That Luang Fesztivál on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''That'' is an
 In
In 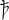 ) was used as an abbreviation, before it was phased out by the Romantic ''þt''. Similarly, ''yͭ'' was a ligature to represent ''that'', as seen in the gravestone of
) was used as an abbreviation, before it was phased out by the Romantic ''þt''. Similarly, ''yͭ'' was a ligature to represent ''that'', as seen in the gravestone of
English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the is ...
word used for several grammatical
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular variety (linguistics), speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the go ...
purposes. These include use as an adjective
In linguistics, an adjective (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that generally grammatical modifier, modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Tra ...
, conjunction
Conjunction may refer to:
* Conjunction (grammar), a part of speech
* Logical conjunction, a mathematical operator
** Conjunction introduction, a rule of inference of propositional logic
* Conjunction (astronomy), in which two astronomical bodies ...
, pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not co ...
, adverb An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, level of certainty, etc., answering ...
, and intensifier
In linguistics, an intensifier (abbreviated ) is a lexical category (but ''not'' a traditional part of speech) for a modifier that makes no contribution to the propositional meaning of a clause but serves to enhance and give additional emotional co ...
; it has distance from the speaker, as opposed to words like ''this''. The word did not originally exist in Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
, and its concept was represented by '. Once it came into being, it was spelt as (among others, such as ''þet''), taking the role of the modern ''that''. It also took on the role of the modern word ''what'', though this has since changed, and ''that'' has recently replaced some usage of the modern ''which''. Pronunciation of the word varies according to its role within a sentence, with two main varieties (a strong and a weak form), though there are also regional differences, such as where the sound is substituted instead by a in English spoken in Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
.
Modern usage
The word ''that'' serves several grammatical purposes. Owing to its wide versatility in usage, the writerJoseph Addison
Joseph Addison (1 May 1672 – 17 June 1719) was an English essayist, poet, playwright and politician. He was the eldest son of The Reverend Lancelot Addison. His name is usually remembered alongside that of his long-standing friend Richard S ...
named it "that jacksprat" in 1771, and gave this example of a grammatically correct sentence: "That that I say is this: that that that that gentleman has advanced, is not that, that he should have proved." ''That'' can be used as a demonstrative pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not co ...
,
demonstrative adjective
In linguistics, an adjective (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that generally grammatical modifier, modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Tra ...
,
conjunction
Conjunction may refer to:
* Conjunction (grammar), a part of speech
* Logical conjunction, a mathematical operator
** Conjunction introduction, a rule of inference of propositional logic
* Conjunction (astronomy), in which two astronomical bodies ...
,
relative pronoun
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that marks a relative clause. It serves the purpose of conjoining modifying information about an antecedent referent.
An example is the word ''which'' in the sentence "This is the house which Jack built." Here the ...
,
relative adverb
A subordinate clause, dependent clause, subclause, or embedded clause is a clause that is embedded within a complex sentence. For instance, in the English sentence "I know that Bette is a dolphin", the clause "that Bette is a dolphin" occurs as th ...
,
and an intensifier
In linguistics, an intensifier (abbreviated ) is a lexical category (but ''not'' a traditional part of speech) for a modifier that makes no contribution to the propositional meaning of a clause but serves to enhance and give additional emotional co ...
.
*''That'' as a demonstrative
Demonstratives (abbreviated ) are words, such as ''this'' and ''that'', used to indicate which entities are being referred to and to distinguish those entities from others. They are typically deictic; their meaning depending on a particular frame ...
pronoun refers to a specific object being discussed, such as in "that is a cat"; the word is a distal demonstrative
Demonstratives (abbreviated ) are words, such as ''this'' and ''that'', used to indicate which entities are being referred to and to distinguish those entities from others. They are typically deictic; their meaning depending on a particular frame ...
pronoun, as opposed to proximal, because there is distance between the speaker and the object being discussed (as opposed to words such as ''this'', where there is a relative sense of closeness).
*When used as a demonstrative adjective, ''that'' describes which specific object is being discussed; for example, in the phrase "that spotted dog is Fido", ''that'' specifies which particular dog is Fido among all spotted dogs.
*In its usage as a conjunction, it connects clauses
In language, a clause is a constituent that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject and a syntactic predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with ...
together, such as in "I know that Peter is right". In sentences with several clauses, ''that'' is also used as a discriminator to differentiate between subjects of a clause.
*As a relative pronoun, ''that'' introduces restrictive clauses, such as in "the different factors that are fundamental and specific to particular features"; in a study of medical science journals in Britain leading up to 2004, it was found that ''that'' had been largely replaced by the word ''which'' when used in this context, while writing that is increasingly formal—ranging from verse to fiction to nonfiction—finds ''that'' usage decreasing as ''wh-'' words (interrogatives
An interrogative word or question word is a function word used to ask a question, such as ''what, which'', ''when'', ''where'', ''who, whom, whose'', ''why'', ''whether'' and ''how''. They are sometimes called wh-words, because in English most of ...
) relatively increase.
*''That'' is used as a relative adverb, such as in "it doesn't cost that much". When used in this way, ''that'' requires inferences be drawn by the listener to determine the meaning of the speaker.
*The word also intensifies elements of a sentence, similar in function to the word ''so'', such as when one says "I was that ill ... I couldn't even stand up." But just as in its use as a relative adverb, ''that'' as an intensifier is best understood when the addressee infers meaning from its usage. In the example given, ''that'' intensifies and refers to a possible view already held by the addressee (whether the speaker was not seriously ill), even though the speaker does not explicitly confirm or intensify this previously-held belief.
