the Low Countries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
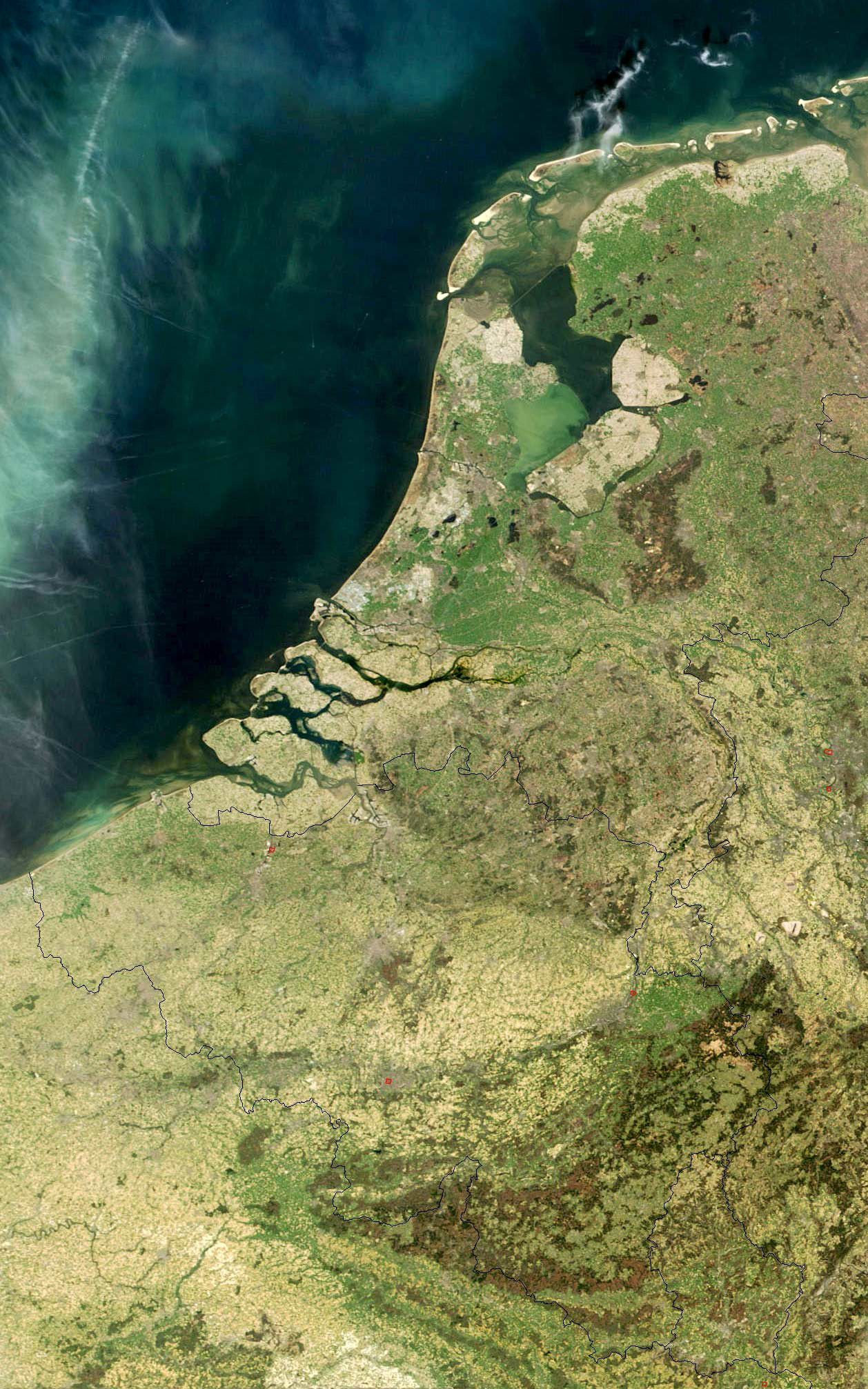 The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern
 Historically, the term ''Low Countries'' arose at the Court of the
Historically, the term ''Low Countries'' arose at the Court of the
File:Kenau_Hasselaar_op_de_wallen_van_Haarlem.gif,
The Cinema of the Low Countries
Early Modern Women in the Low Countries
The Reformation and Revolt in the Low Countries
 The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
forming the lower basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting of three countries: Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
. Geographically and historically, the area also includes parts of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
such as the French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France an ...
and the German regions of East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
and Cleves
Kleve (; traditional en, Cleves ; nl, Kleef; french: Clèves; es, Cléveris; la, Clivia; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century ...
