St. James's Day Battle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
St James' Day Battle (also known as St James' Day Fight, the Battle of the North Foreland and the Battle of Orfordness) took place on 25 July 1666 — St James' day in the
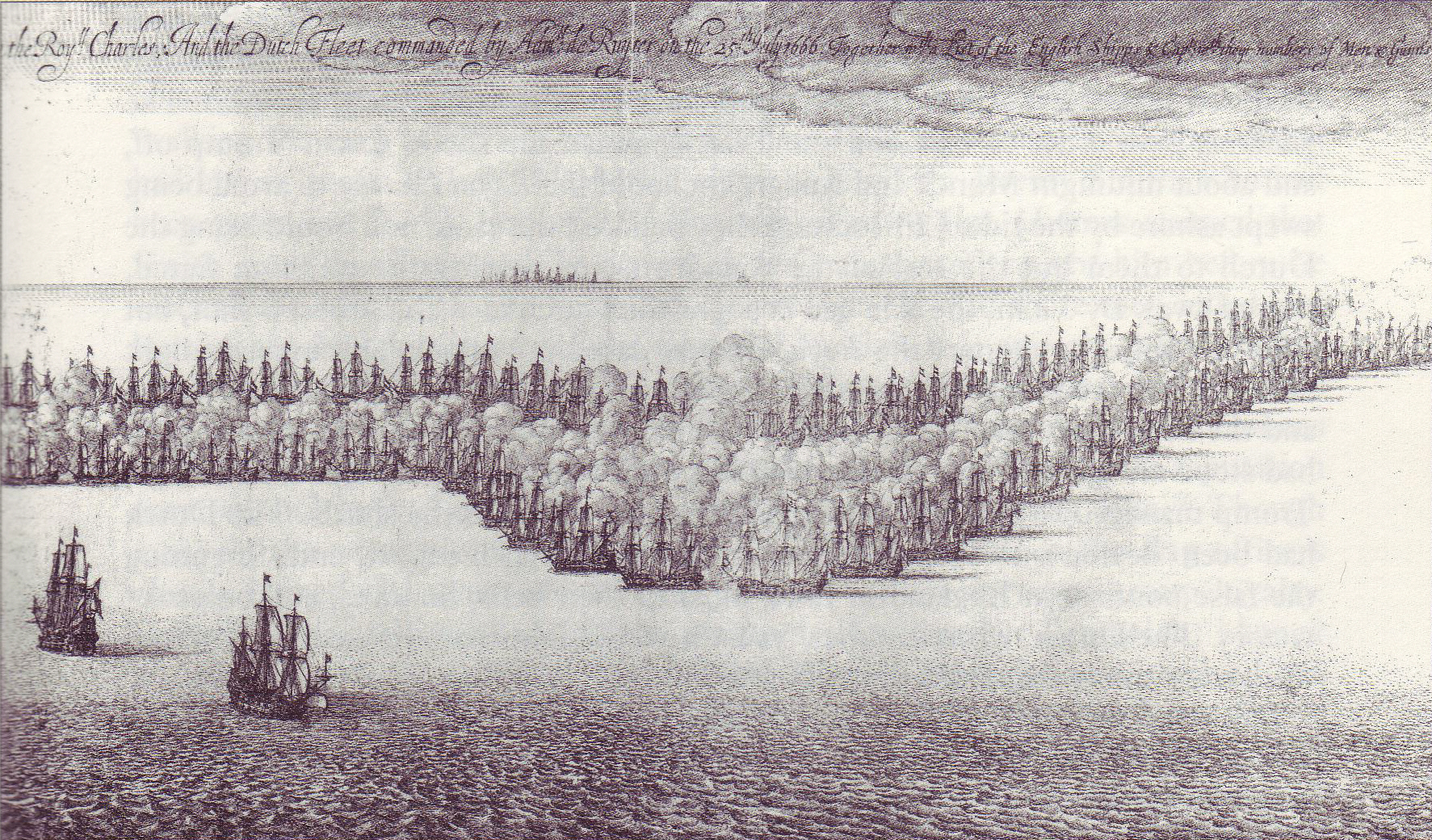 On the morning of 5 August, after a short summer's night, De Ruyter discovered that his position had become hopeless. Lieutenant-Admiral Johan Evertsen had died after losing a leg, De Ruyter's force was now reduced to about forty ships, crowding together and most of these were inoperational, being survivors of the van. Some fifteen good ships had apparently deserted during the night. A strong gale from the east prevented an easy retreat to the continental coast, and to the west the British van and centre (about fifty ships) surrounded him in a half-circle, safely bombarding him from a leeward position.
