Sundarbans mangroves on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sundarbans (pronounced ) is a
mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
area in the delta formed by the confluence of the Padma
The Padma ( bn, পদ্মা ''Pôdma'') is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is sit ...
, Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. I ...
and Meghna River
The Meghna River ( bn, মেঘনা নদী) is one of the major rivers in Bangladesh, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest delta on earth, which fans out to the Bay of Bengal. A part of the Surma-Meghna River System, ...
s in the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line betwee ...
. It spans the area from the Baleswar River
The Baleshwari River is located in Bangladesh, forming part of the eastern border of Bagerhat District and the western border of Barguna District. It borders on the east the largest mangrove forest in the world, in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta, t ...
in Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
's division of Khulna to the Hooghly River in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
's state of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
. It comprises closed and open mangrove forests, land used for agricultural purpose, mudflats and barren land, and is intersected by multiple tidal
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide.
Tidal may also refer to:
* ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple
* Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim
* TidalCycles, a live coding environment for music
* Tidal (servic ...
streams and channels. Sundarbans is home to the world's largest area of mangrove forests. Four protected areas in the Sundarbans are enlisted as UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
s, viz. Sundarbans West (Bangladesh), Sundarbans South (Bangladesh), Sundarbans East (Bangladesh) and Sundarbans National Park
The Sundarbans National Park is a national park, tiger reserve and biosphere reserve in West Bengal, India. It is part of the Sundarbans on the Ganges Delta and adjacent to the Sundarban Reserve Forest in Bangladesh. It is located to south-w ...
(India).
Despite these protections, the Indian Sundarbans were considered endangered in a 2020 assessment under the IUCN Red List of Ecosystems framework. The Sundarbans mangrove forest covers an area of about , of which forests in Bangladesh's Khulna Division
The Khulna Division ( bn, খুলনা বিভাগ) is the second largest of the eight divisions of Bangladesh. It has an area of and a population of 15,563,000 at the 2011 Bangladesh census (preliminary returns). Its headquarters and lar ...
extend over and in West Bengal, they extend over across the South 24 Parganas and North 24 Parganas districts. The most abundant tree species are sundri (''Heritiera fomes
''Heritiera fomes'' is a species of mangrove tree in the family Malvaceae. Its common names include sunder, sundri, jekanazo and pinlekanazo. It is the dominant mangrove tree species of the Sundarbans of Bangladesh and India, and comprises about ...
'') and gewa (''Excoecaria agallocha
''Excoecaria agallocha'', a mangrove species, belongs to the genus '' Excoecaria'' of the family Euphorbiaceae. The species has many common names, including blind-your-eye mangrove, blinding tree, buta buta tree, milky mangrove, poisonfish tree ...
''). The forests provide habitat to 453 fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''Biota (ecology ...
wildlife, including 290 bird, 120 fish, 42 mammal, 35 reptile and eight amphibian species. Despite a total ban on all killing or capture of wildlife other than fish and some invertebrates, it appears that there is a consistent pattern of depleted biodiversity or loss of species in the 20th century, and that the ecological quality of the forest is declining.
Despite preservation commitments from both governments, the Sundarbans are under threat from both natural and human-made causes. In 2007, the landfall of Cyclone Sidr
Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Sidr was a tropical cyclone that resulted in one of the worst natural disasters in Bangladesh. The fourth named storm of the 2007 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Sidr formed in the central Bay of Bengal, and q ...
damaged around 40% of the Sundarbans. The forest is also suffering from increased salinity due to rising sea levels
Rising may refer to:
* Rising, a stage in baking - see Proofing (baking technique)
*Elevation
* Short for Uprising, a rebellion
Film and TV
* "Rising" (''Stargate Atlantis''), the series premiere of the science fiction television program ''Starga ...
due to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
and reduced freshwater supply. In May 2009 Cyclone Aila
Severe Cyclonic Storm Aila (JTWC designation: 02B) was the second named tropical cyclone of the 2009 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. Warned by both the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RMSC) and Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) ...
devastated the Sundarbans with massive casualties. At least 100,000 people were affected by this cyclone. The proposed coal-fired Rampal power station
The Rampal Power Station ( Bengali, রামপাল বিদ্যুৎ কেন্দ্র) is a 1320 megawatt coal-fired power station currently under construction at Rampal Upazila of Bagerhat District in Khulna, Bangladesh. The po ...
situated north of the Sundarbans at Rampal Upazila of Bagerhat District
Bagerhat District ( bn, বাগেরহাট, pron: ''bageɾɦaʈ'') is a district in south-western Bangladesh. It is a part of the Khulna Division.
Geography
Bagerhat district has a total area of 3959.11 square kilometres. It is bounded by ...
in Khulna, Bangladesh, is anticipated to further damage this unique mangrove forest according to a 2016 report by UNESCO. Climate change is expected to both continue to negatively effect both natural systems and human populations in the region, resulting in further ecosystem degradation and climate migration
Climate migrants are a subset of environmental migrants who were forced to flee "due to sudden or gradual alterations in the natural environment related to at least one of three impacts of climate change: sea-level rise, extreme weather events, a ...
. Experts examining the region recommend further focus on mangrove restoration
Mangrove restoration is the regeneration of mangrove forest ecosystems in areas where they have previously existed. The practice of mangrove restoration is grounded in the discipline of restoration ecology, which aims to “ ssistthe recovery of re ...
and management and advocating for adaptation of human populations, through processes like managed retreat
Managed retreat involves the purposeful, coordinated movement of people and buildings away from risks. This may involve the movement of a person, infrastructure (e.g., building or road), or community. It can occur in response to a variety of hazar ...
and investments in resilient infrastructure.
