Thatcherites on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thatcherism is a form of
 Whilst Thatcher was Prime Minister, she greatly embraced transatlantic relations with the U.S. President
Whilst Thatcher was Prime Minister, she greatly embraced transatlantic relations with the U.S. President
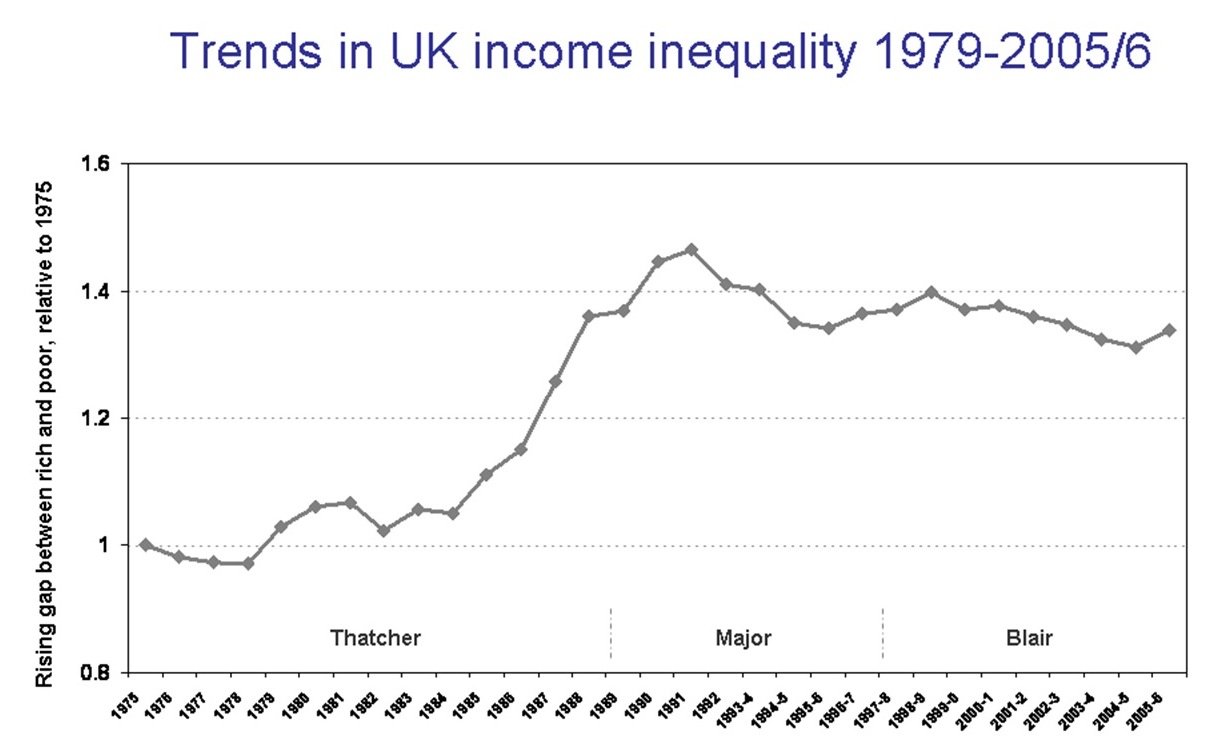 Critics of Thatcherism claim that its successes were obtained only at the expense of great social costs to the British population. There were nearly 3.3 million unemployed in Britain in 1984, compared to 1.5 million when she first came to power in 1979, though that figure had reverted to some 1.6 million by the end of 1990.
While credited with reviving Britain's economy, Thatcher also was blamed for spurring a doubling in the relative poverty rate. Britain's childhood-poverty rate in 1997 was the highest in Europe. When she resigned in 1990, 28% of the children in Great Britain were considered to be below the poverty line, a number that kept rising to reach a peak of nearly 30% during the government of Thatcher's successor,
Critics of Thatcherism claim that its successes were obtained only at the expense of great social costs to the British population. There were nearly 3.3 million unemployed in Britain in 1984, compared to 1.5 million when she first came to power in 1979, though that figure had reverted to some 1.6 million by the end of 1990.