De Ruyter was desperate. When his second-in-command of the centre, Lieutenant-Admiral
On the morning of 5 August, after a short summer's night, De Ruyter discovered that his position had become hopeless. Lieutenant-Admiral Johan Evertsen had died after losing a leg, De Ruyter's force was now reduced to about forty ships, crowding together and most of these were inoperational, being survivors of the van. Some fifteen good ships had apparently deserted during the night. A strong gale from the east prevented an easy retreat to the continental coast, and to the west the British van and centre (about fifty ships) surrounded him in a half-circle, safely bombarding him from a leeward position.
De Ruyter was desperate. When his second-in-command of the centre, Lieutenant-Admiral
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandri ...
then in use in England (4 August 1666 in the Gregorian calendar), during the Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas and trade routes, whe ...
. It was fought between fleets of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, commanded jointly by Prince Rupert of the Rhine
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 (O.S.) / 27 December (N.S.) – 29 November 1682 (O.S.)) was an English army officer, admiral, scientist and colonial governor. He first came to prominence as a Royalist cava ...
and George Monck
George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle JP KG PC (6 December 1608 – 3 January 1670) was an English soldier, who fought on both sides during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A prominent military figure under the Commonwealth, his support was cruc ...
, 1st Duke of Albemarle, and the United Provinces commanded by Lieutenant-Admiral Michiel de Ruyter
Michiel Adriaenszoon de Ruyter (; 24 March 1607 – 29 April 1676) was a Dutch admiral. Widely celebrated and regarded as one of the most skilled admirals in history, De Ruyter is arguably most famous for his achievements with the Dutch N ...
. In the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, the battle is known as the Two Days' Battle.
Background
This attack followed on the heels of theFour Days' Battle
The Four Days' Battle, also known as the Four Days' Fight in some English sources and as Vierdaagse Zeeslag in Dutch, was a naval battle of the Second Anglo-Dutch War. Fought from 1 June to 4 June 1666 in the Julian or Old Style calendar that w ...
of 1–4 June 1666 which is normally considered a Dutch victory.
Battle
First day
In the early morning of 25 July, the Dutch fleet of 88 ships discovered the English fleet of 89 ships near North Foreland, sailing to the north. De Ruyter gave orders for a chase and the Dutch fleet pursued the English from the southeast in a leeward position, as the wind blew from the northwest. Suddenly, the wind turned to the northeast. The English commander,Prince Rupert of the Rhine
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 (O.S.) / 27 December (N.S.) – 29 November 1682 (O.S.)) was an English army officer, admiral, scientist and colonial governor. He first came to prominence as a Royalist cava ...
, then turned sharply east to regain the weather gauge
The weather gage (sometimes spelled weather gauge) is the advantageous position of a fighting sailing vessel relative to another. It is also known as "nautical gauge" as it is related to the sea shore. The concept is from the Age of Sail and is no ...
. De Ruyter followed, but the wind fell and the fleet fell behind. The Dutch van, commanded by Lieutenant-Admiral Johan Evertsen
Johan Evertsen (1 February 1600 – 5 August 1666) was a Dutch admiral who was born in the 17th century.
Early life
Like his five brothers, Evertsen started his military career as a lieutenant after the death of his father, "Captain Jan". He q ...
, was becalmed and drifted away from the line of battle
The line of battle is a tactic in naval warfare in which a fleet of ships forms a line end to end. The first example of its use as a tactic is disputed—it has been variously claimed for dates ranging from 1502 to 1652. Line-of-battle tacti ...
, splitting De Ruyter's fleet in two. This awkward situation lasted for hours; then, again, a soft breeze began to blow from the northeast. Immediately, the English van, commanded by Thomas Allin, and part of the centre formed a line of battle and engaged the Dutch van, still in disarray.
