Through the Looking Glass on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Through the Looking-Glass, and What Alice Found There'' (also known as ''Alice Through the Looking-Glass'' or simply ''Through the Looking-Glass'') is a novel published on 27 December 1871 (though indicated as 1872) by
 Chapter Two – The Garden of Live Flowers: Upon leaving the house (where it had been a cold, snowy night), she enters a sunny spring garden where the flowers can speak; they perceive Alice as being a "flower that can move about". Elsewhere in the garden, Alice meets the Red Queen, who is now human-sized, and who impresses Alice with her ability to run at breathtaking speeds.
Chapter Three – Looking-Glass Insects: The Red Queen reveals to Alice that the entire countryside is laid out in squares, like a gigantic chessboard, and offers to make Alice a queen if she can move all the way to the eighth rank/row in a chess match. Alice is placed in the second rank as one of the White Queen's pawns, and begins her journey across the chessboard by boarding a train that jumps over the third row and directly into the fourth rank, thus acting on the rule that pawns can advance two spaces on their first move. She arrives in a forest where a depressed gnat teaches her about the looking glass insects, strange creatures part bug part object (e.g., bread and butterfly, rocking horse fly), before flying away sadly. Alice continues her journey and along the way, crosses the "wood where things have no names". There she forgets all nouns, including her own name. With the help of a fawn who has also forgotten his identity, she makes it to the other side, where they both remember everything. Realizing that he is a fawn, she is a human, and that fawns are afraid of humans, it runs off (to Alice's frustration).
Chapter Two – The Garden of Live Flowers: Upon leaving the house (where it had been a cold, snowy night), she enters a sunny spring garden where the flowers can speak; they perceive Alice as being a "flower that can move about". Elsewhere in the garden, Alice meets the Red Queen, who is now human-sized, and who impresses Alice with her ability to run at breathtaking speeds.
Chapter Three – Looking-Glass Insects: The Red Queen reveals to Alice that the entire countryside is laid out in squares, like a gigantic chessboard, and offers to make Alice a queen if she can move all the way to the eighth rank/row in a chess match. Alice is placed in the second rank as one of the White Queen's pawns, and begins her journey across the chessboard by boarding a train that jumps over the third row and directly into the fourth rank, thus acting on the rule that pawns can advance two spaces on their first move. She arrives in a forest where a depressed gnat teaches her about the looking glass insects, strange creatures part bug part object (e.g., bread and butterfly, rocking horse fly), before flying away sadly. Alice continues her journey and along the way, crosses the "wood where things have no names". There she forgets all nouns, including her own name. With the help of a fawn who has also forgotten his identity, she makes it to the other side, where they both remember everything. Realizing that he is a fawn, she is a human, and that fawns are afraid of humans, it runs off (to Alice's frustration).
 Chapter Four – Tweedledum and Tweedledee: She then meets the fat twin brothers Tweedledum and Tweedledee, whom she knows from the
Chapter Four – Tweedledum and Tweedledee: She then meets the fat twin brothers Tweedledum and Tweedledee, whom she knows from the  Chapter Five – Wool and Water: Alice next meets the White Queen, who is very absent-minded but boasts of (and demonstrates) her ability to remember future events before they have happened. Alice and the White Queen advance into the chessboard's fifth rank by crossing over a brook together, but at the very moment of the crossing, the Queen transforms into a talking Sheep in a small shop. Alice soon finds herself struggling to handle the oars of a small rowboat, where the Sheep annoys her with (seemingly) nonsensical shouting about "
Chapter Five – Wool and Water: Alice next meets the White Queen, who is very absent-minded but boasts of (and demonstrates) her ability to remember future events before they have happened. Alice and the White Queen advance into the chessboard's fifth rank by crossing over a brook together, but at the very moment of the crossing, the Queen transforms into a talking Sheep in a small shop. Alice soon finds herself struggling to handle the oars of a small rowboat, where the Sheep annoys her with (seemingly) nonsensical shouting about "
Lewis Carroll
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (; 27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet and mathematician. His most notable works are ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865) and its sequel ...
and the sequel to ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creatur ...
'' (1865). Alice
Alice may refer to:
* Alice (name), most often a feminine given name, but also used as a surname
Literature
* Alice (''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''), a character in books by Lewis Carroll
* ''Alice'' series, children's and teen books by ...
again enters a fantastical world, this time by climbing through a mirror into the world that she can see beyond it. There she finds that, just like a reflection, everything is reversed, including logic (for example, running helps one remain stationary, walking away from something brings one towards it, chessmen are alive, nursery rhyme characters exist, and so on).
''Through the Looking-Glass'' includes such verses as "Jabberwocky
"Jabberwocky" is a nonsense poem written by Lewis Carroll about the killing of a creature named "the Jabberwock". It was included in his 1871 novel '' Through the Looking-Glass'', the sequel to ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865). The ...
" and "The Walrus and the Carpenter
"The Walrus and the Carpenter" is a narrative poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in his book ''Through the Looking-Glass'', published in December 1871. The poem is recited in chapter four, by Tweedledum and Tweedledee to Alice. The poem is co ...
", and the episode involving Tweedledum and Tweedledee. The mirror above the fireplace that is displayed at Hetton Lawn in Charlton Kings, Gloucestershire (a house that was owned by Alice Liddell
Alice Pleasance Hargreaves (''née'' Liddell, ; 4 May 1852 – 16 November 1934), was an English woman who, in her childhood, was an acquaintance and photography subject of Lewis Carroll. One of the stories he told her during a boating trip bec ...
's grandparents, and was regularly visited by Alice and Lewis Carroll) resembles the one drawn by John Tenniel
Sir John Tenniel (; 28 February 182025 February 1914)Johnson, Lewis (2003), "Tenniel, John", ''Grove Art Online, Oxford Art Online'', Oxford University Press. Web. Retrieved 12 December 2016. was an English illustrator, graphic humorist and pol ...
and is cited as a possible inspiration for Carroll.
It was the first of the "Alice" stories to gain widespread popularity, and prompted a newfound appreciation for its predecessor when it was published.
Plot summary
Chapter One – Looking-Glass House:Alice
Alice may refer to:
* Alice (name), most often a feminine given name, but also used as a surname
Literature
* Alice (''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''), a character in books by Lewis Carroll
* ''Alice'' series, children's and teen books by ...
is playing with a white kitten (whom she calls "Snowdrop") and a black kitten (whom she calls "Kitty") when she ponders what the world is like on the other side of a mirror's reflection. Climbing up onto the fireplace mantel
The fireplace mantel or mantelpiece, also known as a chimneypiece, originated in medieval times as a hood that projected over a fire grate to catch the smoke. The term has evolved to include the decorative framework around the fireplace, and ca ...
