t-72 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The T-72 is a family of
 GABTU sent a T-64A prototype with a team to Uralvagonzavod. Kartsev was to lead this team.
Kartsev was unsatisfied with the innovations of the T-64, and began instead a more comprehensive project to redesign the tank. Kartsev melded what he believed were the best aspects of the T-64A, Object 167, and an upgunned T-62.
During development the tank was code-named "Ural" after the Ural mountain region. Uralvagonzavod produced the first prototype with a T-62 turret, D-81 125-mm gun and V-45 engine in January 1968. Ob. 439 differed so greatly from the T-64 that it was redesignated as "Object 172".
Kartsev's defiance angered GABTU, which initially reprimanded him for his insubordination. However, after the tank proved indeed to possess potential as a less costly alternative to the T-64, Kartsev was allowed to continue work on his design. Politically motivated opposition continued to beset the tank throughout its development. Vagonka tank plant manager I.F. Krutyakov sought to subordinate Uralvagonzavod under Josef Kotin. Kartsev skillfully beat back this play for power, embarrassing Krutyakov in the process. Kartsev retired in August 1969, and was succeeded by Venediktov.
The team soon found out that the more powerful V-45 engine put a lot of stress on the T-64 hull, so that after some time cracks started to materialize. A more stable solution was sought.
Finally, an idea from 1960 was used, when a modification of the T-62 had been discussed: In 1961, two prototypes of "Object 167" had been built by Uralvagonzavod to test a stronger hull and running gear combination for that tank. Under influence from Kharkiv, the idea had been turned down by Moscow. But this construction, with its big, rubbercoated roadwheels now formed the basis for the mobilisation model of the T-64.
Additional changes were made to the automatic loading system, which also was taken from an earlier project, originally intended for a T-62 upgrade. The 125 mm ammunition, consisting of a separate projectile and a propellant charge, was now stored horizontally on two levels, not vertically on one level as in the T-64. It was said to be more reliable than the T-64 autoloader. In 1964, two 125-mm guns of the D-81 type had been used to evaluate their installation in to the T-62, so the Ural plant was ready to adopt the 125 mm calibre for the T-64A as well.
Venediktov's team later replaced the T-64-style suspension with the Obj. 167's suspension. The tank was trialed in Kubinka in 1968, and Central Asia in 1969. After intensive comparative testing with the T-64A, Object 172 was re-engineered in 1970 to deal with some minor problems. Further trials took place in Transbaikal in 1971.
GABTU sent a T-64A prototype with a team to Uralvagonzavod. Kartsev was to lead this team.
Kartsev was unsatisfied with the innovations of the T-64, and began instead a more comprehensive project to redesign the tank. Kartsev melded what he believed were the best aspects of the T-64A, Object 167, and an upgunned T-62.
During development the tank was code-named "Ural" after the Ural mountain region. Uralvagonzavod produced the first prototype with a T-62 turret, D-81 125-mm gun and V-45 engine in January 1968. Ob. 439 differed so greatly from the T-64 that it was redesignated as "Object 172".
Kartsev's defiance angered GABTU, which initially reprimanded him for his insubordination. However, after the tank proved indeed to possess potential as a less costly alternative to the T-64, Kartsev was allowed to continue work on his design. Politically motivated opposition continued to beset the tank throughout its development. Vagonka tank plant manager I.F. Krutyakov sought to subordinate Uralvagonzavod under Josef Kotin. Kartsev skillfully beat back this play for power, embarrassing Krutyakov in the process. Kartsev retired in August 1969, and was succeeded by Venediktov.
The team soon found out that the more powerful V-45 engine put a lot of stress on the T-64 hull, so that after some time cracks started to materialize. A more stable solution was sought.
Finally, an idea from 1960 was used, when a modification of the T-62 had been discussed: In 1961, two prototypes of "Object 167" had been built by Uralvagonzavod to test a stronger hull and running gear combination for that tank. Under influence from Kharkiv, the idea had been turned down by Moscow. But this construction, with its big, rubbercoated roadwheels now formed the basis for the mobilisation model of the T-64.
Additional changes were made to the automatic loading system, which also was taken from an earlier project, originally intended for a T-62 upgrade. The 125 mm ammunition, consisting of a separate projectile and a propellant charge, was now stored horizontally on two levels, not vertically on one level as in the T-64. It was said to be more reliable than the T-64 autoloader. In 1964, two 125-mm guns of the D-81 type had been used to evaluate their installation in to the T-62, so the Ural plant was ready to adopt the 125 mm calibre for the T-64A as well.
Venediktov's team later replaced the T-64-style suspension with the Obj. 167's suspension. The tank was trialed in Kubinka in 1968, and Central Asia in 1969. After intensive comparative testing with the T-64A, Object 172 was re-engineered in 1970 to deal with some minor problems. Further trials took place in Transbaikal in 1971.
 The first series production of T-72 Object 172M began in July at UKBM in Nizhny Tagil. However, due to difficulties in getting the factory organised for the change in production from T-64 to T-72, only 30 completed tanks were delivered in 1973. Troubles continued in 1974 where out of a state production quota of 440 only 220 were officially declared, with the actual number of completed tanks being close to 150. As a result, substantial investment in tooling was undertaken. Only after modernisation, could the factory begin full-scale production of the T-72. Nizhny Tagil produced the tank in various modifications until 1992.
The T-72 was the most common tank used by the Warsaw Pact from the 1970s until the
The first series production of T-72 Object 172M began in July at UKBM in Nizhny Tagil. However, due to difficulties in getting the factory organised for the change in production from T-64 to T-72, only 30 completed tanks were delivered in 1973. Troubles continued in 1974 where out of a state production quota of 440 only 220 were officially declared, with the actual number of completed tanks being close to 150. As a result, substantial investment in tooling was undertaken. Only after modernisation, could the factory begin full-scale production of the T-72. Nizhny Tagil produced the tank in various modifications until 1992.
The T-72 was the most common tank used by the Warsaw Pact from the 1970s until the  Licensed versions of the T-72 were made in Poland and Czechoslovakia, for Warsaw Pact consumers. These tanks had better and more consistent quality of make but with inferior armour, lacking the resin-embedded ceramics layer inside the turret front and
Licensed versions of the T-72 were made in Poland and Czechoslovakia, for Warsaw Pact consumers. These tanks had better and more consistent quality of make but with inferior armour, lacking the resin-embedded ceramics layer inside the turret front and
 ;T-72A (1979)
:Coincidence rangefinder replaced with
;T-72A (1979)
:Coincidence rangefinder replaced with
* BREM-1 (''Bronirovannaya Remonto-Evakuatsionnaya Mashina'') –
 The T-72 shares many design features with other tank designs of Soviet origin. Some of these are viewed as deficiencies in a straight comparison to NATO tanks, but most are a product of the way these tanks were envisioned to be employed, based on the Soviets' practical experiences in World War II.
The T-72 shares many design features with other tank designs of Soviet origin. Some of these are viewed as deficiencies in a straight comparison to NATO tanks, but most are a product of the way these tanks were envisioned to be employed, based on the Soviets' practical experiences in World War II.
 The T-72 has a nuclear, biological, and chemical ( NBC) protection system. The inside of both hull and turret is lined with a synthetic fabric made of
The T-72 has a nuclear, biological, and chemical ( NBC) protection system. The inside of both hull and turret is lined with a synthetic fabric made of
 Like all Soviet-legacy tanks, the T-72's design has traded off interior space in return for a very small silhouette and efficient use of armour, to the point of replacing the fourth crewman with a mechanical loader. The low height of the tank places constraints on the height of crews, with the USSR having a height limit of 5ft 4in for crews for the T-72. The basic T-72 design has extremely small periscope viewports, even by the constrained standards of battle tanks and the driver's field of vision is significantly reduced when his hatch is closed. The steering system is a traditional dual-tiller layout instead of the easier-to-use steering wheel or steering yoke common in modern Western tanks. This set-up requires the near-constant use of both hands, which complicates employment of the seven speed
Like all Soviet-legacy tanks, the T-72's design has traded off interior space in return for a very small silhouette and efficient use of armour, to the point of replacing the fourth crewman with a mechanical loader. The low height of the tank places constraints on the height of crews, with the USSR having a height limit of 5ft 4in for crews for the T-72. The basic T-72 design has extremely small periscope viewports, even by the constrained standards of battle tanks and the driver's field of vision is significantly reduced when his hatch is closed. The steering system is a traditional dual-tiller layout instead of the easier-to-use steering wheel or steering yoke common in modern Western tanks. This set-up requires the near-constant use of both hands, which complicates employment of the seven speed

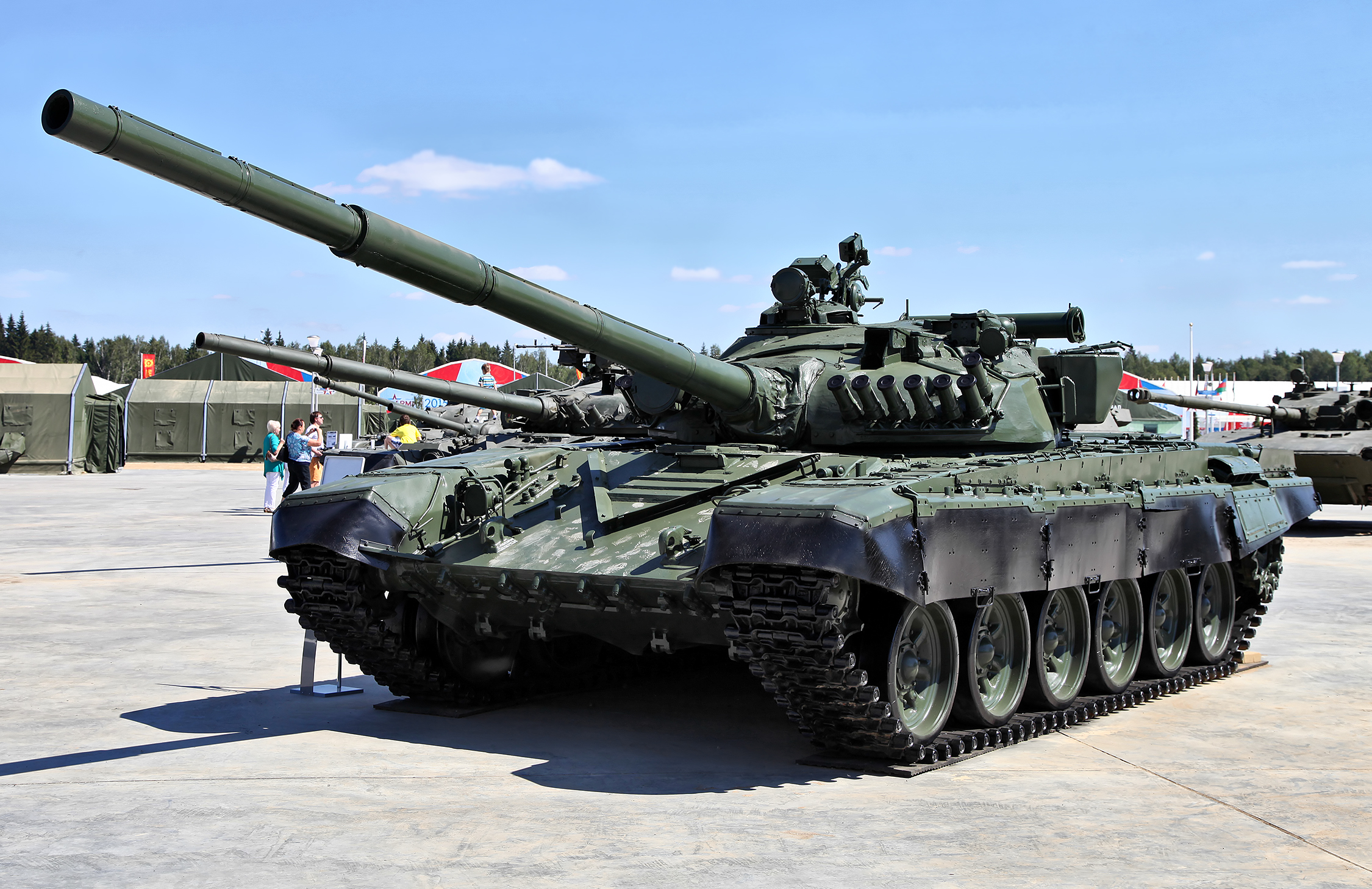
 Armour protection of the T-72 was strengthened with each succeeding generation. The original T-72 "Ural" Object 172M's (from 1973) turret is made from conventional cast high hardness steel (HHS) armour with no laminate inserts. It is believed that the maximum thickness is and the nose is . The glacis of the new laminated armour is thick, comprising HHS, double layer of laminate and RHA steel, which when inclined gives about thickness along the line of sight. In 1977 the armour of the T-72 Object 172M was slightly changed. The turret now featured insert filled with ceramic sand bars "kwartz" rods and the glacis plate composition was changed. It was now made up of HHA steel, glass Tekstolit laminate and RHA steel. This version was often known in Soviet circles as T-72 "Ural-1". The next armour update was introduced by the T-72A (Object 176), which was designed in 1976 and replaced the original on the production lines during 1979–1985. T-72 Object 1976 is also known as T-72A. With the introduction of the T-72B (Object 184) in 1985, the composite armour was again changed. According to retired major, James M. Warford, variants developed after the T-72 base model and T-72M/T-72G MBT, featured a cast steel turret that included a cavity filled with quartz or sand in a form similar to US "fused-silica" armour. The T-72 Model 1978 (Obiekt 172M sb-4), which entered production in 1977, featured a new turret with special armour composed of ceramic rods.
