Technetium Antigranulocyte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A gallium scan is a type of
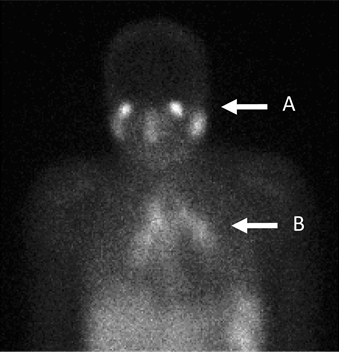 In the past, the gallium scan was the
In the past, the gallium scan was the
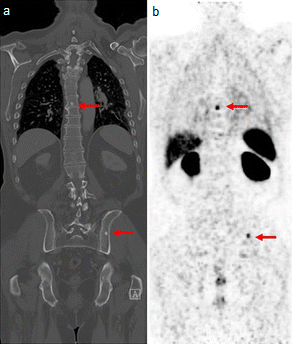 The positron emitting isotope, 68Ga, can be used to target
The positron emitting isotope, 68Ga, can be used to target
nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emit ...
test that uses either a gallium-67
Natural gallium (31Ga) consists of a mixture of two stable isotopes: gallium-69 and gallium-71. The most commercially important radioisotopes are gallium-67 and gallium-68.
Gallium-67 (half-life 3.3 days) is a gamma-emitting isotope (the gamma ...
(67Ga) or gallium-68
Natural gallium (31Ga) consists of a mixture of two stable isotopes: gallium-69 and gallium-71. The most commercially important radioisotopes are gallium-67 and gallium-68.
Gallium-67 (half-life 3.3 days) is a gamma-emitting isotope (the gamma r ...
(68Ga) radiopharmaceutical
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is ...
to obtain images of a specific type of tissue, or disease state of tissue. Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group ( alum ...
salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quanti ...
s like gallium citrate
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in t ...
and gallium nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble ...
may be used. The form of salt is not important, since it is the freely dissolved gallium ion Ga3+ which is active. Both 67Ga and 68Ga salts have similar uptake mechanisms. Gallium can also be used in other forms, for example 68Ga-PSMA is used for cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
imaging. The gamma emission
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically s ...
of gallium-67 is imaged by a gamma camera
A gamma camera (γ-camera), also called a scintillation camera or Anger camera, is a device used to image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy. The applications of scintigraphy include early drug development ...
, while the positron emission
Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (). Positron e ...
of gallium-68 is imaged by positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, ...
(PET).
Gallium salts are taken up by tumors, inflammation, and both acute and chronic infection, allowing these pathological processes to be imaged. Gallium is particularly useful in imaging osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
that involves the spine, and in imaging older and chronic infections that may be the cause of a fever of unknown origin
Fever of unknown origin (FUO) refers to a condition in which the patient has an elevated temperature (fever) but, despite investigations by a physician, no explanation has been found.
.
Gallium-68 DOTA scans are increasingly replacing octreotide scans (a type of indium-111
Indium-111 (111In) is a radioactive isotope of indium (In). It decays by electron capture to stable cadmium-111 with a half-life of 2.8 days.
Indium-111 chloride (111InCl) solution is produced by proton irradiation of a cadmium target (112Cd( ...
scan using octreotide as a somatostatin receptor ligand). The gallium-68 is bound to an octreotide derivative chemical such as DOTATOC and the positrons it emits are imaged by PET-CT
Positron emission tomography–computed tomography (better known as PET-CT or PET/CT) is a nuclear medicine technique which combines, in a single gantry, a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and an x-ray computed tomography (CT) scann ...
scan. Such scans are useful in locating neuroendocrine tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine ( hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lun ...
and pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of panc ...
.
Gallium citrate scan
 In the past, the gallium scan was the
In the past, the gallium scan was the gold standard
A gold standard is a Backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
for lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enl ...
staging, until it was replaced by positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, ...
(PET) using fludeoxyglucose
18F">sup>18Fluorodeoxyglucose (INN), or fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 ( USAN and USP), also commonly called fluorodeoxyglucose and abbreviated 18F">sup>18FDG, 2- 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG, is a radiopharmaceutical, specifically a radiotracer, used in ...
(FDG). Gallium imaging is still used to image inflammation and chronic infections, and it still sometimes locates unsuspected tumors as it is taken up by many kinds of cancer cells in amounts that exceed those of normal tissues. Thus, an increased uptake of gallium-67 may indicate a new or old infection, an inflammatory focus from any cause, or a cancerous tumor.