. During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities.
Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated ...
, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhineland ...
. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevated regions are considered part of the Low Countries, including Luxembourg and the south of Belgium. Within the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
, the region's political grouping is still referred to as the Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a Political union, politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in ...
(short for Belgium-Netherlands-Luxembourg).
During the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
, the region contained a militarised frontier and contact point between Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
. With the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
, the Low Countries were the scene of the early independent trading centres that marked the reawakening of Europe in the 12th century. In that period, they rivalled northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative Regions ...
as one of the most densely populated regions of Western Europe. Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s and councils governed most of the cities along with a figurehead ruler; interaction with their ruler was regulated by a strict set of rules describing what the latter could and could not expect. All of the regions mainly depended on trade, manufacturing and the encouragement of the free flow of goods and craftsmen. Dutch and French dialects were the main languages used in secular city life.
Terminology

Dukes of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy (french: duc de Bourgogne) was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by France in 1477, and later by Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of Spain from the House of Habsburg ...
, who used the term ' ("the lands over here") for the Low Countries as opposed to ' ("the lands over there") for the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
and the Free County of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy or Franche-Comté (french: Franche Comté de Bourgogne; german: Freigrafschaft Burgund) was a medieval county (from 982 to 1678) of the Holy Roman Empire, predecessor to the modern region of Franche-Comté. The name ' ...
, which were part of their realm but geographically disconnected from the Low Countries. Governor Mary of Hungary used both the expressions ' and ' ("lands down here"), which evolved to ' or ''Low Countries''. Today the term is typically fitted to modern political boundaries and used in the same way as the term ''Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a Political union, politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in ...
''.
The name of the country of the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
has the same etymology and origin as the name for the region Low Countries, due to "nether" meaning "low". In the Dutch language itself ''De Lage Landen'' is the modern term for Low Countries, and ''De Nederlanden'' (plural) is in use for the 16th century domains of Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infant ...
, the historic Low Countries, while ''Nederland'' (singular) is the normal Dutch name for the country of the Netherlands. However, in official use, the name of the Dutch kingdom is still Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
, (plural). This name derives from the 19th-century origins of the kingdom which originally included present-day Belgium.
In Dutch, and to a lesser extent in English, the Low Countries colloquially means the Netherlands and Belgium, sometimes the Netherlands and Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
—the Dutch-speaking north of Belgium. For example, a ' (''Derby der Lage Landen''), is a sports event between Belgium and the Netherlands.
Belgium separated in 1830 from the (northern) Netherlands. The new country took its name from ''Belgica'', the Latinised name for the Low Countries, as it was known during the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Re ...
(1568–1648). The Low Countries were in that war divided in two parts. On one hand, the northern Federated Netherlands or ''Belgica Foederata'' rebelled against King Philip II of Spain; on the other, the southern Royal Netherlands or ''Belgica Regia'' remained loyal to the Spanish king. This divide laid the early foundation for the later modern states of Belgium and the Netherlands.
History
The region politically had its origins in theCarolingian empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
; more precisely, most of the people were within the Duchy of Lower Lotharingia
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier''
. After the disintegration of Lower Lotharingia, the Low Countries were brought under the rule of various lordships until they came to be in the hands of the Valois Dukes of Burgundy. Hence, a large part of the Low Countries came to be referred to as the Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
. After the reign of the Valois Dukes ended, much of the Low Countries were controlled by the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. This area was referred to as the Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austr ...
, which was also called the Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
up to 1581. Even after the political secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics l ...
of the autonomous Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
(or "United Provinces") in the north, the term "Low Countries" continued to be used to refer collectively to the region. The region was temporarily united politically between 1815 and 1839, as the United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
, before this split into the three modern countries of the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg.
Early history
The Low Countries were part of theRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
provinces of Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 5 ...
and Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippine ...
. They were inhabited by Belgic and Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
. In the 4th and 5th century, Frankish tribes had entered this Roman region and came to run it increasingly independently. They came to be ruled by the Merovingian dynasty
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
, under which dynasty the southern part (below the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
) was re- Christianised.
Frankish empire
By the end of the 8th century, the Low Countries formed a core part of a much expandedFrancia
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
and the Merovingians were replaced by the Carolingian dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pi ...
. In 800, the Pope crowned and appointed Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( e ...
of the re-established Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
.
After the death of Charlemagne, Francia was divided in three parts among his three grandsons. The middle slice, Middle Francia
Middle Francia ( la, Francia media) was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Franc ...
, was ruled by Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I ( Dutch and Medieval Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire''; Italian: ''Lotario'') (795 – 29 September 855) was emperor (817–855, co-ruling with his father until 840), and the governor of Bav ...
