Thirteen Factories on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Thirteen Factories, also known as the , was a neighbourhood along the
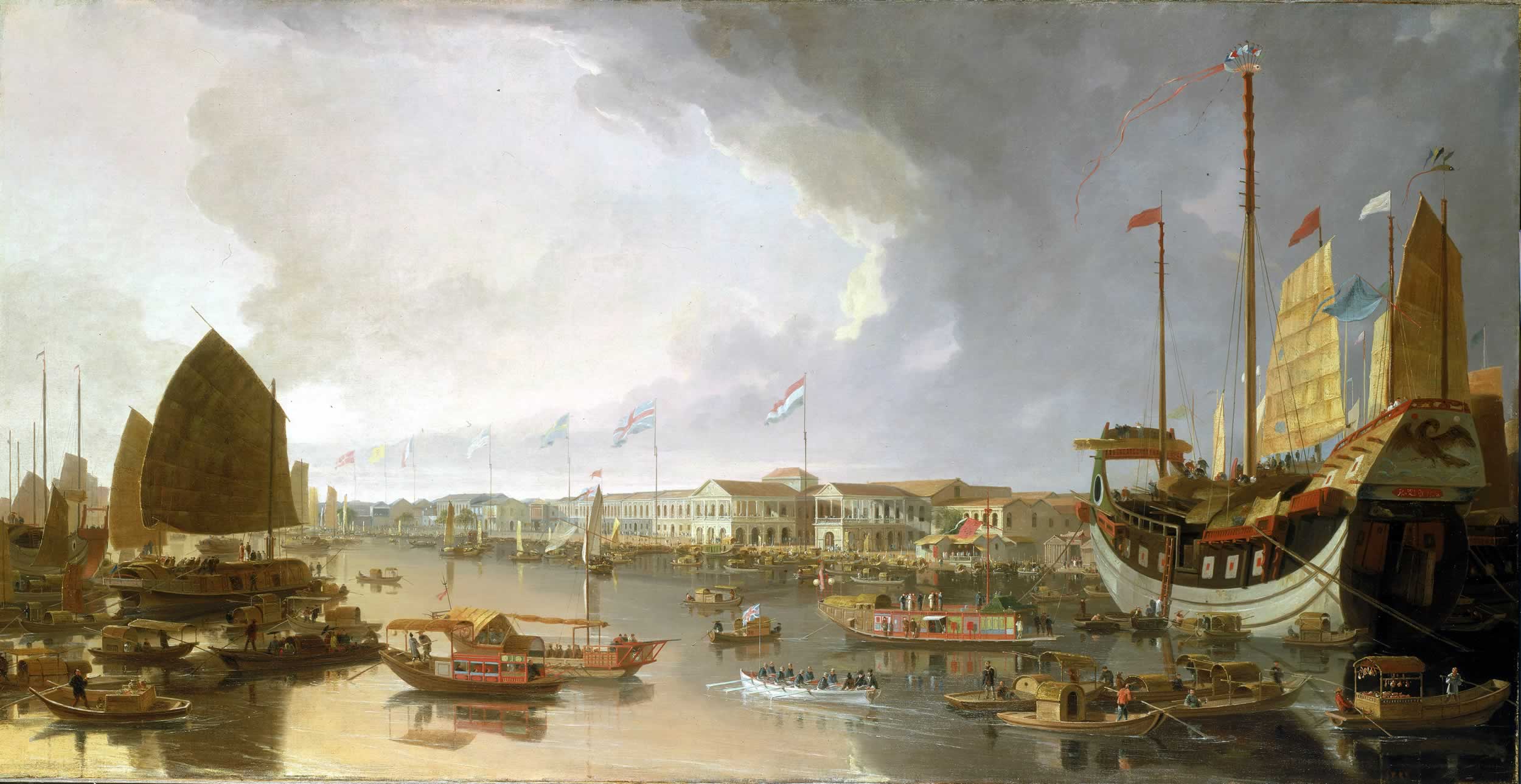


 The "factories" were not workshops or manufacturing centres but the offices,
The "factories" were not workshops or manufacturing centres but the offices,
Ch'ien Lung, (Qianlong) Letter to George III
/ref> A second embassy under
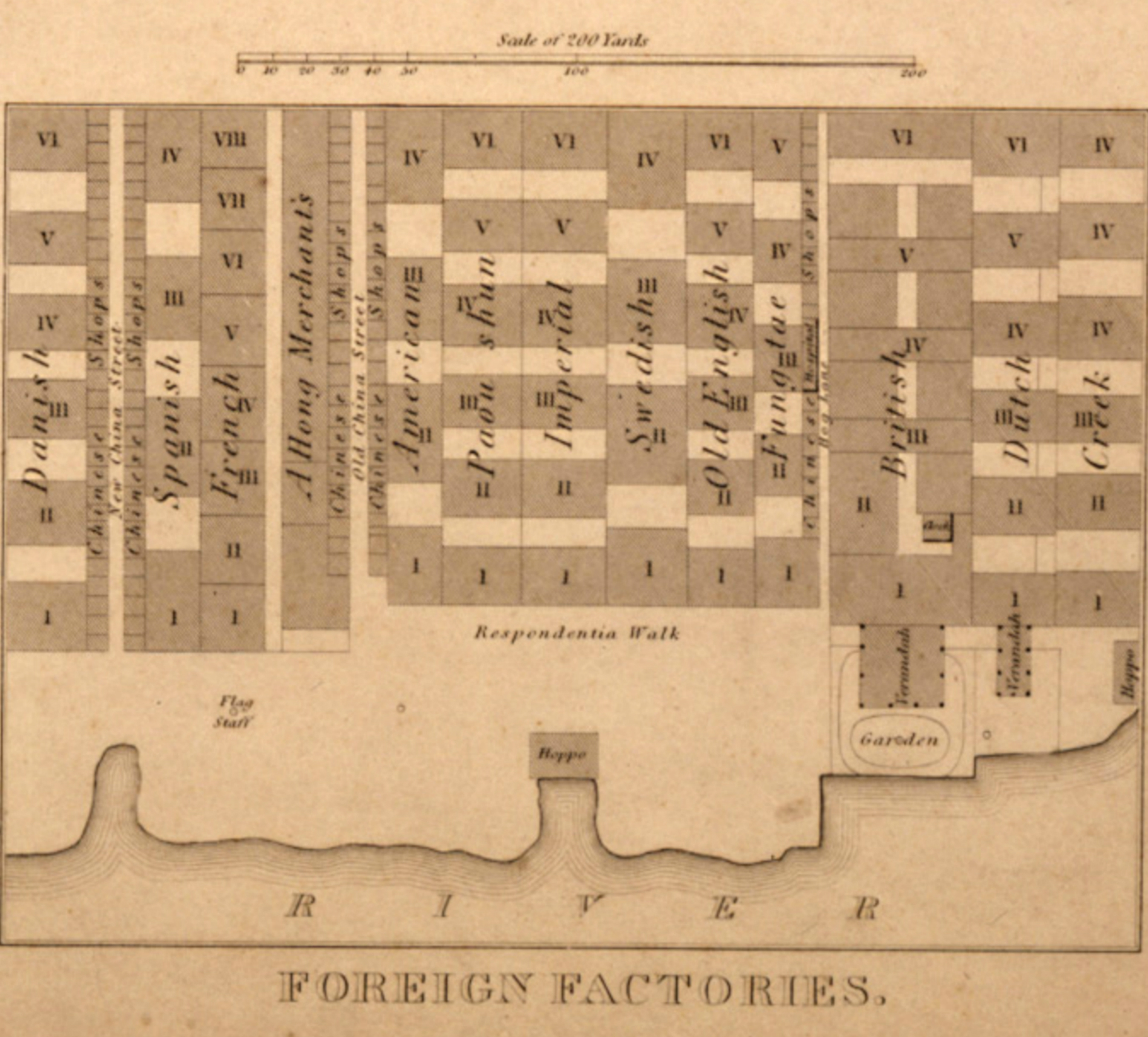
 The Western merchants were allowed to occupy two- or three-story buildings set back about from the river. Each factory contained a number of houses. The warehouses occupied the ground floors; the upper floors were taken up by living areas. The square in front of the factories was fenced off, with Chinese access restricted. There were no wells or access to running water. Chinese servants were used to bring in drinking and wash water and to empty the factories'
The Western merchants were allowed to occupy two- or three-story buildings set back about from the river. Each factory contained a number of houses. The warehouses occupied the ground floors; the upper floors were taken up by living areas. The square in front of the factories was fenced off, with Chinese access restricted. There were no wells or access to running water. Chinese servants were used to bring in drinking and wash water and to empty the factories'
 The area was bound on the north by on the west by and on the east by a small creek. and divided the groups of factories from one another and were lined by retail stores selling a wide variety of Chinese goods.
