ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
for therapeutic
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many differe ...
benefit. Physiotherapeutic ultrasound was introduced into clinical practice in the 1950s, with lithotripsy introduced in the 1980s. Others are at various stages in transitioning from research to clinical use: HIFU, targeted ultrasound drug delivery, trans-dermal ultrasound drug delivery, ultrasound hemostasis, cancer therapy, and ultrasound assisted thrombolysis It may use focused ultrasound (FUS) or unfocused ultrasound.
In the above applications, the ultrasound passes through human tissue where it is the main source of the observed biological effect (the oscillation of abrasive dental tools at ultrasonic frequencies therefore do not belong to this class). The ultrasound within tissue consists of very high frequency sound waves, between 800,000 Hz and 20,000,000 Hz, which cannot be heard by humans.
There is some evidence that ultrasound is more effective than placebo treatment for treating patients with arthritis pain, a range of musculoskeletal injuries and for promoting tissue healing.
Medical uses
Relatively high power ultrasound can break up stony deposits or tissue, accelerate the effect of drugs in a targeted area, assist in the measurement of the elastic properties of tissue, and can be used to sort cells or small particles for research. * Focused high-energy ultrasound pulses can be used to break calculi such as kidney stones and gallstones into fragments small enough to be passed from the body without undue difficulty, a process known as lithotripsy. * Focused ultrasound sources may be used forcataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble w ...
treatment by phacoemulsification
Phacoemulsification is a modern cataract surgery method in which the eye's internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution to mainta ...
.
* Ultrasound can ablate
Ablation ( la, ablatio – removal) is removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosive processes or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, and include spacecraft material for a ...
tumors or other tissue non-invasively. This is accomplished using a technique known as High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU), also called ''focused ultrasound surgery'' (FUS surgery). This procedure uses generally lower frequencies than medical diagnostic ultrasound (250–2000 kHz), but significantly higher time-averaged intensities. The treatment is often guided by Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI); the combination is then referred to as ''Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound'' (MRgFUS).
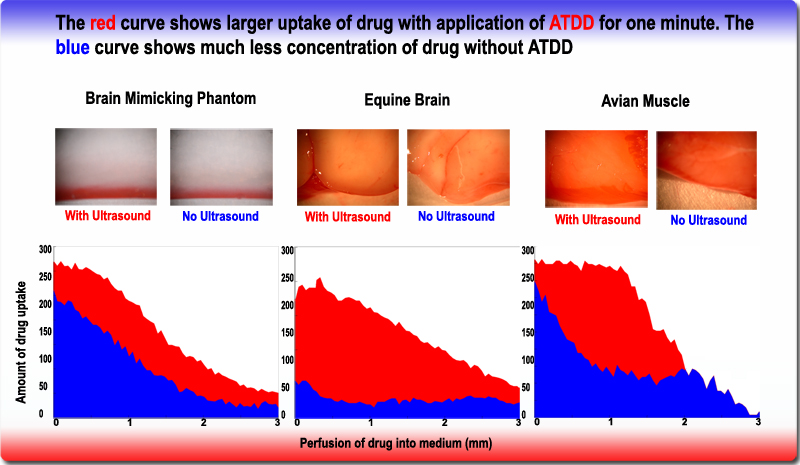 * Delivering chemotherapy to brain cancer cells and various drugs to other tissues is called
* Delivering chemotherapy to brain cancer cells and various drugs to other tissues is called acoustic targeted drug delivery
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) is a noninvasive treatment, often used for tumor irradiation, that utilizes a sonosensitizer and the deep penetration of ultrasound to treat lesions of varying depths by reducing target cell number and preventing future t ...
(ATDD). These procedures generally use high frequency ultrasound (1–10 MHz) and a range of intensities (0–20 W/cm2). The acoustic energy is focused on the tissue of interest to agitate its matrix and make it more permeable for therapeutic drugs.
* Ultrasound has been used to trigger the release of anti-cancer drugs from delivery vectors including liposomes, polymeric microspheres and self-assembled polymeric.
* Ultrasound is essential to the procedures of ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy and endovenous laser treatment for the non-surgical treatment of varicose veins.
* Ultrasound-assisted lipectomy is Liposuction assisted by ultrasound.
There are three potential effects of ultrasound. The first is the increase in blood flow in the treated area. The second is the decrease in pain from the reduction of swelling and edema. The third is the gentle massage of muscle tendons and/ or ligaments in the treated area because no strain is added and any scar tissue is softened. These three benefits are achieved by two main effects of therapeutic ultrasound. The two types of effects are: thermal and non thermal effects. Thermal effects are due to the absorption of the sound waves. Non thermal effects are from cavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
, microstreaming and acoustic streaming.
