The Holocaust In Russia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
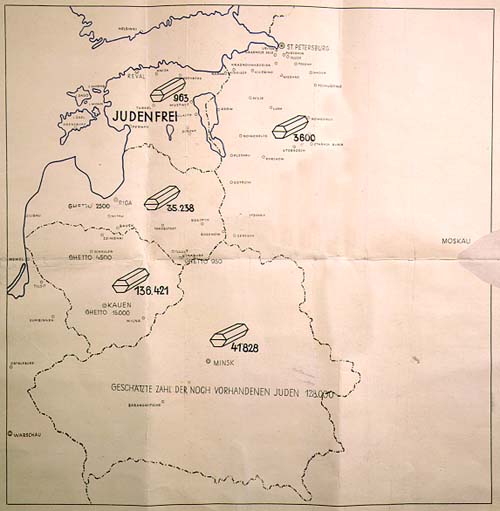 The Holocaust in Russia is the
The Holocaust in Russia is the
 Following the war, the Soviet Union suppressed or downplayed the impact of Nazi crimes on its Jewish citizens. An anti-Semitic campaign against "rootless cosmopolitans" (i.e. "
Following the war, the Soviet Union suppressed or downplayed the impact of Nazi crimes on its Jewish citizens. An anti-Semitic campaign against "rootless cosmopolitans" (i.e. "
 The Holocaust in Russia is the
The Holocaust in Russia is the Nazi crime
Nazi crime or Hitlerite crime ( pl, Zbrodnia nazistowska or ''zbrodnia hitlerowska'') is a legal concept used in the Polish legal system, referring to an action which was carried out, inspired, or tolerated by public functionaries of Nazi Germany ...
s during the occupation of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
(Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
) by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
.
On the Eve of the Holocaust
TheSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
did grant official "equality of all citizens regardless of status
Status (Latin plural: ''statūs''), is a state, condition, or situation, and may refer to:
* Status (law)
** City status
** Legal status, in law
** Political status, in international law
** Small entity status, in patent law
** Status conference ...
, sex, race
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to:
* Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species
* Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or s ...
, religion, and nationality." The years before the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
were an era of rapid change for Soviet Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, leaving behind the dreadful poverty of the Pale of Settlement
The Pale of Settlement (russian: Черта́ осе́длости, '; yi, דער תּחום-המושבֿ, '; he, תְּחוּם הַמּוֹשָב, ') was a western region of the Russian Empire with varying borders that existed from 1791 to 19 ...
. 40% of the population in the former Pale left for large cities within the Soviet Union. Emphasis on education and movement from countryside ''shtetl
A shtetl or shtetel (; yi, שטעטל, translit=shtetl (singular); שטעטלעך, romanized: ''shtetlekh'' (plural)) is a Yiddish term for the small towns with predominantly Ashkenazi Jewish populations which existed in Eastern Europe before ...
s'' to newly industrialized cities allowed many Soviet Jews to enjoy overall advances under Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
and to become one of the most educated population groups in the world. Due to Stalinist
Stalinism is the means of governing and Marxist-Leninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union from 1927 to 1953 by Joseph Stalin. It included the creation of a one-party totalitarian police state, rapid industrialization, the theory o ...
emphasis on its urban population
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, t ...
, interwar
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relativel ...
migration inadvertently rescued countless Soviet Jews—Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
penetrated the entire former Jewish Pale, but were kilometers short of Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
.
World War II
On 22 June 1941,Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
abruptly broke the non−aggression pact and invaded the Soviet Union. The Soviet territories occupied by early 1942, including all of Belarus, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Ukraine and most Russian territory west of the line Leningrad–Moscow–Rostov, contained about four million Jews, including hundreds of thousands who had fled Poland in 1939. Despite the chaos of the Soviet retreat, some effort was made to evacuate Jews, who were either employed in the military industries or were family members of servicemen. Of 4 million about a million succeeded in escaping further east. The "Holocaust by bullet" was the task of SS death squads called ''Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the im ...
'', under the overall command of Reinhard Heydrich
Reinhard Tristan Eugen Heydrich ( ; ; 7 March 1904 – 4 June 1942) was a high-ranking German SS and police official during the Nazi era and a principal architect of the Holocaust.