The area was bound on the north by on the west by and on the east by a small creek. and divided the groups of factories from one another and were lined by retail stores selling a wide variety of Chinese goods.
Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
in southwestern Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
(Canton) in the Qing Empire
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
from to 1856 around modern day Xiguan
Saikwan or Xiguan is an ancient town and an area in the Liwan district of Guangzhou, China, which was located west of the old walled city. The Thirteen Factories trading enclave was located on its southern shore and the Shamian enclave was co ...
, in Guangzhou's Liwan District
Liwan District is one of 11 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province, China. The district is split into two parts by the Pearl River: Xiguan in the northeast and Fangcun in the southwest.
...
. These warehouses and stores were the principal and sole legal site of most Western trade with China from 1757 to 1842. The factories were destroyed by fire in 1822 by accident, in 1841 amid the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
, and in 1856 at the onset of the Second Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Sino War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a colonial war lasting from 1856 to 1860, which pitted the British Empire and the French Emp ...
. The factories' importance diminished after the opening of the treaty ports
Treaty ports (; ja, 条約港) were the port cities in China and Japan that were opened to foreign trade mainly by the unequal treaties forced upon them by Western powers, as well as cities in Korea opened up similarly by the Japanese Empire.
...
and the end of the Canton System
The Canton System (1757–1842; zh, t=一口通商, p=Yīkǒu tōngshāng, "Single orttrading relations") served as a means for Qing China to control trade with the West within its own country by focusing all trade on the southern port of C ...
under the terms of the 1842 Anglo-Chinese Treaty of Nanking
The Treaty of Nanjing was the peace treaty which ended the First Opium War (1839–1842) between Great Britain and the Qing dynasty of China on 29 August 1842. It was the first of what the Chinese later termed the Unequal Treaties.
In the ...
. After the Second Opium War, the factories were not rebuilt at their former site south of Guangzhou's old walled city but moved, first to Henan Island
Haizhu District is one of 11 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province, China.
Geography
Haizhu District is located in the southern part of Guangzhou city. After the adjustment of Guangzhou' ...
across the Pearl River and then to Shamian Island
Shamian (also romanized as Shameen or Shamin, both from its Cantonese pronunciation) is a sandbank island in the Liwan District of Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. The island's name literally means "sandy surface" in Chinese.
The territory ...
south of Guangzhou's western suburbs. Their former site is now part of .
Terminology



 The "factories" were not workshops or manufacturing centres but the offices,
The "factories" were not workshops or manufacturing centres but the offices, trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
s, and warehouse
A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities ...
s of foreign factors
Factor, a Latin word meaning "who/which acts", may refer to:
Commerce
* Factor (agent), a person who acts for, notably a mercantile and colonial agent
* Factor (Scotland), a person or firm managing a Scottish estate
* Factors of production, suc ...
, mercantile fiduciaries
A fiduciary is a person who holds a legal or ethical relationship of trust with one or more other parties (person or group of persons). Typically, a fiduciary prudently takes care of money or other assets for another person. One party, for exampl ...
who bought and sold goods on consignment for their principals. The word derives from “feitoria” which means trading post in Portuguese (the first westerners to engage in trade with China).
