Sulfonated on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aromatic sulfonation is an organic reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an
 Typical conditions involve heating the aromatic compound with sulfuric acid:
:C6H6 + H2SO4 → C6H5SO3H + H2O
Sulfur trioxide or its protonated derivative is the actual
Typical conditions involve heating the aromatic compound with sulfuric acid:
:C6H6 + H2SO4 → C6H5SO3H + H2O
Sulfur trioxide or its protonated derivative is the actual

 Sulfonation of polystyrene is used to make sodium polystyrene sulfonate, a common ion exchange resin for
Sulfonation of polystyrene is used to make sodium polystyrene sulfonate, a common ion exchange resin for
arene
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member of aromatic compounds is benzene. The word "aromatic" originates from the past groupin ...
is replaced by a sulfonic acid functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
in an electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic system (usually hydrogen) is replaced by an electrophile. Some of the most important electrophilic aromatic substitutions are aromatic n ...
. Aryl sulfonic acids are used as detergents, dye, and drugs.
Stoichiometry and mechanism
electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carrie ...
in this electrophilic aromatic substitution.
To drive the equilibrium, dehydrating agents such as thionyl chloride
Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately per year bein ...
can be added.
:C6H6 + H2SO4 + SOCl2 → C6H5SO3H + SO2 + 2 HCl
Chlorosulfuric acid is also an effective agent:
:C6H6 + HSO3Cl → C6H5SO3H + HCl
In contrast to aromatic nitration and most other electrophilic aromatic substitutions this reaction is reversible. Sulfonation takes place in concentrated acidic conditions and desulfonation is the mode of action in a dilute hot aqueous acid. The reaction is very useful in protecting the aromatic system because of this reversibility. Due to their electron withdrawing effects, sulfonate protecting groups can be used to prevent electrophilic aromatic substitution. They can also be installed as directing groups to affect the position where a substitution may take place.T.W> Graham Solomons: ''Organic Chemistry'', 11th Edition, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2013, p. 676, .
Specialized sulfonation methods
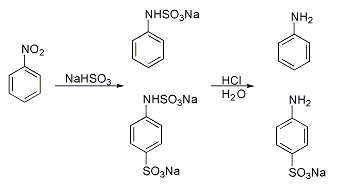
Many method have been developed for introducing sulfonate groups aside from direction sulfonation.Piria reaction
A classic named reaction is the Piria reaction ( Raffaele Piria, 1851) in which nitrobenzene is reacted with a metalbisulfite
The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogensulfite) is the ion . Salts containing the ion are also known as "sulfite lyes". Sodium bisulfite is used interchangeably with sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5). Sodium metabisulfite disso ...
forming an aminosulfonic acid as a result of combined nitro group reduction and sulfonation.

Tyrer sulfonation process
In the Tyrer sulfonation process (1917), at some time of technological importance, benzene vapor is led through a vessel containing 90% sulfuric acid the temperature of which is increased from 100 to 180°C. Water and benzene are continuously removed in a condenser and the benzene layer fed back to the vessel. In this way an 80% yield is obtained.Applications
Aromatic sulfonic acids are intermediates in the preparation of dyes and many pharmaceuticals. Sulfonation ofaniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...
s lead to a large group of sulfa drugs.
water softening
Water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. The resulting soft water requires less soap for the same cleaning effort, as soap is not wasted bonding with calcium ions. Soft water also exten ...
.
Reactions of aryl sulfonic acids
As afunctional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
, aryl sulfonic acids undergo desulfonation when heated in water:
:RC6H4SO3H + H2O → RC6H5 + H2SO4
When treated with strong base, benzenesulfonic acid derivatives convert to phenols.
:C6H5SO3H + 2 NaOH → C6H5OH + Na2SO4 + H2O
See also
*Electrophilic halogenation
In organic chemistry, an electrophilic aromatic halogenation is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution. This organic reaction is typical of aromatic compounds and a very useful method for adding substituents to an aromatic system.
:
A few ...
*Nitration
In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols an ...
* Perchlorylbenzene
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Aromatic Sulfonation Substitution reactions