Tahiti Boy And The Palmtree Family on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in

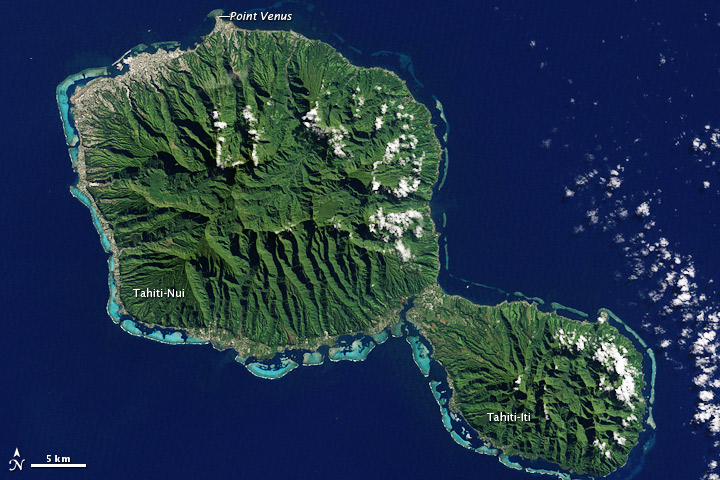 Tahiti is the highest and largest island in French Polynesia lying close to Moorea island. It is located south of Hawaii, from Chile, from Australia.
The island is across at its widest point and covers an area of . The highest peak is Mont Orohena (Moua Orohena) (). Mount Roonui, or Mount Ronui (Moua Rōnui), in the southeast rises to . The island consists of two roughly round portions centered on volcanic mountains and connected by a short isthmus named after the small town of Taravao, which is situated there.
The northwestern portion is known as ''Tahiti Nui'' ("big Tahiti"), while the much smaller southeastern portion is known as ''Tahiti Iti'' ("small Tahiti") or ''Taiarapū''. ''Tahiti Nui'' is heavily populated along the coast, especially around the capital, Papeete.
The interior of ''Tahiti Nui'' is almost entirely uninhabited.Population Densité de population
Tahiti is the highest and largest island in French Polynesia lying close to Moorea island. It is located south of Hawaii, from Chile, from Australia.
The island is across at its widest point and covers an area of . The highest peak is Mont Orohena (Moua Orohena) (). Mount Roonui, or Mount Ronui (Moua Rōnui), in the southeast rises to . The island consists of two roughly round portions centered on volcanic mountains and connected by a short isthmus named after the small town of Taravao, which is situated there.
The northwestern portion is known as ''Tahiti Nui'' ("big Tahiti"), while the much smaller southeastern portion is known as ''Tahiti Iti'' ("small Tahiti") or ''Taiarapū''. ''Tahiti Nui'' is heavily populated along the coast, especially around the capital, Papeete.
The interior of ''Tahiti Nui'' is almost entirely uninhabited.Population Densité de population
Atlas démographique 2007. ispf.pf ''Tahiti Iti'' has remained isolated, as its southeastern half (''Te Pari'') is accessible only to those travelling by boat or on foot. The rest of the island is encircled by a main road which cuts between the mountains and the sea. Tahiti's landscape features lush

. Weatherbase.com. Retrieved 26 September 2007.

 On 2 April 1768, the expedition of Louis-Antoine de Bougainville, aboard and on the first French circumnavigation, sighted Tahiti. On 5 April, they anchored off Hitiaa O Te Ra and were welcomed by its chief Reti. Bougainville was also visited by Tutaha. Bougainville stayed about ten days.
By 12 April 1769 Captain
On 2 April 1768, the expedition of Louis-Antoine de Bougainville, aboard and on the first French circumnavigation, sighted Tahiti. On 5 April, they anchored off Hitiaa O Te Ra and were welcomed by its chief Reti. Bougainville was also visited by Tutaha. Bougainville stayed about ten days.
By 12 April 1769 Captain
 On 26 October 1788, , under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian
On 26 October 1788, , under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian
 In 1819, Pōmare II, encouraged by the missionaries, introduced the first Tahitian legal code, known under the name of the Pōmare Legal Code, which consists of nineteen laws. The missionaries and Pōmare II thus imposed a ban on nudity (obliging them to wear clothes covering their whole body), banned dances and chants (described as immodest), tattoos, and costumes made of flowers.
In the 1820s, the entire population of Tahiti converted to Protestantism. Duperrey, who berthed in Tahiti in May 1823, attests to the change in Tahitian society in a letter dated 15 May 1823: "The missionaries of the Royal Society of London have totally changed the morals and customs of the inhabitants. Idolatry no longer exists among them, and they generally profess the Christian religion. The women no longer come aboard the vessel, and even when we meet them on land they are extremely reserved. (...) The bloody wars that these people used to carry out and human sacrifices have no longer taken place since 1816."
When, on 7 December 1821, Pōmare II died, his son Pōmare III was only eighteen months old. His uncle and the religious people therefore supported the regency, until 2 May 1824, the date on which the missionaries conducted his coronation, a ceremony unprecedented in Tahiti. Taking advantage of the weakness of the Pōmare, local chiefs won back some of their power and took the hereditary title of ''Tavana'' (from the English word "governor"). The missionaries also took advantage of the situation to change the way in which powers were arranged, and to make the Tahitian monarchy closer to the English model of a constitutional monarchy. They therefore created the Tahitian Legislative Assembly, which first sat on 23 February 1824.
In 1827, the young
In 1819, Pōmare II, encouraged by the missionaries, introduced the first Tahitian legal code, known under the name of the Pōmare Legal Code, which consists of nineteen laws. The missionaries and Pōmare II thus imposed a ban on nudity (obliging them to wear clothes covering their whole body), banned dances and chants (described as immodest), tattoos, and costumes made of flowers.
In the 1820s, the entire population of Tahiti converted to Protestantism. Duperrey, who berthed in Tahiti in May 1823, attests to the change in Tahitian society in a letter dated 15 May 1823: "The missionaries of the Royal Society of London have totally changed the morals and customs of the inhabitants. Idolatry no longer exists among them, and they generally profess the Christian religion. The women no longer come aboard the vessel, and even when we meet them on land they are extremely reserved. (...) The bloody wars that these people used to carry out and human sacrifices have no longer taken place since 1816."
When, on 7 December 1821, Pōmare II died, his son Pōmare III was only eighteen months old. His uncle and the religious people therefore supported the regency, until 2 May 1824, the date on which the missionaries conducted his coronation, a ceremony unprecedented in Tahiti. Taking advantage of the weakness of the Pōmare, local chiefs won back some of their power and took the hereditary title of ''Tavana'' (from the English word "governor"). The missionaries also took advantage of the situation to change the way in which powers were arranged, and to make the Tahitian monarchy closer to the English model of a constitutional monarchy. They therefore created the Tahitian Legislative Assembly, which first sat on 23 February 1824.
In 1827, the young  In November 1835 Charles Darwin visited Tahiti aboard HMS ''Beagle'' on her circumnavigation, captained by Robert FitzRoy. He was impressed by what he perceived to be the positive influence the missionaries had had on the sobriety and moral character of the population. Darwin praised the scenery, but was not flattering towards Tahiti's Queen Pōmare IV. Captain Fitzroy negotiated payment of compensation for an attack on an English ship by Tahitians, which had taken place in 1833.
In November 1835 Charles Darwin visited Tahiti aboard HMS ''Beagle'' on her circumnavigation, captained by Robert FitzRoy. He was impressed by what he perceived to be the positive influence the missionaries had had on the sobriety and moral character of the population. Darwin praised the scenery, but was not flattering towards Tahiti's Queen Pōmare IV. Captain Fitzroy negotiated payment of compensation for an attack on an English ship by Tahitians, which had taken place in 1833.
 In Sept. 1839, the island was visited by the United States Exploring Expedition. One of its members,
In Sept. 1839, the island was visited by the United States Exploring Expedition. One of its members,
 In 1877, Queen Pōmare died after ruling for fifty years. Her son, Pōmare V, then succeeded her on the throne. The new king seemed little concerned with the affairs of the kingdom, and when in 1880 the governor Henri Isidore Chessé, supported by the Tahitian chiefs, pushed him to abdicate in favour of France, he accepted. On 29 June 1880, he ceded Tahiti to France along with the islands that were its dependencies. He was given the titular position of Officer of the Orders of the Legion of Honour and Agricultural Merit of France. Having become a colony, Tahiti thus lost all sovereignty. Tahiti was nevertheless a special colony, since all the subjects of the Kingdom of Pōmare would be given French citizenship. On 14 July 1881, among cries of "Vive la République!" the crowds celebrated the fact that Polynesia now belonged to France; this was the first celebration of the Tiurai (national and popular festival). In 1890, Papeete became a commune of the Republic of France.