While credited with reviving Britain's economy, Thatcher also was blamed for spurring a doubling in the relative poverty rate. Britain's childhood-poverty rate in 1997 was the highest in Europe. When she resigned in 1990, 28% of the children in Great Britain were considered to be below the poverty line, a number that kept rising to reach a peak of nearly 30% during the government of Thatcher's successor,
 The extent to which one can say Thatcherism has a continuing influence on British political and economic life is unclear. In reference to modern British political culture, it could be said that a "post-Thatcherite consensus" exists, especially in regard to economic policy. In the 1980s, the now defunct
The extent to which one can say Thatcherism has a continuing influence on British political and economic life is unclear. In reference to modern British political culture, it could be said that a "post-Thatcherite consensus" exists, especially in regard to economic policy. In the 1980s, the now defunct
What is Thatcherism? (BBC News Online)
What is Thatcherism? (Britpolitics.co.uk)
{{Use dmy dates, date=February 2021 1970s economic history 1980s economic history 1990s economic history 1970s neologisms British nationalism Conservative Party (UK) factions Eponymous political ideologies Euroscepticism in the United Kingdom Margaret Thatcher Neoliberalism History of the Conservative Party (UK) History of libertarianism Liberal conservatism Libertarian theory Libertarianism in the United Kingdom Politics of the United Kingdom Right-libertarianism Right-wing ideologies Right-wing politics in the United Kingdom Right-wing populism in the United Kingdom
British conservative
The Conservative Party, officially the Conservative and Unionist Party and also known colloquially as the Tories, is one of the two main political parties in the United Kingdom, along with the Labour Party. It is the current governing party, ...
ideology named after Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
leader Margaret Thatcher that relates to not just her political platform and particular policies but also her personal character
Moral character or character (derived from charaktêr) is an analysis of an individual's steady Morality, moral qualities. The concept of ''character'' can express a variety of attributes, including the presence or lack of virtues such as empat ...
and general style of management while in office. Proponents of Thatcherism are referred to as Thatcherites. The term has been used to describe the principles of the British government under Thatcher from the 1979 general election to her resignation in 1990, but it also receives use in describing administrative efforts continuing into the Conservative governments under statesmen John Major
Sir John Major (born 29 March 1943) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of the Conservative Party from 1990 to 1997, and as Member of Parliament ...
and David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
throughout the 1990s and 2010s. In international terms, Thatcherites have been described as a part of the general socio-economic movement known as neoliberalism, with different countries besides the United Kingdom (such as the United States) sharing similar policies around expansionary capitalism.
Thatcherism represents a systematic, decisive rejection and reversal of the post-war consensus inside Great Britain in terms of governance, whereby the major political parties largely agreed on the central themes of Keynesianism, the welfare state, nationalised industry, and close regulation of the British economy before Thatcher's rise to prominence. Under her administration, there was one major exception to Thatcherite changes: the National Health Service (NHS), which was widely popular with the British public. In 1982, Thatcher promised that the NHS was "safe in our hands".
The exact terms of what makes up Thatcherism, as well as its specific legacy in British history over the past decades, are controversial. Ideologically, Thatcherism has been described by Nigel Lawson, Thatcher's Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
from 1983 to 1989, as a political platform emphasising free markets with restrained government spending
Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual o ...
and tax cuts that gets coupled with British nationalism both at home and abroad. Thatcher herself rarely used the word "Thatcherism". However, she gave a speech in Solihull during her campaign for the 1987 general election and included in a discussion of the economic successes there the remark: "that's what I call Thatcherism".
'' The Daily Telegraph'' stated in April 2008 that the programme of the next non-Conservative government, with statesman Tony Blair's " New Labour" organisation governing the nation throughout the 1990s and 2000s, basically accepted the central reform measures of Thatcherism such as deregulation
Deregulation is the process of removing or reducing state regulations, typically in the economic sphere. It is the repeal of governmental regulation of the economy. It became common in advanced industrial economies in the 1970s and 1980s, as a ...
, privatisation
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
of key national industries, maintaining a flexible labour market, marginalising the trade unions and centralising power from local authorities to central government. While Blair distanced himself from certain aspects of Thatcherism earlier in his career, in his 2010 autobiography '' A Journey'' he argued both that "Britain needed the industrial and economic reforms of the Thatcher period" and as well that "much of what she wanted to do in the 1980s was inevitable, a consequence not of ideology but of social and economic change."
Overview
Thatcherism attempts to promote low inflation, the small state and free markets through tight control of the money supply,privatisation
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
and constraints on the labour movement. It is often compared with Reaganomics in the United States, economic rationalism
Economic rationalism is an Australian term often used in the discussion of Macroeconomics, macroeconomic policy, applicable to the economic policy of many governments around the world, in particular during the 1980s and 1990s. Economic rationalist ...
in Australia and Rogernomics in New Zealand and as a key part of the worldwide economic liberal movement.
Nigel Lawson, Thatcher's Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
from 1983 to 1989, listed the Thatcherite ideals as "free markets, financial discipline, firm control over public expenditure, tax cuts, nationalism, 'Victorian values' (of the Samuel Smiles self-help variety), privatisation and a dash of populism". Thatcherism is thus often compared to classical liberalism. Milton Friedman said that "Margaret Thatcher is not in terms of belief a Tory. She is a nineteenth-century Liberal".
