St. Catharines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
St. Catharines is the largest city in Canada's Niagara Region and the sixth largest urban area in the province of
 The Merritt family arrived after this time, among the later Loyalists to relocate following the American Revolution. They were from the Carolinas, New York state and
The Merritt family arrived after this time, among the later Loyalists to relocate following the American Revolution. They were from the Carolinas, New York state and
 Numerous efforts have been made to improve the downtown; the restructuring of manufacturing resulted in a loss of jobs and retail businesses. In the early 21st century, city, university, and private developers undertook several initiatives to revive downtown, related to urban design, clustering activities to attract people to the area as a destination from day through evening events.
In 2006, city council approved converting one-way arteries through the city centre to allow for two-way traffic, to make it easier for people to make their way around the city to explore it. In terms of urban planning and use, two-way traffic improves circulation within the area. The city wanted to improve downtown as a destination, rather than a place to pass through. The council also want to have downtown St. Catharines on the Wine Route, a driving tour of Niagara wineries and an Ontario Wine Council initiative to boost the number of visitors to the region's many wineries. The Wine Route was modified to officially redirect winery goers through the downtown starting in 2012. The first phase of two-way traffic was completed in 2009, with St. Paul and King streets being converted. The cost of the conversion was $3.5 million and was shared with Niagara Region. In 2012, most observers concluded that the change had achieved its goals; it garnered national media attention.
In 2009, $54 million in joint federal, provincial and municipal funding was announced for the construction of a performing arts centre in the city's core, officially opened in September 2015 as the FirstOntario Performing Arts Centre. Complementing the centre, which features concert, dance and film venues, is
Numerous efforts have been made to improve the downtown; the restructuring of manufacturing resulted in a loss of jobs and retail businesses. In the early 21st century, city, university, and private developers undertook several initiatives to revive downtown, related to urban design, clustering activities to attract people to the area as a destination from day through evening events.
In 2006, city council approved converting one-way arteries through the city centre to allow for two-way traffic, to make it easier for people to make their way around the city to explore it. In terms of urban planning and use, two-way traffic improves circulation within the area. The city wanted to improve downtown as a destination, rather than a place to pass through. The council also want to have downtown St. Catharines on the Wine Route, a driving tour of Niagara wineries and an Ontario Wine Council initiative to boost the number of visitors to the region's many wineries. The Wine Route was modified to officially redirect winery goers through the downtown starting in 2012. The first phase of two-way traffic was completed in 2009, with St. Paul and King streets being converted. The cost of the conversion was $3.5 million and was shared with Niagara Region. In 2012, most observers concluded that the change had achieved its goals; it garnered national media attention.
In 2009, $54 million in joint federal, provincial and municipal funding was announced for the construction of a performing arts centre in the city's core, officially opened in September 2015 as the FirstOntario Performing Arts Centre. Complementing the centre, which features concert, dance and film venues, is
 Tourism was considered to be an influential factor in
Tourism was considered to be an influential factor in
Time for a poultry-pitching party"
The St. Catharines Standard. Retrieved 27 December 2009. Chicken Chucking consists of pitching or sliding frozen chickens along the ice-covered Martindale Pond and is hosted by the
 * Burgoyne Bridge – a bridge in downtown St. Catharines
*
* Burgoyne Bridge – a bridge in downtown St. Catharines
*
 The city's trail system offers over 90 kilometres (55 mi) of accessible pathways that are suitable for walking, jogging, cycling, hiking and cross-country skiing.
*
The city's trail system offers over 90 kilometres (55 mi) of accessible pathways that are suitable for walking, jogging, cycling, hiking and cross-country skiing.