Etymology
The literal meaning of Sundarbans ( bn, সুন্দরবন, Sundôrbôn) is "beautiful forest". Alternatively, it was proposed that the name is a corruption of ''Samudraban'', ''Shomudrobôn'' ("Sea Forest"), or ''Chandra-bandhe'', the name of a tribe. However, the likely origin of the word is ''Sundari'' or ''Sundri'', the local name of the mangrove species ''Heritiera fomes
''Heritiera fomes'' is a species of mangrove tree in the family Malvaceae. Its common names include sunder, sundri, jekanazo and pinlekanazo. It is the dominant mangrove tree species of the Sundarbans of Bangladesh and India, and comprises about ...
'' abundant in the area.
History
The history of human settlement in the Sundarbans area can be traced back to Mauryan era (4th-2nd century BCE). A ruin of an abandoned city was found in the Baghmara Forest Block that is attributed toChand Sadagar
Chand Sadagar ( Assamese: চান্দ সদাগৰ, Bengali: চাঁদ সদাগর) was a rich and powerful sea merchant of Champaknagar in Eastern India. This merchant has been claimed by both the Assamese and Bengali people of ...
, a pre-Mauryan semi-historical figure in Bengali folklore. Archaeological excavation at Kapilmuni, Paikgacha Upazilla, north of the Sundarbans in Bangladesh, revealed ruins of urban settlement dating back to the early middle ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. During the Mughal period, forest tracts were leased out by the local rulers for establishing settlements. In 1757, The British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
obtained proprietary rights over Sundarbans from the Mughal Emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
Alamgir II and completed mapping the area in 1764. However, systematic forest management started a century later. The first Forest Management Division to have jurisdiction over the Sundarbans was established in 1869. In 1875 a large portion of the mangrove forests was declared as reserved
Reserved is a Polish apparel retailer headquartered in Gdańsk, Pomerania, Poland. It was founded in 1999 and remains the largest company of the LPP group, which has more than 1,700 retail stores located in over 20 countries and also owns such ...
forests under the Indian Forest Act of 1865 (Act VIII of 1865). The remaining portions of the forests were declared a reserve forest the following year and the forest, which was so far administered by the civil administration district, was placed under the control of the Forest Department. A Forest Division, which is the basic forest management and administration unit, was created in 1879 with the headquarters in Khulna, Bangladesh. The first management plan was written for the period 1893–1898.
Geography
The Sundarban forest lies in the vast delta on theBay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line betwee ...
formed by the super confluence of the Hooghly, Padma
The Padma ( bn, পদ্মা ''Pôdma'') is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is sit ...
(both are distributaries of Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
), Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. I ...
and Meghna
The Meghna River ( bn, মেঘনা নদী) is one of the major rivers in Bangladesh, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest delta on earth, which fans out to the Bay of Bengal. A part of the Surma-Meghna River System, ...
rivers across southern Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. The seasonally flooded Sundarbans freshwater swamp forests lie inland from the mangrove forests on the coastal fringe. The forest covers of which about are in Bangladesh. The Indian part of Sundarbans is estimated to be about , of which about is occupied by water bodies in the forms of river, canals and creeks of width varying from a few metres to several kilometres.
The Sundarbans is intersected by a complex network of tidal
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide.
Tidal may also refer to:
* ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple
* Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim
* TidalCycles, a live coding environment for music
* Tidal (servic ...
waterways, mudflats and small islands of salt-tolerant mangrove forests. The interconnected network of waterways makes almost every corner of the forest accessible by boat. The area is known for the Bengal tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present in ...
(''Panthera tigris''), as well as numerous fauna including species of birds, spotted deer
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
, crocodiles and snakes. The fertile soils of the delta have been subject to intensive human use for centuries, and the ecoregion has been mostly converted to intensive agriculture, with few enclaves of forest remaining. The remaining forests, taken together with the Sundarbans mangroves, are important habitat for the endangered tiger. Additionally, the Mangroves species present in the Sundarban area serve a crucial function as a protective barrier for the millions of inhabitants in and around Khulna and Mongla against the floods that result from the cyclones. It also protects from Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater exp ...
and soil erosion for the coastal population.
Physiography
The mangrove-dominated Ganges Delta – the Sundarbans – is a complexecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
comprising one of the three largest single tracts of mangrove forests of the world. The larger part is situated in Bangladesh, a smaller portion of it lies in India. The Indian part of the forest is estimated to be about 40 percent, while the Bangladeshi part is 60 percent. To the south the forest meets the Bay of Bengal; to the east it is bordered by the Baleswar River
The Baleshwari River is located in Bangladesh, forming part of the eastern border of Bagerhat District and the western border of Barguna District. It borders on the east the largest mangrove forest in the world, in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta, t ...
and to the north there is a sharp interface with intensively cultivated land. The natural drainage in the upstream areas, other than the main river channels, is everywhere impeded by extensive embankments and polders. The Sundarbans was originally measured (about 200 years ago) to be of about . Now it has dwindled into about one-third of its original size. The total land area today is , including exposed sandbar
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. ...
s with a total area of ; the remaining water area of encompasses rivers, small streams and canals. Rivers in the Sundarbans are meeting places of salt water and freshwater. Thus, it is a region of transition between the freshwater of the rivers originating from the Ganges and the saline water of the Bay of Bengal.
The Sundarbans along the Bay of Bengal has evolved over the millennia through natural deposition of upstream sediments accompanied by intertidal segregation. The physiography is dominated by deltaic formations that include innumerable drainage lines associated with surface and subaqueous levees, splays and tidal flats. There are also marginal marshes above mean tide level, tidal sandbars and islands with their networks of tidal channels, subaqueous distal bars and proto-delta clays and silt sediments. The Sundarbans' floor varies from above sea level.