The Dutch failed to form a coherent line of battle in response, and ship after ship was mauled by the combined firepower of the English line. Vice-Admiral Rudolf Coenders was killed, and Lieutenant-Admiral Tjerk Hiddes de Vries
Tjerk Hiddes de Vries (Sexbierum, 6 August 1622 - Flushing, 6 August 1666) was a naval hero and Dutch admiral from the seventeenth century. The French, who could not pronounce his name, called him Kiërkides. His name was also given as ''Tsjerk' ...
had an arm and a leg shot off. De Ruyter formed the Dutch centre and attempted to reach the van, but the wind was against him and he failed to reunite his forces.
With the Dutch van defeated, the English converged to deliver the coup-de-grâce to De Ruyter's centre. George Monck
George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle JP KG PC (6 December 1608 – 3 January 1670) was an English soldier, who fought on both sides during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A prominent military figure under the Commonwealth, his support was cruc ...
, accompanying Rupert, predicted that De Ruyter would give two broadsides and run, but the latter put up a furious fight on the Dutch flagship '' De Zeven Provinciën''. He withstood a combined attack by ''Sovereign of the Seas'' and ''Royal Charles'' and forced Rupert to leave the damaged ''Royal Charles'' for ''Royal James''. The Dutch centre's resistance enabled the seaworthy remnants of the van to make an escape to the south.
Lieutenant-Admiral Cornelis Tromp
Cornelis Maartenszoon Tromp, ''Count of Sølvesborg'' (3 September 1629 – 29 May 1691) was a Dutch naval officer who served as lieutenant-admiral general in the Dutch Navy, and briefly as a general admiral in the Royal Danish Navy. Trom ...
, commanding the Dutch rear, now brought his vessels to De Ruyter's rescue. Tromp ordered his vessels to the west crossing the line of the English rear under the command of Jeremiah Smith. The English rear was now cut off from the centre, and Tromp's squadron began a dogged attack that forced Smith's ships to flee to the west. The pursuit of the English rear lasted well into the night, with Tromp ultimately destroying with a fireship
A fire ship or fireship, used in the days of wooden rowed or sailing ships, was a ship filled with combustibles, or gunpowder deliberately set on fire and steered (or, when possible, allowed to drift) into an enemy fleet, in order to destroy sh ...
. After Tromp thrice shot the entire crew from its rigging, Smith's flagship caught fire and had to be towed home. The vice commander of the English rear was Edward Spragge
Sir Edward Spragge (name also written as Spragg or Sprague) (circa 1620 – 21 August 1673) was an Irish-born English admiral of the Royal Navy. He was a fiery, brilliantly accomplished seaman who fought in many great actions after the restoratio ...
, who felt so humiliated by the course of events that he became a personal enemy of Tromp. He would later be killed pursuing Tromp in the Battle of Texel
The naval Battle of Texel or Battle of Kijkduin took place off the southern coast of island of Texel on 21 August 1673 (11 August O.S.) between the Dutch and the combined English and French fleets. It was the last major battle of the Third ...
.
Second day
On the morning of 26 July, Tromp broke off pursuit, well-pleased with his first real victory as a squadron commander. During the night, a ship had brought him the message that De Ruyter had likewise been victorious, so Tromp was in a euphoric mood. That abruptly changed upon the discovery of the drifting flagship of the dyingTjerk Hiddes de Vries
Tjerk Hiddes de Vries (Sexbierum, 6 August 1622 - Flushing, 6 August 1666) was a naval hero and Dutch admiral from the seventeenth century. The French, who could not pronounce his name, called him Kiërkides. His name was also given as ''Tsjerk' ...
. Suddenly he feared that his ship was now the only remnant of the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
fleet and that he was in mortal peril. Behind him, those ships of the English rear still operational had again turned to the east. In front, the other enemy squadrons surely awaited him. On the horizon, only English flags were to be seen. Manoeuvring wildly, Tromp, drinking a lot of gin to restore his nerve, dodged any attempt to trap him and brought his squadron safely home in the port of Flushing
Flushing may refer to:
Places
* Flushing, Cornwall, a village in the United Kingdom
* Flushing, Queens, New York City
** Flushing Bay, a bay off the north shore of Queens
** Flushing Chinatown (法拉盛華埠), a community in Queens
** Flushin ...
on the morning of 26 July. There, to great mutual relief, he discovered the rest of the Dutch fleet.