It has been suggested that gallium imaging may become an obsolete technique, with indium leukocyte imaging
The indium white blood cell scan is a nuclear medicine procedure in which white blood cells (mostly neutrophils) are removed from the patient, tagged with the radioisotope Indium-111, and then injected intravenously into the patient. The tagged le ...
and technetium antigranulocyte antibodies replacing it as a detection mechanism for infections. For detection of tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, especially lymphomas, gallium imaging is still in use, but may be replaced by fludeoxyglucose
18F">sup>18Fluorodeoxyglucose (INN), or fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 ( USAN and USP), also commonly called fluorodeoxyglucose and abbreviated 18F">sup>18FDG, 2- 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG, is a radiopharmaceutical, specifically a radiotracer, used in ...
PET imaging in the future.
In infections, the gallium scan has an advantage over indium leukocyte imaging in imaging osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
(bone infection) of the spine, lung infections and inflammation, and for chronic infections. In part this is because gallium binds to neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
membranes, even after neutrophil death. Indium leukocyte imaging is better for acute infections (where neutrophils are still rapidly and actively localizing to the infection), and also for osteomyelitis that does not involve the spine, and for abdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso ...
and pelvic
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
infections. Both the gallium scan and indium leukocyte imaging may be used to image fever of unknown origin
Fever of unknown origin (FUO) refers to a condition in which the patient has an elevated temperature (fever) but, despite investigations by a physician, no explanation has been found.
(elevated temperature without an explanation). However, the indium leukocyte scan will image only the 25% of such cases which are caused by acute infections, while gallium will also localize to other sources of fever, such as chronic infections and tumors.
Mechanism
The body generally handles Ga3+ as though it wereferric
In chemistry, iron(III) refers to the element iron in its +3 oxidation state. In ionic compounds (salts), such an atom may occur as a separate cation (positive ion) denoted by Fe3+.
The adjective ferric or the prefix ferri- is often used to s ...
iron (Fe-III), and thus the free isotope ion is bound (and concentrates) in areas of inflammation, such as an infection site, and also areas of rapid cell division. Gallium (III) (Ga3+) binds to transferrin
Transferrins are glycoproteins found in vertebrates which bind to and consequently mediate the transport of iron (Fe) through blood plasma. They are produced in the liver and contain binding sites for two Fe3+ ions. Human transferrin is encoded ...
, leukocyte
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mul ...
lactoferrin
Lactoferrin (LF), also known as lactotransferrin (LTF), is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, ...
, bacterial
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
siderophore
Siderophores (Greek: "iron carrier") are small, high-affinity iron- chelating compounds that are secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. They help the organism accumulate iron. Although a widening range of siderophore functions is n ...
s, inflammatory protein
Inflammatory may refer to:
* Inflammation, a biological response to harmful stimuli
* The word ''inflammatory'' is also used to refer literally to fire and flammability, and figuratively in relation to comments that are provocative and arouse pa ...
s, and cell-membranes in neutrophils, both living and dead.
Lactoferrin is contained within leukocytes. Gallium may bind to lactoferrin and be transported to sites of inflammation, or binds to lactoferrin released during bacterial phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis i ...
at infection sites (and remains due to binding with macrophage receptors). Gallium-67 also attaches to the siderophore molecules of bacteria themselves, and for this reason can be used in leukopenic
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of leukocytes (WBC). Found in the blood, they are the white blood cells, and are the body's primary defense against an infection. Thus the condition of leukopenia places individuals at increased risk of ...
patients with bacterial infection (here it attaches directly to bacterial proteins, and leukocytes are not needed). Uptake is thought to be associated with a range of tumour properties including transferring receptors, anaerobic tumor metabolism and tumor perfusion and vascular permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the capacity of a blood vessel wall to allow for the flow of small molecules (drugs, nutrients, water, ions) or even whole cells ( lymp ...
.
Common indications
*Whole-body survey to localize source of fever in patients with fever of unknown origin. *Detection ofpulmonary
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
and mediastinal
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
inflammation/infection, especially in the immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
patient.
*Evaluation and follow-up of active lymphocytic or granulomatous inflammatory processes such as sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly af ...
or tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
.
*Diagnosing vertebral osteomyelitis and/or disk space infection where gallium-67 is preferred over labeled leukocytes.
*Diagnosis and follow-up of medical treatment of retroperitoneal fibrosis
Retroperitoneal fibrosis or Ormond's disease is a disease featuring the proliferation of fibrous tissue in the retroperitoneum, the compartment of the body containing the kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and various other structures. It may present wi ...
.
*Evaluation and follow-up of drug-induced pulmonary toxicity Pulmonary toxicity is the medical name for side effects on the lungs.
