thrombocytopenic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of

 Thrombocytopenia usually has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine
Thrombocytopenia usually has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine
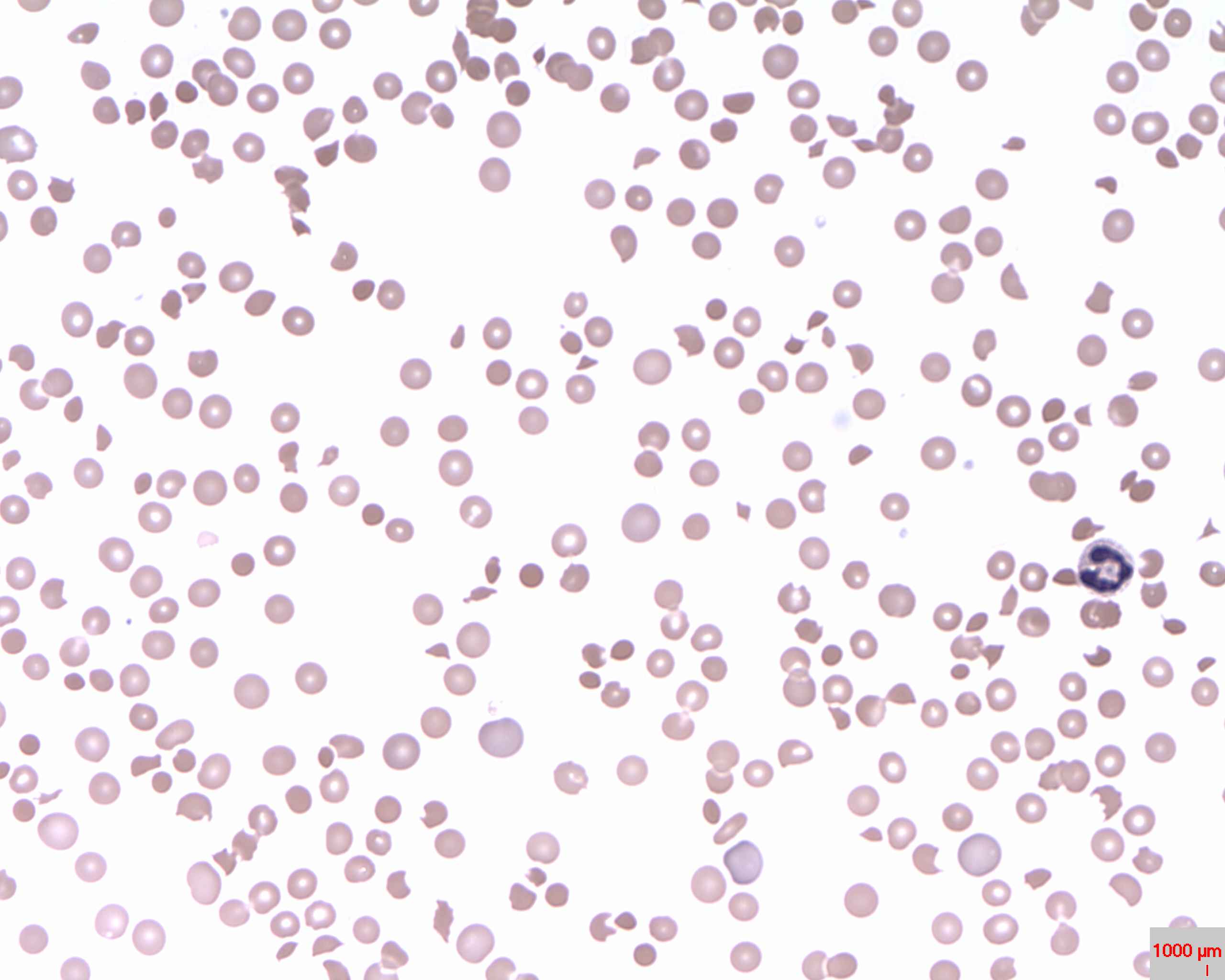 Abnormally high rates of platelet destruction may be due to immune or nonimmune conditions, including:
*
Abnormally high rates of platelet destruction may be due to immune or nonimmune conditions, including:
*
platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ...
s, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
. It is the most common coagulation disorder
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood's ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding (bleeding diathesis), which may occur spo ...
among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients.
