Sultan Mehmet The Conqueror on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Sultan Mehmed, links=no), was an
 Mehmed II was born on 30 March 1432, in
Mehmed II was born on 30 March 1432, in

 When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he devoted himself to strengthening the Ottoman navy and made preparations for an attack on Constantinople. In the narrow Bosphorus Straits, the fortress
When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he devoted himself to strengthening the Ottoman navy and made preparations for an attack on Constantinople. In the narrow Bosphorus Straits, the fortress  After the conquest of Constantinople, Mehmed claimed the title of
After the conquest of Constantinople, Mehmed claimed the title of
 Mehmed II's first campaigns after Constantinople were in the direction of Serbia, which had been an Ottoman
Mehmed II's first campaigns after Constantinople were in the direction of Serbia, which had been an Ottoman
 The
The

 The Ottomans since the early 15th century tried to bring Wallachia ( ota, والاچیا) under their control by putting their own candidate on the throne, but each attempt ended in failure. The Ottomans regarded Wallachia as a buffer zone between them and the Kingdom of Hungary and for a yearly tribute did not meddle in their internal affairs. The two primary Balkan powers, Hungary and the Ottomans, maintained an enduring struggle to make Wallachia their own vassal. To prevent Wallachia from falling into the Hungarian fold, the Ottomans freed young
The Ottomans since the early 15th century tried to bring Wallachia ( ota, والاچیا) under their control by putting their own candidate on the throne, but each attempt ended in failure. The Ottomans regarded Wallachia as a buffer zone between them and the Kingdom of Hungary and for a yearly tribute did not meddle in their internal affairs. The two primary Balkan powers, Hungary and the Ottomans, maintained an enduring struggle to make Wallachia their own vassal. To prevent Wallachia from falling into the Hungarian fold, the Ottomans freed young
 The despot of Serbia, Lazar Branković, died in 1458, and a civil war broke out among his heirs that resulted in the Ottoman conquest of Serbia in 1459/1460.
The despot of Serbia, Lazar Branković, died in 1458, and a civil war broke out among his heirs that resulted in the Ottoman conquest of Serbia in 1459/1460.
 During the post- Seljuks era in the second half of the middle ages, numerous Turkmen principalities collectively known as
During the post- Seljuks era in the second half of the middle ages, numerous Turkmen principalities collectively known as
 In 1456,
In 1456,
Calendar 26 iulie 2005.Moment istoric
(Anniversaries on 26 July 2005. A historical moment)'' and began forming another army. The Ottomans were unable to conquer any of the major Moldavian strongholds ( Suceava, Neamț, Hotin) and were constantly harassed by small scale Moldavians attacks. Soon they were also confronted with starvation, a situation made worse by an outbreak of the


 An Ottoman army under
An Ottoman army under
 After conquering Constantinople, when Mehmed II finally entered the city through what is now known as the Topkapi Gate, he immediately rode his horse to the Hagia Sophia, where he ordered the building to be protected. He ordered that an imam meet him there in order to chant the Muslim Creed: "I testify that there is no
After conquering Constantinople, when Mehmed II finally entered the city through what is now known as the Topkapi Gate, he immediately rode his horse to the Hagia Sophia, where he ordered the building to be protected. He ordered that an imam meet him there in order to chant the Muslim Creed: "I testify that there is no
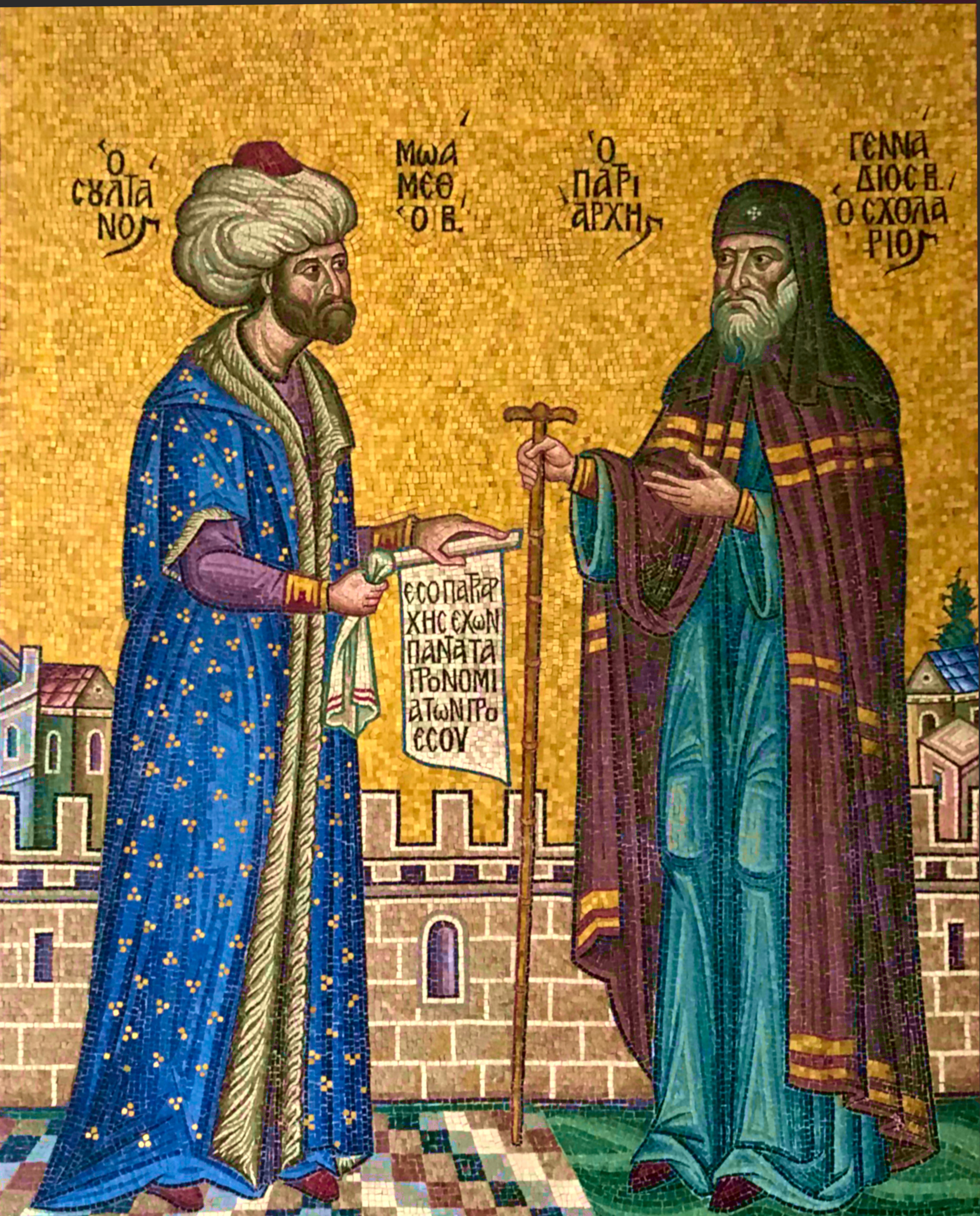 Mehmed II introduced the word Politics into Arabic "Siyasah" from a book he published and claimed to be the collection of Politics doctrines of the Byzantine Caesars before him. He gathered Italian artists, humanism, humanists and Greek scholars at his court, allowed the Eastern Orthodox, Byzantine Church to continue functioning, ordered the patriarch Gennadius Scholarius, Gennadius to translate Christianity, Christian doctrine into Turkish, and called Gentile Bellini from Venice to paint his portrait as well as Venetian frescoes that are vanished today. He collected in his palace a library which included works in Greek, Persian and Latin. Mehmed invited Muslim scientists and astronomers such as Ali Qushji and artists to his court in Constantinople, started a university, built mosques (for example, the Fatih Mosque), waterways, and Istanbul's Topkapı Palace and the Tiled Kiosk.
Around the Fatih Mosque, grand mosque that he constructed, he erected Sahn-ı Seman Medrese, eight madrasas, which, for nearly a century, kept their rank as the highest teaching institutions of the Islamic sciences in the empire.
Mehmed II allowed his subjects a considerable degree of religious freedom, provided they were obedient to his rule. After his conquest of Bosnia in 1463 he issued the Ahdname of Milodraž to the Bosnian Franciscans, granting them freedom to move freely within the Empire, offer worship in their churches and monastery, monasteries, and to practice their religion free from official and unofficial persecution, insult or disturbance. However, his standing army was recruited from the ''Devshirme'', a group that took Christian subjects at a young age (8–20 yrs): they were converted to Islam, then schooled for administration or the military Janissaries. This was a meritocracy which "produced from among their alumni four out of five Grand Viziers from this time on".
Within Constantinople, Mehmed established a ''Millet (Ottoman Empire), millet'' or an autonomous religious community, and appointed the former Patriarch
Mehmed II introduced the word Politics into Arabic "Siyasah" from a book he published and claimed to be the collection of Politics doctrines of the Byzantine Caesars before him. He gathered Italian artists, humanism, humanists and Greek scholars at his court, allowed the Eastern Orthodox, Byzantine Church to continue functioning, ordered the patriarch Gennadius Scholarius, Gennadius to translate Christianity, Christian doctrine into Turkish, and called Gentile Bellini from Venice to paint his portrait as well as Venetian frescoes that are vanished today. He collected in his palace a library which included works in Greek, Persian and Latin. Mehmed invited Muslim scientists and astronomers such as Ali Qushji and artists to his court in Constantinople, started a university, built mosques (for example, the Fatih Mosque), waterways, and Istanbul's Topkapı Palace and the Tiled Kiosk.
Around the Fatih Mosque, grand mosque that he constructed, he erected Sahn-ı Seman Medrese, eight madrasas, which, for nearly a century, kept their rank as the highest teaching institutions of the Islamic sciences in the empire.
Mehmed II allowed his subjects a considerable degree of religious freedom, provided they were obedient to his rule. After his conquest of Bosnia in 1463 he issued the Ahdname of Milodraž to the Bosnian Franciscans, granting them freedom to move freely within the Empire, offer worship in their churches and monastery, monasteries, and to practice their religion free from official and unofficial persecution, insult or disturbance. However, his standing army was recruited from the ''Devshirme'', a group that took Christian subjects at a young age (8–20 yrs): they were converted to Islam, then schooled for administration or the military Janissaries. This was a meritocracy which "produced from among their alumni four out of five Grand Viziers from this time on".
Within Constantinople, Mehmed established a ''Millet (Ottoman Empire), millet'' or an autonomous religious community, and appointed the former Patriarch
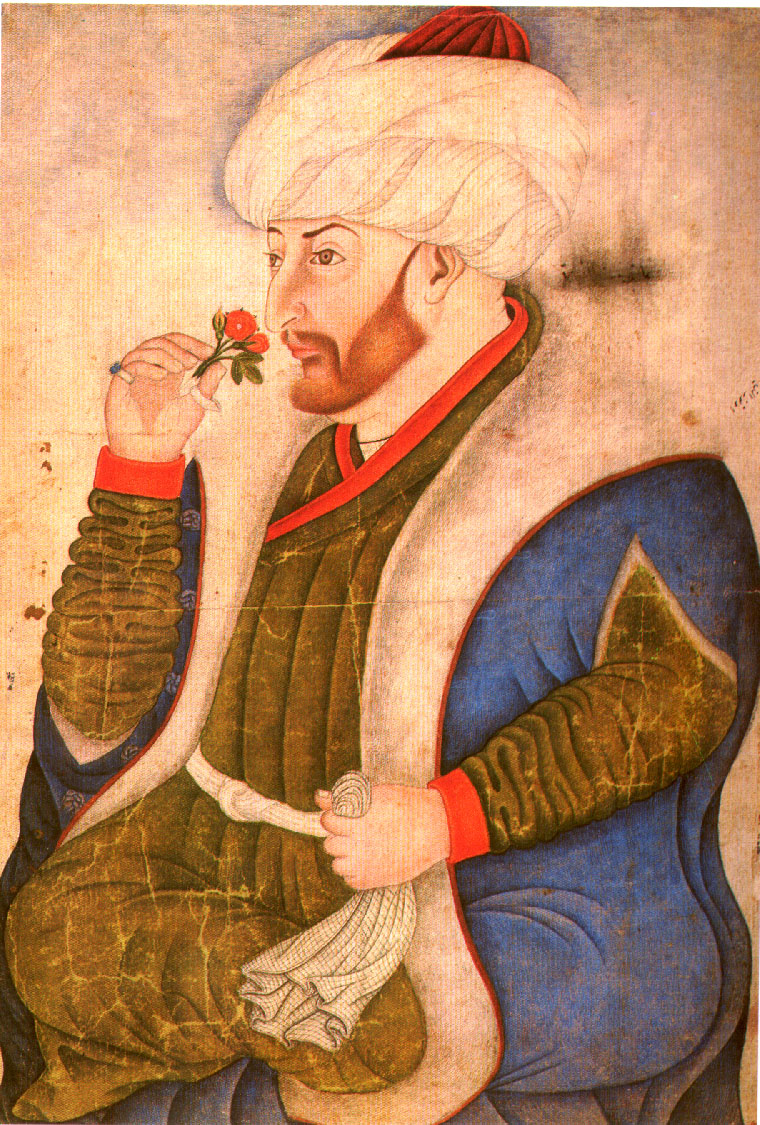 Aside from his efforts to expand Ottoman dominion throughout the Eastern Mediterranean, Mehmed II also cultivated a large collection of Western art and literature, many of which were produced by Renaissance artists. From a young age, Mehmed had shown interest in Renaissance art and Classical literature and histories, with his school books having caricaturistic illustrations of ancient coins and portraiture sketched in distinctly European styles. Furthermore, he reportedly had two tutors, one trained in Greek and another in Latin, who read him Classical histories including those of Laertius, Livy, and Herodotus in the days leading up to the fall of Constantinople.
From early on in his reign, Mehmed invested in the patronage of Italian Renaissance artists. His first documented request in 1461 was a commission from artist Matteo de' Pasti, who resided in the court of the lord of Rimini, Sigismondo Malatesta. This first attempt was unsuccessful, though, as Pasti was arrested in Crete by Venetian authorities accusing him of being an Ottoman spy. Later attempts would prove more fruitful, with some notable artists including Costanzo da Ferrara and Gentile Bellini both being invited to the Ottoman court.
Aside from his patronage of Renaissance artists, Mehmed was also an avid scholar of contemporary and Classical literature and history. This interest culminated in Mehmed's work on building a massive multilingual library that contained over 8000 manuscripts in Persian, Ottoman Turkish, Arabic, Latin, and Greek, among other languages. Of note in this large collection was Mehmed's Greek scriptorium, which included copies of Arrians’ ''Anabasis of Alexander the Great'' and Homer's ''Iliad''. His interest in Classical works extended in many directions, including the patronage of the Greek writer Kritiboulos of Imbros, who produced the Greek manuscript ''History of Mehmed the Conqueror'', alongside his efforts to salvage and rebind Greek manuscripts acquired after his conquest of Constantinople.