The T-72A featured a new turret with thicker, nearly vertical, frontal armour. Due to its appearance, it was unofficially nicknamed "
Armour protection of the T-72 was strengthened with each succeeding generation. The original T-72 "Ural" Object 172M's (from 1973) turret is made from conventional cast high hardness steel (HHS) armour with no laminate inserts. It is believed that the maximum thickness is and the nose is . The glacis of the new laminated armour is thick, comprising HHS, double layer of laminate and RHA steel, which when inclined gives about thickness along the line of sight. In 1977 the armour of the T-72 Object 172M was slightly changed. The turret now featured insert filled with ceramic sand bars "kwartz" rods and the glacis plate composition was changed. It was now made up of HHA steel, glass Tekstolit laminate and RHA steel. This version was often known in Soviet circles as T-72 "Ural-1". The next armour update was introduced by the T-72A (Object 176), which was designed in 1976 and replaced the original on the production lines during 1979–1985. T-72 Object 1976 is also known as T-72A. With the introduction of the T-72B (Object 184) in 1985, the composite armour was again changed. According to retired major, James M. Warford, variants developed after the T-72 base model and T-72M/T-72G MBT, featured a cast steel turret that included a cavity filled with quartz or sand in a form similar to US "fused-silica" armour. The T-72 Model 1978 (Obiekt 172M sb-4), which entered production in 1977, featured a new turret with special armour composed of ceramic rods.
The T-72A featured a new turret with thicker, nearly vertical, frontal armour. Due to its appearance, it was unofficially nicknamed "
However, after the Soviet collapse, the tank was not accepted. In 2021, Russian Army T-72B3s were seen fitted with raised mesh screens above their turrets. The screens appeared to act as a type of slat armour attempting to protect the tanks from top attack weapons such as the
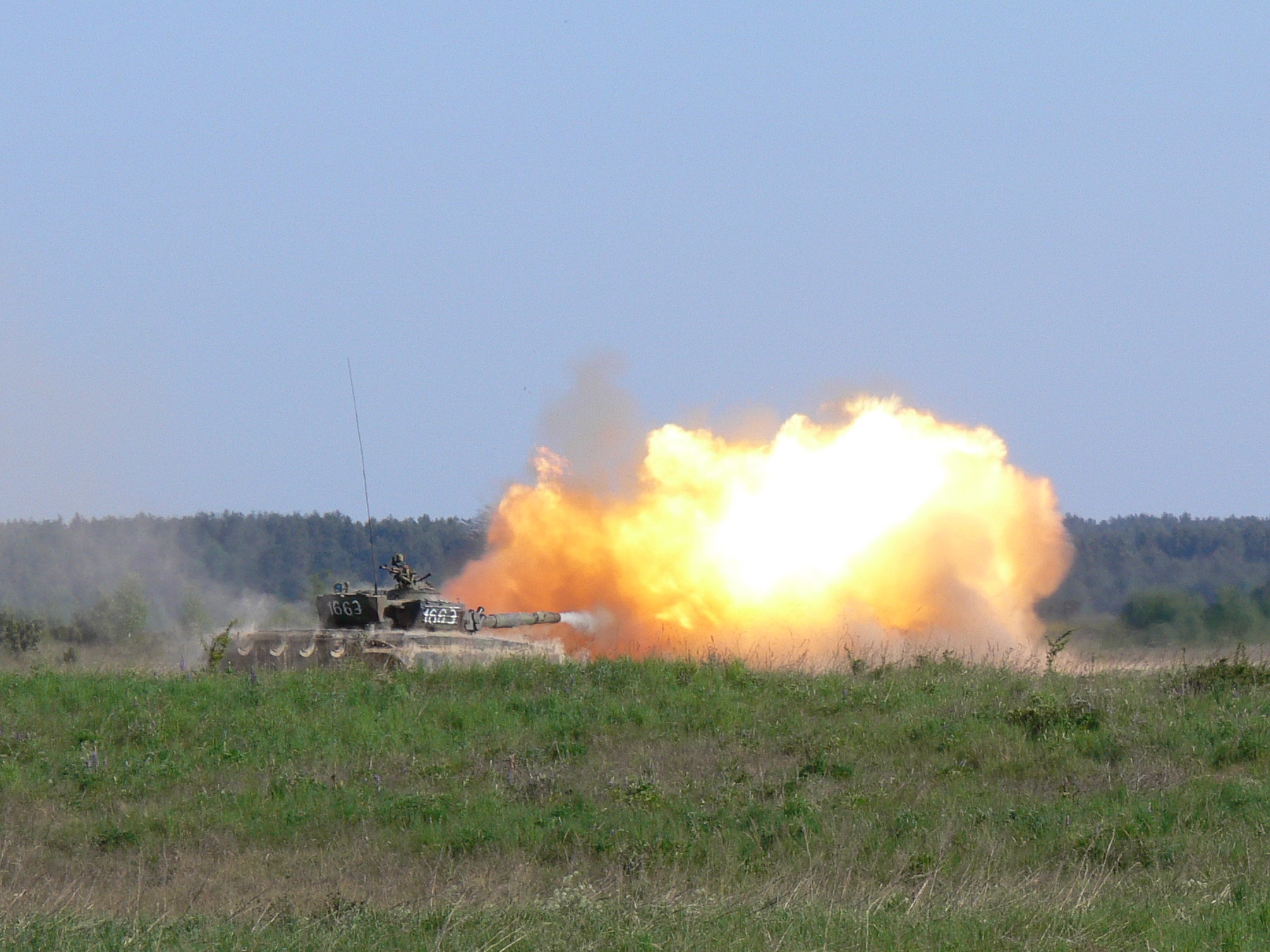 The T-72 is equipped with the 2A46 series main gun, a significantly larger (20-mm larger) calibre than the standard gun found in contemporary Western MBTs, and still slightly larger than the 120 mm/L44 found in many modern Western MBTs. As is typical of Soviet tanks, the gun can fire anti-tank guided missiles, and standard main gun ammunition, including HEAT and APFSDS rounds.
The original T-72 Object 172M (1973) used 2A26M2 model gun first mounted on T-64. The barrel had a length of 6350mm or 50.8 calibers and had maximum rated chamber pressure of 450 MPa. The cannon had an electroplated chrome lining but lacked a thermal sleeve. The cannon was capable of firing 3VBM-3 round with 3BM-9 steel projectile sabot and 3VBM-6 round with 3BM-12 Tungsten sabot APFSDS projectile. Allowing respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. In addition to APFSDS rounds T-72 Object 172M could also fire 3VBK-7 round incorporating 3BK-12 HEAT warhead and 3VBK-10 round incorporating 3BK-14 HEAT warhead. HEAT rounds allowed respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 0 degree angle. The High Explosive rounds provided included 3WOF-22 with 3OF-19 warhead or 3WOF-36 with the 3OF-26 warhead. For all rounds, the Zh40 propellant was used. Complementing the original gun setup was 2E28M "Siren" two-plane electrohydraulic stabilizer allowing automatic stabilization with speeds from 0.05 to 6 degrees per second.
Even as the T-72 Object 172M (1973) was entering production new ammunition was developed to offset armour developments in the West. Beginning in 1972, two new APFSDS rounds were introduced, the 3VBM-7 round with 3BM-15 Tungsten sabot projectile and the "cheaper" 3VBM-8 round with 3BM-17 sabot but without the tungsten carbide plug. These allowed penetration of respectively and RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. At the same time, a universal Zh52 propellant charge was introduced. The 3VBM-7 was the most common APFSDS round found in T-72 Object 172M tanks during the 70s.
The stated barrel life expectancy of the 2A26M2 model gun was 600 rounds of HE/HEAT equivalent to 600 EFC (Effective Full Charge) or 150 rounds of APFSDS.
The main gun of the T-72 has a mean error of at a range of , considered substandard today. Its maximum firing distance is , due to limited positive elevation. The limit of aimed fire is (with the gun-launched
The T-72 is equipped with the 2A46 series main gun, a significantly larger (20-mm larger) calibre than the standard gun found in contemporary Western MBTs, and still slightly larger than the 120 mm/L44 found in many modern Western MBTs. As is typical of Soviet tanks, the gun can fire anti-tank guided missiles, and standard main gun ammunition, including HEAT and APFSDS rounds.