, she pokes at the wall-hung mirror behind the fireplace and discovers, to her surprise, that she is able to step through it to an alternative world. In this reflected version of her own house, she finds a book with looking-glass poetry, "Jabberwocky
"Jabberwocky" is a nonsense poem written by Lewis Carroll about the killing of a creature named "the Jabberwock". It was included in his 1871 novel '' Through the Looking-Glass'', the sequel to ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865). The ...
", whose reversed printing she can read only by holding it up to the mirror. She also observes that the chess piece
A chess piece, or chessman, is a game piece that is placed on a chessboard to play the game of chess. It can be either white or black, and it can be one of six types: king, queen, rook, bishop, knight, or pawn.
Chess sets generally come with si ...
s have come to life, though they remain small enough for her to pick up.
 Chapter Two – The Garden of Live Flowers: Upon leaving the house (where it had been a cold, snowy night), she enters a sunny spring garden where the flowers can speak; they perceive Alice as being a "flower that can move about". Elsewhere in the garden, Alice meets the Red Queen, who is now human-sized, and who impresses Alice with her ability to run at breathtaking speeds.
Chapter Three – Looking-Glass Insects: The Red Queen reveals to Alice that the entire countryside is laid out in squares, like a gigantic chessboard, and offers to make Alice a queen if she can move all the way to the eighth rank/row in a chess match. Alice is placed in the second rank as one of the White Queen's pawns, and begins her journey across the chessboard by boarding a train that jumps over the third row and directly into the fourth rank, thus acting on the rule that pawns can advance two spaces on their first move. She arrives in a forest where a depressed gnat teaches her about the looking glass insects, strange creatures part bug part object (e.g., bread and butterfly, rocking horse fly), before flying away sadly. Alice continues her journey and along the way, crosses the "wood where things have no names". There she forgets all nouns, including her own name. With the help of a fawn who has also forgotten his identity, she makes it to the other side, where they both remember everything. Realizing that he is a fawn, she is a human, and that fawns are afraid of humans, it runs off (to Alice's frustration).
Chapter Two – The Garden of Live Flowers: Upon leaving the house (where it had been a cold, snowy night), she enters a sunny spring garden where the flowers can speak; they perceive Alice as being a "flower that can move about". Elsewhere in the garden, Alice meets the Red Queen, who is now human-sized, and who impresses Alice with her ability to run at breathtaking speeds.
Chapter Three – Looking-Glass Insects: The Red Queen reveals to Alice that the entire countryside is laid out in squares, like a gigantic chessboard, and offers to make Alice a queen if she can move all the way to the eighth rank/row in a chess match. Alice is placed in the second rank as one of the White Queen's pawns, and begins her journey across the chessboard by boarding a train that jumps over the third row and directly into the fourth rank, thus acting on the rule that pawns can advance two spaces on their first move. She arrives in a forest where a depressed gnat teaches her about the looking glass insects, strange creatures part bug part object (e.g., bread and butterfly, rocking horse fly), before flying away sadly. Alice continues her journey and along the way, crosses the "wood where things have no names". There she forgets all nouns, including her own name. With the help of a fawn who has also forgotten his identity, she makes it to the other side, where they both remember everything. Realizing that he is a fawn, she is a human, and that fawns are afraid of humans, it runs off (to Alice's frustration).
 Chapter Four – Tweedledum and Tweedledee: She then meets the fat twin brothers Tweedledum and Tweedledee, whom she knows from the
Chapter Four – Tweedledum and Tweedledee: She then meets the fat twin brothers Tweedledum and Tweedledee, whom she knows from the nursery rhyme
A nursery rhyme is a traditional poem or song for children in Britain and many other countries, but usage of the term dates only from the late 18th/early 19th century. The term Mother Goose rhymes is interchangeable with nursery rhymes.
From ...
. After reciting the long poem "The Walrus and the Carpenter
"The Walrus and the Carpenter" is a narrative poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in his book ''Through the Looking-Glass'', published in December 1871. The poem is recited in chapter four, by Tweedledum and Tweedledee to Alice. The poem is co ...
", they draw Alice's attention to the Red King—loudly snoring away under a nearby tree—and maliciously provoke her with idle philosophical banter that she exists only as an imaginary figure in the Red King's dreams. Finally, the brothers begin suiting up for battle, only to be frightened away by an enormous crow, as the nursery rhyme about them predicts. Chapter Five – Wool and Water: Alice next meets the White Queen, who is very absent-minded but boasts of (and demonstrates) her ability to remember future events before they have happened. Alice and the White Queen advance into the chessboard's fifth rank by crossing over a brook together, but at the very moment of the crossing, the Queen transforms into a talking Sheep in a small shop. Alice soon finds herself struggling to handle the oars of a small rowboat, where the Sheep annoys her with (seemingly) nonsensical shouting about "
Chapter Five – Wool and Water: Alice next meets the White Queen, who is very absent-minded but boasts of (and demonstrates) her ability to remember future events before they have happened. Alice and the White Queen advance into the chessboard's fifth rank by crossing over a brook together, but at the very moment of the crossing, the Queen transforms into a talking Sheep in a small shop. Alice soon finds herself struggling to handle the oars of a small rowboat, where the Sheep annoys her with (seemingly) nonsensical shouting about "crabs
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting " tail" ( abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in al ...
" and "feathers
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premie ...
".
Chapter Six – Humpty Dumpty: After crossing yet another brook into the sixth rank, Alice immediately encounters Humpty Dumpty
Humpty Dumpty is a character in an English nursery rhyme, probably originally a riddle and one of the best known in the English-speaking world. He is typically portrayed as an anthropomorphic egg, though he is not explicitly described as such. ...