Historians believe that Mehmed's widespread cultural and artistic tastes, especially those aimed towards the West, served various important diplomatic and administrative functions. His patronage of Renaissance artists have been interpreted as a method of diplomacy with other influential Mediterranean states, significantly many Italian states including the Kingdom of Naples and the Republic of Florence. Furthermore, historians speculate that his Greek scriptorium was used to educate Greek chancellery officials in an attempt to reintegrate former Byzantine diplomatic channels with several Italian states that conducted their correspondences in Greek. Importantly, historians also assert that Mehmed's vast collection of art and literature worked towards promoting his imperial authority and legitimacy, especially in his newly conquered lands. This was accomplished through various means, including the invocation of Mehmed's image as an Oriental neo-Alexandrian figure, which is seen through shared helmet ornaments in depictions of Mehmed and Alexander on medallion portraits produced during Mehmed's reign, as well as being a leitmotiv in Kritiboulous’ work. Additionally, his commissioning of Renaissance artwork was, itself, possibly an attempt to break down Western-Oriental cultural binaries in order for Mehmed to present himself as a Western-oriented ruler, among the ranks of contemporary European Christian monarchs.
Mehmed's affinity towards the Renaissance arts, and his strong initiative in its creation and collection, did not have a large base of support within his own court. One of the many opponents to Mehmed's collection was his own son and future Sultan, Bayezid II, who was backed by powerful religious and Turkish factions in his opposition. Upon his accession, Bayezid II sold Mehmed's collection of portraits and disposed of his statuary.
Aside from his efforts to expand Ottoman dominion throughout the Eastern Mediterranean, Mehmed II also cultivated a large collection of Western art and literature, many of which were produced by Renaissance artists. From a young age, Mehmed had shown interest in Renaissance art and Classical literature and histories, with his school books having caricaturistic illustrations of ancient coins and portraiture sketched in distinctly European styles. Furthermore, he reportedly had two tutors, one trained in Greek and another in Latin, who read him Classical histories including those of Laertius, Livy, and Herodotus in the days leading up to the fall of Constantinople.
From early on in his reign, Mehmed invested in the patronage of Italian Renaissance artists. His first documented request in 1461 was a commission from artist Matteo de' Pasti, who resided in the court of the lord of Rimini, Sigismondo Malatesta. This first attempt was unsuccessful, though, as Pasti was arrested in Crete by Venetian authorities accusing him of being an Ottoman spy. Later attempts would prove more fruitful, with some notable artists including Costanzo da Ferrara and Gentile Bellini both being invited to the Ottoman court.
Aside from his patronage of Renaissance artists, Mehmed was also an avid scholar of contemporary and Classical literature and history. This interest culminated in Mehmed's work on building a massive multilingual library that contained over 8000 manuscripts in Persian, Ottoman Turkish, Arabic, Latin, and Greek, among other languages. Of note in this large collection was Mehmed's Greek scriptorium, which included copies of Arrians’ ''Anabasis of Alexander the Great'' and Homer's ''Iliad''. His interest in Classical works extended in many directions, including the patronage of the Greek writer Kritiboulos of Imbros, who produced the Greek manuscript ''History of Mehmed the Conqueror'', alongside his efforts to salvage and rebind Greek manuscripts acquired after his conquest of Constantinople.
Historians believe that Mehmed's widespread cultural and artistic tastes, especially those aimed towards the West, served various important diplomatic and administrative functions. His patronage of Renaissance artists have been interpreted as a method of diplomacy with other influential Mediterranean states, significantly many Italian states including the Kingdom of Naples and the Republic of Florence. Furthermore, historians speculate that his Greek scriptorium was used to educate Greek chancellery officials in an attempt to reintegrate former Byzantine diplomatic channels with several Italian states that conducted their correspondences in Greek. Importantly, historians also assert that Mehmed's vast collection of art and literature worked towards promoting his imperial authority and legitimacy, especially in his newly conquered lands. This was accomplished through various means, including the invocation of Mehmed's image as an Oriental neo-Alexandrian figure, which is seen through shared helmet ornaments in depictions of Mehmed and Alexander on medallion portraits produced during Mehmed's reign, as well as being a leitmotiv in Kritiboulous’ work. Additionally, his commissioning of Renaissance artwork was, itself, possibly an attempt to break down Western-Oriental cultural binaries in order for Mehmed to present himself as a Western-oriented ruler, among the ranks of contemporary European Christian monarchs.
Mehmed's affinity towards the Renaissance arts, and his strong initiative in its creation and collection, did not have a large base of support within his own court. One of the many opponents to Mehmed's collection was his own son and future Sultan, Bayezid II, who was backed by powerful religious and Turkish factions in his opposition. Upon his accession, Bayezid II sold Mehmed's collection of portraits and disposed of his statuary.
 Some sources indicate that Mehmed had a passion for his hostage and favourite, Radu the Fair. Young men condemned to death were spared and added to Mehmed's seraglio if he found them attractive, and the Porte went to great lengths to procure young noblemen for him.
Mehmed had a strong interest in ancient Greek and medieval Byzantine civilization. His heroes were Achilles and Alexander the Great and he could discuss Christian religion with some authority. He was reputed to be fluent in several languages, including Ottoman Turkish language, Turkish, Serbian language, Serbian, Arab language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian, Greek language, Greek and Latin language, Latin.
At times, he assembled the Ulama, or learned Muslim teachers, and caused them to discuss theological problems in his presence. During his reign, mathematics, astronomy, and theology reached their highest level among the Ottomans. His social circle included a number of humanists and sages such as Ciriaco de' Pizzicolli of Ancona, Benedetto Dei of Florence and
Some sources indicate that Mehmed had a passion for his hostage and favourite, Radu the Fair. Young men condemned to death were spared and added to Mehmed's seraglio if he found them attractive, and the Porte went to great lengths to procure young noblemen for him.
Mehmed had a strong interest in ancient Greek and medieval Byzantine civilization. His heroes were Achilles and Alexander the Great and he could discuss Christian religion with some authority. He was reputed to be fluent in several languages, including Ottoman Turkish language, Turkish, Serbian language, Serbian, Arab language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian, Greek language, Greek and Latin language, Latin.
At times, he assembled the Ulama, or learned Muslim teachers, and caused them to discuss theological problems in his presence. During his reign, mathematics, astronomy, and theology reached their highest level among the Ottomans. His social circle included a number of humanists and sages such as Ciriaco de' Pizzicolli of Ancona, Benedetto Dei of Florence and
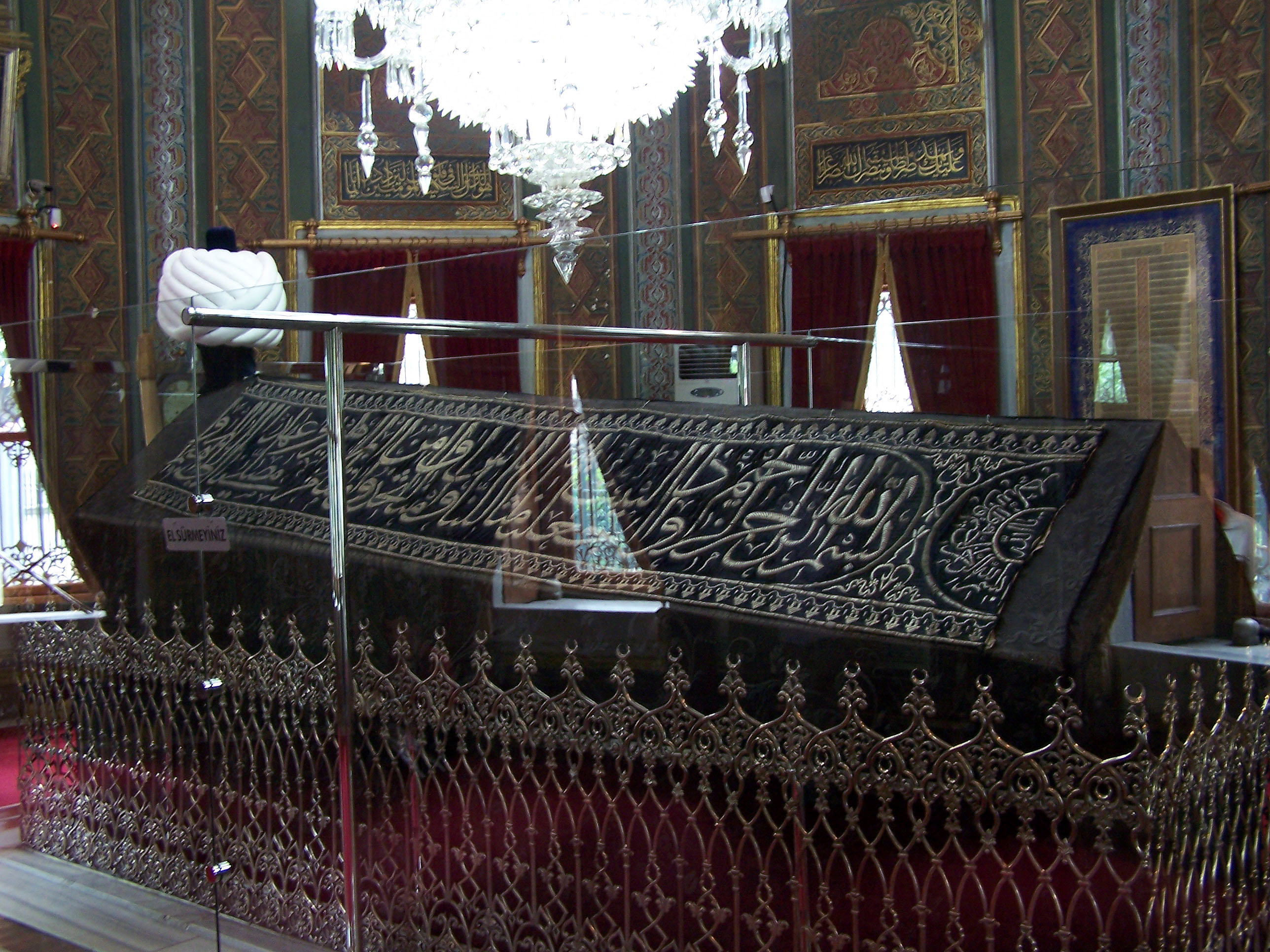
 In 1481 Mehmed marched with the Ottoman army, but upon reaching Maltepe, Istanbul he became ill. He was just beginning new campaigns to capture Rhodes and southern Italy, however according to some historians his next voyage was planned to overthrow the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt and to capture Egypt and claim the caliphate. But after some days he died, on 3 May 1481, at the age of forty-nine, and was buried in his ''türbe'' near the
In 1481 Mehmed marched with the Ottoman army, but upon reaching Maltepe, Istanbul he became ill. He was just beginning new campaigns to capture Rhodes and southern Italy, however according to some historians his next voyage was planned to overthrow the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt and to capture Egypt and claim the caliphate. But after some days he died, on 3 May 1481, at the age of forty-nine, and was buried in his ''türbe'' near the
''A history of modern Europe From the fall of Constantinople''
London: G. Bell and Sons. * * Fredet, Peter (1888)
''Modern History; From the Coming of Christ and Change of the Roman Republic into an Empire, to the Year of Our Lord 1888''
Baltimore: J. Murphy & Co
383 pp
* Harris, Jonathan, ''The End of Byzantium''. New Haven CT and London: Yale University Press, 2010.
İnalcık; Halil, Review of ''Mehmed the Conqueror and his Time''
* Imber, Colin, ''The Ottoman Empire, 1300–1650: The Structure of Power''. 2nd Edition. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2009. * * * * Philippides, Marios, ''Emperors, Patriarchs, and Sultans of Constantinople, 1373–1513: An Anonymous Greek Chronicle of the Sixteenth Century''. Brookline MA: Hellenic College Press, 1990. * * Silburn, P. A. B. (1912)
''The evolution of sea-power''
London: Longmans, Green and Co. *
by Edward Gibbon
Constantinople Siege & Fall
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Roger Crowley, Judith Herrin & Colin Imber (''In Our Time (radio series), In Our Time'', 28 December 2006) {{DEFAULTSORT:Mehmed 02 Mehmed the Conqueror, Hanafis Maturidis Sunni Sufis 1432 births 1481 deaths Turkish Muslims 15th-century murdered monarchs 15th-century Ottoman sultans Burials in Turkey Deaths by poisoning Fall of Constantinople Medieval child rulers Mujaddid Ottoman people of the Byzantine–Ottoman wars Ottoman people of the Ottoman–Venetian Wars People from Edirne Turkish poets The Sultan of Two Lands and the Khan of Two Seas
Ottoman sultan
The sultans of the Ottoman Empire ( tr, Osmanlı padişahları), who were all members of the Ottoman dynasty (House of Osman), ruled over the transcontinental empire from its perceived inception in 1299 to its dissolution in 1922. At its hei ...
who ruled from August 1444 to September 1446, and then later from February 1451 to May 1481. In Mehmed II's first reign, he defeated the crusade led by John Hunyadi after the Hungarian incursions into his country broke the conditions of the truce Peace of Szeged
The Treaty of Edirne and the Peace of Szeged were two halves of a peace treaty between Sultan Murad II of the Ottoman Empire and King Vladislaus of the Kingdom of Hungary. Despot Đurađ Branković of the Serbian Despotate was a party to the ...
. When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he strengthened the Ottoman navy and made preparations to attack Constantinople. At the age of 21, he conquered
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, ...
Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and brought an end to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
.
After the conquest Mehmed claimed the title Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
( ota, قیصر روم, Qayser-i Rûm, links=no), based on the fact that Constantinople had been the seat and capital of the surviving Eastern Roman Empire since its consecration in 330 AD by Emperor Constantine I. The claim was only recognized by the Patriarchate of Constantinople. Nonetheless, Mehmed II viewed the Ottoman state as a continuation of the Roman Empire for the remainder of his life, seeing himself as "continuing" the Empire rather than "replacing" it.
Mehmed continued his conquests in Anatolia with its reunification and in Southeast Europe as far west as Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
. At home he made many political and social reforms, encouraged the arts and sciences, and by the end of his reign, his rebuilding program had changed Constantinople into a thriving imperial capital. He is considered a hero in modern-day Turkey and parts of the wider Muslim world. Among other things, Istanbul's Fatih district, Fatih Sultan Mehmet Bridge
The Fatih Sultan Mehmet Bridge ("Sultan Mehmed the Conqueror Bridge"), also known as the Second Bosphorus Bridge (in Turkish: ''Fatih Sultan Mehmet Köprüsü'', ''F.S.M. Köprüsü'' or ''2. Köprü''), is a bridge in Istanbul, Turkey spannin ...
and Fatih Mosque
The large Fatih Mosque ( tr, Fatih Camii, "Conqueror's Mosque" in English) is an Ottoman mosque off Fevzi Paşa Caddesi in the Fatih district of Istanbul, Turkey. The original mosque was constructed between 1463 and 1470 on the site of the C ...
are named after him.
Early reign
 Mehmed II was born on 30 March 1432, in
Mehmed II was born on 30 March 1432, in Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
, then the capital city of the Ottoman state. His father was Sultan Murad II (1404–1451) and his mother Hüma Hatun
Hüma Hatun ( ota, هما خاتون, 1410 ‒ September 1449) was the fourth wife of Ottoman Sultan Murad II and mother of Mehmed II.
Life
Although, some Turkish sources claim that she was of Turkish origin, Hüma Hatun was a slave girl, whi ...
, a slave of uncertain origin.
