Tapetum Of The Corpus Callosum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The corpus callosum (

 The corpus callosum forms the floor of the
The corpus callosum forms the floor of the
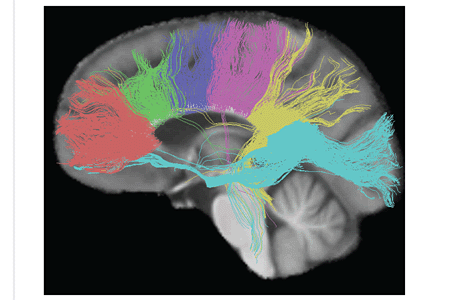 The size, amount of myelination, and density of the fibers in the subregions relate to the functions of the brain regions they connect. Myelination is the process of coating neurons with myelin, which helps the transfer of information between neurons. The process is believed to occur until an individual's thirties with peak growth in the first decade of one's life. Thinner, lightly myelinated fibers are slower conducting and they connect the association and prefrontal areas. Thicker and fast-conducting fibers connect the visual and motor areas.
The tractogram pictured shows the nerve tracts from six segments of the corpus callosum, providing linking of the cortical regions between the cerebral hemispheres. Those of the genu are shown in coral, of the premotor – green, of the sensory-motor – purple, of the parietal – pink, of the temporal – yellow, and of the splenium – blue.
Thinner
The size, amount of myelination, and density of the fibers in the subregions relate to the functions of the brain regions they connect. Myelination is the process of coating neurons with myelin, which helps the transfer of information between neurons. The process is believed to occur until an individual's thirties with peak growth in the first decade of one's life. Thinner, lightly myelinated fibers are slower conducting and they connect the association and prefrontal areas. Thicker and fast-conducting fibers connect the visual and motor areas.
The tractogram pictured shows the nerve tracts from six segments of the corpus callosum, providing linking of the cortical regions between the cerebral hemispheres. Those of the genu are shown in coral, of the premotor – green, of the sensory-motor – purple, of the parietal – pink, of the temporal – yellow, and of the splenium – blue.
Thinner
 The symptoms of refractory (difficult to treat)
The symptoms of refractory (difficult to treat)
File:Slide1oo.JPG, Corpus callosum
File:26638.medium-emphasizing-corpus-callosum.png, Coronal T2 (grey scale inverted) MRI of the brain at the level of the caudate nuclei emphasizing corpus callosum
File:Dti-tractography-normal-corpus-callosum.ogv, Tractography of Corpus callosum
File:Corpus callosum.png, Corpus callosum with Anatomography
File:LocationOfHypothalamus.jpg,
NIF Search – Corpus callosum
via the
National Organization for Disorders of the Corpus Callosum
A 3D model of corpus callosum
{{Authority control Cerebral white matter Articles containing video clips
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fiber
The commissural fibers or transverse fibers are axons that connect the two hemispheres of the brain. In contrast to commissural fibers, association fibers connect regions within the same hemisphere of the brain, and projection fibers connec ...
s, beneath the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consistin ...
in the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, great longitudinal fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continu ...
, connecting the left and right cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distributi ...
structure in the human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the act ...
, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
al projections.
A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium.
Structure

 The corpus callosum forms the floor of the
The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, great longitudinal fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continu ...
that separates the two cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricle
The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively.
Each lateral ventricle resemble ...
s.
The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerve tracts that connect different parts of the hemispheres. These are the rostrum, the genu, the trunk or body, and the splenium. A narrowed part between the trunk and the splenium is known as the isthmus. Fibres from the trunk and the splenium known together as the tapetum form the roof of each lateral ventricle.
The front part of the corpus callosum, towards the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
s, is called the genu ("knee"). The genu curves downward and backward in front of the septum pellucidum
The septum pellucidum (Latin for "translucent wall") is a thin, triangular, vertical double membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain. It runs as a sheet from the corpus callosum down to the f ...
, diminishing greatly in thickness. The lower, much thinner part is the rostrum and is connected below with the lamina terminalis
The median portion of the wall of the forebrain consists of a thin lamina, the lamina terminalis, which stretches from the interventricular foramen (Foramen of Monro) to the recess at the base of the optic stalk (optic nerve) and contains the vas ...
, which stretches from the interventricular foramina to the recess at the base of the optic stalk. The rostrum is named for its resemblance to a bird's beak.
The end part of the corpus callosum, towards the cerebellum, is called the splenium. This is the thickest part, and overlaps the tela choroidea
The tela choroidea (or tela chorioidea) is a region of meningeal pia mater that adheres to the underlying ependyma, and gives rise to the choroid plexus in each of the brain’s four ventricles. ''Tela'' is Latin for ''woven'' and is used to descr ...
of the third ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ...
and the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
, and ends in a thick, convex, free border. Splenium translates as "bandage" in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
.