Thatcher herself stated during a speech in 1983: "I would not mind betting that if Mr Gladstone were alive today he would apply to join the Conservative Party". In the 1996 Keith Joseph memorial lecture, Thatcher argued: "The kind of Conservatism which he and I ..favoured would be best described as 'liberal', in the old-fashioned sense. And I mean the liberalism of Mr Gladstone, not of the latter day collectivists". Thatcher once told Friedrich Hayek: "I know you want me to become a Whig; no, I am a Tory". Hayek believed "she has felt this very clearly". The relationship between Thatcherism and liberalism is complicated. Thatcher's former Defence Secretary John Nott
Sir John William Frederic Nott (born 1 February 1932) is a former British Conservative Party politician. He was a senior politician of the late 1970s and early 1980s, playing a prominent role as Secretary of State for Defence during the 1982 in ...
claimed that "it is a complete misreading of her beliefs to depict her as a nineteenth-century Liberal".
As Ellen Meiksins Wood has argued, Thatcherite capitalism was compatible with traditional British political institutions. As Prime Minister, Thatcher did not challenge ancient institutions such as the monarchy or the House of Lords, but some of the most recent additions such as the trade unions. Indeed, many leading Thatcherites, including Thatcher herself, went on to join the House of Lords, an honour which William Ewart Gladstone, for instance, had declined. Thinkers closely associated with Thatcherism include Keith Joseph
Keith Sinjohn Joseph, Baron Joseph, (17 January 1918 – 10 December 1994), known as Sir Keith Joseph, 2nd Baronet, for most of his political life, was a British politician, intellectual and barrister. A member of the Conservative Party, he ...
, Enoch Powell, Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman. In an interview with Simon Heffer in 1996, Thatcher stated that the two greatest influences on her as Conservative leader had been Joseph and Powell, who were both "very great men".
Thatcher was a strong critic of communism, Marxism and socialism. Biographer John Campbell reports that in July 1978 when asked by a Labour MP in Commons what she meant by socialism "she was at a loss to reply. What in fact she meant was Government support for inefficient industries, punitive taxation, regulation of the labour market, price controlseverything that interfered with the functioning of the free economy".
Thatcherism before Thatcher
A number of commentators have traced the origins of Thatcherism in post-war British politics. The historian Ewen Green claimed there was resentment of the inflation, taxation and the constraints imposed by the labour movement, which was associated with the so-called Buttskellite consensus in the decades before Thatcher came to prominence. Although the Conservative leadership accommodated itself to theClement Attlee
Clement Richard Attlee, 1st Earl Attlee, (3 January 18838 October 1967) was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1945 to 1951 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1935 to 1955. He was Deputy Prime Mini ...
government's post-war reforms, there was continuous right-wing opposition in the lower ranks of the party, in right-wing pressure groups like the Middle Class Alliance and the People's League for the Defence of Freedom and later in think tanks like the Centre for Policy Studies. For example, in the 1945 general election
The following elections occurred in the year 1945.
Africa
* 1945 South-West African legislative election
Asia
* 1945 Indian general election
Australia
* 1945 Fremantle by-election
Europe
* 1945 Albanian parliamentary election
* 1945 Bulgaria ...
the Conservative Party chairman Ralph Assheton had wanted 12,000 abridged copies of ''The Road to Serfdom
''The Road to Serfdom'' ( German: ''Der Weg zur Knechtschaft'') is a book written between 1940 and 1943 by Austrian-British economist and philosopher Friedrich Hayek. Since its publication in 1944, ''The Road to Serfdom'' has been popular among ...
'' (a book by the anti-socialist economist Friedrich Hayek later closely associated with Thatcherism), taking up one-and-a-half tons of the party's paper ration, distributed as election propaganda.
The historian Christopher Cooper traced the formation of the monetarist
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of governments in controlling the amount of money in circulation. Monetarist theory asserts that variations in the money supply have major influences on national ...
economics at the heart of Thatcherism back to the resignation of Conservative Chancellor of the Exchequer Peter Thorneycroft in 1958.
As early as 1950, Thatcher accepted the consensus of the day about the welfare state, claiming the credit belonged to the Conservatives in a speech to the Conservative Association annual general meeting. Biographer Charles Moore states:
Historian Richard Vinen is sceptical about there being Thatcherism before Thatcher.
Ideological definition
Thatcher saw herself as creating alibertarian
Libertarianism (from french: libertaire, "libertarian"; from la, libertas, "freedom") is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, and minimize the state's e ...
movement, rejecting traditional Toryism. Thatcherism is associated with libertarianism within the Conservative Party, albeit one of libertarian ends achieved by using strong and sometimes authoritarian leadership. British political commentator Andrew Marr has called libertarianism the "dominant, if unofficial, characteristic of Thatcherism". Whereas some of her heirs, notably Michael Portillo and Alan Duncan
Sir Alan James Carter Duncan (born 31 March 1957) is a British former Conservative Party politician who served as Minister of State for International Development from 2010 to 2014 and as Minister of State for Europe and the Americas from 201 ...
, embraced this libertarianism, others in the Thatcherite movement such as John Redwood sought to become more populist.
Some commentators have argued that Thatcherism should not be considered properly libertarian. Noting the tendency towards strong central government in matters concerning the trade unions and local authorities, Andrew Gamble summarised Thatcherism as "the free economy and the strong state". Simon Jenkins
Sir Simon David Jenkins (born 10 June 1943) is a British author, a newspaper columnist and editor. He was editor of the ''Evening Standard'' from 1976 to 1978 and of ''The Times'' from 1990 to 1992.
Jenkins chaired the National Trust from 20 ...
accused the Thatcher government of carrying out a nationalisation of Britain. Libertarian political theorist Murray Rothbard did not consider Thatcherism to be libertarian and heavily criticised Thatcher and Thatcherism stating that "Thatcherism is all too similar to Reaganism
Ronald Reagan was the 40th President of the United States (1981–1989). A Republican and former actor and governor of California, he energized the conservative movement in the United States from 1964. His basic foreign policy was to equal and ...
: free-market rhetoric masking statist content". Stuart McAnulla states that Thatcherism is actually liberal conservatism
Liberal conservatism is a political ideology combining conservative policies with liberal stances, especially on economic issues but also on social and ethical matters, representing a brand of political conservatism strongly influenced by libe ...
, a combination of liberal economics and a strong state.
Thatcherism as a form of government
Another important aspect of Thatcherism is the style of governance. Britain in the 1970s was often referred to as "ungovernable". Thatcher attempted to redress this by centralising a great deal of power to herself, as the Prime Minister, often bypassing traditional cabinet structures (such as cabinet committees). This personal approach also became identified with personal toughness at times such as theFalklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial de ...
in 1982, the IRA bomb at the Conservative conference in 1984 and the miners' strike
Miners' strikes are when miners conduct strike actions.
See also
* List of strikes
References
{{Reflist
Miners
A miner is a person who extracts ore, coal, chalk, clay, or other minerals from the earth through mining. There are tw ...
in 1984–85.
Sir Charles Powell, the Foreign Affairs Private Secretary to the Prime Minister (1984–1991 and 1996) described her style as such: "I've always thought there was something Leninist about Mrs Thatcher which came through in the style of government: the absolute determination, the belief that there's a vanguard which is right and if you keep that small, tightly knit team together, they will drive things through ... there's no doubt that in the 1980s, No. 10 could beat the bushes of Whitehall pretty violently. They could go out and really confront people, lay down the law, bully a bit".
Criticism
By 1987, after Thatcher's successful third re-election, criticism of Thatcherism increased. At the time, Thatcher claimed it was necessary tackle the "culture of dependency" by government intervention to stop socialised welfare. In 1988, she caused controversy when she made the remarks, "You do not blame society. Society is not anyone. You are personally responsible." and, "Don't blame society — that's no one." These comments attracted significant criticism including from other conservatives due to their belief in individual and collective responsibility. In 1988, Thatcher told the party conference that her third term was to be about 'social affairs'. During her last three years in power, she attempted to reform socialised welfare, differing from her earlier stated goal of "rolling back the state".Economic positions
Thatcherite economics
Thatcherism is associated with the economic theory of monetarism, notably put forward by Friedrich Hayek's ''The Constitution of Liberty
''The Constitution of Liberty'' is the magnum opus of Austrian economist and 1974 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences recipient Friedrich A. Hayek. First published in 1960 by the University of Chicago Press, the book is considered Hayek’s ...
'' which Thatcher had banged on a table while saying "this is what we believe". In contrast to previous government policy, monetarism placed a priority on controlling inflation over controlling unemployment. According to monetarist theory, inflation is the result of there being too much money in the economy. It was claimed that the government should seek to control the money supply to control inflation. By 1979, it was not only the Thatcherites who were arguing for stricter control of inflation. The Labour Chancellor Denis Healey
Denis Winston Healey, Baron Healey, (30 August 1917 – 3 October 2015) was a British Labour Party (UK), Labour politician who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1974 to 1979 and as Secretary of State for Defence from 1964 to 1970; he ...
had already adopted some monetarist policies, such as reducing public spending and selling off the government's shares in BP.
Moreover, it has been argued that the Thatcherites were not strictly monetarist in practice. A common theme centres on the Medium Term Financial Strategy, issued in the 1980 budget, which consisted of targets for reducing the growth of the money supply in the following years. After overshooting many of these targets, the Thatcher government revised the targets upwards in 1982. Analysts have interpreted this as an admission of defeat in the battle to control the money supply. The economist C. F. Pratten claimed that "since 1984, behind a veil of rhetoric, the government has lost any faith it had in technical monetarism. The money supply, as measured by M3, has been allowed to grow erratically, while calculation of the public sector borrowing requirement is held down by the ruse of subtracting the proceeds of privatisation as well as taxes from government expenditure. The principles of monetarism have been abandoned".
Thatcherism is also associated with supply-side economics
Supply-side economics is a macroeconomic theory that postulates economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-side economics, consumers will benefit fr ...
. Whereas Keynesian economics holds that the government should stimulate economic growth by increasing demand through increased credit and public spending, supply-side economists argue that the government should instead intervene only to create a free market by lowering taxes, privatising state industries and increasing restraints on trade unionism.
Trade union legislation
Reduction in the power of the trades unions was made gradually, unlike the approach of the Edward Heath government and the greatest single confrontation with the unions was the National Union of Mineworkers (NUM) strike of 1984–1985, in which the miners' union was eventually defeated. There is evidence that this confrontation with the trade unions was anticipated by both the Conservative Party and the NUM. The outcome contributed to the resurgence of the power of capital over labour.Domestic and social positions
Thatcherite morality
Thatcherism is associated with a conservative stance on morality. argues that Thatcherism married conservatism withfree-market economics
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
. Thatcherism did not propose dramatic new panaceas such as Milton Friedman's negative income tax. Instead the goal was to create a rational tax-benefit economic system that would increase British efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time in doing something or in producing a desired result. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without ...
while supporting a conservative social system based on traditional morality. There would still be a minimal safety net
A safety net is a net to protect people from injury after falling from heights by limiting the distance they fall, and deflecting to dissipate the impact energy. The term also refers to devices for arresting falling or flying objects for the ...
for the poor, but major emphasis was on encouraging individual effort and thrift. Thatcherism sought to minimise the importance of welfare for the middle classes, and reinvigorate Victorian bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
virtues. Thatcherism was family centred, unlike the extreme individualism of most neoliberal models. It had its roots in that historical experiences such as Methodism, as well as the fear of the too-powerful state that had troubled Hayek.
Norman Tebbit
Norman Beresford Tebbit, Baron Tebbit (born 29 March 1931) is a British politician. A member of the Conservative Party, he served in the Cabinet from 1981 to 1987 as Secretary of State for Employment (1981–1983), Secretary of State for Trad ...
, a close ally of Thatcher, laid out in a 1985 lecture what he thought to be the permissive society that conservatives should oppose:
Despite her association with social conservatism
Social conservatism is a political philosophy and variety of conservatism which places emphasis on traditional power structures over social pluralism. Social conservatives organize in favor of duty, traditional values and social institutio ...
, Thatcher voted in 1966 to legalise homosexuality, one of the few Conservative MPs to do so. That same year, she also voted in support of legal abortion. However, in the 1980s during her time as Prime Minister, the Thatcher government enacted Section 28, a law that opposed the "intentional promotion" of homosexuality by local authorities and "promotion" of the teaching of "the acceptability of homosexuality as a pretended family relationship" in schools. In her 1987 speech to the Conservative Party conference, Thatcher stated:
The law was opposed by many gay rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, , 3 ...
advocates such as Stonewall
Stonewall or Stone wall may refer to:
* Stone wall, a kind of masonry construction
* Stonewalling, engaging in uncooperative or delaying tactics
* Stonewall riots, a 1969 turning point for the modern LGBTQ rights movement in Greenwich Village, Ne ...
and OutRage! and was later repealed by Tony Blair's Labour government in 2000 (in Scotland) and 2003. Conservative Prime Minister David Cameron later issued an official apology for previous Conservative policies on homosexuality, specifically the introduction of the controversial Section 28 laws from the 1980s, viewing past ideological views as "a mistake" with his own ideological direction.
Sermon on the Mound
In May 1988, Thatcher gave an address to theGeneral Assembly
A general assembly or general meeting is a meeting of all the members of an organization or shareholders of a company.
Specific examples of general assembly include:
Churches
* General Assembly (presbyterian church), the highest court of presby ...
of the Church of Scotland. In the address, Thatcher offered a theological justification for her ideas on capitalism and the market economy. She said "Christianity is about spiritual redemption, not social reform" and she quoted St. Paul by saying "If a man will not work he shall not eat". Choice played a significant part in Thatcherite reforms and Thatcher said that choice was also Christian, stating that Jesus Christ chose to lay down his life and that all individuals have the God-given right to choose between good and evil
In religion, ethics, philosophy, and psychology "good and evil" is a very common dichotomy. In cultures with Manichaean and Abrahamic religious influence, evil is perceived as the dualistic antagonistic opposite of good, in which good shoul ...
.