When Mehmed II was eleven years old he was sent to Amasya
Amasya () is a city in northern Turkey and is the capital of Amasya Province, in the Black Sea Region. It was called Amaseia or Amasia in antiquity."Amasya" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th ...
with his two ''lalas'' (advisors) to govern and thus gain experience, per the custom of Ottoman rulers before his time. Sultan Murad II also sent a number of teachers for him to study under. This Islamic education had a great impact in molding Mehmed's mindset and reinforcing his Muslim beliefs. He was influenced in his practice of Islamic epistemology by practitioners of science, particularly by his mentor, Molla Gürani, and he followed their approach. The influence of Akshamsaddin
Akshamsaddin (Muhammad Shams al-Din bin Hamzah, tr, Akşemseddin) (1389, Damascus – 16 February 1459, Göynük, Bolu), was an influential Ottoman Sunni Muslim scholar, poet, and mystic saint.
Biography
He was the grandson of Shahab al-Di ...
in Mehmed's life became predominant from a young age, especially in the imperative of fulfilling his Islamic duty to overthrow the Byzantine empire by conquering Constantinople.
After Murad II made peace with Hungary on June 12, 1444, he abdicated the throne to his 12-year-old son Mehmed II in July/August 1444.
In Mehmed II's first reign, he defeated the crusade led by John Hunyadi after the Hungarian incursions into his country broke the conditions of the truce Peace of Szeged
The Treaty of Edirne and the Peace of Szeged were two halves of a peace treaty between Sultan Murad II of the Ottoman Empire and King Vladislaus of the Kingdom of Hungary. Despot Đurađ Branković of the Serbian Despotate was a party to the ...
in September 1444. Cardinal Julian Cesarini
Julian Cesarini the Elder ( It.: ''Giuliano Cesarini, seniore'') (1398 in Rome – 10 November 1444 in Varna, Ottoman Empire) was one of the group of brilliant cardinals created by Pope Martin V on the conclusion of the Western Schism. His ...
, the representative of the Pope, had convinced the king of Hungary that breaking the truce with Muslims was not a betrayal. At this time Mehmed II asked his father Murad II to reclaim the throne, but Murad II refused. According to the 17th-century chronicles,Erhan Afyoncu
Erhan Afyoncu (born 1967, in Tokat) is a Turkish historian, writer, academician, television programmer and columnist. Rector of the National Defense University.
Personal life
He saw his primary and secondary education in Tokat, the place of birth. ...
, (2009), Truvanın İntikamı (), p. 2, (In Turkish) Mehmed II wrote, "If you are the sultan, come and lead your armies. If I am the sultan I hereby order you to come and lead my armies." Then, Murad II led the Ottoman army and won the Battle of Varna
The Battle of Varna took place on 10 November 1444 near Varna in eastern Bulgaria. The Ottoman Army under Sultan Murad II (who did not actually rule the sultanate at the time) defeated the Hungarian–Polish and Wallachian armies commanded ...
on 10 November 1444. Halil Inalcik Halil is a common Turkish male given name. It is equivalent to the Arabic given name and surname Khalil or its variant Khaleel.
Notable persons with the name include:
* Halil Akbunar (born 1993), Turkish footballer
* Halil Akkaş (born 1983), ...
states that Mehmed II did not ask for his father. Instead, it was Çandarlı Halil Pasha's effort to bring Murad II back to the throne.
In 1446 Murad II returned to the throne. Mehmed II retained the title of sultan but only acted as a governor of Manisa. Following the death of Murad II in 1451, Mehmed II became sultan for the second time. Ibrahim II of Karaman
Ibrahim II (died 1464) was a bey of Karaman.
Background
During the post- Seljuk era in the second half of the 13th century, numerous Turkoman principalities, which are collectively known as the Anatolian beyliks, emerged in Anatolia. Initially ...
invaded the disputed area and instigated various revolts against Ottoman rule. Mehmed II conducted his first campaign against İbrahim of Karaman; Byzantines threatened to release Ottoman claimant Orhan.
Conquests
Conquest of Constantinople

 When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he devoted himself to strengthening the Ottoman navy and made preparations for an attack on Constantinople. In the narrow Bosphorus Straits, the fortress
When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he devoted himself to strengthening the Ottoman navy and made preparations for an attack on Constantinople. In the narrow Bosphorus Straits, the fortress Anadoluhisarı
Anadoluhisarı ( en, Anatolian Castle), known historically as Güzelce Hisar ("the Beauteous Castle") is a medieval Ottoman fortress located in Istanbul, Turkey on the Anatolian (Asian) side of the Bosporus. The complex is the oldest survivin ...
had been built by his great-grandfather Bayezid I
Bayezid I ( ota, بايزيد اول, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, یلدیرم بايزيد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; – 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted t ...
on the Asian side; Mehmed erected an even stronger fortress called Rumelihisarı
Rumelihisarı (also known as Rumelian Castle and Roumeli Hissar Castle) or Boğazkesen Castle (meaning "Strait-Blocker Castle" or literally "Throat-Cutter Castle") is a medieval fortress located in Istanbul, Turkey, on a series of hills on the Eu ...
on the European side, and thus gained complete control of the strait. Having completed his fortresses, Mehmed proceeded to levy a toll on ships passing within reach of their cannon. A Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
vessel ignoring signals to stop was sunk with a single shot and all the surviving sailors beheaded,Silburn, P. A. B. (1912). except for the captain, who was impaled and mounted as a human scarecrow as a warning to further sailors on the strait.
Abu Ayyub al-Ansari
Abu Ayyub al-Ansari ( ar, أبو أيوب الأنصاري, Abū Ayyūb al-Anṣārī, tr, Ebu Eyyûb el-Ensarî, died c. 674) — born Khalid ibn Zayd ibn Kulayb ibn Tha'laba ( ar, خالد ابن زيد ابن كُليب ابن ثعلبه, Kh ...
, the companion and standard bearer of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, had died during the first Siege of Constantinople (674–678)
The first Arab siege of Constantinople in 674–678 was a major conflict of the Arab–Byzantine wars, and the first culmination of the Umayyad Caliphate's expansionist strategy towards the Byzantine Empire, led by Caliph Mu'awiya I. Mu'awiya, ...
. As Mehmed II's army approached Constantinople, Mehmed's sheikh Akshamsaddin
Akshamsaddin (Muhammad Shams al-Din bin Hamzah, tr, Akşemseddin) (1389, Damascus – 16 February 1459, Göynük, Bolu), was an influential Ottoman Sunni Muslim scholar, poet, and mystic saint.
Biography
He was the grandson of Shahab al-Di ...
discovered the tomb of Abu Ayyub al-Ansari. After the conquest, Mehmed built Eyüp Sultan Mosque
The Eyüp Sultan Mosque ( tr, Eyüp Sultan Camii) is in the Eyüp district of Istanbul, outside the city walls and near the Golden Horn. On a much older site, the present building dates from the beginning of the 19th century. The mosque complex in ...
at the site to emphasize the importance of the conquest to the Islamic world and highlight his role as ghazi.
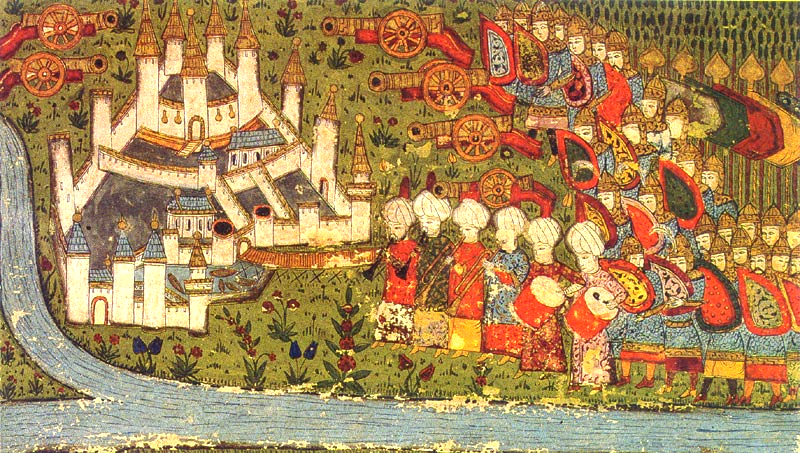
In 1453 Mehmed commenced the siege of Constantinople with an army between 80,000 and 200,000 troops, an artillery train of over seventy large field pieces, and a navy of 320 vessels, the bulk of them transports and storeships. The city was surrounded by sea and land; the fleet at the entrance of the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
stretched from shore to shore in the form of a crescent, to intercept or repel any assistance for Constantinople from the sea. In early April, the Siege of Constantinople
The following is a list of sieges of Constantinople, a historic city located in an area which is today part of Istanbul, Turkey. The city was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the ...
began. At first, the city's walls held off the Turks, even though Mehmed's army used the new bombard designed by Orban Orban, also known as Urban ( hu, Orbán; died 1453), was an iron founder and engineer from Brassó, Transylvania, in the Kingdom of Hungary (today Brașov, Romania), who cast large-calibre artillery for the Ottoman siege of Constantinople in 1453.
...
, a giant cannon similar to the Dardanelles Gun
The Basillica or Great Turkish Bombard ( tr, Şahi topu or simply ''Şahi'') is a 15th-century siege cannon, specifically a super-sized bombard, which saw action in the 1807 Dardanelles operation.Schmidtchen (1977b), p. 228 It was built in ...
. The harbor of the Golden Horn was blocked by a boom chain and defended by twenty-eight warships.
On 22 April, Mehmed transported his lighter warships overland, around the Genoese colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
of Galata, and into the Golden Horn's northern shore; eighty galleys were transported from the Bosphorus after paving a route, little over one mile, with wood. Thus, the Byzantines stretched their troops over a longer portion of the walls. About a month later, Constantinople fell, on 29 May, following a fifty-seven-day siege. After this conquest, Mehmed moved the Ottoman capital from Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
to Constantinople.
When Sultan Mehmed II stepped into the ruins of the Boukoleon, known to the Ottomans and Persians as the Palace of the Caesars, probably built over a thousand years before by Theodosius II, he uttered the famous lines of Saadi:
Some Muslim scholars claimed that a hadith in Musnad Ahmad
''Musnad Ahmad ibn Hanbal'' ( ar, مسند أحمد بن حنبل) is a collection of musnad hadith compiled by the Islamic scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal (d. 241 AH/855 AD) to whom the Hanbali fiqh (legislation) is attributed.
Description
It is one ...
referred specifically to Mehmed's conquest of Constantinople, seeing it as the fulfillment of a prophecy and a sign of the approaching apocalypse.
 After the conquest of Constantinople, Mehmed claimed the title of
After the conquest of Constantinople, Mehmed claimed the title of caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
(''Qayser-i Rûm''), based on the assertion that Constantinople had been the seat and capital of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
since 330 AD, and whoever possessed the Imperial capital was the ruler of the Empire. The contemporary scholar George of Trebizond
George of Trebizond ( el, Γεώργιος Τραπεζούντιος; 1395–1486) was a Byzantine Greek philosopher, scholar, and humanist. Life
He was born on the Greek island of Crete (then a Venetian colony known as the Kingdom of Candia), an ...
supported his claim. The claim was not recognized by the Catholic Church and most of, if not all, Western Europe, but was recognized by the Eastern Orthodox Church. Mehmed had installed Gennadius Scholarius
Gennadius II (Greek Γεννάδιος Βʹ; lay name Γεώργιος Κουρτέσιος Σχολάριος, ''Georgios Kourtesios Scholarios''; c. 1400 – c. 1473) was a Byzantine Greek philosopher and theologian, and Ecumenical Patriarch o ...
, a staunch antagonist of the West, as the ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople with all the ceremonial elements, ethnarch (or ''milletbashi'') status and rights of property that made him the second largest landlord in the said empire by the sultan himself in 1454, and in turn Gennadius II recognized Mehmed the Conqueror as successor to the throne.
Emperor Constantine XI Palaiologos
Constantine XI Dragases Palaiologos or Dragaš Palaeologus ( el, Κωνσταντῖνος Δραγάσης Παλαιολόγος, ''Kōnstantînos Dragásēs Palaiológos''; 8 February 1405 – 29 May 1453) was the last Roman (Byzantine) e ...
died without producing an heir, and had Constantinople not fallen to the Ottomans he likely would have been succeeded by the sons of his deceased elder brother. Those children were taken into the palace service of Mehmed after the fall of Constantinople. The oldest boy, renamed Has Murad, became a personal favorite of Mehmed and served as beylerbey
''Beylerbey'' ( ota, بكلربكی, beylerbeyi, lit=bey of beys, meaning the 'commander of commanders' or 'lord of lords') was a high rank in the western Islamic world in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, from the Anatolian Seljuk ...
of the Balkans. The younger son, renamed Mesih Pasha
Mesih Pasha or Misac Pasha (died November 1501) was an Ottoman of Eastern Roman origin, being a nephew of the last Roman emperor, Constantine XI Palaiologos. He served as Kapudan Pasha of the Ottoman Navy and was Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Emp ...
, became admiral of the Ottoman fleet and sanjak-bey of the Gallipoli
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles s ...
. He eventually served twice as Grand Vizier under Mehmed's son, Bayezid II
Bayezid II ( ota, بايزيد ثانى, Bāyezīd-i s̱ānī, 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512, Turkish: ''II. Bayezid'') was the eldest son and successor of Mehmed II, ruling as Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, B ...
.
After the fall of Constantinople, Mehmed would also go on to conquer the Despotate of Morea
The Despotate of the Morea ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μορέως) or Despotate of Mystras ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μυστρᾶ) was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centu ...
in the Peloponnese in 1460, and the Empire of Trebizond in northeastern Anatolia in 1461. The last two vestiges of Byzantine rule were thus absorbed by the Ottoman Empire. The conquest of Constantinople bestowed immense glory and prestige on the country. There is some historical evidence that, 10 years after the conquest of Constantinople, Mehmed II visited the site of Troy and boasted that he had avenged the Trojans by conquering the Greeks (Byzantines).
Conquest of Serbia (1454–1459)
 Mehmed II's first campaigns after Constantinople were in the direction of Serbia, which had been an Ottoman
Mehmed II's first campaigns after Constantinople were in the direction of Serbia, which had been an Ottoman vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
since the Battle of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo ( tr, Kosova Savaşı; sr, Косовска битка) took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan ...
in 1389. The Ottoman ruler had a connection with the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and ...
– one of Murad II's wives was Mara Branković
Mara Branković ( sr-Cyrl, Мара Бранковић) or Mara Despina Hatun (c. 1416 – 14 September 1487), also known as ''Sultana Marija'' or ''Amerissa'', was the daughter of Serbian monarch Đurađ Branković and Eirene Kantakouzene. As ...
– and he used that fact to claim some Serbian islands. That Đurađ Branković
Đurađ Branković (; sr-cyr, Ђурађ Бранковић; hu, Brankovics György; 1377 – 24 December 1456) was the Serbian Despot from 1427 to 1456. He was one of the last Serbian medieval rulers. He was a participant in the battle of Ank ...
had recently made an alliance with the Hungarians, and had paid the tribute irregularly, may have been important considerations. When Serbia refused these demands, the Ottoman army set out from Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
towards Serbia in 1454. Smederevo
Smederevo ( sr-Cyrl, Смедерево, ) is a city and the administrative center of the Podunavlje District in eastern Serbia. It is situated on the right bank of the Danube, about downstream of the Serbian capital, Belgrade.
