The Great Wall (film, 1962) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of
 The collection of fortifications known as the Great Wall of China has historically had a number of different names in both Chinese and English.
In Chinese histories, the term "Long Wall(s)" ( ''Chángchéng'') appears in
The collection of fortifications known as the Great Wall of China has historically had a number of different names in both Chinese and English.
In Chinese histories, the term "Long Wall(s)" ( ''Chángchéng'') appears in
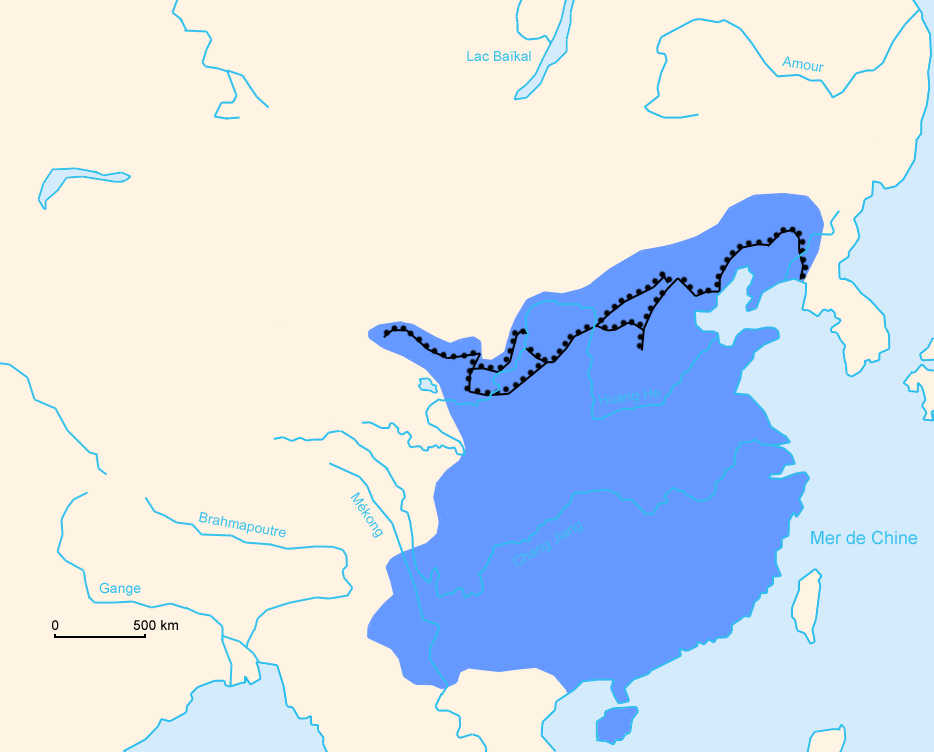 The Great Wall concept was revived again under the Ming in the 14th century, and following the Ming army's defeat by the
The Great Wall concept was revived again under the Ming in the 14th century, and following the Ming army's defeat by the
 None of the
None of the
File:Hanmuren.JPG, Great Wall of Han dynasty near
Accessed May 12, 2010.
, Answers.com. Accessed May 12, 2010.
Cecil Adams,
Is the Great wall of China the only manmade object byou can see from space?
, ''The Straight Dope''. Accessed May 12, 2010.
Snopes,
Great wall from space
, last updated July 21, 2007. Accessed May 12, 2010.
Is China's Great Wall Visible from Space?
, ''Scientific American'', February 21, 2008. "... the wall is only visible from low orbit under a specific set of weather and lighting conditions. And many other structures that are less spectacular from an earthly vantage point—desert roads, for example—appear more prominent from an orbital perspective." it is still ingrained in popular culture."Metro Tescos", '' The Times'' (London), April 26, 2010. Found a
The Times website
Accessed May 12, 2010. The apparent width of the Great Wall from the Moon would be the same as that of a human hair viewed from away. One of the earliest known references to the myth that the Great Wall can be seen from the moon appears in a letter written in 1754 by the English antiquary
''
 A more controversial question is whether the wall is visible from low Earth orbit (an altitude of as little as ). NASA claims that it is barely visible, and only under nearly perfect conditions; it is no more conspicuous than many other human-made objects.
Veteran US astronaut Gene Cernan has stated: "At Earth orbit of high, the Great Wall of China is, indeed, visible to the naked eye." Ed Lu, Expedition 7 Science Officer aboard the International Space Station, adds that, "It's less visible than a lot of other objects. And you have to know where to look."
In October 2003, Chinese astronaut Yang Liwei stated that he had not been able to see the Great Wall of China. In response, the
A more controversial question is whether the wall is visible from low Earth orbit (an altitude of as little as ). NASA claims that it is barely visible, and only under nearly perfect conditions; it is no more conspicuous than many other human-made objects.
Veteran US astronaut Gene Cernan has stated: "At Earth orbit of high, the Great Wall of China is, indeed, visible to the naked eye." Ed Lu, Expedition 7 Science Officer aboard the International Space Station, adds that, "It's less visible than a lot of other objects. And you have to know where to look."
In October 2003, Chinese astronaut Yang Liwei stated that he had not been able to see the Great Wall of China. In response, the
Great Wall visible in space photo
BBC News, Asia-Pacific section. Retrieved March 17, 2007.
File:Remains of Beacon tower near Yumenguan. 2011.jpg, Remains of Beacon tower near
International Friends of the Great Wall
– organization focused on conservation
UNESCO World Heritage Centre profile
Enthusiast/scholar website
*
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Great Wall Of China 7th-century BC establishments in China Border barriers Chinese architectural history Fortification lines Qin Shi Huang Walls World Heritage Sites in China
ancient Chinese states
Ancient Chinese states () were typified by variously sized city-states and territories that existed in China prior to its unification by Qin Shi Huang in 221 BCE. In many cases these were vassal states and fiefs established in the '' fengjian'' s ...
and Imperial China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
as protection against various nomadic groups from the Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistri ...
. Several walls were built from as early as the 7th century BC, with selective stretches later joined by Qin Shi Huang (220–206 BC), the first emperor of China. Little of the Qin wall remains. Later on, many successive dynasties built and maintained multiple stretches of border walls. The best-known sections of the wall were built by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644).
Apart from defense, other purposes of the Great Wall have included border control
Border control refers to measures taken by governments to monitor and regulate the movement of people, animals, and goods across land, air, and maritime borders. While border control is typically associated with international borders, it a ...
s, allowing the imposition of duties on goods transported along the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
, regulation or encouragement of trade and the control of immigration and emigration. Furthermore, the defensive characteristics of the Great Wall were enhanced by the construction of watchtowers, troop barracks, garrison stations, signaling capabilities through the means of smoke or fire, and the fact that the path of the Great Wall also served as a transportation corridor.
The frontier walls built by different dynasties have multiple courses. Collectively, they stretch from Liaodong in the east to Lop Lake in the west, from the present-day SinoRussian border in the north to Tao River (Taohe) in the south; along an arc that roughly delineates the edge of the Mongolian steppe; spanning in total. Today, the defensive system of the Great Wall is generally recognized as one of the most impressive architectural feats in history.
Names
 The collection of fortifications known as the Great Wall of China has historically had a number of different names in both Chinese and English.
In Chinese histories, the term "Long Wall(s)" ( ''Chángchéng'') appears in
The collection of fortifications known as the Great Wall of China has historically had a number of different names in both Chinese and English.
In Chinese histories, the term "Long Wall(s)" ( ''Chángchéng'') appears in Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years b ...
's '' Records of the Grand Historian'', where it referred both to the separate great walls built between and north of the Warring States and to the more unified construction of the First Emperor. The Chinese character , meaning city or fortress, is a phono-semantic compound of the "earth" radical and phonetic , whose Old Chinese pronunciation has been reconstructed as *''deŋ''. It originally referred to the rampart which surrounded traditional Chinese cities and was used by extension for these walls around their respective states; today, however, it is much more often the Chinese word for "city".
The longer Chinese name "Ten-Thousand Mile Long Wall" ( ''Wànlǐ Chángchéng'') came from Sima Qian's description of it in the ''Records'', though he did not name the walls as such. The AD 493 ''Book of Song
The ''Book of Song'' (''Sòng Shū'') is a historical text of the Liu Song Dynasty of the Southern Dynasties of China. It covers history from 420 to 479, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories, a traditional collection of historical records. I ...
'' quotes the frontier general Tan Daoji referring to "the long wall of 10,000 miles", closer to the modern name, but the name rarely features in pre-modern times otherwise. The traditional Chinese mile
''Li'' (, ''lǐ'', or , ''shìlǐ''), also known as the Chinese mile, is a traditional Chinese unit of distance. The li has varied considerably over time but was usually about one third of an English mile and now has a standardized length of a ...
(, ''lǐ'') was an often irregular distance that was intended to show the length of a standard village and varied with terrain but was usually standardized at distances around a third of an English mile (540 m). However, this use of "ten-thousand" (''wàn'') is figurative in a similar manner to the Greek and English ''myriad
A myriad (from Ancient Greek grc, μυριάς, translit=myrias, label=none) is technically the number 10,000 (ten thousand); in that sense, the term is used in English almost exclusively for literal translations from Greek, Latin or Sinospher ...
'' and simply means "innumerable" or "immeasurable".
Because of the wall's association with the First Emperor's supposed tyranny, the Chinese dynasties after Qin usually avoided referring to their own additions to the wall by the name "Long Wall". Instead, various terms were used in medieval records, including "frontier(s)" (, ''Sài''), "rampart(s)" (, ''Yuán''), "barrier(s)" (, ''Zhàng''), "the outer fortresses" ''Wàibǎo''), and "the border wall(s)" ''Biānqiáng''). Poetic and informal names for the wall included "the Purple Frontier" ''Zǐsài'') and "the Earth Dragon" ''Tǔlóng''). Only during the Qing period did "Long Wall" become the catch-all term to refer to the many border walls regardless of their location or dynastic origin, equivalent to the English "Great Wall".
Sections of the wall in south Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
and Mongolian steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
are sometimes referred to as "Wall of Genghis Khan", even though Genghis Khan did not construct any walls or permanent defense lines himself.
The current English name evolved from accounts of from early modern European travelers. By the nineteenth century, "the Great Wall of China" had become standard in English and French, although other European languages such as German continue to refer to it as "the Chinese wall".
History
Early walls
The Chinese were already familiar with the techniques of wall-building by the time of theSpring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
between the 8th and 5th centuries BC. During this time and the subsequent Warring States period, the states of Qin, Wei
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (衛, 1040–209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (魏, 403–225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
, Zhao, Qi, Han, Yan, and Zhongshan all constructed extensive fortifications to defend their own borders. Built to withstand the attack of small arms such as swords and spears, these walls were made mostly of stone or by stamping earth and gravel between board frames.
King Zheng of Qin conquered the last of his opponents and unified China as the First Emperor of the Qin dynasty ("Qin Shi Huang") in 221 BC. Intending to impose centralized rule and prevent the resurgence of feudal lords, he ordered the destruction of the sections of the walls that divided his empire among the former states. To position the empire against the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
people from the north, however, he ordered the building of new walls to connect the remaining fortifications along the empire's northern frontier. "Build and move on" was a central guiding principle in constructing the wall, implying that the Chinese were not erecting a permanently fixed border.
Transporting the large quantity of materials required for construction was difficult, so builders always tried to use local resources. Stones from the mountains were used over mountain ranges, while rammed earth was used for construction in the plains. There are no surviving historical records indicating the exact length and course of the Qin walls. Most of the ancient walls have eroded away over the centuries, and very few sections remain today. The human cost of the construction is unknown, but it has been estimated by some authors that hundreds of thousands workers died building the Qin wall. Later, the Han, the Northern dynasties and the Sui all repaired, rebuilt, or expanded sections of the Great Wall at great cost to defend themselves against northern invaders. The Tang and Song dynasties did not undertake any significant effort in the region. Dynasties founded by non-Han ethnic groups also built their border walls: the Xianbei-ruled Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties ...
, the Khitan-ruled Liao, Jurchen-led Jin and the Tangut-established Western Xia, who ruled vast territories over Northern China throughout centuries, all constructed defensive walls but those were located much to the north of the other Great Walls as we know it, within China's autonomous region of Inner Mongolia and in modern-day Mongolia itself.
Ming era
 The Great Wall concept was revived again under the Ming in the 14th century, and following the Ming army's defeat by the
The Great Wall concept was revived again under the Ming in the 14th century, and following the Ming army's defeat by the Oirats
Oirats ( mn, Ойрад, ''Oirad'', or , Oird; xal-RU, Өөрд; zh, 瓦剌; in the past, also Eleuths) are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
Histor ...
in the Battle of Tumu. The Ming had failed to gain a clear upper hand over the Mongol tribes after successive battles, and the long-drawn conflict was taking a toll on the empire. The Ming adopted a new strategy to keep the nomadic tribes out by constructing walls along the northern border of China. Acknowledging the Mongol control established in the Ordos Desert, the wall followed the desert's southern edge instead of incorporating the bend of the Yellow River.
Unlike the earlier fortifications, the Ming construction was stronger and more elaborate due to the use of bricks and stone instead of rammed earth. Up to 25,000 watchtowers are estimated to have been constructed on the wall. As Mongol raids
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
continued periodically over the years, the Ming devoted considerable resources to repair and reinforce the walls. Sections near the Ming capital of Beijing were especially strong. Qi Jiguang between 1567 and 1570 also repaired and reinforced the wall, faced sections of the ram-earth wall with bricks and constructed 1,200 watchtowers from Shanhaiguan Pass to Changping to warn of approaching Mongol raiders. During the 1440s–1460s, the Ming also built a so-called "Liaodong Wall". Similar in function to the Great Wall (whose extension, in a sense, it was), but more basic in construction, the Liaodong Wall enclosed the agricultural heartland of the Liaodong province, protecting it against potential incursions by Jurchen-Mongol Oriyanghan from the northwest and the Jianzhou Jurchens from the north. While stones and tiles were used in some parts of the Liaodong Wall, most of it was in fact simply an earth dike with moats on both sides.
Towards the end of the Ming, the Great Wall helped defend the empire against the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
invasions that began around 1600. Even after the loss of all of Liaodong, the Ming army held the heavily fortified Shanhai Pass
Shanhai Pass or Shanhaiguan () is one of the major passes in the Great Wall of China, being the easternmost stronghold along the Ming Great Wall, and commands the narrowest choke point in the Liaoxi Corridor. It is located in Shanhaiguan Di ...
, preventing the Manchus from conquering the Chinese heartland. The Manchus were finally able to cross the Great Wall in 1644, after Beijing had already fallen to Li Zicheng's short-lived Shun dynasty. Before this time, the Manchus had crossed the Great Wall multiple times to raid, but this time it was for conquest. The gates at Shanhai Pass were opened on May 25 by the commanding Ming general, Wu Sangui
Wu Sangui (; 8 June 1612 – 2 October 1678), courtesy name Changbai () or Changbo (), was a notorious Ming Dynasty military officer who played a key role in the fall of the Ming dynasty and the founding of the Qing dynasty in China. In Chinese ...
, who formed an alliance with the Manchus, hoping to use the Manchus to expel the rebels from Beijing. The Manchus quickly seized Beijing, and eventually defeated both the Shun dynasty and the remaining Ming resistance, consolidating the rule of the Qing dynasty over all of China proper.
Under Qing rule, China's borders extended beyond the walls and Mongolia was annexed into the empire, so constructions on the Great Wall were discontinued. On the other hand, the so-called Willow Palisade, following a line similar to that of the Ming Liaodong Wall, was constructed by the Qing rulers in Manchuria. Its purpose, however, was not defense but rather to prevent Han Chinese migration into Manchuria.
Foreign accounts
 None of the
None of the Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) ...
who visited China or Mongolia in the 13th and 14th centuries, such as Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, William of Rubruck, Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
, Odoric of Pordenone and Giovanni de' Marignolli, mentioned the Great Wall.
The North African traveler Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
, who also visited China during the Yuan dynasty c. 1346, had heard about China's Great Wall, possibly before he had arrived in China. He wrote that the wall is "sixty days' travel" from Zeitun (modern Quanzhou
Quanzhou, postal map romanization, alternatively known as Chinchew, is a prefecture-level city, prefecture-level port city on the north bank of the Jin River, beside the Taiwan Strait in southern Fujian, China. It is Fujian's largest metrop ...
) in his travelogue ''Gift to Those Who Contemplate the Wonders of Cities and the Marvels of Travelling
''The Rihla'', formal title ''A Masterpiece to Those Who Contemplate the Wonders of Cities and the Marvels of Travelling'', is the travelogue written by Ibn Battuta, documenting his lifetime of travel and exploration, which according to his desc ...
''. He associated it with the legend of the wall mentioned in the Qur'an, which Dhul-Qarnayn (commonly associated with Alexander the Great) was said to have erected to protect people near the land of the rising sun from the savages of Gog and Magog
Gog and Magog (; he, גּוֹג וּמָגוֹג, ''Gōg ū-Māgōg'') appear in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran as individuals, tribes, or lands. In Ezekiel 38, Gog is an individual and Magog is his land; in Genesis 10, Magog is a man and epo ...
. However, Ibn Battuta could find no one who had either seen it or knew of anyone who had seen it, suggesting that although there were remnants of the wall at that time, they were not significant.
Soon after Europeans reached Ming China by ship in the early 16th century, accounts of the Great Wall started to circulate in Europe, even though no European was to see it for another century. Possibly one of the earliest European descriptions of the wall and of its significance for the defense of the country against the " Tartars" (i.e. Mongols) may be the one contained in João de Barros
João de Barros () (1496 – 20 October 1570), called the ''Portuguese Livy'', is one of the first great Portuguese historians, most famous for his ''Décadas da Ásia'' ("Decades of Asia"), a history of the Portuguese in India, Asia, and southea ...
's 1563 ''Asia''. Other early accounts in Western sources include those of Gaspar da Cruz, Bento de Goes
A is the Japanese iteration of a single-portion take-out or home-packed meal, often for lunch. Outside Japan, it is common in other East and Southeast Asian culinary styles, especially within Chinese, Korean, Singaporean cuisines and more, as r ...
, Matteo Ricci
Matteo Ricci, SJ (; la, Mattheus Riccius; 6 October 1552 – 11 May 1610), was an Italians, Italian Society of Jesus, Jesuit Priesthood in the Catholic Church, priest and one of the founding figures of the Jesuit China missions. He create ...
, and Bishop Juan González de Mendoza, the latter in 1585 describing it as a "superbious and mightie work" of architecture, though he had not seen it. In 1559, in his work "A Treatise of China and the Adjoyning Regions", Gaspar da Cruz offers an early discussion of the Great Wall. Perhaps the first recorded instance of a European actually entering China via the Great Wall came in 1605, when the Portuguese Jesuit brother Bento de Góis reached the northwestern Jiayu Pass from India. Early European accounts were mostly modest and empirical, closely mirroring contemporary Chinese understanding of the Wall, although later they slid into hyperbole, including the erroneous but ubiquitous claim that the Ming walls were the same ones that were built by the first emperor in the 3rd century BC.
When China opened its borders to foreign merchants and visitors after its defeat in the First and Second Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Sino War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a colonial war lasting from 1856 to 1860, which pitted the British Empire and the French Emp ...
s, the Great Wall became a main attraction for tourists. The travelogues of the later 19th century further enhanced the reputation and the mythology of the Great Wall.
Course
A formal definition of what constitutes a "Great Wall" has not been agreed upon, making the full course of the Great Wall difficult to describe in its entirety. The defensive lines contain multiple stretches of ramparts, trenches and ditches, as well as individual fortresses. In 2012, based on existing research and the results of a comprehensive mapping survey, the National Cultural Heritage Administration of China concluded that the remaining Great Wall associated sites include 10,051 wall sections, 1,764 ramparts or trenches, 29,510 individual buildings, and 2,211 fortifications or passes, with the walls and trenches spanning a total length of . Incorporating advanced technologies, the study has concluded that the Ming Great Wall measures . This consists of of wall sections, of trenches and of natural defensive barriers such as hills and rivers. In addition, Qin, Han and earlier Great Wall sites are long in total;Jin dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (,
; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin
in ...
border fortifications are in length; the remainder date back to Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties ...
, Northern Qi, Sui, Tang, the Five Dynasties, Song, Liao and Xixia. About half of the sites are located in Inner Mongolia (31%) and Hebei (19%).
Yumenguan
Yumen Pass (; Uyghur: قاش قوۋۇق), or Jade Gate or Pass of the Jade Gate, is the name of a pass of the Great Wall located west of Dunhuang in today's Gansu Province of China. During the Han dynasty (202 BC – AD 220), this was a p ...
.
File:20090529 Great Wall 8185.jpg, Ming dynasty Great Wall at Jinshanling
Han Great Wall
Han fortifications starts from Yumen Pass andYang Pass
Yangguan, or Yangguan Pass (), is a mountain pass that was fortified by Emperor Wu of the Western Han Dynasty around 120 BC and used as an outpost in the colonial dominions adjacent to ancient China. It is located approximately southwest of Dunh ...
, southwest of Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major ...
, in Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
province. Ruins of the remotest Han border posts are found in Mamitu ( ''Mǎmítú'', ) near Yumen Pass.
Ming Great Wall
The Jiayu Pass, located in Gansu province, is the western terminus of the Ming Great Wall. From Jiayu Pass the wall travels discontinuously down the Hexi Corridor and into the deserts of Ningxia, where it enters the western edge of the Yellow River loop at Yinchuan. Here the first major walls erected during the Ming dynasty cut through the Ordos Desert to the eastern edge of the Yellow River loop. There at Piantou Pass ''Piāntóuguān'') in Xinzhou,Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
province, the Great Wall splits in two with the "Outer Great Wall" ''Wài Chǎngchéng'') extending along the Inner Mongolia border with Shanxi into Hebei province, and the "Inner Great Wall" ''Nèi Chǎngchéng'') running southeast from Piantou Pass for some , passing through important passes like the Pingxing Pass
Pingxing Pass () is a mountain pass in the Shanxi Province of China.
There is a section of the Great Wall of China there.
The Battle of Pingxingguan was fought here between the National Revolutionary Army's 8th Route Army of the Republic ...
and Yanmen Pass before joining the Outer Great Wall at Sihaiye in Beijing's Yanqing County.
The sections of the Great Wall around Beijing municipality are especially famous: they were frequently renovated and are regularly visited by tourists today. The Badaling
Badaling () is the site of the most visited section of the Great Wall of China, approximately northwest of Beijing's city center, in Badaling Town, Yanqing District (within Beijing municipality). The portion of the wall running through the ...
Great Wall near Zhangjiakou is the most famous stretch of the wall, for this was the first section to be opened to the public in the People's Republic of China, as well as the showpiece stretch for foreign dignitaries. The Badaling
Badaling () is the site of the most visited section of the Great Wall of China, approximately northwest of Beijing's city center, in Badaling Town, Yanqing District (within Beijing municipality). The portion of the wall running through the ...
Great Wall saw nearly 10 million visitors in 2018, and in 2019, a daily limit of 65,000 visitors was instated. South of Badaling is the Juyong Pass; when it was used by the Chinese to protect their land, this section of the wall had many guards to defend the capital Beijing. Made of stone and bricks from the hills, this portion of the Great Wall is high and wide.
One of the most striking sections of the Ming Great Wall is where it climbs extremely steep slopes in Jinshanling. There it runs long, ranges from in height, and across the bottom, narrowing up to across the top. Wangjing Lou ''Wàngjīng Lóu'') is one of Jinshanling's 67 watchtowers, above sea level. Southeast of Jinshanling is the Mutianyu Great Wall which winds along lofty, cragged mountains from the southeast to the northwest for . It is connected with Juyongguan Pass to the west and Gubeikou to the east. This section was one of the first to be renovated following the turmoil of the Cultural Revolution.
At the edge of the Bohai Gulf is Shanhai Pass, considered the traditional end of the Great Wall and the "First Pass Under Heaven". The part of the wall inside Shanhai Pass that meets the sea is named the "Old Dragon Head". north of Shanhai Pass is Jiaoshan Great Wall ( ''Jiāoshān Chángchéng''), the site of the first mountain of the Great Wall. northeast from Shanhaiguan is Jiumenkou ''Jiǔménkǒu''), which is the only portion of the wall that was built as a bridge.
In 2009, 180 km of previously unknown sections of the Ming wall concealed by hills, trenches and rivers were discovered with the help of infrared range finders and GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
devices. In March and April 2015, nine sections with a total length of more than , believed to be part of the Great Wall, were discovered along the border of Ningxia autonomous region and Gansu province.
Characteristics
Before the use of bricks, the Great Wall was mainly built from rammed earth, stones, and wood. During the Ming, however, bricks were heavily used in many areas of the wall, as were materials such as tiles, lime, and stone. The size and weight of the bricks made them easier to work with than earth and stone, so construction quickened. Additionally, bricks could bear more weight and endure better than rammed earth. Stone can hold under its own weight better than brick, but is more difficult to use. Consequently, stones cut into rectangular shapes were used for the foundation, inner and outerbrims
Brims may refer to:
People
* Harriett Brims (1864-1939), Australian pioneer photographer
* Robin Brims (born 1951), British Army officer
Places
* Brims, Caithness, the location of Brims Castle, Scotland
* Brims, Orkney, Scotland
* Brims or B ...
, and gateways of the wall. Battlements line the uppermost portion of the vast majority of the wall, with defensive gaps a little over tall, and about wide. From the parapets, guards could survey the surrounding land.
Sticky rice mortar
Sticky rice mortar was invented in ancient China utilizing organic materials in inorganic mortar. Hydraulic mortar was not available in ancient China, possibly due to a lack of volcanic ash.
Around 500 CE, sticky rice soup was mixed with s ...
, consisting of sticky rice soup mixed with slaked lime
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has ma ...
, was extensively used to hold bricks together; no human bones or body parts were ever incorporated into the mortar or any part of the wall, contrary to what a legend states. Communication between the army units along the length of the Great Wall, including the ability to call reinforcements and warn garrisons
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mi ...
of enemy movements, was of high importance. Signal towers were built upon hill tops or other high points along the wall for their visibility. Wooden gates could be used as a trap against those going through. Barracks, stables, and armories were built near the wall's inner surface.
Condition
While portions north of Beijing and near tourist centers have been preserved and even extensively renovated, in many other locations the wall is in disrepair. The wall sometimes provided a source of stones to build houses and roads. Sections of the wall are also prone to graffiti and vandalism, while inscribed bricks were pilfered and sold on the market for up to 50renminbi
The renminbi (; symbol: ¥; ISO code: CNY; abbreviation: RMB) is the official currency of the People's Republic of China and one of the world's most traded currencies, ranking as the fifth most traded currency in the world as of April 2022. ...
. Parts have been destroyed to make way for construction or mining.
A 2012 report by the National Cultural Heritage Administration states that 22% of the Ming Great Wall has disappeared, while of wall have vanished. More than of the wall in Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
province may disappear in the next 20 years, due to erosion from sandstorms. In some places, the height of the wall has been reduced from more than to less than . Various square lookout towers that characterize the most famous images of the wall have disappeared. Many western sections of the wall are constructed from mud, rather than brick and stone, and thus are more susceptible to erosion. In 2014 a portion of the wall near the border of Liaoning and Hebei province was repaired with concrete. The work has been much criticized.
Visibility from space
Variousfactoids
A factoid is either an invented or assumed statement presented as a fact, ''or'' a true but brief or trivial item of news or information.
The term was coined in 1973 by American writer Norman Mailer to mean a piece of information that becomes ac ...
in popular culture claim that the Great Wall can be seen (with the naked eye) from space, with questionable degrees of veracity.
From the Moon
The Great Wall of China cannot be seen by the naked human eye from the Moon. Even though the myth is thoroughly debunked,Urban Legends.com websiteAccessed May 12, 2010.
, Answers.com. Accessed May 12, 2010.
Cecil Adams,
Is the Great wall of China the only manmade object byou can see from space?
, ''The Straight Dope''. Accessed May 12, 2010.
Snopes,
Great wall from space
, last updated July 21, 2007. Accessed May 12, 2010.
Is China's Great Wall Visible from Space?
, ''Scientific American'', February 21, 2008. "... the wall is only visible from low orbit under a specific set of weather and lighting conditions. And many other structures that are less spectacular from an earthly vantage point—desert roads, for example—appear more prominent from an orbital perspective." it is still ingrained in popular culture."Metro Tescos", '' The Times'' (London), April 26, 2010. Found a
The Times website
Accessed May 12, 2010. The apparent width of the Great Wall from the Moon would be the same as that of a human hair viewed from away. One of the earliest known references to the myth that the Great Wall can be seen from the moon appears in a letter written in 1754 by the English antiquary
William Stukeley
William Stukeley (7 November 1687 – 3 March 1765) was an English antiquarian, physician and Anglican clergyman. A significant influence on the later development of archaeology, he pioneered the scholarly investigation of the prehistoric ...
. Stukeley wrote that, "This mighty wall of four score miles 30 kmin length is only exceeded by the Chinese Wall, which makes a considerable figure upon the terrestrial globe
A globe is a spherical model of Earth, of some other celestial body, or of the celestial sphere. Globes serve purposes similar to maps, but unlike maps, they do not distort the surface that they portray except to scale it down. A model glob ...
, and may be discerned at the Moon." The claim was also mentioned by Henry Norman in 1895 where he states "besides its age it enjoys the reputation of being the only work of human hands on the globe visible from the Moon." The issue of "canals" on Mars was prominent in the late 19th century and may have led to the belief that long, thin objects were visible from space. The claim that the Great Wall is visible from the moon also appears in 1932's ''Ripley's Believe It or Not!
''Ripley's Believe It or Not!'' is an American franchise founded by Robert Ripley, which deals in bizarre events and items so strange and unusual that readers might question the claims. Originally a newspaper panel, the ''Believe It or Not'' feat ...
'' strip."The Great Wall of China"''
Ripley's Believe It or Not!
''Ripley's Believe It or Not!'' is an American franchise founded by Robert Ripley, which deals in bizarre events and items so strange and unusual that readers might question the claims. Originally a newspaper panel, the ''Believe It or Not'' feat ...
'', 1932.
From low Earth orbit
 A more controversial question is whether the wall is visible from low Earth orbit (an altitude of as little as ). NASA claims that it is barely visible, and only under nearly perfect conditions; it is no more conspicuous than many other human-made objects.
Veteran US astronaut Gene Cernan has stated: "At Earth orbit of high, the Great Wall of China is, indeed, visible to the naked eye." Ed Lu, Expedition 7 Science Officer aboard the International Space Station, adds that, "It's less visible than a lot of other objects. And you have to know where to look."
In October 2003, Chinese astronaut Yang Liwei stated that he had not been able to see the Great Wall of China. In response, the
A more controversial question is whether the wall is visible from low Earth orbit (an altitude of as little as ). NASA claims that it is barely visible, and only under nearly perfect conditions; it is no more conspicuous than many other human-made objects.
Veteran US astronaut Gene Cernan has stated: "At Earth orbit of high, the Great Wall of China is, indeed, visible to the naked eye." Ed Lu, Expedition 7 Science Officer aboard the International Space Station, adds that, "It's less visible than a lot of other objects. And you have to know where to look."
In October 2003, Chinese astronaut Yang Liwei stated that he had not been able to see the Great Wall of China. In response, the European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
(ESA) issued a press release reporting that from an orbit between , the Great Wall is visible to the naked eye. The image was actually a river in Beijing.
Leroy Chiao, a Chinese-American astronaut, took a photograph from the International Space Station that shows the wall. It was so indistinct that the photographer was not certain he had actually captured it. Based on the photograph, the '' China Daily'' later reported that the Great Wall can be seen from 'space' with the naked eye, under favorable viewing conditions, if one knows exactly where to look.Markus, Francis. (April 19, 2005)Great Wall visible in space photo
BBC News, Asia-Pacific section. Retrieved March 17, 2007.
Gallery
Yumenguan
Yumen Pass (; Uyghur: قاش قوۋۇق), or Jade Gate or Pass of the Jade Gate, is the name of a pass of the Great Wall located west of Dunhuang in today's Gansu Province of China. During the Han dynasty (202 BC – AD 220), this was a p ...
, 2011
File:"The First Mound"--the west end of the Great Wall.jpg, "The First Mound" – at Jiayu Pass, the western terminus of the Ming wall
File:The Journey of Discovery Beijing (6962643268).jpg, The Great Wall near Jiayu Pass
File:明长城 - panoramio (1).jpg, Ming Great Wall remnant near Yinchuan
File:榆林市的明长城遗迹 - panoramio.jpg, The Great Wall remnant at Yulin Yulin may refer to the following places in China:
Cities and prefectures
*Yulin, Guangxi (玉林市), a prefecture-level city in Guangxi
*Yulin, Shaanxi (榆林市), a prefecture-level city in Shaanxi
* Yulin Prefecture (鬱林州), a prefecture b ...
Image:GreatWall 2004 Summer 1A.jpg, The Great Wall at Badaling
Badaling () is the site of the most visited section of the Great Wall of China, approximately northwest of Beijing's city center, in Badaling Town, Yanqing District (within Beijing municipality). The portion of the wall running through the ...
File:Juyongguan Great Wall.jpg, The Juyongguan area of the Great Wall accepts numerous tourists each day
File:Gubeikou Gate.jpg, Gateway of Gubeikou Fortress
File:Environmental protection sign near Great Wall. 2011.jpg, Environmental protection sign near Great Wall, 2011
Image:Great Wall at Simatai overlooking gorge.jpg, Ming Great Wall at Simatai, overlooking the gorge
Image:MutianyuGreatWallWildSection.JPG, Mutianyu Great Wall. This is atop the wall on a section that has not been restored
File:Great wall stops in see.jpg, The Old Dragon Head, the Great Wall where it meets the sea in the vicinity of Shanhai Pass
Shanhai Pass or Shanhaiguan () is one of the major passes in the Great Wall of China, being the easternmost stronghold along the Ming Great Wall, and commands the narrowest choke point in the Liaoxi Corridor. It is located in Shanhaiguan Di ...
File:The Great wall - by Hao Wei.jpg, The Great Wall at dawn
File:InsideGWWatchtower.jpg, Inside the watchtower
File:Great Wall of China view 1.jpg, Badaling Great Wall during winter
See also
* Cheolli Jangseong * Chinese city wall * Defense of the Great Wall * Gates of Alexander *Grand Canal (China)
The Grand Canal, known to the Chinese as the Jing–Hang Grand Canal (, or more commonly, as the「大运河」("Grand Canal")), a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is the longest canal or artificial river in the world. Starting in Beijing, it passes ...
* Great Wall of China hoax
The Great Wall of China hoax was a faked newspaper story concocted on June 25, 1899 by four reporters in Denver, Colorado about bids by American businesses on a contract to demolish the Great Wall of China and construct a road in its place. The st ...
* Great Wall Marathon
* Great Wall of Gorgan
* Great Wall of India
* List of World Heritage Sites in China
This is a list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in China. China has 56, ranking second in the world just below Italy (58). China ratified The Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage on 12 December 1985. Thes ...
* Miaojiang Great Wall
* Offa's Dyke
* Roman military frontiers and fortifications
Roman military borders and fortifications were part of a grand strategy of territorial defense in the Roman Empire, although this is a matter of debate. By the early 2nd century, the Roman Empire had reached the peak of its territorial ex ...
* Zasechnaya cherta
Zasechnaya cherta (russian: Большая засечная черта, loosely translated as Great Abatis Line or Great Abatis Border) was a chain of fortification lines, created by Grand Duchy of Moscow and later the Tsardom of Russia to prote ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Arnold, H. J. P., "The Great Wall: Is It or Isn't It?" ''Astronomy Now'', 1995. *Beckwith, Christopher I.
Christopher I. Beckwith (born October 23, 1945) is an American philologist and distinguished professor in the Department of Central Eurasian Studies at Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana.
He has a B.A. in Chinese from Ohio State Univer ...
(2009): ''Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present''. Princeton: Princeton University Press. .
* Luo, Zewen, et al. and Baker, David, ed. (1981). ''The Great Wall''. Maidenhead: McGraw-Hill Book Company (UK).
*
* Michaud, Roland and Sabrina (photographers), & Michel Jan, ''The Great Wall of China''. Abbeville Press, 2001.
* Schafer, Edward H. (1985). ''The Golden Peaches of Samarkand''. Berkeley: University of California Press. .
*
External links
International Friends of the Great Wall
– organization focused on conservation
UNESCO World Heritage Centre profile
Enthusiast/scholar website
*
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Great Wall Of China 7th-century BC establishments in China Border barriers Chinese architectural history Fortification lines Qin Shi Huang Walls World Heritage Sites in China