The foreign agents were known at the time as "supercargo
A supercargo (from Spanish ''sobrecargo'') is a person employed on board a vessel by the owner of cargo carried on the ship. The duties of a supercargo are defined by admiralty law and include managing the cargo owner's trade, selling the merchand ...
s" in English and as ''daban'' () in Chinese. This term's Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding are ...
pronunciation, ''tai-pan
A tai-pan (,Andrew J. Moody, "Transmission Languages and Source Languages of Chinese Borrowings in English", ''American Speech'', Vol. 71, No. 4 (Winter, 1996), pp. 414-415. literally "top class"汉英词典 — ''A Chinese-English Dictionary' ...
'', only came into common English use after the rise of private trading from 1834 on. A private captain might be his own supercargo; a large East Indiamen
East Indiaman was a general name for any sailing ship operating under charter or licence to any of the East India trading companies of the major European trading powers of the 17th through the 19th centuries. The term is used to refer to vesse ...
might have five or more, which were ranked "chief supercargo", "2nd supercargo", and so on. A team of supercargos divided their work, some overseeing sales, others tea purchases, silk purchases, and so forth. Permanent supercargos might divide their work by the order ships arrived. The bookkeepers who attended them were called "writers"; those serving with the ship, who also checked these accounts, "pursers".
"Hong" is the Cantonese pronunciation of , the Chinese term for a properly-licensed business. By analogy, it was applied to its chief, the Hong merchant, and its property, the factories themselves. It has also been suggested the term was first applied to the factories as they were arranged in a row along the riverbank, "row" or "rank" being an alternative meaning of the same Chinese character.
''Hoppo
Hoppo or Administrator of the Canton Customs ( zh, t=粵海關部, s=粤海关部, p=Yuèhǎi Guānbù), was the Qing dynasty official at Guangzhou (Canton) given responsibility by the emperor for controlling shipping, collecting tariffs, and ma ...
'', or fully the "Canton Sea Customs Minister", was the imperial official responsible for imperial customs and supervised the other officials. The word is Chinese Pidgin English
Chinese Pidgin English (also called Chinese Coastal English or Pigeon English; ) is a pidgin language lexically based on English, but influenced by a Chinese substratum. From the 17th to the 19th centuries, there was also Chinese Pidgin Eng ...
, and some speculated that it derived from ''Hu Bu
The Ministry or Board of Revenue was one of the Six Ministries under the Department of State Affairs in imperial China.
Name
The term "Ministry" or "Board of Revenue" is an English gloss of the department's purview. It is also similarly transla ...
'' (Board of Revenue), but the official had no connection to the Board. The Hoppo was responsible for fixing the charges levied as a ship entered the port, a responsibility that allowed him to become quite rich.
History
Since theMing dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
( founded in 1368 ), a series of sea bans (''haijin'') restricted China's foreign commerce, at times attempting to ban it completely. In 1684, the Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1 ...
of the Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
allowed foreigners to trade with China in the four cities of Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
, Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an, ...
, Songjiang Songjiang, from the Chinese for "Pine River" and formerly romanized as Sungkiang, usually refers to one of the following areas within the municipal limits of Shanghai:
* Songjiang Town (), the former principal town of the Shanghai area
* Songjia ...
, and Ningpo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sa ...
. In the case of Guangzhou, early traders were obliged to follow the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
winds, arriving between June and September, conducting their business, and then departing between November and February. The foreign ships were anchored downstream at Pazhou
Pazhou is a subdistrict of Haizhu in southeastern Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, in China.
, formerly Whampoa Island, has a total area of and is the site of Pazhou Pagoda. Its eastern bay was formerly the chief anchorage for ships parti ...
(then known as "Whampoa"), with business conducted in the city's western suburbs. Western traders were further required to work through Chinese merchants
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
who would guarantee their good behavior and tax obligations; they were also the owners and landlords of the warehouses and apartments the traders were obliged to use. In practice, private traders could often avoid these restrictions but the customs superintendent, the ''hoppo'', was always careful to enforce them upon large-volume purchasers such as the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
. Typically, cargo was ferried from the ships by its own crew and to the ships at the expense of the Chinese merchants on their "chop boats" (lighters). To avoid theft or piracy, foreign traders began assigning a few of their own seamen to these ships as guards.