According t ...
was besieged, as was Novo Brdo
Novo Brdo ( sr-Cyrl, Ново Брдо), or Novobërda and Artana ( sq-definite, Novobërdë or ''Artanë''), is a municipality located in the Pristina district of Kosovo. According to the 2011 census, it has a population of 6,729 inhabitants. ...
, the most important Serbian metal mining and smelting center. Ottomans and Hungarians fought during the years till 1456.
The Ottoman army advanced as far as Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 m ...
, where it attempted but failed to conquer the city from John Hunyadi at the Siege of Belgrade, on 14 July 1456. A period of relative peace ensued in the region until the Fall of Belgrade in 1521, during the reign of Mehmed's great-grandson, known as Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
. The sultan retreated to Edirne, and Đurađ Branković
Đurađ Branković (; sr-cyr, Ђурађ Бранковић; hu, Brankovics György; 1377 – 24 December 1456) was the Serbian Despot from 1427 to 1456. He was one of the last Serbian medieval rulers. He was a participant in the battle of Ank ...
regained possession of some parts of Serbia. Before the end of the year, however, the 79-year-old Branković died. Serbian independence survived him for only two years, when the Ottoman Empire formally annexed his lands following dissension among his widow and three remaining sons. Lazar, the youngest, poisoned his mother and exiled his brothers, but he died soon afterwards. In the continuing turmoil the oldest brother Stefan Branković
Stefan Branković ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Бранковић; c. 1417 – 9 October 1476), also known in historiography as Stefan the Blind (Стефан Слепи), was briefly the despot (ruler) of the Serbian Despotate between 1458 and 1459, m ...
gained the throne but was ousted in March 1459. After that the Serbian throne was offered to Stephen Tomašević
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; h ...
, the future king of Bosnia, which infuriated Sultan Mehmed. He sent his army, which captured Smederevo
Smederevo ( sr-Cyrl, Смедерево, ) is a city and the administrative center of the Podunavlje District in eastern Serbia. It is situated on the right bank of the Danube, about downstream of the Serbian capital, Belgrade.
According t ...
in June 1459, ending the existence of the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and ...
.
Conquest of Morea (1458–1460)
 The
The Despotate of the Morea
The Despotate of the Morea ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μορέως) or Despotate of Mystras ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μυστρᾶ) was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centu ...
bordered the southern Ottoman Balkans. The Ottomans had already invaded the region under Murad II, destroying the Byzantine defenses – the Hexamilion wall
The Hexamilion wall ( el, Εξαμίλιον τείχος, "six-mile wall") was a defensive wall constructed across the Isthmus of Corinth, guarding the only land route onto the Peloponnese peninsula from mainland Greece.
History
Early fortif ...
– at the Isthmus of Corinth in 1446. Before the final siege of Constantinople Mehmed ordered Ottoman troops to attack the Morea. The despots, Demetrios Palaiologos
Demetrios Palaiologos or Demetrius Palaeologus ( el, Δημήτριος Παλαιολόγος, Dēmētrios Palaiologos; 1407–1470) was Despot of the Morea together with his brother Thomas from 1449 until the fall of the despotate in 1460. Deme ...
and Thomas Palaiologos
Thomas Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Θωμᾶς Παλαιολόγος; 1409 – 12 May 1465) was Despot of the Morea from 1428 until the fall of the despotate in 1460, although he continued to claim the title until his death five years late ...
, brothers of the last emperor, failed to send any aid. Their own incompetence resulted in an Albanian-Greek revolt against them, during which they invited in Ottoman troops to help put down the revolt. At this time, a number of influential Moreote Greeks and Albanians made private peace with Mehmed. After more years of incompetent rule by the despots, their failure to pay their annual tribute to the Sultan, and finally their own revolt against Ottoman rule, Mehmed entered the Morea in May 1460. The capital Mistra
Mystras or Mistras ( el, Μυστρᾶς/Μιστρᾶς), also known in the ''Chronicle of the Morea'' as Myzithras (Μυζηθρᾶς), is a fortified town and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Situated on Mt. Taygetus, ...
fell exactly seven years after Constantinople, on 29 May 1460. Demetrios ended up a prisoner of the Ottomans and his younger brother Thomas fled. By the end of the summer, the Ottomans had achieved the submission of virtually all cities possessed by the Greeks.
A few holdouts remained for a time. The island of Monemvasia
Monemvasia ( el, Μονεμβασιά, Μονεμβασία, or ) is a town and municipality in Laconia, Greece. The town is located on a small island off the east coast of the Peloponnese, surrounded by the Myrtoan Sea. The island is connected ...
refused to surrender, and it was ruled for a brief time by a Catalan corsair. When the population drove him out they obtained the consent of Thomas to submit to the Pope's protection before the end of 1460. The Mani Peninsula, on the Morea's south end, resisted under a loose coalition of local clans, and the area then came under the rule of Venice. The last holdout was Salmeniko
The Salmeniko Castle ( el, Κάστρο του Σαλμενίκου, ''Kastro tou Salmenikou'') or Orgia or Oria Castle (Κάστρο Οργιάς/Ωριάς, cf. '' Kastro tis Orias'') was a castle at the foot of Panachaiko mountain, in the mode ...
, in the Morea's northwest. Graitzas Palaiologos Konstantinos Graitzas Palaiologos ( el, Κωνσταντίνος Γραίτζας Παλαιολόγος) was the commander of the Byzantine garrison at Salmeniko Castle near Patras during the invasion of the Despotate of Morea by the forces of Mehm ...
was the military commander there, stationed at Salmeniko Castle
The Salmeniko Castle ( el, Κάστρο του Σαλμενίκου, ''Kastro tou Salmenikou'') or Orgia or Oria Castle (Κάστρο Οργιάς/Ωριάς, cf. '' Kastro tis Orias'') was a castle at the foot of Panachaiko mountain, in the mod ...
(also known as Castle Orgia). While the town eventually surrendered, Graitzas and his garrison and some town residents held out in the castle until July 1461, when they escaped and reached Venetian territory.
Conquest of Trebizond (1460–1461)
Emperors of Trebizond formed alliances through royal marriages with various Muslim rulers. EmperorJohn IV of Trebizond
John IV Megas Komnenos ( el, Ιωάννης Μέγας Κομνηνός, ''Iōannēs Megas Komnēnos'') (died April 1460) was Emperor of Trebizond from 1429 until his death. He was a son of Emperor Alexios IV of Trebizond and Theodora Kantakouze ...
married his daughter to the son of his brother-in-law, Uzun Hasan, khan of the Ak Koyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu ( az, Ağqoyunlular , ) was a culturally Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two tribal confederations: Akkoyunlu (Wh ...
, in return for his promise to defend Trebizond. He also secured promises of support from the Turkish bey
Bey ( ota, بك, beğ, script=Arab, tr, bey, az, bəy, tk, beg, uz, бек, kz, би/бек, tt-Cyrl, бәк, translit=bäk, cjs, пий/пек, sq, beu/bej, sh, beg, fa, بیگ, beyg/, tg, бек, ar, بك, bak, gr, μπέης) is ...
s of Sinope Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
*Sinope (mythology), in ...
and Karamania In the 18th and 19th centuries, Karamania (or Caramania) was an exonym used by Europeans for the southern (Mediterranean) coast of Anatolia, then part of the Ottoman Empire (current Turkey). It can also refer to the general south central Anatolian r ...
, and from the king and princes of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. The Ottomans were motivated to capture Trebizond or to get an annual tribute. In the time of Murad II, they first attempted to take the capital by sea in 1442, but high surf made the landings difficult and the attempt was repulsed. While Mehmed II was away laying siege to Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 m ...
in 1456, the Ottoman governor of Amasya
Amasya () is a city in northern Turkey and is the capital of Amasya Province, in the Black Sea Region. It was called Amaseia or Amasia in antiquity."Amasya" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th ...
attacked Trebizond, and although he was defeated, he took many prisoners and extracted a heavy tribute.
After John's death in 1459, his brother David came to power and intrigued with various European powers for help against the Ottomans, speaking of wild schemes that included the conquest of Jerusalem. Mehmed II eventually heard of these intrigues and was further provoked to action by David's demand that Mehmed remit the tribute imposed on his brother.
Mehmed the Conqueror's response came in the summer of 1461. He led a sizable army from Bursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
by land and the Ottoman navy by sea, first to Sinope Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
*Sinope (mythology), in ...
, joining forces with Ismail's brother Ahmed (the Red). He captured Sinope and ended the official reign of the Jandarid dynasty, although he appointed Ahmed as the governor of Kastamonu and Sinope, only to revoke the appointment the same year. Various other members of the Jandarid dynasty were offered important functions throughout the history of the Ottoman Empire. During the march to Trebizond, Uzun Hasan sent his mother Sara Khatun as an ambassador; while they were climbing the steep heights of Zigana on foot, she asked Sultan Mehmed why he was undergoing such hardship for the sake of Trebizond. Mehmed replied:
Having isolated Trebizond, Mehmed quickly swept down upon it before the inhabitants knew he was coming, and he placed it under siege. The city held out for a month before the emperor David surrendered on 15 August 1461.
Submission of Wallachia (1459–1462)

 The Ottomans since the early 15th century tried to bring Wallachia ( ota, والاچیا) under their control by putting their own candidate on the throne, but each attempt ended in failure. The Ottomans regarded Wallachia as a buffer zone between them and the Kingdom of Hungary and for a yearly tribute did not meddle in their internal affairs. The two primary Balkan powers, Hungary and the Ottomans, maintained an enduring struggle to make Wallachia their own vassal. To prevent Wallachia from falling into the Hungarian fold, the Ottomans freed young
The Ottomans since the early 15th century tried to bring Wallachia ( ota, والاچیا) under their control by putting their own candidate on the throne, but each attempt ended in failure. The Ottomans regarded Wallachia as a buffer zone between them and the Kingdom of Hungary and for a yearly tribute did not meddle in their internal affairs. The two primary Balkan powers, Hungary and the Ottomans, maintained an enduring struggle to make Wallachia their own vassal. To prevent Wallachia from falling into the Hungarian fold, the Ottomans freed young Vlad III
Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler ( ro, Vlad Țepeș ) or Vlad Dracula (; ro, Vlad Drăculea ; 1428/311476/77), was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most im ...
(Dracula), who had spent four years as a prisoner of Murad, together with his brother Radu, so that Vlad could claim the throne of Wallachia. His rule was short-lived, however, as Hunyadi invaded Wallachia and restored his ally Vladislav II, of the Dănești clan, to the throne.
Vlad III Dracula fled to Moldavia, where he lived under the protection of his uncle, Bogdan II
Bogdan II (1409 – 17 October 1451) was a prince of Moldavia from October 12, 1449 to October 17, 1451.
Family
According to some historians, he was the bastard of Alexander the Good, by an unknown mother. On the contrary, according to the other ...
. In October 1451, Bogdan was assassinated and Vlad fled to Hungary. Impressed by Vlad's vast knowledge of the mindset and inner workings of the Ottoman Empire, as well as his hatred towards the Turks and new Sultan Mehmed II, Hunyadi reconciled with his former enemy and tried to make Vlad III his own adviser, but Vlad refused.
In 1456, three years after the Ottomans had conquered Constantinople, they threatened Hungary by besieging Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 m ...
. Hunyadi began a concerted counter-attack in Serbia: while he himself moved into Serbia and relieved the siege (before dying of the plague), Vlad III Dracula led his own contingent into Wallachia, reconquered his native land, and killed Vladislav II.
In 1459, Mehmed II sent envoys to Vlad to urge him to pay a delayed tribute of 10,000 ducats and 500 recruits into the Ottoman forces. Vlad III Dracula refused and had the Ottoman envoys killed by nailing their turban
A turban (from Persian دولبند, ''dulband''; via Middle French ''turbant'') is a type of headwear based on cloth winding. Featuring many variations, it is worn as customary headwear by people of various cultures. Communities with promin ...
s to their heads, on the pretext that they had refused to raise their "hats" to him, as they only removed their headgear before God.
Meanwhile, the Sultan sent the Bey of Nicopolis, Hamza Pasha, to make peace and, if necessary, eliminate Vlad III. Vlad III set an ambush; the Ottomans were surrounded and almost all of them caught and impaled, with Hamza Pasha impaled on the highest stake, as befit his rank.
In the winter of 1462, Vlad III crossed the Danube and scorched the entire Bulgarian land in the area between Serbia and the Black Sea. Allegedly disguising himself as a Turkish Sipahi and utilizing his command of the Turkish language and customs, Vlad III infiltrated Ottoman camps, ambushed, massacred or captured several Ottoman forces. In a letter to Corvinus dated 2 February, he wrote:
Mehmed II abandoned his siege of Corinth to launch a punitive attack against Vlad III in Wallachia but suffered many casualties in a surprise night attack led by Vlad III Dracula, who was apparently bent on personally killing the Sultan. However, Vlad's policy of staunch resistance against the Ottomans was not a popular one, and he was betrayed by the boyars's (local aristocracy) appeasing faction, most of them also pro-Dăneşti (a rival princely branch). His best friend and ally Stephen III of Moldavia, who had promised to help him, seized the chance and instead attacked him trying to take back the Fortress of Chilia
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''face ...
. Vlad III had to retreat to the mountains. After this, the Ottomans captured the Wallachian capital Târgoviște
Târgoviște (, alternatively spelled ''Tîrgoviște''; german: Tergowisch) is a city and county seat in Dâmbovița County, Romania. It is situated north-west of Bucharest, on the right bank of the Ialomița River.
Târgoviște was one of ...
and Mehmed II withdrew, having left Radu as ruler of Wallachia. Turahanoğlu Ömer Bey
Turahanoğlu Ömer Bey ( gr, Ὀμάρης or Ἀμάρης; 1435–1484) was an Ottoman general and governor. The son of the famed Turahan Bey, he was active chiefly in southern Greece: he fought in the Morea against both the Byzantines in the ...
, who served with distinction and wiped out a force 6,000 Wallachians and deposited 2,000 of their heads at the feet of Mehmed II, was also reinstated, as a reward, in his old gubernatorial post in Thessaly. Vlad eventually escaped to Hungary, where he was imprisoned on a false accusation of treason against his overlord, Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus, also called Matthias I ( hu, Hunyadi Mátyás, ro, Matia/Matei Corvin, hr, Matija/Matijaš Korvin, sk, Matej Korvín, cz, Matyáš Korvín; ), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1458 to 1490. After conducting several mi ...
.
Conquest of Bosnia (1463)
 The despot of Serbia, Lazar Branković, died in 1458, and a civil war broke out among his heirs that resulted in the Ottoman conquest of Serbia in 1459/1460.
The despot of Serbia, Lazar Branković, died in 1458, and a civil war broke out among his heirs that resulted in the Ottoman conquest of Serbia in 1459/1460. Stephen Tomašević
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; h ...
, son of the king of Bosnia, tried to bring Serbia under his control, but Ottoman expeditions forced him to give up his plan and Stephen fled to Bosnia, seeking refuge at the court of his father. After some battles, Bosnia became tributary kingdom to the Ottomans.