, who, besides celebrating his unbirthday, provides his own translation of the strange terms in "Jabberwocky". In the process, he introduces Alice to the concept of portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsChapter Seven – The Lion and the Unicorn: ''"All the king's horses and all the king's men"'' come to Humpty Dumpty's assistance, and are accompanied by the White King, along with the Lion and the Unicorn, who again proceed to act out a nursery rhyme by fighting with each other. In this chapter, the March Hare and

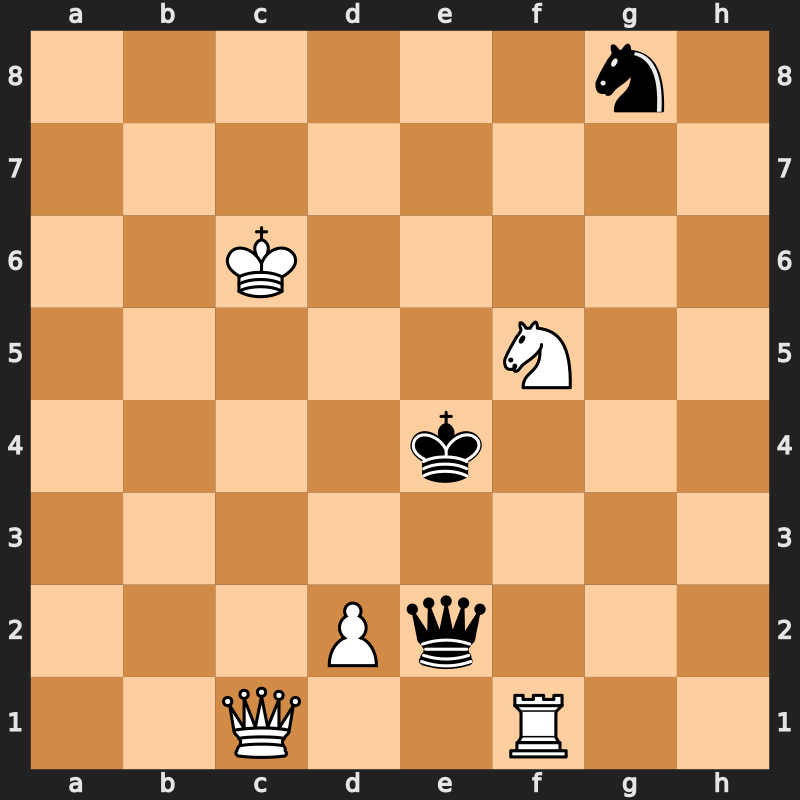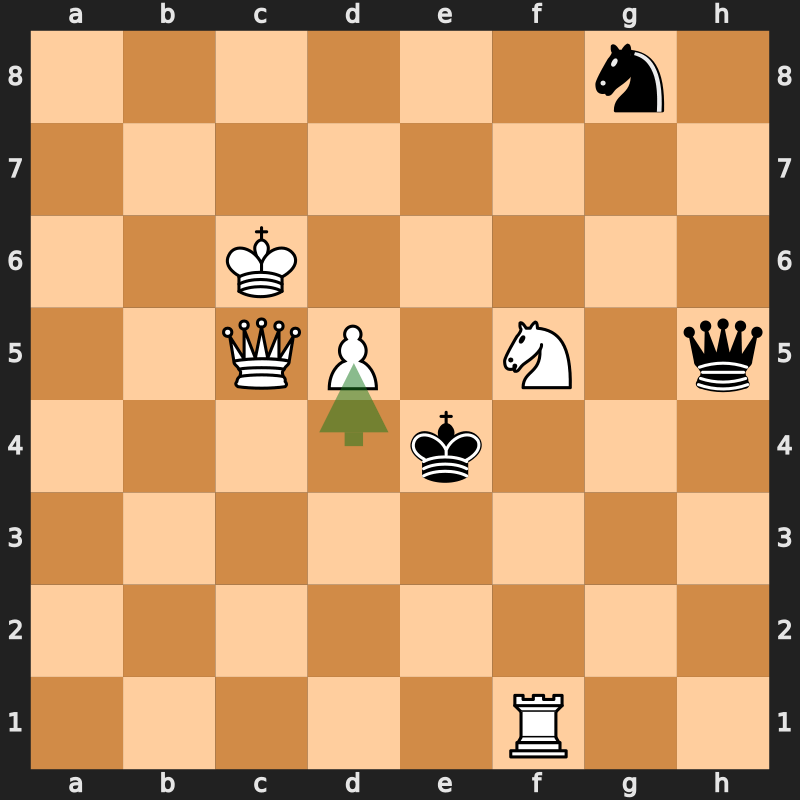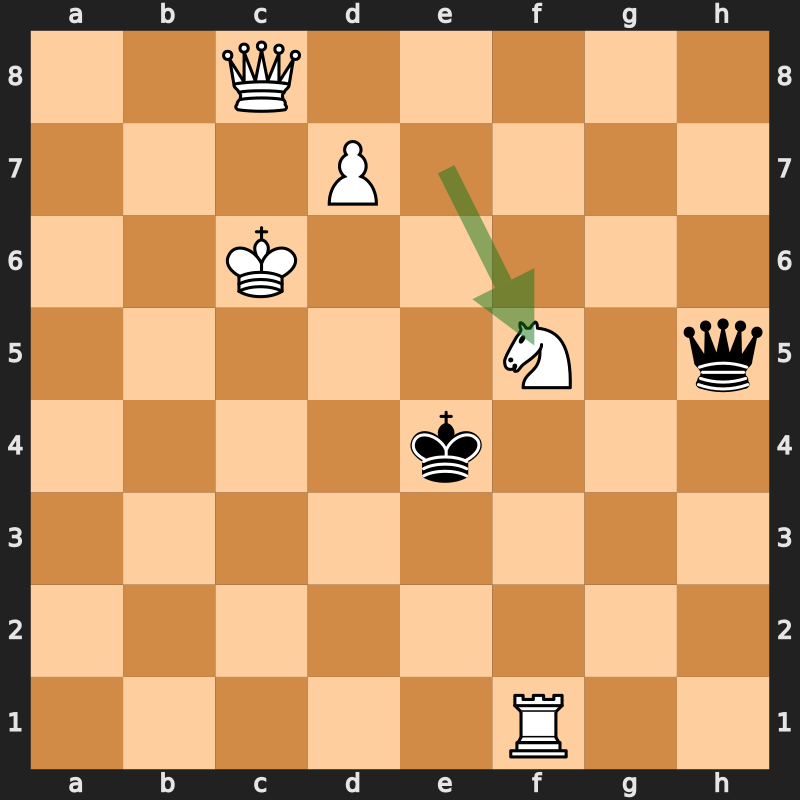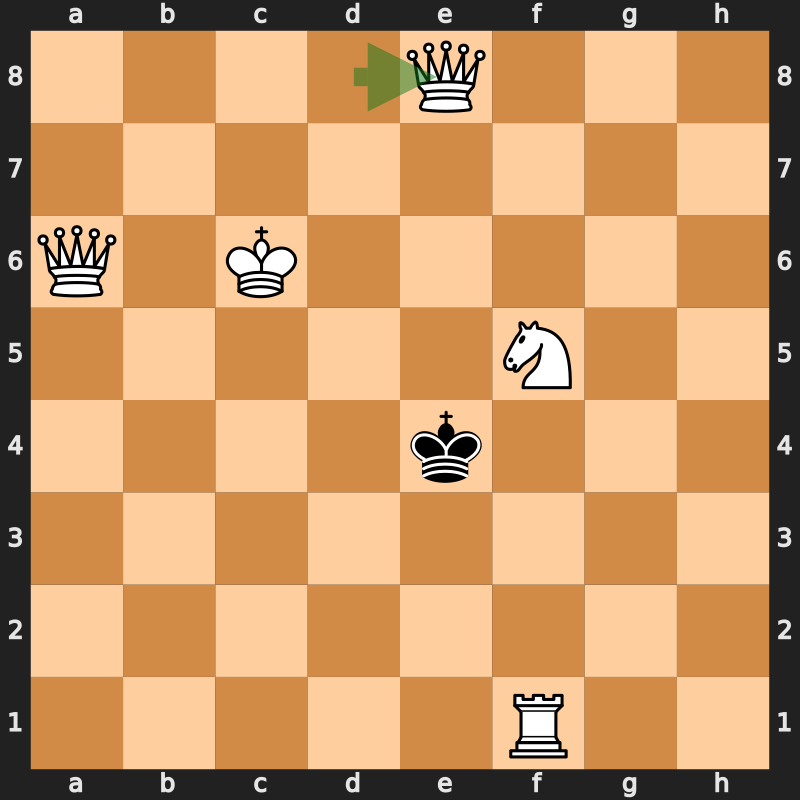 While the first ''Alice'' novel took playing cards as a theme, ''Through the Looking-Glass'' instead used chess; most of the main characters are represented by chess pieces, with Alice being a pawn. The looking-glass world consists of square fields divided by brooks or streams, and the crossing of each brook typically signifies a change in scene, with Alice advancing one square. At the book's beginning, Carroll provided and explained a
While the first ''Alice'' novel took playing cards as a theme, ''Through the Looking-Glass'' instead used chess; most of the main characters are represented by chess pieces, with Alice being a pawn. The looking-glass world consists of square fields divided by brooks or streams, and the crossing of each brook typically signifies a change in scene, with Alice advancing one square. At the book's beginning, Carroll provided and explained a
 Most poems and songs of the book do not include a title.