*
 Martindale Pond in St. Catharines'
Martindale Pond in St. Catharines'
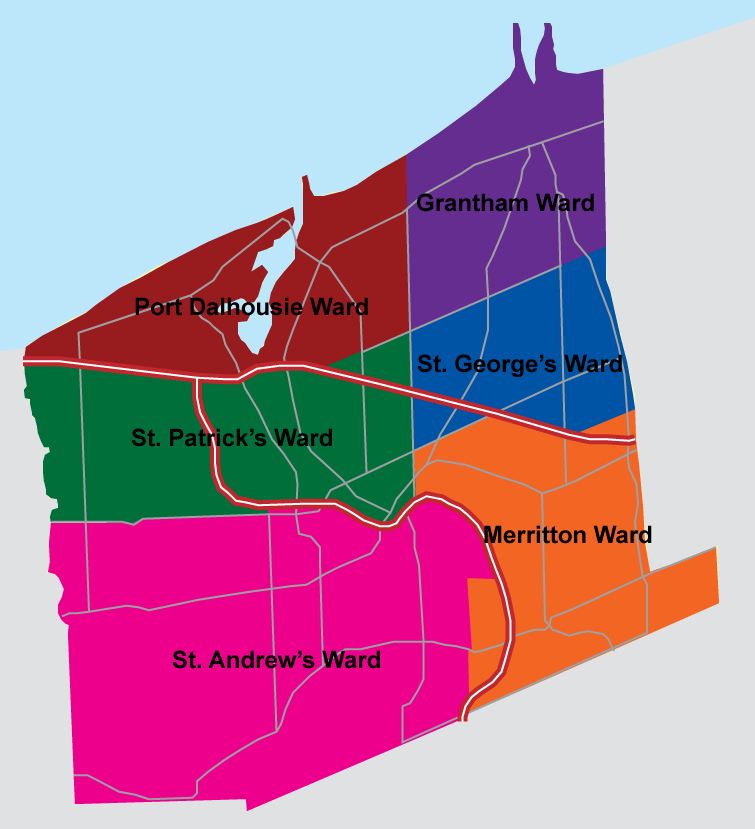 St. Catharines is governed by a mayor and city council of twelve city councillors, with two councillors representing each of the six municipal
St. Catharines is governed by a mayor and city council of twelve city councillors, with two councillors representing each of the six municipal
 The most defining transportation icon of St. Catharines is the Welland Canal, a
The most defining transportation icon of St. Catharines is the Welland Canal, a
Niagara Artists Centre
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Catharines St. Catharines, Cities in Ontario Lower-tier municipalities in Ontario Populated places on Lake Ontario in Canada Populated places on the Underground Railroad
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
. As of 2016, it has an area of , 136,803 residents, and a metropolitan population of 406,074. It lies in Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
, south of Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
across Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
, and is inland from the international boundary with the United States along the Niagara River
The Niagara River () is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada (on the west) and the state of New York in the United States (on the east). There are diffe ...
. It is the northern entrance of the Welland Canal
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines ...
. Residents of St. Catharines are known as ''St. Catharinites''. St. Catharines carries the official nickname "The Garden City" due to its 1,000 acres (4 km2) of parks, gardens, and trails.
St. Catharines is between the Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area
The Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area (GTHA) is a contiguous urban region that is composed of some of the largest cities and metropolitan areas by population in the Canadian province of Ontario. The GTHA consists of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) ...
(GTHA) and the Canada–U.S. border at Fort Erie
Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York, and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
Fort Erie is one of Ni ...
. Manufacturing is the city's dominant industry, as noted by the heraldic motto, "Industry and Liberality". General Motors of Canada, Ltd., the Canadian subsidiary of General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
, was the city's largest employer, a distinction now held by the District School Board of Niagara
The District School Board of Niagara (DSBN, known as English-language Public District School Board No. 22 prior to 1999) is a school board in the public school system of Ontario, Canada, in the Regional Municipality of Niagara. Its head office ...
. THK Rhythm Automotive, formerly TRW, operates a plant in the city, although in recent years, employment there has shifted from heavy industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); o ...
and manufacturing to services.
St. Catharines lies on one of the main telecommunications backbones between Canada and the United States, and as a result a number of call centres operate in the city. It is designated an Urban Growth Centre by the Growth Plan for the Greater Golden Horseshoe The Growth Plan for the Greater Golden Horseshoe, 2006 (the Plan) is a regional growth management policy for the Greater Golden Horseshoe (GGH) area of southern Ontario, Canada. Introduced under the Places to Grow Act in 2005, the Plan was approved ...
, intended to achieve a minimum density target of 150 jobs and residents combined per hectare by 2032 or earlier.