On 10 July 1461, Stephen Thomas died, and Stephen Tomašević succeeded him as King of Bosnia. In 1461, Stephen Tomašević made an alliance with the Hungarians and asked Pope Pius II
Pope Pius II ( la, Pius PP. II, it, Pio II), born Enea Silvio Bartolomeo Piccolomini ( la, Aeneas Silvius Bartholomeus, links=no; 18 October 1405 – 14 August 1464), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 Augu ...
for help in the face of an impending Ottoman invasion. In 1463, after a dispute over the tribute paid annually by the Bosnian Kingdom
The Kingdom of Bosnia ( sh, Kraljevina Bosna / Краљевина Босна), or Bosnian Kingdom (''Bosansko kraljevstvo'' / Босанско краљевство), was a medieval kingdom that lasted for nearly a century, from 1377 to 1463, and ...
to the Ottomans, he sent for help from the Venetians. However, none ever reached Bosnia. In 1463, Sultan Mehmed II led an army into the country. The royal city of Bobovac
Bobovac ( sh-Cyrl, Бобовац) is a fortified city of medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located near today's Vareš and the village of Borovica. It is protected site as a National monument of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
History
The city ...
soon fell, leaving Stephen Tomašević to retreat to Jajce and later to Ključ. Mehmed invaded Bosnia and conquered it very quickly, executing Stephen Tomašević and his uncle Radivoj. Bosnia officially fell in 1463 and became the westernmost province of the Ottoman Empire.
Ottoman-Venetian War (1463–1479)
According to the Byzantine historianMichael Critobulus Michael Critobulus (; c. 1410 – c. 1470) was a Greek politician, scholar and historian. He is known as the author of a history of the Ottoman conquest of the Eastern Roman Empire under Sultan Mehmet II. Critobulus' work, along with the writings o ...
, hostilities broke out after an Albanian slave of the Ottoman commander of Athens fled to the Venetian fortress of Coron (Koroni
Koroni or Corone ( el, Κορώνη) is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is a municipal unit. Known as ''Corone' ...
) with 100,000 silver aspers from his master's treasure. The fugitive then converted to Christianity, so Ottoman demands for his rendition were refused by the Venetian authorities. Using this as a pretext in November 1462, the Ottoman commander in central Greece, Turahanoğlu Ömer Bey
Turahanoğlu Ömer Bey ( gr, Ὀμάρης or Ἀμάρης; 1435–1484) was an Ottoman general and governor. The son of the famed Turahan Bey, he was active chiefly in southern Greece: he fought in the Morea against both the Byzantines in the ...
, attacked and nearly succeeded in taking the strategically important Venetian fortress of Lepanto ( Nafpaktos). On 3 April 1463, however, the governor of the Morea, Isa Beg, took the Venetian-held town of Argos by treason.
The new alliance launched a two-pronged offensive against the Ottomans: a Venetian army, under the Captain General of the Sea Alvise Loredan
Alvise Loredan (1393 – 6 March 1466) was a Venetian nobleman of the Loredan family. At a young age he became a galley captain, and served with distinction as a military commander, with a long record of battles against the Ottomans, from the n ...
, landed in the Morea, while Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus, also called Matthias I ( hu, Hunyadi Mátyás, ro, Matia/Matei Corvin, hr, Matija/Matijaš Korvin, sk, Matej Korvín, cz, Matyáš Korvín; ), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1458 to 1490. After conducting several mi ...
invaded Bosnia. At the same time, Pius II
Pope Pius II ( la, Pius PP. II, it, Pio II), born Enea Silvio Bartolomeo Piccolomini ( la, Aeneas Silvius Bartholomeus, links=no; 18 October 1405 – 14 August 1464), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 Augus ...
began assembling an army at Ancona
Ancona (, also , ) is a city and a seaport in the Marche region in central Italy, with a population of around 101,997 . Ancona is the capital of the province of Ancona and of the region. The city is located northeast of Rome, on the Adriatic ...
, hoping to lead it in person. Negotiations were also begun with other rivals of the Ottomans, such as Karamanids, Uzun Hassan and the Crimean Khanate.
In early August, the Venetians retook Argos and refortified the Isthmus of Corinth, restoring the Hexamilion wall
The Hexamilion wall ( el, Εξαμίλιον τείχος, "six-mile wall") was a defensive wall constructed across the Isthmus of Corinth, guarding the only land route onto the Peloponnese peninsula from mainland Greece.
History
Early fortif ...
and equipping it with many cannons. They then proceeded to besiege the fortress of the Acrocorinth
Acrocorinth ( el, Ακροκόρινθος), "Upper Corinth", the acropolis of ancient Corinth, is a monolithic rock overseeing the ancient city of Corinth, Greece. In the estimation of George Forrest, "It is the most impressive of the acropoli ...
, which controlled the northwestern Peloponnese. The Venetians engaged in repeated clashes with the defenders and with Ömer Bey's forces, until they suffered a major defeat on 20 October and were then forced to lift the siege and retreat to the Hexamilion and to Nauplia ( Nafplion). In Bosnia, Matthias Corvinus seized over sixty fortified places and succeeded in taking its capital, Jajce, after a 3-month siege, on 16 December.
Ottoman reaction was swift and decisive: Mehmed II dispatched his Grand Vizier, Mahmud Pasha Angelović
Mahmud Pasha Angelović ( sr, Махмуд-паша Анђеловић/Mahmud-paša Anđelović; tr, Veli Mahmud Paşa; 1420–1474) was the Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire from 1456 to 1466 and again from 1472 to 1474, who also wrote Persian ...
, with an army against the Venetians. To confront the Venetian fleet, which had taken station outside the entrance of the Dardanelles Straits, the Sultan further ordered the creation of the new shipyard of Kadirga Limani in the Golden Horn (named after the "kadirga" type of galley), and of two forts to guard the Straits, Kilidulbahr and Sultaniye
Soltaniyeh ( fa, سلطانيه, also Romanized as Solţānīyeh, Solţāneyyeh, Sultaniye, and Sultānīyeh; also known as Sa‘īdīyeh; ) is the capital city of Soltaniyeh District of Soltaniyeh County, Zanjan Province, northwestern Iran.
...
.Setton, Hazard & Norman (1969), p. 326 The Morean campaign was swiftly victorious for the Ottomans; they razed the Hexamilion, and advanced into the Morea. Argos fell, and several forts and localities that had recognized Venetian authority reverted to their Ottoman allegiance.
Sultan Mehmed II, who was following Mahmud Pasha with another army to reinforce him, had reached Zeitounion ( Lamia) before being apprised of his Vizier's success. Immediately, he turned his men north, towards Bosnia. However, the Sultan's attempt to retake Jajce in July and August 1464 failed, with the Ottomans retreating hastily in the face of Corvinus' approaching army. A new Ottoman army under Mahmud Pasha then forced Corvinus to withdraw, but Jajce was not retaken for many years after. However, the death of Pope Pius II on 15 August in Ancona spelled the end of the Crusade.
In the meantime, the Venetian Republic had appointed Sigismondo Malatesta for the upcoming campaign of 1464. He launched attacks against Ottoman forts and engaged in a failed siege of Mistra
Mystras or Mistras ( el, Μυστρᾶς/Μιστρᾶς), also known in the ''Chronicle of the Morea'' as Myzithras (Μυζηθρᾶς), is a fortified town and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Situated on Mt. Taygetus, ...
in August through October. Small-scale warfare continued on both sides, with raids and counter-raids, but a shortage of manpower and money meant that the Venetians remained largely confined to their fortified bases, while Ömer Bey's army roamed the countryside.
In the Aegean, the Venetians tried to take Lesbos in the spring of 1464, and besieged the capital Mytilene
Mytilene (; el, Μυτιλήνη, Mytilíni ; tr, Midilli) is the capital of the Greek island of Lesbos, and its port. It is also the capital and administrative center of the North Aegean Region, and hosts the headquarters of the University of ...
for six weeks, until the arrival of an Ottoman fleet under Mahmud Pasha on 18 May forced them to withdraw. Another attempt to capture the island shortly after also failed. The Venetian navy spent the remainder of the year in ultimately fruitless demonstrations of force before the Dardanelles. In early 1465, Mehmed II sent peace feelers to the Venetian Senate; distrusting the Sultan's motives, these were rejected.
In April 1466, the Venetian war effort was reinvigorated under Vettore Cappello: the fleet took the northern Aegean islands of Imbros
Imbros or İmroz Adası, officially Gökçeada (lit. ''Heavenly Island'') since 29 July 1970,Alexis Alexandris, "The Identity Issue of The Minorities in Greece And Turkey", in Hirschon, Renée (ed.), ''Crossing the Aegean: An Appraisal of the 1 ...
, Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
, and Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki, el, Σαμοθράκη, ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long and is in size and has a population of 2,859 (2011 ...
, and then sailed into the Saronic Gulf
The Saronic Gulf (Greek: Σαρωνικός κόλπος, ''Saronikós kólpos'') or Gulf of Aegina in Greece is formed between the peninsulas of Attica and Argolis and forms part of the Aegean Sea. It defines the eastern side of the isthmus of Co ...
. On 12 July, Cappello landed at Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; el, Πειραιάς ; grc, Πειραιεύς ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens' city centre, along the east coast of the Saroni ...
and marched against Athens, the Ottomans' major regional base. He failed to take the Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
and was forced to retreat to Patras, the capital of Peloponnese and the seat of the Ottoman bey
Bey ( ota, بك, beğ, script=Arab, tr, bey, az, bəy, tk, beg, uz, бек, kz, би/бек, tt-Cyrl, бәк, translit=bäk, cjs, пий/пек, sq, beu/bej, sh, beg, fa, بیگ, beyg/, tg, бек, ar, بك, bak, gr, μπέης) is ...
, which was being besieged by a joint force of Venetians and Greeks. Before Cappello could arrive, and as the city seemed on the verge of falling, Ömer Bey suddenly appeared with 12,000 cavalry and drove the outnumbered besiegers off. Six hundred Venetians and a hundred Greeks were taken prisoner out of a force of 2,000, while Barbarigo himself was killed. Cappello, who arrived some days later, attacked the Ottomans but was heavily defeated. Demoralized, he returned to Negroponte with the remains of his army. There Cappello fell ill and died on 13 March 1467. In 1470 Mehmed personally led an Ottoman army to besiege Negroponte. The Venetian relief navy was defeated, and Negroponte was captured.
In spring 1466, Sultan Mehmed marched with a large army against the Albanians. Under their leader, Skanderbeg
, reign = 28 November 1443 – 17 January 1468
, predecessor = Gjon Kastrioti
, successor = Gjon Kastrioti II
, spouse = Donika Arianiti
, issue = Gjon Kastrioti II
, royal house = Kastrioti
, father ...
, they had long resisted the Ottomans, and had repeatedly sought assistance from Italy. Mehmed II responded by marching again against Albania but was unsuccessful. The winter brought an outbreak of plague, which would recur annually and sap the strength of the local resistance. Skanderbeg himself died of malaria in the Venetian stronghold of Lissus ( Lezhë), ending the ability of Venice to use the Albanian lords for its own advantage. After Skanderbeg died, some Venetian-controlled northern Albanian garrisons continued to hold territories coveted by the Ottomans, such as Žabljak Crnojevića
Žabljak Crnojevića ( sr-cyrl, Жабљак Црнојевића, ), commonly referred to as Žabljak, is an abandoned medieval fortified town (fortress) in Montenegro. The fortress is located on the confluence of the Morača river in Lake Skad ...
, Drisht
Drisht ( sq-definite, Drishti) is a village, former bishopric and Latin titular see with an Ancient and notable medieval history (Latin ''Drivastum,'' Italian ''Drivasto'') in Albania, 6 km from Mes Bridge (Albanian: ''Ura e Mesit''). It is ...
, Lezhë, and Shkodra – the most significant. Mehmed II sent his armies to take Shkodra in 1474 but failed. Then he went personally to lead the siege of Shkodra
The fourth siege of Shkodra of 1478–79 was a confrontation between the Ottoman Empire and the Venetians together with the League of Lezhe and other Albanians at Shkodra (Scutari in Italian) and its Rozafa Castle during the First Ottoman-V ...
of 1478–79. The Venetians and Shkodrans resisted the assaults and continued to hold the fortress until Venice ceded Shkodra to the Ottoman Empire in the Treaty of Constantinople as a condition of ending the war.
The agreement was established as a result of the Ottomans having reached the outskirts of Venice. Based on the terms of the treaty, the Venetians were allowed to keep Ulcinj, Antivan, and Durrës. However, they ceded Shkodra, which had been under Ottoman siege for many months, as well as other territories on the Dalmatian coastline, and they relinquished control of the Greek islands of Negroponte ( Euboea) and Lemnos. Moreover, the Venetians were forced to pay 100,000 ducat indemnity and agreed to a tribute of around 10,000 ducat
The ducat () coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages from the 13th to 19th centuries. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained wi ...
s per year in order to acquire trading privileges in the Black Sea. As a result of this treaty, Venice acquired a weakened position in the Levant.
Anatolian conquests (1464–1473)
 During the post- Seljuks era in the second half of the middle ages, numerous Turkmen principalities collectively known as
During the post- Seljuks era in the second half of the middle ages, numerous Turkmen principalities collectively known as Anatolian beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A sec ...
emerged in Anatolia. Karamanids initially centred around the modern provinces of Karaman
Karaman, historically known as Laranda ( Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. Accordin ...
and Konya, the most important power in Anatolia. But towards the end of the 14th century, Ottomans began to dominate on most of Anatolia, reducing the Karaman influence and prestige.
İbrahim II of Karaman
Ibrahim II (died 1464) was a bey of Karaman.
Background
During the post- Seljuk era in the second half of the 13th century, numerous Turkoman principalities, which are collectively known as the Anatolian beyliks, emerged in Anatolia. Initially ...
was the ruler of Karaman, and during his last years, his sons began struggling for the throne. His heir apparent was İshak of Karaman, the governor of Silifke
Silifke ( grc-gre, Σελεύκεια, ''Seleukeia'', la, Seleucia ad Calycadnum) is a town and district in south-central Mersin Province, Turkey, west of the city of Mersin, on the west end of Çukurova.
Silifke is near the Mediterranean coast ...
. But Pir Ahmet, a younger son, declared himself as the bey of Karaman in Konya. İbrahim escaped to a small city in western territories where he died in 1464. The competing claims to the throne resulted in an interregnum in the ''beylik''. Nevertheless, with the help of Uzun Hasan, the sultan of the Akkoyunlu (White Sheep) Turkmens, İshak was able to ascend to the throne. His reign was short, however, as Pir Ahmet appealed to Sultan Mehmed II for help, offering Mehmed some territory that İshak refused to cede. With Ottoman help, Pir Ahmet defeated İshak in the battle of Dağpazarı
Dağpazarı is a village in the Mut district of Mersin Province, Turkey
Geography
Dağpazarı is a part of Mut district of Mersin Province. Situated in the Taurus Mountains, northeast of Mut, the road distance to Mut is about and to Mersin is ...
. İshak had to be content with Silifke up to an unknown date. Pir Ahmet kept his promise and ceded a part of the ''beylik'' to the Ottomans, but he was uneasy about the loss. So, during the Ottoman campaign in the West, he recaptured his former territory. Mehmed returned, however, and captured both Karaman (Larende) and Konya in 1466. Pir Ahmet barely escaped to the East. A few years later, Ottoman vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was a ...
(later grand vizier) Gedik Ahmet Pasha
Gedik Ahmed Pasha (; died 18 November 1482) was an Ottoman statesman and admiral who served as Grand Vizier and Kapudan Pasha (Grand Admiral of the Ottoman Navy) during the reigns of sultans Mehmed II and Bayezid II.
Very little was known abou ...
captured the coastal region of the ''beylik''.
Pir Ahmet as well as his brother Kasım escaped to Uzun Hasan's territory. This gave Uzun Hasan a chance to interfere. In 1472, the Akkoyunlu army invaded and raided most of Anatolia (this was the reason behind the Battle of Otlukbeli
The Battle of Otlukbeli or Otluk Beli was a battle between Aq Qoyunlu and the Ottoman Empire that was fought on August 11, 1473.
Background
In autumn of 1463, Republic of Venice opened negotiations with Uzun Hasan. In 1464, Uzun Hasan intervene ...
in 1473). But then Mehmed led a successful campaign against Uzun Hasan in 1473 that resulted in the decisive victory of the Ottoman Empire in the Battle of Otlukbeli
The Battle of Otlukbeli or Otluk Beli was a battle between Aq Qoyunlu and the Ottoman Empire that was fought on August 11, 1473.
Background
In autumn of 1463, Republic of Venice opened negotiations with Uzun Hasan. In 1464, Uzun Hasan intervene ...
. Before that, Pir Ahmet with Akkoyunlu help had captured Karaman. However, Pir Ahmet couldn't enjoy another term. Because immediately after the capture of Karaman, the Akkoyunlu army was defeated by the Ottomans near Beyşehir
Beyşehir () is a large town and district of Konya Province in the Akdeniz region of Turkey. The town is located on the southeastern shore of Lake Beyşehir and is marked to the west and the southwest by the steep lines and forests of the Tauru ...
and Pir Ahmet had to escape once more. Although he tried to continue his struggle, he learned that his family members had been transferred to Istanbul by Gedik Ahmet Pasha, so he finally gave up. Demoralized, he escaped to Akkoyunlu territory where he was given a '' tımar'' (fief) in Bayburt
Bayburt () is a city in northeast Turkey lying on the Çoruh River and is the provincial capital of Bayburt Province. According to the 2021 census the population is determined as around 82,274.
Bayburt was once an important center on the ancient ...
. He died in 1474.
Uniting the Anatolian ''beylik''s was first accomplished by Sultan Bayezid I
Bayezid I ( ota, بايزيد اول, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, یلدیرم بايزيد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; – 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted t ...
, more than fifty years before Mehmed II but after the destructive Battle of Ankara
The Battle of Ankara or Angora was fought on 20 July 1402 at the Çubuk plain near Ankara, between the forces of the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I and the Emir of the Timurid Empire, Timur. The battle was a major victory for Timur, and it led to the ...
in 1402, the newly formed unification was gone. Mehmed II recovered Ottoman power over the other Turkish states, and these conquests allowed him to push further into Europe.
Another important political entity that shaped the Eastern policy of Mehmed II were the White Sheep Turcomans. Under the leadership of Uzun Hasan, this kingdom gained power in the East; but because of their strong relations with the Christian powers like the Empire of Trebizond and the Republic of Venice, and the alliance between the Turcomans and the Karamanid tribe, Mehmed saw them as a threat to his own power.
War with Moldavia (1475–1476)
 In 1456,
In 1456, Peter III Aaron
Peter III Aaron ( ro, Petru Aron; died 1467), bastard son of Alexandru cel Bun, was a Voivode (Prince) of Moldavia on three occasions: October 1451 to February 1452, August 1454 to February 1455, and May 1455 to April 1457. The first two were d ...
agreed to pay the Ottomans an annual tribute of 2,000 gold ducats to ensure his southern borders, thus becoming the first Moldavian ruler to accept the Turkish demands. His successor Stephen the Great rejected Ottoman suzerainty and a series of fierce wars ensued. Stephen tried to bring Wallachia under his sphere of influence and so supported his own choice for the Wallachian throne. This resulted in an enduring struggle between different Wallachian rulers backed by Hungarians, Ottomans, and Stephen. An Ottoman army under Hadim Pasha (governor of Rumelia) was sent in 1475 to punish Stephen for his meddling in Wallachia; however, the Ottomans suffered a great defeat at the Battle of Vaslui
The Battle of Vaslui (also referred to as the Battle of Podul Înalt or the Battle of Racova) was fought on 10 January 1475, between Stephen III of Moldavia and the Ottoman governor of Rumelia, Hadım Suleiman Pasha. The battle took place at ...
. Stephen inflicted a decisive defeat on the Ottomans, described as "the greatest ever secured by the Cross against Islam," with casualties, according to Venetian and Polish records, reaching beyond 40,000 on the Ottoman side. Mara Brankovic (Mara Hatun), the former younger wife of Murad II, told a Venetian envoy that the invasion had been worst ever defeat for the Ottomans. Stephen was later awarded the title "Athleta Christi" (Champion of Christ) by Pope Sixtus IV, who referred to him as "verus christianae fidei athleta" ("the true defender of the Christian faith").
Mehmed II assembled a large army and entered Moldavia in June 1476. Meanwhile, groups of Tartars
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounde ...
from the Crimean Khanate (the Ottomans' recent ally) were sent to attack Moldavia. Romanian sources may state that they were repelled.M. Barbulescu, D. Deletant, K. Hitchins, S. Papacostea, P. Teodor, ''Istoria României (History of Romania)'', Ed. Corint, Bucharest, 2002, , p. 157 Other sources state that joint Ottoman and Crimean Tartar forces "occupied Bessarabia and took Akkerman, gaining control of the southern mouth of the Danube. Stephan tried to avoid open battle with the Ottomans by following a scorched-earth policy".
Finally, Stephen faced the Ottomans in battle. The Moldavians luring the main Ottoman forces into a forest that was set on fire, causing some casualties. According to another battle description, the defending Moldavian forces repelled several Ottoman attacks with steady fire from hand-guns. The attacking Turkish Janissaries
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ...
were forced to crouch on their stomachs instead of charging headlong into the defenders positions. Seeing the imminent defeat of his forces, Mehmed charged with his personal guard against the Moldavians, managing to rally the Janissaries, and turning the tide of the battle. Turkish Janissaries penetrated inside the forest and engaged the defenders in man-to-man fighting.
The Moldavian army was utterly defeated (casualties were very high on both sides), and the chronicle
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and l ...
s say that the entire battlefield was covered with the bones of the dead, a probable source for the toponym (''Valea Albă'' is Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
** Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditiona ...
and ''Akdere'' Turkish for "The White Valley").
Stephen the Great retreated into the north-western part of Moldavia or even into the Polish Kingdom Jurnalul Național
''Jurnalul Național'' is a Romanian newspaper, part of the INTACT Media Group led by Dan Voiculescu, which also includes the popular television station Antena 1. The newspaper was launched in 1993. Its headquarters is in Bucharest
Buchare ...
, Calendar 26 iulie 2005.Moment istoric
(Anniversaries on 26 July 2005. A historical moment)'' and began forming another army. The Ottomans were unable to conquer any of the major Moldavian strongholds ( Suceava, Neamț, Hotin) and were constantly harassed by small scale Moldavians attacks. Soon they were also confronted with starvation, a situation made worse by an outbreak of the
plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
, and the Ottoman army returned to Ottoman lands. The threat of Stephen to Wallachia continued for decades. That very same year Stephen helped his cousin Vlad the Impaler
Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler ( ro, Vlad Țepeș ) or Vlad Dracula (; ro, Vlad Drăculea ; 1428/311476/77), was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most im ...
return to the throne of Wallachia for the third and final time. Even after Vlad's untimely death several months later Stephen continued to support, with force of arms, a variety of contenders to the Wallachian throne succeeding after Mehmet's death to instate Vlad Călugărul
Vlad IV Călugărul ("Vlad IV the Monk"; prior to 1425 – September 1495) was the Prince of Wallachia in 1481 and then from 1482 to 1495.
His father Vlad Dracul had previously held the throne, as had his brothers Mircea II and Radu the Handso ...
, half brother to Vlad the Impaler, for a period of 13 years from 1482 to 1495.
Conquest of Albania (1466–1478)

Skanderbeg
, reign = 28 November 1443 – 17 January 1468
, predecessor = Gjon Kastrioti
, successor = Gjon Kastrioti II
, spouse = Donika Arianiti
, issue = Gjon Kastrioti II
, royal house = Kastrioti
, father ...
, a member of the Albanian nobility
The Albanian nobility was an elite hereditary ruling class in Albania, parts of the western Balkans and later in parts of the Ottoman world. The Albanian nobility was composed of landowners of vast areas, often in allegiance to states like the By ...
and a former member of the Ottoman ruling elite, led Skanderbeg's rebellion
Skanderbeg's rebellion was an almost 25-year long anti-Ottoman rebellion led by the renegade Ottoman sanjakbey Skanderbeg in the territory which belonged to the Ottoman sanjaks of Albania, Dibra and Ohrid (modern-day Albania and North Macedonia) ...
against the expansion of the Ottoman Empire into Europe. Skanderbeg, son of Gjon Kastrioti
Gjon Kastrioti (1375/80 – 4 May 1437), was a member of the Albanian nobility, from the House of Kastrioti, and the father of future Albanian leader Gjergj Kastrioti (better known as Skanderbeg). He governed the territory between the Cape ...
(who had joined the unsuccessful Albanian revolt of 1432–1436), united the Albanian principalities
The term Albanian principalities refers to a number of principalities created in the Middle Ages in Albania and the surrounding regions in the western Balkans that were ruled by Albanian nobility. The 12th century marked the first Albanian princ ...
in a military and diplomatic alliance, the League of Lezhë
The League of Lezhë ( sq, Lidhja e Lezhës), also commonly referred to as the Albanian League ( sq, Lidhja Arbërore), was a military and diplomatic alliance of the Albanian aristocracy, created in the city of Lezhë on 2 March 1444. The Leag ...
, in 1444. Mehmed II was never successful in his efforts to subjugate Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares la ...
while Skanderbeg was alive, even though he twice (1466 and 1467) led the Ottoman armies himself against Krujë. After Skanderbeg died in 1468, the Albanians couldn't find a leader to replace him, and Mehmed II eventually conquered Krujë and Albania in 1478.
In spring 1466, Sultan Mehmed marched with a large army against Skanderbeg and the Albanians. Skanderbeg had repeatedly sought assistance from Italy, and believed that the ongoing Ottoman–Venetian War (1463–1479)
The First Ottoman–Venetian War was fought between the Republic of Venice and her allies and the Ottoman Empire from 1463 to 1479. Fought shortly after the capture of Constantinople and the remnants of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottomans, it ...
offered a golden opportunity to reassert Albanian independence; for the Venetians, the Albanians provided a useful cover to the Venetian coastal holdings of Durrës ( it, Durazzo) and Shkodër
Shkodër ( , ; sq-definite, Shkodra) is the fifth-most-populous city of the Republic of Albania and the seat of Shkodër County and Shkodër Municipality. The city sprawls across the Plain of Mbishkodra between the southern part of Lake Shk ...
( it, Scutari). The major result of this campaign was the construction of the fortress of Elbasan
Elbasan ( ; sq-definite, Elbasani ) is the fourth most populous city of Albania and seat of Elbasan County and Elbasan Municipality. It lies to the north of the river Shkumbin between the Skanderbeg Mountains and the Myzeqe Plain in central A ...
, allegedly within just 25 days. This strategically sited fortress, at the lowlands near the end of the old ''Via Egnatia
The Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a con ...
'', cut Albania effectively in half, isolating Skanderbeg's base in the northern highlands from the Venetian holdings in the south. However, following the Sultan's withdrawal Skanderbeg himself spent the winter in Italy, seeking aid. On his return in early 1467, his forces sallied from the highlands, defeated Ballaban Pasha, and lifted the siege of the fortress of Croia ( Krujë); they also attacked Elbasan but failed to capture it.Setton, Hazard & Norman (1969), p. 327 Mehmed II responded by marching again against Albania. He energetically pursued the attacks against the Albanian strongholds, while sending detachments to raid the Venetian possessions to keep them isolated. The Ottomans failed again to take Croia, and they failed to subjugate the country. However, the winter brought an outbreak of plague, which would recur annually and sap the strength of the local resistance. Skanderbeg himself died of malaria in the Venetian stronghold of Lissus ( Lezhë), ending the ability of Venice to use the Albanian lords for its own advantage. The Albanians were left to their own devices and were gradually subdued over the next decade.
After Skanderbeg died, Mehmed II personally led the siege of Shkodra in 1478–79, of which early Ottoman chronicler Aşıkpaşazade
Dervish Ahmed ( tr, Derviş Ahmed; "Ahmed the Dervish; 1400–1484), better known by his pen name Âşıki or family name Aşıkpaşazade, was an Ottoman historian, a prominent representative of the early Ottoman historiography. He was a descen ...
(1400–81) wrote, "All the conquests of Sultan Mehmed were fulfilled with the seizure of Shkodra." The Venetians and Shkodrans resisted the assaults and continued to hold the fortress until Venice ceded Shkodra to the Ottoman Empire in the Treaty of Constantinople as a condition of ending the war.
Crimean policy (1475)
A number of Turkic peoples, collectively known as theCrimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
, had been inhabiting the peninsula since the early Middle Ages. After the destruction of the Golden Horde by Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
earlier in the 15th century, the Crimean Tatars founded an independent Crimean Khanate under Hacı I Giray
Hacı I Giray (1397–1466, ruled circa 1441–1466) was the founder of the Crimean Khanate and the Giray dynasty of Crimea. As the Golden Horde was breaking up, he established himself in Crimea and spent most of his life fighting off other warl ...
, a descendant of Genghis Khan.
The Crimean Tatars controlled the steppes that stretched from the Kuban to the Dniester River
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and th ...
, but they were unable to take control over the commercial Genoese towns called Gazaria (Genoese colonies)
Gazaria (also Cassaria, Cacsarea, and Gasaria) was the name given to the colonial possessions of the Republic of Genoa in Crimea and around the Black Sea coasts in the territories of the modern regions of Russia, Ukraine and Romania, from the ...
, which had been under Genoese control since 1357. After the conquest of Constantinople, Genoese communications were disrupted, and when the Crimean Tatars asked for help from the Ottomans, they responded with an invasion of the Genoese towns, led by Gedik Ahmed Pasha
Gedik Ahmed Pasha (; died 18 November 1482) was an Ottoman statesman and admiral who served as Grand Vizier and Kapudan Pasha (Grand Admiral of the Ottoman Navy) during the reigns of sultans Mehmed II and Bayezid II.
Very little was known abou ...
in 1475, bringing Kaffa and the other trading towns under their control. After the capture of the Genoese towns, the Ottoman Sultan held Meñli I Giray
Meñli I Giray ( crh3, I Meñli Geray, ۱منكلى كراى) (1445–1515), also spelled as Mengli I Giray, was a '' khan'' of the Crimean Khanate (1466, 1469–1475, 1478–1515) and the sixth son of Hacı I Giray.
Biography
Struggle ...
captive, later releasing him in return for accepting Ottoman suzerainty over the Crimean Khans and allowing them to rule as tributary princes of the Ottoman Empire. However, the Crimean khans still had a large amount of autonomy from the Ottoman Empire, while the Ottomans directly controlled the southern coast.