Foreign policy
Atlanticism
 Whilst Thatcher was Prime Minister, she greatly embraced transatlantic relations with the U.S. President
Whilst Thatcher was Prime Minister, she greatly embraced transatlantic relations with the U.S. President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
. She often publicly supported Reagan's policies even when other Western allies were not as vocal. For example, she granted permission for American planes to use British bases for raids, such as the 1986 United States bombing of Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, and allowed American cruise missiles and Pershing missiles to be housed on British soil in response to Soviet deployment of SS-20 nuclear missiles targeting Britain and other Western European nations.
Europe
While Euroscepticism has for many become a characteristic of Thatcherism, Thatcher was far from consistent on the issue, only becoming truly Eurosceptic in the last years of her time as Prime Minister. Thatcher supported Britain's entry into theEuropean Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
in 1973, campaigned for a "Yes" vote in the 1975 referendum and signed the Single European Act in 1986.
Towards the end of the 1980s, Thatcher (and so Thatcherism) became increasingly vocal in its opposition to allowing the European Community to supersede British sovereignty. In a famous 1988 Bruges speech, Thatcher declared: "We have not successfully rolled back the frontiers of the state in Britain, only to see them reimposed at a European level, with a European superstate exercising a new dominance from Brussels".
Dispute over the term
It is often claimed that the word ''Thatcherism'' was coined by cultural theorist Stuart Hall in a 1979 '' Marxism Today'' article. However, this is not true as the term was first used by Tony Heath in an article he wrote that appeared in '' Tribune'' on 10 August 1973. Writing as ''Tribune''s education correspondent, Heath wrote: "It will be argued that teachers are members of a profession which must not be influenced by political considerations. With the blight of Thatcherism spreading across the land that is a luxury that only the complacent can afford". Although the term had in fact been widely used before then, not all social critics have accepted the term as valid, with the High Tory journalist T. E. Utley believing "There is no such thing as Thatcherism". Utley contended that the term was a creation of Thatcher's enemies who wished to damage her by claiming that she had an inflexible devotion to a certain set of principles and also by some of her friends who had little sympathy for what he called "the English political tradition" because it facilitated "compromise and consensus". Utley argued that a free and competitive economy, rather than being an innovation of Thatcherism, was one "more or less permanent ingredient in modern Conservative philosophy":It was on that principle that Churchill fought the 1945 election, having just read Hayek's ''Road to Serfdom''. ..What brought the Tories to 13 years of political supremacy inIn foreign policy, Utley claimed Thatcher's desire to restore British greatness did not mean "primarily a power devoted to the preservation of its own interests", but that she belonged "to that militant Whig branch of English Conservatism...her view of foreign policy has a high moral content". In practical terms, he claimed this expressed itself in her preoccupation in "the freedom of Afghanistan rather than the security of Ulster". Such leftist critics as1951 Events January * January 4 – Korean War: Third Battle of Seoul – Chinese and North Korean forces capture Seoul for the second time (having lost the Second Battle of Seoul in September 1950). * January 9 – The Government of the United ...was the slogan 'Set the people free'. ..There is absolutely nothing new about the doctrinal front that she presents on these matters. ..As for 'privatisation', Mr. Powell proposed it in ..1968. As for 'property-owning democracy', I believe it wasAnthony Eden Robert Anthony Eden, 1st Earl of Avon, (12 June 1897 – 14 January 1977) was a British Conservative Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1955 until his resignation in 1957. Achieving rapid promo ...who coined the phrase.
Anthony Giddens
Anthony Giddens, Baron Giddens (born 18 January 1938) is an English sociologist who is known for his theory of structuration and his holistic view of modern societies. He is considered to be one of the most prominent modern sociologists and is t ...
claim that Thatcherism was purely an ideology and argue that her policies marked a change which was dictated more by political interests than economic reasons:
The Conservative historian of Peterhouse, Maurice Cowling
Maurice John Cowling (6 September 1926 – 24 August 2005) was a British historian and a Fellow of Peterhouse, Cambridge.
Early life
Cowling was born in West Norwood, South London, son of Reginald Frederick Cowling (1901–1962), a patent agent ...
, also questioned the uniqueness of "Thatcherism". Cowling claimed that Thatcher used "radical variations on that patriotic conjunction of freedom, authority, inequality, individualism and average decency and respectability, which had been the Conservative Party's theme since at least 1886". Cowling further contended that the "Conservative Party under Mrs Thatcher has used a radical rhetoric to give intellectual respectability to what the Conservative Party has always wanted".
Historians Emily Robinson, Camilla Schofield, Florence Sutcliffe-Braithwaite and Natalie Thomlinson have argued that by the 1970s Britons were keen about defining and claiming their individual rights, identities and perspectives. They demanded greater personal autonomy and self-determination and less outside control. They angrily complained that the establishment was withholding it. They argue this shift in concerns helped cause Thatcherism and was incorporated into Thatcherism's appeal.
