Stella (software) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
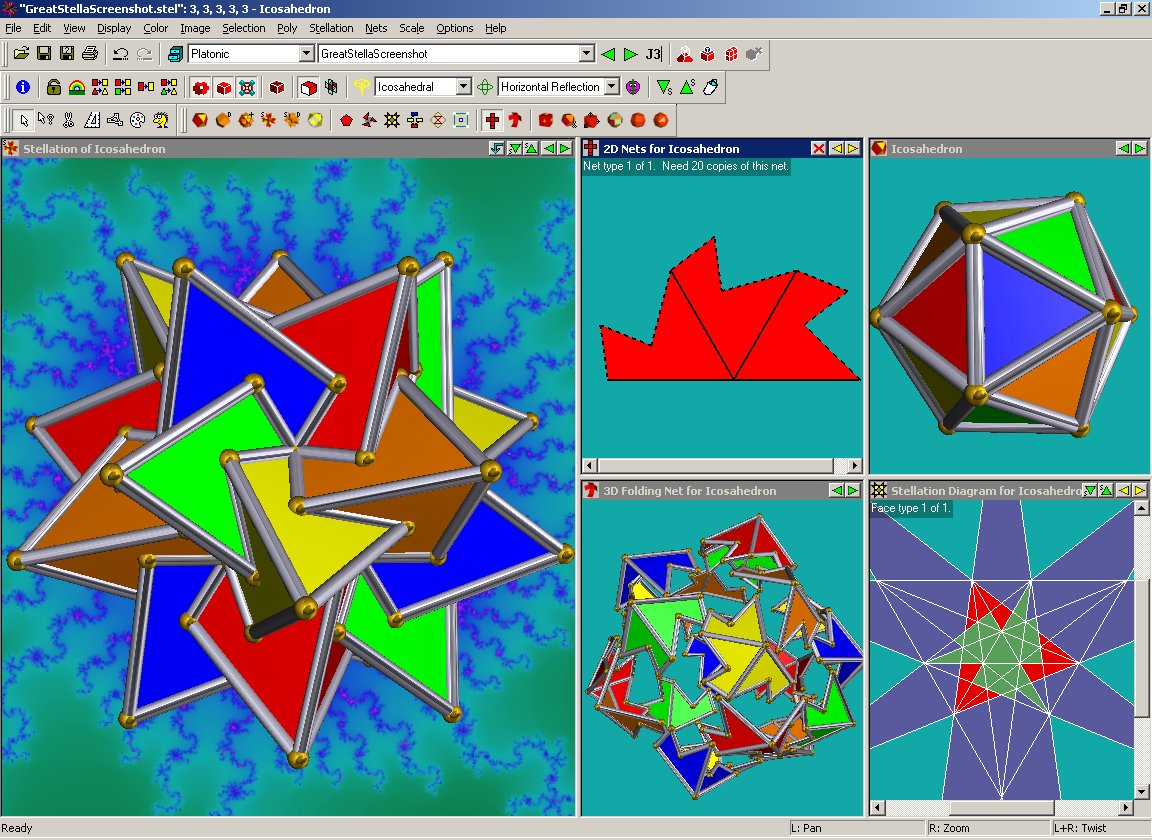
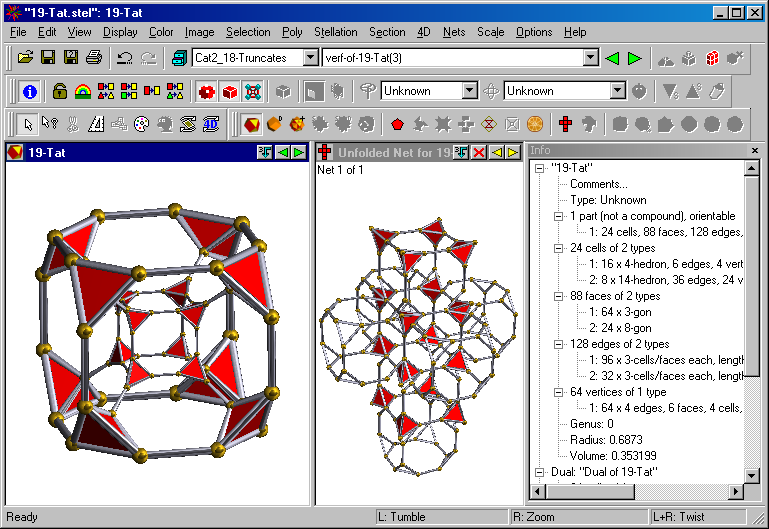 Stella, a
Stella, a

 Stella, a
Stella, a computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program ...
available in three versions (Great Stella, Small Stella and Stella4D), was created by Robert Webb of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
. The programs contain a large library of polyhedra
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices.