* "Introduction" (prelude; "Child of the pure unclouded brow…")
* "
Most poems and songs of the book do not include a title.
* "Introduction" (prelude; "Child of the pure unclouded brow…")
* "
 The book has been adapted several times, both in combination with ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' and as a stand-alone feature.
The book has been adapted several times, both in combination with ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' and as a stand-alone feature.
 * ''Alice in Concert'' (1980), also known as ''Alice at the Palace'', was a production written and produced by Elizabeth Swados. Performed on a bare stage, the production starred
* ''Alice in Concert'' (1980), also known as ''Alice at the Palace'', was a production written and produced by Elizabeth Swados. Performed on a bare stage, the production starred
A catalogue of illustrated editions of the Alice books from 1899 to 2009The Lewis Carroll Society UK
;Online texts * * * * {{Authority control Alice's Adventures in Wonderland 1872 British novels 1870s children's books 1872 fantasy novels British children's books Victorian novels Children's fantasy novels British children's novels Works by Lewis Carroll Books illustrated by John Tenniel Macmillan Publishers books Sequel novels Novels about chess Surreal comedy British novels adapted into films British novels adapted into television shows 1872 in the United Kingdom Novels set in fictional countries
Hatter
Hat-making or millinery is the design, manufacture and sale of hats and other headwear. A person engaged in this trade is called a milliner or hatter.
Historically, milliners, typically women shopkeepers, produced or imported an inventory of g ...
of the first book make a brief re-appearance in the guise of "Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
messengers" called "Haigha" and "Hatta".
Chapter Eight – "It's my own Invention": Upon leaving the Lion and Unicorn to their fight, Alice reaches the seventh rank by crossing another brook into the forested territory of the Red Knight, who is intent on capturing the "white pawn"—Alice—until the White Knight
A white knight is a mythological figure and literary stock character. They are portrayed alongside a black knight as diametric opposites. A white knight usually represents a heroic warrior fighting against evil, with the role in medieval literatu ...
comes to her rescue. Escorting her through the forest towards the final brook-crossing, the Knight recites a long poem of his own composition called Haddocks' Eyes, and repeatedly falls off his horse.
Chapter Nine – Queen Alice: Bidding farewell to the White Knight, Alice steps across the last brook, and is automatically crowned a queen, with the crown materialising abruptly on her head (a reference to pawn promotion). She soon finds herself in the company of both the White and Red Queens, who relentlessly confound Alice by using word play
Word play or wordplay (also: play-on-words) is a literary technique and a form of wit in which words used become the main subject of the work, primarily for the purpose of intended effect or amusement. Examples of word play include puns, pho ...
to thwart her attempts at logical discussion. They then invite one another to a party that will be hosted by the newly crowned Alice—of which Alice herself had no prior knowledge.
Chapter Ten – Shaking: Alice arrives and seats herself at her own party, which quickly turns into chaos. Alice finally grabs the Red Queen, believing her to be responsible for all the day's nonsense, and begins shaking her.
Chapter Eleven – Waking: Alice awakes in her armchair to find herself holding the black kitten, who she deduces to have been the Red Queen all along, with the white kitten having been the White Queen.
Chapter Twelve – Which dreamed it?: The story ends with Alice recalling the speculation of the Tweedle brothers, that everything may have been a dream of the Red King, and that Alice might herself be no more than a figment of ''his'' imagination. The book ends with the line "Life, what is it but a dream?"
Characters
Main characters
*Alice
Alice may refer to:
* Alice (name), most often a feminine given name, but also used as a surname
Literature
* Alice (''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''), a character in books by Lewis Carroll
* ''Alice'' series, children's and teen books by ...
* March Hare
* The Hatter
* Humpty Dumpty
Humpty Dumpty is a character in an English nursery rhyme, probably originally a riddle and one of the best known in the English-speaking world. He is typically portrayed as an anthropomorphic egg, though he is not explicitly described as such. ...
* Red King
* Red Queen
* The Sheep
* Tweedledum and Tweedledee
* The Walrus and the Carpenter
"The Walrus and the Carpenter" is a narrative poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in his book ''Through the Looking-Glass'', published in December 1871. The poem is recited in chapter four, by Tweedledum and Tweedledee to Alice. The poem is co ...
* White King
* White Knight
A white knight is a mythological figure and literary stock character. They are portrayed alongside a black knight as diametric opposites. A white knight usually represents a heroic warrior fighting against evil, with the role in medieval literatu ...
* White Queen
* The Lion and the Unicorn
Minor characters
Symbolism
Mirrors
One of the key motifs of ''Through the Looking-Glass'' is that of mirrors, including the use of opposites, time running backwards, and so on, not to mention the title of the book itself. In fact, the themes and settings of the book make it somewhat of amirror image
A mirror image (in a plane mirror) is a reflected duplication of an object that appears almost identical, but is reversed in the direction perpendicular to the mirror surface. As an optical effect it results from reflection off from substances ...
to its predecessor, ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creatur ...
'' (1865). The first book begins in the warm outdoors, on 4 May;During the "Mad Tea-Party", Alice reveals that the date is "the fourth" and that the month is "May" (chap.7). uses frequent changes in size as a plot device
A plot device or plot mechanism
is any technique in a narrative used to move the plot forward. A clichéd plot device may annoy the reader and a contrived or arbitrary device may confuse the reader, causing a loss of the suspension of disbelief ...