The trunk of the corpus callosum lies between the splenium and the genu.
The callosal sulcus separates the corpus callosum from the cingulate gyrus
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the ...
.
Relations
On either side of the corpus callosum, the fibers radiate in thewhite matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distributi ...
and pass to the various parts of the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consistin ...
; those curving forward from the genu into the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
s constitute the forceps minor (also forceps anterior) and those curving backward from the splenium into the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the vi ...
s, the forceps major (also forceps posterior). Between these two parts is the main body of the fibers, which constitute the tapetum and extend laterally on either side into the temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pro ...
, and cover in the central part of the lateral ventricle. The tapetum and anterior commissure
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a white matter tract (a bundle of axons) connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. In most exis ...
share the function of connecting left and right temporal lobes.
The anterior cerebral arteries
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from t ...
are in contact with the undersurface of the rostrum; they arch over the front of the genu and are carried along the trunk, supplying the front four-fifths of the corpus callosum.
Neuronal fibers
 The size, amount of myelination, and density of the fibers in the subregions relate to the functions of the brain regions they connect. Myelination is the process of coating neurons with myelin, which helps the transfer of information between neurons. The process is believed to occur until an individual's thirties with peak growth in the first decade of one's life. Thinner, lightly myelinated fibers are slower conducting and they connect the association and prefrontal areas. Thicker and fast-conducting fibers connect the visual and motor areas.
The tractogram pictured shows the nerve tracts from six segments of the corpus callosum, providing linking of the cortical regions between the cerebral hemispheres. Those of the genu are shown in coral, of the premotor – green, of the sensory-motor – purple, of the parietal – pink, of the temporal – yellow, and of the splenium – blue.
Thinner
The size, amount of myelination, and density of the fibers in the subregions relate to the functions of the brain regions they connect. Myelination is the process of coating neurons with myelin, which helps the transfer of information between neurons. The process is believed to occur until an individual's thirties with peak growth in the first decade of one's life. Thinner, lightly myelinated fibers are slower conducting and they connect the association and prefrontal areas. Thicker and fast-conducting fibers connect the visual and motor areas.
The tractogram pictured shows the nerve tracts from six segments of the corpus callosum, providing linking of the cortical regions between the cerebral hemispheres. Those of the genu are shown in coral, of the premotor – green, of the sensory-motor – purple, of the parietal – pink, of the temporal – yellow, and of the splenium – blue.
Thinner axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
s in the genu connect the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
between the two halves of the brain; these fibers arise from a fork-like bundle of fibers from the tapetum, the forceps minor. Thicker axons in the trunk of the corpus callosum, interconnect areas of the motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex believed to be involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
, with proportionately more of the corpus callosum dedicated to supplementary motor regions including Broca's area
Broca's area, or the Broca area (, also , ), is a region in the frontal lobe of the dominant hemisphere, usually the left, of the brain with functions linked to speech production.
Language processing has been linked to Broca's area since Pierr ...
. The splenium, communicates somatosensory
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It i ...
information between the two halves of the parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integrates sensory informa ...
and the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and ...
at the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the vi ...
, these are the fibers of the forceps major.
A study of five- to eighteen-year-olds found a positive correlation between age and callosal thickness.
Variation between sexes
The corpus callosum and its relation to sex has been a subject of debate in the scientific and lay communities for over a century. Initial research in the early 20th century claimed the corpus to be different in size between men and women. That research was, in turn, questioned, and ultimately gave way to more advanced imaging techniques that appeared to refute earlier correlations. However, advanced analytical techniques ofcomputational neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defin ...
developed in the 1990s showed that sex differences were clear, but confined to certain parts of the corpus callosum, and that they correlated with cognitive performance in certain tests. An MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
study found that the midsagittal corpus callosum cross-sectional area is, after controlling for brain size, on average, proportionately larger in females.
Using diffusion tensor sequences on MRI machines, the rate at which molecules diffuse in and out of a specific area of tissue, anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the property of a material which allows it to change or assume different properties in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physic ...
can be measured and used as an indirect measurement of anatomical connection strength. These sequences have found consistent sex differences in human corpus callosal shape and microstructure.
Analysis by shape and size has also been used to study specific three-dimensional mathematical relationships with MRIs, and have found consistent and statistically significant differences between sexes. Specific algorithms have found significant differences between the two sexes in over 70% of cases in one review.
A 2005 study on the sizes and structures of the corpus callosum in transgender people found it to be structurally more in line with their declared gender than their assigned sex.