A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μl) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μl. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood - thrombocythemia
Thrombocythemia is a condition of high platelet (thrombocyte) count in the blood. Normal count is in the range of 150x109 to 450x109 platelets per liter of blood, but investigation is typically only considered if the upper limit exceeds 750x109/L. ...
(when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis
Thrombocythemia is a condition of high platelet (thrombocyte) count in the blood. Normal count is in the range of 150x109 to 450x109 platelets per liter of blood, but investigation is typically only considered if the upper limit exceeds 750x109/L. ...
(when the cause is known).
Signs and symptoms

complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cell ...
. Some individuals with thrombocytopenia may experience external bleeding, such as nosebleed
A nosebleed, also known as epistaxis, is bleeding from the nose. Blood can flow down into the stomach, and cause nausea and vomiting. In more severe cases, blood may come out of both nostrils. Rarely, bleeding may be so significant that low bloo ...
s or bleeding gums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue linin ...
. Some women may have heavier or longer periods or breakthrough bleeding. Bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close e ...
, particularly purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, ...
in the forearms and petechia
A petechia () is a small red or purple spot (≤4 mm in diameter) that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and Mucous membrane, mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian , 'freckle,' ...
e in the feet, legs, and mucous membranes
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
, may be caused by spontaneous bleeding under the skin.
Eliciting a full medical history is vital to ensure the low platelet count is not secondary to another disorder. Ensuring that the other blood cell types, such as red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek language, Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''k ...
and white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
, are not also suppressed, is also important.
Painless, round, and pinpoint (1 to 3 mm in diameter) petechiae usually appear and fade, and sometimes group to form ecchymoses
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close e ...
. Larger than petechiae, ecchymoses are purple, blue, or yellow-green areas of skin that vary in size and shape. They can occur anywhere on the body.
A person with this disease may also complain of malaise
As a medical term, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. The word has existed in French since at least the 12th century.
The term is often used ...
, fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
, and general weakness (with or without accompanying blood loss). Acquired thrombocytopenia may be associated with the use of certain drugs. Inspection typically reveals evidence of bleeding (petechiae or ecchymoses), along with slow, continuous bleeding from any injuries or wounds. Adults may have large, blood-filled bullae in the mouth. If the person's platelet count is between 30,000 and 50,000/μl, bruising with minor trauma may be expected; if it is between 15,000 and 30,000/μl, spontaneous bruising will be seen (mostly on the arms and legs).
Causes
Thrombocytopenia can be inherited or acquired.Decreased production
Abnormally low platelet production may be caused by: *Dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
, vitamin B12 or folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
deficiency
* Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ' ...
, myelodysplastic syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may ...
, or aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia is a cancer in which the body fails to make blood cells in sufficient numbers. Blood cells are produced in the bone marrow by stem cells that reside there. Aplastic anemia causes a deficiency of all blood cell types: red blood ...
* Decreased production of thrombopoietin
Thrombopoietin (THPO) also known as megakaryocyte growth and development factor (MGDF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''THPO'' gene.
Thrombopoietin is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the liver and kidney which regulates the pro ...
by the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
in liver failure
* Sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, systemic viral or bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of ...
* Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria ''Leptospira''. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild (headaches, muscle pains, and fevers) to severe ( bleeding in the lungs or meningitis). Weil's disease, the acute, severe ...
* Hereditary syndromesAlmazni I, Stapley R, Morgan NV (2019) Inherited Thrombocytopenia: Update on genes and genetic variants which may be associated With bleeding. Front Cardiovasc Med
** ACTN1-related thrombocytopenia
** Amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia with radio-ulnar synostosis
** ANKRD26 related thrombocytopenia
** Autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia
** Bernard–Soulier syndrome
Bernard–Soulier syndrome (BSS) is a rare autosomal recessive bleeding disorder that is caused by a deficiency of the ''glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex'' (GPIb-IX-V), the receptor for von Willebrand factor. The incidence of BSS is estimated to be ...
(associated with giant platelet disorder
Giant platelet disorders, also known as macrothrombocytopenia, are rare disorders featuring abnormally large platelets, thrombocytopenia and a tendency to bleeding. Giant platelets cannot stick adequately to an injured blood vessel walls, resultin ...
)
** Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT) is a rare inherited disorder.
Presentation
The primary manifestations are thrombocytopenia and megakaryocytopenia, or low numbers of platelets and megakaryocytes. There is an absence of megakaryo ...
** Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia and radioulnar synostosis
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can r ...
** CYCS-related thrombocytopenia
** Epstein syndrome
Epstein syndrome is a rare genetic disease characterized by a mutation in the MYH9 gene in nonmuscle myosin. This disease affects the patient's renal system and can result in kidney failure. Epstein Syndrome was first discovered in 1972 when two ...
(associated with giant platelet disorder)
** ETV6 related thrombocytopenia
** Fanconi anemia
Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a rare genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of nor ...
** Filaminopathies A
** FYB related thrombocytopenia
** Glanzmann's thrombasthenia
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia is an abnormality of the platelets. It is an extremely rare coagulopathy (bleeding disorder due to a blood abnormality), in which the platelets contain defective or low levels of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GpIIb/IIIa), which ...
** GNE myopathy with congenital thrombocytopenia
** Gray platelet syndrome
Gray platelet syndrome (GPS), or platelet alpha-granule deficiency, is a rare congenital autosomal recessive bleeding disorder caused by a reduction or absence of alpha-granules in blood platelets, and the release of proteins normally contained in ...
(associated with giant platelet disorder)
** Harris platelet syndrome
Harris platelet syndrome (HPS) is the most common inherited giant platelet disorder.
Presentation
HPS was identified among healthy blood donors in the north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, characterized by absent bleeding symptoms, mild t ...
(associated with giant platelet disorder)
** Macrothrombocytopenia and hearing loss
** May–Hegglin anomaly (associated with giant platelet disorder)
** MYH9
Myosin-9 also known as myosin, heavy chain 9, non-muscle or non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIa (NMMHC-IIA) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''MYH9'' gene.
Non-muscle myosin IIA (NM IIA) is expressed in most cells and tissues where it ...
-related disease (associated with giant platelet disorder)
** PRKACG-related thrombocytopenia
** Paris-Trousseau thrombocytopenia
Paris-Trousseau syndrome (PTS) is an inherited disorder characterized by mild hemorrhagic tendency associated with 11q chromosome deletion. It manifests as a granular defect within an individual's platelets. It is characterized by thrombocytes with ...
/Jacobsen syndrome
Jacobsen syndrome is a rare chromosomal disorder resulting from deletion of genes from chromosome 11 that includes band 11q24.1. It is a congenital disorder. Since the deletion takes place on the q arm of chromosome 11, it is also called 11q te ...
** Sebastian syndrome
Sebastian may refer to:
People
* Sebastian (name), including a list of persons with the name
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films and television
* ''Sebastian'' (1968 film), British spy film
* ''Sebastian'' (1995 film), Swedish drama film
...
** SLFN14-related thrombocytopenia
** Stormorken syndrome
** TRPM7-related thrombocytopenia
** Thrombocytopenia absent radius
TAR syndrome (thrombocytopenia with absent radius) is a rare genetic disorder that is characterized by the absence of the radius bone in the forearm and a dramatically reduced platelet count.
Signs and symptoms
* Presents with symptoms of thro ...
syndrome
** Tropomyosin 4-related thrombocytopenia
** TUBB1-related thrombocytopenia
** Upshaw–Schulman syndrome
Upshaw–Schulman syndrome (USS) is the recessively inherited form of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), a rare and complex blood coagulation disease. USS is caused by the absence of the ADAMTS13 protease resulting in the persistence of u ...
** Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome
Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome (WAS) is a rare X-linked recessive disease characterized by eczema, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), immune deficiency, and bloody diarrhea (secondary to the thrombocytopenia). It is also sometimes called the eczem ...
** X-linked thrombocytopenia
X-linked thrombocytopenia, also referred to as XLT or thrombocytopenia 1, is an inherited clotting disorder that primarily affects males. It is a ''WAS''-related disorder, meaning it is caused by a mutation in the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome
Wisk ...
** X-linked thrombocytopenia with thalassemia
Increased destruction
 Abnormally high rates of platelet destruction may be due to immune or nonimmune conditions, including:
*
Abnormally high rates of platelet destruction may be due to immune or nonimmune conditions, including:
* Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), also known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura or immune thrombocytopenia, is a type of thrombocytopenic purpura defined as an isolated low platelet count with a normal bone marrow in the absence of othe ...
* Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder that results in blood clots forming in small blood vessels throughout the body. This results in a low platelet count, low red blood cells due to their breakdown, and often kidney, h ...