; and draws on the imagery of playing cards. The second book, however, opens indoors on a snowy, wintry night exactly six months later, on 4 November (the day before Guy Fawkes Night
Guy Fawkes Night, also known as Guy Fawkes Day, Bonfire Night and Fireworks Night, is an annual commemoration observed on 5 November, primarily in Great Britain, involving bonfires and fireworks displays. Its history begins with the ev ...
);In the first chapter, Alice speaks of the snow outside and the "bonfire" that "the boys" are building for a celebration "to-morrow," a clear reference to the traditional bonfires of Guy Fawkes Night
Guy Fawkes Night, also known as Guy Fawkes Day, Bonfire Night and Fireworks Night, is an annual commemoration observed on 5 November, primarily in Great Britain, involving bonfires and fireworks displays. Its history begins with the ev ...
that take place on 5 November. In Chapter 5, she affirms that her age is "seven and a half exactly." uses frequent changes in time and spatial directions as a plot device; and draws on the imagery of chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
.
Chess

 While the first ''Alice'' novel took playing cards as a theme, ''Through the Looking-Glass'' instead used chess; most of the main characters are represented by chess pieces, with Alice being a pawn. The looking-glass world consists of square fields divided by brooks or streams, and the crossing of each brook typically signifies a change in scene, with Alice advancing one square. At the book's beginning, Carroll provided and explained a
While the first ''Alice'' novel took playing cards as a theme, ''Through the Looking-Glass'' instead used chess; most of the main characters are represented by chess pieces, with Alice being a pawn. The looking-glass world consists of square fields divided by brooks or streams, and the crossing of each brook typically signifies a change in scene, with Alice advancing one square. At the book's beginning, Carroll provided and explained a chess composition
A chess problem, also called a chess composition, is a puzzle set by the composer using chess pieces on a chess board, which presents the solver with a particular task. For instance, a position may be given with the instruction that White is to ...
with descriptive notation, corresponding to the events of the story. Although the piece movements follow the rules of chess, other basic rules are ignored: one player (White) makes several consecutive moves while the (Red/Black) opponent's moves are skipped, and a late check (12... Qe8+) is left undealt with. Carroll also explained that certain items listed in the composition do not have corresponding piece moves but simply refer to the story, e.g. the "castling of the three Queens, which is merely a way of saying that they entered the palace". Despite these liberties, the final position is an authentic checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game.
In chess, the king is ...
.
The most extensive treatment of the chess motif in Carroll's novel was made by Glen Downey in his master's thesis, later expanded and incorporated into his dissertation on the use of chess as a device in Victorian fiction. In the former piece, Downey gave the composition's moves in algebraic notation: 1... Qh5 2. d4 3. Qc4 4. Qc5 5. d5 6. Qf8 7. d6 8. Qc8 9. d7 Ne7+ 10. Nxe7 11. Nf5 12. d8=Q Qe8+ 13. Qa6 14. Qxe8#. In the latter piece, Downey treated the 21 items in the composition sequentially, identifying the above 16 coherent chess moves, and another five items as "non-moves" or pure story descriptors, per Carroll's qualification.
The mating position nearly satisfies the conditions of a pure mate, a special type of checkmate where the mated king is prevented from moving to any of the adjacent squares in its field by exactly one enemy attack, among other conditions. The position is also nearly an ideal mate, a stronger form of pure mate in which every piece on the board of either color contributes to the checkmate. The one feature of the position which prevents it from being either a pure or an ideal mate is that the Red (Black) King is unable to move to e3 for two reasons: the knight's attack, and the (sustained) attack of the newly promoted, mating queen. Although pure and ideal mates are "incidental" in real games, they are objects of aesthetic
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed t ...
interest to composers
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and Defi ...
of chess problems.
Language
The White Queen offers to hire Alice as her lady's maid and to pay her "twopence a week, and jam every other day". Alice says that she doesn't want any jam today, to which the Queen replies, "you couldn't have it if you ''did'' want it. The rule is,jam tomorrow
Jam tomorrow (or the older spelling jam to-morrow) is an expression for a never-fulfilled promise, or for some pleasant event in the future, which is never likely to materialize. Originating from a bit of wordplay involving Lewis Carroll's Alice, i ...
and jam yesterdaybut never jam ''to-day''." This is a reference to the rule in Latin that the word ''iam'' or ''jam—''which means ''now'', in the sense of ''already'' or ''at that time''—cannot be used to describe ''now'' in the present, which is ''nunc'' in Latin. Therefore, "''jam''" is never available today. This exchange is also a demonstration of the logical fallacy of equivocation
In logic, equivocation ("calling two different things by the same name") is an informal fallacy resulting from the use of a particular word/expression in multiple senses within an argument.
It is a type of ambiguity that stems from a phrase havi ...
.
Poems and songs
 Most poems and songs of the book do not include a title.
* "Introduction" (prelude; "Child of the pure unclouded brow…")
* "
Most poems and songs of the book do not include a title.
* "Introduction" (prelude; "Child of the pure unclouded brow…")
* "Jabberwocky
"Jabberwocky" is a nonsense poem written by Lewis Carroll about the killing of a creature named "the Jabberwock". It was included in his 1871 novel '' Through the Looking-Glass'', the sequel to ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865). The ...
"See "Jabberwocky" full poem including readings, via Wikisource.Carroll, Lewis
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (; 27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet and mathematician. His most notable works are '' Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865) and its seque ...
. 1897 872 ''Through the Looking-Glass and What Alice Found There''. Philadelphia: Henry Altemus Company
The Henry Altemus Company was a publishing company based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for almost a century, from 1842 to 1936.
History
The firm started as a bookbindery. In 1863, Altemus was awarded a patent for a particular type of binding ...
.
* " Tweedledum and Tweedledee"
* "The Walrus and the Carpenter
"The Walrus and the Carpenter" is a narrative poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in his book ''Through the Looking-Glass'', published in December 1871. The poem is recited in chapter four, by Tweedledum and Tweedledee to Alice. The poem is co ...
"See "Walrus and the Carpenter" full poem, via Wikisource.
* "Humpty Dumpty
Humpty Dumpty is a character in an English nursery rhyme, probably originally a riddle and one of the best known in the English-speaking world. He is typically portrayed as an anthropomorphic egg, though he is not explicitly described as such. ...
"
* Humpty Dumpty's poem ("In Winter when the fields are white…")
* " The Lion and the Unicorn"
* " Haddocks' Eyes" (i.e., "A-sitting on a Gate")
* Red Queen's lullaby
A lullaby (), or cradle song, is a soothing song or piece of music that is usually played for (or sung to) children (for adults see music and sleep). The purposes of lullabies vary. In some societies they are used to pass down cultural knowledg ...