Expedition to Italy (1480)

 An Ottoman army under
An Ottoman army under Gedik Ahmed Pasha
Gedik Ahmed Pasha (; died 18 November 1482) was an Ottoman statesman and admiral who served as Grand Vizier and Kapudan Pasha (Grand Admiral of the Ottoman Navy) during the reigns of sultans Mehmed II and Bayezid II.
Very little was known abou ...
invaded Italy in 1480, capturing Otranto
Otranto (, , ; scn, label=Salentino, Oṭṛàntu; el, label=Griko, Δερεντό, Derentò; grc, Ὑδροῦς, translit=Hudroûs; la, Hydruntum) is a coastal town, port and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce (Apulia, Italy), in a fertile ...
. Because of lack of food, Gedik Ahmed Pasha returned with most of his troops to Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares la ...
, leaving a garrison of 800 infantry and 500 cavalry behind to defend Otranto in Italy. It was assumed he would return after the winter. Since it was only 28 years after the fall of Constantinople, there was some fear that Rome would suffer the same fate. Plans were made for the Pope and citizens of Rome to evacuate the city. Pope Sixtus IV repeated his 1481 call for a crusade. Several Italian city-states, Hungary, and France responded positively to the appeal. The Republic of Venice did not, however, as it had signed an expensive peace treaty with the Ottomans in 1479.
In 1481 king Ferdinand I of Naples
Ferdinando Trastámara d'Aragona, of the Naples branch, universally known as Ferrante and also called by his contemporaries Don Ferrando and Don Ferrante (2 June 1424, in Valencia – 25 January 1494, in Naples), was the only son, illegitimate, of ...
raised an army to be led by his son Alphonso II of Naples
Alfonso II (4 November 1448 – 18 December 1495) was Duke of Calabria and ruled as King of Naples from 25 January 1494 to 23 January 1495. He was a soldier and a patron of Renaissance architecture and the arts.
Heir to his father Fer ...
. A contingent of troops was provided by king Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus, also called Matthias I ( hu, Hunyadi Mátyás, ro, Matia/Matei Corvin, hr, Matija/Matijaš Korvin, sk, Matej Korvín, cz, Matyáš Korvín; ), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1458 to 1490. After conducting several mi ...
of Hungary. The city was besieged starting 1 May 1481. After the death of Mehmed on 3 May, ensuing quarrels about his succession possibly prevented the Ottomans from sending reinforcements to Otranto. So, the Turkish occupation of Otranto ended by negotiation with the Christian forces, permitting the Turks to withdraw to Albania, and Otranto was retaken by Papal forces in 1481.
Return to Constantinople (1453–1478)
 After conquering Constantinople, when Mehmed II finally entered the city through what is now known as the Topkapi Gate, he immediately rode his horse to the Hagia Sophia, where he ordered the building to be protected. He ordered that an imam meet him there in order to chant the Muslim Creed: "I testify that there is no
After conquering Constantinople, when Mehmed II finally entered the city through what is now known as the Topkapi Gate, he immediately rode his horse to the Hagia Sophia, where he ordered the building to be protected. He ordered that an imam meet him there in order to chant the Muslim Creed: "I testify that there is no god
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
but Allah
Allah (; ar, الله, translit=Allāh, ) is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from '' al- ilāh'', which means "the god", a ...
. I testify that Muhammad is the messenger of Allah." The Eastern Orthodoxy, Orthodox cathedral was transformed into a Muslim mosque through a Waqf, charitable trust, solidifying Islamic rule in Constantinople.
Mehmed's main concern with Constantinople was with rebuilding the city's defenses and repopulation. Building projects were commenced immediately after the conquest, which included the repair of the walls, construction of the citadel, a remarkable hospital with students and medical staff, a large cultural complex, two sets of barracks for the Janissaries, janissaries, a ''tophane'' gun foundry outside Galata and building a new palace.Inalcik, Halil. "The Policy of Mehmed II toward the Greek Population of Istanbul and the Byzantine Buildings of the City". ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers'' 23, (1969): 229–249. p. 236 To encourage the return of the Greeks and the Genoese who had fled from Galata, the trading quarter of the city, he returned their houses and provided them with guarantees of safety. Mehmed issued orders across his empire that Muslims, Christians, and Jews should resettle in the City demanding that five thousand households needed to be transferred to Constantinople by September. From all over the Islamic empire, prisoners of war and deported people were sent to the city; these people were called "Sürgün" in Turkish ( gr, σουργούνιδες ''sourgounides''; "immigrants").
Mehmed restored the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, Ecumenical Orthodox Patriarchate (6 January 1454), Gennadius Scholarius, monk Gennadios being appointed as the first Orthodox Patriarch and established a Jewish Grand Rabbinate (Hakham Bashi, Ḥakham Bashi) and the prestigious Armenian Patriarchate of Constantinople in the capital, as part of the Millet (Ottoman Empire), millet system. In addition he founded, and encouraged his viziers to found, a number of Muslim institutions and commercial installations in the main districts of Constantinople, such as the Rum Mehmed Pasha Mosque built by the Grand Vizier Rum Mehmed Pasha. From these nuclei, the metropolis developed rapidly. According to a survey carried out in 1478, there were then in Constantinople and neighboring Galata 16,324 households, 3,927 shops, and an estimated population of 80,000. The population was about 60% Muslim, 20% Christian, and 10% Jewish.
By the end of his reign, Mehmed's ambitious rebuilding program had changed the city into a thriving imperial capital. According to the contemporary Ottoman historian Neşri, "Sultan Mehmed created all of Istanbul". Fifty years later, Constantinople had again become the largest city in Europe.
Two centuries later, the well-known Ottoman itinerant Evliya Çelebi gave a list of groups introduced into the city with their respective origins. Even today, many quarters of Istanbul, such as Aksaray, Istanbul, Aksaray and Çarşamba, Istanbul, Çarşamba, bear the names of the places of origin of their inhabitants. However, many people escaped again from the city, and there were several outbreaks of plague, so that in 1459 Mehmed allowed the deported Greeks to come back to the city. This measure apparently had no great success, since French people, French voyager Pierre Gilles writes in the middle of the 16th century that the Greek population of Constantinople was unable to name any of the ancient Byzantine churches that had been transformed into mosques or abandoned. This shows that the population substitution had been total.
Administration and culture
 Mehmed II introduced the word Politics into Arabic "Siyasah" from a book he published and claimed to be the collection of Politics doctrines of the Byzantine Caesars before him. He gathered Italian artists, humanism, humanists and Greek scholars at his court, allowed the Eastern Orthodox, Byzantine Church to continue functioning, ordered the patriarch Gennadius Scholarius, Gennadius to translate Christianity, Christian doctrine into Turkish, and called Gentile Bellini from Venice to paint his portrait as well as Venetian frescoes that are vanished today. He collected in his palace a library which included works in Greek, Persian and Latin. Mehmed invited Muslim scientists and astronomers such as Ali Qushji and artists to his court in Constantinople, started a university, built mosques (for example, the Fatih Mosque), waterways, and Istanbul's Topkapı Palace and the Tiled Kiosk.
Around the Fatih Mosque, grand mosque that he constructed, he erected Sahn-ı Seman Medrese, eight madrasas, which, for nearly a century, kept their rank as the highest teaching institutions of the Islamic sciences in the empire.
Mehmed II allowed his subjects a considerable degree of religious freedom, provided they were obedient to his rule. After his conquest of Bosnia in 1463 he issued the Ahdname of Milodraž to the Bosnian Franciscans, granting them freedom to move freely within the Empire, offer worship in their churches and monastery, monasteries, and to practice their religion free from official and unofficial persecution, insult or disturbance. However, his standing army was recruited from the ''Devshirme'', a group that took Christian subjects at a young age (8–20 yrs): they were converted to Islam, then schooled for administration or the military Janissaries. This was a meritocracy which "produced from among their alumni four out of five Grand Viziers from this time on".
Within Constantinople, Mehmed established a ''Millet (Ottoman Empire), millet'' or an autonomous religious community, and appointed the former Patriarch
Mehmed II introduced the word Politics into Arabic "Siyasah" from a book he published and claimed to be the collection of Politics doctrines of the Byzantine Caesars before him. He gathered Italian artists, humanism, humanists and Greek scholars at his court, allowed the Eastern Orthodox, Byzantine Church to continue functioning, ordered the patriarch Gennadius Scholarius, Gennadius to translate Christianity, Christian doctrine into Turkish, and called Gentile Bellini from Venice to paint his portrait as well as Venetian frescoes that are vanished today. He collected in his palace a library which included works in Greek, Persian and Latin. Mehmed invited Muslim scientists and astronomers such as Ali Qushji and artists to his court in Constantinople, started a university, built mosques (for example, the Fatih Mosque), waterways, and Istanbul's Topkapı Palace and the Tiled Kiosk.
Around the Fatih Mosque, grand mosque that he constructed, he erected Sahn-ı Seman Medrese, eight madrasas, which, for nearly a century, kept their rank as the highest teaching institutions of the Islamic sciences in the empire.
Mehmed II allowed his subjects a considerable degree of religious freedom, provided they were obedient to his rule. After his conquest of Bosnia in 1463 he issued the Ahdname of Milodraž to the Bosnian Franciscans, granting them freedom to move freely within the Empire, offer worship in their churches and monastery, monasteries, and to practice their religion free from official and unofficial persecution, insult or disturbance. However, his standing army was recruited from the ''Devshirme'', a group that took Christian subjects at a young age (8–20 yrs): they were converted to Islam, then schooled for administration or the military Janissaries. This was a meritocracy which "produced from among their alumni four out of five Grand Viziers from this time on".
Within Constantinople, Mehmed established a ''Millet (Ottoman Empire), millet'' or an autonomous religious community, and appointed the former Patriarch Gennadius Scholarius
Gennadius II (Greek Γεννάδιος Βʹ; lay name Γεώργιος Κουρτέσιος Σχολάριος, ''Georgios Kourtesios Scholarios''; c. 1400 – c. 1473) was a Byzantine Greek philosopher and theologian, and Ecumenical Patriarch o ...
as religious leader for the Orthodox Christians of the city. His authority extended to all Ottoman Orthodox Christians, and this excluded the Genoese and Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
settlements in the suburbs, and excluded Muslim and Jewish settlers entirely. This method allowed for an indirect rule of the Christian Byzantines and allowed the occupants to feel relatively autonomous even as Mehmed II began the Turkish remodeling of the city, turning it into the Turkish capital, which it remained until the 1920s.
Centralization of government
Mehmed the Conqueror consolidated power by building his imperial court, the divan, with officials who would be solely loyal to him and allow him greater autonomy and authority. Under previous sultans the divan had been filled with members of aristocratic families that sometimes had other interests and loyalties than that of the sultan. Mehmed the Conqueror transitioned the empire away from the Ghazi (warrior), Ghazi mentality that emphasizes ancient traditions and ceremonies in governance and moved the empire towards a centralized bureaucracy largely made of officials of devşirme background. Additionally, Mehmed the Conqueror took the step of converting the religious scholars who were part of the Ottoman madrasas into salaried employees of the Ottoman bureaucracy who were loyal to him. This centralization was possible and formalized through a Ottoman law, kanunname, issued during 1477–1481, which for the first time listed the chief officials in the Ottoman government, their roles and responsibilities, salaries, protocol and punishments, as well as how they related to each other and the sultan. Once Mehmed had created an Ottoman bureaucracy and transformed the empire from a frontier society to a centralized government, he took care to appoint officials who would help him implement his agenda. His first grand vizier was Zaganos Pasha, who was of devşirme background as opposed to an aristocrat, and Zaganos Pasha's successor, Mahmud Pasha Angelović, was also of devşirme background. Mehmed was the first sultan who was able to codify and implement kanunname solely based on his own independent authority. Additionally, Mehmed was able to later implement kanunname that went against previous tradition or precedent. This was monumental in an empire that was so steeped in tradition and could be slow to change or adapt. Having viziers and other officials who were loyal to Mehmed was an essential part of this government because he transferred more power to the viziers than previous sultans had. He delegated significant powers and functions of government to his viziers as part of his new policy of imperial seclusions. A wall was built around the palace as an element of the more closed era, and unlike previous sultans Mehmed was no longer accessible to the public or even lower officials. His viziers directed the military and met foreign ambassadors, two essential parts of governing especially with his numerous military campaigns. One such notable ambassador was Kinsman Karabœcu Pasha (Turkish: "Karaböcü Kuzen Paşa"), who came from a rooted family of spies, which enabled him to play a notable role in Mehmed's campaign of conquering Constantinople.Patronage of Renaissance artists
 Aside from his efforts to expand Ottoman dominion throughout the Eastern Mediterranean, Mehmed II also cultivated a large collection of Western art and literature, many of which were produced by Renaissance artists. From a young age, Mehmed had shown interest in Renaissance art and Classical literature and histories, with his school books having caricaturistic illustrations of ancient coins and portraiture sketched in distinctly European styles. Furthermore, he reportedly had two tutors, one trained in Greek and another in Latin, who read him Classical histories including those of Laertius, Livy, and Herodotus in the days leading up to the fall of Constantinople.
From early on in his reign, Mehmed invested in the patronage of Italian Renaissance artists. His first documented request in 1461 was a commission from artist Matteo de' Pasti, who resided in the court of the lord of Rimini, Sigismondo Malatesta. This first attempt was unsuccessful, though, as Pasti was arrested in Crete by Venetian authorities accusing him of being an Ottoman spy. Later attempts would prove more fruitful, with some notable artists including Costanzo da Ferrara and Gentile Bellini both being invited to the Ottoman court.
Aside from his patronage of Renaissance artists, Mehmed was also an avid scholar of contemporary and Classical literature and history. This interest culminated in Mehmed's work on building a massive multilingual library that contained over 8000 manuscripts in Persian, Ottoman Turkish, Arabic, Latin, and Greek, among other languages. Of note in this large collection was Mehmed's Greek scriptorium, which included copies of Arrians’ ''Anabasis of Alexander the Great'' and Homer's ''Iliad''. His interest in Classical works extended in many directions, including the patronage of the Greek writer Kritiboulos of Imbros, who produced the Greek manuscript ''History of Mehmed the Conqueror'', alongside his efforts to salvage and rebind Greek manuscripts acquired after his conquest of Constantinople.
Historians believe that Mehmed's widespread cultural and artistic tastes, especially those aimed towards the West, served various important diplomatic and administrative functions. His patronage of Renaissance artists have been interpreted as a method of diplomacy with other influential Mediterranean states, significantly many Italian states including the Kingdom of Naples and the Republic of Florence. Furthermore, historians speculate that his Greek scriptorium was used to educate Greek chancellery officials in an attempt to reintegrate former Byzantine diplomatic channels with several Italian states that conducted their correspondences in Greek. Importantly, historians also assert that Mehmed's vast collection of art and literature worked towards promoting his imperial authority and legitimacy, especially in his newly conquered lands. This was accomplished through various means, including the invocation of Mehmed's image as an Oriental neo-Alexandrian figure, which is seen through shared helmet ornaments in depictions of Mehmed and Alexander on medallion portraits produced during Mehmed's reign, as well as being a leitmotiv in Kritiboulous’ work. Additionally, his commissioning of Renaissance artwork was, itself, possibly an attempt to break down Western-Oriental cultural binaries in order for Mehmed to present himself as a Western-oriented ruler, among the ranks of contemporary European Christian monarchs.