The original T-72 Object 172M (1973) used 2A26M2 model gun first mounted on T-64. The barrel had a length of 6350mm or 50.8 calibers and had maximum rated chamber pressure of 450 MPa. The cannon had an electroplated chrome lining but lacked a thermal sleeve. The cannon was capable of firing 3VBM-3 round with 3BM-9 steel projectile sabot and 3VBM-6 round with 3BM-12 Tungsten sabot APFSDS projectile. Allowing respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. In addition to APFSDS rounds T-72 Object 172M could also fire 3VBK-7 round incorporating 3BK-12 HEAT warhead and 3VBK-10 round incorporating 3BK-14 HEAT warhead. HEAT rounds allowed respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 0 degree angle. The High Explosive rounds provided included 3WOF-22 with 3OF-19 warhead or 3WOF-36 with the 3OF-26 warhead. For all rounds, the Zh40 propellant was used. Complementing the original gun setup was 2E28M "Siren" two-plane electrohydraulic stabilizer allowing automatic stabilization with speeds from 0.05 to 6 degrees per second.
Even as the T-72 Object 172M (1973) was entering production new ammunition was developed to offset armour developments in the West. Beginning in 1972, two new APFSDS rounds were introduced, the 3VBM-7 round with 3BM-15 Tungsten sabot projectile and the "cheaper" 3VBM-8 round with 3BM-17 sabot but without the tungsten carbide plug. These allowed penetration of respectively and RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. At the same time, a universal Zh52 propellant charge was introduced. The 3VBM-7 was the most common APFSDS round found in T-72 Object 172M tanks during the 70s.
The stated barrel life expectancy of the 2A26M2 model gun was 600 rounds of HE/HEAT equivalent to 600 EFC (Effective Full Charge) or 150 rounds of APFSDS.
The main gun of the T-72 has a mean error of at a range of , considered substandard today. Its maximum firing distance is , due to limited positive elevation. The limit of aimed fire is (with the gun-launched
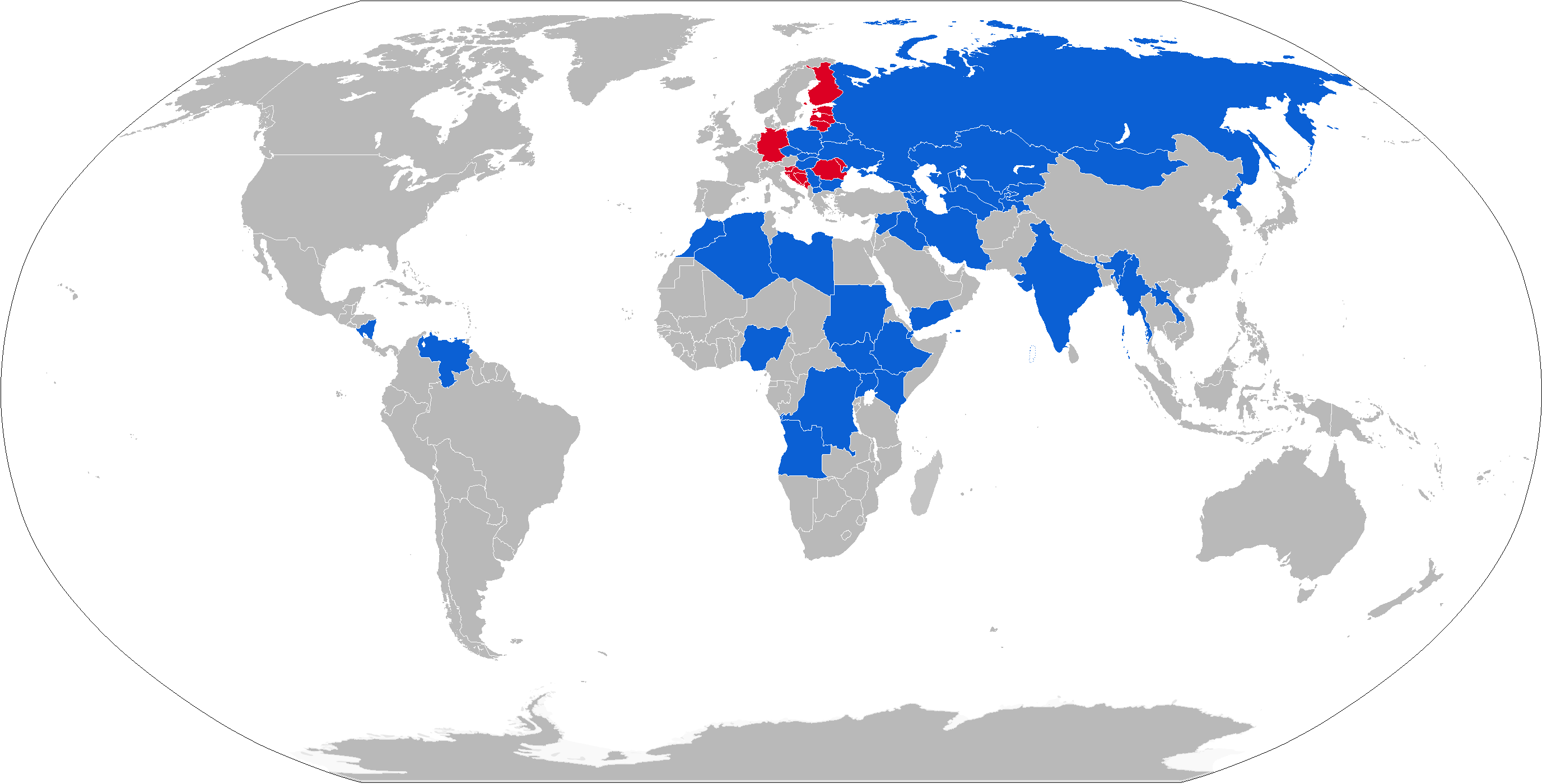
 The T-72 was never used in the
The T-72 was never used in the
 During the war in South Ossetia in 2008 both sides deployed great numbers of T-72 tanks. At the time of the conflict, the Georgian military fielded 191 T-72 tanks of which 120 were modified to T-72Sim1s. The Georgian army deployed a total of 75 of its T-72 tanks into South Ossetia. The Georgian military lost 30 T-72's, ten in combat during the fighting around Tskhinvali, and another 20 destroyed by Russian paratroopers after their capture.
During the war in South Ossetia in 2008 both sides deployed great numbers of T-72 tanks. At the time of the conflict, the Georgian military fielded 191 T-72 tanks of which 120 were modified to T-72Sim1s. The Georgian army deployed a total of 75 of its T-72 tanks into South Ossetia. The Georgian military lost 30 T-72's, ten in combat during the fighting around Tskhinvali, and another 20 destroyed by Russian paratroopers after their capture.

 * 1980–1988:
* 1980–1988:
Vasiliy Fofanov's Modern Russian Armour Page
Huge pile of Hungarian T-72 walkarounds
T-72 variants
* {{Cold War tanks, style=wide T-72 Cold War tanks of the Soviet Union Main battle tanks of the Soviet Union Main battle tanks of Russia Tanks with autoloaders Uralvagonzavod products Tanks of Russia Tanks of the Soviet Union Tanks of the Cold War Military vehicles introduced in the 1970s
Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
/Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
n main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank, is a tank that fills the role of armor-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more powerful engines, better suspension sys ...
s that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks have been built, and refurbishment has enabled many to remain in service for decades. It has been widely exported and has seen service in 40 countries and in numerous conflicts. The T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and comp ...
introduced in 1992 is a development of the T-72B; production and development of various modernized T-72 models continues today.
Development
Development from the T-64
The T-72 was a product of a rivalry between design teams. Morozov KB was led by Alexander Morozov inKharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.
. Uralvagon KB was led by Leonid Kartsev in Nizhny Tagil.
To improve on the T-62, two designs based on the tank were tested in 1964: Nizhny Tagil's Object 167 (T-62B) and Kharkiv's Object 434.
Ob. 434 was a technically ambitious prototype. Under the direction of Morozov in Kharkiv, a new design emerged with the hull reduced to the minimum size possible. To do this, the crew was reduced to three soldiers, removing the loader by introducing an automated loading system.
Ob. 167 was designed based on an Object 140 rebuilt by Kartsev and Valeri Venediktov. Ob. 167 was more advanced than Kartsev's Ob. 165 and Ob. 166, and was also Kartsev's favored model. In October 1961, when asked to ready Ob. 166 for production, Kartsev disagreed and instead offered to prepare the Ob. 167. This suggestion was rejected, and the Ob. 166 and Ob. 165 were readied as the T-62 and T-62A respectively. Unlike the Kharkiv tank, it eschewed the state-of-the-art. Prototypes used the turret from the T-62, and a manual loader. In 1964, the tank underwent comparative testing with the Ob. 434, in which the former proved its superiority to both the T-62 and T-55
The T-54 and T-55 tanks are a series of Soviet main battle tanks introduced in the years following the Second World War. The first T-54 prototype was completed at Nizhny Tagil by the end of 1945.Steven Zaloga, T-54 and T-55 Main Battle Tank ...
. Ob. 167 was favored by Uralvagonzavod director I.V. Okunev and Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev s ...
, who believed the tank was more affordable. Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union
The First Deputy Premier of the Soviet Union was the deputy head of government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR); despite the title, the office was not necessarily held by a single individual. The office had three different names ...
Dmitry Ustinov, believed the parallel development of Ob. 167 jeopardized the future of the Kharkiv tank. In December 1962, the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union
The Council of Ministers of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( rus, Совет министров СССР, r=Sovet Ministrov SSSR, p=sɐˈvʲet mʲɪˈnʲistrəf ɛsɛsɛˈsɛr; sometimes abbreviated to ''Sovmin'' or referred to as the '' ...
ordered Ob. 432 (later serialized as the T-64) into production, dooming Kartsev's tank.
Kartsev continued to work on the Ob. 167. Ob. 167M incorporated an autoloader. This model too was rejected in May 1964.
Problems with the early production run were evident from the start, but a strong lobby formed around Morozov who advocated for Ob. 434 in Moscow, preventing rival developments and ideas from being discussed. Ob. 434 was accepted into Soviet Army service in May 1968 as the T-64A.
The T-64's smaller design presented a problem when selecting a suitable engine. The chosen 700 hp 5TDF engine was unreliable, difficult to repair, and had a guaranteed lifespan similar to World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
designs.
Object 172
In 1967, the Uralvagonzavod formed "Section 520", which was to prepare the serial production of the T-64 for 1970. Because of the time-consuming construction of the 5TDF engines, which took about twice as long as the contemporary V-45, the Malyshev Factory in Kharkiv could not provide a sufficient number of 5TDF engines for all Soviet tank factories. The Military-Industrial Commission (VPK) authorized work on two alternative engines for a wartime T-64, a so-called "mobilization model" that could be produced more quickly and at half the cost. Obj. 219 (which became the T-80, with a GTD-1000T gas-turbine) was designed in Leningrad. Ob. 439 with a diesel V-45 engine was designed by Uralvagon KB at Uralvagonzavod in Nizhny Tagil. GABTU sent a T-64A prototype with a team to Uralvagonzavod. Kartsev was to lead this team.
Kartsev was unsatisfied with the innovations of the T-64, and began instead a more comprehensive project to redesign the tank. Kartsev melded what he believed were the best aspects of the T-64A, Object 167, and an upgunned T-62.
During development the tank was code-named "Ural" after the Ural mountain region. Uralvagonzavod produced the first prototype with a T-62 turret, D-81 125-mm gun and V-45 engine in January 1968. Ob. 439 differed so greatly from the T-64 that it was redesignated as "Object 172".
Kartsev's defiance angered GABTU, which initially reprimanded him for his insubordination. However, after the tank proved indeed to possess potential as a less costly alternative to the T-64, Kartsev was allowed to continue work on his design. Politically motivated opposition continued to beset the tank throughout its development. Vagonka tank plant manager I.F. Krutyakov sought to subordinate Uralvagonzavod under Josef Kotin. Kartsev skillfully beat back this play for power, embarrassing Krutyakov in the process. Kartsev retired in August 1969, and was succeeded by Venediktov.
The team soon found out that the more powerful V-45 engine put a lot of stress on the T-64 hull, so that after some time cracks started to materialize. A more stable solution was sought.
Finally, an idea from 1960 was used, when a modification of the T-62 had been discussed: In 1961, two prototypes of "Object 167" had been built by Uralvagonzavod to test a stronger hull and running gear combination for that tank. Under influence from Kharkiv, the idea had been turned down by Moscow. But this construction, with its big, rubbercoated roadwheels now formed the basis for the mobilisation model of the T-64.
Additional changes were made to the automatic loading system, which also was taken from an earlier project, originally intended for a T-62 upgrade. The 125 mm ammunition, consisting of a separate projectile and a propellant charge, was now stored horizontally on two levels, not vertically on one level as in the T-64. It was said to be more reliable than the T-64 autoloader. In 1964, two 125-mm guns of the D-81 type had been used to evaluate their installation in to the T-62, so the Ural plant was ready to adopt the 125 mm calibre for the T-64A as well.
Venediktov's team later replaced the T-64-style suspension with the Obj. 167's suspension. The tank was trialed in Kubinka in 1968, and Central Asia in 1969. After intensive comparative testing with the T-64A, Object 172 was re-engineered in 1970 to deal with some minor problems. Further trials took place in Transbaikal in 1971.
GABTU sent a T-64A prototype with a team to Uralvagonzavod. Kartsev was to lead this team.
Kartsev was unsatisfied with the innovations of the T-64, and began instead a more comprehensive project to redesign the tank. Kartsev melded what he believed were the best aspects of the T-64A, Object 167, and an upgunned T-62.
During development the tank was code-named "Ural" after the Ural mountain region. Uralvagonzavod produced the first prototype with a T-62 turret, D-81 125-mm gun and V-45 engine in January 1968. Ob. 439 differed so greatly from the T-64 that it was redesignated as "Object 172".
Kartsev's defiance angered GABTU, which initially reprimanded him for his insubordination. However, after the tank proved indeed to possess potential as a less costly alternative to the T-64, Kartsev was allowed to continue work on his design. Politically motivated opposition continued to beset the tank throughout its development. Vagonka tank plant manager I.F. Krutyakov sought to subordinate Uralvagonzavod under Josef Kotin. Kartsev skillfully beat back this play for power, embarrassing Krutyakov in the process. Kartsev retired in August 1969, and was succeeded by Venediktov.
The team soon found out that the more powerful V-45 engine put a lot of stress on the T-64 hull, so that after some time cracks started to materialize. A more stable solution was sought.
Finally, an idea from 1960 was used, when a modification of the T-62 had been discussed: In 1961, two prototypes of "Object 167" had been built by Uralvagonzavod to test a stronger hull and running gear combination for that tank. Under influence from Kharkiv, the idea had been turned down by Moscow. But this construction, with its big, rubbercoated roadwheels now formed the basis for the mobilisation model of the T-64.
Additional changes were made to the automatic loading system, which also was taken from an earlier project, originally intended for a T-62 upgrade. The 125 mm ammunition, consisting of a separate projectile and a propellant charge, was now stored horizontally on two levels, not vertically on one level as in the T-64. It was said to be more reliable than the T-64 autoloader. In 1964, two 125-mm guns of the D-81 type had been used to evaluate their installation in to the T-62, so the Ural plant was ready to adopt the 125 mm calibre for the T-64A as well.
Venediktov's team later replaced the T-64-style suspension with the Obj. 167's suspension. The tank was trialed in Kubinka in 1968, and Central Asia in 1969. After intensive comparative testing with the T-64A, Object 172 was re-engineered in 1970 to deal with some minor problems. Further trials took place in Transbaikal in 1971.
T-72
Being only a mobilisation model, serial production of Object 172 was not possible in peacetime. However, by 1971, even Ustinov was growing tired of problems with the T-64. In an unclear political process decree number 326-113 was issued, which allowed the production of Object 172 in the Soviet Union from 1 January 1972, and freed Uralvagonzavod from the T-64A production. An initial production run began in 1972 at Nizhni Tagil. These were trialed in the Soviet Army. A final trial batch was built as "Object 172M" and tested in 1973 and accepted into service as the "T-72" in 1974. Uralvagon KB continued to iterate on the T-72 in a series of block improvements. Obj. 174 introduced ceramic/steellaminate
Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materia ...
turret armour. The coincidence rangefinder was replaced with a laser rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in ...
. Obj. 174 was designated as the T-72A when it entered production in 1978. Turret armour was greatly improved with Obj. 174M. A more powerful V-84 engine was introduced to offset the increased weight. Obj. 174M entered service in 1985 as the T-72B.
At least some technical documentation on the T-72 is known to have been passed to the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
by the Polish Colonel Ryszard Kukliński between 1971 and 1982.
Production history
 The first series production of T-72 Object 172M began in July at UKBM in Nizhny Tagil. However, due to difficulties in getting the factory organised for the change in production from T-64 to T-72, only 30 completed tanks were delivered in 1973. Troubles continued in 1974 where out of a state production quota of 440 only 220 were officially declared, with the actual number of completed tanks being close to 150. As a result, substantial investment in tooling was undertaken. Only after modernisation, could the factory begin full-scale production of the T-72. Nizhny Tagil produced the tank in various modifications until 1992.
The T-72 was the most common tank used by the Warsaw Pact from the 1970s until the
The first series production of T-72 Object 172M began in July at UKBM in Nizhny Tagil. However, due to difficulties in getting the factory organised for the change in production from T-64 to T-72, only 30 completed tanks were delivered in 1973. Troubles continued in 1974 where out of a state production quota of 440 only 220 were officially declared, with the actual number of completed tanks being close to 150. As a result, substantial investment in tooling was undertaken. Only after modernisation, could the factory begin full-scale production of the T-72. Nizhny Tagil produced the tank in various modifications until 1992.
The T-72 was the most common tank used by the Warsaw Pact from the 1970s until the collapse of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
in 1991. It was also exported to other countries, such as Finland, India, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
, as well as being copied elsewhere, both with and without licenses.
 Licensed versions of the T-72 were made in Poland and Czechoslovakia, for Warsaw Pact consumers. These tanks had better and more consistent quality of make but with inferior armour, lacking the resin-embedded ceramics layer inside the turret front and
Licensed versions of the T-72 were made in Poland and Czechoslovakia, for Warsaw Pact consumers. These tanks had better and more consistent quality of make but with inferior armour, lacking the resin-embedded ceramics layer inside the turret front and glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glacis ...
plate armour, replaced with all steel. The Polish-made T-72G tanks also had thinner armour compared to Soviet Army standard (410 mm for turret). Before 1990, Soviet-made T-72 export versions were similarly downgraded for non-Warsaw Pact customers (mostly the Arab countries). Many parts and tools are not interchangeable between the Soviet, Polish and Czechoslovakian versions, which caused logistics problems.
Yugoslavia developed the T-72 into the more advanced M-84
The M-84 is a Yugoslav main battle tank, a variant of the Soviet T-72. The M-84 is still in service in Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kuwait.
Development and production
Development
The M-84 is based on the Soviet T-72M (expo ...
, and sold hundreds of them around the world during the 1980s. The Iraqis called their T-72 copies the " Lion of Babylon" (''Asad Babil''). These Iraqi tanks were assembled from kits sold to them by the Soviet Union as a means of evading the UN-imposed weapons embargo. More modern derivatives include the Polish PT-91 ''Twardy''. Several countries, including Russia and Ukraine, also offer modernization packages for older T-72s.
Various versions of the T-72 have been in production for decades, and the specifications for its armour have changed considerably. Original T-72 tanks had homogeneous cast steel armour incorporating spaced armour technology and were moderately well protected by the standards of the early 1970s. In 1979, the Soviets began building T-72 modification with composite armour similar to the T-64 composite armour, in the front of the turret and the front of the hull. Late in the 1980s, T-72 tanks in Soviet inventory (and many of those elsewhere in the world as well) were fitted with reactive armour tiles.
TPD-K1 laser rangefinder system have appeared in T-72 tanks since 1974; earlier examples were equipped with parallax optical rangefinders, which could not be used for distances under . Some export versions of the T-72 lacked the laser rangefinder until 1985 or sometimes only the squadron and platoon commander tanks (version K) received them. After 1985, all newly made T-72s came with reactive armour as standard, the more powerful V-84 engine and an upgraded design main gun, which can fire guided anti-tank missiles from the barrel. With these developments, the T-72 eventually became almost as powerful as the more expensive T-80 tank, but few of these late variants reached the economically ailing Warsaw Pact allies and foreign customers before the Soviet bloc fell apart in 1990.
Since 2000, export vehicles have been offered with thermal imaging night-vision gear of French manufacture as well (though it may be more likely that they might simply use the locally manufactured 'Buran-Catherine' system, which incorporates a French thermal imager). Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium (DU; also referred to in the past as Q-metal, depletalloy or D-38) is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope than natural uranium.: "Depleted uranium possesses only 60% of the radioactivity of natural uranium, hav ...
armour-piercing ammunition for the gun has been manufactured in Russia in the form of the BM-32 projectile since around 1978, though it has never been deployed, and is less penetrating than the later tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
BM-42 and the newer BM-42M.
In 2010, Russia started a upgrade using the enormous stocks of T-72B's held in reserve. The rebuild tank is called T72B3 (Ob'yekt 184-M3).
In 2018, the 3rd Central Research Institute in Moscow had tested a proof-of-concept demonstration for robotic tank mobility, and was planning to further develop it based on the T-72B3 and other platforms.
In 2022, according to intelligence sources, the upgrade of the Russian T-72 fleet has slowed during the war in Ukraine while production of the more modern T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and comp ...
s and T-14 Armatas has almost stopped because the International sanctions
International sanctions are political and economic decisions that are part of diplomatic efforts by countries, multilateral or regional organizations against states or organizations either to protect national security interests, or to protect i ...
affecting the Russian military industry. However, more tanks of T-72 and T-90 types were ordered in August 2022. A new batch of T-72B3M tanks was reportedly delivered in late 2022.
Models
Main models of the T-72, built in the Soviet Union and Russia. Command tanks have ''K'' added to their designation for ''komandirskiy'', "command", for example ''T-72K'' is the command version of the basic T-72. Versions with reactive armour have ''V'' added, for ''vzryvnoy'', "explosive". ;T-72 Ural (1973) :Original version, armed with 125 mm smoothbore tank gun and optical coincidence rangefinder."Czolgi Swiata" (World's Tanks or Tanks of the World) magazine issue 20 ;T-72A (1979)
:Coincidence rangefinder replaced with
;T-72A (1979)
:Coincidence rangefinder replaced with laser rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in ...
and electronic fire control added, turret front and top being heavily reinforced with composite armour (nicknamed ''Dolly Parton'' by US intelligence), provisions for mounting reactive armour, smoke grenade launchers, flipper armour mount on front mudguards, internal changes.