Cavitational effects result from the vibration of the tissue causing microscopic bubbles to form, which transmit the vibrations in a way that directly stimulates cell membranes. This physical stimulation appears to enhance the cell-repair effects of the inflammatory response.
History
The first large scale application of ultrasound was around World War II. Sonar systems were being built and used to navigate submarines. It was realized that the high intensity ultrasound waves that they were using were heating and killing fish. This led to research in tissue heating and healing effects. Since the 1940s, ultrasound has been used by physical and occupational therapists for therapeutic effects.Physical therapy
Ultrasound is applied using a transducer or applicator that is in direct contact with the patient's skin. Gel is used on all surfaces of the head to reduce friction and assist transmission of the ultrasonic waves. Therapeutic ultrasound in physical therapy is alternating compression andrarefaction
Rarefaction is the reduction of an item's density, the opposite of compression. Like compression, which can travel in waves ( sound waves, for instance), rarefaction waves also exist in nature. A common rarefaction wave is the area of low relat ...
of sound waves with a frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is ...
of 0.7 to 3.3 MHz. Maximum energy absorption in soft tissue occurs from 2 to 5 cm. Intensity decreases as the waves penetrate deeper. They are absorbed primarily by connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue ...
: ligaments, tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s, and fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organ ...
(and also by scar tissue).
Conditions for which ultrasound may be used for treatment include the following examples: ligament sprains, muscle strains, tendonitis, joint inflammation, plantar fasciitis, metatarsalgia, facet irritation, impingement syndrome, bursitis, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and ...
, osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
, and scar tissue adhesion. There is no evidence to support the use of ultrasound for the treatment of low back pain, and current clinical guidelines recommend that ultrasound is not used for this condition. Ultrasound used for calcific tendonitis had a positive short term effect. For the long term, there was no significant difference with ultrasound use. This shows that for pain relief and short-term treatment ultrasound can be an effective treatment for Calcific Tendonitis A review with five small placebo‐controlled trials from 2011, did not support the use of ultrasound in the treatment of acute ankle sprains and the potential treatment effects of ultrasound appear to be generally small and of probably of limited clinical importance, especially in the context of the usually short‐term recovery period for these injuries. A meta-analysis found that ultrasound therapy is effective in reducing pain, increasing ROM, and reducing WOMAC functional scores in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Research tools
* Acoustic tweezers is an emerging tool for contactless separation, concentration and manipulation of microparticles andbiological cells
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients ...
, using ultrasound in the low MHz range to form standing waves. This is based on the acoustic radiation force which causes particles to be attracted to either the nodes or anti-nodes of the standing wave depending on the acoustic contrast factor, which is a function of the sound velocities and densities of the particle and of the medium in which the particle is immersed.
* Application of focused ultrasound in conjunction with microbubbles has been shown to enable non-invasive delivery of epirubicin across the blood–brain barrier in mouse models and non invasive delivery of GABA in non human primates.
Research
* Using ultrasound to generate cellular effects in soft tissue has fallen out of favor as research has shown a lack of efficacy and a lack of scientific basis for proposed biophysical effects. * According to a 2017 meta-analysis and associated practice guideline,Low intensity pulsed ultrasound
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) is a technology that can be used for therapeutic purposes. It exploits low intensity and pulsed mechanical waves in order to induce regenerative and anti-inflammatory effects on biological tissues, such as ...
should no longer been used for bone regeneration because high quality clinical studies failed to demonstrate a clinical benefit.
* An additional effect of low-intensity ultrasound could be its potential to disrupt the blood–brain barrier for drug delivery.
* Transcranial ultrasound is being tested for use in aiding tissue plasminogen activator treatment in stroke patients in the procedure called ultrasound-enhanced systemic thrombolysis
Background
Ultrasound enhanced systemic thrombolysis (UEST), also known as sonothrombolysis, is a method that uses ultrasound waves to mechanically break the thrombi, or clots, using the vibration carried via soundwaves. A large portion of initi ...
.
* Ultrasound has been shown to act synergistically with antibiotics in killing bacteria.
* Ultrasound has been postulated to allow thicker eukaryotic cell tissue cultures by promoting nutrient penetration.
* Long-duration therapeutic ultrasound called sustained acoustic medicine is a daily slow-release therapy that can be applied to increase local circulation and theoretically accelerates healing of musculoskeletal tissues after an injury. However, there is some evidence to suggest this may not be effective.
See also
*Home ultrasound
Home ultrasound is the provision of therapeutic ultrasound via the use of a portable or home ultrasound machine. This method of medical ultrasound therapy can be used for various types of pain relief and physical therapy.
In physics, the term "ult ...
* LILFU
References
External links
* * * {{cite web , url = http://www.istu.org/ , title = International Society for Therapeutic Ultrasound Medical ultrasonography Athletic training