Although most cases of pulmonary toxicity in medicine are due to side effects of medicinal drugs, many cases can be due to side effects of radiation (radiotherapy). Other (non-me ...
(e.g. Bleomycin, Amiodarone)
*Evaluation of patients who are not candidates for WBC scans (WBC count less than 6,000).
Note that all of these conditions are also seen in PET scans using the gallium-68.
Technique
The main (67Ga) technique usesscintigraphy
Scintigraphy (from Latin ''scintilla'', "spark"), also known as a gamma scan, is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally and ...
to produce two-dimensional images. After the tracer has been injected, images are typically taken by a gamma camera
A gamma camera (γ-camera), also called a scintillation camera or Anger camera, is a device used to image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy. The applications of scintigraphy include early drug development ...
at 24, 48, and in some cases, 72, and 96 hours later. Each set of images takes 30–60 minutes, depending on the size of the area being imaged. The resulting image will have bright areas that collected large amounts of tracer, because inflammation is present or rapid cell division is occurring. Single-photon emission computed tomography
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, ...
(SPECT) images may also be acquired. In some imaging centers, SPECT images may be combined with computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
(CT) scan using either fusion software or SPECT/CT hybrid cameras to superimpose both physiological image-information from the gallium scan, and anatomical information from the CT scan.
A common injection dose is around 150 megabecquerels. Imaging should not usually be sooner than 24 hours as high background at this time produces false negatives. Forty-eight-hour whole body images are appropriate. Delayed imaging can be obtained even 1 week or longer after injection if bowel is confounding. SPECT can be performed as needed. Oral laxatives or enemas can be given before imaging to reduce bowel activity and reduce dose to large bowel; however, the usefulness of bowel preparation is controversial.
10% to 25% of the dose of gallium-67 is excreted within 24 hours after injection (the majority of which is excreted through the kidneys). After 24 hours the principal excretory pathway is colon. The "target organ" (organ that receives the largest radiation dose in the average scan) is the colon (large bowel).
In a normal scan, uptake of gallium is seen in wide range of locations which do not indicate a positive finding. These typically include soft tissues, liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, and bone. Other sites of localisation can be nasopharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
and lacrimal glands, breasts (particularly in lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The pr ...
or pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
), normally healing wounds, kidneys, bladder and colon.
Gallium PSMA scan
 The positron emitting isotope, 68Ga, can be used to target
The positron emitting isotope, 68Ga, can be used to target prostate-specific membrane antigen
Glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII), also known as N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate peptidase I (NAALADase I), NAAG peptidase, or prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''FOLH1'' (folate hydrol ...
(PSMA), a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
which is present in prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
cells. The technique has been shown to improve detection of metastatic
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
disease compared to MRI or CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
s.
In December 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) approved 68Ga PSMA-11 for medical use in the United States. It is indicated
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. There can be multiple indications to use a procedure or medication. An indication can commonly be confused with the term diagnosis. A diagnosis ...
for positron emission tomography (PET) of prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) positive lesions in men with prostate cancer. It is manufactured by the UCLA Biomedical Cyclotron Facility. The FDA approved 68Ga PSMA-11 based on evidence from two clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT0336847 identical to NCT02919111 and Trial 2/NCT02940262 identical to NCT02918357) of male participants with prostate cancer. Some participants were recently diagnosed with the prostate cancer. Other participants were treated before, but there was suspicion that the cancer was spreading because of rising prostate specific antigen or PSA. The trials were conducted at two sites in the United States.
The FDA considers 68Ga PSMA-11 to be a first-in-class medication A first-in-class medication is a pharmaceutical that uses a "new and unique mechanism of action" to treat a particular medical condition. While the Food and Drug Administration's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research tracks first-in-class medica ...
.
Common indications
Gallium PSMA scanning is recommended primarily in cases of biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer, particularly for patients with lowPSA
PSA, PsA, Psa, or psa may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* Posterior spinal artery
* Primary systemic amyloidosis, a disease caused by the accumulation of abnormal proteins
* Prostate-specific antigen, an enzyme used as a blood tracer for prost ...
values, and in patients with high risk disease where metastases are considered likely.
Technique
An intravenous administration of 1.8–2.2 megabecquerels of 68Ga PSMA-11 perkilogram
The kilogram (also kilogramme) is the unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquially ...
of bodyweight is recommended. Imaging should commence approximately 60 minutes after administration with an acquisition from mid-thigh to the base of the skull.