The French painter Paul Gauguin lived on Tahiti in the 1890s and painted many Tahitian subjects. Papeari has a small Gauguin museum.
In 1891 Matthew Turner, an American shipbuilder from San Francisco who had been seeking a fast passage between the city and Tahiti, built , a two-masted
In 1877, Queen Pōmare died after ruling for fifty years. Her son, Pōmare V, then succeeded her on the throne. The new king seemed little concerned with the affairs of the kingdom, and when in 1880 the governor Henri Isidore Chessé, supported by the Tahitian chiefs, pushed him to abdicate in favour of France, he accepted. On 29 June 1880, he ceded Tahiti to France along with the islands that were its dependencies. He was given the titular position of Officer of the Orders of the Legion of Honour and Agricultural Merit of France. Having become a colony, Tahiti thus lost all sovereignty. Tahiti was nevertheless a special colony, since all the subjects of the Kingdom of Pōmare would be given French citizenship. On 14 July 1881, among cries of "Vive la République!" the crowds celebrated the fact that Polynesia now belonged to France; this was the first celebration of the Tiurai (national and popular festival). In 1890, Papeete became a commune of the Republic of France.
The French painter Paul Gauguin lived on Tahiti in the 1890s and painted many Tahitian subjects. Papeari has a small Gauguin museum.
In 1891 Matthew Turner, an American shipbuilder from San Francisco who had been seeking a fast passage between the city and Tahiti, built , a two-masted
 During the First World War, the Papeete region of the island was attacked by two German warships. A French gunboat as well as a captured German freighter were sunk in the harbour and the two German
During the First World War, the Papeete region of the island was attacked by two German warships. A French gunboat as well as a captured German freighter were sunk in the harbour and the two German

 Tahiti is part of French Polynesia. French Polynesia is a semi-autonomous territory of France with its own assembly, president, budget and laws. France's influence is limited to subsidies, education, and security.
Tahitians are French citizens with complete civil and political rights. French is the official language, but Tahitian and French are both in use. However there was a time during the 1960s and 1970s when children were forbidden to speak Tahitian in schools. Tahitian is now taught in schools; it is sometimes even a requirement for employment.
During a press conference on 26 June 2006 during the second France-Oceania Summit, French President
Tahiti is part of French Polynesia. French Polynesia is a semi-autonomous territory of France with its own assembly, president, budget and laws. France's influence is limited to subsidies, education, and security.
Tahitians are French citizens with complete civil and political rights. French is the official language, but Tahitian and French are both in use. However there was a time during the 1960s and 1970s when children were forbidden to speak Tahitian in schools. Tahitian is now taught in schools; it is sometimes even a requirement for employment.
During a press conference on 26 June 2006 during the second France-Oceania Summit, French President
 The places of birth of the 189,517 residents of the island of Tahiti at the 2017 census were the following:
*75.4% were born in Tahiti (up from 71.5% at the 2007 census)
*9.3% in Metropolitan France (down from 10.9% in 2007)
*5.9% elsewhere in the Society Islands (down from 6.4% in 2007)
*2.8% in the Tuamotu-Gambier (down from 3.3% in 2007)
*1.8% in the Marquesas Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.6% in the Austral Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.3% in the
The places of birth of the 189,517 residents of the island of Tahiti at the 2017 census were the following:
*75.4% were born in Tahiti (up from 71.5% at the 2007 census)
*9.3% in Metropolitan France (down from 10.9% in 2007)
*5.9% elsewhere in the Society Islands (down from 6.4% in 2007)
*2.8% in the Tuamotu-Gambier (down from 3.3% in 2007)
*1.8% in the Marquesas Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.6% in the Austral Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.3% in the
 The main trading partners are Metropolitan France for about 40% of imports and about 25% of exports. The other main trading partners are the US, Japan, Australia and New Zealand.
The main trading partners are Metropolitan France for about 40% of imports and about 25% of exports. The other main trading partners are the US, Japan, Australia and New Zealand.
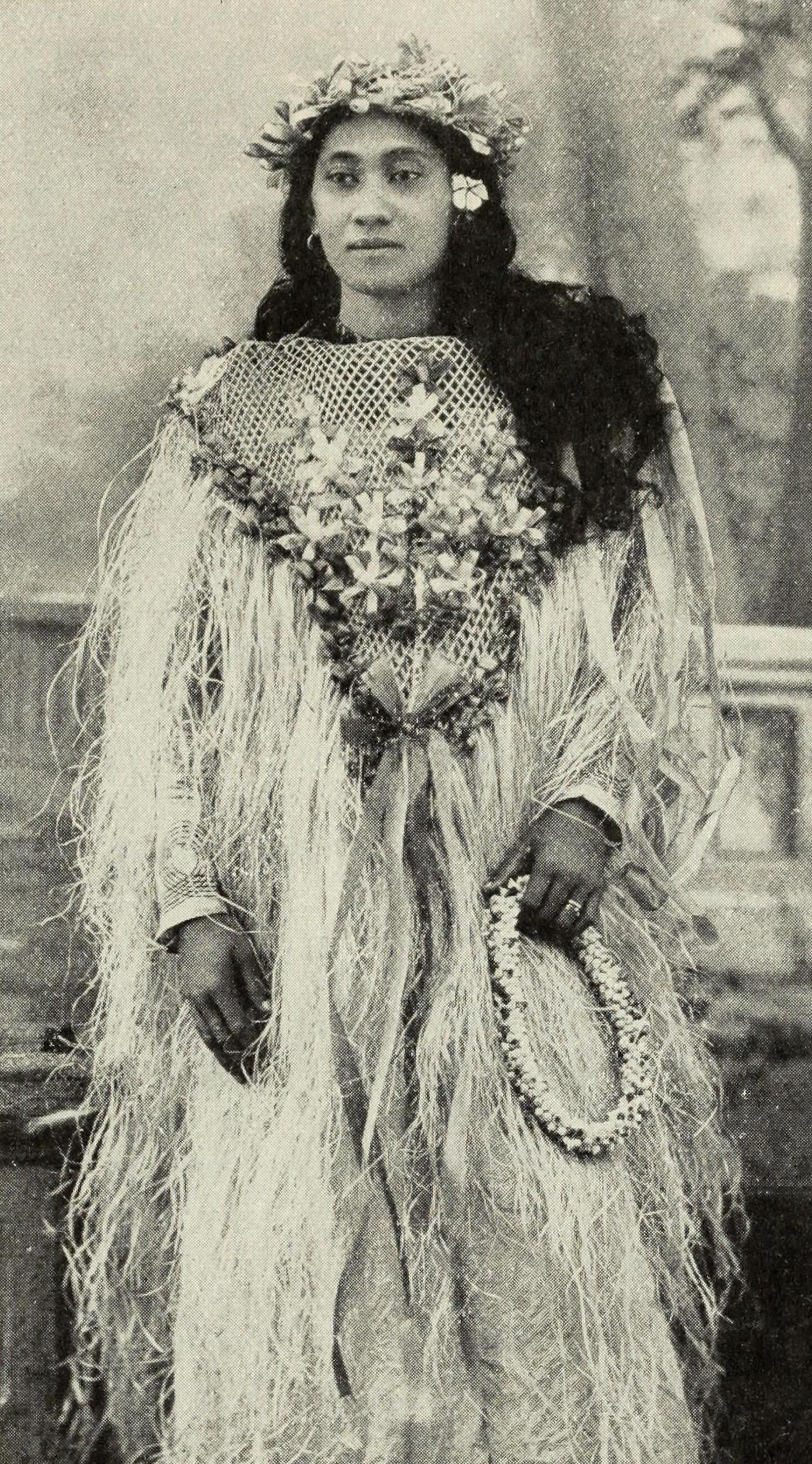 Tahitian cultures included an oral tradition that involved the mythology of gods, such as
Tahitian cultures included an oral tradition that involved the mythology of gods, such as
 One of the most widely recognised images of the islands is the world-famous Tahitian dance. The '' ōtea'' (sometimes written as ''otea'') is a traditional dance from Tahiti, where the dancers, standing in several rows, execute figures. This dance, easily recognised by its fast hip-shaking and grass skirts, is often confused with the Hawaiian hula, a generally slower, more graceful dance which focuses more on the hands and storytelling than the hips.
