TT72 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Theban Tomb TT72 is located in the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It was the tomb of Re, who was the First Prophet of
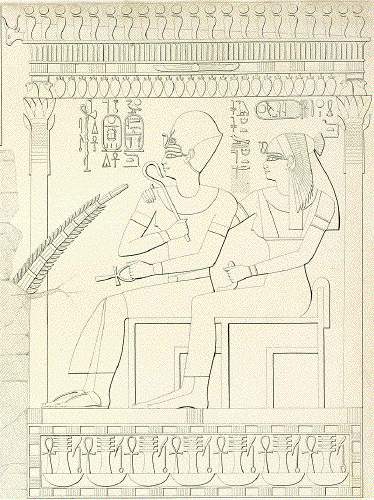 One side of the hall shows several different scenes (numbering refers to the numbering used in Porter and Moss):
# The deceased offering on behalf Thutmosis II
# Several registers showing a banquet with a harpist
# Re seated and offerings to Renenutet as a serpent
# Amenhotep II hunting ibex and ostriches while riding a chariot
# Re with relatives making an offering to Amenhotep II and his mother Merytre-Hatshepsut
# Re seated and family spearing fish
# Re offering to Osiris.
One side of the hall shows several different scenes (numbering refers to the numbering used in Porter and Moss):
# The deceased offering on behalf Thutmosis II
# Several registers showing a banquet with a harpist
# Re seated and offerings to Renenutet as a serpent
# Amenhotep II hunting ibex and ostriches while riding a chariot
# Re with relatives making an offering to Amenhotep II and his mother Merytre-Hatshepsut
# Re seated and family spearing fish
# Re offering to Osiris.
Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as (Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → (Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian ...
in the Mortuary temple of Thutmosis III. The tomb is located in the necropolis area around Sheikh Abd el-Qurna
The necropolis of Sheikh Abd el-Qurna ( ar, شيخ عبدالقرنة) is located on the West Bank at Thebes in Upper Egypt. It is part of the archaeological area of Deir el-Bahari, and named after the domed tomb of the local saint. This is the mo ...
and dates to the time of Amenhotep II.Porter and Moss, Topographical Bibliography: The Theban Necropolis, p. 142
Re was the son of Ahmose (TT121
The Theban Tomb TT120 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The tomb is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Ahmose, who was the second proph ...
), who was a first prophet of Amun and Iret, who was a royal ornament and Singer of Hathor.Peter A. Piccione, A Family of Priests in the Theban Tombs of Ahmose and R‘a (TT 121 and 72), Essays for the Library of Seshat: Studies Presented to Janet H. Johnson on the Occasion of Her 70th Birthday, The Oriental Institute, Chicago, 2017.
Tomb
TT72 has been known for a long time. Lepsius visited and recorded the tomb including the scene depicting Pharaoh Amenhotep II and his motherMerytre-Hatshepsut
Queen Merytre-Hatshepsut (or sometimes Hatshepsut-Meryet-Ra) became the principal wife of Pharaoh Thutmose III after the death of Satiah. She was also the daughter of Adoratrix Huy and the mother of Amenhotep II.
Family
Merytre-Hatshepsut was of ...
. The tomb was first excavated by Weigall in 1907, who noted the fact that one has a clear view of the temple of Thutmosis III from the tomb. TT72 is located fairly close to the tomb of Re's father Ahmose, TT121. In 1913–14 Winlock worked at the tomb and mapped it for the Metropolitan Museum of Arts. Winlock investigated monks cells related to the Coptic Monasteries nearby. Smoke damage in the tomb indicates it was used as a kitchen or smoke house during Coptic times.
The exterior of the tomb shows the use of colonnades, terraces and ramps. This construction emulates the overall structure of royal temples, including the temple of Tuthmosis III called Djeser-Akhet, where Re served as First Prophet. Just above the tomb is the cenotaph to an Egyptian Saint. This structure was built on top of the shrine that Re had constructed.
Hall
 One side of the hall shows several different scenes (numbering refers to the numbering used in Porter and Moss):
# The deceased offering on behalf Thutmosis II
# Several registers showing a banquet with a harpist
# Re seated and offerings to Renenutet as a serpent
# Amenhotep II hunting ibex and ostriches while riding a chariot
# Re with relatives making an offering to Amenhotep II and his mother Merytre-Hatshepsut
# Re seated and family spearing fish
# Re offering to Osiris.
One side of the hall shows several different scenes (numbering refers to the numbering used in Porter and Moss):
# The deceased offering on behalf Thutmosis II
# Several registers showing a banquet with a harpist
# Re seated and offerings to Renenutet as a serpent
# Amenhotep II hunting ibex and ostriches while riding a chariot
# Re with relatives making an offering to Amenhotep II and his mother Merytre-Hatshepsut
# Re seated and family spearing fish
# Re offering to Osiris.
Inner room
The inner room is decorated with funerary scenes including the opening of the mouth. The coffin that was presumably initially put in this room was later found in tombKV35
Tomb KV35 is the tomb of Pharaoh Amenhotep II located in the Valley of the Kings in Luxor, Egypt. Later, it was used as a cache for other royal mummies. It was discovered by Victor Loret in March 1898.
Layout and history
It has a dog's leg shape, ...
, the tomb of Amenhotep II. The coffin contained the mummy of Ramesses VI.
See also
* List of Theban tombsReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:TT071 Buildings and structures completed in the 15th century BC Theban tombs