, and thereby also came to be referred to as "Lotharingia" or "Lorraine". Apart from the original coastal County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Y ...
, which was within West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about ...
, the rest of the Low Countries were within the lowland part of this, "Lower Lorraine
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier''
".
After the death of Lothair, the Low Countries were coveted by the rulers of both West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about ...
and East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire int ...
. Each tried to swallow the region and to merge it with their spheres of influence. Thus, the Low Countries consisted of fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of f ...
s whose sovereignty resided with either the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period ...
or the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
. While the further history the Low Countries can be seen as the object of a continual struggle between these two powers, the title of Duke of Lothier
Lothier refers to the territory within the Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, governed by the dukes of Brabant and their successors after 1190 until the end of the Ancien Régime in 1796.
In 1190, at the Diet of Hall in the abbey of Comburg, the Germa ...
was coveted in the low countries for centuries.
Duchy of Burgundy
In the 14th and 15th century, separate fiefs came gradually to be ruled by a single family throughroyal intermarriage
Royal intermarriage is the practice of members of ruling dynasties marrying into other reigning families. It was more commonly done in the past as part of strategic diplomacy for national interest. Although sometimes enforced by legal requireme ...
. This process culminated in the rule of the House of Valois
The Capetian house of Valois ( , also , ) was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. They succeeded the House of Capet (or "Direct Capetians") to the French throne, and were the royal house of France from 1328 to 1589. Junior members of the ...
, who were the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
. At the height of Burgundian influence, the Low Countries became the political, cultural, and economic centre of Northern Europe, noted for its crafts and luxury goods, notably early Netherlandish painting
Early Netherlandish painting, traditionally known as the Flemish Primitives, refers to the work of artists active in the Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands during the 15th- and 16th-century Northern Renaissance period. It flourished especial ...
, which is the work of artists who were active in the flourishing cities of Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Scienc ...
, Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest i ...
, Mechelen
Mechelen (; french: Malines ; traditional English name: MechlinMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical contex ...
, Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. Th ...
, Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eu ...
and Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, all in present-day Belgium. Musicians of the Franco-Flemish School
The designation Franco-Flemish School, also called Netherlandish School, Burgundian School, Low Countries School, Flemish School, Dutch School, or Northern School, refers, somewhat imprecisely, to the style of polyphonic vocal music composition ...
were highly sought by the leading classes of all Europe.
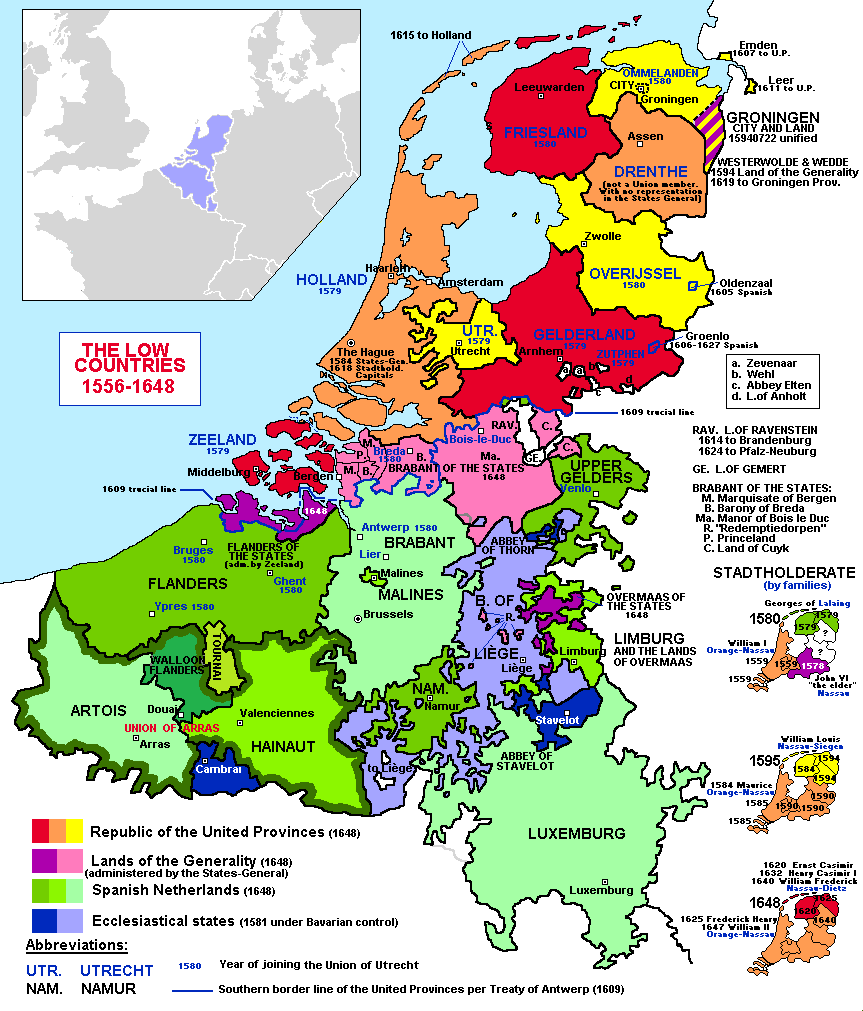
Seventeen Provinces
In 1477 the Burgundian holdings in the area passed through an heiress—Mary of Burgundy
Mary (french: Marie; nl, Maria; 13 February 1457 – 27 March 1482), nicknamed the Rich, was a member of the House of Valois-Burgundy who ruled a collection of states that included the duchies of Limburg, Brabant, Luxembourg, the counties o ...