Biotic factors here play a significant role in physical coastal evolution, and for wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
a variety of habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
s have developed which include beaches, estuaries, permanent and semi-permanent swamps, tidal flats, tidal creek
A tidal creek or tidal channel is a narrow inlet or estuary that is affected by the ebb and flow of ocean tides. Thus, it has variable salinity and electrical conductivity over the tidal cycle, and flushes salts from inland soils. Tidal cree ...
s, coastal dunes, back dunes and levees. The mangrove vegetation itself assists in the formation of new landmass and the intertidal vegetation plays a significant role in swamp morphology. The activities of mangrove fauna in the intertidal mudflats develop micromorphological
{{Wikidata redirect
This is causing the flight of human capital to the mainland, about 13% in the decade of 2000–2010.
A 2015 ethnographic study, conducted by a team of researchers from Heiderberg university in Germany, found a crisis brewing in the Sunderbans. The study contended that poor planning on the part of the India and Bangladesh governments coupled with natural ecological changes were forcing the flight of human capital from the region
 Part of the Sundarbans is shielded from tidal inflow by leaves and there one finds villages and agriculture. During the
Part of the Sundarbans is shielded from tidal inflow by leaves and there one finds villages and agriculture. During the
 The Sundarbans area is one of the most densely populated areas in the world, and the population is increasing. As a result, half of this ecoregion's mangrove forests have been cut down to supply fuelwood and other natural resources. Despite the intense and large-scale exploitation, this still is one of the largest contiguous areas of mangroves in the world. Another threat comes from deforestation and water diversion from the rivers inland, which causes far more silt to be brought to the estuary, clogging up the waterways.
The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of Sundarban National Park in West Bengal. The
The Sundarbans area is one of the most densely populated areas in the world, and the population is increasing. As a result, half of this ecoregion's mangrove forests have been cut down to supply fuelwood and other natural resources. Despite the intense and large-scale exploitation, this still is one of the largest contiguous areas of mangroves in the world. Another threat comes from deforestation and water diversion from the rivers inland, which causes far more silt to be brought to the estuary, clogging up the waterways.
The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of Sundarban National Park in West Bengal. The
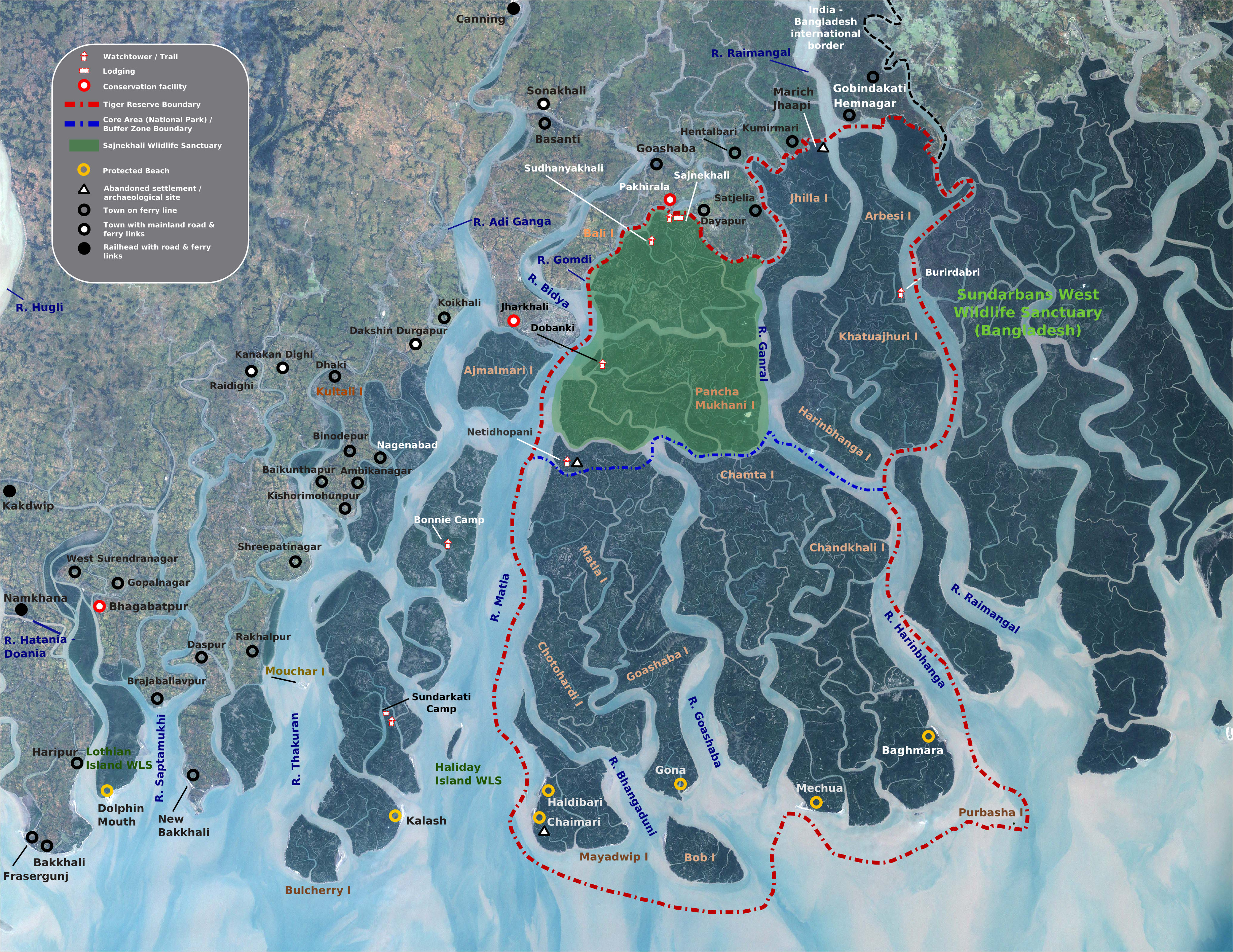 The Bangladesh part of the forest lies under two forest divisions, and four administrative ranges viz Chandpai (Khulna District), Sarankhola (Khulna), and Burigoalini (
The Bangladesh part of the forest lies under two forest divisions, and four administrative ranges viz Chandpai (Khulna District), Sarankhola (Khulna), and Burigoalini (
The Sundarbans: A Unique Wilderness of the World
; a
USDA Forest Reserve
; McCool, Stephen F.; Cole, David N.; Borrie, William T.; O'Loughlin, Jennifer, comps. 2000. Wilderness science in a time of change conference, Volume 2: Wilderness within the context of larger systems; 1999 May 23–27; Missoula, MT. Proceedings RMRS-P-15-VOL-2. Ogden, UT: US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service,
Integrated Resource Development of the Sundarbans Reserved Forest
: Project Findings and Recommendations,
; Also in French: http://base.d-p-h.info/en/fiches/dph/fiche-dph-8148.html * Jalais, Annu. (2010). "Braving Crocodiles with Kali: Being a prawn-seed collector and a modern woman in the 21st century Sundarbans", ''Socio-Legal Review'', Vol. 6. * Montgomery, Sy (1995). ''Spell of the Tiger: The Man-Eaters of Sundarbans''. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York. * Rivers of Life: Living with Floods in Bangladesh. M. Q. Zaman. ''Asian Survey'', Vol. 33, No. 10 (October 1993), pp. 985–996 *
Sundarbans on United Nations Environment Programme
*
Environmental classification of mangrove wetlands of India
. V. Selvam. ''Current Science'', Vol. 84, No. 6, 25 March 2003. *
UNESCO World Heritage Centre: The Sundarbans
UNESCO: Sundarban Biosphere Reserve Information
World Heritage Site: The Sundarbans
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110714132030/http://srmilan.multiply.com/journal/item/15/15 The Sundarban of Bangladesh: A Rich Biodiversity of the World's Largest Mangrove Ecosystem
Greenpeace: Sinking Sundarbans – Climate voices
Tiger Conservation Project in the Bangladeshi Sundarbans
Research on water management and control in the Sunderbans, West Bengal, India
Finfishes of Sundarbans
* Nasa images
set 01
an
set 2