;T-72M
:Export version, similar to T-72A but lacking composite armour (decreasing the weight to 37 tonnes), much simpler fire control system, and usually supplied with inferior ammunition compared to the Soviet army standard. Also built in Poland and former Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
.
;T-72B (1985)
:New main gun, stabilizer, sights, and fire control, capable of firing 9M119 Svir guided missile, additional armour including of appliqué armour in the front of hull, improved composites in the turret armour, improved engine.
;T-72B3 model 2011 (~2010)
:This upgrade was initiated in 2010 using the enormous stocks of T-72B's held in reserve. They are rebuilt with new technologies including Sosna-U multichannel gunner's sight, new digital VHF radio, improved autoloader, 2A46M-5 gun to accommodate new ammunition. Retains older V-84-1 engine and Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armour, and lacks satellite navigation.
;T-72B3 model 2016 or T-72B3M
:Upgrade for T-72B3, with Relikt explosive reactive armour on the sides, side skirts with soft-container reactive armour and slat screens, 2A46M-5 gun capable of firing 9M119M Refleks guided missile, V-92S2F engine, automatic transmission, digital display and rear-view video. Often incorrectly referred to as "T-72B4"
The T-72 design has been used into the following foreign models: T-72M4CZ (Czech Republic), PT-91 Twardy (Poland), M-84
The M-84 is a Yugoslav main battle tank, a variant of the Soviet T-72. The M-84 is still in service in Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kuwait.
Development and production
Development
The M-84 is based on the Soviet T-72M (expo ...
(Yugoslavia), M-84AS1 (Serbia), M-84D (Croatia) and Lion of Babylon (Iraq).
Variants
In addition, the T-72 hull has been used as the basis for other heavy vehicle designs, including the following: *BMPT Terminator
The BMPT "Terminator" ( - Tank Support Fighting Vehicle) is an armored fighting vehicle (AFV), designed and manufactured by the Russian company Uralvagonzavod. This vehicle was designed for supporting tanks and other AFVs in urban areas. The BM ...
– Heavy convoy and close tank support vehicle.
* TOS-1 – Thermobaric
A thermobaric weapon, also called an aerosol bomb, a vacuum bomb or a fuel air explosive (FAE), is a type of explosive that uses oxygen from the surrounding air to generate a high-temperature explosion. The fuel–air explosive is one of the be ...
multiple rocket launcher
A multiple rocket launcher (MRL) or multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) is a type of rocket artillery system that contains multiple launchers which are fixed to a single platform, and shoots its rocket ordnance in a fashion similar to a vo ...
, with 30-tube launcher in place of the turret."JED The Military Equipment Directory"* BREM-1 (''Bronirovannaya Remonto-Evakuatsionnaya Mashina'') –
Armoured recovery vehicle
An armoured recovery vehicle (ARV) is typically a powerful tank or armoured personnel carrier (APC) chassis modified for use during combat for military vehicle recovery (towing) or repair of battle-damaged, stuck, and/or inoperable armoured ...
with a 12-tonne crane, 25-tonne winch, dozer blade, towing equipment, and tools.
* IMR-2
The IMR-2 is a Soviet and Russian tracked military engineering vehicle built on T-72 main battle tank chassis. IMR stands for ''Inzhenernaya Mashina Razgrazhdeniya'' (russian: link=no, инженерная машина разграждения-2; ...
(''Inzhenernaya Mashina Razgrashdeniya'') – Combat engineering vehicle
A military engineering vehicle is a vehicle built for construction work or for the transportation of combat engineers on the battlefield. These vehicles may be modified civilian equipment (such as the armoured bulldozers that many nations field) ...
with an 11-tonne telescoping crane and pincers, configurable dozer blade/plough, and mine-clearing system.
* MTU-72 (''Tankovyy Mostoukladchik'') – Armoured bridge layer, capable of laying a capacity bridge spanning in three minutes.
* BMR-3 Vepr (''Bronirovannaja Mashina Razminirovanija'') – Mine clearing vehicle.
Design characteristics
 The T-72 shares many design features with other tank designs of Soviet origin. Some of these are viewed as deficiencies in a straight comparison to NATO tanks, but most are a product of the way these tanks were envisioned to be employed, based on the Soviets' practical experiences in World War II.
The T-72 shares many design features with other tank designs of Soviet origin. Some of these are viewed as deficiencies in a straight comparison to NATO tanks, but most are a product of the way these tanks were envisioned to be employed, based on the Soviets' practical experiences in World War II.
Weight
The T-72 is extremely lightweight, at forty-one tonnes, and very small compared to Western main battle tanks. Some of the roads and bridges in former Warsaw Pact countries were designed such that T-72s can travel along in formation, but NATO tanks could not pass at all, or just one-by-one, significantly reducing their mobility. The basic T-72 is relatively underpowered, with a supercharged version of the basic V12diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-cal ...
originally designed for the World War II-era T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank introduced in 1940. When introduced its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was less powerful than its contemporaries while its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against anti-tank weapons. The C ...
. The wide tracks run on large-diameter road wheels, which allows for easy identification of the T-72 and descendants (the T-64 family has relatively small road wheels).
The T-72 is designed to cross rivers up to deep submerged using a small diameter snorkel assembled on-site. The crew is individually supplied with simple rebreather
A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen i ...
chest-pack apparatuses for emergency situations. If the engine stops underwater, it must be restarted within six seconds, or the T-72's engine compartment becomes flooded due to pressure loss. The snorkeling procedure is considered dangerous, but is important for maintaining operational mobility.
Nuclear, biological, and chemical protection
 The T-72 has a nuclear, biological, and chemical ( NBC) protection system. The inside of both hull and turret is lined with a synthetic fabric made of
The T-72 has a nuclear, biological, and chemical ( NBC) protection system. The inside of both hull and turret is lined with a synthetic fabric made of boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the '' boron group'' it has t ...
compound, meant to reduce the penetrating radiation from neutron bomb explosions. The crew is supplied clean air via an air filter system. A slight over-pressure prevents entry of contamination via bearings and joints. Use of an autoloader for the main gun allows for more efficient forced smoke removal compared to traditional manually loaded ("pig-loader") tank guns, so NBC isolation of the fighting compartment can, in theory, be maintained indefinitely.
Interior
manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission (mechanics), transmission ...
.
Armour

 Armour protection of the T-72 was strengthened with each succeeding generation. The original T-72 "Ural" Object 172M's (from 1973) turret is made from conventional cast high hardness steel (HHS) armour with no laminate inserts. It is believed that the maximum thickness is and the nose is . The glacis of the new laminated armour is thick, comprising HHS, double layer of laminate and RHA steel, which when inclined gives about thickness along the line of sight. In 1977 the armour of the T-72 Object 172M was slightly changed. The turret now featured insert filled with ceramic sand bars "kwartz" rods and the glacis plate composition was changed. It was now made up of HHA steel, glass Tekstolit laminate and RHA steel. This version was often known in Soviet circles as T-72 "Ural-1". The next armour update was introduced by the T-72A (Object 176), which was designed in 1976 and replaced the original on the production lines during 1979–1985. T-72 Object 1976 is also known as T-72A. With the introduction of the T-72B (Object 184) in 1985, the composite armour was again changed. According to retired major, James M. Warford, variants developed after the T-72 base model and T-72M/T-72G MBT, featured a cast steel turret that included a cavity filled with quartz or sand in a form similar to US "fused-silica" armour. The T-72 Model 1978 (Obiekt 172M sb-4), which entered production in 1977, featured a new turret with special armour composed of ceramic rods.
The T-72A featured a new turret with thicker, nearly vertical, frontal armour. Due to its appearance, it was unofficially nicknamed "
Armour protection of the T-72 was strengthened with each succeeding generation. The original T-72 "Ural" Object 172M's (from 1973) turret is made from conventional cast high hardness steel (HHS) armour with no laminate inserts. It is believed that the maximum thickness is and the nose is . The glacis of the new laminated armour is thick, comprising HHS, double layer of laminate and RHA steel, which when inclined gives about thickness along the line of sight. In 1977 the armour of the T-72 Object 172M was slightly changed. The turret now featured insert filled with ceramic sand bars "kwartz" rods and the glacis plate composition was changed. It was now made up of HHA steel, glass Tekstolit laminate and RHA steel. This version was often known in Soviet circles as T-72 "Ural-1". The next armour update was introduced by the T-72A (Object 176), which was designed in 1976 and replaced the original on the production lines during 1979–1985. T-72 Object 1976 is also known as T-72A. With the introduction of the T-72B (Object 184) in 1985, the composite armour was again changed. According to retired major, James M. Warford, variants developed after the T-72 base model and T-72M/T-72G MBT, featured a cast steel turret that included a cavity filled with quartz or sand in a form similar to US "fused-silica" armour. The T-72 Model 1978 (Obiekt 172M sb-4), which entered production in 1977, featured a new turret with special armour composed of ceramic rods.
The T-72A featured a new turret with thicker, nearly vertical, frontal armour. Due to its appearance, it was unofficially nicknamed "Dolly Parton
Dolly Rebecca Parton (born January 19, 1946) is an American singer-songwriter, actress, philanthropist, and businesswoman, known primarily for her work in country music. After achieving success as a songwriter for others, Parton made her album ...
" armour by the US Army. This used the new ceramic-rod turret filler, incorporated improved glacis laminate armour, and mounted new anti-shaped-charge sideskirts.
The T-72M was identical to the base T-72 Ural model in terms of protection, retaining the monolithic steel turret. The modernized T-72M1 was closer to the T-72A in terms of protection. It featured an additional of high hardness steel appliqué armour on the glacis plate, which produced an increase of in line of sight thickness. It was also the first export variant with composite armour in the turret, containing ceramic rods sometimes called "sandbar armour". The turret armour composition was essentially identical to the T-72 "Ural-1" whereas Soviet-only T-72As had slightly increased turret protection.
Several T-72 models featured explosive reactive armour (ERA), which increased protection primarily against high-explosive anti-tank
High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity ...
(HEAT) type weapons. Certain late-model T-72 tanks featured Kontakt-5 ERA, a form of ''universal'' ERA partly effective against kinetic penetrators. It was added to the T-72 as a response to testing conducted by the Soviet Union against captured Israeli Magach-4 tanks which found that the glacis of the T-72 could be penetrated by the 105mm M111 APDSFS ''Hetz'' ammunition.
Late model T-72s, such as the T-72B, featured improved turret armour, visibly bulging the turret front—nicknamed "super-Dolly Parton" armour by Western intelligence. The turret armour of the T-72B was the thickest and most effective of all Soviet tank armour; it was even thicker than the frontal armour of the T-80B. The T-72B used a new "reflecting-plate armour" (''bronya s otrazhayushchimi listami''), in which the frontal cavity of the cast turret was filled with a laminate of alternating steel and non-metallic (rubber) layers. The glacis was also fitted with of appliqué armour. The late production versions of the T-72B/B1 and T-72A variants also featured an anti-radiation layer on the hull roof.
Early model T-72s did not feature side skirts; instead, the original base model featured gill or flipper-type armour panels on either side of the forward part of the hull. When the T-72A was introduced in 1979, it was the first model to feature the plastic side skirts covering the upper part of the suspension, with separate panels protecting the side of the fuel and stowage panniers.
After the collapse of the USSR, US and German analysts had a chance to examine Soviet-made T-72 tanks equipped with Kontakt-5 ERA, and they proved impenetrable to most Cold War US and German tank projectiles and anti-tank weapons. A U.S. Army spokesperson claimed at the show, "the myth of Soviet inferiority in this sector of arms production that has been perpetuated by the failure of downgraded T-72 export tanks in the Gulf Wars has, finally, been laid to rest. The results of these tests show that if a NATO/Warsaw Pact confrontation had erupted in Europe, the Soviets would have had parity (or perhaps even superiority) in armour". KE-effective ERA, such as Kontakt-5, drove the development of M829A3 ammunition.
Late 1980s, Soviet developed Object 187 (Объект 187, or ''T-72BI''), it was a parallel project to Object 188 (the T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and comp ...
tank). It was based on the T-72B, with a heavily modified turret. The 'Object 187' used composite armour for the turret ("Super Dolly Parton" composite armour) and the hull front, and RHA for the rest of the tank. It possibly consisted of special materials including ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
or high density uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
alloys. Maximum physical thickness of the passive armour (not counting the reactive armour – ERA) was up to 950 mm RHA. With Kontakt-5 ERA, T-72BI's frontal armour was immune to the NATO's 120 mm L/44 tank gun.Экспериментальный основной боевой танк "Объект 187"However, after the Soviet collapse, the tank was not accepted. In 2021, Russian Army T-72B3s were seen fitted with raised mesh screens above their turrets. The screens appeared to act as a type of slat armour attempting to protect the tanks from top attack weapons such as the
FGM-148 Javelin
The FGM-148 Javelin, or Advanced Anti-Tank Weapon System-Medium (AAWS-M), is an American-made portable anti-tank missile system in service since 1996, and continuously upgraded. It replaced the M47 Dragon anti-tank missile in US service. Its fire- ...
ATGM and small air-to-ground munitions fired from unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controll ...
s (UAVs). During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
the cages proved ineffective at defending the tanks and were removed.
Estimated protection level
The following table shows the estimated protection level of different T-72 models inrolled homogeneous armour
Rolled homogeneous armour (RHA) is a type of vehicle armour made of a single steel composition hot-rolled to improve its material characteristics, as opposed to layered or cemented armour. Its first common application was in tanks. After World ...
equivalency, i.e., the composite armour of the turret of a T-72B offers as much protection against an armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot
Armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS), long dart penetrator, or simply dart ammunition, is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition used to attack modern vehicle armour. As an armament for main battle tanks, it succeeds ...
(APFSDS) round as a thick armour steel layer.
Possible easy replacement of Kontakt 5 (or 1) with Relikt. Relikt defends against tandem-charge warheads and reduces penetration of APFSDS rounds by over 50 percent. ''Calculation'' T-72B + Relikt vs APFSDS, on turret 1,000–1,050 mm, on hull 950–1,000 mm. For T-90MS Relikt is a basic set, for the T-90S basic set – Kontakt 5.
Gun
 The T-72 is equipped with the 2A46 series main gun, a significantly larger (20-mm larger) calibre than the standard gun found in contemporary Western MBTs, and still slightly larger than the 120 mm/L44 found in many modern Western MBTs. As is typical of Soviet tanks, the gun can fire anti-tank guided missiles, and standard main gun ammunition, including HEAT and APFSDS rounds.
The original T-72 Object 172M (1973) used 2A26M2 model gun first mounted on T-64. The barrel had a length of 6350mm or 50.8 calibers and had maximum rated chamber pressure of 450 MPa. The cannon had an electroplated chrome lining but lacked a thermal sleeve. The cannon was capable of firing 3VBM-3 round with 3BM-9 steel projectile sabot and 3VBM-6 round with 3BM-12 Tungsten sabot APFSDS projectile. Allowing respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. In addition to APFSDS rounds T-72 Object 172M could also fire 3VBK-7 round incorporating 3BK-12 HEAT warhead and 3VBK-10 round incorporating 3BK-14 HEAT warhead. HEAT rounds allowed respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 0 degree angle. The High Explosive rounds provided included 3WOF-22 with 3OF-19 warhead or 3WOF-36 with the 3OF-26 warhead. For all rounds, the Zh40 propellant was used. Complementing the original gun setup was 2E28M "Siren" two-plane electrohydraulic stabilizer allowing automatic stabilization with speeds from 0.05 to 6 degrees per second.
Even as the T-72 Object 172M (1973) was entering production new ammunition was developed to offset armour developments in the West. Beginning in 1972, two new APFSDS rounds were introduced, the 3VBM-7 round with 3BM-15 Tungsten sabot projectile and the "cheaper" 3VBM-8 round with 3BM-17 sabot but without the tungsten carbide plug. These allowed penetration of respectively and RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. At the same time, a universal Zh52 propellant charge was introduced. The 3VBM-7 was the most common APFSDS round found in T-72 Object 172M tanks during the 70s.
The stated barrel life expectancy of the 2A26M2 model gun was 600 rounds of HE/HEAT equivalent to 600 EFC (Effective Full Charge) or 150 rounds of APFSDS.
The main gun of the T-72 has a mean error of at a range of , considered substandard today. Its maximum firing distance is , due to limited positive elevation. The limit of aimed fire is (with the gun-launched
The T-72 is equipped with the 2A46 series main gun, a significantly larger (20-mm larger) calibre than the standard gun found in contemporary Western MBTs, and still slightly larger than the 120 mm/L44 found in many modern Western MBTs. As is typical of Soviet tanks, the gun can fire anti-tank guided missiles, and standard main gun ammunition, including HEAT and APFSDS rounds.
The original T-72 Object 172M (1973) used 2A26M2 model gun first mounted on T-64. The barrel had a length of 6350mm or 50.8 calibers and had maximum rated chamber pressure of 450 MPa. The cannon had an electroplated chrome lining but lacked a thermal sleeve. The cannon was capable of firing 3VBM-3 round with 3BM-9 steel projectile sabot and 3VBM-6 round with 3BM-12 Tungsten sabot APFSDS projectile. Allowing respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. In addition to APFSDS rounds T-72 Object 172M could also fire 3VBK-7 round incorporating 3BK-12 HEAT warhead and 3VBK-10 round incorporating 3BK-14 HEAT warhead. HEAT rounds allowed respectively and penetration of RHA steel at 0 degree angle. The High Explosive rounds provided included 3WOF-22 with 3OF-19 warhead or 3WOF-36 with the 3OF-26 warhead. For all rounds, the Zh40 propellant was used. Complementing the original gun setup was 2E28M "Siren" two-plane electrohydraulic stabilizer allowing automatic stabilization with speeds from 0.05 to 6 degrees per second.
Even as the T-72 Object 172M (1973) was entering production new ammunition was developed to offset armour developments in the West. Beginning in 1972, two new APFSDS rounds were introduced, the 3VBM-7 round with 3BM-15 Tungsten sabot projectile and the "cheaper" 3VBM-8 round with 3BM-17 sabot but without the tungsten carbide plug. These allowed penetration of respectively and RHA steel at 2000m at 0 degree angle. At the same time, a universal Zh52 propellant charge was introduced. The 3VBM-7 was the most common APFSDS round found in T-72 Object 172M tanks during the 70s.
The stated barrel life expectancy of the 2A26M2 model gun was 600 rounds of HE/HEAT equivalent to 600 EFC (Effective Full Charge) or 150 rounds of APFSDS.
The main gun of the T-72 has a mean error of at a range of , considered substandard today. Its maximum firing distance is , due to limited positive elevation. The limit of aimed fire is (with the gun-launched anti-tank guided missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder ...
, which is rarely used outside of former Soviet states). The T-72's main gun is fitted with an integral pressure reserve drum, which assists in rapid smoke evacuation from the bore after firing. The 125 millimeter gun barrel is certified strong enough to ram the tank through forty centimeters of iron-reinforced brick wall, though doing so will negatively affect the gun's accuracy when subsequently fired. Rumours in NATO armies of the late Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
claimed that the tremendous recoil of the huge 125 mm gun could damage the fully mechanical transmission of the T-72. The tank commander reputedly had to order firing by repeating his command, when the T-72 is on the move: "Fire! Fire!" The first shout supposedly allowed the driver to disengage the clutch to prevent wrecking the transmission when the gunner fired the cannon on the second order. In reality, this still-common tactic substantially improves the tank's firing accuracy and has nothing to do with recoil or mechanical damage to anything. This might have to do with the lower quality (compared to Western tanks) of the T-72's stabilizers.
The vast majority of T-72s do not have FLIR thermal imaging
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared ...
sights, though all T-72s (even those exported to the Third World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " First ...
) possess the characteristic (and inferior) 'Luna' Infrared illuminator. Thermal imaging sights are extremely expensive, and the new Russian FLIR system, the 'Buran-Catherine Thermal Imaging Suite' was introduced only recently on the T-80UM tank.
Autoloader
Like the earlier domestic-use-only T-64, the T-72 is equipped with an automatic loading system, eliminating the need for a dedicated crewmember, decreasing the size and weight of the tank. However, the autoloader is of a noticeably different design. Both the T-64 and T-72 carry their two-section 125 mm ammunition (shell and full propellant charge, or missile and reduced propellant charge) in separate loading trays positioned on top of each other; but firstly, in T-64, 28 of these were arranged vertically as a ring under the turret ring proper, and were rotated to put the correct tray into position under the hoist system in the turret rear. This had the disadvantage of cutting the turret off from the rest of the tank, most notably, the driver. Accessing the hull required partial removal of the trays. The T-72 uses a design that has lower width requirements and does not isolate the turret compartment: the trays are arranged in a circle at the very bottom of the fighting compartment; the trade-off is the reduction of the number of trays to 22. The second difference is that in the T-64 the trays were hinged together and were flipped open as they were brought into position, allowing both the shell/missile and propellant charge to be rammed into the breech in one motion; in the T-72 the tray is brought to the breech as-is, with the shell in the lower slot and the charge in the upper one, and the mechanical rammer sequentially loads each of them, resulting in a longer reloading cycle. The autoloader has a minimum cycle of 6.5 seconds (ATGM 8 seconds) and a maximum cycle of 15 seconds for reload, in later versions the sequence mode allows to reload in less than 5 seconds, allowing to reach 3 shots in 13 seconds. The autoloader system also includes an automated casing removal mechanism that ejects the propellant case through an opening port in the back of the turret during the following reload cycle. The autoloader disconnects the gun from the vertical stabilizer and cranks it up three degrees above the horizontal in order to depress the breech end of the gun and line it up with the loading tray and rammer. While loading, the gunner can still aim because he has a vertically independent sight. With a laser rangefinder and ballistic computer, final aiming takes at least another three to five seconds, but it is pipelined into the last steps of auto-loading and proceeds concurrently. In addition to the 22 auto-loaded rounds, the T-72 carries 17 rounds conventionally in the hull, which can be loaded into the emptied autoloader trays or directly into the gun. The T-72B3 modernization replaced the old autoloader with a new one to fit longer projectiles such as 3BM59 and 3BM60. Previous variants are limited and may only carry older APFSDS rounds that can't exceed a certain length, therefore allowing less performance from anti-tank rounds. The way that the unused rounds are stored in the autoloader system has been exposed as a flaw, as observers have noted that penetrating hits can easily set off a chain reaction that detonates all of the ammunition. The result is the turret is blown off resulting in a so-called "jack-in-the-box" explosion. This vulnerability was first observed during theGulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: ...
