless Creatures, symbolising anger, with the monkey representing greed and the deer lovesickness. The Tungusic peoples considered the Siberian tiger a near-deity and often referred to it as "Grandfather" or "Old man". The Udege people, Udege and Nani people, Nanai called it "Amba". The Manchu people, Manchu considered the Siberian tiger as "Hu Lin," the king. In Hinduism, the god Shiva wears and sits on tiger skin. The ten-armed warrior goddess Durga rides the tigress (or lioness) Damon into battle. In southern India the god Ayyappan was associated with a tiger. Dingu-Aneni is the god in North-East India is also associated with tiger. The Werecat, weretiger replaces the werewolf in shapeshifting folklore in Asia; in India they were evil sorcerers, while in Indonesia and Malaysia they were somewhat more benign. In Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman tradition, the tiger was depicted being ridden by the god Dionysus.
In Chinese mythology and Chinese culture, culture, the Tiger (zodiac), tiger is one of the 12 animals of the Chinese astrology, Chinese zodiac. In Chinese art, the tiger is depicted as an earth symbol and equal rival of the Chinese dragon – the two representing matter and spirit respectively. The Southern Chinese martial art Hung Ga is based on the movements of the tiger and the crane. In History of China, Imperial China, a tiger was the personification of war and often represented the highest army General Officer, general (or present day United States Secretary of Defense, defense secretary), while the emperor and empress were represented by a dragon and Fenghuang, phoenix, respectively. The White Tiger (Chinese constellation), White Tiger () is one of the Four Symbols (Chinese constellation), Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (), and it represents the west and the autumn season.
The tiger's tail appears in stories from countries including China and Korea, it being generally inadvisable to grasp a tiger by the tail. In Korean mythology, Korean myth and Korean culture, culture, the tiger is regarded as a guardian that drives away evil spirits and a sacred creature that brings good luck – the symbol of courage and absolute power. For the people who live in and around the forests of Korea, the tiger considered the symbol of the Mountain Spirit or King of mountain animals. So, Koreans also called the tigers "San Gun" (산군) means Mountain Lord.
In Buddhism, the tiger is one of the Three Senseless Creatures, symbolising anger, with the monkey representing greed and the deer lovesickness. The Tungusic peoples considered the Siberian tiger a near-deity and often referred to it as "Grandfather" or "Old man". The Udege people, Udege and Nani people, Nanai called it "Amba". The Manchu people, Manchu considered the Siberian tiger as "Hu Lin," the king. In Hinduism, the god Shiva wears and sits on tiger skin. The ten-armed warrior goddess Durga rides the tigress (or lioness) Damon into battle. In southern India the god Ayyappan was associated with a tiger. Dingu-Aneni is the god in North-East India is also associated with tiger. The Werecat, weretiger replaces the werewolf in shapeshifting folklore in Asia; in India they were evil sorcerers, while in Indonesia and Malaysia they were somewhat more benign. In Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman tradition, the tiger was depicted being ridden by the god Dionysus.

Literature and media
In the Hindu epic Mahabharata, the tiger is fiercer and more ruthless than the lion. William Blake's poem in his ''Songs of Experience'' (1794), titled "The Tyger", portrays the tiger as a menacing and fearful animal. In Rudyard Kipling's 1894 ''The Jungle Book'', the tiger Shere Khan is the mortal enemy of the human protagonist Mowgli. Yann Martel's 2001 Booker Prize winning novel ''Life of Pi'', features the title character surviving shipwreck for months on a small boat with a large Bengal tiger while avoiding being eaten. The story was adapted in Ang Lee's 2012 Life of Pi (film), feature film of the same name. Friendly tiger characters include Tigger in A. A. Milne's Winnie-the-Pooh and Hobbes (Calvin and Hobbes), Hobbes of the comic strip ''Calvin and Hobbes'', both represented as stuffed animals come to life. Tony the Tiger is a famous mascot for Kellogg's breakfast cereal Frosted Flakes, known for his catchphrase "They're Gr-r-reat!".Heraldry and emblems
 The tiger is one of the animals displayed on the Pashupati seal of the Indus Valley civilisation. The tiger was the emblem of the Chola Dynasty and was depicted on coins, seals and banners. The seals of several Chola copper coins show the tiger, the Pandyan emblem fish and the Chera dynasty, Chera emblem bow, indicating that the Cholas had achieved political supremacy over the latter two dynasties. Gold coins found in Kavilayadavalli in the Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh have motifs of the tiger, bow and some indistinct marks. The tiger symbol of Chola Empire was later adopted by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam and the tiger became a symbol of the unrecognised state of Tamil Eelam and Tamil independence movement. The Bengal tiger is the
The tiger is one of the animals displayed on the Pashupati seal of the Indus Valley civilisation. The tiger was the emblem of the Chola Dynasty and was depicted on coins, seals and banners. The seals of several Chola copper coins show the tiger, the Pandyan emblem fish and the Chera dynasty, Chera emblem bow, indicating that the Cholas had achieved political supremacy over the latter two dynasties. Gold coins found in Kavilayadavalli in the Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh have motifs of the tiger, bow and some indistinct marks. The tiger symbol of Chola Empire was later adopted by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam and the tiger became a symbol of the unrecognised state of Tamil Eelam and Tamil independence movement. The Bengal tiger is the national animal
This is a list of countries that have officially designated one or more animals as their national animals.
National animal
{, class="wikitable sortable"
! Country
! Name of animal
! Scientific name (Latin name)
! class="unsortable", Picture
...
of India and Bangladesh. The Malaysian tiger is the national animal of Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
. The Siberian tiger is the national animal of South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
. The Tiger is featured on the logo of the Delhi Capitals Indian Premier League, IPL team.
In European heraldry, the Tyger (heraldry), tyger, a depiction of a tiger as imagined by European artists, is among the creatures used in charges and supporters. This creature has several notable differences from real tigers, lacking stripes and having a leonine tufted tail and a head terminating in large, pointed jaws. A more realistic tiger entered the heraldic armory through the British Empire's expansion into Asia, and is referred to as the Bengal tiger to distinguish it from its older counterpart. The Bengal tiger is not a common creature in heraldry, but is used as a supporter in the arms of Bombay and emblazoned on the shield of the University of Madras.Arthur Fox-Davies, ''A Complete Guide to Heraldry'', T.C. and E.C. Jack, London, 1909, 191–192, https://archive.org/details/completeguidetoh00foxduoft.
See also
* Siegfried & Roy, two famous tamers of tigers * List of largest cats * ''Tiger King'', a 2020 crime documentary series on the exotic pet trade * Tiger versus lionReferences
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
* * * * * {{Portal bar, Cats, Mammals, Animals, Biology, Asia Apex predators Big cats Conservation-reliant species EDGE species Extant Pleistocene first appearances Fauna of South Asia Fauna of Southeast Asia Felids of Asia Mammals described in 1758 Mammals of East Asia National symbols of India National symbols of Bangladesh National symbols of Malaysia National symbols of Singapore Panthera Species endangered by agricultural development Species endangered by deliberate extirpation efforts Species endangered by human consumption for medicinal or magical purposes Species endangered by logging Species endangered by urbanization Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus