Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A thin-film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR or TFBAR) is a device consisting of a piezoelectric material manufactured by thin film methods between two conductive – typically metallic – electrodes and acoustically isolated from the surrounding medium. The operation is based on the piezoelectricity of the piezolayer between the electrodes.
 FBAR devices using piezoelectric films with thicknesses ranging from several micrometres down to tens of micrometres resonate in the frequency range of 100 MHz to 20 GHz. FBAR or TFBAR resonators fall in the category of bulk acoustic resonators (BAW) and piezoelectric resonators and they are used in applications where high frequency, small size and weight is needed.
FBAR devices using piezoelectric films with thicknesses ranging from several micrometres down to tens of micrometres resonate in the frequency range of 100 MHz to 20 GHz. FBAR or TFBAR resonators fall in the category of bulk acoustic resonators (BAW) and piezoelectric resonators and they are used in applications where high frequency, small size and weight is needed.
 Doping or adding new materials like scandium (Sc) are new directions to improve material properties of AlN for FBARs. Research of new electrode materials or alternative materials to aluminium like by replacing one of the metal electrodes with very light materials like graphene for minimising the loading of the resonator has been demonstrated to lead better control of the resonance frequency.
Doping or adding new materials like scandium (Sc) are new directions to improve material properties of AlN for FBARs. Research of new electrode materials or alternative materials to aluminium like by replacing one of the metal electrodes with very light materials like graphene for minimising the loading of the resonator has been demonstrated to lead better control of the resonance frequency.


 As per 2022 there are two known structures of thin-film bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonators: free-standing and solidly mounted (SMR) resonators. In a free-standing resonator structure air is used to separate the resonator from the substrate/surrounding. The structure of a free-standing resonator is based on some typical manufacturing steps used in micro-electromechanical systems MEMS.
As per 2022 there are two known structures of thin-film bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonators: free-standing and solidly mounted (SMR) resonators. In a free-standing resonator structure air is used to separate the resonator from the substrate/surrounding. The structure of a free-standing resonator is based on some typical manufacturing steps used in micro-electromechanical systems MEMS. 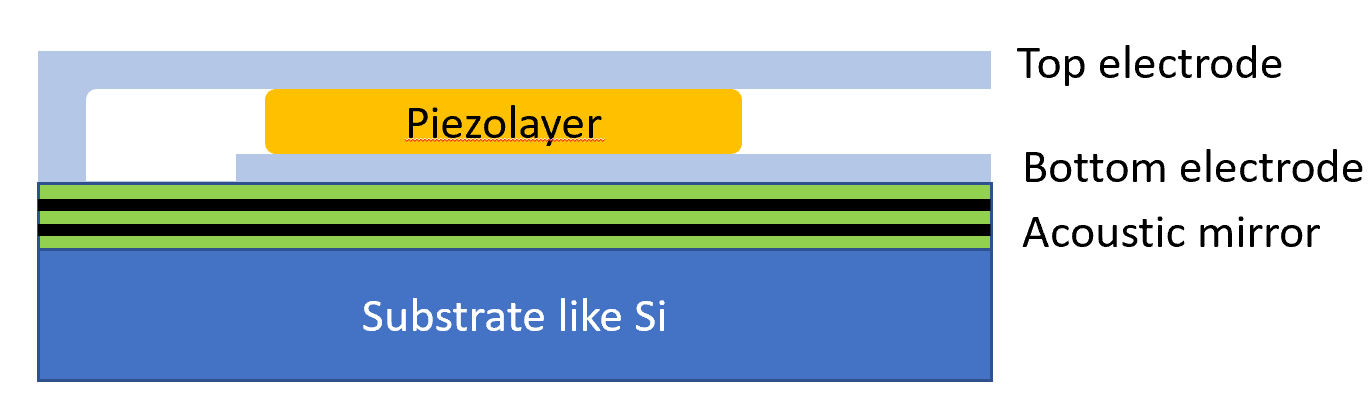 In an SMR structure acoustic mirror(s) providing an acoustic isolation is constructed between the resonator and the surrounding like the substrate. The acoustic mirror (like a
In an SMR structure acoustic mirror(s) providing an acoustic isolation is constructed between the resonator and the surrounding like the substrate. The acoustic mirror (like a
 A common application of FBARs is radio frequency (RF) filters for use in
A common application of FBARs is radio frequency (RF) filters for use in
University of Southern California explanation on the operation of FBAR's
PhD thesis of J. V. Tirado, Bulk Acoustic Wave Resonators and their Application to Microwave Devices, 2010, Universitat Autonoma Barcelona, Spain, 201 pages.
PhD thesis of J. Liu, Application of Bragg Reflection for Suppression of Spurious Transverse Mode Resonances in RF BAW Resonators, 2014, Chiba University, Japan, 151 pages.
Broadcom's products based on FBAR technology
FBAR technology opportunity in 5G telecommunication
Products of Qorvo based on BAW (FBAR)
Description of Texas Instrument's SimpleLink module
Akoustis Technologies Inc.
Example of Ansys acoustic tools
Example of FBAR/BAW related simulation tools with Comsol Multiphysics
IPR (Intellectual Property Rights) landscape of acoustic wave filters by KnowMade, 2019
Sound Acoustics Resonators
 FBAR devices using piezoelectric films with thicknesses ranging from several micrometres down to tens of micrometres resonate in the frequency range of 100 MHz to 20 GHz. FBAR or TFBAR resonators fall in the category of bulk acoustic resonators (BAW) and piezoelectric resonators and they are used in applications where high frequency, small size and weight is needed.
FBAR devices using piezoelectric films with thicknesses ranging from several micrometres down to tens of micrometres resonate in the frequency range of 100 MHz to 20 GHz. FBAR or TFBAR resonators fall in the category of bulk acoustic resonators (BAW) and piezoelectric resonators and they are used in applications where high frequency, small size and weight is needed.
Piezoelectricity in thin films
The crystallographic orientation of a thin film depends on the piezomaterial selected and many other items like the surface on which the film is grown and various manufacturing - thin film growth - conditions (temperatures selected, pressure, gases used, vacuum conditions etc.). Any material like lead zirconate titanate (PZT) orbarium strontium titanate
A perovskite is any material with a crystal structure following the formula ABX3, which was first discovered as the Perovskite, mineral called perovskite, which consists of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in t ...
(BST) from the list of piezoelectric materials could act as an active material in an FBAR resonator. However two compound materials aluminium nitride
Aluminium nitride ( Al N) is a solid nitride of aluminium. It has a high thermal conductivity of up to 321 W/(m·K) and is an electrical insulator. Its wurtzite phase (w-AlN) has a band gap of ~6 eV at room temperature and has a potenti ...
(AlN) and zinc oxide (ZnO) are the two most studied piezoelectric materials manufactured for high frequency FBAR realisations. This is due to the fact that the properties like stoichiometry of two compound materials can be easier to control compared to three compound materials manufactured by thin film methods. For example it is known that thin film ZnO with C axis of the crystal structure (crystalline Z axis) normal to the substrate surface excites longitudinal (L) waves. Shear (transverse) (S) waves are excited if C axis of the film crystal structure is 41º tilted. It is also possible – depending on the crystal structure of the film – that both waves (L & S) are excited. Therefore the understanding and control of the crystal structure of the manufactured piezoelectric film is crucial for the operation of the FBAR.
For high frequency purposes like filtering of signals the energy conversion efficiency is the most important item and therefore longitudinal (L) waves are favored and targeted to be used. For sensing and actuation purposes the structural deformation might be more important than energy conversion efficiency and shear-mode wave excitation will be the target of the manufacturing of the piezoelectric film.
Despite the lower electromechanical coupling coefficient The electromechanical coupling coefficient is a numerical measure of the conversion Energy conversion efficiency, efficiency between electrical and Acoustics, acoustic energy in piezoelectric materials.
Qualitatively the electromechanical coupling ...
compared to zinc oxide, aluminum nitride, with a wider band gap has become the most used material in industrial applications, which require a wide bandwidth in signal processing. Compatibility with the silicon integrated circuit technology has supported AlN in FBAR resonator based products like radio frequency filters, duplexers, RF power amplifier or RF receiver modules.
Thin film piezoelectric sensor
A piezoelectric sensor is a device that uses the piezoelectric effect to measure changes in pressure, acceleration, temperature, strain, or force by converting them to an electrical charge. The prefix ''piezo-'' is Greek for 'press' or 'squeeze'. ...
s may be based on various piezoelectric materials depending on the application, but two compound piezoelectric materials are favored due to simplicity of manufacturing.
 Doping or adding new materials like scandium (Sc) are new directions to improve material properties of AlN for FBARs. Research of new electrode materials or alternative materials to aluminium like by replacing one of the metal electrodes with very light materials like graphene for minimising the loading of the resonator has been demonstrated to lead better control of the resonance frequency.
Doping or adding new materials like scandium (Sc) are new directions to improve material properties of AlN for FBARs. Research of new electrode materials or alternative materials to aluminium like by replacing one of the metal electrodes with very light materials like graphene for minimising the loading of the resonator has been demonstrated to lead better control of the resonance frequency.
Substrates for FBAR resonators and their applications
FBAR resonators can be manufactured on ceramic (Al2O3 or alumina), sapphire, glass or silicon substrates. However silicon wafer is the most common substrate due to its scalability towards mass manufacturing and compatibility with various manufacturing steps needed. During early studies and experimentation phase of thin film resonators in 1967 cadmium sulfide (CdS) was evaporated on a resonant piece of bulk quartz crystal which served as a transducer providing aQ factor
In physics and engineering, the quality factor or ''Q'' factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy los ...
(quality factor) of 5000 at the resonance frequency (279 MHz). This was an enabler for tighter frequency control, for needs to use higher frequencies and utilising FBAR resonators. With the development of thin film technologies it was possible to keep the Q factor high enough, leave out the crystal and increase resonance frequency.

Application areas
Most of the smartphones in 2020 include at least one FBAR-based duplexer or filter and some 4/ 5G products may even include 20–30 functionalities based on FBAR technology mainly due to the increased complexity of radio frequency front end (RFFE, RF front end) electronics – both receiver and transmitter paths – and the antenna/antenna system. Trends to utilize RF spectrum more efficiently with higher frequencies than roughly 1.5–2.5 GHz and in some cases also simultaneously with increasing RF output power have supported FBAR technology to become one of the key enabling technologies in telecommunication realisations. FBAR technology complements and in some cases competes with surface acoustic wave (SAW) technology and FBAR resonators can replace crystals in crystal oscillators andcrystal filter
A crystal filter allows some frequencies to 'pass' through an electrical circuit while attenuating undesired frequencies. An electronic filter can use quartz crystals as resonator components of a filter circuit. Quartz crystals are piezoelectric ...
s at frequencies more than 100 MHz.
Sensory is a developing area for FBAR resonators and structures based on them. Targets to measure and also possibly control small amount of materials/liquids/gas, and replacing as miniaturized in various sensing and actuation tasks like in micro mirror displays (DMD)s are under research and development as well as energy harvesting by utilizing nanogenerator A Nanogenerator is a type of technology that converts mechanical/thermal energy as produced by small-scale physical change into electricity. A Nanogenerator has three typical approaches: piezoelectric, triboelectric, and pyroelectric nanogenerators. ...
s.
Basic structures

 As per 2022 there are two known structures of thin-film bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonators: free-standing and solidly mounted (SMR) resonators. In a free-standing resonator structure air is used to separate the resonator from the substrate/surrounding. The structure of a free-standing resonator is based on some typical manufacturing steps used in micro-electromechanical systems MEMS.
As per 2022 there are two known structures of thin-film bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonators: free-standing and solidly mounted (SMR) resonators. In a free-standing resonator structure air is used to separate the resonator from the substrate/surrounding. The structure of a free-standing resonator is based on some typical manufacturing steps used in micro-electromechanical systems MEMS.  In an SMR structure acoustic mirror(s) providing an acoustic isolation is constructed between the resonator and the surrounding like the substrate. The acoustic mirror (like a
In an SMR structure acoustic mirror(s) providing an acoustic isolation is constructed between the resonator and the surrounding like the substrate. The acoustic mirror (like a Bragg reflector
A distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) is a reflector used in waveguides, such as optical fibers. It is a structure formed from multiple layers of alternating materials with varying refractive index, or by periodic variation of some characteristi ...
) typically consists of odd total number of materials with alternating a high and low acoustic impedance. The thickness of mirror materials must also be optimized to the quarter wavelength for maximum acoustic reflectivity. The basic principle of the SMR structure was introduced in 1965.
Schematic pictures of the thin film resonators show only the basic principles of the potential structures. In reality some dielectric layers may be needed like for strengthening various parts of the structure. Additionally if needed – for simplifying the final filter layout in the application – resonator structures can be stacked e.g. built on top of each other like in some filter applications. However this approach increases the complexity of manufacturing.
Some performance requirements like tuning of the resonance frequency may also require additional process steps like ion milling, which complicates the manufacturing process.
Newest directions to develop better performing FBARs is to utilize single crystal AlN instead of polycrystalline AlN and to place electrodes on the same side of the piezolayer.
Because realizing FBAR structures needs many precise steps simulation is actively used during the design phase to predict purity of resonance frequency and other performance. At early phase of the development basic finite element method (FEM) based modelling techniques used for crystals were also applied and modified for FBARs. Several new methods like a scanning laser interferometry were needed to visualise the functionality of the resonators and helping to improve the design (layout and cross-sectional structure of the resonator) to achieve purity of the resonance and wanted resonance modes.
Application drivers
In many applications temperature behavior, stability vs. time, strength and purity of the wanted resonance frequency are forming the base for the performance of the applications based on FBAR resonators. Material choices, layout and design of resonator structures are contributing to the resonator performance and the final performance of the application. Mechanical performance and reliability are determined by the packaging and structure of the resonators in the applications. A common application of FBARs is radio frequency (RF) filters for use in
A common application of FBARs is radio frequency (RF) filters for use in cell phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whil ...
s and other wireless applications like positioning (GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
, Glonass, BeiDou, Galileo (satellite navigation) etc.), Wi-Fi systems, small telecommunication cells and modules for those. Such filters are made from a network of resonators (either in half- ladder, full-ladder, lattice, a combination of lattice and ladder or stacked topologies) and are designed to remove unwanted frequencies from being transmitted in such devices, while allowing other specific frequencies to be received and transmitted. FBAR filters can also be found in duplexer
A duplexer is an electronic device that allows bi-directional ( duplex) communication over a single path. In radar and radio communications systems, it isolates the receiver from the transmitter while permitting them to share a common antenna. M ...
s. FBAR filter technology is complementing surface acoustic wave (SAW) filter technology in areas where increased power handling capability, and electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden and momentary flow of electric current between two electrically charged objects caused by contact, an short circuit, electrical short or dielectric breakdown. A buildup of static electricity can be caused ...
(ESD) tolerance is needed. Frequencies more than 1.5–2.5 GHz are well-suited for FBAR devices. FBARs on a silicon substrate can be manufactured in high volumes and the manufacturing is supported by all development of semiconductor device fabrication methods. Future requirements of new applications like filtering bandwidth with steep stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level. Depending on applic ...
attenuation and lowest possible insertion loss have effects on resonator performance and show development steps needed.
FBARs can also be used in oscillators and synchronizers to replace a crystal/crystals in applications where frequencies more than 100 MHz and/or very low jitter is one of the performance targets.
FBARs can also be used as sensors. For instance, when a FBAR device is put under mechanical pressure its resonance frequency will shift. Sensing of humidity and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are demonstrated by using FBARs. A tactile sensor array may also consist of FBAR devices, and gravimetric or mass sensing can be based on FBAR resonators.
As discrete components FBAR technology based parts like basic resonators and filters are packaged in miniaturised/small form factor like wafer level package
Wafer-level packaging (WLP) is a process where packaging components are attached to an integrated circuit (IC) ''before'' the wafer – on which the IC is fabricated – is diced. In WSP, the top and bottom layers of the packaging and the solder ...
s. FBARs can also be integrated with power amplifiers (PA) or low noise amplifiers (LNA) to form a module solution with the related electronic circuitry. Although monolithic integrated of FBARs on the same substrate with the electronic circuitry like CMOS has been demonstrated it requires several additional process steps and mask layers on top of IC technology increasing the cost of the solution. Therefore monolithic solutions have not been progressed as much as module solutions in commercial applications. Typical module solutions are a power amplifier-duplexer
A duplexer is an electronic device that allows bi-directional ( duplex) communication over a single path. In radar and radio communications systems, it isolates the receiver from the transmitter while permitting them to share a common antenna. M ...
module (PAD), or a low-noise amplifier (LNA)-filter module where and the related circuitry are packaged in the same package possibly on a separate module substrate.
FBARs can be integrated in complex communication like SimpleLink modules for avoiding area/space requirements of an external, packaged crystal. Therefore FBAR technology has a key role in electronics miniaturisation
Miniaturization ( Br.Eng.: ''Miniaturisation'') is the trend to manufacture ever smaller mechanical, optical and electronic products and devices. Examples include miniaturization of mobile phones, computers and vehicle engine downsizing. In el ...
specifically in applications where oscillators and precise high performance filters are needed.
Historical and industrial landscape
Resonators and filters/duplexers
The use of piezoelectric materials in electronics began in the early 1960s at Bell Telephone Laboratories/ Bell Labs, where piezoelectric crystals were developed and used as resonators in applications like oscillators with frequencies up to 100 MHz. Thinning was applied for increasing the resonance frequency of the crystals. However there were limitations of the thinning of crystals and new methods of thin film manufacturing were applied in the early 1970s for increasing accuracy of resonance frequency and targeting increasing manufacturing volumes. TFR Technologies Inc., founded in 1989, was one of the pioneering companies in the field of FBAR resonators and filters mostly for space and military applications. The first products were delivered to customers in 1997. TFR Technologies Inc. was in 2005 acquired byTriQuint Semiconductor
TriQuint Semiconductor was a semiconductor company that designed, manufactured, and supplied high-performance RF modules, components and foundry services. The company was founded in 1985 in Beaverton, Oregon before moving to neighboring Hillsboro, ...
Inc. In early 2015, RF Micro Devices
RF Micro Devices (also known as RFMD or RF Micro), was an American company that designed and manufactured high-performance radio frequency systems and solutions for applications that drive wireless and broadband communications. Headquartered in Gr ...
(RFMD), Inc. and TriQuint Semiconductor, Inc. announced a merger to form Qorvo active providing FBAR-based products.
HP Laboratories started a project on FBARs in 1993 concentrating in free-standing resonators and filters. In 1999 FBAR activity became part of Agilent Technologies Inc., which in 2001 delivered 25,000 FBAR duplexers for N-CDMA phones. Later in 2005, FBAR activity at Agilent was one of the technologies of Avago Technologies Ltd., which acquired Broadcom Corporation in 2015. In 2016 Avago Technologies Ltd. changed its name to Broadcom Inc.
Broadcom Inc. is an American designer, developer, manufacturer and global supplier of a wide range of semiconductor and infrastructure software products. Broadcom's product offerings serve the data center, networking, software, broadband, wirel ...
, currently active in providing FBAR-based products.
Infineon Technologies
Infineon Technologies AG is a German semiconductor manufacturer founded in 1999, when the semiconductor operations of the former parent company Siemens AG were spun off. Infineon has about 50,280 employees and is one of the ten largest semicond ...
AG started to work with SMR-FBARs in 1999, concentrating in telecommunication filters for mobile applications. The first product was delivered to Nokia Mobile Phones Ltd, which launched the first SMR-FBAR-based GSM three-band mobile phone product in 2001. Infineon's FBAR (BAW) filter group was acquired by Avago Technologies Ltd 2008 which later became part of Broadcom as described before.
After acquiring Panasonic's filtering business in 2016 Skyworks Solutions became one of the major players in BAW/FBAR devices additionally to Broadcom and Qorvo.
Additionally after acquiring rest of RF360 Holdings in 2019 Qualcomm and Kyocera are offering thin film resonator based products like RFFE modules and separate filters.
Still many companies like Akoustis Technologies, Inc. (founded in 2014), Texas Instruments (TI), several universities and research institutes are offering and studying to improve FBAR technology, its performance, manufacturing, advancing design capabilities of FBARs and exploring new application areas jointly with system manufacturers and companies providing simulation tools ( Ansys, Comsol Multiphysics, and Resonant Inc. etc.).
Thin film resonator based sensors
Because thin film resonators can replace crystals in sensoring, the most potential application area for FBAR resonators is similar to area for thequartz crystal microbalance A quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) (also known as ''quartz microbalance'' (QMB), sometimes also as ''quartz crystal nanobalance'' (QCN)) measures a mass variation per unit area by measuring the change in frequency of a quartz crystal resonator. The ...
(QCM). One of the pioneering companies utilizing thin film resonators in sensoring is Sorex Sensors Ltd.
See also
* Resonance *Acoustic resonance
Acoustic resonance is a phenomenon in which an acoustic system amplifies sound waves whose frequency matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration (its ''resonance frequencies'').
The term "acoustic resonance" is sometimes used to nar ...
* Acoustic impedance
* RF and microwave filter Radio frequency (RF) and microwave filters represent a class of electronic filter, designed to operate on signals in the megahertz to gigahertz frequency ranges (medium frequency to extremely high frequency). This frequency range is the range used ...
* RF front end
* Duplexer
A duplexer is an electronic device that allows bi-directional ( duplex) communication over a single path. In radar and radio communications systems, it isolates the receiver from the transmitter while permitting them to share a common antenna. M ...
* Piezoelectric sensor
A piezoelectric sensor is a device that uses the piezoelectric effect to measure changes in pressure, acceleration, temperature, strain, or force by converting them to an electrical charge. The prefix ''piezo-'' is Greek for 'press' or 'squeeze'. ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
University of Southern California explanation on the operation of FBAR's
PhD thesis of J. V. Tirado, Bulk Acoustic Wave Resonators and their Application to Microwave Devices, 2010, Universitat Autonoma Barcelona, Spain, 201 pages.
PhD thesis of J. Liu, Application of Bragg Reflection for Suppression of Spurious Transverse Mode Resonances in RF BAW Resonators, 2014, Chiba University, Japan, 151 pages.
Broadcom's products based on FBAR technology
FBAR technology opportunity in 5G telecommunication
Products of Qorvo based on BAW (FBAR)
Description of Texas Instrument's SimpleLink module
Akoustis Technologies Inc.
Example of Ansys acoustic tools
Example of FBAR/BAW related simulation tools with Comsol Multiphysics
IPR (Intellectual Property Rights) landscape of acoustic wave filters by KnowMade, 2019
Sound Acoustics Resonators