{{West Bengal Geography of South 24 Parganas district Bay of Bengal Protected areas of Bangladesh Protected areas of West Bengal Indomalayan ecoregions Mangrove ecoregions Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Ecoregions of Bangladesh Ecoregions of India Natural regions Environment of West Bengal Forests of Bangladesh Forests of India Forests of West Bengal Ramsar sites in Bangladesh Wetlands of India Ramsar sites in India Tourist attractions in Bangladesh Tourist attractions in West Bengal World Heritage Sites in Bangladesh World Heritage Sites in India Regions of West Bengal Regions of India
Hazards
Natural hazards
According to a report created by UNESCO, the landfall ofCyclone Sidr
Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Sidr was a tropical cyclone that resulted in one of the worst natural disasters in Bangladesh. The fourth named storm of the 2007 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Sidr formed in the central Bay of Bengal, and q ...
damaged around 40% of Sundarbans in 2007.
Human made hazards
In August 2010, a memorandum of understanding was signed betweenBangladesh Power Development Board
The Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) is a government agency operating under the Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources, Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. It was created as a public-sector organization to boos ...
(BPDB) and India's state-owned National Thermal Power Corporation
NTPC Limited, formerly known as National Thermal Power Corporation Limited, is an Indian central public sector undertaking under the ownership of the Ministry of Power, Government of India which is engaged in generation of electricity and ...
(NTPC) where they designated to implement the coal-fired Rampal power station by 2016. The proposed project, on an area of over 1,834 acres of land, is situated north of the Sundarbans. This project violates the environmental impact assessment guidelines for coal-based thermal power plants. Environmental activists contend that the proposed location of the Rampal Station would violate provisions of the Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar site, Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on W ...
. The government of Bangladesh rejected the allegations that the coal-based power plant would adversely affect the world's largest mangrove forest.
On 9 December 2014 an oil-tanker named ''Southern Star VII'', carrying of furnace oil, was sunk in the Sela river of Sundarbans after it had been hit by a cargo vessel. The oil spread over area after the clash, as of 17 December. The slick spread to a second river and a network of canals in the Sundarbans and blackened the shoreline. The event was very threatening to trees, plankton, vast populations of small fishes and dolphins. The event occurred at a protected Sundarbans mangrove area, home to rare Irrawaddy and Ganges dolphins. Until 15 December 2014 only of oil from the area were cleaned up by local residents, Bangladesh Navy
The Bangladesh Navy ( bn, বাংলাদেশ নৌবাহিনী, Bangladesh Nou Bahini) is the naval warfare branch of the Bangladesh Armed Forces, responsible for Bangladesh's of maritime territorial area, and the defence of imp ...
and the government of Bangladesh. Some reports indicated that the event killed some wildlife. On 13 December 2014, a dead Irrawaddy dolphin
The Irrawaddy dolphin (''Orcaella brevirostris'') is a euryhaline species of oceanic dolphin found in scattered subpopulations near sea coasts and in estuaries and rivers in parts of the Bay of Bengal and Southeast Asia. It closely resembles the ...
was seen floating on the Harintana-Tembulbunia channel of the Sela River.
Economy
The Sundarbans plays an important role in the economy of the southwestern region of Bangladesh as well as in the national economy. It is the single largest source offorest produce
Forest produce is defined under section 2(4) of the Indian Forest Act, 1927. Its legal definition includes timber, charcoal, caoutchouc, catechu, wood-oil, resin, natural varnish, bark, lac, myrobalans, mahua flowers (whether found inside or bro ...
in the country. The forest provides raw materials for wood-based industries. In addition to traditional forest produce like timber, fuelwood, pulpwood etc., large-scale harvest of non-wood forest products such as thatching materials, honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
, beeswax, fish, crustacean and mollusc resources of the forest takes place regularly. The vegetated tidal lands of the Sundarbans function as an essential habitat, produces nutrients and purifies water. The forest also traps nutrient and sediment, acts as a storm barrier, shore stabiliser and energy storage unit. Last but not the least, the Sunderbans provides an aesthetic attraction for local and foreign tourists. The water houseboat in the Sundarbans is also a recent attraction among the tourists.