The ōtea is one of the few dances which existed in pre-European times as a male dance. On the other hand, the ''hura'' (Tahitian vernacular for ''hula''), a dance for women, has disappeared, and the couple's dance ''
One of the most widely recognised images of the islands is the world-famous Tahitian dance. The '' ōtea'' (sometimes written as ''otea'') is a traditional dance from Tahiti, where the dancers, standing in several rows, execute figures. This dance, easily recognised by its fast hip-shaking and grass skirts, is often confused with the Hawaiian hula, a generally slower, more graceful dance which focuses more on the hands and storytelling than the hips.
The ōtea is one of the few dances which existed in pre-European times as a male dance. On the other hand, the ''hura'' (Tahitian vernacular for ''hula''), a dance for women, has disappeared, and the couple's dance ''
 Faaā International Airport is located from Papeete in the commune of Faaā and is the only
Faaā International Airport is located from Papeete in the commune of Faaā and is the only
Official Tahiti website
Tahiti documentary
CIA Factbook entry
Tahitian Heritage
in French with Google Translation available {{Communes of Tahiti Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Islands of the Society Islands
French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of Frenc ...
. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
. Divided into two parts, ''Tahiti Nui'' (bigger, northwestern part) and ''Tahiti Iti'' (smaller, southeastern part), the island was formed from volcanic activity; it is high and mountainous with surrounding coral reefs. Its population was 189,517 in 2017, making it by far the most populous island in French Polynesia and accounting for 68.7% of its total population.
Tahiti is the economic, cultural and political centre of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity and an overseas country of the French Republic
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
. The capital of French Polynesia, Papeete
Papeete (Tahitian language, Tahitian: ''Papeete'', pronounced ) is the capital city of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of the France, French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. The Communes of France, commune of Papeete is located on the isl ...
, is located on the northwest coast of Tahiti. The only international airport in the region, Faaā International Airport, is on Tahiti near Papeete. Tahiti was originally settled by Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
between 300 and 800CE. They represent about 70% of the island's population, with the rest made up of Europeans, Chinese and those of mixed heritage. The island was part of the Kingdom of Tahiti until its annexation
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
by France in 1880, when it was proclaimed a colony of France, and the inhabitants became French citizens. French is the sole official language, although the Tahitian language (''Reo Tahiti'') is also widely spoken.
Geography

 Tahiti is the highest and largest island in French Polynesia lying close to Moorea island. It is located south of Hawaii, from Chile, from Australia.
The island is across at its widest point and covers an area of . The highest peak is Mont Orohena (Moua Orohena) (). Mount Roonui, or Mount Ronui (Moua Rōnui), in the southeast rises to . The island consists of two roughly round portions centered on volcanic mountains and connected by a short isthmus named after the small town of Taravao, which is situated there.
The northwestern portion is known as ''Tahiti Nui'' ("big Tahiti"), while the much smaller southeastern portion is known as ''Tahiti Iti'' ("small Tahiti") or ''Taiarapū''. ''Tahiti Nui'' is heavily populated along the coast, especially around the capital, Papeete.
The interior of ''Tahiti Nui'' is almost entirely uninhabited.Population Densité de population
Tahiti is the highest and largest island in French Polynesia lying close to Moorea island. It is located south of Hawaii, from Chile, from Australia.
The island is across at its widest point and covers an area of . The highest peak is Mont Orohena (Moua Orohena) (). Mount Roonui, or Mount Ronui (Moua Rōnui), in the southeast rises to . The island consists of two roughly round portions centered on volcanic mountains and connected by a short isthmus named after the small town of Taravao, which is situated there.
The northwestern portion is known as ''Tahiti Nui'' ("big Tahiti"), while the much smaller southeastern portion is known as ''Tahiti Iti'' ("small Tahiti") or ''Taiarapū''. ''Tahiti Nui'' is heavily populated along the coast, especially around the capital, Papeete.
The interior of ''Tahiti Nui'' is almost entirely uninhabited.Population Densité de populationAtlas démographique 2007. ispf.pf ''Tahiti Iti'' has remained isolated, as its southeastern half (''Te Pari'') is accessible only to those travelling by boat or on foot. The rest of the island is encircled by a main road which cuts between the mountains and the sea. Tahiti's landscape features lush
rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
s and many rivers and waterfalls, including the Papenoo on the north side and the Fautaua Falls near Papeete
Papeete (Tahitian language, Tahitian: ''Papeete'', pronounced ) is the capital city of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of the France, French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. The Communes of France, commune of Papeete is located on the isl ...
.
Geology
The Society archipelago is ahotspot volcanic chain
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying Mantle (geology), mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii hotspot, Hawaii, Iceland hotspot, Iceland, ...
consisting of ten islands and atolls. The chain is oriented along the N. 65° W. direction, parallel to the movement of the Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
. Due to the plate movement over the Society hotspot
The Society hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the south Pacific Ocean which is responsible for the formation of the Society Islands, an archipelago of fourteen volcanic islands and atolls spanning around 720 km of the ocean which formed between ...
, the age of the islands decreases from 5 Ma at Maupiti to 0 Ma at Mehetia, where Mehetia is the inferred current location of the hotspot as evidenced by recent seismic activity. Maupiti, the oldest island in the chain, is a highly eroded shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more v ...
with at least 12 thin aa flows, which accumulated fairly rapidly between 4.79 and 4.05 Ma. Bora Bora is another highly eroded shield volcano consisting of basaltic lavas accumulated between 3.83 and 3.1 Ma. The lavas are intersected by post-shield dikes. Tahaa consists of shield-stage basalt with an age of 3.39 Ma, followed by additional eruptions 1.2 Ma later. Raiatea consists of shield-stage basalt followed by post-shield trachytic lava flows, all occurring from 2.75 to 2.29 Ma. Huahine consists of two coalesced basalt shield volcanoes, Huahine Nui and Huahine Iti, with several flows followed by post-shield trachyphonolitic lava domes from 3.08 to 2.06 Ma. Moorea consists of at least 16 flows of shield-stage basalt and post-shield lavas from 2.15 to 1.36 Ma. Tahiti consists of two basalt shield volcanoes, Tahiti Nui and Tahiti Iti, with an age range of 1.67 to 0.25 Ma.

Climate
November to April is the wet season, the wettest month of which is January with of rain in Papeete. August is the driest with . The average temperature ranges between , with little seasonal variation. The lowest and highest temperatures recorded in Papeete are , respectively.Papeete, French Polynesia. Weatherbase.com. Retrieved 26 September 2007.
History
Geological history
About 1.4 million to 870,000 years ago, the island of Tahiti was formed as a volcanic shield.Early settling of Tahiti
The first Tahitians arrived from Western Polynesia some time before 500BCE. Linguistic, biological and archaeological evidence supports a long migration from Southeast Asia via the Fijian, Samoan and Tongan Archipelagos using outrigger canoes that were up to twenty or thirty metres long and could transport families as well as domestic animals.
Civilization before the arrival of the Europeans
Before the arrival of the Europeans, the island was divided into territories, each dominated by a single clan. The most important clans were the closely related Teva i Uta (Teva of the Interior) and the Teva i Tai (Teva of the Sea)Bernard Gille, Antoine Leca (2009) ''Histoire des institutions de l'Océanie française: Polynésie, Nouvelle-Calédonie, Wallis et Futuna'', L'Harmattan, whose combined territory extended from the peninsula in the south of Tahiti Nui. Salvat, p. 187 Clan leadership consisted of a chief (''arii rahi''), nobles (''arii''), and under-chiefs (''Īatoai''). The arii were also the religious leaders, revered for the mana (spiritual power) they inherited as descendants of the gods. As symbols of their power, they wore belts of red feathers. Nonetheless, to exercise their political power, councils or general assemblies composed of the arii and the Īatoai had to be called, especially in case of war. The chief's spiritual power was also limited; each clan's practice was organized around their ''marae'' (stone temple) and its priests.First European visits
The first European to arrive at Tahiti may have been Spanish explorer Juan Fernández in his expedition of 1576–1577. Alternatively, Portuguese navigator Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, serving theSpanish Crown
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
in an expedition to Terra Australis, was perhaps the first European to see Tahiti. He sighted an inhabited island on 10 February 1606. However, it has been suggested that he actually saw the island of Rekareka to the southeast of Tahiti. Hence, although the Spanish and Portuguese made contact with nearby islands, they may not have arrived at Tahiti.
The next stage of European visits to the region came during the period of intense Anglo-French rivalry
Anglo-French (or sometimes Franco-British) may refer to:
*France–United Kingdom relations
*Anglo-Norman language or its decendants, varieties of French used in medieval England
*Anglo-Français and Français (hound), an ancient type of hunting d ...
that filled the twelve years between the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War. The first of these visits, and perhaps the first European visit to Tahiti, was under the command of Captain Samuel Wallis. While circumnavigating the globe in , they sighted the island on 18 June 1767 and then harbored in Matavai Bay between the chiefdom Pare
Pare may refer to:
People with the name
* Emmett Paré (1907-1973), tennis player
* Pare, former member of Kotak, an Indonesian band
* Pare Lorentz (1905-1992), American film director
* Richard Pare (born 1948), English photographer
* Paré, a ...