In 1686, Westerners were allowed to rent accommodations in the factory quarter to avoid the necessity of shuttling back to Pazhou each night. For the most part, the supercargos, their assistants, and the bookkeepers stayed at the factories, the crew—except for a few guards or those on shore leave—stayed with the ships, and the captains continued to ferry between the two. A Chinese comprador hired each factory's staff of Chinese servants and bought its provisions from local vendors; senior supercargos sometimes brought their own staff or slaves as well. Another comprador dealt with the ship's provisions at Pazhou, where sampan
A sampan is a relatively flat-bottomed Chinese and Malay wooden boat. Some sampans include a small shelter on board and may be used as a permanent habitation on inland waters. The design closely resembles Western hard chine boats like th ...
ladies crowded around the ships to do laundry and odd jobs for the sailors. A few weeks before departure, the crew came to the factories in shifts of a few days each for shore leave, chaperoned by some of the ship's officers. Hog Lane was lined with open-fronted booths and shops catering to them, selling food, drink, clothing, and "chowchows" (novelties), and was policed by Chinese guards stationed at both ends of the alley. At first the supercargos came and left with the ships, but over the course of the 18th century companies began to rent their factory spaces year-round to avoid being displaced on their return. The supercargos were then permitted to outstay their company's ships a few weeks to conduct business for the next season; after that, they were obliged to remove themselves to Macao
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a pop ...
through the spring and summer until the appearance of the next ship. By the 1760s, every East India company had permanent supercargos and rooms were being rented in Macao year-round as well.
In the mid-1750s, the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
realized that the fees and prices were both better at Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
; it was also nearer the main centres of Chinese tea production and silk manufacture. The impact of their shift on Guangzhou's tax receipts and a fear of a second Macao being created prompted attempts to force Ningbo to make itself less attractive. When that failed, the Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
issued a 1757 edict closing all ports but Guangzhou's to most Westerners. In order to keep the traders in the factory area and out of the rest of the western suburbs, the 17 Chinese merchants
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
of the port were obliged to establish the guild known to foreigners as the "Cohong
The ''Cohong'', sometimes spelled or , a guild of China, Chinese merchants or Hong (business) , ''hongs'', operated the Canton System, import-export monopoly in Canton (present-day Guangzhou) during the Qing dynasty (16441911). During the centu ...
" in 1760, each paying an entrance fee of around 10,000 Spanish dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
s (74,000 tls.) and submitting to a levy of about 3% on their future business. Ten of the merchants did so, the fees establishing the Consoo Fund and Hall
In architecture, a hall is a relatively large space enclosed by a roof and walls. In the Iron Age and early Middle Ages in northern Europe, a mead hall was where a lord and his retainers ate and also slept. Later in the Middle Ages, the gr ...
, walkways, and a new street to which small-scale merchants were obliged to move in order to continue selling to the foreign traders. Since the new street was particularly full of porcelain dealers, it came to be known as China Street. The Hong merchants included Howqua
Wu Bingjian (; 17694 September 1843), trading as "Houqua" and better known in the West as "Howqua", was a hong merchant in the Thirteen Factories, head of the '' E-wo hong'' and leader of the Canton Cohong. He was once the richest man in the wor ...
(Wu Bingjian), Puankhequa, Mowqua, Goqua, Fatqua, Kingqua, Sunshing, Mingqua, Saoqua, and Punboqua.. Despite the existence of Sinophones and the linguists usually accompanying each ship, foreigners were notionally banned by imperial decree from learning the Chinese language, there being officially appointed translators for that purpose. The foreign traders—despite most working for government monopolies themselves—protested strongly at the Cohong's control over prices, advances, and exchange rates and predicted the death of trade with China. In fact, the Cohong helped ensure Chinese production met the traders' needs—some ships had previously been obliged to wait as much as a year to be fully stocked—and by 1769, the area was being expanded to make up for an extreme shortness of apartments. In 1748, there had only been eight factories, but there were seventeen by 1770, a number kept up until the great fire of 1822.