Mehmed's affinity towards the Renaissance arts, and his strong initiative in its creation and collection, did not have a large base of support within his own court. One of the many opponents to Mehmed's collection was his own son and future Sultan, Bayezid II, who was backed by powerful religious and Turkish factions in his opposition. Upon his accession, Bayezid II sold Mehmed's collection of portraits and disposed of his statuary.
Aside from his efforts to expand Ottoman dominion throughout the Eastern Mediterranean, Mehmed II also cultivated a large collection of Western art and literature, many of which were produced by Renaissance artists. From a young age, Mehmed had shown interest in Renaissance art and Classical literature and histories, with his school books having caricaturistic illustrations of ancient coins and portraiture sketched in distinctly European styles. Furthermore, he reportedly had two tutors, one trained in Greek and another in Latin, who read him Classical histories including those of Laertius, Livy, and Herodotus in the days leading up to the fall of Constantinople.
From early on in his reign, Mehmed invested in the patronage of Italian Renaissance artists. His first documented request in 1461 was a commission from artist Matteo de' Pasti, who resided in the court of the lord of Rimini, Sigismondo Malatesta. This first attempt was unsuccessful, though, as Pasti was arrested in Crete by Venetian authorities accusing him of being an Ottoman spy. Later attempts would prove more fruitful, with some notable artists including Costanzo da Ferrara and Gentile Bellini both being invited to the Ottoman court.
Aside from his patronage of Renaissance artists, Mehmed was also an avid scholar of contemporary and Classical literature and history. This interest culminated in Mehmed's work on building a massive multilingual library that contained over 8000 manuscripts in Persian, Ottoman Turkish, Arabic, Latin, and Greek, among other languages. Of note in this large collection was Mehmed's Greek scriptorium, which included copies of Arrians’ ''Anabasis of Alexander the Great'' and Homer's ''Iliad''. His interest in Classical works extended in many directions, including the patronage of the Greek writer Kritiboulos of Imbros, who produced the Greek manuscript ''History of Mehmed the Conqueror'', alongside his efforts to salvage and rebind Greek manuscripts acquired after his conquest of Constantinople.
Historians believe that Mehmed's widespread cultural and artistic tastes, especially those aimed towards the West, served various important diplomatic and administrative functions. His patronage of Renaissance artists have been interpreted as a method of diplomacy with other influential Mediterranean states, significantly many Italian states including the Kingdom of Naples and the Republic of Florence. Furthermore, historians speculate that his Greek scriptorium was used to educate Greek chancellery officials in an attempt to reintegrate former Byzantine diplomatic channels with several Italian states that conducted their correspondences in Greek. Importantly, historians also assert that Mehmed's vast collection of art and literature worked towards promoting his imperial authority and legitimacy, especially in his newly conquered lands. This was accomplished through various means, including the invocation of Mehmed's image as an Oriental neo-Alexandrian figure, which is seen through shared helmet ornaments in depictions of Mehmed and Alexander on medallion portraits produced during Mehmed's reign, as well as being a leitmotiv in Kritiboulous’ work. Additionally, his commissioning of Renaissance artwork was, itself, possibly an attempt to break down Western-Oriental cultural binaries in order for Mehmed to present himself as a Western-oriented ruler, among the ranks of contemporary European Christian monarchs.
Mehmed's affinity towards the Renaissance arts, and his strong initiative in its creation and collection, did not have a large base of support within his own court. One of the many opponents to Mehmed's collection was his own son and future Sultan, Bayezid II, who was backed by powerful religious and Turkish factions in his opposition. Upon his accession, Bayezid II sold Mehmed's collection of portraits and disposed of his statuary.
Family
Mehmed II had at least eight known consorts, at least one of whom were his legal wife.Consorts
Mehmed II was the last sultan to legally marry until 1533/1534, whenSuleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
married his favorite concubine Hurrem Sultan, Hürrem Sultan
Mehmed II's eight know consorts are:
*Gülbahar Hatun (wife of Mehmed II), Gülbahar Hatun Mother of Bayezid II.
*Gülşah Hatun. Mother of Şehzade Mustafa.
*Sittişah Hatun, Sittişah Mukrime Hatun. Sometimes mistakenly believed to be the mother of Bayezid II. Called also Sitti Hatun. Daughter of Dulkadiroğlu Süleyman Bey, sixth ruler of Dulkadir, she was his first legal wife, but the marriage was unhappy and it remained childless. Her niece Ayşe Hatun, daughter of her brother, became a consort of Bayezid II.
*Çiçek Hatun. Mother of Şehzade Cem.
*Anna Komnenos (daughter of David of Trebizond), Anna Hatun. Daughter of the Greek emperor of Trabzon, Trebizond David of Trebizond, David II Komnenos and his wife Helena Kantakouzene, Empress of Trebizond, Helena Kantakuzenos. The marriage was initially proposed by her father, but Mehmed refused. However, after the Trebizond Campaign, conquest of Trebizond in 1461, Anna entered in Mehmed's harem as "noble tribute" or guest and stayed there for two years, after which Mehmed married her to Zagan Pasha, Zaganos Mehmed Pasha. In exchange, Mehmed had the Zaganos's daughter as his consort. It is therefore unlikely that Mehmed ever legally married her, and the union may never have been consummated. She had not children by Mehmed.
*Helena Palaiologina (daughter of Demetrios), Helena Hatun (? - Edirne, before 1470). Daughter of the despot of Morea Demetrios Palaiologos
Demetrios Palaiologos or Demetrius Palaeologus ( el, Δημήτριος Παλαιολόγος, Dēmētrios Palaiologos; 1407–1470) was Despot of the Morea together with his brother Thomas from 1449 until the fall of the despotate in 1460. Deme ...
, Mehmed asked her for himself after the Morea campaign, having heard of her beauty. She was probraly his second legal wife, however, the union was never consummated because Mehmed feared that she might poison him.
*Maria Hatun. Born Maria Gattilusio, she was widow of Alexander Komnenos Asen. She was judicated as the most beautiful woman of her age.
*Hatice Hatun. Daughter of Zagan Pasha, Zaganos Mehmed Pasha, she entered the harem in 1463 as probraly Mehmed's third legal wife. In return, her father was able to marry Anna Hatun, Mehmed's consort or "noble guest". After Mehmed's death she remarried with a statesman.
Sons
Mehmed II had at least four sons:Alderson, The structure of the Ottoman Dynasty *Bayezid II
Bayezid II ( ota, بايزيد ثانى, Bāyezīd-i s̱ānī, 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512, Turkish: ''II. Bayezid'') was the eldest son and successor of Mehmed II, ruling as Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, B ...
(3 December 1447 - 10 June 1512) - son of Gülbahar Hatun. He succeeded his father as the Ottoman Sultan.
*Şehzade Mustafa (1450, Manisa - 25 December 1474, Konya) - son of Gülşah Hatun. Governor of Konya until his death. He had a son, Şehzade Hali, and a daughter, Nergiszade Ferahşad Hatun (who married his cousin Şehzade Abdullah, son of Bayezid II). He was the favorite son of his father.
*Cem Sultan, Şehzade Cem (22 December 1459, Constantinople - 25 February 1495; Capua, Kingdom of Naples, Italy) - son of Çiçek Hatun. Governor of Konya after the death of his brother Mustafa, he fought for the throne against his half-brother Bayezid. He died in exile.
*Şehzade Nureddin. Probably died as an infant.
Daughters
Mehmed II had at least four daughters: *Gevherhan Hatun (daughter of Mehmed the Conqueror), Gevherhan Hatun (1446 - Constantinople, 1514) - daughter of Gülbahar Hatun. *Ayşe Hatun. She married Hasan Bey, son of Isfendiyarids, Candaroğlu İsmail Bey. *Kamerhan Hatun. *''Fülane'' Hatun.Personal life
 Some sources indicate that Mehmed had a passion for his hostage and favourite, Radu the Fair. Young men condemned to death were spared and added to Mehmed's seraglio if he found them attractive, and the Porte went to great lengths to procure young noblemen for him.
Mehmed had a strong interest in ancient Greek and medieval Byzantine civilization. His heroes were Achilles and Alexander the Great and he could discuss Christian religion with some authority. He was reputed to be fluent in several languages, including Ottoman Turkish language, Turkish, Serbian language, Serbian, Arab language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian, Greek language, Greek and Latin language, Latin.
At times, he assembled the Ulama, or learned Muslim teachers, and caused them to discuss theological problems in his presence. During his reign, mathematics, astronomy, and theology reached their highest level among the Ottomans. His social circle included a number of humanists and sages such as Ciriaco de' Pizzicolli of Ancona, Benedetto Dei of Florence and
Some sources indicate that Mehmed had a passion for his hostage and favourite, Radu the Fair. Young men condemned to death were spared and added to Mehmed's seraglio if he found them attractive, and the Porte went to great lengths to procure young noblemen for him.
Mehmed had a strong interest in ancient Greek and medieval Byzantine civilization. His heroes were Achilles and Alexander the Great and he could discuss Christian religion with some authority. He was reputed to be fluent in several languages, including Ottoman Turkish language, Turkish, Serbian language, Serbian, Arab language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian, Greek language, Greek and Latin language, Latin.
At times, he assembled the Ulama, or learned Muslim teachers, and caused them to discuss theological problems in his presence. During his reign, mathematics, astronomy, and theology reached their highest level among the Ottomans. His social circle included a number of humanists and sages such as Ciriaco de' Pizzicolli of Ancona, Benedetto Dei of Florence and Michael Critobulus Michael Critobulus (; c. 1410 – c. 1470) was a Greek politician, scholar and historian. He is known as the author of a history of the Ottoman conquest of the Eastern Roman Empire under Sultan Mehmet II. Critobulus' work, along with the writings o ...
of Imbros, who mentions Mehmed as a Philhellene thanks to his interest in Grecian antiquities and relics. It was on his orders that the Parthenon and other Athenian monuments were spared destruction. Besides, Mehmed II himself was a poet writing under the name "Avni" (the helper, the helpful one) and he left a classical diwan (poetry), diwan poetry collection.
Death and legacy

 In 1481 Mehmed marched with the Ottoman army, but upon reaching Maltepe, Istanbul he became ill. He was just beginning new campaigns to capture Rhodes and southern Italy, however according to some historians his next voyage was planned to overthrow the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt and to capture Egypt and claim the caliphate. But after some days he died, on 3 May 1481, at the age of forty-nine, and was buried in his ''türbe'' near the
In 1481 Mehmed marched with the Ottoman army, but upon reaching Maltepe, Istanbul he became ill. He was just beginning new campaigns to capture Rhodes and southern Italy, however according to some historians his next voyage was planned to overthrow the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt and to capture Egypt and claim the caliphate. But after some days he died, on 3 May 1481, at the age of forty-nine, and was buried in his ''türbe'' near the Fatih Mosque
The large Fatih Mosque ( tr, Fatih Camii, "Conqueror's Mosque" in English) is an Ottoman mosque off Fevzi Paşa Caddesi in the Fatih district of Istanbul, Turkey. The original mosque was constructed between 1463 and 1470 on the site of the C ...
complex. According to the historian Colin Heywood, "there is substantial circumstantial evidence that Mehmed was poisoned, possibly at the behest of his eldest son and successor, Bayezid."
The news of Mehmed's death caused great rejoicing in Europe; church bells were rung, and celebrations held. The news was proclaimed in Venice thus: "La Grande Aquila è morta!" ('The Great Eagle is dead!')
Mehmed II is recognized as the first sultan to codify criminal and constitutional law, long before Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
; he thus established the classical image of the autocratic Ottoman sultan. Mehmed's thirty-one year rule and numerous wars expanded the Ottoman Empire to include Constantinople, the Turkish kingdoms and territories of Asia Minor, Bosnia, Serbia, and Albania. Mehmed left behind an imposing reputation in both the Islamic and Christian worlds. According to historian Franz Babinger, Mehmed was regarded as a bloodthirsty tyrant by the Christian world and by a part of his subjects. Istanbul's Fatih Sultan Mehmet Bridge
The Fatih Sultan Mehmet Bridge ("Sultan Mehmed the Conqueror Bridge"), also known as the Second Bosphorus Bridge (in Turkish: ''Fatih Sultan Mehmet Köprüsü'', ''F.S.M. Köprüsü'' or ''2. Köprü''), is a bridge in Istanbul, Turkey spannin ...
(completed 1988), which crosses the Bosporus Straits, is named after him, and his name and picture appeared on the Turkish 1000 Turkish lira, lira note from 1986 to 1992.
Portrayal in popular culture
* Mehmed is the eponymous subject of Gioachino Rossini, Rossini's 1820 opera, ''Maometto II''. Rossini and librettist Cesare della Valle offer a nuanced picture of Mehmed, portraying him as a fearless and magnanimous leader, even on the verge of conquering Euboea, Negroponte. * Portrayed by Sami Ayanoğlu in the Turkish film ''The Conquest of Constantinople'' (1951). * Portrayed by Devrim Evin the Turkish film ''Fetih 1453'' (2012). His childhood is portrayed by Ege Uslu. * Portrayed by Mehmet Akif Alakurt in the Turkish television series ''Fatih (TV series), Fatih'' (2013). * Portrayed by Dominic Cooper in ''Dracula Untold''. * Portrayed by Kenan İmirzalıoğlu in the Turkish television series '':tr:Mehmed Bir Cihan Fatihi'' (2018). * Portrayed by Cem Yiğit Üzümoğlu in the docuseries ''Rise of Empires: Ottoman'' (2020).See also
* Classical Age of the Ottoman Empire * Decline of the Byzantine Empire * Kashifi (Ottoman poet), Kashifi (author of the ''Ḡazā-nāma-ye Rum'')References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * Dyer, T. H., & Hassall, A. (1901)''A history of modern Europe From the fall of Constantinople''
London: G. Bell and Sons. * * Fredet, Peter (1888)
''Modern History; From the Coming of Christ and Change of the Roman Republic into an Empire, to the Year of Our Lord 1888''
Baltimore: J. Murphy & Co
383 pp
* Harris, Jonathan, ''The End of Byzantium''. New Haven CT and London: Yale University Press, 2010.
İnalcık; Halil, Review of ''Mehmed the Conqueror and his Time''
* Imber, Colin, ''The Ottoman Empire, 1300–1650: The Structure of Power''. 2nd Edition. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2009. * * * * Philippides, Marios, ''Emperors, Patriarchs, and Sultans of Constantinople, 1373–1513: An Anonymous Greek Chronicle of the Sixteenth Century''. Brookline MA: Hellenic College Press, 1990. * * Silburn, P. A. B. (1912)
''The evolution of sea-power''
London: Longmans, Green and Co. *
External links
by Edward Gibbon
Constantinople Siege & Fall
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Roger Crowley, Judith Herrin & Colin Imber (''In Our Time (radio series), In Our Time'', 28 December 2006) {{DEFAULTSORT:Mehmed 02 Mehmed the Conqueror, Hanafis Maturidis Sunni Sufis 1432 births 1481 deaths Turkish Muslims 15th-century murdered monarchs 15th-century Ottoman sultans Burials in Turkey Deaths by poisoning Fall of Constantinople Medieval child rulers Mujaddid Ottoman people of the Byzantine–Ottoman wars Ottoman people of the Ottoman–Venetian Wars People from Edirne Turkish poets The Sultan of Two Lands and the Khan of Two Seas