Historical usage
 In
In Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
, ''that'' did not exist, and was only represented by '. It originated in the north of England sometime before the 1200s and spread around the country in the thirteenth century; it then rapidly became the dominant demonstrative pronoun. Before the writings of Ælfric of Eynsham
Ælfric of Eynsham ( ang, Ælfrīc; la, Alfricus, Elphricus; ) was an English abbot and a student of Æthelwold of Winchester, and a consummate, prolific writer in Old English of hagiography, homilies, biblical commentaries, and other genres. H ...
, ' was normally regularized as ' in writing, but by the time Ælfric lived, ' was common. As a pronoun, was widely used in Old English, though it was later replaced by ''wh-'' words. Where ' had only stood in for subjects of a clause, instead took on the role of both a subject and an object, and when ' and were both used, was always relative in orientation. The symbol '' ꝥ'' (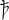 ) was used as an abbreviation, before it was phased out by the Romantic ''þt''. Similarly, ''yͭ'' was a ligature to represent ''that'', as seen in the gravestone of
) was used as an abbreviation, before it was phased out by the Romantic ''þt''. Similarly, ''yͭ'' was a ligature to represent ''that'', as seen in the gravestone of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
: "". In Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
, ' was entirely replaced by (among other representations), before again being replaced by the modern ''that''. Among all relative markers in the English language, including ''who
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book ''Horton Hear ...
'', ''which'', ''whose'', and ''what'', ''that''—through its ancient form of '—appears to be the oldest.
In Old English translations of Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
(but only sparsely in original Old English texts), the phrase ' is frequently used—typically meaning "only"—but its origins and characteristics are not well-understood. Frequently, the construction of ' was in the original Latin, which referred then to a following clause. The use of ' was for cases in which there was exclusivity (to distinguish between general and specific objects), but translators also used it in situations where exclusivity was already given through other syntactical elements of the sentence. In these texts, seems to be used pleonastically (redundantly), and it began to be used as an independent adverb. In the context of weather events, was never used, such as in the example sentence ' (translated as "that rains").
Similarly, for several centuries in Old English and early Middle English texts, the phrase (translated as "among that") persisted. In the hundreds of years of its existence, it was used infrequently, though the usage was stable. Even in Old English, usage of ' ("while") was much more commonplace, with its frequency some six times as large as in a surveyed corpus. experienced grammaticalisation
In historical linguistics, grammaticalization (also known as grammatization or grammaticization) is a process of language change by which words representing objects and actions (i.e. nouns and verbs) become grammatical markers (such as affixes or p ...
(turning a word into a grammatical marker), and as a result of its low usage, possibly underwent a period of specialization, where it competed with other grammaticalised phrases.
After verbs
A verb () is a word (part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descrip ...
such as ''said'', and more generally in introducing a dependent clause
A subordinate clause, dependent clause, subclause, or embedded clause is a clause that is embedded within a complex sentence. For instance, in the English sentence "I know that Bette is a dolphin", the clause "that Bette is a dolphin" occurs as t ...
, contemporary English grammar
English grammar is the set of structural rules of the English language. This includes the structure of words, phrases, clauses, Sentence (linguistics), sentences, and whole texts.
This article describes a generalized, present-day Standard English ...
allows the speaker to either include ''that'' or to omit it. This construction—as in "I suspect (that) he is right"—is called the zero form when ''that'' is not used. While there has been some analysis of the relative frequency of Old and Middle English usage of the zero form, these studies are of limited value, since they rely on unique text corpora
In linguistics, a corpus (plural ''corpora'') or text corpus is a language resource consisting of a large and structured set of texts (nowadays usually electronically stored and processed). In corpus linguistics, they are used to do statistical ...
, failing to give a general view of its usage. In the late period of Middle English, the linguist Norihiko Otsu determined, the zero form was generally as popular as the form in which ''that'' is included. The zero form was common in documents closely relating to speech, such as sermons, suggesting spoken English often omitted ''that'' in these contexts.
Pronunciation
''That'' has several pronunciations. While inreceived pronunciation
Received Pronunciation (RP) is the Accent (sociolinguistics), accent traditionally regarded as the Standard language, standard and most Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestigious form of spoken British English. For over a century, there has been ...
, it is pronounced either as or , in Cameroonian English
Cameroon English is an English dialect spoken predominantly in Cameroon, mostly learned as a second language. It shares some similarities with English varieties in neighbouring West Africa, as Cameroon lies at the west of Central Africa. It is ...
, for example, the is alveolarised as , resulting in a pronunciation of . The weak and strong forms (the two of received pronunciation) of ''that'' vary according to their grammatical roles, with one as a demonstrative and the other as an anaphoric (referencing adverb). In this way, represents a determining pronoun (such as in "what is that?"), while is a subordinating word (as in "that is as it should be").
See also
*Dependent statement In grammar, a dependent statement is a statement converted into a noun clause, normally, in English, by the addition of ''that'' at the beginning, and made dependent on another clause (e.g. as subject or object). For example, the statement ''I had ...
* Deixis
In linguistics, deixis (, ) is the use of general words and phrases to refer to a specific time, place, or person in context, e.g., the words ''tomorrow'', ''there'', and ''they''. Words are deictic if their semantic meaning is fixed but their de ...
References
Citations
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{italic title English grammar English words