Criticism
 Critics of Thatcherism claim that its successes were obtained only at the expense of great social costs to the British population. There were nearly 3.3 million unemployed in Britain in 1984, compared to 1.5 million when she first came to power in 1979, though that figure had reverted to some 1.6 million by the end of 1990.
While credited with reviving Britain's economy, Thatcher also was blamed for spurring a doubling in the relative poverty rate. Britain's childhood-poverty rate in 1997 was the highest in Europe. When she resigned in 1990, 28% of the children in Great Britain were considered to be below the poverty line, a number that kept rising to reach a peak of nearly 30% during the government of Thatcher's successor,
Critics of Thatcherism claim that its successes were obtained only at the expense of great social costs to the British population. There were nearly 3.3 million unemployed in Britain in 1984, compared to 1.5 million when she first came to power in 1979, though that figure had reverted to some 1.6 million by the end of 1990.
While credited with reviving Britain's economy, Thatcher also was blamed for spurring a doubling in the relative poverty rate. Britain's childhood-poverty rate in 1997 was the highest in Europe. When she resigned in 1990, 28% of the children in Great Britain were considered to be below the poverty line, a number that kept rising to reach a peak of nearly 30% during the government of Thatcher's successor, John Major
Sir John Major (born 29 March 1943) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of the Conservative Party from 1990 to 1997, and as Member of Parliament ...
. During her government, Britain's Gini coefficient reflected this growing difference, going from 0.25 in 1979 to 0.34 in 1990, at about which value it remained for the next 20 years, under both Conservative and Labour governments.
Thatcher's legacy
 The extent to which one can say Thatcherism has a continuing influence on British political and economic life is unclear. In reference to modern British political culture, it could be said that a "post-Thatcherite consensus" exists, especially in regard to economic policy. In the 1980s, the now defunct
The extent to which one can say Thatcherism has a continuing influence on British political and economic life is unclear. In reference to modern British political culture, it could be said that a "post-Thatcherite consensus" exists, especially in regard to economic policy. In the 1980s, the now defunct Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
For ...
adhered to a "tough and tender" approach in which Thatcherite reforms were coupled with extra welfare provision. Neil Kinnock, leader of the Labour Party from 1983 to 1992, initiated Labour's rightward shift across the political spectrum by largely concurring with the economic policies of the Thatcher governments. The New Labour governments of Tony Blair and Gordon Brown were described as "neo-Thatcherite" by some on the left, since many of their economic policies mimicked those of Thatcher.
In 1999, twenty years after Thatcher had come to power, the Conservative Party held a dinner in London Hilton to honour the anniversary. During the dinner several speeches were given. To Thatcher's astonishment, the Conservatives had decided that it was time to shelve the economic policies of the 1980s. The Conservative Party leader at the time William Hague said that the party had learnt its lesson from the 1980s and called it a "great mistake to think that all Conservatives have to offer is solutions based on free markets". His deputy at the time Peter Lilley elaborated and said, "belief in the free market has only ever been part of Conservatism".
In 2002, Peter Mandelson, who had served in Blair's Cabinet, famously declared that "we are all Thatcherites now".
Most of the major British political parties today accept the trade union legislation, privatisations and general free market approach to government that Thatcher's governments
Margaret Thatcher's term as the prime minister of the United Kingdom began on 4 May 1979 when she accepted an invitation of Queen Elizabeth II to form a government, and ended on 28 November 1990 upon her resignation. She was elected to the pos ...
installed. Before 2010, no major political party in the United Kingdom had committed to reversing the Thatcher government's reforms of the economy, although in the aftermath of the Great Recession from 2007 to 2012, the then Labour Party leader Ed Miliband had indicated he would support stricter financial regulation
Financial regulation is a form of regulation or supervision, which subjects financial institutions to certain requirements, restrictions and guidelines, aiming to maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system. This may be handled ...
and industry-focused policy in a move to a more mixed economy. Although Miliband was said by the '' Financial Times'' to have "turned his back on many of New Labour's tenets, seeking to prove that an openly socialist party could win the backing of the British electorate for the first time since the 1970s", in 2011 Miliband had declared his support for Thatcher's reductions in income tax on top earners, her legislation to change the rules on the closed shop and strikes before ballots, as well as her introduction of Right to Buy, saying Labour had been wrong to oppose these reforms at the time.
Moreover, the UK's comparative macroeconomic performance has improved since the implementation of Thatcherite economic policies. Since Thatcher resigned as British Prime Minister in 1990, British economic growth was on average higher than the other large European economies (i.e. Germany, France and Italy). Such comparisons have been controversial for decades.