- Arue (governed by Tu (Tu-nui-e-aa-i-te-Atua) and his regent Tutaha) and the chiefdom Haapape, governed by Amo and his wife "Oberea" ( Purea). The first contacts were difficult, Salvat, pp. 44–45 but to avert all-out war after a British show of force, Oberea laid down peace offerings leading to cordial relations.
 On 2 April 1768, the expedition of Louis-Antoine de Bougainville, aboard and on the first French circumnavigation, sighted Tahiti. On 5 April, they anchored off Hitiaa O Te Ra and were welcomed by its chief Reti. Bougainville was also visited by Tutaha. Bougainville stayed about ten days.
By 12 April 1769 Captain
On 2 April 1768, the expedition of Louis-Antoine de Bougainville, aboard and on the first French circumnavigation, sighted Tahiti. On 5 April, they anchored off Hitiaa O Te Ra and were welcomed by its chief Reti. Bougainville was also visited by Tutaha. Bougainville stayed about ten days.
By 12 April 1769 Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
had arrived in Tahiti's Matavai Bay, commanding . He had been sent on a scientific mission with astronomy, botany, and artistic details. On 14 April Cook met Tutaha and Tepau and the next day he picked the site for a fortified camp at Point Venus for Charles Green's observatory. Botanist Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences.
Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James ...
and artist Sydney Parkinson, along with Cook, gathered valuable information on fauna and flora as well as on native society, language and customs, including the proper name of the island. Cook also met many island chiefs. Cook and ''Endeavour'' left Tahiti on 13 July 1769. Cook estimated the population to be 200,000 including all the nearby islands in the chain. This estimate was reduced to 35,000 by Cook's contemporary, anthropologist and Tahiti expert Douglas L. Oliver.
The Viceroy of Peru, Manuel de Amat y Juniet, under order of the Spanish Crown, organized an expedition to colonize the island in 1772. He would ultimately send three expeditions aboard the ship ''Aguila'', the first two under the command of navigator Domingo de Bonechea. Four Tahitians, Pautu, Tipitipia, Heiao, and Tetuanui, accompanied Bonechea back to Peru in early 1773 after the first ''Aguila'' expedition.
Cook returned to Tahiti between 15 August and 1 September 1773. Greeted by the chiefs, Cook anchored in Vaitepiha Bay before returning to Point Venus. Cook left Tahiti on 14 May 1774.
Pautu and Tetuanui returned to Tahiti with Bonechea aboard ''Aguila'' on 14 November 1774; Tipitipia and Heiao had died. Bonechea died on 26 January 1775 in Tahiti and was buried near the mission he had established at Tautira Bay. Lt Tomas Gayangos took over command and set sail for Peru on 27 January, leaving the Fathers Geronimo Clota and Narciso Gonzalez and the sailors Maximo Rodriguez and Francisco Perez in charge of the mission. On the third ''Aguila'' expedition, under Don Cayetano de Langara, the mission on Tahiti was abandoned on 12 November 1775, when the Fathers successfully begged to be taken back to Lima.
During his final visit in 1777 Cook first moored in Vaitepiha Bay. From there he reunited with many Tahitian clans and established British presence on the remains of the Spanish mission. On 29 September 1777 Cook sailed for Papetoai Bay on Moorea.
British influence and the rise of the Pōmare
Mutineers of the ''Bounty''
 On 26 October 1788, , under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian
On 26 October 1788, , under the command of Captain William Bligh, landed in Tahiti with the mission of carrying Tahitian breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family (Moraceae) believed to be a domesticated descendant of ''Artocarpus camansi'' originating in New Guinea, the Maluku Islands, and the Philippi ...
trees ( Tahitian: ''uru'') to the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
. Sir Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences.
Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James ...
, the botanist from James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
's first expedition, had concluded that this plant would be ideal to feed the African slaves working in the Caribbean plantations at very little cost. The crew remained in Tahiti for about five months, the time needed to transplant the seedlings of the trees. Three weeks after leaving Tahiti, on 28 April 1789, the crew mutinied on the initiative of Fletcher Christian. The mutineers seized the ship and set the captain and most of those members of the crew who remained loyal to him adrift in a ship's boat. A group of mutineers then went back to settle in Tahiti.
Although various explorers had refused to get involved in tribal conflicts, the mutineers from the ''Bounty'' offered their services as mercenaries and furnished arms to the family which became the Pōmare Dynasty. The chief Tū knew how to use their presence in the harbours favoured by sailors to his advantage. As a result of his alliance with the mutineers, he succeeded in considerably increasing his supremacy over the island of Tahiti.
In about 1790, the ambitious chief Tū took the title of king and gave himself the name ''Pōmare''. Captain Bligh explains that this name was a homage to his eldest daughter Teriinavahoroa, who had died of tuberculosis, "an illness that made her cough (''mare'') a lot, especially at night (''pō'')". Thus he became Pōmare I
Pōmare I (c. 1753 – September 3, 1803) (fully in old orthography: Tu-nui-ea-i-te-atua-i-Tarahoi Vaira'atoa Taina Pōmare I; also known as Tu or Tinah or Outu, or more formally as Tu-nui-e-a'a-i-te-atua) was the unifier and first king of T ...
, founding the Pōmare Dynasty and his lineage would be the first to unify Tahiti from 1788 to 1791. He and his descendants founded and expanded Tahitian influence to all of the lands that now constitute modern French Polynesia.
In 1791, under Captain Edward Edwards called at Tahiti and took custody of fourteen of the mutineers. Four were drowned in the sinking of ''Pandora'' on her homeward voyage, three were hanged, four were acquitted, and three were pardoned.
Landings of the whalers
In the 1790s, whalers began landing at Tahiti during their hunting expeditions in the southern hemisphere. The arrival of these whalers, who were subsequently joined by merchants coming from the penal colonies in Australia, marked the first major overturning of traditional Tahitian society. The crews introducedalcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
, arms and infectious diseases to the island, and encouraged prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
, which brought with it venereal disease. These commercial interactions with westerners had catastrophic consequences for the Tahitian population, which shrank rapidly, ravaged by diseases and other cultural factors. During the first decade of the 19th century, the Tahitian population dropped from 16,000 to 8,000–9,000; the French census in 1854 counted a population just under 6,000.
Arrival of the missionaries
On 5 March 1797, representatives of the London Missionary Society landed at Matavai Bay ( Mahina) on board ''Duff'', with the intention of converting the pagan native populations to Christianity. The arrival of these missionaries marked a new turning point for the island of Tahiti, having a lasting impact on the local culture. The first years proved hard work for the missionaries, despite their association with the Pōmare, the importance of whom they were aware of thanks to the reports of earlier sailors. In 1803, upon the death ofPōmare I
Pōmare I (c. 1753 – September 3, 1803) (fully in old orthography: Tu-nui-ea-i-te-atua-i-Tarahoi Vaira'atoa Taina Pōmare I; also known as Tu or Tinah or Outu, or more formally as Tu-nui-e-a'a-i-te-atua) was the unifier and first king of T ...
, his son Vairaatoa succeeded him and took the title of Pōmare II. He allied himself more and more with the missionaries, and from 1803 they taught him reading and the Gospels. Furthermore, the missionaries encouraged his wish to conquer his opponents, so that they would only have to deal with a single political contact, enabling them to develop Christianity in a unified country. The conversion of Pōmare II to Protestantism in 1812 marks moreover the point when Protestantism truly took off on the island.
In about 1810, Pōmare II
Pōmare II (c. 1782 – December 7, 1821) (fully Tu Tunuieaiteatua Pōmare II or in modern orthography Tū Tū-nui-ʻēʻa-i-te-atua Pōmare II; historically misspelled as Tu Tunuiea'aite-a-tua), was the second king of Tahiti between 1782 and 182 ...
married Teremoemoe daughter of the chief of Raiatea, to ally himself with the chiefdoms of the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
. On 12 November 1815, thanks to these alliances, Pōmare II won a decisive battle at Fei Pī (Punaauia), notably against Opuhara, the chief of the powerful clan of Teva. This victory allowed Pōmare II to be styled ''Arii Rahi'', or the king of Tahiti. It was the first time that Tahiti had been united under the control of a single family. This marked the end of Tahitian feudalism and the military aristocracy, which were replaced by an absolute monarchy. At the same time, Protestantism quickly spread, thanks to the support of Pōmare II, and replaced the traditional beliefs. In 1816 the London Missionary Society sent John Williams
John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932)Nylund, Rob (15 November 2022)Classic Connection review ''WBOI'' ("For the second time this year, the Fort Wayne Philharmonic honored American composer, conductor, and arranger John Williams, who wa ...
as a missionary and teacher, and starting in 1817, the Gospels were translated into Tahitian (''Reo Maohi'') and taught in the religious schools. In 1818, the minister William Pascoe Crook
William Pascoe Crook (1775–1846), a missionary, schoolmaster and pastor. He was born in Dartmouth, Devon, England on 29 April 1775. He was the first missionary to document the Marquesas Islands in an ethnographical account after he was sent by ...
founded the city of Papeete
Papeete (Tahitian language, Tahitian: ''Papeete'', pronounced ) is the capital city of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of the France, French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. The Communes of France, commune of Papeete is located on the isl ...