.
Operators and service
 The T-72 was never used in the
The T-72 was never used in the Afghanistan War
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
* Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see a ...
. The 40th Soviet Army that was deployed there had mainly T-55, and T-62 tanks.
The Russian Federation had over 10,000 T-72 tanks in use, including around 2,000 in active service and 8,000 in reserve (mostly T-72Bs). The T-72 has been used by the Russian Army in the fighting during the First and Second Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 ...
s, the Russo-Georgian War, and the Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Rev ...
. The T-72 has been used by over 40 countries worldwide.
Syria
In the1982 Lebanon War
The 1982 Lebanon War, dubbed Operation Peace for Galilee ( he, מבצע שלום הגליל, or מבצע של"ג ''Mivtsa Shlom HaGalil'' or ''Mivtsa Sheleg'') by the Israeli government, later known in Israel as the Lebanon War or the First L ...
, Syrian T-72s are believed to have engaged Israeli tanks ( M60A1, Magach or probably Merkava tanks) in the south of Lebanon. It is assumed that Syrian T-72 never met the Merkava in battle. On 9 June 1982, the Syrian General HQ ordered a brigade of the 1st Armoured Division, recently equipped with T-72 tanks, to move straight ahead, cross the border, and hit the right flank of the Israeli units advancing along the eastern side of Beka'a valley. The ensuing battle staved off further Israeli advance and 10 IDF main battle tanks were destroyed. After the war, Syrian president Hafez Al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad ', , (, 6 October 1930 – 10 June 2000) was a Syrian statesman and military officer who served as President of Syria from taking power in 1971 until his death in 2000. He was also Prime Minister of Syria from 1970 to 1 ...
called it "the best tank in the world".
The T-72 has been in extensive use in the Syrian Civil War by the Syrian Arab Army since 2011. Quite a few captured units have been used by anti-government forces, including the rebel Free Syrian Army
The Free Syrian Army (FSA) ( ar, الجيش السوري الحر, al-jaysh as-Sūrī al-ḥur) is a loose faction in the Syrian Civil War founded on 29 July 2011 by officers of the Syrian Armed Forces with the goal of bringing down the govern ...
, and jihadist groups such as the Islamic Front and the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ' ...
.
Initially, the insurgent forces used IEDs and RPG-7 ambush tactics against the government armoured forces. Later, the rebels obtained modern Russian RPGs and Yugoslav M79 Osa
The M79 Osa ( sr, Оса; "wasp") is a Yugoslav-made portable 90 mm anti-tank weapon made of fibre-reinforced plastics. It resembles the French portable anti-tank launcher 89 mm LRAC F1. It consists of the launcher, a CN-6 sighting p ...
s, which were used successfully against T-72s. Starting in 2012, the capture from Syrian stocks and later direct delivery by external sponsors of modern anti-tank guided missiles, including Chinese-made HJ-8
The HJ-8 or Hongjian-8 and Baktar Shikan (Pakistani version) () is a second generation tube-launched, optically tracked, wire-guided anti-tank missile system which was originally deployed by China's People's Liberation Army since the late 1980s.
...
, Soviet-made 9K111 Fagot, 9M113 Konkurs, and 9K115 Metis, and U.S.-made BGM-71 TOW
The BGM-71 TOW ("Tube-launched, Optically tracked, Wire-guided") is an American anti-tank missile. TOW replaced much smaller missiles like the SS.10 and ENTAC, offering roughly twice the effective range, a more powerful warhead, and a greatly ...
missile enabled the opposition forces to engage and destroy any government armoured vehicle types, T-72 included, from safer distances. As of March 2020, at least 837 T-72 tanks operated by the Syrian Armed forces were destroyed according to visual recordings.
Iraq
Iraqi T-72Ms and T-72M1s had success in the battle for Basra and the last stages of the war. 105mm M68 tank guns and TOW missiles proved ineffective against the frontal armour of Iraqi T-72s. Sixty T-72 tanks were lost during the eight years of war. Ra'ad Al-Hamdani, an Iraqi general in the Iraqi Republican Guard, stating "The 16th Iranian Armoured Division, which was equipped with Chieftain tanks, lost a battle against the 10th Iraqi Armoured Brigade with T-72 tanks. It is hard for an armoured brigade to destroy a division in 12 hours but it happened; it was a disaster for the Iranians". Out of the 894 Chieftain tanks that had started the war only 200 were left by the war's end. According to Iranians and Iraqis, the T-72 was the most feared tank of the Iran–Iraq War. During theinvasion of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait was an operation conducted by Iraq on 2 August 1990, whereby it invaded the neighboring State of Kuwait, consequently resulting in a seven-month-long Iraqi military occupation of the country. The invasion and Ira ...
Iraq used 690 tanks, mainly T-55s, T-62s and T-72s. Kuwait had 281 tanks, including 6 T-72s, 165 Chieftains, 70 Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public i ...
and 40 Centurions. On the morning of 2 August, near the Mutla Pass
Al-Jahra Governorate ( ar, محافظة الجهراء Muḥāfaẓat al-Ǧahrāʾ) is one of the six Governorates of Kuwait. It is the largest Governorate in Kuwait. It includes the town of Al-Jahra, most of the northern and western parts of Ku ...
, a tank battle took place between the Vickers tanks of the 6th Kuwaiti Mechanized Brigade and the T-72s of the Republican Guard's 17th Armoured Brigade, 1st Hammurabi Armoured Division
The 'Hammurabi' Armored Division ( ar, فرقة حمورابي المدرعة) was an elite formation of the Iraqi Republican Guard. It was named after Hammurabi; a Babylonian King known for the set of laws called Hammurabi's Code, which constitu ...
. Kuwaiti tanks were able to knock out one T-72 during the ambush, but were defeated in response with the commander of the 6th brigade captured. Only 20 surviving Vickers tanks were able to retreat to Saudi Arabia.
The Iraqi-assembled T-72 version Lion of Babylon engaged coalition forces in both Iraq wars. The Battle of 73 Easting took place during a sandstorm in the Iraqi desert. U.S. M1A1s and Bradley Fighting Vehicle
The Bradley Fighting Vehicle (BFV) is a tracked armoured fighting vehicle platform of the United States developed by FMC Corporation and manufactured by BAE Systems Land & Armaments, formerly United Defense. It is named after U.S. General Om ...
s came up against Iraqi Republican Guard T-72Ms and BMPs and inflicted 37 losses on the Iraqi armoured forces, while losing a single Bradley to enemy fire. The primary attack was conducted by 2ACR's three squadrons of about 400 soldiers, along with the 1st Infantry Division's two leading brigades, who attacked and destroyed the Iraqi 18th Mechanized Brigade and 37th Armoured Brigade of the Tawakalna Division, each consisting of between 2,500 and 3,000 personnel.The Iraqi T-72Ms used 3BM9 shells (removed from Soviet service in 1973), with a penetration of 245 mm at a distance of up to . M60A1s of the 1st Marine Division Task Force Ripper led the drive to the Kuwait International Airport on 27 February 1991. Task Force Ripper's M60A1 tanks destroyed about 100 Iraqi tanks and armored personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Ac ...
s, including T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks h ...
tanks. The total number of T-72s lost during Operation Desert Storm was approximately 150.
As of 1996, Iraq had 776 T-72 tanks in service from 1,038 originally received.
Chechen wars
During theFirst Chechen War
The First Chechen War, also known as the First Chechen Campaign,, rmed conflict in the Chechen Republic and on bordering territories of the Russian FederationФедеральный закон № 5-ФЗ от 12 января 1995 (в редакц ...
(December 1994 to September 1996) fought between the Russian Federation and the self-proclaimed Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, led by Dzhokhar Dudayev
Dzhokhar Musayevich Dudayev (, ; russian: Джохар Мусаевич Дудаев; ; 15 February 1944 – 21 April 1996) was a Soviet Air Force general and Chechen separatist leader who was the first president of the Chechen Republic of Ichk ...
, the Russian Federation deployed both T-72 and T-80 tanks. Russian AFV losses during the first three months fighting amounted to 62 tank (T-72/T-80) losses (44 T-72s of 141, 18 T-80s of 71 and 0 PT-76s of 9). Analysis of damage to non repairable vehicles showed that no T-72 were lost to frontal penetration of the hull from man portable anti tank weapons.
Analysis of the causes of these losses indicated the majority were caused by Chechen four-man anti-armour hunter-killer teams consisting of a gunner armed with a Russian RPG-7 or RPG-18 shoulder-fired antitank rocket launcher, and a machine gunner and a sniper, with five or six such teams simultaneously attacking a single armored vehicle. The majority of losses recorded occurred from three to six kill shot hits to the sides, top and rear of a vehicle.
Highlighted were serious tactical deployment failures, once again demonstrating doctrine and tactics being a primary factor in determining a tank's worth. Following the serious losses to the Russian Federation during their first assault upon Grozny, armoured tactics were revised. Russian armored vehicle losses dropped off with their change in tactics to have Russian infantry move in front, with armored combat vehicles in support of the infantry. In particular use of AAA armoured vehicles, these vehicles can elevate their main armament to higher angles than the T-72 .
The Russian army captured seven of Dudayev's T-72s and used them in combat. During the First Chechen War, at least two tank duels took place. In the first, Dudayev's T-72A knocked out one T-62M belonging to pro-Russian Chechens. In the second, one of Dudayev's T-72As was destroyed by a Russian T-72B. Three Russian T-72s are recorded as destroyed, at the hands of Chechen separatists, including one tank during the Second Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 ...
, during the period 1997 to 2003.
Russo-Georgian War
 During the war in South Ossetia in 2008 both sides deployed great numbers of T-72 tanks. At the time of the conflict, the Georgian military fielded 191 T-72 tanks of which 120 were modified to T-72Sim1s. The Georgian army deployed a total of 75 of its T-72 tanks into South Ossetia. The Georgian military lost 30 T-72's, ten in combat during the fighting around Tskhinvali, and another 20 destroyed by Russian paratroopers after their capture.
During the war in South Ossetia in 2008 both sides deployed great numbers of T-72 tanks. At the time of the conflict, the Georgian military fielded 191 T-72 tanks of which 120 were modified to T-72Sim1s. The Georgian army deployed a total of 75 of its T-72 tanks into South Ossetia. The Georgian military lost 30 T-72's, ten in combat during the fighting around Tskhinvali, and another 20 destroyed by Russian paratroopers after their capture.
Russo-Ukrainian War
War in Donbas
On 26 August 2014, theInternational Institute for Strategic Studies
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is a British research institute or think tank in the area of international affairs. Since 1997, its headquarters have been Arundel House in London, England.