A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on t ...
which can be manipulated and altered in various ways.
Polyhedra
Polyhedra in Great Stella's library include thePlatonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all edges c ...
s, the Archimedean solid
In geometry, an Archimedean solid is one of the 13 solids first enumerated by Archimedes. They are the convex uniform polyhedra composed of regular polygons meeting in identical vertices, excluding the five Platonic solids (which are composed ...
s, the Kepler-Poinsot solids, the Johnson solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that isohedral, each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each Vertex (geometry), ver ...
s, some Johnson Solid near-misses, numerous compounds including the uniform polyhedra
In geometry, a uniform polyhedron has regular polygons as faces and is vertex-transitive (i.e., there is an isometry mapping any vertex onto any other). It follows that all vertices are congruent.
Uniform polyhedra may be regular (if also fa ...
, and other polyhedra. Operations which can be performed on these polyhedra include stellation
In geometry, stellation is the process of extending a polygon in two dimensions, polyhedron in three dimensions, or, in general, a polytope in ''n'' dimensions to form a new figure. Starting with an original figure, the process extends specific el ...
, faceting, augmentation, dualization (also called "reciprocation"), creating convex hull
In geometry, the convex hull or convex envelope or convex closure of a shape is the smallest convex set that contains it. The convex hull may be defined either as the intersection of all convex sets containing a given subset of a Euclidean space ...
s, and others.
All versions of the program enable users to print net
Net or net may refer to:
Mathematics and physics
* Net (mathematics), a filter-like topological generalization of a sequence
* Net, a linear system of divisors of dimension 2
* Net (polyhedron), an arrangement of polygons that can be folded up ...
s for polyhedra. These nets may then be assembled into actual three-dimensional polyhedral model
The polyhedral model (also called the polytope method) is a mathematical framework for programs that perform large numbers of operations -- too large to be explicitly enumerated -- thereby requiring a ''compact'' representation. Nested loop progra ...
s of great beauty and complexity.
Stella4D
In 2007, a Stella4D version was added, allowing the generation and display of four-dimensional polytopes ( polychora), including a library of all convex uniform polychora, and all currently known nonconvex star polychora, as well as the uniform duals. They can be selected from a library or generated from user created polyhedralvertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
files.
Features
Stella provides a configurable workspace comprising several panels. Once a model has been selected from the range available, different views of it may be displayed in each panel. These views can also include measurements, symmetries and unfolded nets. A variety of operations may be performed on any polyhedron. In 3D these include:stellation
In geometry, stellation is the process of extending a polygon in two dimensions, polyhedron in three dimensions, or, in general, a polytope in ''n'' dimensions to form a new figure. Starting with an original figure, the process extends specific el ...
, faceting
Stella octangula as a faceting of the cube
In geometry, faceting (also spelled facetting) is the process of removing parts of a polygon, polyhedron or polytope, without creating any new Vertex (geometry), vertices.
New edges of a faceted pol ...
, augmentation, excavation, drilling and dualising.
Other features include spring network relaxation, generation of the convex hull, and generation of cupolaic blends and related figures.
Release history
* v1.0 – 20 August 2001 – First release of Stella ** v1.1 – 14 January 2002 * v2.0 – 12 September 2002 ** v2.8.7 – 16 November 2004 * v3.0 – 12 June 2005 ** v3.5.1 – 10 May 2006 * v4.0 – 13 March 2007 – (Including new "Stella4D") ** v4.4 – 11 January 2008 * v5.0 – 30 September 2012 ** v5.4 – 10 May 2014References
* * * (Note: journal was back-dated. Paper actually written 2003)Further reading
* (Note: journal was back-dated. Paper actually written 2004)External links
*{{official website, http://www.software3d.com/Stella.php Polyhedra 4-polytopes 3D graphics software