, which became the capital of the island.
 In 1819, Pōmare II, encouraged by the missionaries, introduced the first Tahitian legal code, known under the name of the Pōmare Legal Code, which consists of nineteen laws. The missionaries and Pōmare II thus imposed a ban on nudity (obliging them to wear clothes covering their whole body), banned dances and chants (described as immodest), tattoos, and costumes made of flowers.
In the 1820s, the entire population of Tahiti converted to Protestantism. Duperrey, who berthed in Tahiti in May 1823, attests to the change in Tahitian society in a letter dated 15 May 1823: "The missionaries of the Royal Society of London have totally changed the morals and customs of the inhabitants. Idolatry no longer exists among them, and they generally profess the Christian religion. The women no longer come aboard the vessel, and even when we meet them on land they are extremely reserved. (...) The bloody wars that these people used to carry out and human sacrifices have no longer taken place since 1816."
When, on 7 December 1821, Pōmare II died, his son Pōmare III was only eighteen months old. His uncle and the religious people therefore supported the regency, until 2 May 1824, the date on which the missionaries conducted his coronation, a ceremony unprecedented in Tahiti. Taking advantage of the weakness of the Pōmare, local chiefs won back some of their power and took the hereditary title of ''Tavana'' (from the English word "governor"). The missionaries also took advantage of the situation to change the way in which powers were arranged, and to make the Tahitian monarchy closer to the English model of a constitutional monarchy. They therefore created the Tahitian Legislative Assembly, which first sat on 23 February 1824.
In 1827, the young
In 1819, Pōmare II, encouraged by the missionaries, introduced the first Tahitian legal code, known under the name of the Pōmare Legal Code, which consists of nineteen laws. The missionaries and Pōmare II thus imposed a ban on nudity (obliging them to wear clothes covering their whole body), banned dances and chants (described as immodest), tattoos, and costumes made of flowers.
In the 1820s, the entire population of Tahiti converted to Protestantism. Duperrey, who berthed in Tahiti in May 1823, attests to the change in Tahitian society in a letter dated 15 May 1823: "The missionaries of the Royal Society of London have totally changed the morals and customs of the inhabitants. Idolatry no longer exists among them, and they generally profess the Christian religion. The women no longer come aboard the vessel, and even when we meet them on land they are extremely reserved. (...) The bloody wars that these people used to carry out and human sacrifices have no longer taken place since 1816."
When, on 7 December 1821, Pōmare II died, his son Pōmare III was only eighteen months old. His uncle and the religious people therefore supported the regency, until 2 May 1824, the date on which the missionaries conducted his coronation, a ceremony unprecedented in Tahiti. Taking advantage of the weakness of the Pōmare, local chiefs won back some of their power and took the hereditary title of ''Tavana'' (from the English word "governor"). The missionaries also took advantage of the situation to change the way in which powers were arranged, and to make the Tahitian monarchy closer to the English model of a constitutional monarchy. They therefore created the Tahitian Legislative Assembly, which first sat on 23 February 1824.
In 1827, the young Pōmare III
Pōmare III (1820–1827), born Teriʻitariʻa, was the king of Tahiti between 1821 and 1827. He was the second son of King Pōmare II and his second wife, Queen Teriʻitoʻoterai Tere-moe-moe. Sources differ on his relation to his sister with mi ...
suddenly died, and it was his half-sister, Aimata, aged thirteen, who took the title of Pōmare IV. The Birmingham born missionary George Pritchard, who was the acting British consul, became her main adviser and tried to interest her in the affairs of the kingdom. But the authority of the Queen, who was certainly less charismatic than her father, was challenged by the chiefs, who had won back an important part of their prerogatives since the death of Pōmare II. The power of the Pōmare had become more symbolic than real; time and time again Queen Pōmare, Protestant and anglophile, sought in vain the protection of England.
 In November 1835 Charles Darwin visited Tahiti aboard HMS ''Beagle'' on her circumnavigation, captained by Robert FitzRoy. He was impressed by what he perceived to be the positive influence the missionaries had had on the sobriety and moral character of the population. Darwin praised the scenery, but was not flattering towards Tahiti's Queen Pōmare IV. Captain Fitzroy negotiated payment of compensation for an attack on an English ship by Tahitians, which had taken place in 1833.
In November 1835 Charles Darwin visited Tahiti aboard HMS ''Beagle'' on her circumnavigation, captained by Robert FitzRoy. He was impressed by what he perceived to be the positive influence the missionaries had had on the sobriety and moral character of the population. Darwin praised the scenery, but was not flattering towards Tahiti's Queen Pōmare IV. Captain Fitzroy negotiated payment of compensation for an attack on an English ship by Tahitians, which had taken place in 1833.
 In Sept. 1839, the island was visited by the United States Exploring Expedition. One of its members,
In Sept. 1839, the island was visited by the United States Exploring Expedition. One of its members, Alfred Thomas Agate
Alfred Thomas Agate (February 14, 1812 – January 5, 1846) was a noted American artist, painter and miniaturist.
Agate lived in New York from 1831 to 1838. He studied with his brother, Frederick Styles Agate, a portrait and historical painter ...
, produced a number of sketches of Tahitian life, some of which were later published in the United States.
French protectorate and the end of the Pōmare kingdom
In 1836, the Queen's advisor Pritchard had two French Catholic priests expelled,François Caret
François d'Assise Caret, SS.CC., (born François Toussaint Caret; 4 July 1802 – 26 October 1844) was a French Catholic priest of the Congregation of the Sacred Hearts of Jesus and Mary, a religious institute of the Roman Catholic Church.
Lif ...
and Honoré Laval. As a result, in 1838 France sent Admiral Abel Aubert du Petit-Thouars to obtain reparations. Once his mission had been completed, Admiral Du Petit-Thouars sailed towards the Marquesas Islands, which he annexed in 1842. Also in 1842, a European crisis involving Morocco escalated between France and Great Britain, souring their relations. In August 1842, Admiral Du Petit-Thouars returned and landed in Tahiti. He then made friends with Tahitian chiefs who were hostile to the Pōmare family and favourable to a French protectorate. He had them sign a request for protection in the absence of their Queen, before then approaching her and obliging her to ratify the terms of the treaty of protectorate. The treaty had not even been ratified by France itself when Jacques-Antoine Moerenhout was named royal commissaire alongside Queen Pōmare.
Within the framework of this treaty, France recognised the sovereignty of the Tahitian state. The Queen was responsible for internal affairs, while France would deal with foreign relations and assure the defence of Tahiti, as well as maintain order on the island. Once the treaty had been signed there began a struggle for influence between the English Protestants and the Catholic representatives of France. During the first years of the Protectorate, the Protestants managed to retain a considerable hold over Tahitian society, thanks to their knowledge of the country and its language. George Pritchard had been away at the time. He returned however to work towards indoctrinating the locals against the Roman Catholic French.
Tahitian War of independence (1844–47)
In 1843, the Queen's Protestant advisor, Pritchard, persuaded her to display the Tahitian flag in place of the flag of the Protectorate. By way of reprisal, Admiral Dupetit-Thouars announced the annexation of the Kingdom of Pōmare on 6 November 1843 and set up the governor Armand Joseph Bruat there as the chief of the new colony. He threw Pritchard into prison, and later sent him back to Britain. The annexation caused the Queen to be exiled to the Leeward Islands, and after a period of troubles, a real Franco-Tahitian war began in March 1844. News of Tahiti reached Europe in early 1844. The Frenchstatesman
A statesman or stateswoman typically is a politician who has had a long and respected political career at the national or international level.
Statesman or Statesmen may also refer to:
Newspapers United States
* ''The Statesman'' (Oregon), a n ...