It was discovered that, rather than depending on the monsoon winds, ships could arrive or depart at any time of year by rounding the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. This opened the trade for smaller craft who might only need a few weeks to complete a visit, where the large company vessels still needed 4 to 5 months at minimum. Subsequently, the British and Americans typically always had ships anchored off Pazhou, allowing them to keep their supercargos and staff in the Guangzhou factories all year. During the 1780s, the Spanish also began to send several ships from Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
each year rather than the single vessel they had previously used; they began renting a permanent factory in 1788. (In practice, senior supercargos tended to prefer Macao during the summer regardless and to send their junior officers to deal with off-season trade.)
In 1793, sent George Macartney to request that ports in northern China be opened to trade but was rejected by the Qianlong Emperor, not due to Macartney's refusal to kowtow
A kowtow is the act of deep respect shown by prostration, that is, kneeling and bowing so low as to have one's head touching the ground. In Sinospheric culture, the kowtow is the highest sign of reverence. It was widely used to show reverence ...
in the presence of the Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
, as is commonly believed./ref> A second embassy under
Lord Amherst
Field Marshal Jeffery Amherst, 1st Baron Amherst, (29 January 1717 – 3 August 1797) was a British Army officer and Commander-in-Chief of the Forces in the British Army. Amherst is credited as the architect of Britain's successful campaig ...
fared no better in 1816–1817. The growth of European (particularly British) tea consumption supplemented the port's heavy trade in silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
and porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises mainl ...
. The balancing trade in goods from Europe was poor so payments had to be settled in large volumes of bullion
Bullion is non-ferrous metal that has been refined to a high standard of elemental purity. The term is ordinarily applied to bulk metal used in the production of coins and especially to precious metals such as gold and silver. It comes from t ...
until the trade in opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
rose to take its place.
In 1835, the medical missionary
A missionary is a member of a Religious denomination, religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Tho ...
Peter Parker
Spider-Man is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer-editor Stan Lee and artist Steve Ditko, he first appearance, first appeared in the anthology comic book ''Amazing Fantasy'' #15 (August ...
opened an ophthalmic hospital in the area. Parker commissioned Lam Qua
Lam Qua (; 1801–1860), or Kwan Kiu Cheong (), was a Chinese painter from the Canton province in Qing Dynasty China, who specialized in Western-style portraits intended largely for Western clients. Lam Qua was the first Chinese portrait painte ...
, a Western-trained Chinese painter who also had workshops in the area, to paint pre-operative portraits of patients who had large tumors or other major deformities.
The viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "k ...
Lin Zexu
Lin Zexu (30 August 1785 – 22 November 1850), courtesy name Yuanfu, was a Chinese political philosopher and politician. He was the head of states (Viceroy), Governor General, scholar-official, and under the Daoguang Emperor of the Qing dynast ...
's vigorous suppression of the British opium trade
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid m ...
precipitated the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
(1839–1842), during which the factories were burnt to the ground. The 1842 Treaty of Nanking
The Treaty of Nanjing was the peace treaty which ended the First Opium War (1839–1842) between Great Britain and the Qing dynasty of China on 29 August 1842. It was the first of what the Chinese later termed the Unequal Treaties.
In the ...
ending that war forced the ceding of Hong Kong Island
Hong Kong Island is an Islands and peninsulas of Hong Kong, island in the southern part of Hong Kong. Known colloquially and on road signs simply as Hong Kong, the island has a population of 1,289,500 and its population density is 16,390/km ...
to the British and opened the treaty ports
Treaty ports (; ja, 条約港) were the port cities in China and Japan that were opened to foreign trade mainly by the unequal treaties forced upon them by Western powers, as well as cities in Korea opened up similarly by the Japanese Empire.
...
of Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ...
, Ningbo
Ningbo (; Ningbonese: ''gnin² poq⁷'' , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), formerly romanized as Ningpo, is a major sub-provincial city in northeast Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It comprises 6 urban districts, 2 sate ...
("Ningpo"), Xiamen
Xiamen ( , ; ), also known as Amoy (, from Hokkien pronunciation ), is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an, ...
("Amoy"), and Fuzhou
Fuzhou (; , Fuzhounese: Hokchew, ''Hók-ciŭ''), alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute t ...
("Fuchow"). It nominally opened the walled city of Guangzhou to the foreigners, but this was subsequently resisted by the city's viceroys
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
on a number of pretexts. The factories were rebuilt at their former location but, with their diminished importance, they were not rebuilt a third time after their destruction at the onset of the Second Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Sino War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a colonial war lasting from 1856 to 1860, which pitted the British Empire and the French Emp ...
. Instead, the foreign traders first operated off of Henan Island
Haizhu District is one of 11 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province, China.
Geography
Haizhu District is located in the southern part of Guangzhou city. After the adjustment of Guangzhou' ...
on the other side of the Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
and then, after the war's conclusion, rebuilt their Guangzhou operations at a new enclave on the Shamian
Shamian (also romanized as Shameen or Shamin, both from its Cantonese pronunciation) is a sandbank island in the Liwan District of Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. The island's name literally means "sandy surface" in Chinese.
The territory ...
sandbar south of the city's western suburbs.
Organization
Under theCanton System
The Canton System (1757–1842; zh, t=一口通商, p=Yīkǒu tōngshāng, "Single orttrading relations") served as a means for Qing China to control trade with the West within its own country by focusing all trade on the southern port of C ...
, between 1757 and 1842, Western merchants in China were restricted to live and conduct their business only in the approved area of the port of Guangzhou
Port of Guangzhou is the main seaport of Guangzhou city, Guangdong province, China. The port is operated by Guangzhou Port Group Co. Ltd which is a state owned company. The company was established on February 26, 2004 from the former Guangzhou Ha ...
and only through government-approved merchant houses. Their factories formed a tight-knit community, which the historian Jacques Downs called a "golden ghetto" because it was both isolated and lucrative.
These hong Hong may refer to:
Places
*Høng, a town in Denmark
*Hong Kong, a city and a special administrative region in China
*Hong, Nigeria
*Hong River in China and Vietnam
*Lake Hong in China
Surnames
*Hong (Chinese name)
*Hong (Korean name)
Organiz ...
s—first established by Pan Zhencheng () and nine others in 1760—were granted a lucrative monopoly on foreign trade in exchange for various payments and obligations to the Qing state. The hongs were organised into a guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
known as the cohong
The ''Cohong'', sometimes spelled or , a guild of China, Chinese merchants or Hong (business) , ''hongs'', operated the Canton System, import-export monopoly in Canton (present-day Guangzhou) during the Qing dynasty (16441911). During the centu ...
, which also oversaw the Thai
Thai or THAI may refer to:
* Of or from Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia
** Thai people, the dominant ethnic group of Thailand
** Thai language, a Tai-Kadai language spoken mainly in and around Thailand
*** Thai script
*** Thai (Unicode block ...
and domestic trade in the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
. The Hoppo
Hoppo or Administrator of the Canton Customs ( zh, t=粵海關部, s=粤海关部, p=Yuèhǎi Guānbù), was the Qing dynasty official at Guangzhou (Canton) given responsibility by the emperor for controlling shipping, collecting tariffs, and ma ...
was appointed by the emperor to oversee taxation and customs collection; he also oversaw disputes among the merchants, in an attempt to restrain the foreigners from contacting the imperial government in Beijing directly.
Architecture
 The Western merchants were allowed to occupy two- or three-story buildings set back about from the river. Each factory contained a number of houses. The warehouses occupied the ground floors; the upper floors were taken up by living areas. The square in front of the factories was fenced off, with Chinese access restricted. There were no wells or access to running water. Chinese servants were used to bring in drinking and wash water and to empty the factories'
The Western merchants were allowed to occupy two- or three-story buildings set back about from the river. Each factory contained a number of houses. The warehouses occupied the ground floors; the upper floors were taken up by living areas. The square in front of the factories was fenced off, with Chinese access restricted. There were no wells or access to running water. Chinese servants were used to bring in drinking and wash water and to empty the factories' chamber pot
A chamber pot is a portable toilet, meant for nocturnal use in the bedroom. It was common in many cultures before the advent of indoor plumbing and flushing toilets.
Names and etymology
"Chamber" is an older term for bedroom. The chamber pot ...
s.
The facades of the buildings used Western classical designs, but the structures otherwise were merchant buildings of local style. The layout featured courtyards, long, narrow hallways, with rooms on either side. Construction materials were local, such as brick with tile roofs, but the windows and stairs came from British sources abroad.
Layout
 The area was bound on the north by on the west by and on the east by a small creek. and divided the groups of factories from one another and were lined by retail stores selling a wide variety of Chinese goods.
The area was bound on the north by on the west by and on the east by a small creek. and divided the groups of factories from one another and were lined by retail stores selling a wide variety of Chinese goods. Peter Parker
Spider-Man is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer-editor Stan Lee and artist Steve Ditko, he first appearance, first appeared in the anthology comic book ''Amazing Fantasy'' #15 (August ...
's hospital was located at Lane.
The exact number of factories varied, but by the early 19th century it became stable at 17 or 18 including, from east to west:
The Chow-Chow Factory was indirectly linked to the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
.
Legacy
The former site of the thirteen factories is now part of the Cultural Park. Thirteen Factories Street, which ran north of the enclave, is now named Shisanhang (Thirteen Factories) Road..See also
*Canton System
The Canton System (1757–1842; zh, t=一口通商, p=Yīkǒu tōngshāng, "Single orttrading relations") served as a means for Qing China to control trade with the West within its own country by focusing all trade on the southern port of C ...
& Old China Trade
The Old China Trade () refers to the early commerce between the Qing Empire and the United States under the Canton System, spanning from shortly after the end of the American Revolutionary War in 1783 to the Treaty of Wanghia in 1844. The Old C ...
* Hong Hong may refer to:
Places
*Høng, a town in Denmark
*Hong Kong, a city and a special administrative region in China
*Hong, Nigeria
*Hong River in China and Vietnam
*Lake Hong in China
Surnames
*Hong (Chinese name)
*Hong (Korean name)
Organiz ...
& Cohong
The ''Cohong'', sometimes spelled or , a guild of China, Chinese merchants or Hong (business) , ''hongs'', operated the Canton System, import-export monopoly in Canton (present-day Guangzhou) during the Qing dynasty (16441911). During the centu ...
* Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
, Pazhou
Pazhou is a subdistrict of Haizhu in southeastern Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, in China.
, formerly Whampoa Island, has a total area of and is the site of Pazhou Pagoda. Its eastern bay was formerly the chief anchorage for ships parti ...
, Changzhou
Changzhou ( Changzhounese: ''Zaon Tsei'', ) is a prefecture-level city in southern Jiangsu province, China. It was previously known as Yanling, Lanling and Jinling. Located on the southern bank of the Yangtze River, Changzhou borders the provin ...
, & Xiaoguwei
Xiaoguwei Island, formerly known in English as , is an island in the Pearl River Delta in Guangdong Province, China. It is administered as Xiaoguwei Subdistrict, a subdistrict in Panyu District, Guangzhou. The Guangzhou Higher Education Mega Cen ...
islands
* Dejima
, in the 17th century also called Tsukishima ( 築島, "built island"), was an artificial island off Nagasaki, Japan that served as a trading post for the Portuguese (1570–1639) and subsequently the Dutch (1641–1854). For 220 years, it ...
& Zaibatsu
is a Japanese language, Japanese term referring to industrial and financial vertical integration, vertically integrated business conglomerate (company), conglomerates in the Empire of Japan, whose influence and size allowed control over signi ...
, Japanese equivalents
* Economy of China
The China, People's Republic of China has an upper middle income Developing country, developing Mixed economy, mixed socialist market economy that incorporates economic planning through Industrial policy, industrial policies and strategic Five- ...
& the Economic history of imperial China
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * * . * . * . * . * * . * . * .External links
* . * . * . {{coord, 23.109743, N, 113.251607, E, display=title, region:CN_type:landmark History of Guangzhou History of foreign trade in China Business families Foreign relations of the Qing dynasty Cantonese merchants Former neighborhoods