("Hush-a-by lady, in Alice's lap…")
* " To the Looking-Glass world it was Alice that said…"
* White Queen's riddle ("'First, the fish must be caught'…")
* " A boat beneath a sunny sky"(postlude; acrostic
An acrostic is a poem or other word composition in which the ''first'' letter (or syllable, or word) of each new line (or paragraph, or other recurring feature in the text) spells out a word, message or the alphabet. The term comes from the Fr ...
poem in which putting the beginning letters of each line spell Alice Pleasance Liddell, the girl after whom the book's Alice is named).
The Wasp in a Wig
Lewis Carroll decided to suppress a scene involving what was described as "a wasp in a wig" (possibly a play on the commonplace expression "bee in the bonnet"). A biography of Carroll, written by Carroll's nephew, Stuart Dodgson Collingwood, suggests that one of the reasons for this suppression was a suggestion from his illustrator,John Tenniel
Sir John Tenniel (; 28 February 182025 February 1914)Johnson, Lewis (2003), "Tenniel, John", ''Grove Art Online, Oxford Art Online'', Oxford University Press. Web. Retrieved 12 December 2016. was an English illustrator, graphic humorist and pol ...
, who wrote in a letter to Carroll dated 1 June 1870:
For many years, no one had any idea what this missing section was or whether it had survived. In 1974, a document purporting to be the galley proof
In printing and publishing, proofs are the preliminary versions of publications meant for review by authors, editors, and proofreaders, often with extra-wide margins. Galley proofs may be uncut and unbound, or in some cases electronically tran ...
s of the missing section was auctioned at Sotheby's
Sotheby's () is a British-founded American multinational corporation with headquarters in New York City. It is one of the world's largest brokers of fine and decorative art, jewellery, and collectibles. It has 80 locations in 40 countries, an ...
; the catalogue description, in part, read, "the proofs were bought at the sale of the author's…personal effects…Oxford, 1898". The document would be won by John Fleming, a Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the List of co ...
book dealer, for a bid of about . The contents were subsequently published in Martin Gardner
Martin Gardner (October 21, 1914May 22, 2010) was an American popular mathematics and popular science writer with interests also encompassing scientific skepticism, micromagic, philosophy, religion, and literatureespecially the writings of L ...
's '' More Annotated Alice'' (1990), and are also available as a hardback book.''
The rediscovered section describes Alice's encounter with a wasp wearing a yellow wig, and includes a full previously unpublished poem. If included in the book, it would have followed, or been included at the end of, Chapter 8the chapter featuring the encounter with the White Knight. The discovery is generally accepted as genuine, but the proofs have yet to receive any physical examination to establish age and authenticity.
The missing episode was included in the 1998 TV film adaptation '' Alice through the Looking Glass''.
Dramatic adaptations
 The book has been adapted several times, both in combination with ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' and as a stand-alone feature.
The book has been adapted several times, both in combination with ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' and as a stand-alone feature.
Stand-alone adaptations
* ''Alice Through a Looking Glass'' (1928), a silent movie directed byWalter Lang
Walter Lang (August 10, 1896 – February 7, 1972) was an American film director.
Early life
Walter Lang was born in Tennessee. As a young man he went to New York City where he found clerical work at a film production company. The business piqu ...
, would be one of the earliest stand-alone adaptations of the book.
* A dramatised audio-recorded version, directed by Douglas Cleverdon, was released in 1959 by Argo Records
Argo Records was a record label in Chicago that was established in 1955 as a division of Chess Records.
Originally the label was called Marterry, but bandleader Ralph Marterie objected, and within a couple of months the imprint was renamed Ar ...
. The book is narrated by Margaretta Scott
Margaretta Mary Winifred ScottBrian McFarlane, "Scott, Margaretta Mary Winifred (1912–2005)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, Jan 201available online Retrieved 30 August 2020. (13 February 1912 – 15 Apri ...
, starring Jane Asher
Jane Asher (born 5 April 1946)The International Who's Who of Women, 3rd edition, ed. Elizabeth Sleeman, Europa Publications, 2002, p. 29 is an English actress and author. She achieved early fame as a child actress and has worked extensively in f ...
as Alice, along with actors Frank Duncan (Humpty Dumpty, Red King, Frog), Tony Church, Norman Shelley, and Carleton Hobbs.
* '' Alice Through the Looking Glass'' (1966) was a NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American English-language commercial broadcast television and radio network. The flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, its headquarters ...
TV musical special, first airing on 6 November. The special includes music by Moose Charlap Morris Isaac "Moose" Charlap (December 19, 1928 – July 8, 1974) was an American Broadway composer best known for ''Peter Pan'' (1954), for which Carolyn Leigh wrote the lyrics. The idea for the show came from Jerome Robbins, who planned to have a ...
, and stars Ricardo Montalban, Agnes Moorehead
Agnes Robertson Moorehead (December 6, 1900April 30, 1974) was an American actress. In a career spanning four decades, her credits included work in radio, stage, film, and television.Obituary '' Variety'', May 8, 1974, page 286. Moorehead was t ...
, Jack Palance
Jack Palance ( ; born Volodymyr Palahniuk ( uk, Володимир Палагню́к); February 18, 1919 – November 10, 2006) was an American actor known for playing tough guys and villains. He was nominated for three Academy Awards, all fo ...
, Jimmy Durante
James Francis Durante ( , ; February 10, 1893 – January 29, 1980) was an American comedian, actor, singer, vaudevillian, and pianist. His distinctive gravelly speech, Lower East Side accent, comic language-butchery, jazz-influenced songs ...
, and the Smothers Brothers, along with Judi Rolin in the role of Alice.
* ''Alice Through the Looking Glass'' (1973) is a BBC TV movie, directed by James MacTaggart
James MacTaggart (25 April 1928 – 29 May 1974) was a Scottish television producer, director and writer. He worked in London from 1961.
Early life
MacTaggart was born in Glasgow and served in the Royal Army Service Corps from 1946, rising to ...
and starring Sarah Sutton as Alice.
* ''Alice in the Land in the Other Side of the Mirror'' (1982) is a 38-minute Soviet cutout-animated TV film produced by Kievnauchfilm studio and directed by Yefrem Pruzhanskiy. Despite its translated name, the film's original, Russian title is '.
* ''Alice Through the Looking Glass'' (1987) is an animated TV movie starring Janet Waldo
Janet Waldo (born Jeanette Marie Waldo; February 4, 1919 – June 12, 2016) was an American radio and voice actress. In animation, she voiced Judy Jetson in various Hanna-Barbera media, Nancy in '' Shazzan'', Penelope Pitstop, Princess from '' ...
as the voice of Alice, as well as the voices of Mr. T as the Jabberwock, Jonathan Winters
Jonathan Harshman Winters III (November 11, 1925 – April 11, 2013) was an American comedian, actor, author, television host, and artist. Beginning in 1960, Winters recorded many classic comedy albums for the Verve Records label. He also ...
, and Phyllis Diller
Phyllis Ada Diller (née Driver; July 17, 1917 – August 20, 2012) was an American stand-up comedian, actress, author, musician, and visual artist, best known for her eccentric stage persona, self-deprecating humor, wild hair and clothes, and ...