François Guizot
François Pierre Guillaume Guizot (; 4 October 1787 – 12 September 1874) was a French historian, orator, and statesman. Guizot was a dominant figure in French politics prior to the Revolution of 1848.
A conservative liberal who opposed the a ...
, supported by King Louis-Philippe of France, had denounced annexation of the island.
The war ended in December 1846 in favour of the French. The Queen returned from exile in 1847 and agreed to sign a new covenant, considerably reducing her powers, while increasing those of the commissaire. The French nevertheless still reigned over the Kingdom of Tahiti. In 1863, they put an end to the British influence and replaced the British Protestant Missions with the Société des missions évangéliques de Paris (Society of Evangelical Missions of Paris).
During the same period about a thousand Chinese, mainly Cantonese, were recruited at the request of a plantation owner in Tahiti, William Stewart, to work on the great cotton plantation at Atimaono. When the enterprise resulted in bankruptcy in 1873, some Chinese workers returned to their country, but a large number stayed in Tahiti and mixed with the population.
In 1866 the district councils were formed, elected, which were given the powers of the traditional hereditary chiefs. In the context of the republican assimilation, these councils tried their best to protect the traditional way of life of the local people, which was threatened by European influence.
 In 1877, Queen Pōmare died after ruling for fifty years. Her son, Pōmare V, then succeeded her on the throne. The new king seemed little concerned with the affairs of the kingdom, and when in 1880 the governor Henri Isidore Chessé, supported by the Tahitian chiefs, pushed him to abdicate in favour of France, he accepted. On 29 June 1880, he ceded Tahiti to France along with the islands that were its dependencies. He was given the titular position of Officer of the Orders of the Legion of Honour and Agricultural Merit of France. Having become a colony, Tahiti thus lost all sovereignty. Tahiti was nevertheless a special colony, since all the subjects of the Kingdom of Pōmare would be given French citizenship. On 14 July 1881, among cries of "Vive la République!" the crowds celebrated the fact that Polynesia now belonged to France; this was the first celebration of the Tiurai (national and popular festival). In 1890, Papeete became a commune of the Republic of France.
The French painter Paul Gauguin lived on Tahiti in the 1890s and painted many Tahitian subjects. Papeari has a small Gauguin museum.
In 1891 Matthew Turner, an American shipbuilder from San Francisco who had been seeking a fast passage between the city and Tahiti, built , a two-masted
In 1877, Queen Pōmare died after ruling for fifty years. Her son, Pōmare V, then succeeded her on the throne. The new king seemed little concerned with the affairs of the kingdom, and when in 1880 the governor Henri Isidore Chessé, supported by the Tahitian chiefs, pushed him to abdicate in favour of France, he accepted. On 29 June 1880, he ceded Tahiti to France along with the islands that were its dependencies. He was given the titular position of Officer of the Orders of the Legion of Honour and Agricultural Merit of France. Having become a colony, Tahiti thus lost all sovereignty. Tahiti was nevertheless a special colony, since all the subjects of the Kingdom of Pōmare would be given French citizenship. On 14 July 1881, among cries of "Vive la République!" the crowds celebrated the fact that Polynesia now belonged to France; this was the first celebration of the Tiurai (national and popular festival). In 1890, Papeete became a commune of the Republic of France.
The French painter Paul Gauguin lived on Tahiti in the 1890s and painted many Tahitian subjects. Papeari has a small Gauguin museum.
In 1891 Matthew Turner, an American shipbuilder from San Francisco who had been seeking a fast passage between the city and Tahiti, built , a two-masted schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoon ...
that made the trip in seventeen days.
Twentieth century to present
In 1903, the Établissements Français d'Océanie (French Establishments in Oceania) were created, which collected together Tahiti, the other Society Islands, the Austral Islands, the Marquesas Islands and the Tuamotu Archipelago. During the First World War, the Papeete region of the island was attacked by two German warships. A French gunboat as well as a captured German freighter were sunk in the harbour and the two German
During the First World War, the Papeete region of the island was attacked by two German warships. A French gunboat as well as a captured German freighter were sunk in the harbour and the two German armoured cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast eno ...
s bombarded the colony. Between 1966 and 1996 the French Government conducted 193 nuclear bomb tests above and below the atolls of Moruroa and Fangataufa. The last test was conducted on 27 January 1996.
In 1946, Tahiti and the whole of French Polynesia became an overseas territory (''Territoire d'outre-mer''). Tahitians were granted French citizenship, a right that had been campaigned for by nationalist leader Pouvanaa a Oopa
Pouvana'a a O'opa (May 10, 1895 – January 10, 1977) was a Tahitian politician and advocate for French Polynesian independence. He is viewed as the ''metua'' (father) of French Polynesia's independence movement.
Pouvanaa served as a Deputy ...
for many years. On 17 July 1974, the French did a nuclear test over Mururoa Atoll, codenamed , but the atomic cloud and fallout didn't take the direction planned. 42 hours later, the cloud reached Tahiti and the surrounding islands. As much as 111,000 people were affected. Reports showed that some people on Tahiti were exposed to 500 times the maximum allowed level for plutonium. In 2003, French Polynesia's status was changed to that of an overseas collectivity (''collectivité d'outre-mer''), and in 2004 it was declared an overseas country (''pays d'outre-mer'' or ''POM'').
In 2009, Tauatomo Mairau
Tauatomo Mairau (died May 17, 2013) was a member of the royal Tahitian family of Mairau, a descendant of Tahiti’s Queen Pōmare IV. He was born on the island of Rurutu. As of February 2009, Tauatomo Mairau claimed to be the heir to the Tahitia ...
claimed the Tahitian throne and attempted to re-assert the status of the monarchy in court.
Politics
 Tahiti is part of French Polynesia. French Polynesia is a semi-autonomous territory of France with its own assembly, president, budget and laws. France's influence is limited to subsidies, education, and security.
Tahitians are French citizens with complete civil and political rights. French is the official language, but Tahitian and French are both in use. However there was a time during the 1960s and 1970s when children were forbidden to speak Tahitian in schools. Tahitian is now taught in schools; it is sometimes even a requirement for employment.
During a press conference on 26 June 2006 during the second France-Oceania Summit, French President
Tahiti is part of French Polynesia. French Polynesia is a semi-autonomous territory of France with its own assembly, president, budget and laws. France's influence is limited to subsidies, education, and security.
Tahitians are French citizens with complete civil and political rights. French is the official language, but Tahitian and French are both in use. However there was a time during the 1960s and 1970s when children were forbidden to speak Tahitian in schools. Tahitian is now taught in schools; it is sometimes even a requirement for employment.
During a press conference on 26 June 2006 during the second France-Oceania Summit, French President Jacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac (, , ; 29 November 193226 September 2019) was a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. Chirac was previously Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988, as well as Ma ...
said he did not think the majority of Tahitians wanted independence. He would keep an open door to a possible referendum in the future.
Elections for the Assembly of French Polynesia, the Territorial Assembly of French Polynesia, were held on 23 May 2004.
In a surprise result, Oscar Temaru's pro-independence progressive coalition, Union for Democracy
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** Union ...
, formed a government with a one-seat majority in the 57-seat parliament, defeating the conservative party, Tāhōeraa Huiraatira, led by Gaston Flosse. On 8 October 2004, Flosse succeeded in passing a censure motion against the government, provoking a crisis. A controversy is whether the national government of France should use its power to call for new elections in a local government in case of a political crisis.
Demographics
The indigenous Tahitians are of Polynesian ancestry and make up 70% of the population alongside Europeans, East Asians (mostly Chinese), and people of mixed heritage, sometimes referred to as ''Demis''. The places of birth of the 189,517 residents of the island of Tahiti at the 2017 census were the following:
*75.4% were born in Tahiti (up from 71.5% at the 2007 census)
*9.3% in Metropolitan France (down from 10.9% in 2007)
*5.9% elsewhere in the Society Islands (down from 6.4% in 2007)
*2.8% in the Tuamotu-Gambier (down from 3.3% in 2007)
*1.8% in the Marquesas Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.6% in the Austral Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.3% in the
The places of birth of the 189,517 residents of the island of Tahiti at the 2017 census were the following:
*75.4% were born in Tahiti (up from 71.5% at the 2007 census)
*9.3% in Metropolitan France (down from 10.9% in 2007)
*5.9% elsewhere in the Society Islands (down from 6.4% in 2007)
*2.8% in the Tuamotu-Gambier (down from 3.3% in 2007)
*1.8% in the Marquesas Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.6% in the Austral Islands (down from 2.0% in 2007)
*1.3% in the overseas departments and territories of France
Overseas France (french: France d'outre-mer) consists of 13 French-administered territories outside Europe, mostly the remains of the French colonial empire that chose to remain a part of the French state under various statuses after decolon ...
other than French Polynesia (1.0% in New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
and Wallis and Futuna; 0.3% in the other overseas departments and collectivities) (down from 1.6% in 2007)
*0.5% in East and Southeast Asia (same percentage as in 2007)
*0.3% in North Africa (most of them Pieds-Noirs
The ''Pieds-Noirs'' (; ; ''Pied-Noir''), are the people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French rule from 1830 to 1962; the vast majority of whom departed for mainland France as soon as Alger ...