The 2017 Global Go To Think ...
claimed that it had identified a mixed Russian column composed of at least 3 T-72Bs and a lone T-72B3 in the War in Donbas. The significance of this sighting was that Russia attempted to maintain plausible deniability
Plausible deniability is the ability of people, typically senior officials in a formal or informal chain of command, to denial, deny knowledge of or responsibility for any damnable actions committed by members of their organizational hierarchy. Th ...
over the issue of supplying tanks and other arms to the separatists. Russia continuously claimed that any tanks operated by the separatists must have been captured from Ukraine's own army. The T-72B3 is in service with the Russian Army in large numbers. This modernized T-72 is not known to have been exported to nor operated by any other country.
In an interview with Dorzhi Batomunkuev in March 2015, it was revealed that he had operated a T-72B as part of a 32 tank Russian army unit when fighting for Debaltseve in Ukraine in February 2015. His tank was destroyed and he suffered severe burns.
Before the conflict Ukraine had 600 T-72s in storage. However, encountering a deficiency of serviceable armoured vehicles, the Ukrainian Ministry of Defence began returning some of the T-72s to service.
Russian invasion of Ukraine
The T-72 has seen extensive service in the2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
with both sides.
Russia's most numerous tanks are the T-72B3 (mod. 2011 and 2016) and the older T-72B (mod. 1985 and 1989). In the buildup to the invasion, Russian forces applied improvised
Improvisation is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. Improvisation in the performing arts is a very spontaneous performance without specific or scripted preparation. The skills of impr ...
steel grilles to the top of the turret, known as "cope cages" by some commentators (including British Defence Secretary Ben Wallace). Military analysts have speculated that such grilles were added in an attempt to counter the usage of top-attack
Plunging fire is a form of indirect fire, where gunfire is fired at a trajectory to make it fall on its target from above. It is normal at the high trajectories used to attain long range, and can be used deliberately to attack a target not susce ...
weapons, such as the US made FGM-148 Javelin
The FGM-148 Javelin, or Advanced Anti-Tank Weapon System-Medium (AAWS-M), is an American-made portable anti-tank missile system in service since 1996, and continuously upgraded. It replaced the M47 Dragon anti-tank missile in US service. Its fire- ...
and British-Swedish NLAW
The Saab Bofors Dynamics NLAW (pronounced: ''"N-LAW"'', ), also known as the MBT LAW or RB 57, is a fire-and-forget, lightweight shoulder-fired, and disposable (single-use) line of sight (LOS) missile system, designed for infantry use. The ...
, by Ukrainian forces. These implementations add weight to the tank, increase its visual profile, and make it more difficult for the crew to escape from the tank. Analysts have also speculated that they may be potentially used as a countermeasure against RPG-7s fired from above during urban combat, loitering munition
A loitering munition (also known as a suicide droneLoitering Muniti ...
s, or against drone attacks, as a response to lessons learned from the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of an unresolved conflict over the region, involving Azerba ...
. The lack of uniformity between the makeshift cage variants made from different meshes and iron fences suggest that they are largely improvised by the tank crews, and are not standard issue. In May 2022, some Russian tankers said they eventually removed the cages, as they obstructed the use of machine guns and radios, and prevented evacuation if the tank caught fire.
Before the invasion, Ukraine operated small numbers of T-72s which were left from the Soviet Union but were partly modernized. These mainly included T-72As and T-72AVs, as well as modernized T-72AMTs (mod. 2017). On 3 April, an image of a rare T-72 "Ural" (1973) equipped with Kontakt-1 ERA having been damaged appeared. As of April 2022, an unspecified number of Czech T-72M1s had been provided to Ukraine. Poland also donated over 200 T-72M1/M1R tanks to Ukraine.
Further service
In September 2009, it was announced thatVenezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
was planning to purchase 92 Russian T-72B1V tanks. The first T-72s destined for Venezuela arrived at the port of Puerto Cabello on 25 May 2011. In June 2012, Russia and Venezuela agreed on a deal for 100 more T-72B1Vs.
In 2012 Xu Bin-shi, a high ranking Chinese military engineer, revealed during an interview that China first obtained a T-72 from Romania in the 1980s, in exchange for plasma spray technology.
In June 2013, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
bought from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
a $1 billion package of tanks, artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
, and rocket launchers starting on 18 June. Although the T-72 tanks Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
had were outdated, they were modified by Israel's Elbit Systems
Elbit Systems Ltd. is an Israel-based international defense electronics company engaged in a wide range of programs throughout the world. The company, which includes Elbit Systems and its subsidiaries, operates in the areas of aerospace, land ...
and Rafael. Together the two tweaked T-72A and T-72M1 tanks with improved sights, thermal imaging cameras, wind sensors, and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
communication systems to name a few. Even with these upgrades, military experts still consider the tanks "do not meet modern requirements".
Combat history

 * 1980–1988:
* 1980–1988: Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Counci ...
(Iraq)
* 1982: Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
(Syria)
*1982: 1982 Ethiopian-Somali Border War (Ethiopia)
* 1987–1990: Sri Lankan Civil War (India)
* 1988–1994: First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War, referred to in Armenia as the Artsakh Liberation War ( hy, Արցախյան ազատամարտ, Artsakhyan azatamart) was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 t ...
(Armenia and Azerbaijan)
* 1988–1993: Georgian Civil War
* 1992–1997: Civil war in Tajikistan (Russia, Tajikistan)
* 1990–1991: First Persian Gulf War (Iraq, Kuwait)
* 1990–2002: Sierra Leone Civil War
The Sierra Leone Civil War (1991–2002), or the Sierra Leonean Civil War, was a civil war in Sierra Leone that began on 23 March 1991 when the Revolutionary United Front (RUF), with support from the special forces of Liberian dictator Char ...
( Executive Outcomes)
* 1991–2001: Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
(Yugoslavia)
** 1991: Ten-Day War
The Ten-Day War ( sl, desetdnevna vojna), or the Slovenian War of Independence (), was a brief armed conflict that followed Slovenia's declaration of independence from Yugoslavia on 25 June 1991. It was fought between the separatists of the ...
(Yugoslavia)
** 1991–1995 Croatian War of Independence
The Croatian War of Independence was fought from 1991 to 1995 between Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serb-controlled Yug ...
(Yugoslavia, Krajina Serbs, Croatia and Republika Srpska)
** 1998: Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
(Yugoslavia)
** 2001: 2001 Macedonia conflict
The 2001 insurgency in Macedonia was an armed conflict which began when the ethnic Albanian National Liberation Army (NLA) militant group, formed from veterans of the Kosovo War and Insurgency in the Preševo Valley, attacked Macedonian se ...
(Macedonia)
* 1991–2002: Algerian Civil War
The Algerian Civil War ( ar, rtl=yes, الْحَرْبُ الْأَهْلِيَّةُ الجَزَائِرِيَّةُ, al-Ḥarb al-ʾAhlīyah al-Jazāʾirīyah) was a civil war in Algeria fought between the Algerian government and various I ...
(Algeria)
* 1994: Rwanda Civil War (Uganda)
* 1994–1996: First Chechen War
The First Chechen War, also known as the First Chechen Campaign,, rmed conflict in the Chechen Republic and on bordering territories of the Russian FederationФедеральный закон № 5-ФЗ от 12 января 1995 (в редакц ...
(Russia, Chechnya (limited)) First known case of using tank-launched missiles, which effectively destroy targets at 4 km range.
* 1999–2009: Second Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 ...
(Russia)
* 2003: Invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one month, including 26 ...
(Iraq)
* 2008: War in South Ossetia (Russia and Georgia)
* 2011–Present: Syrian Civil War Government forces using T-72 tanks. Opposition forces using captured government's tanks
* 2011: 2011 Libyan civil war
The First Libyan Civil War was an armed conflict in 2011 in the North African country of Libya that was fought between forces loyal to Colonel Muammar Gaddafi and rebel groups that were seeking to oust Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, his government. It ...
(Gaddafi Government
Muammar Gaddafi became the ''de facto'' leader of Libya on 1 September 1969 after leading a group of young Libyan Army officers against King Idris I in a bloodless coup d'état. After the king had fled the country, the Revolutionary Comma ...
and Anti-Gaddafi forces
The anti-Gaddafi forces were Libyan groups that opposed and militarily defeated the government of Muammar Gaddafi, killing him in the process. These opposition forces included organized and armed militia groups, participants in the Libyan Civil ...
)
* 2013: South Sudanese conflict
* 2014–Present: Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Rev ...
(Ukraine, Russia, pro-Russian separatists)
** 2014: 2014 Pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine
From the end of February 2014, demonstrations by pro-Russian and anti-government groups took place in major cities across the eastern and southern regions of Ukraine in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity, which resulted in the succe ...
(Ukraine, pro-Russian separatists)
** 2014: Annexation of Crimea (Russia)
** 2014–Present: War in Donbas
** 2022–Present: 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
* 2014–2017: Iraqi Civil War (2014-2017) Iraqi civil war may refer to:
* Iraqi–Kurdish conflict (1918–2003), wars and rebellions by Iraqi Kurds against the government
** First Iraqi–Kurdish War (1961–70)
** Second Iraqi–Kurdish War (1974–75)
* 1991 Iraqi uprisings, rebellions i ...
(Iraq)
* 2015: Boko Haram insurgency
The Boko Haram insurgency began in July 2009, when the militant Islamist and jihadist rebel group Boko Haram started an armed rebellion against the government of Nigeria. The conflict is taking place within the context of long-standing is ...
(Nigerian Armed Forces)
* 2016: 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh clashes
The 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, also known as the Four-Day War,, IPA: ʰɑroɾjɑ pɑtɛɾɑzm az, Dördgünlük müharibə April War,; or April clashes, began along the Nagorno-Karabakh line of contact on 1 April 2016 with the Artsakh ...
(Armenia, Azerbaijan)
* 2020: 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of an unresolved conflict over the region, involving Azerba ...
(Armenia, Azerbaijan)
* 2020–Present: 2020–2021 China–India skirmishes (India)
* 2020–Present: Tigray War (Ethiopia, Tigray Defense Forces)
* 2022: 2022 Kyrgyzstan–Tajikistan clashes
A series of sporadic border clashes resumed between Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan on 27 January 2022, following a series of clashes in 2021 between the two countries.
Kyrgyzstan officials said that the clashes escalated on 14 September 2022, with T ...
(Tajikistan)
See also
* 125 mm smoothbore ammunition *AT-8 Songster
The 9K112 Kobra (NATO reporting name: AT-8 Songster) is a SACLOS anti-tank missile system of the Soviet Union. It is fired from the 125 mm main guns of the T-64 and T-80 series of tanks. A newer design based on the same concept is the 9M119 ( ...
* Tank machine gun type 95/98
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Vasiliy Fofanov's Modern Russian Armour Page
Huge pile of Hungarian T-72 walkarounds
T-72 variants
* {{Cold War tanks, style=wide T-72 Cold War tanks of the Soviet Union Main battle tanks of the Soviet Union Main battle tanks of Russia Tanks with autoloaders Uralvagonzavod products Tanks of Russia Tanks of the Soviet Union Tanks of the Cold War Military vehicles introduced in the 1970s