History
The city was first settled byLoyalists
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ...
in the 1780s. The Crown granted land in compensation for services and for losses in the United States. Early histories credit loyalists Serjeant Jacob Dittrick and Private John Hainer as among the first settlers to come to the area in 1790. They took their Crown Patents where Dick's Creek and 12 Mile Creek merge, now the city centre of St. Catharines. Historians have speculated that Dick's Creek was named after Richard Pierpoint
Richard Pierpoint (Bundu – Canada ), also known as Black Dick, Captain Dick, Captain Pierpoint, Pawpine, and Parepoint was a British soldier of Senegalese descent. Brought to America as a slave, he was granted freedom to fight on the side of t ...
, a Black Loyalist
Black Loyalists were people of African descent who sided with the Loyalists during the American Revolutionary War. In particular, the term refers to men who escaped enslavement by Patriot masters and served on the Loyalist side because of the C ...
and former American slave, due to an oral history account and events that had taken place around that time that would be consistent with Pierpoint being the source of the name. Secondary to water routes, indigenous trails provided transportation networks, which resulted in the nearby radial road patterns. The surrounding land was surveyed and Townships created between 1787 and 1789.
After the Butler's Rangers
Butler's Rangers (1777–1784) was a Loyalist provincial military unit of the American Revolutionary War, raised by American loyalist John Butler. Most members of the regiment were Loyalists from upstate New York and northeastern Pennsylvania. Th ...
disbanded in 1784 and settled the area, Duncan Murray as a former Quartermaster in the 84th Regiment of Foot (Royal Highland Emigrants)
The 84th Regiment of Foot (Royal Highland Emigrants) was a British regiment in the American Revolutionary War that was raised to defend present day Ontario, Quebec and Atlantic Canada from the constant land and sea attacks by American Revolutiona ...
was appointed by the Crown to distribute free Government supplies (victuals) for 2 years to the resettled Loyalists. He did this from his mill, built on the 12 Mile Creek in Power Glen. After his death in 1786, his holdings were forfeited to merchant Robert Hamilton of Queenston. Hamilton tried to operate for profit the already well-established Murray's Distribution Centre and Mill under the management of his cousin. Among other ventures, Hamilton became land wealthy, expropriating lands from subsistence Loyalist settlers who were incapable of settling their debts. Murray's distribution centre, later Hamilton's warehouse, and its location have long been a mystery. Hamilton's major profits were derived from transhipping supplies for the military and civic establishments from his Queenston
Queenston is a compact rural community and unincorporated place north of Niagara Falls in the Town of Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada. It is bordered by Highway 405 to the south and the Niagara River to the east; its location at the eponym ...
enterprise, not from charitably supplying the subsistence Loyalist settlers. Hamilton lacked interest in social development and sold his business to Jesse Thompson before the turn of the 19th century.
 The Merritt family arrived after this time, among the later Loyalists to relocate following the American Revolution. They were from the Carolinas, New York state and
The Merritt family arrived after this time, among the later Loyalists to relocate following the American Revolution. They were from the Carolinas, New York state and New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
. In 1796, Thomas Merritt arrived to build on his relationship with his former Commander and Queen's Ranger, John Graves Simcoe
John Graves Simcoe (25 February 1752 – 26 October 1806) was a British Army general and the first lieutenant governor of Upper Canada from 1791 until 1796 in southern Ontario and the watersheds of Georgian Bay and Lake Superior. He founded Yor ...
, now the Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada
The following is a list of lieutenant governors of Ontario and the lieutenant governors of the former colony of Upper Canada. The office of Lieutenant Governor of Ontario was created in 1867, when the Province of Ontario was created upon Confed ...