) (down from 0.4% in 2007)
*1.1% in other foreign countries (down from 1.5% in 2007)
Most people from metropolitan France live in Papeete and its suburbs, notably Punaauia, where they made up 16.8% of the population at the 2017 census, and Arue, where they made up 15.9%; these percentages do not include their children born in French Polynesia.
Historical population
Administrative divisions
The island consists of 12 communes, which, along with Moorea-Maiao, make up the Windward Islands administrative subdivision. The capital isPapeete
Papeete (Tahitian language, Tahitian: ''Papeete'', pronounced ) is the capital city of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of the France, French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. The Communes of France, commune of Papeete is located on the isl ...
and the largest commune by population is Faaā while Taiarapu-Est has the largest area.
Communes of Tahiti
The following is a list of communes and their subdivisions sorted alphabetically:Economy
Tourism is a significant industry.Tahitian pearl
The Tahitian pearl (or black pearl) is an organic gem formed from the black lip oyster ('' Pinctada margaritifera'').Newman, Renee. ''Pearl Buying Guide''. "Black Pearls." Los Angeles: International Jewelry Publications, c2005, p. 73 These pearls d ...
(Black pearl) farming is also a substantial source of revenues, most of the pearls being exported to Japan, Europe and the United States. Tahiti also exports vanilla, fruits, flowers, monoi, fish, copra oil, and noni. Tahiti is also home to a single winery, whose vineyards are located on the Rangiroa atoll.
Unemployment affects about 13% of the active population, especially women and unqualified young people.
Tahiti's currency, the French Pacific Franc (CFP, also known as XPF), is pegged to the euro at 1 CFP = EUR .0084 (1 EUR = 119.05 CFP, approx. 113 CFP to the United States dollar in March 2017). Hotels and financial institutions offer exchange services.
Sales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
in Tahiti is called ''Taxe sur la valeur ajoutée'' (TVA or value added tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end ...
(VAT) in English). VAT in 2009 was 10% on tourist services, and 6% on hotels, small boarding houses, food and beverages. VAT on the purchase of goods and products is 16%.
Energy and electricity
French Polynesia imports its petroleum and has no local refinery or production. Daily consumption of imported oil products was 7,430 barrels, according to the US Energy Information Administration.Culture
 Tahitian cultures included an oral tradition that involved the mythology of gods, such as
Tahitian cultures included an oral tradition that involved the mythology of gods, such as Oro
Oro or ORO, meaning gold in Spanish and Italian, may refer to:
Music and dance
* Oro (dance), a Balkan circle dance
* Oro (eagle dance), an eagle dance from Montenegro and Herzegovina
* "Oro" (song), the Serbian entry in the 2008 Eurovision S ...
and beliefs, as well as ancient traditions such as tattooing and navigation. The annual Heivā I Tahiti Festival in July is a celebration of traditional culture, dance, music and sports including a long-distance race between the islands of French Polynesia, in modern outrigger canoes (vaa Vaa may refer to:
* Loch Vaa, a body of water in Highland, Scotland
People with the surname
* Aslaug Vaa (1889–1965), Norwegian poet and playwright
* Dyre Vaa (1903–1980), Norwegian sculptor and painter
See also
* VAA (disambiguation)
* Va' ...
).
The Paul Gauguin Museum is dedicated to the life and works of French artist Paul Gauguin (1848–1903) who resided in Tahiti for years and painted such works as ''Two Tahitian Women
''Two Tahitian Women'' is an 1899 painting by Paul Gauguin. It depicts two topless women, one holding mango blossoms, on the Pacific Island of Tahiti. The painting is part of the permanent collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York ...
'', '' Tahitian Women on the Beach'', and ''Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?
''Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?'' (french: D'où venons-nous ? Que sommes-nous ? Où allons-nous ?) is a painting by French artist Paul Gauguin. The painting was created in Tahiti, and is in the Museum of Fine Arts in B ...
''
The Musée de Tahiti et des Îles (Museum of Tahiti and the Islands) is in Punaauia. It is an ethnographic museum that was founded in 1974 to conserve and restore Polynesian artefacts and cultural practices.
The Robert Wan Pearl Museum is the world's only museum dedicated to pearls. The Papeete Market
Marché Papeete ("municipal market") or Papeete Market is an extensive market place in Papeete, the capital of Tahiti.
The market sells fruit, vegetables, fish, oils, handicrafts (including hats and handbags) and various souvenir items. Vendors a ...
sells local arts and crafts.
Dance
 One of the most widely recognised images of the islands is the world-famous Tahitian dance. The '' ōtea'' (sometimes written as ''otea'') is a traditional dance from Tahiti, where the dancers, standing in several rows, execute figures. This dance, easily recognised by its fast hip-shaking and grass skirts, is often confused with the Hawaiian hula, a generally slower, more graceful dance which focuses more on the hands and storytelling than the hips.
The ōtea is one of the few dances which existed in pre-European times as a male dance. On the other hand, the ''hura'' (Tahitian vernacular for ''hula''), a dance for women, has disappeared, and the couple's dance ''
One of the most widely recognised images of the islands is the world-famous Tahitian dance. The '' ōtea'' (sometimes written as ''otea'') is a traditional dance from Tahiti, where the dancers, standing in several rows, execute figures. This dance, easily recognised by its fast hip-shaking and grass skirts, is often confused with the Hawaiian hula, a generally slower, more graceful dance which focuses more on the hands and storytelling than the hips.
The ōtea is one of the few dances which existed in pre-European times as a male dance. On the other hand, the ''hura'' (Tahitian vernacular for ''hula''), a dance for women, has disappeared, and the couple's dance ''upaupa
The upaupa (often written as upa upa) is a traditional dance from Tahiti. It was mentioned by European explorers, who described it as very indecent. It is not quite clear how similar the gestures at that time were with the now immensely popular ...
'' is likewise gone but may have re-emerged as the tamure. Nowadays, the ōtea can be danced by men (''ōtea tāne''), by women (''ōtea vahine''), or by both genders (''ōtea āmui'', "united ō"). The dance is with music only, drums, but no singing. The drum can be one of the types of the tōere, a laying log of wood with a longitudinal slit, which is struck by one or two sticks. Or it can be the ''pahu'', the ancient Tahitian standing drum covered with a shark skin and struck by the hands or with sticks. The rhythm from the tōere is fast; from the pahu it is slower. A smaller drum, the ''faatete'', can also be used.
The dancers make gestures, re-enacting daily occupations of life. For the men the themes can be chosen from warfare or sailing, and then they may use spears or paddles.
For women the themes are closer to home or from nature: combing their hair or the flight of a butterfly, for example. More elaborate themes can be chosen, for example, one where the dancers end up in a map of Tahiti, highlighting important places. In a proper ōtea the story of the theme should pervade the whole dance.
The group dance called Aparima is often performed with the dancers dressed in pareo and maro. There are two types of aparima: the ''aparima hīmene'' (sung handdance) and the ''aparima vāvā'' (silent handdance), the latter being performed with music only and no singing.
Newer dances include the hivinau The hivinau is a dance from Tahiti where the dancers turn in pairs around the orchestra. It is often either the first or the last dance of a dance festival or used as a transition between two dances.
Although an old dance, it is not traditional, th ...
and the paoa.
Death
The Tahitians believed in the afterlife, a paradise called Rohutu-noanoa. When a Tahitian died, the corpse was wrapped in barkcloth and placed on a funeral bier, ''fare tupapa u'', which was a raised canoe awning on posts surrounded by bamboo. Food for the gods was placed nearby to prevent them from eating the body, which would condemn the spirit to the underworld. Mourners would slash themselves with shark's teeth and smear the blood on barkcloth placed nearby. Most importantly, the Chief Mourner donned the ''parae'', an elaborate costume that included aniridescent
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear to gradually change color as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfl ...
mask made of four polished pearl shell discs. One disk was black, signifying Po, the spirit world, while one was white, signifying Ao, the world of people. A crown of red feathers signified Oro. A curved wooden board, ''pautu'', below the mask contained five polished pearl shells, which signified Hina, the moon goddess. Hanging below were more shells in rows, ''ahu-parau'', representing the Pleiades, believed to be the eyes of former chiefs. Finally, a ceremonial garment, ''tiputa'', covered the body and was decorated with an apron of polished coconut shells, ''ahu-aipu''.