—to the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. Charles V, who inherited the territory in 1506, was named ruler by the States General and styled himself as ''Heer der Nederlanden'' ("Lord of the Netherlands"). He continued to rule the territories as a multitude of duchies and principalities until the Low Countries were eventually united into one indivisible territory, the Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
, covered by the Pragmatic Sanction of 1549
The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549 was an edict, promulgated by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, reorganising the Seventeen Provinces of the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg into one indivisible territory, while retaining existing cus ...
, while retaining existing customs, laws, and forms of government within the provinces.
The Pragmatic Sanction transformed the agglomeration of lands into a unified entity, of which the Habsburgs would be the heirs. By streamlining the succession law in all Seventeen Provinces and declaring that all of them would be inherited by one heir, Charles effectively united the Netherlands as one entity. After Charles' abdication in 1555, the Seventeen Provinces passed to his son, Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal fro ...
.
Division
The Pragmatic Sanction is said to be one example of the Habsburg contest with particularism that contributed to the Dutch Revolt. Each of the provinces had its own laws, customs and political practices. The new policy, imposed from the outside, angered many inhabitants, who viewed their provinces as distinct entities. It and other monarchical acts, such as the creation of bishoprics and promulgation of laws againstheresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
, stoked resentments, which fired the eruption of the Dutch Revolt.
After the northern Seven United Provinces
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
of the seventeen declared their independence from Habsburg Spain in 1581, the ten provinces of the Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
remained occupied by the Army of Flanders
The Army of Flanders ( es, Ejército de Flandes nl, Leger van Vlaanderen) was a multinational army in the service of the kings of Spain that was based in the Spanish Netherlands during the 16th to 18th centuries. It was notable for being the long ...
under Spanish service and are therefore sometimes called the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
. In 1713, under the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of ...
following the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
, what was left of the Spanish Netherlands was ceded to Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and thus became known as the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
.
Kenau Simonsdochter Hasselaer
Kenau Simonsdochter Hasselaer (1526–1588) was a wood merchant of Haarlem, who became a legendary folk hero for her fearless defense of the city against the Spanish invaders during the siege of Haarlem in 1573.
Biography
She was the daughte ...
defending the walls during the Siege of Haarlem
The siege of Haarlem was an episode of the Eighty Years' War. From 11 December 1572 to 13 July 1573 an army of Philip II of Spain laid bloody siege to the city of Haarlem in the Netherlands, whose loyalties had begun wavering during the previ ...
(1572–1573)
File:De stadt Maastricht, door den prins van Parma (Alexander Farnese) met storm verovert, den 29 july des jaars 1579 (Jan Luyken, 1679).jpg, Sack of Maastricht by the ''Tercios de Flandes'' (Flemish Regiments) in 1579
File:Famien Strada Histoire-Capture of Tournai 1581-ppn087811480 MG 8936T3p287.tif, Siege and capture of Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eu ...
(1581)
File:Oostende.1601.JPG, Map of Ostend during the siege in 1601
Late Modern Period
TheUnited Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
(1815–1830) temporarily united the Low Countries again before it split into the three modern countries of the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg.
During the early months of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
(around 1914), the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
invaded the Low Countries of Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
in what has been come to be known as the German invasion of Belgium German invasion of Belgium may refer to:
* German invasion of Belgium (1914) during World War I
*German invasion of Belgium (1940)
The invasion of Belgium or Belgian campaign (10–28 May 1940), often referred to within Belgium as the 18 Days' ...