The forest has immense protective and productive functions. Constituting 51% of the total reserved forest estate of Bangladesh, it contributes about 41% of total forest revenue and accounts for about 45% of all timber and fuel wood output of the country. A number of industries (e.g., newsprint mill, match factory, hardboard, boat building, furniture making) are based on raw materials obtained from the Sundarbans ecosystem. Non-timber forest product
Non-timber forest products (NTFPs) are useful foods, substances, materials and/or commodities obtained from forests other than timber. Harvest ranges from wild collection to farming. They typically include game animals, fur-bearers, nuts, see ...
s and plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
s help generate considerable employment and income opportunities for at least half a million poor coastal people. It provides natural protection to life and properties of the coastal population in cyclone-prone Bangladesh.
Agriculture
 Part of the Sundarbans is shielded from tidal inflow by leaves and there one finds villages and agriculture. During the
Part of the Sundarbans is shielded from tidal inflow by leaves and there one finds villages and agriculture. During the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
season, the low lying agricultural lands are waterlogged and the summer crop (''kharif crop
Kharif crops, also known as monsoon crops or autumn crops, are domesticated plants that are cultivated and harvested in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh during the Indian subcontinent's monsoon season, which lasts from June to November depending o ...
'') is therefore mainly deepwater rice or floating rice. In the dry winter season the land is normally uncropped and used for cattle grazing. However, the lands near the villages are irrigated from ponds that were filled up during monsoon, and vegetable crops (''Rabi crop
Rabi crops or
rabi harvest, also known as winter crops, are agricultural crops that are sown in winter and harvested in the spring in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. The complimentary of the rabi crop is the kharif crop, which is grown after t ...
s'') can be grown here.
Habitation
The Sundarbans has a population of over 4 million but much of it is mostly free of permanent human habitation. Despite human habitations and a century of economic exploitation of the forest well into the late 1940s, the Sundarbans retained a forest closure of about 70% according to theOverseas Development Administration
, type = Department
, logo = DfID.svg
, logo_width = 180px
, logo_caption =
, picture = File:Admiralty Screen (411824276).jpg
, picture_width = 180px
, picture_caption = Department for International Development (London office) (far right ...
(ODA) of the United Kingdom in 1980.
Administration
 The Sundarbans area is one of the most densely populated areas in the world, and the population is increasing. As a result, half of this ecoregion's mangrove forests have been cut down to supply fuelwood and other natural resources. Despite the intense and large-scale exploitation, this still is one of the largest contiguous areas of mangroves in the world. Another threat comes from deforestation and water diversion from the rivers inland, which causes far more silt to be brought to the estuary, clogging up the waterways.
The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of Sundarban National Park in West Bengal. The
The Sundarbans area is one of the most densely populated areas in the world, and the population is increasing. As a result, half of this ecoregion's mangrove forests have been cut down to supply fuelwood and other natural resources. Despite the intense and large-scale exploitation, this still is one of the largest contiguous areas of mangroves in the world. Another threat comes from deforestation and water diversion from the rivers inland, which causes far more silt to be brought to the estuary, clogging up the waterways.
The Directorate of Forest is responsible for the administration and management of Sundarban National Park in West Bengal. The Principal Chief Conservator of Forests
The Indian Forest Service (IFS) is one of the three All India Services of the Government of India. The other two All India Services being the Indian Administrative Service and the Indian Police Service. It was constituted in the year 1966 und ...
(PCCF), Wildlife & Bio-Diversity & ex-officio Chief Wildlife Warden, West Bengal is the senior most executive officer looking over the administration of the park. The Chief Conservator of Forests (South) & Director, Sundarban Biosphere Reserve is the administrative head of the park at the local level and is assisted by a Deputy Field Director and an Assistant Field Director. The park area is divided into two ranges, overseen by range forest officers. Each range is further sub-divided into beats. The park also has floating watch stations and camps to protect the property from poachers.
The park receives financial aid from the State Government as well as the Ministry of Environment and Forests
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) is an Indian government ministry. This ministry is headed by Secretary Rank senior most IAS officer. The ministry portfolio is currently held by Bhupender Yadav, Union Minister ...
under various Plan and Non-Plan Budgets. Additional funding is received under the Project Tiger
Project Tiger is a tiger conservation programme launched in April 1973 by the Government of India during Prime Minister Indira Gandhi's tenure. The project aims at ensuring a viable population of the Bengal tiger in its natural habitats, protect ...
from the Central Government. In 2001, a grant of US$20,000 was received as a preparatory assistance for promotion between India and Bangladesh from the World Heritage Fund.
A new Khulna Forest Circle was created in Bangladesh back in 1993 to preserve the forest, and Chief Conservators of Forests have been posted since. The direct administrative head of the Division is the Divisional Forest Officer, based at Khulna, who has a number of professional, subprofessional and support staff and logistic supports for the implementation of necessary management and administrative activities. The basic unit of management is the compartment. There are 55 compartments in four Forest Ranges and these are clearly demarcated mainly by natural features such as rivers, canals and creeks.
Recently West Bengal Cabinet has approved a new district in South 24 Parganas and proposed district was named Sundarban.
Protected areas
 The Bangladesh part of the forest lies under two forest divisions, and four administrative ranges viz Chandpai (Khulna District), Sarankhola (Khulna), and Burigoalini (
The Bangladesh part of the forest lies under two forest divisions, and four administrative ranges viz Chandpai (Khulna District), Sarankhola (Khulna), and Burigoalini (Satkhira District
Satkhira ( bn, সাতক্ষীরা জেলা, pron: ''Satkhira'') is a district in southwestern Bangladesh and is part of Khulna Division. It lies along the border with West Bengal, India. It is on the bank of the Arpangachhia River. T ...
) and has sixteen forest stations. It is further divided into fifty-five compartments and nine blocks. There are three wildlife sanctuaries established in 1977 under the Bangladesh Wildlife (Preservation) Order, 1973 (P.O. 23 of 1973). The West Bengal part of the forest lies under the district of South & North 24 Parganas.
Protected areas cover 15% of the Sundarbans mangroves including Sundarbans National Park
The Sundarbans National Park is a national park, tiger reserve and biosphere reserve in West Bengal, India. It is part of the Sundarbans on the Ganges Delta and adjacent to the Sundarban Reserve Forest in Bangladesh. It is located to south-w ...
and Sajnakhali Wildlife Sanctuary
Sajnekhali Wildlife Sanctuary is a 362 km2 area in the northern part of the Sundarbans delta in South 24 Parganas district, West Bengal, India. It is located at the confluence of the Matla and Gumdi rivers. The area is mainly mangrove scrub, fore ...
, in West Bengal, Sundarbans East, Sundarbans South and Sundarbans West Wildlife Sanctuaries in Bangladesh.
In May 2019, the local authorities in Bangladesh killed 4 tiger poachers in a shootout in the Sunderbans mangrove area where currently 114 tigers dwell.
Sundarban National Park
The Sundarban National Park is a National Park, Tiger Reserve, and aBiosphere Reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
in West Bengal, India. It is part of the Sundarbans on the Ganges Delta, and adjacent to the Sundarbans Reserve Forest in Bangladesh. The delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D ( NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also ...
is densely covered by mangrove forests, and is one of the largest reserves for the Bengal tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna.
The tiger is estimated to have been present in ...
. It is also home to a variety of bird, reptile and invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
species, including the salt-water crocodile. The present Sundarbans National Park was declared as the core area of Sundarbans Tiger Reserve in 1973 and a wildlife sanctuary in 1977. On 4 May 1984 it was declared a National Park.
Sundarbans West Wildlife Sanctuary
Sundarbans West Wildlife Sanctuary is a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Bangladesh. The region supports mangroves, including: sparse stands of Gewa (''Excoecaria agallocha
''Excoecaria agallocha'', a mangrove species, belongs to the genus '' Excoecaria'' of the family Euphorbiaceae. The species has many common names, including blind-your-eye mangrove, blinding tree, buta buta tree, milky mangrove, poisonfish tree ...
'') and dense stands of Goran ('' Ceriops tagal''), with discontinuous patches of Hantal palm ('' Phoenix paludosa'') on drier ground, river banks and levees. The fauna of the sanctuary is very diverse with some 40 species of mammals, 260 species of birds and 35 species of reptiles. The greatest of these being the Bengal tiger of which an estimated 350 remain in the Bangladesh Sundarbans. Other large mammals are wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
, chital horin (spotted deer
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
), Indian otter and macaque monkey
The macaques () constitute a genus (''Macaca'') of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and (in one instance) Gibraltar. Macaques are principall ...
. Five species of marine turtles frequent the coastal zone and two endangered reptiles are present – the estuarine crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats and brackish wetlands from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been liste ...
and the Indian python
The Indian python (''Python molurus'') is a large python species native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It is also known by the common names black-tailed python, Indian rock python, and Asian r ...
.
Sundarbans East Wildlife Sanctuary
Sundarbans East Wildlife Sanctuary extends over an area of in Bangladesh. Sundari trees (''Heritiera fomes'') dominate the flora, interspersed with Gewa (''Excoecaria agallocha
''Excoecaria agallocha'', a mangrove species, belongs to the genus '' Excoecaria'' of the family Euphorbiaceae. The species has many common names, including blind-your-eye mangrove, blinding tree, buta buta tree, milky mangrove, poisonfish tree ...
'') and Passur (''Xylocarpus mekongensis'') with Kankra ('' Bruguiera gymnorhiza'') occurring in areas subject to more frequent flooding. There is an understory of Shingra (''Cynometra ramiflora'') where, soils are drier and Amur (''Aglaia cucullata'') in wetter areas and Goran ('' Ceriops decandra'') in more saline places. Nypa palm (''Nypa fruticans'') is widespread along drainage lines.
Sundarbans South Wildlife Sanctuary
Sundarbans South Wildlife Sanctuary extends over an area of in Bangladesh. There is evidently the greatest seasonal variation in salinity levels and possibly represents an area of relatively longer duration of moderate salinity where Gewa (''Excoecaria agallocha
''Excoecaria agallocha'', a mangrove species, belongs to the genus '' Excoecaria'' of the family Euphorbiaceae. The species has many common names, including blind-your-eye mangrove, blinding tree, buta buta tree, milky mangrove, poisonfish tree ...
'') is the dominant woody species. It is often mixed with Sundri, which is able to displace in circumstances such as artificially opened canopies where Sundri does not regenerate as effectively. It is also frequently associated with a dense understory of Goran ('' Ceriops tagal'') and sometimes Passur.
Sajnakhali Wildlife Sanctuary
Sajnakhali Wildlife Sanctuary is a area in the northern part of the Sundarbans delta inSouth 24 Parganas district
South 24 Parganas (Pron: pɔrɡɔnɔs; abbr. 24 PGS (S)), or sometimes South Twenty Four Parganas and Dakshin 24 Parganas, is a district in the Indian state of West Bengal, headquartered in Alipore. It is the largest district of West Bengal by ...
, West Bengal, India. It is mainly mangrove scrub, forest and swamp. It was set up as a sanctuary in 1976. It is home to a rich population of different species of wildlife, such as water fowl
The Anatidae are the biological family of water birds that includes ducks, geese, and swans. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on all the world's continents except Antarctica. These birds are adapted for swimming, floating ...
, heron, pelican, spotted deer
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
, rhesus macaque
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally ...
s, wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
, tigers, water monitor lizards, fishing cat
The fishing cat (''Prionailurus viverrinus'') is a medium-sized wild cat of South and Southeast Asia. Since 2016, it is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Fishing cat populations are threatened by destruction of wetlands and have declin ...
s, otters, olive ridley turtle
The olive ridley sea turtle (''Lepidochelys olivacea''), also known commonly as the Pacific ridley sea turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Cheloniidae. The species is the second-smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found in th ...
s, crocodiles, batagur terrapins, and migratory birds.
In popular culture
The Sundarbans is celebrated through numerous Bengali folk songs and dances, often centred around the folk heroes, gods and goddesses specific to the Sunderbans (like Bonbibi andDakshin Rai
Dakshin Ray ( bn, দক্ষিণ রায়, "King of the South") is a revered deity in the Sundarbans in India and Bangladesh who rules over beasts and demons. He is regarded as the overall ruler of the Sundarbans. The God is worshipped by ...
) and to the Lower Gangetic Delta (like Manasa
Manasa () is a Hindu goddess of snakes. She is worshipped mainly in Bihar, Bengal, Jharkhand, Lower Assam and other parts of northeastern India and in Uttarakhand, chiefly for the prevention and cure of snakebite, and also for fertility and p ...
and Chand Sadagar
Chand Sadagar ( Assamese: চান্দ সদাগৰ, Bengali: চাঁদ সদাগর) was a rich and powerful sea merchant of Champaknagar in Eastern India. This merchant has been claimed by both the Assamese and Bengali people of ...
). The Bengali folk epic Manasamangal mentions ''Netidhopani'' and has some passages set in the Sundarbans during the heroine Behula
Behula is the protagonist in the Shiva Purana and the Manasamangal genre of Assamese and Bengali medieval epics. A number of works belonging to this genre were written between the thirteenth and eighteenth centuries. Though the religious purpos ...
's quest to bring her husband ''Lakhindar'' back to life.
The area provides the setting for several novels by Emilio Salgari
Emilio Salgari (, but often erroneously ; 21 August 1862 – 25 April 1911) was an Italian writer of action adventure swashbucklers and a pioneer of science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of spe ...
, (e.g. ''The Mystery of the Black Jungle
''The Mystery of the Black Jungle'' ( it, I misteri della jungla nera) is an exotic adventure novel written by Italian author Emilio Salgari, published in 1895. It features two of his most well-known characters, the hunter Tremal-Naik and his loy ...
''). ''Sundarbaney Arjan Sardar'', a novel by Shibshankar Mitra, and ''Padma Nadir Majhi
''Padma Nadir Majhi'' is an Indo-Bangladesh joint production feature film directed by Goutom Ghosh from the novel of the same name, Manik Bandopadhyay's ''Padma Nadir Majhi'', shows life of fishermen of the Padma River.
Plot
Hossain Miya (Utpa ...
'', a novel by Manik Bandopadhyay
Manik Bandyopadhyay lias Banerjee(; 19 May 1908 – 3 December 1956) is an Indian Litterateur regarded as one of the major figures of 20th century Bengali literature. During a lifespan of 48 years and 28 years of literary career, battling with ...
, are based on the rigors of lives of villagers and fishermen living in the Sunderbans region, and are woven into the Bengali psyche to a great extent. Part of the plot of Salman Rushdie
Sir Ahmed Salman Rushdie (; born 19 June 1947) is an Indian-born British-American novelist. His work often combines magic realism with historical fiction and primarily deals with connections, disruptions, and migrations between Eastern and We ...
's Booker Prize winning novel, ''Midnight's Children
''Midnight's Children'' is a 1981 novel by Indian-British writer Salman Rushdie, published by Jonathan Cape with cover design by Bill Botten, about India's transition from British colonial rule to independence and partition. It is a postc ...
'' is set in the Sundarbans. This forest is adopted as the setting of Kunal Basu
''Kunal Basu'' ('' Bengali:'' কুনাল বসু) is an Indian author of English fiction who has written five novels – ''The Opium Clerk'' (2001), ''The Miniaturist'' (2003), '' Racists'' (2006), ''The Yellow Emperor's Cure'' (2011) '' ...
's short story "The Japanese Wife" and the subsequent film adaptation. Most of the plot of an internationally acclaimed novelist, Amitav Ghosh
Amitav Ghosh (born 11 July 1956)Ghosh, Amitav
, '''s 2004 novel, '' The Hungry Tide'', is set in the Sundarbans. The plot centres on a headstrong American cetologist who arrives to study a rare species of river dolphin, enlisting a local fisherman and translator to aid her. The book also mentions two accounts of the Bonbibi story of "Dukhey's Redemption". Manik Bandopadhyay's ''
TV series '', '''s 2004 novel, '' The Hungry Tide'', is set in the Sundarbans. The plot centres on a headstrong American cetologist who arrives to study a rare species of river dolphin, enlisting a local fisherman and translator to aid her. The book also mentions two accounts of the Bonbibi story of "Dukhey's Redemption". Manik Bandopadhyay's ''
Padma Nadir Majhi
''Padma Nadir Majhi'' is an Indo-Bangladesh joint production feature film directed by Goutom Ghosh from the novel of the same name, Manik Bandopadhyay's ''Padma Nadir Majhi'', shows life of fishermen of the Padma River.
Plot
Hossain Miya (Utpa ...
'' was made into a movie by Goutam Ghose
Goutam Ghose (also spelled Gautam Ghosh born 24 July 1950) is an Indian film director, Actor, music director and cinematographer, who works primarily in Bengali cinema. He is the only Indian to have received the "Vittorio Di Sica" Award, Italy ...
.