.
* '' Alice through the Looking Glass'' (1998) is a Channel 4
Channel 4 is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network operated by the state-owned enterprise, state-owned Channel Four Television Corporation. It began its transmission on 2 November 1982 and was established to provide a four ...
TV movie, starring Kate Beckinsale
Kathrin Romany Beckinsale (born 26 July 1973) is an English actress and model. After some minor television roles, her film debut was ''Much Ado About Nothing'' (1993) while a student at the University of Oxford. She appeared in British costum ...
as the role of Alice, which restored the lost "Wasp in a Wig" episode.
* A 2-hour multimedia stage production (2007), conceived by Andy Burden, was produced by the Tobacco Factory. The show would be directed by Burden and written by Hattie Naylor, with music and lyrics by Paul Dodgson.
* '' Through the Looking Glass'' (2008) was a chamber opera Chamber opera is a designation for operas written to be performed with a chamber ensemble rather than a full orchestra. Early 20th-century operas of this type include Paul Hindemith's '' Cardillac'' (1926). Earlier small-scale operas such as Pergol ...
composed by Alan John
Alan John (born 7 May 1958 in Sydney) is an Australian composer. He studied music at the University of Sydney, graduating in 1980. His compositions include original music for various plays, films (such as '' Holding the Man'', ''Three Dollars'' a ...
to a libretto by Andrew Upton.
* '' Alice Through the Looking Glass'' (2016), directed by James Bobin, is a sequel to the Tim-Burton-directed Disney reboot ''Alice in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creature ...
'' (2010). It does not follow the plot of the book.
* The BBC Radio 4
BBC Radio 4 is a British national radio station owned and operated by the BBC that replaced the BBC Home Service in 1967. It broadcasts a wide variety of Talk radio, spoken-word programmes, including news, drama, comedy, science and history fro ...
show ''Saturday Drama'' broadcast an adaptation by Stephen Wyatt
Stephen Wyatt, born 4 February 1948 in Beckenham, Kent (now Greater London), is a British writer for theatre, radio and television.
Early life and education
Wyatt was raised in Ealing, West London. He was educated at Latymer Upper School an ...
on 22 December 2011. The broadcast featured Lewis Carroll, voiced by Julian Rhind-Tutt, as both the narrator and an active character in the story. Other actors include Lauren Mote
Lauren Mote (born 10 February 1997) is a British actress who is best known for voice-acting roles such as Lizzy in the 2010 Disney animated film ''Tinker Bell and the Great Fairy Rescue''. Snyopsis and review. In her teens, she switched to a f ...
(Alice), Carole Boyd (Red Queen), Sally Phillips (White Queen), Nicholas Parsons
Christopher Nicholas Parsons (10 October 1923 – 28 January 2020) was an English actor, straight man and radio and television presenter. He was the long-running presenter of the comedy radio show '' Just a Minute'' and hosted the game show '' ...
(Humpty-Dumpty), Alistair McGowan
Alistair Charles McGowan (born 24 November 1964) is an English impressionist, comic, actor, singer and writer best known to British audiences for ''The Big Impression'' (formerly ''Alistair McGowan's Big Impression''), which was, for four years ...
(Tweedledum & Tweedledee), and John Rowe (White Knight).
Adaptations with ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''
Film and TV
* ''Alice in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creature ...
'' (1933) is a pre-code
Pre-Code Hollywood was the brief era in the American film industry between the widespread adoption of sound in film in 1929LaSalle (2002), p. 1. and the enforcement of the Motion Picture Production Code censorship guidelines, popularly known ...
live-action film directed by Norman Z. McLeod
Norman Zenos McLeod (September 20, 1898 – January 27, 1964) was an American film director, screenwriter and cartoonist.
McLeod's most acclaimed work was made in collaboration with major comic performers of the 1930s, and included such films as ...
, with Charlotte Henry
Charlotte Virginia Henry (March 3, 1914 – April 11, 1980) was an American actress who is best remembered for her roles in ''Alice in Wonderland'' (1933) and '' Babes in Toyland'' (1934). She also starred in the Frank Buck serial '' Jun ...
in the role of Alice, along with Cary Grant
Cary Grant (born Archibald Alec Leach; January 18, 1904November 29, 1986) was an English-American actor. He was known for his Mid-Atlantic accent, debonair demeanor, light-hearted approach to acting, and sense of comic timing. He was one o ...
, Gary Cooper
Gary Cooper (born Frank James Cooper; May 7, 1901May 13, 1961) was an American actor known for his strong, quiet screen persona and understated acting style. He won the Academy Award for Best Actor twice and had a further three nominations, a ...
, and others. Despite the title, the film features most elements from ''Through the Looking Glass'' as well, including Humpty Dumpty (played by W. C. Fields) and a Harman-Ising animated version of "The Walrus and the Carpenter
"The Walrus and the Carpenter" is a narrative poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in his book ''Through the Looking-Glass'', published in December 1871. The poem is recited in chapter four, by Tweedledum and Tweedledee to Alice. The poem is co ...
".
* The animated ''Alice in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creature ...
'' (1951) is the 13th animated feature film of Walt Disney
Walter Elias Disney (; December 5, 1901December 15, 1966) was an American animator, film producer and entrepreneur. A pioneer of the American animation industry, he introduced several developments in the production of cartoons. As a film p ...
and the most famous among all direct adaptions of Carroll's work. The film features several elements from ''Through the Looking-Glass'', including the talking flowers, Tweedledee & Tweedledum, and "The Walrus and the Carpenter".
* ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creatur ...
'' (1972), a musical film starring Fiona Fullerton
Fiona Elizabeth Fullerton (born 10 October 1956) is a British actress and singer, known for her role as Alice in the 1972 film ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' and as Bond girl KGB spy Pola Ivanova in the 1985 James Bond film ''A View to a ...
as Alice, includes the twins Fred and Frank Cox as Tweedledum & Tweedledee.
* ("In the World of Alice") is a 1974 Italian TV series that covers both novels, particularly ''Through the Looking-Glass'' in episodes 3 and 4.
* ''Alice in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creature ...
'' (1985) is a two-part TV musical produced by Irwin Allen
Irwin Allen (born Irwin O. Cohen, June 12, 1916 – November 2, 1991) was an American film and television producer and director, known for his work in science fiction, then later as the "Master of Disaster" for his work in the disaster film gen ...
that covers both books, and stars Natalie Gregory as Alice. In this adaptation, the Jabberwock materialises into reality after Alice reads "Jabberwocky", pursuing her throughout the second half of the musical.
* ''Fushigi no Kuni no Arisu'' (1985; ') is an anime
is hand-drawn and computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside of Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, in Japan and in Japanese, (a term derived from a shortening of ...
adaptation of the two novels in which later episodes adhere more closely with ''Through the Looking Glass''.