It took Tromp six hours to gather enough courage to face De Ruyter. It was obvious to him that he should never have allowed himself to get completely separated from the main force. Indeed, De Ruyter, not being his usual charitable self, immediately blamed him for the defeat and ordered Tromp and his subcommanders Isaac Sweers
Isaac Sweers (occasionally Ysaack Sweerts; 1 January 1622 – 22 August 1673) was a 17th-century Dutch vice-admiral with the Admiralty of Amsterdam who fought in the Anglo-Dutch Wars.
was a of the Royal Netherlands Navy
The Royal Net ...
and Willem van der Zaan
Willem van der Zaan (29 June 1621 – 17 March 1669) was a Dutch Admiral. His name is often given in the 17th century spelling Zaen.
Biography
Willem was born in Amsterdam. He joined the Dutch navy at a young age and had risen to the rank of ca ...
from his sight, and told them to never again set foot on ''De Zeven Provinciën''. The commander of the Dutch fleet still had not mentally recovered from the events of the previous day.
 On the morning of 5 August, after a short summer's night, De Ruyter discovered that his position had become hopeless. Lieutenant-Admiral Johan Evertsen had died after losing a leg, De Ruyter's force was now reduced to about forty ships, crowding together and most of these were inoperational, being survivors of the van. Some fifteen good ships had apparently deserted during the night. A strong gale from the east prevented an easy retreat to the continental coast, and to the west the British van and centre (about fifty ships) surrounded him in a half-circle, safely bombarding him from a leeward position.
De Ruyter was desperate. When his second-in-command of the centre, Lieutenant-Admiral
On the morning of 5 August, after a short summer's night, De Ruyter discovered that his position had become hopeless. Lieutenant-Admiral Johan Evertsen had died after losing a leg, De Ruyter's force was now reduced to about forty ships, crowding together and most of these were inoperational, being survivors of the van. Some fifteen good ships had apparently deserted during the night. A strong gale from the east prevented an easy retreat to the continental coast, and to the west the British van and centre (about fifty ships) surrounded him in a half-circle, safely bombarding him from a leeward position.
De Ruyter was desperate. When his second-in-command of the centre, Lieutenant-Admiral Aert Jansse van Nes
Aert Jansse van Nes (1626 – 13 or 14 September 1693) was a 17th-century Dutch naval commander, notable for commanding the second squadron in the raid on the Medway in 1667.
He was born at Rotterdam. Three modern ships of the Royal Nether ...
visited him for a council of war, he exclaimed: "With seven or eight against the mass!" He then sagged, mumbling: "What's wrong with us? I wish I were dead." His close personal friend Van Nes tried to cheer him up, joking: "Me too. But you never die when you want to!" No sooner had both men left the cabin than the table they had been sitting at was smashed by a cannonball.
The English, however, had their own problems. The strong gale prevented them from closing with the Dutch. They tried to use fire ships, but these, too, had trouble reaching the enemy. Only the sloop ''Fan-Fan'', Rupert's personal pleasure yacht, rowed to the Dutch flagship ''De Zeven Provinciën'' to harass it with its two little guns, much to the hilarious laughter of the English crews.
When his ship had again warded off an attack by a fire ship (the ''Land of Promise'') and Tromp still did not show up, for De Ruyter tension became unbearable. He sought death, exposing himself deliberately on the deck. When he failed to be hit, he exclaimed: "Oh, God, how unfortunate I am! Amongst so many thousands of cannonballs, is there not one that would take me?" His son-in-law, Captain of the Marines Johann de Witte, heard him and said: "Father, what desperate words! If you merely want to die, let us then turn, sail in the midst of our enemies and fight ourselves to death!". This brave but foolish proposal brought the Admiral back to his senses, for he discovered that he was not so desperate and answered: "You don't know what you are talking about! If I did that, all would be lost. But if I can bring myself and these ships safely home, we'll finish the job later."