He was chief of the Reich Security Main Office (inclu ...
. These had been used on a limited scale in Poland in 1939, but were now organized on a much larger scale. Most of their victims were defenseless Jewish civilians (not a single ''Einsatzgruppe'' member was killed in action during these operations). They used their skills to become efficient killers, according to Michael Berenbaum
Michael Berenbaum (born July 31, 1945, in Newark, New Jersey) is an American scholar, professor, rabbi, writer, and filmmaker, who specializes in the study of the Holocaust. He served as deputy director of the President's Commission on the Holo ...
. Berenbaum, Michael. ''The World Must Know''. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, Johns Hopkins University Press, 2nd edition, 2006, p. 93. By the end of 1941, however, the ''Einsatzgruppen'' had killed only 15 percent of the Jews in the occupied Soviet territories, and it was apparent that these methods could not be used to kill all the Jews of Europe. Even before the invasion of the Soviet Union, experiments with killing Jews in the back of vans using gas from the van's exhaust had been carried out, and when this proved too slow, more lethal gasses were tried. Units of the Wehrmacht also participated in many aspects of the Holocaust in Russia.
The Holocaust in the RSFSR
The Black Book of Soviet Jewry
''The Black Book of Soviet Jewry'' or simply ''The Black Book'' ( rus, Чёрная Кни́га, r=Chyórnaya Kníga, p=ˈt͡ɕɵrnəjə ˈknʲiɡə; yi, דאָס שוואַרצע בוך, ''Dos shvartse bukh''), also known as ''The Complete B ...
contains a section on occupied Russia, with testimonies about the Holocaust in Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest c ...
, Rostov-on-Don
Rostov-on-Don ( rus, Ростов-на-Дону, r=Rostov-na-Donu, p=rɐˈstof nə dɐˈnu) is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East Eu ...
, Yessentuki
Yessentuki ( rus, Ессентуки́, p=jɪsɪntʊˈkʲiˑ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Stavropol Krai, Russia, located in the shadow of Mount Elbrus at the base of the Caucasus Mountains. The city serves as a railway ...
, Kislovodsk
Kislovodsk (russian: Кислово́дск, lit. ''sour waters''; ; krc, Ачысуу) is a spa city in Stavropol Krai, Russia, in the North Caucasus region of Russia which is located between the Black and Caspian Seas.
Population:
History
I ...
and Stavropol
Stavropol (; rus, Ставрополь, p=ˈstavrəpəlʲ) is a city and the administrative centre of Stavropol Krai, Russia. As of the 2021 Census, its population was 547,820, making it one of Russia's fastest growing cities.
It was known as ...
among others.
It is estimated by some that before the war, 130,000 Jews lived in parts of the RSFRS that would be later be occupied. The majority evacuated eastward, and a report written by Einsatzgruppen mentions the massive flight. Most of the Jews who remained in occupied RSFSR territories with the advance of the Wehrmacht were murdered by the beginning of 1942, except for some in the southern areas who were murdered between spring 1942 and winter 1942-1943.
The YIVO encyclopedia
''The YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe'' is a two-volume, English-language reference work on the history and culture of Eastern Europe Jewry in this region, prepared by the YIVO Institute for Jewish Research and published by Yale Univ ...
places the number of Holocaust victims in the Russian Soviet Federated Socialist Republic at over 119,000. This is because while much of the local Jewish population escaped, many refugees from places further west fled to these areas, only for them to be captured later. According to this source, most Holocaust victims in the RSFSR were murdered in the areas of Rostov-on-Don
Rostov-on-Don ( rus, Ростов-на-Дону, r=Rostov-na-Donu, p=rɐˈstof nə dɐˈnu) is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East Eu ...
, Krasnodar
Krasnodar (; rus, Краснода́р, p=krəsnɐˈdar; ady, Краснодар), formerly Yekaterinodar (until 1920), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Krasnodar Krai, Russia. The city stands on the Kuban River in southern ...
, Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest c ...
and Bryansk
Bryansk ( rus, Брянск, p=brʲansk) is a city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, situated on the River Desna, southwest of Moscow. Population:
Geography Urban layout
The location of the settlement was originally ass ...