Correlates of size with handedness
One study reported that the front portion of the human corpus callosum was 0.75 cm2 or 11% larger inleft-handed
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to it being stronger, faster or more dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dextrous or simply less subject ...
and ambidextrous
Ambidexterity is the ability to use both the right and left hand equally well. When referring to objects, the term indicates that the object is equally suitable for right-handed and left-handed people. When referring to humans, it indicates that ...
people than right-handed people. This difference was evident in the anterior and posterior regions of the corpus callosum, but not in the splenium. This has been challenged and others have instead suggested that the degree of handedness negatively correlates with the size of the corpus callosum, meaning that individuals who are capable of using both hands with dexterity would have the largest corpus callosum and vice versa for either left or right hand. However, a recent meta-analysis failed to confirm any substantial handedness-related differences in the corpus callosum.
Clinical significance
Epilepsy
 The symptoms of refractory (difficult to treat)
The symptoms of refractory (difficult to treat) epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
can be reduced by cutting through the corpus callosum in an operation known as a corpus callosotomy
Corpus callosotomy is a palliative surgical procedure for the treatment of medically refractory epilepsy. In this procedure the corpus callosum is cut through in an effort to limit the spread of epileptic activity between the two halves of the ...
lobotomy paralysis. This is usually reserved for cases in which complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
or grand mal
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and commun ...
seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with l ...
are produced by an epileptogenic focus on one side of the brain, causing an interhemispheric electrical storm. The diagnostic work up for this procedure involves an electroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
, MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
, PET scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, ...
, and evaluation by a neurologist, neurosurgeon, psychiatrist, and neuroradiologist before a partial lobotomy surgery can be considered.
Failure to develop
The formation of the corpus callosum begins with the first midline crossing of pioneer axons around week 12 in the prenatal development of the human, or day 15 in the embryogenesis of the mouse. Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rarecongenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities ca ...
that is one of the most common brain malformations observed in human beings, in which the corpus callosum is partially or completely absent. ACC is usually diagnosed within the first two years of life, and may manifest as a severe syndrome in infancy or childhood, as a milder condition in young adults, or as an asymptomatic incidental finding. Initial symptoms of ACC usually include seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with l ...
, which may be followed by feeding problems and delays in holding the head erect, sitting, standing, and walking. Other possible symptoms may include impairments in mental and physical development, hand-eye coordination, and visual and auditory memory. Hydrocephaly may also occur. In mild cases, symptoms such as seizures, repetitive speech, or headaches may not appear for years. Some syndromes often associated with ACC include Aicardi syndrome
Aicardi syndrome is a rare genetic malformation syndrome characterized by the partial or complete absence of a key structure in the brain called the corpus callosum, the presence of retinal lacunes, and epileptic seizures in the form of infanti ...
, Andermann syndrome, Shapiro syndrome
Shapiro syndrome is an extremely rare disorder consisting of paroxysmal hypothermia (due to hypothalamic dysfunction of thermoregulation), hyperhydrosis (sweating), and agenesis of the corpus callosum with onset typically on adulthood. The diseas ...
, and acrocallosal syndrome
Acrocallosal syndrome (also known as ACLS) is an extremely rare autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by corpus callosum agenesis, polydactyly, multiple dysmorphic features, motor and intellectual disabilities, and other symptoms. The syndr ...
.
ACC is usually not fatal. Treatment usually involves management of symptoms, such as hydrocephaly and seizures, if they occur. Although many children with the disorder lead normal lives and have average intelligence, careful neuropsychological testing reveals subtle differences in higher cortical function compared to individuals of the same age and education without ACC. Children with ACC accompanied by developmental delay and/or seizure disorders should be screened for metabolic disorders.
In addition to agenesis of the corpus callosum, similar conditions are hypogenesis (partial formation), dysgenesis (malformation), and hypoplasia (underdevelopment, including too thin).
Other studies have also linked possible correlations between corpus callosum malformation and autism spectrum
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulti ...
disorders.
Kim Peek, a savant
Savant syndrome () is a rare condition in which someone with significant mental disabilities demonstrates certain abilities far in excess of average. The skills that savants excel at are generally related to memory. This may include rapid calcu ...
and the inspiration behind the movie ''Rain Man
''Rain Man'' is a 1988 American road drama film directed by Barry Levinson and written by Barry Morrow and Ronald Bass. It tells the story of abrasive, selfish young wheeler-dealer Charlie Babbitt (Tom Cruise), who discovers that his estranged ...
'', was found with agenesis of the corpus callosum, as part of FG syndrome
FG syndrome (FGS) is a rare genetic syndrome caused by one or more recessive genes located on the X chromosome and causing physical anomalies and developmental delays. FG syndrome was named after the first letters of the surnames of the first pat ...
.
Other disease
Anterior corpus callosum lesions may result in akinetic mutism oranomic aphasia
Anomic aphasia (also known as dysnomia, nominal aphasia, and amnesic aphasia) is a mild, fluent type of aphasia where individuals have word retrieval failures and cannot express the words they want to say (particularly nouns and verbs). By contra ...
.