* Hemolytic–uremic syndrome
Hemolytic–uremic syndrome (HUS) is a group of blood disorders characterized by low red blood cells, acute kidney failure, and low platelets. Initial symptoms typically include bloody diarrhea, fever, vomiting, and weakness. Kidney problems and ...
* Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts o ...
* Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood characterized by destruction of red blood cells by the complement system, a part of the body's innate immune system. This destructive process occu ...
* Antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome, or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies. APS provokes blood clots (thrombosis) in both arteries and veins as well as pregnancy- ...
* Systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
* Post-transfusion purpura Post-transfusion purpura (PTP) is a delayed adverse reaction to a blood transfusion or platelet transfusion that occurs when the body has produced alloantibodies to the allogeneic transfused platelets' antigens. These alloantibodies destroy the pa ...
* Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (NAITP, NAIT, NATP or NAT) is a disease that affects babies in which the platelet count is decreased because the mother's immune system attacks her fetus' or newborn's platelets. A low platelet count increases ...
* Hypersplenism
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulati ...
* Dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characterist ...
* Gaucher's disease
Gaucher's disease or Gaucher disease () (GD) is a genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polyg ...
* Zika virus
''Zika virus'' (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, whe ...
Medication-induced
These medications can induce thrombocytopenia through direct myelosuppression: *Valproic acid
Valproate (VPA) and its valproic acid, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in those ...
* Methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
* Carboplatin
Carboplatin, sold under the trade name Paraplatin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of forms of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, brain cancer, and neuroblastoma. It is used b ...
* Interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten the ...
* Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers (squamous-cell carcinoma), and in th ...
* Panobinostat
Panobinostat, sold under the brand name Farydak, is a medication used for the treatment of multiple myeloma. It is a hydroxamic acid and acts as a non-selective histone deacetylase inhibitor (pan-HDAC inhibitor).H2 blockers and
 Many cases of
Many cases of
proton-pump inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitors ...
s
Other causes
* Laboratory error, possibly due to the anticoagulantEDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula H2N(CH2CO2H)2sub>2. This white, water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-soluble complexes eve ...
in CBC specimen tubes; a ''citrated'' platelet count is a useful follow-up study
* Snakebite
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occu ...
* Niacin
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid, is an organic compound and a form of vitamin B3, an essential human nutrient. It can be manufactured by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variet ...
toxicity
* Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migran ...
* Thrombocytapheresis (also called plateletpheresis)
* Niemann–Pick disease
Niemann–Pick disease is a group of severe inherited metabolic disorders, in which sphingomyelin accumulates in lysosomes in cells (the lysosomes normally degrade material that comes from out of cells).
These disorders involve the dysfunctional ...
Diagnosis
Laboratory tests for thrombocytopenia might includefull blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and plat ...
, liver enzyme
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
s, kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Functions of a healthy kidney include maintaining a person's fluid ...
, vitamin B12 levels, folic acid levels, erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of ...
, and peripheral blood smear. If the cause for the low platelet count remains unclear, a bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of condition ...
is usually recommended to differentiate cases of decreased platelet production from cases of peripheral platelet destruction.
Thrombocytopenia in hospitalized alcoholics may be caused by spleen enlargement, folate deficiency
Folate deficiency, also known as vitamin B9 deficiency, is a low level of folate and derivatives in the body. Signs of folate deficiency are often subtle. A low number of red blood cells (anemia) is a late finding in folate deficiency and folate ...
, and most frequently, the direct toxic effect of alcohol on production, survival time, and function of platelets. Platelet count begins to rise after 2 to 5 days' abstinence from alcohol. The condition is generally benign, and clinically significant hemorrhage is rare.
In severe thrombocytopenia, a bone marrow study can determine the number, size, and maturity of the megakaryocyte
A megakaryocyte (''mega-'' + '' karyo-'' + '' -cyte'', "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. In hum ...
s. This information may identify ineffective platelet production as the cause of thrombocytopenia and rule out a malignant disease process at the same time.
Treatment
Treatment is guided by the severity and specific cause of the disease. Treatment focuses on eliminating the underlying problem, whether that means discontinuing drugs suspected to cause it or treating underlying sepsis. Diagnosis and treatment of serious thrombocytopenia is usually directed by ahematologist
Hematology (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to ...
. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
may be used to increase platelet production. Lithium carbonate
Lithium carbonate is an inorganic compound, the lithium salt (chemistry), salt of carbonate with the chemical formula, formula . This white Salt (chemistry), salt is widely used in the processing of metal oxides. It is listed on the World Health O ...
or folate may also be used to stimulate platelet production in the bone marrow.
Platelet transfusions
Platelet transfusion
Platelet transfusion, also known as platelet concentrate, is used to prevent or treat bleeding in people with either a low platelet count or poor platelet function. Often this occurs in people receiving cancer chemotherapy. Preventive transfusi ...
s may be suggested for people who have a low platelet count due to thrombocytopenia.
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Treatment ofthrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder that results in blood clots forming in small blood vessels throughout the body. This results in a low platelet count, low red blood cells due to their breakdown, and often kidney, h ...
(TTP) is a medical emergency, since the associated hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly ...
and platelet activation can lead to kidney failure and changes in the level of consciousness. Treatment of TTP was revolutionized in the 1980s with the application of plasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis (from the Greek πλάσμα, ''plasma'', something molded, and ἀφαίρεσις ''aphairesis'', taking away) is the removal, treatment, and return or exchange of blood plasma or components thereof from and to the blood circulati ...
. According to the Furlan-Tsai hypothesis, this treatment works by removing antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against the von Willebrand factor
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) () is a blood glycoprotein involved in hemostasis, specifically, platelet adhesion. It is deficient and/or defective in von Willebrand disease and is involved in many other diseases, including thrombotic thrombocytopen ...
-cleaving protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
ADAMTS-13
ADAMTS13 (''a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13'')—also known as ''von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease'' (VWFCP)—is a zinc-containing metalloprotease enzyme that cleaves von Willebrand factor ( ...
. The plasmapheresis procedure also adds active ADAMTS-13 protease proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
to the patient, restoring a normal level of von Willebrand factor multimers. Patients with persistent antibodies against ADAMTS-13 do not always manifest TTP, and these antibodies alone are not sufficient to explain how plasmapheresis treats TTP.
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), also known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura or immune thrombocytopenia, is a type of thrombocytopenic purpura defined as an isolated low platelet count with a normal bone marrow in the absence of othe ...
(ITP), also known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, can be left untreated, and spontaneous remission (especially in children) is not uncommon. However, counts under 50,000/μl are usually monitored with regular blood tests, and those with counts under 10,000/μl are usually treated, as the risk of serious spontaneous bleeding is high with such low platelet counts. Any patient experiencing severe bleeding symptoms is also usually treated. The threshold for treating ITP has decreased since the 1990s; hematologist
Hematology (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to ...
s recognize that patients rarely spontaneously bleed with platelet counts greater than 10,000/μl, although exceptions to this observation have been documented.
Thrombopoetin analogues have been tested extensively for the treatment of ITP. These agents had previously shown promise, but had been found to stimulate antibodies against endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, es ...
thrombopoietin
Thrombopoietin (THPO) also known as megakaryocyte growth and development factor (MGDF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''THPO'' gene.
Thrombopoietin is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the liver and kidney which regulates the pro ...
or lead to thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thro ...
. Romiplostim
Romiplostim, sold under the brand name Nplate among others, is a fusion protein analog of thrombopoietin, a hormone that regulates platelet production.
Indications and Marketing
The drug was developed by Amgen through a restricted usage program ...
(trade name Nplate, formerly AMG 531) was found to be safe and effective for the treatment of ITP in refractory patients, especially those who relapse
In internal medicine, relapse or recidivism is a recurrence of a past (typically medical) condition. For example, multiple sclerosis and malaria often exhibit peaks of activity and sometimes very long periods of dormancy, followed by relapse or r ...
d following splenectomy.
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Discontinuation of heparin is critical in a case of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). Beyond that, however, clinicians generally treat to avoid thrombosis. Treatment may include adirect thrombin inhibitor Direct thrombin inhibitors (DTIs) are a class of medication that act as anticoagulants (delaying blood clotting) by directly inhibiting the enzyme thrombin (factor IIa). Some are in clinical use, while others are undergoing clinical development. Sev ...
, such as lepirudin
Lepirudin is an anticoagulant that functions as a direct thrombin inhibitor.
Brand name: Refludan, Generic: Lepirudin rDNA for injection.