The Sunderbans has been the subject of a detailed and well-researched scholarly work on Bonbibi (a 'forest goddess' venerated by Hindus), on the relation between the islanders and tigers and on conservation and how it is perceived by the inhabitants of the Sundarbans, as well as numerous non-fiction books, including ''The Man-Eating Tigers of Sundarbans'' by Sy Montegomery for a young audience, which was shortlisted for the Dorothy Canfield Fisher Children's Book Award
The Vermont Golden Dome Book Award (formerly the Dorothy Canfield Fisher Children's Book Award) annually recognizes one new American children's book selected by the vote of Vermont schoolchildren. It was inaugurated in 1957.
The award is co-spon ...
. In ''Up The Country'', Emily Eden
Emily Eden (3 March 1797 – 5 August 1869) was an English poet and novelist who gave witty accounts of English life in the early 19th century. She wrote a celebrated account of her travels in India, and two novels that sold well. She was also a ...
discusses her travels through the Sunderbans. Numerous documentary movies have been made about the Sunderbans, including the 2003 IMAX production ''Shining Bright'' about the Bengal tiger. The acclaimed BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
'' documents the lives of villagers, especially honey collector
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primaril ...
s, in the Sundarbans.
See also
* Sundarbans Tiger Project *Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education
The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) is an autonomous organisation or governmental agency under the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India. Headquartered in Dehradun, its functions are to conduct fore ...
* Sangu Wildlife Sanctuary
Sangu Matamuhari or Sangu Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary—IUCN category II (habitat/species management area)—situated in Bandarban District, Chittagong Division, Bangladesh. It is part of the Sangu reserve forest. It is under the Lam ...
* Environmental impact of development in the Sundarbans Environmental impact of development in the Sundarbans, is the study of environmental impact on Sundarban, the largest single tract mangrove forest. It consist of a geographical area of , including of reserve forest land, and is a natural region l ...
References
Sources
* * Laskar Muqsudur RahmanThe Sundarbans: A Unique Wilderness of the World
; a
USDA Forest Reserve
; McCool, Stephen F.; Cole, David N.; Borrie, William T.; O'Loughlin, Jennifer, comps. 2000. Wilderness science in a time of change conference, Volume 2: Wilderness within the context of larger systems; 1999 May 23–27; Missoula, MT. Proceedings RMRS-P-15-VOL-2. Ogden, UT: US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service,
Rocky Mountain Research Station
The Rocky Mountain Research Station (RMRS) is one of five regional units that make up the US Forest Service Research and Development organization — the most extensive natural resources research organization in the world. The station headquarte ...
.
* Terminal ReportIntegrated Resource Development of the Sundarbans Reserved Forest
: Project Findings and Recommendations,
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
(acting as executing agency for the United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
), United Nations, Rome, 1998 (prepared for the Government of Bangladesh)
* Blasco, F. (1975). ''The Mangroves of India''. Institut Francis de Pondichéry, Travaux de las Section Scientifique et Technique, Tome XIV, Facicule 1. Pondicherry, India.
* Jalais, Annu. (2005). "Dwelling on Morichjhanpi: When Tigers Became 'Citizens', Refugees 'Tiger-Food'"; ''Economic and Political Weekly'', 23 April 2005, pp. 1757 – 1762.
* Jalais, Annu. (2007). "The Sundarbans: Whose World Heritage Site?", ''Conservation and Society'' (vol. 5, no. 4).
* Jalais, Annu. (2008). "Unmasking the Cosmopolitan Tiger", ''Nature and Culture'' (vol. 3, no. 1), pp. 25–40.
* Jalais, Annu. (2008). "Bonbibi: Bridging Worlds", ''Indian Folklore'', serial no. 28, Jan 2008.
* Jalais, Annu. (2009). "Confronting Authority, Negotiating Morality: tiger prawn seed collection in the Sundarbans", International Collective in Support of Fishworkers, Yemaya, 32, Nov; Also in French: http://base.d-p-h.info/en/fiches/dph/fiche-dph-8148.html * Jalais, Annu. (2010). "Braving Crocodiles with Kali: Being a prawn-seed collector and a modern woman in the 21st century Sundarbans", ''Socio-Legal Review'', Vol. 6. * Montgomery, Sy (1995). ''Spell of the Tiger: The Man-Eaters of Sundarbans''. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York. * Rivers of Life: Living with Floods in Bangladesh. M. Q. Zaman. ''Asian Survey'', Vol. 33, No. 10 (October 1993), pp. 985–996 *
Sundarbans on United Nations Environment Programme
*
Environmental classification of mangrove wetlands of India
. V. Selvam. ''Current Science'', Vol. 84, No. 6, 25 March 2003. *
External links
*UNESCO World Heritage Centre: The Sundarbans
UNESCO: Sundarban Biosphere Reserve Information
World Heritage Site: The Sundarbans
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110714132030/http://srmilan.multiply.com/journal/item/15/15 The Sundarban of Bangladesh: A Rich Biodiversity of the World's Largest Mangrove Ecosystem
Greenpeace: Sinking Sundarbans – Climate voices
Tiger Conservation Project in the Bangladeshi Sundarbans
Research on water management and control in the Sunderbans, West Bengal, India
Finfishes of Sundarbans
* Nasa images
set 01
an
set 2
{{West Bengal Geography of South 24 Parganas district Bay of Bengal Protected areas of Bangladesh Protected areas of West Bengal Indomalayan ecoregions Mangrove ecoregions Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Ecoregions of Bangladesh Ecoregions of India Natural regions Environment of West Bengal Forests of Bangladesh Forests of India Forests of West Bengal Ramsar sites in Bangladesh Wetlands of India Ramsar sites in India Tourist attractions in Bangladesh Tourist attractions in West Bengal World Heritage Sites in Bangladesh World Heritage Sites in India Regions of West Bengal Regions of India