See also:
* Alien hand syndrome
* Dyslexia without agraphia (seen with damage to splenium of corpus callosum)
*Marchiafava–Bignami disease Marchiafava–Bignami disease is a progressive neurological disease of alcohol use disorder, characterized by corpus callosum demyelination and necrosis and subsequent atrophy. The disease was first described in 1903 by the Italian pathologists Amic ...
a degenerative disease characterised by loss of myelin and necrosis of the corpus callosum
* Multiple sclerosis with the Dawson's fingers sign
*Reversible splenial lesion syndrome
Reversibility can refer to:
* Time reversibility, a property of some mathematical or physical processes and systems for which time-reversed dynamics are well defined
:* Reversible diffusion, an example of a reversible stochastic process
* Reversib ...
– a rare encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; from grc, ἐνκέφαλος "brain" + πάθος "suffering") means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but r ...
of unknown origin with a transient lesion in the splenium, mostly associated with infectious diseases
*Septo-optic dysplasia
Septo-optic dysplasia (SOD), known also as de Morsier syndrome, is a rare congenital malformation syndrome that features a combination of the underdevelopment of the optic nerve, pituitary gland dysfunction, and absence of the septum pellucidum (a ...
(de Morsier syndrome)
*Split-brain
Split-brain or callosal syndrome is a type of disconnection syndrome when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree. It is an association of symptoms produced by disruption of, or interference wit ...
* Susac's syndrome characterised by lesions as small holes in the corpus callosum
History
The first study of the corpus with relation to gender was by R. B. Bean, a Philadelphia anatomist, who suggested in 1906 that "exceptional size of the corpus callosum may mean exceptional intellectual activity" and that there were measurable differences between men and women. Perhaps reflecting the political climate of the times, he went on to claim differences in the size of the callosum across different races. His research was ultimately refuted by Franklin Mall, the director of his own laboratory. Of more mainstream impact was a 1982 ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
'' article by Holloway and Utamsing that suggested sex difference in human brain morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
, which related to differences in cognitive ability. ''Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, ...
'' published an article in 1992 that suggested that, because the corpus is "often wider in the brains of women than in those of men, it may allow for greater cross-talk between the hemispheres—possibly the basis for women’s intuition."
Later publications in the psychology literature have raised doubt as to whether the anatomic size of the corpus is actually different. A meta-analysis of 49 studies since 1980 found that, contrary to de Lacoste-Utamsing and Holloway, no sex difference could be found in the size of the corpus callosum, whether or not any account was taken of larger male brain size. A study in 2006 using thin slice MRI showed no difference in thickness of the corpus when accounting for the size of the subject.
Other animals
The corpus callosum is found only inplacental mammals
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
, while it is absent in monotremes and marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
s, as well as other vertebrates such as birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish. (Other groups do have other brain structures that allow for communication between the two hemispheres, such as the anterior commissure
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a white matter tract (a bundle of axons) connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. In most exis ...
, which serves as the primary mode of interhemispheric communication in marsupials, and which carries all the commissural fiber
The commissural fibers or transverse fibers are axons that connect the two hemispheres of the brain. In contrast to commissural fibers, association fibers connect regions within the same hemisphere of the brain, and projection fibers connec ...
s arising from the neocortex (also known as the neopallium), whereas in placental mammals, the anterior commissure carries only some of these fibers.) In primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s, the speed of nerve transmission depends on its degree of myelination
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
, or lipid coating. This is reflected by the diameter of the nerve axon. In most primates, axonal diameter increases in proportion to brain size to compensate for the increased distance to travel for neural impulse transmission. This allows the brain to coordinate sensory and motor impulses. However, the scaling of overall brain size and increased myelination
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
have not occurred between chimpanzees and human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s. This has resulted in the human corpus callosum's requiring double the time for interhemispheric communication as a macaque's. The fibrous bundle at which the corpus callosum appears, can and does increase to such an extent in humans that it encroaches upon and wedges apart the hippocampal structures.Morris, H., & Schaeffer, J. P. (1953). The Nervous system-The Brain or Encephalon. Human anatomy; a complete systematic treatise. (11th ed., pp. 920–921, 964–965). New York: Blakiston.
Additional images
Sagittal
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divi ...
''post mortem'' section through the midline brain. The corpus callosum is the curved band of lighter tissue at the center of the brain above the hypothalamus. Its lighter texture is due to higher myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
content, resulting in faster neuronal impulse transmission
References
External links
* * Comparative Neuroscience atWikiversity
Wikiversity is a Wikimedia Foundation project that supports learning communities, their learning materials, and resulting activities. It differs from Wikipedia in that it offers tutorials and other materials for the fostering of learning, rather ...
NIF Search – Corpus callosum
via the
Neuroscience Information Framework
The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/genomic resources and provides many auth ...
National Organization for Disorders of the Corpus Callosum
A 3D model of corpus callosum
{{Authority control Cerebral white matter Articles containing video clips