.
Aftermath
The Nazi Genocide of the Jews carried by German ''Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the im ...
'', and ''Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previous ...
'' along with local collaborators resulted in almost complete annihilation of the Jewish population over the entire territory temporarily occupied by Germany and its allies. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Léon Poliakov
Léon Poliakov (russian: Лев Поляков; 25 November 1910, Saint Petersburg – 8 December 1997, Orsay) was a French historian who wrote extensively on the Holocaust and antisemitism and wrote ''The Aryan Myth''.
Born into a Russian Jewi ...
established the Center of Contemporary Jewish Documentation
The Center for Contemporary Jewish Documentation is an independent French organization
founded by Isaac Schneersohn in 1943 in the town of Grenoble, France during the Second World War to preserve the evidence of Nazi war crimes for future gener ...
(1943) and after the war, he assisted Edgar Faure
Edgar Jean Faure (; 18 August 1908 – 30 March 1988) was a French politician, lawyer, essayist, historian and memoirist who served as Prime Minister of France in 1952 and again between 1955 and 1956.Nuremberg Trial
The Nuremberg trials were held by the Allies against representatives of the defeated Nazi Germany, for plotting and carrying out invasions of other countries, and other crimes, in World War II.
Between 1939 and 1945, Nazi Germany invaded m ...
.
In July 1943, a Soviet military court in Krasnodar
Krasnodar (; rus, Краснода́р, p=krəsnɐˈdar; ady, Краснодар), formerly Yekaterinodar (until 1920), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Krasnodar Krai, Russia. The city stands on the Kuban River in southern ...
held the first war crimes trial
A war crimes trial is the trial of persons charged with criminal violation of the laws and customs of war and related principles of international law committed during armed conflict.
History
The trial of Peter von Hagenbach by an ad hoc tribunal ...
of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. There were 11 defendants, all of whom were collaborators. They were each charged with treason for helping the Germans murder 7000 people during the occupation of Krasnodar. All but one of the defendants were members of the death squad Sonderkommando 10a, a subunit of Einsatzgruppe D
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the im ...
.
All of the defendants pleaded guilty and begged for leniency. Eight of them were sentenced to death and publicly hanged on 18 July 1943, the day after sentencing. The other three were deemed to have had relatively minor roles and were instead each sentenced to 20 years of hard labour. While outside observers viewed the proceedings as a show trial, they did not doubt the severity or the extent of the crimes themselves, nor the guilt of the defendants. Observers said the true purpose of the trial was to showcase the suffering of Soviet civilians and deter further collaboration.
Massacres
*Gully of Petrushino
Gully of Petrushino (Russian: ''Петрушинская балка'' or ''Балка смерти'' from German: ''Todesschlucht'') is a site on the outskirts of Taganrog, Russia, at which 7,000 Soviet civilians, mostly Jews, were massacred betwe ...
, near Taganrog
Taganrog ( rus, Таганрог, p=təɡɐnˈrok) is a port city in Rostov Oblast, Russia, on the north shore of the Taganrog Bay in the Sea of Azov, several kilometers west of the mouth of the Don River. Population:
History of Taganrog
The ...
, October 1941
After World War II
 Following the war, the Soviet Union suppressed or downplayed the impact of Nazi crimes on its Jewish citizens. An anti-Semitic campaign against "rootless cosmopolitans" (i.e. "
Following the war, the Soviet Union suppressed or downplayed the impact of Nazi crimes on its Jewish citizens. An anti-Semitic campaign against "rootless cosmopolitans" (i.e. "Zionists
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after ''Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Jew ...
") followed. On 12 August 1952, in the event known as the Night of the Murdered Poets
The Night of the Murdered Poets (; yi, הרוגי מלכות פֿונעם ראַטנפאַרבאַנד, translit=Harugey malkus funem Ratnfarband, lit=Soviet Union Martyrs) was the execution of thirteen Soviet Jews in the Lubyanka Prison in Mosco ...
, thirteen most prominent Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
writers, poets, actors and other intellectuals were executed on the orders of Joseph Stalin, among them Peretz Markish
Peretz Davidovich Markish ( yi, פּרץ מאַרקיש ) (russian: Перец Давидович Маркиш) (7 December 1895 (25 November OS) – 12 August 1952) was a Russian Jewish poet and playwright who wrote predominantly in Yiddish.
...
, Leib Kvitko
Leyb Moiseyevich Kvitko (russian: Лев Моисе́евич Кви́тко, yi, לייב קוויטקאָ) (October 15, 1890 – August 12, 1952) was a prominent Yiddish poet, an author of well-known children's poems and a member of the Je ...
, David Hofstein
Dovid Hofshteyn ( yi, דוד האָפשטיין ''Dovid Hofshteyn'', russian: Давид Гофштейн; June 12, 1889 in Korostyshiv – August 12, 1952), also known as David Hofstein, was a Yiddish poet. He was one of the 13 Jewish intellectua ...
, Itzik Feffer
Itzik Feffer (10 September 1900 – 12 August 1952), also Fefer (Yiddish איציק פֿעפֿער, Russian Ицик Фефер, Исаàк Соломòнович Фèфер) was a Soviet Yiddish poet executed on the Night of the Murdered Poet ...
and David Bergelson
David (or Dovid) Bergelson (, russian: Давид Бергельсон, 12 August 1884 – 12 August 1952) was a Yiddish language writer born in the Russian Empire. He lived for a time in Berlin, Germany before moving to the Soviet Union following ...
.
Research
TheUnited States Holocaust Memorial Museum
The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM) is the United States' official memorial to the Holocaust. Adjacent to the National Mall in Washington, D.C., the USHMM provides for the documentation, study, and interpretation of Holocaust hi ...
's Mandel Center's Initiative on the Holocaust in the Soviet Union works to gain a better understanding of this developing subfield and unearth the crimes and casualties. The Mandel Center partnered with various international organizations such as the International Centre for History and Sociology of World War II and its Consequences at the National Research University Higher School of Economics
HSE University (russian: link=no, «Высшая школа экономики», ВШЭ), officially the National Research University Higher School of Economics (russian: link=no, Национальный исследовательский ун ...
, The Yiddish Language Institute, the Center for Judaic Studies at the University of Latvia
University of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Universitāte, shortened ''LU'') is a state-run university located in Riga, Latvia established in 1919.
The ''QS World University Rankings'' places the university between 801st and 1000th globally, seventh ...
, the Museum “Jews in Latvia", Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv
Kyiv University or Shevchenko University or officially the Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv ( uk, Київський національний університет імені Тараса Шевченка), colloquially known as KNU ...
, the Ukrainian Center for Holocaust Studies, and the National University of Kyiv-Mohyla Academy
National University of Kyiv-Mohyla Academy ( NaUKMA) ( uk, Національний університет «Києво-Могилянська академія» (НаУКМА)) is a national, research university located in Kyiv, Ukraine. The ...
.
See also
*Krasnodar Trial
The Krasnodar Trial was a war crimes trial that was held in front of a military tribunal in July 1943 in Krasnodar, Soviet Union. All of the defendants had been Soviets who collaborated with Germany. All 11 defendants were accused of treason for co ...
— the 1943 war crimes trial in the Russian SSR
* Generalplan Ost
The ''Generalplan Ost'' (; en, Master Plan for the East), abbreviated GPO, was the Nazi German government's plan for the genocide and ethnic cleansing on a vast scale, and colonization of Central and Eastern Europe by Germans. It was to be un ...
* Russian Research and Educational Holocaust Center
The Russian Research and Educational Holocaust Center was founded in 1992 in Moscow and has since then been working on awareness raising of the Holocaust in the Russian society. It is the only non-governmental organization in the Russian Federation ...
* War crimes of the Wehrmacht
During World War II, the German combined armed forces ( ''Heer'', ''Kriegsmarine'' and ''Luftwaffe'') committed systematic war crimes, including massacres, mass rape, looting, the exploitation of forced labor, the murder of three million Sov ...
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Holocaust in RussiaRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
World War II prisoner of war massacres
Eastern Front (World War II)
Soviet Union in World War II