Then the wind, that had brought so much misfortune to the Dutch, saved them by turning to the west. They formed a line of battle and brought their fleet to safety through the Flemish shoals, Vice-Admiral Adriaen Banckert
Adriaen van Trappen Banckert (c.1615 – 22 April 1684) was a Dutch admiral. In English literature he is sometimes known as ''Banckers''. His first name is often rendered in the modern spelling ''Adriaan''. ''Van Trappen'' was the original family ...
of the Zealandic fleet covering the retreat of all damaged ships with the operational vessels, the number of the latter slowly growing as it turned out that only very few ships had actually deserted in the night; most had merely drifted away, and now, one after the other, they rejoined the battle.
Aftermath
The battle was a clear English victory. Dutch casualties were enormous, estimated immediately after the battle of about 5,000 men, compared with 300 English killed; later, more precise information showed that only about 1,200 of them had been killed or seriously wounded. However the twin disasters of theGreat Plague of London
The Great Plague of London, lasting from 1665 to 1666, was the last major epidemic of the bubonic plague to occur in England. It happened within the centuries-long Second Pandemic, a period of intermittent bubonic plague epidemics that origi ...
and the Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through central London from Sunday 2 September to Thursday 6 September 1666, gutting the medieval City of London inside the old Roman city wall, while also extending past th ...
, combined with his financial mismanagement, left Charles II without the funds to continue the war. In fact, he had had only enough reserves for this one last battle.
In fact, the Dutch had lost only two ships: De Ruyter had been successful at saving almost the complete van, only ''Sneek'' and ''Tholen'' struck their flag, and they could quickly repair the damage. The Dutch soon recovered; within a month, they again took sea, but only a minor skirmish resulted. During this later fight, De Ruyter inhaled a burning fuse filament that burnt a fistula
A fistula (plural: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") in anatomy is an abnormal connection between two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow or ...
in his throat; he would recover just in time to inflict a severe blow on the English navy in the Raid on the Medway
The Raid on the Medway, during the Second Anglo-Dutch War in June 1667, was a successful attack conducted by the Dutch navy on English warships laid up in the fleet anchorages off Chatham Dockyard and Gillingham in the county of Kent. At t ...
in 1667, when, at last, he could carry out the plan he was prevented from executing in 1666.
But during the weeks that the Dutch fleet was in repair, Admiral Robert Holmes, aided by the Dutch traitor Laurens van Heemskerck, penetrated the Vlie estuary, burnt a fleet of 150 merchants (Holmes's Bonfire
Holmes's Bonfire was a raid on the Vlie estuary in the Netherlands, executed by the English Fleet during the Second Anglo-Dutch War on 19 and 20 August 1666 New Style (9 and 10 August Old Style). The attack, named after the commander of the ...
) and sacked the town of Ter Schelling (the present West-Terschelling
West-Terschelling ( fry, West-Skylge) is the largest village on Terschelling in the province Friesland, the Netherlands. It had a population of around 2,602 in January 2017.
The skyline of the village is dominated by the Brandaris lighthouse, the ...
) on the Frisian island of Terschelling
Terschelling (; fry, Skylge; Terschelling dialect: ''Schylge'') is a municipality and an island in the northern Netherlands, one of the West Frisian Islands. It is situated between the islands of Vlieland and Ameland.
Wadden Islanders are k ...
. ''Fan-Fan'' was again present.
In the Republic, the defeat also had a far-reaching political effect. Tromp was the champion of the Orangist party; now that he was accused of severe negligence, the country split over this issue. To defend himself, Tromp let his brother-in-law, Johan Kievit, publish an account of his conduct. Shortly afterward, Kievit was discovered to have planned a coup, secretly negotiating a peace treaty with the English king. He fled to England and was condemned to death in absentia; Tromp's family was fined and he himself forbidden to serve in the fleet. In November 1669, a supporter of Tromp tried to stab De Ruyter in the entrance hall of his house. Only in 1672 would Tromp have his revenge, when Johan de Witt was murdered; some claim Tromp had had a hand in this. The new ruler, William III of Orange
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from ...
, succeeded, with great difficulty, in reconciling De Ruyter with Tromp in 1673.
References
{{Citation , last = Brandt , first = Gerard , year = 1687 , title = Het Leven en bedryf van den Heere Michiel de Ruiter , edition = 1st , publisher = Uitgeverij van Wijnen, Franeker 1666 in England St James Conflicts in 1666 17th century in Kent