Taxation In Luxembourg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tax revenue in 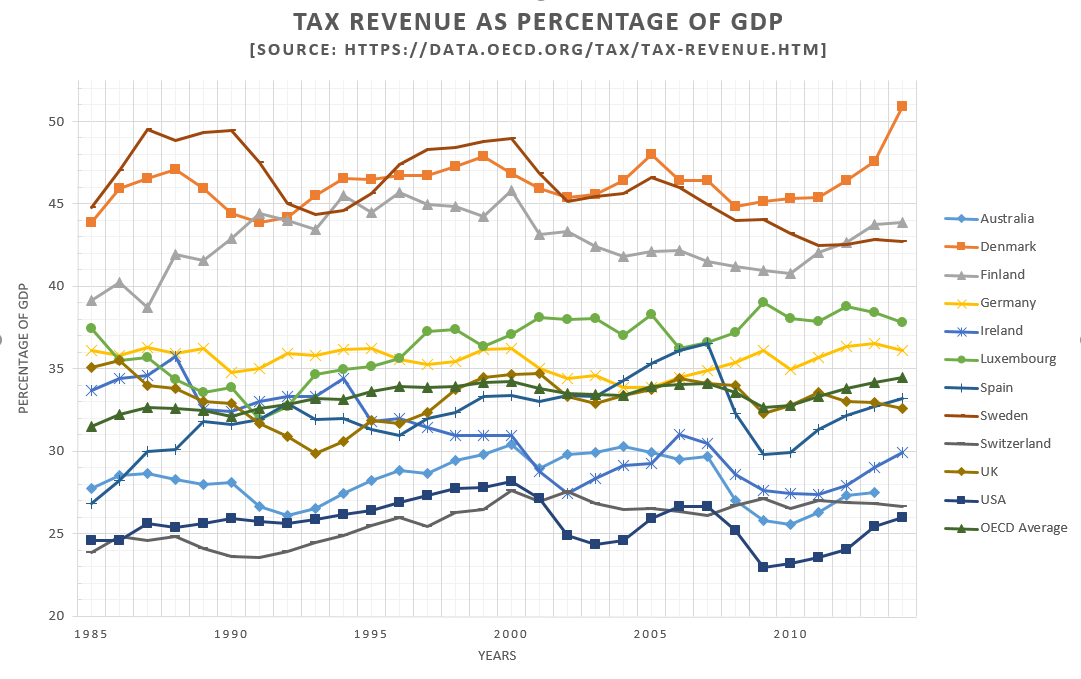
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
(officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg) was 38.65% of GDP in 2017, which is just above the average OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
in 2017 (34.19% of GDP).

Most important revenue sources for the government
The most important revenue sources for the government are: * Corporate income tax * Local business tax * Net wealth tax * Personal income tax * Value added tax Taxes are administrated by government agencies. TheMinister of Finance
A finance minister is an executive or cabinet position in charge of one or more of government finances, economic policy and financial regulation.
A finance minister's portfolio has a large variety of names around the world, such as "treasury", " ...
levies the taxes through the director of Taxation, the revenue offices, and the tax collection offices.
Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
There are two possibilities: either the company is a resident or non-resident. Resident companies: Luxembourg considers a company to be resident if its management headquarter is in the Grand Duchy. Luxembourg resident companies have to pay taxes on their worldwide income once foreign taxes (where the company is present and earns an income) are deducted. Non-resident companies: Luxembourg considers a company to be non-resident if its principle place of management is located outside the country. The only companies that are tax-free are: * Companies with charitable purposes or which work for the general interest * Private-wealth management companies * Undertakings for collective investment In addition to this, there is a solidarity surtax and a municipality business tax on income.Solidarity surtax
There is a 7% solidarity surtax amount that is imposed on the corporate income tax. For instance, for companies with a taxable income that exceeds € 30,000, the aggregate corporate income tax rate is 19.26% (18% + 7% × 18%).Municipal business tax on income
This tax is levied by the municipality and varies within each municipality. For the companies that have their management headquartered in Luxembourg City, the municipal business tax is about 6.75%. For instance, for the companies that have a taxable income that exceeds € 30,000, the effective combined corporate income tax rate is 26.01% (19.26% + 6.75%).Other taxes on business
There are additional taxes on business than the corporate income taxes. For example, there isvalue added tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end ...
(VAT), implemented under the framework provided by the VAT Directive (2006/112/EC), with a general rate of 17% (with reduced rates of 14%, 8%, or 3%).
There is also the net wealth tax (IF) which depends on the assets held:
Personal Income Tax
Resident individuals: Luxembourg considers individuals as tax resident if they have their permanent residence (where they are physically present for an uninterrupted period of more than six months) in Luxembourg. Therefore, owning a residence in Luxembourg is not the only condition for tax residence. People that are resident in Luxembourg are taxed on their worldwide income as though it were earned in Luxembourg. Non-resident individuals are only taxed on their Luxembourg-source income, while part-year residents are taxed at a percentage equivalent to what they would be taxed at if all of their income is earned in Luxembourg. It is possible for non-residents to elect to be treated as though their income is fully from Luxembourg if at least 90% of all income is derived from Luxembourg sources (50% for Belgian-resident individuals).Structure of income tax
In Luxembourg, income tax is divided into eight categories: * Trade and business income * Income from agriculture and forestry * Income from self-employment * Income from employment * Income from pensions and annuities * Income from movable property * Rental income * Miscellaneous income Taxpayers are classified into three main classes that depends on their personal situation: * Class 1: Single individuals without children * Class 1a: Individuals aged > 65, individuals with children, and widow(er)s not covered under class 2 * Class 2: Married couples and for individuals having a partnership contract (joint taxation), for widow(er)s during the first three years of widowhood, and for people who were separated during the first three years of separation (if such a benefit was not accorded in the preceding five years)https://impotsdirects.public.lu/fr/az/c/class_resid.html Tax is calculated with a progressive rate table, ranging from 0% to 42% depending on income. A solidarity surcharge of 7% of income tax is added to income tax, which increases to 9% for tax class 1 and tax class 1a on incomes greater than € 150,000 and for tax class 2 taxpayers on incomes greater than € 300,000. As of 2024, the income tax applicable on class 1 taxpayers is according to the following table: Deductions are possible for, for example, job-related expenses, commuting allowances, insurance premiums, and loan interest. An income-based tax credit for salaried employment of up to €696 applies to incomes of up to €80,000 (in class 1).Social Security Contributions
In Luxembourg, social security contributions are payable by employers and employees. They are divided into five types of fund: * Health insurance * Old-age pension insurance * Long-term care insurance * Accident insurance * Employers’ mutual insurance fund There are different rates that are applicable depending on the type of fund and the employment status. In 2024, the rates are as follows:See also
*Economy of Luxembourg
The economy of Luxembourg is largely dependent on the banking, steel, and industrial sectors. Luxembourgers enjoy the highest Lists of countries by GDP per capita, per capita gross domestic product in the world, according to an International Mon ...
* Social welfare in Luxembourg
* Economy of Europe
References
* * * * * * * {{Taxation in Europe Tax Society of Luxembourg