* ''Alice in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creature ...
'' (1999), a made-for-TV Hallmark
A hallmark is an official mark or series of marks struck on items made of metal, mostly to certify the content of noble metals—such as platinum, gold, silver and in some nations, palladium. In a more general sense, the term '' hallmark'' can a ...
/NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American English-language commercial broadcast television and radio network. The flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, its headquarters ...
film with Tina Majorino
Albertina Marie Majorino (; born February 7, 1985) is an American film and television actress. She started her career as a child actor, starring in films such as '' Andre'', '' When a Man Loves a Woman'', ''Waterworld'', and '' Corrina, Corrina' ...
as Alice, uses elements from ''Through the Looking Glass'', such as the talking flowers, Tweedledee & Tweedledum, and "The Walrus and the Carpenter", as well as the chess theme, including the snoring Red King and White Knight.
* ''Alice
Alice may refer to:
* Alice (name), most often a feminine given name, but also used as a surname
Literature
* Alice (''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''), a character in books by Lewis Carroll
* ''Alice'' series, children's and teen books by ...
'' (2009) is a Syfy TV miniseries that contains elements from both novels.
* ''Alice in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named Alice who falls through a rabbit hole into a fantasy world of anthropomorphic creature ...
'' (2010), directed by Tim Burton
Timothy Walter Burton (born August 25, 1958) is an American filmmaker and animator. He is known for his gothic fantasy and horror films such as ''Beetlejuice'' (1988), ''Edward Scissorhands'' (1990), ''The Nightmare Before Christmas'' (1993), ...
, is a live-action Disney reboot that follows Alice at an adult age, containing elements from both books.
Stage productions
 * ''Alice in Concert'' (1980), also known as ''Alice at the Palace'', was a production written and produced by Elizabeth Swados. Performed on a bare stage, the production starred
* ''Alice in Concert'' (1980), also known as ''Alice at the Palace'', was a production written and produced by Elizabeth Swados. Performed on a bare stage, the production starred Meryl Streep
Mary Louise Meryl Streep (born June 22, 1949) is an American actress. Often described as "the best actress of her generation", Streep is particularly known for her versatility and accent adaptability. She has received numerous accolades throu ...
in the role of Alice, with additional supporting cast by Mark Linn-Baker and Betty Aberlin.
* ''Lookingglass Alice'' (2007) was an acrobatic
Acrobatics () is the performance of human feats of balance, agility, and motor coordination. Acrobatic skills are used in performing arts, sporting events, and martial arts. Extensive use of acrobatic skills are most often performed in acro d ...
interpretation of both novels, produced by the Lookingglass Theater Company, that performed in New York City, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, and Chicago, with a version of the show touring the rest of the United States.
* A 2-part production by Iris Theatre in London was staged in the summer of 2013, in which the second part consisted of ''Through the Looking-Glass''. Both parts included Laura Wickham in the role of Alice.
* ''Alice'' (2010), written by Laura Wade, was a modern adaptation of both books that premiered at the Crucible Theatre in Sheffield in 2010.
* '' Wonder.land'' (2015), a live musical by Moira Buffini
Moira Buffini (born 29 May 1965) is an English dramatist, director, and actor.
Early life
Buffini was born in Cheshire to Irish parents, and attended St Mary's College at Rhos-on-Sea in Wales as a day girl. She studied English and Drama at Go ...
and Damon Albarn, takes some characters from the second novel, notably Dum and Dee and Humpty Dumpty, while the Queen of Hearts and the Red Queen are merged into one character.
* ''Alice in Wonderland and Through the Looking-Glass'' (2001) was a stage adaption by Adrian Mitchell for the Royal Shakespeare Company, in which the second act consists of ''Through the Looking-Glass.''
* ''Alice's Adventures Under Ground ''Alice's Adventures Under Ground'' may refer to:
*''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (commonly ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English novel by Lewis Carroll. It details the story of a young girl named ...
'' (2020), a one-act opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a libre ...
written in 2016 by Gerald Barry and first staged at the Royal Opera House
The Royal Opera House (ROH) is an opera house and major performing arts venue in Covent Garden, central London. The large building is often referred to as simply Covent Garden, after a previous use of the site. It is the home of The Royal ...
, is a conflation of the two novels.
* Looking-Glass, a 1982 Off-Broadway play based on Charles Dodgson, the real-life name of author Lewis Carroll Other
*''Jabberwocky
"Jabberwocky" is a nonsense poem written by Lewis Carroll about the killing of a creature named "the Jabberwock". It was included in his 1871 novel '' Through the Looking-Glass'', the sequel to ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865). The ...
'' (1977) is a film that expands the story of the poem "Jabberwocky".
*'' Thru the Mirror'' (1936) is a Mickey Mouse short film in which Mickey travels through his mirror and into a bizarre world.
*'' Donald in Mathmagic Land'' (1959) is a film that includes a segment with Donald Duck
Donald Fauntleroy Duck is a cartoon character created by The Walt Disney Company. Donald is an Anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic American Pekin, white duck with a yellow-orange bill, legs, and feet. He typically wears a sailor suit, sailor shi ...
dressed as Alice meeting the Red Queen on a chessboard.
*''American McGee's Alice
''American McGee's Alice'' is a 2000 third-person action-adventure video game developed by Rogue Entertainment under the direction of designer American McGee and published by Electronic Arts under the EA Games banner. The game was originall ...
'' (2000) is a computer game in which the player takes the role of a teenage Alice fighting to reclaim her sanity. It was followed by a sequel, '' Alice: Madness Returns'', in 2011.
*''Through the Looking-Glass'' (2011) was a ballet by American composer John Craton.
*''Through the Zombie Glass'' (2013) is a book by Gena Showalter
Gena Showalter (born 1975 in Oklahoma) is an American author in the genres of contemporary romance, paranormal romance, and young adult.
Showalter sold her first book at the age of 27, and has published over 70 books. She has been named by ' ...
.
See also
* Alice Chess * "I Am the Walrus
"I Am the Walrus" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles from their 1967 television film '' Magical Mystery Tour''. Written by John Lennon and credited to Lennon–McCartney, it was released as the B-side to the single " Hello, Goodbye ...
"
* Translations of ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''
* Translations of ''Through the Looking-Glass''
* Vorpal sword
* Works based on ''Alice in Wonderland''
References
Footnotes
Citations
Other sources
* * *External links
* *A catalogue of illustrated editions of the Alice books from 1899 to 2009
;Online texts * * * * {{Authority control Alice's Adventures in Wonderland 1872 British novels 1870s children's books 1872 fantasy novels British children's books Victorian novels Children's fantasy novels British children's novels Works by Lewis Carroll Books illustrated by John Tenniel Macmillan Publishers books Sequel novels Novels about chess Surreal comedy British novels adapted into films British novels adapted into television shows 1872 in the United Kingdom Novels set in fictional countries