. It led to the German occupation of the two countries. However, the German advance into France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
was quickly halted, causing a military stalemate for most of the war. In the end, a total of approximately 56,000 people were killed in the invasion.
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
started in this region, when Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's gaze turned his strategy west toward France. The Low Countries were an easy route around the imposing French Maginot Line
The Maginot Line (french: Ligne Maginot, ), named after the French Minister of War André Maginot, is a line of concrete fortifications, obstacles and weapon installations built by France in the 1930s to deter invasion by Germany and force the ...
. He ordered a conquest of the Low Countries with the shortest possible notice, to forestall the French, and prevent Allied air power
Airpower or air power consists of the application of military aviation, military strategy and strategic theory to the realm of aerial warfare and close air support. Airpower began in the advent of powered flight early in the 20th century. Air ...
from threatening the strategic Ruhr Area
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/k ...
of Germany. It would also provide the basis for a long-term air and sea campaign against Britain. As much as possible of the border areas in northern France should be occupied. Germany's Blitzkrieg
Blitzkrieg ( , ; from 'lightning' + 'war') is a word used to describe a surprise attack using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armoured warfare, armored and motorised infantry, motorized or mechanised infantry, ...
tactics rapidly overpowered the defences of Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg.
All three countries were occupied from May 1940 until early 1945. During the occupation, their governments were forced into exiled in Britain. In 1944, they signed the London Customs Convention
Officially titled the ''Netherlands–Belgium–Luxembourg Customs Convention'', the London Customs Convention was the treaty that established the Benelux Customs Union on 5 September 1944. The word "Benelux" comes from an acronym of the countri ...
, laying the foundation for the eventual Benelux Economic Union
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe: B ...
, an important forerunner of the EEC
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
(later the EU).
Literature
One of the Low Countries' earliest literary figures is the blind poet Bernlef, from , who sang both Christianpsalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived f ...
and pagan verses. Bernlef is representative of the coexistence of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
and Germanic polytheism
Germanic paganism or Germanic religion refers to the traditional, culturally significant religion of the Germanic peoples. With a chronological range of at least one thousand years in an area covering Scandinavia, the British Isles, modern Germ ...
in this time period.
The earliest examples of written literature include the Wachtendonck Psalms, a collection of twenty five psalms that originated in the Moselle-Frankish region around the middle of the 9th century.
See also
*Burgundian Circle
The Burgundian Circle (german: Burgundischer Kreis, nl, Bourgondische Kreits, french: Cercle de Bourgogne) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire created in 1512 and significantly enlarged in 1548. In addition to the Free County of Bur ...
* Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
* Early Netherlandish painting
Early Netherlandish painting, traditionally known as the Flemish Primitives, refers to the work of artists active in the Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands during the 15th- and 16th-century Northern Renaissance period. It flourished especial ...
* Greater Netherlands
Greater Netherlands () is an irredentist concept which unites the Netherlands, Flanders, and sometimes including Brussels. Additionally, a Greater Netherlands state may include the annexation of the French Westhoek, Suriname, formerly Dutch-speak ...
* Lower Lorraine
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier''
* Pan-Netherlands
* Union of Brussels
References
Citations
Sources
* Paul Arblaster. ''A History of the Low Countries''. Palgrave Essential Histories Series New York:Palgrave Macmillan
Palgrave Macmillan is a British academic and trade publishing company headquartered in the London Borough of Camden. Its programme includes textbooks, journals, monographs, professional and reference works in print and online. It maintains off ...
, 2006. 298 pp. .
* J. C. H. Blom and E. Lamberts, eds. ''History of the Low Countries'' (1999)
* B. A. Cook. ''Belgium: A History'' (2002)
* Jonathan Israel. ''The Dutch Republic: Its Rise, Greatness, and Fall 1477–1806'' (1995)
* Oscar Gelderblom. ''Cities of Commerce: The Institutional Foundations of International Trade in the Low Countries, 1250–1650'' (Princeton University Press, 2013) 293 pp.
* J. A. Kossmann-Putto and E. H. Kossmann
Ernst Heinrich Kossmann (31 January 1922 – 8 November 2003), often named as E. H. Kossmann in his books, was a Dutch historian. He was professor of Modern History at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands. His magnum opus is ''The Low Co ...
. ''The Low Countries: History of the Northern and Southern Netherlands'' (1987)
The Cinema of the Low Countries
Early Modern Women in the Low Countries
The Reformation and Revolt in the Low Countries
External links
* {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Historical regions Former polities in the Netherlands Geographic history of Belgium History of Luxembourg