. The first Welland Canal was constructed from 1824 to 1833. William Hamilton Merritt
William Hamilton Merritt (July 3, 1793July 5, 1862) was a businessman and politician in the Niagara Peninsula of Upper Canada in the early 19th century. Although he was born in the United States, his family was Loyalist and eventually settled ...
worked to promote the ambitious venture, both by raising funds and by enlisting government support. The canal established St. Catharines as the hub of commerce and industry for the Niagara Peninsula. Merritt played a role in making St. Catharines a centre of abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
activity. In 1855, the British Methodist Episcopal Church, Salem Chapel
The British Methodist Episcopal (BME) Church, Salem Chapel was founded in 1820 Church pamphlet by African-American freedom seekers in Saint Catharines, Ontario, St. Catharines, Ontario. It is located at 92 Geneva St., in the heart of Old St. Catha ...
was established at the corner of Geneva and North streets, on land granted to the congregation by Merritt in the early 1840s. The area became known to refugee slaves from the United States as a place of "refuge and rest"; it was a destination, one of the final stops in Canada on the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
for refugee African-American slaves. During this time, abolitionist Harriet Tubman
Harriet Tubman (born Araminta Ross, March 10, 1913) was an American abolitionist and social activist. Born into slavery, Tubman escaped and subsequently made some 13 missions to rescue approximately 70 slaves, including family and friends, u ...
lived in St. Catharines. By the mid-1850s, the town's population was about six thousand, 800 of whom were of African descent. St. Catharines remains an important place in Black Canadian
Black Canadians (also known as Caribbean-Canadians or Afro-Canadians) are people of full or partial sub-Saharan African descent who are citizens or permanent residents of Canada. The majority of Black Canadians are of Caribbean origin, though ...
history.
At an unknown early date, an inn was built by Thomas Adams on the east side of what is now Ontario Street. It became a community meeting place, election centre, stagecoach stop, and mail delivery deposit. This was preceded by the church and a log school house completed before 1797, all on the east bank of the 12 Mile Creek at the extreme west end of what was known at that time as Main Street. This was an extension of the old Iroquois Trail
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
and was renamed St. Paul Street by the settlers and descendant by the mid-19th century. Several mills, salt works, numerous retail outlets, a ship building yard, distillery and various other businesses were developed next.
Incorporated as a village in 1845, St. Catharines had a population of about 3500 in 1846. The primary industry was flour milling. Other industry included ship repairs, four grist mills, a brewery, three distilleries, a tannery, a foundry, a machine and pump factory. There were a variety of tradesmen, three bank agencies, and eight taverns. Stage coaches offered service to other towns and villages. There were already six churches or chapels, a post office that received mail daily, a grammar school and a weekly newspaper.
St. Catharines was incorporated as a city in 1876. The city expanded when it annexed Grantham Township
Grantham Township is a former incorporated and now geographic township on the Niagara Peninsula in Upper Canada, later Ontario.
In 1961, part of it was amalgamated into the city of St. Catharines. In 1970, the remaining portion was amalgamated i ...
, Merritton
Merritton is both a distinct community within and a council ward of St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It was named after William Hamilton Merritt, a prominent local entrepreneur and founder of the Welland Canal Company. Until 1858, Merritton was n ...
, and Port Dalhousie
Port Dalhousie is a community in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. Known for its waterfront appeal, it is home to the Royal Canadian Henley Regatta and is historically significant as the terminus for the first three (19th century) routes of the ...
. There was some westward expansion, which was divided between St. Catharines and Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincol ...
.
Origin of the name
Before it was called St. Catharines, the settlement near Twelve Mile Creek was known by various names, including Shipman's Corners and The Twelve. The name St. Catharines was first recorded in 1796 (as St. Catherines) and became a common name for the settlement by 1809—though it would often be spelled with an -er, or with an apostrophe before the s. The name and the spelling was standardized as St. Catharines when the town incorporated in 1845. It is not clear which Catherine the city is named after. Common theories includeSaint Catherine of Alexandria
Catherine of Alexandria (also spelled Katherine); grc-gre, ἡ Ἁγία Αἰκατερίνη ἡ Μεγαλομάρτυς ; ar, سانت كاترين; la, Catharina Alexandrina). is, according to tradition, a Christian saint and virgin, wh ...
, Catherine Butler (wife of Colonel John Butler), or Catherine Askin Hamilton (wife of Robert Hamilton). Catharine Rodman Prendergast Merritt, wife of William Hamilton Merritt, may be the source of the -ar spelling. An alternate theory to explain the spelling was that Catharine with an -ar was the typical spelling of the name for Palatine German settlers in the region.