Gallium DOTA scans
68GaDOTA
''Dota'' is a series of strategy video games by Valve. The series began in 2003 with the release of '' Defense of the Ancients'' (''DotA''), a fan-developed multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) mod for the video game '' Warcraft III: Reig ...
conjugated peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
s (including 68Ga DOTA-TATE, DOTA-TOC
Edotreotide ( USAN, also known as ( DOTA0- Phe1- Tyr3) octreotide, DOTA-TOC, DOTATOC) is a substance which, when bound to various radionuclides, is used in the treatment and diagnosis of certain types of cancer. When used therapeutically it is ...
and DOTA-NOC) are used in positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, ...
(PET) imaging of neuroendocrine tumour
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine ( hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lun ...
s (NETs). The scan is similar to the SPECT octreotide scan in that an octreotide-based somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-co ...
analogue (such as edotreotide) is used as the radioligand
A radioligand is a radioactive biochemical substance (in particular, a ligand that is radiolabeled) that is used for diagnosis or for research-oriented study of the receptor systems of the body.
In a neuroimaging application the radioligand is ...
, and there are similar indications and uses as ocreotide scans, however image quality is significantly improved. Somatostatin receptors are overexpressed in many NETs, so that the 68Ga DOTA conjugated peptide is preferentially taken up in these locations, and visualised on the scan. As well as diagnosis and staging of NETs, 68Ga DOTA conjugated peptide imaging may be used for planning and dosimetry Radiation dosimetry in the fields of health physics and radiation protection is the measurement, calculation and assessment of the ionizing radiation dose absorbed by an object, usually the human body. This applies both internally, due to ingested ...
in preparation for lutetium
Lutetium is a chemical element with the symbol Lu and atomic number 71. It is a silvery white metal, which resists corrosion in dry air, but not in moist air. Lutetium is the last element in the lanthanide series, and it is traditionally counted am ...
-177 or yttrium-90
Yttrium-90 () is an isotope of yttrium. Yttrium-90 has found a wide range of uses in radiation therapy to treat some forms of cancer.
Decay
undergoes β− decay to zirconium-90 with a half-life of 64.1 hours and a decay energy of 2.28 ...
DOTA therapy
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many differe ...
.
In June 2016, Netspot (kit for the preparation of gallium Ga-68 dotatate injection) was approved for medical use in the United States.
In August 2019, 68Ga edotreotide injection (68Ga DOTATOC) was approved for medical use in the United States for use with PET imaging for the localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in adults and children.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) approved 68Ga edotreotide (DOTATOC) based on evidence from three clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT#1619865, Trial 2/NCT#1869725, Trial 3/NCT#2441062) of 334 known or suspected neuro-endocrine tumors. The trials were conducted in the United States.
Gallium (68Ga) oxodotreotide was approved for medical use in Canada as Netspot in July 2019, and as Netvision in May 2022.
Radiochemistry of gallium-67
Gallium-67 citrate is produced by a cyclotron. Charged particle bombardment of enriched Zn-68 is used to produce gallium-67. The gallium-67 is then complexed with citric acid to form gallium citrate. The half life of gallium-67 is 78 hours. It decays byelectron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. T ...
, then emits de-excitation gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic wav ...
s that are detected by a gamma camera. Primary emission is at 93 keV Kev can refer to:
Given name
* Kev Adams, French comedian, actor, screenwriter and film producer born Kevin Smadja in 1991
* Kevin Kev Carmody (born 1946), Indigenous Australian singer-songwriter
* Kev Coghlan (born 1988), Scottish Grand Prix mot ...
(39% abundance), followed by 185 keV (21%) and 300 keV (17%). For imaging, multiple gamma camera energy windows are used, typically centred around 93 and 184 keV or 93, 184, and 296 keV.
Radiochemistry of gallium-68
68Ga is produced from decay of germanium-68, which has a 270.8 day half-life, or by the irradiation ofzinc-68
Naturally occurring zinc (30Zn) is composed of the 5 stable isotopes 64Zn, 66Zn, 67Zn, 68Zn, and 70Zn with 64Zn being the most abundant (48.6% natural abundance). Twenty-five radioisotopes have been characterised with the most abundant and sta ...
through a low energy cyclotron. Use of a generator means a supply of 68Ga can be produced easily with minimal infrastructure, for example at sites without a cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: J ...
, commonly used to produce other PET isotopes.
It decays by positron emission
Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (). Positron e ...
and electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. T ...
into zinc-68. Maximum energy of positron emission is at 1.9 MeV.
See also
* Indium scan *Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiati ...
* Nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emit ...
* Gallium-68 generator
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Gallium Scan 2d nuclear medical imaging Radiation therapy Gallium Orphan drugs