Lepirudin is a recombinant hirudin derived from yeast cells. Lepirudin is almost identical to hirudin extr ...
or argatroban
Argatroban is an anticoagulant that is a small molecule direct thrombin inhibitor. In 2000, argatroban was licensed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for prophylaxis or treatment of thrombosis in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytop ...
. Other "blood thinners
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
" sometimes used in this setting include bivalirudin
Bivalirudin (Bivalitroban), sold under the brand names Angiomax and Angiox and manufactured by The Medicines Company, is a direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI).
Chemically, it is a synthetic congener of the naturally occurring drug hirudin, found in ...
and fondaparinux
Fondaparinux (trade name Arixtra) is an anticoagulant medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparins. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline. A generic version developed by Alchemia is marketed within the US by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.
...
. Platelet transfusion
Platelet transfusion, also known as platelet concentrate, is used to prevent or treat bleeding in people with either a low platelet count or poor platelet function. Often this occurs in people receiving cancer chemotherapy. Preventive transfusi ...
s are not routinely used to treat HIT because thrombosis, not bleeding, is the primary problem. Warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent strok ...
is not recommended until platelets have normalized.
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
Bone marrow/stem cell transplants are the only known cures for this genetic disease. Frequent platelet transfusions are required to keep the patient from bleeding to death before the transplant can be performed, although this is not always the case.Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived platelets
Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived platelets is a technology currently being researched by the private sector, in association with theBiomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority
The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) is a U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) office responsible for the procurement and development of medical countermeasures, principally against bioterrorism, in ...
and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is " ...
, that would create platelets outside the human body.
Neonatal thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia affects a few newborns, and its prevalence in neonatal intensive care units is high. Normally, it is mild and resolves without consequences. Most cases affect preterm birth infants and result from placental insufficiency and/or fetal hypoxia. Other causes, such as alloimmunity, genetics, autoimmunity, and infection, are less frequent. Thrombocytopenia that starts after the first 72 hours, since birth is often the result of underlyingsepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
or necrotizing enterocolitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating intestinal disease that affects premature or very low birth weight infants.Gephart S.M., Quinn M. A call to action to fight for equity and end necrotizing enterocolitis disparities. ''Adv. Neonata ...
. In the case of infection, polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
tests may be useful for rapid pathogen identification and detection of antibiotic-resistance genes. Possible pathogens include viruses (e.g. cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (''CMV'') (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order ''Herpesvirales'', in the family ''Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily ''Betaherpe ...
, rubella virus
Rubella virus (RuV) is the pathogenic agent of the disease rubella, transmitted only between humans via the respiratory route, and is the main cause of congenital rubella syndrome when infection occurs during the first weeks of pregnancy.
Rube ...
, HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
), bacteria (e.g. ''Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative ...
'' spp., ''Enterococcus
''Enterococcus'' is a large genus of lactic acid bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Enterococci are gram-positive cocci that often occur in pairs (diplococci) or short chains, and are difficult to distinguish from streptococci on physical charact ...
'' spp., ''Streptococcus agalactiae
''Streptococcus agalactiae'' (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS) is a gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) with a tendency to form chains (as reflected by the genus name ''Streptococcus''). It is a beta-hemolytic, catalase-negative, a ...
'', ''Listeria monocytogenes
''Listeria monocytogenes'' is the species of pathogenic bacteria that causes the infection listeriosis. It is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, capable of surviving in the presence or absence of oxygen. It can grow and reproduce inside the host' ...
'', ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
'', ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria ...
'', ''Klebsiella pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose-fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar.
Although found in the normal flora of the mouth ...
'', ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerugi ...
'', ''Yersinia enterocolitica
''Yersinia enterocolitica'' is a Gram-negative, bacillus-shaped bacterium, belonging to the family Yersiniaceae. It is motile at temperatures of 22–29° C (72–84 °F), but becomes nonmotile at normal human body temperature. ''Y. enterocolitic ...
''), fungi (e.g. '' Candida'' spp.), and ''Toxoplasma gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan (specifically an apicomplexan) that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as d ...
''. The severity of thrombocytopenia may be correlated with pathogen type; some research indicates that the most severe cases are related to fungal or Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
bacterial infection. The pathogen may be transmitted during or before birth, by breast feeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that brea ...
, or during transfusion. Interleukin-11 is being investigated as a drug for managing thrombocytopenia, especially in cases of sepsis or necrotizing enterocolitis.
References
External links
{{Medicine Coagulopathies Medical signs Hematopathology