Sport
The Tahitian national sport isVaa Vaa may refer to:
* Loch Vaa, a body of water in Highland, Scotland
People with the surname
* Aslaug Vaa (1889–1965), Norwegian poet and playwright
* Dyre Vaa (1903–1980), Norwegian sculptor and painter
See also
* VAA (disambiguation)
* Va' ...
. In English, this paddle sport is also known as outrigger canoe. The Tahitians consistently achieve record-breaking and top times as world champions in this sport.
Major sports in Tahiti include rugby union and association football and the island has fielded a national basketball team, which is a member of FIBA Oceania.
Another sport is surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitabl ...
, with famous surfers such as Malik Joyeux
Malik Joyeux (31 March 1980 – 2 December 2005) was an accomplished all-around waterman and a professional Big Wave surfer. Known by many as the "petit prince", the Footedness, goofy-foot surfer often gained attention for charging the treacherous ...
and Michel Bourez
Michel Bourez (born 30 December 1985) is a French professional surfer.
Biography
Bourez was born on the island of Rurutu in the Tuamotus Islands in French Polynesia and started surfing at age 13. European champion in 2006, Michel entered the ...
. Teahupoo is one of the deadliest surf breaks in the world.
Rugby union in Tahiti is governed by the Fédération Tahitienne de Rugby de Polynésie Française which was formed in 1989. The Tahiti national rugby union team has been active since 1971 but have only played 12 games since then.
Football in Tahiti
The sport of football in French Polynesia is run by the Fédération Tahitienne de Football
The Tahitian Football Federation (french: Fédération tahitienne de football) is the governing body of football in French Polynesia. The Tahiti's men ...
is administered by the Fédération Tahitienne de Football and was founded in 1938. The Tahiti Division Fédérale
The Tahitian Ligue 1 is the top division of the Fédération Tahitienne de Football in French Polynesia. The league is currently named Ligue 1 Vini for sponsorship reasons.
Competition format
Competition is divided into a regular season and play ...
is the top division on the island and the Tahiti Championnat Enterprise
The Tahitian Ligue 2 is the second tier of the Fédération Tahitienne de Football in French Polynesia.
Competition format
The season begins with a regular league. At the end of the regular season the teams enter a play-off league with the bott ...
is the second tier. Some of the major clubs are AS Manu-Ura, who play in Stade Hamuta
Stade Hamuta is a multi-use stadium in Papeete, Tahiti, in French Polynesia. It is currently used mostly for football matches and hosts the home matches of AS Manu-Ura of the Tahiti Division Fédérale
The Tahitian Ligue 1 is the top division o ...
, AS Pirae
Association Sportive Pirae is a football club from Pirae in Tahiti. They are one of the most successful teams in Tahiti having won the Tahiti Division Fédérale nine times. They are also the first French Polynesian team to have reached the fi ...
, who play in the Stade Pater Te Hono Nui and AS Tefana, who play in the Stade Louis Ganivet
Stade Louis Ganivet is a multi-use stadium in Faaa, Tahiti, in French Polynesia. It is currently used mostly for football matches and hosts the home matches of AS Tefana of the Tahiti Division Fédérale
The Tahitian Ligue 1 is the top division ...
. Lesser clubs include Matavai. In 2012, the national team won the OFC Nations Cup qualifying for the 2013 FIFA Confederations Cup
The 2013 FIFA Confederations Cup was the ninth FIFA Confederations Cup, which was held in Brazil from 15 to 30 June 2013 as a prelude to the 2014 FIFA World Cup. The most recent winners of the six continental championships appeared in the tourna ...
in Brazil and becoming the first team other than Australia or New Zealand to win it.
The Tahiti Cup is the islands' premier football knockout tournament and has been played for since 1938. The winner of the Tahiti Cup goes on to play the winner of the Tahiti Division Fédérale in the Tahiti Coupe des Champions.
In 2010, Tahiti was chosen as the host of the 2013 FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup
The 2013 FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup was the seventh edition of the FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup. Overall, this was the 17th edition of a world cup in beach soccer since the establishment of the ''Beach Soccer World Championships'' which ran from ...
, which was held in September 2013.
Tahiti has also been represented at the World Championship of Pétanque. They are the pre-eminent country in the Oceania region for Pétanque, undoubtedly due to their strong connections to France.
As part of the 2024 Summer Olympics
The 2024 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 2024), officially the Games of the XXXIII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la XXXIIIe Olympiade, links=no) and also known as Paris 2024, is an upcoming international multi-sport event that is s ...
, Tahiti will host the surfing competition. It will be the only sport to be held outside of France as Paris hosts the international competition 15,716 km (9,765 mi) away.
Film
Tahiti is depicted in the biography of Paul Gauguin in the 2017 French film ''Gauguin: Voyage to Tahiti'' portraying his life during his years on Tahiti. Also linked to Tahiti are the various films narrating the story of the 1789 mutiny on HMS ''Bounty'' – e.g. ''Mutiny on the Bounty'' (1962) with actorMarlon Brando
Marlon Brando Jr. (April 3, 1924 – July 1, 2004) was an American actor. Considered one of the most influential actors of the 20th century, he received numerous accolades throughout his career, which spanned six decades, including two Academ ...
, ''The Bounty'' (1984) with Mel Gibson.
Education
Tahiti is home to theUniversity of French Polynesia
The University of French Polynesia (french: Université de la Polynésie française) is a French university located in Puna'auia, French Polynesia.
History
Created by a decree of May 29, 1987, the university was originally called French Pac ...
(Université de la Polynésie Française). It is a growing university, with 3,200 students and 62 researchers. Many courses are available such as law, commerce, science, and literature. There is also the Collège La Mennais
Le Collège La Mennais is a private Roman Catholic mixed secondary school in Papeete, Tahiti.
See also
* List of universities in Polynesia
References
''ENSEIGNEMENT SECONDAIRE''. Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Papeete
The Roman Catholic Arch ...
located in Papeete.
Notable people
*Farahia Teuiria
Farahia Teuiria (born 29 August 1972) in Tahiti is a footballer who plays as a midfielder. He previously played for AS Vaiete. He currently plays for AS Tiaré in the Tahiti Division Fédérale and the Tahiti national football team
The Tahit ...
(born 1972), footballer
Transport
Air
 Faaā International Airport is located from Papeete in the commune of Faaā and is the only
Faaā International Airport is located from Papeete in the commune of Faaā and is the only international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
in French Polynesia. Because of limited level terrain, rather than levelling large stretches of sloping agricultural land, the airport is built primarily on reclaimed land on the coral reef just off-shore.
International destinations such as Auckland, Hanga Roa, Honolulu, Los Angeles, Paris, Santiago de Chile, San Francisco, Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
and Tokyo are served by Air France, Air New Zealand, Air Tahiti Nui French Polynesia's flag carrier, Hawaiian Airlines, United Airlines, French Bee, and LATAM Airlines.
Flights within French Polynesia and to New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
are available from Aircalin and Air Tahiti; Air Tahiti has their headquarters at the airport.
Ferry
The Moorea Ferry operates from Papeete and takes about 45 minutes to travel to Moorea. Other ferries are the Aremiti 5 and the Aremiti 7 and these two ferries sail to Moorea in about half an hour. There are also several ferries that transport people and goods throughout the islands. The Bora Bora cruiseline sails to Bora Bora about once a week. The main hub for these ferries is the Papeete Wharf.Roads
Tahiti has a freeway that runs across the west coast. This freeway starts in Arue and continues across the Papeete urban area. Then it continues along the west coast of Tahiti Nui through smaller villages. The freeway turns east toward Taravao where Tahiti Nui meets Tahiti Iti. Tahiti's west coast freeway keeps going until Teahupoo where the freeway becomes a thin paved road.See also
* * List of volcanoes in French Polynesia * Nuclear-free zone *Omoo
''Omoo: A Narrative of Adventures in the South Seas'' is the second book by American writer Herman Melville, first published in London in 1847, and a sequel to his first South Sea narrative ''Typee'', also based on the author's experiences in the ...
* Postage stamps and postal history of French Polynesia
This is a survey of the postal history and postage stamps of French Polynesia, formerly known as the French Oceania.
The first postage stamps used in French Polynesia were the general stamps of the French Colonies from 1862.
In 1882 a shortage of ...
References
Bibliography
* *Further reading
*External links
Official Tahiti website
Tahiti documentary
CIA Factbook entry
Tahitian Heritage
in French with Google Translation available {{Communes of Tahiti Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Islands of the Society Islands