Tony Blair wrote in his 2010 autobiography '' A Journey'' that "Britain needed the industrial and economic reforms of the Thatcher period". He described Thatcher's efforts as "ideological, sometimes unnecessarily so" while also stating that "much of what she wanted to do in the 1980s was inevitable, a consequence not of ideology but of social and economic change." Blair additionally labeled these viewpoints as a matter of "basic fact".
On the occasion of the 25th anniversary of Thatcher's 1979 election victory, the BBC conducted a survey of opinions which opened with the following comments:
From the viewpoint of late 2019, the state of British politics showed that Thatcherism had suffered a "sad fate," according to '' The Economist'' Bagehot column. As a political-economic philosophy Thatcherism was originally built upon four components: commitment to free enterprise
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ...
; British nationalism; a plan to strengthen the state by improving efficiency; and a belief in traditional Victorian values
Victorian morality is a distillation of the moral views of the middle class in 19th-century Britain, the Victorian era.
Victorian values emerged in all classes and reached all facets of Victorian living. The values of the period—which can be ...
especially hard work and civic responsibility. The tone of Thatcherism was establishment bashing, with intellectuals a prime target, and that tone remains sharp today. Bagehot argues that some Thatcherisms have become mainstream, such as a more efficient operation of the government. Others have been sharply reduced, such as insisting that deregulation
Deregulation is the process of removing or reducing state regulations, typically in the economic sphere. It is the repeal of governmental regulation of the economy. It became common in advanced industrial economies in the 1970s and 1980s, as a ...
is always the answer to everything. The dream of restoring traditional values by creating a property-owning democracy has failed in Britain – ownership in the stock market has plunged, as has the proportion of young people who are homebuyers. Her program of privatisation became suspect when it appeared to favour investors rather than customers.
Recent developments in Britain reveal a deep conflict between Thatcherite free enterprise and Thatcherite nationalism. She wanted to reverse Britain's decline by fostering entrepreneurship – but immigrants have often played an important role as entrepreneurial leaders in Britain. Bagehot says Britain is "more successful at hosting world-class players than producing them." In the course of the Brexit process, nationalists have denounced European controls over Britain's future, while business leaders often instead prioritise maintenance of their leadership of the European market. Thatcher herself showed a marked degree of Euroscepticism, as when she warned against a "European superstate
The United States of Europe (USE), the European State, the European Federation and Federal Europe, is the hypothetical scenario of the European integration leading to formation of a sovereign superstate (similar to the United States of Amer ...
."
Evaluating whether or not political conservatives of the 2020s continue the neoliberal legacy of prior years, stateswoman Theresa May's Conservative Party election manifesto has attracted attention due to its inclusion of the lines: "We do not believe in untrammelled free markets. We reject the cult of selfish individualism. We abhor social division, injustice, unfairness and inequality." Journalists such as Ross Gittins of '' The Sydney Morning Herald'' have cited this as a move away from the standard arguments made historically by Thatcherites and related advocates.
See also
* Blairism * Brownism * Gladstonian liberalism *Liberal conservatism
Liberal conservatism is a political ideology combining conservative policies with liberal stances, especially on economic issues but also on social and ethical matters, representing a brand of political conservatism strongly influenced by libe ...
* Neoliberalism
* New Public Management
* Orbanomics
Orbanomics is the name given to the economic policies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and his government since it took power in 2010. These policies are in reaction to the global economic crisis and the state of Hungary's economy in it. I ...
* Pinochetism
Pinochetism ( es, Pinochetismo) is a Right-wing politics, right-wing to Far-right politics, far-right personalism, personalist political ideology based on the principles of anti-communism, conservatism, authoritarianism, militarism, patriotism, na ...
* Political positions of David Cameron
This article concerns the policies, views and voting record of David Cameron, former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (May 2010 to July 2016). Cameron describes himself as a "modern compassionate conservative" and has said that he is "fe ...
* Powellism
Powellism is the name given to the political views of Conservative and Ulster Unionist politician Enoch Powell. They derive from his High Tory and libertarian outlook.
According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the word ''Powellism'' was ...
* Reaganomics
* Right-wing populism
Right-wing populism, also called national populism and right-wing nationalism, is a political ideology that combines right-wing politics and populist rhetoric and themes. Its rhetoric employs anti-elitist sentiments, opposition to the Establi ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * *External links
*What is Thatcherism? (BBC News Online)
What is Thatcherism? (Britpolitics.co.uk)
{{Use dmy dates, date=February 2021 1970s economic history 1980s economic history 1990s economic history 1970s neologisms British nationalism Conservative Party (UK) factions Eponymous political ideologies Euroscepticism in the United Kingdom Margaret Thatcher Neoliberalism History of the Conservative Party (UK) History of libertarianism Liberal conservatism Libertarian theory Libertarianism in the United Kingdom Politics of the United Kingdom Right-libertarianism Right-wing ideologies Right-wing politics in the United Kingdom Right-wing populism in the United Kingdom