Geography
Climate
St. Catharines' climate ishumid continental
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
borderline ''Dfa''/''Dfb''). It has a unique micro-climate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squ ...
because of the moderating influence of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
/Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also ha ...
and the sheltering effect of the Niagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that runs predominantly east–west from New York through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and into Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff ove ...
to the south. This climate allows wineries to flourish. As a result, the city records numerous frost-free days and frequent thaws in the winter, although it sometimes receives heavy lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up throug ...
during certain wind conditions, and micro-cooling lakeside on some spring afternoons. The summer season is predominantly warm, sometimes hot and humid, with an average high temperature of in July. Summer thunderstorms are commonplace but generally less prevalent and less severe than further west in southern Ontario due to the diminishing effect of the surrounding lakes.
The highest temperature ever recorded in St. Catharines was on 10 July 1936. The coldest temperature ever recorded was on 18 February 1979.
The complex and extensive glacial history of the Niagara Peninsula
The Niagara Peninsula is an area of land lying between the southwestern shore of Lake Ontario and the northeastern shore of Lake Erie, in Ontario, Canada. Technically an isthmus rather than a peninsula, it stretches from the Niagara River in t ...
has resulted in similarly complex soil stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers ( strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithost ...
in the area occupied by the city today. St. Catharines was once at the base of a glacial lake known as Glacial Lake Iroquois
Glacial Lake Iroquois was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago.
The lake was essentially an enlargement of the present Lake Ontario that formed because the St. Lawrence River down ...
, which deposited thick layers of clay between the Escarpment and Lake Ontario. As a result of these factors, the city's soil is particularly conducive to fruit growing and is capable of producing grapes that are used to make award-winning wines. Three wineries operate in the city's west end: Henry of Pelham Winery
Henry of Pelham Family Estate Winery is a family owned, Ontario winery that released their first vintage in 1988. Located where the valley of the Short Hills Bench meets the weathered mountain of the Niagara Escarpment.
History
The namesake of ...
, Hernder Estates and Harvest Estates.
Since the opening of the first Welland Canal in 1829, the city has had four different canal systems, whether modified or newly constructed, carved into its geographical landscape. The fourth and present-day canal forms the majority of the city's eastern boundary. The first three of the city's canals have largely been buried, portions of it beside the present-day Highway 406 and near Lake Street and the QEW highway. Other remnants of the original canals can still be seen in various locations throughout the city; many remains are hidden within forested areas designated as city parks. Some residents in the region are interested in restoring the original routing of the Welland Canal through the city. They intend that the restored waterway and locks would be open to a new tourist attraction within the city.
St. Catharines was affected by the Blizzard of 1977
The blizzard of 1977 hit Western New York and Southern Ontario from January 28 to February 1. Daily peak wind gusts ranging from were recorded by the National Weather Service in Buffalo, with snowfall as high as recorded in areas, and the hig ...
, an event which resulted in more than 150 cm of snow, wind that travelled the speed of 110km/h, and a wind chill of approximately -45 degrees Celsius. The Queen Elizabeth Way
The Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) is a 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario linking Toronto with the Niagara Peninsula and Buffalo, New York. The freeway begins at the Peace Bridge in Fort Erie and travels around the western ...
(QEW) was closed and a state of emergency was declared. The Canadian Armed Forces
}
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; french: Forces armées canadiennes, ''FAC'') are the unified military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air elements referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force.
...
was involved in rescue efforts.
Communities
St. Catharines' development history has resulted in a number of unique and distinct communities within the city. The historical area of St. Catharines consisted of nothing more than what is now the downtown core, with the remaining land being part of Louth Township on the west andGrantham Township
Grantham Township is a former incorporated and now geographic township on the Niagara Peninsula in Upper Canada, later Ontario.
In 1961, part of it was amalgamated into the city of St. Catharines. In 1970, the remaining portion was amalgamated i ...
on the east. St. Catharines continued to steadily grow through the late 19th and early 20th centuries, eventually annexing land to the southwest that would become Western Hill and Old Glenridge, and to the east and north that would collectively become the central part of St. Catharines. In addition to the growth of St. Catharines, the town of Merritton
Merritton is both a distinct community within and a council ward of St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It was named after William Hamilton Merritt, a prominent local entrepreneur and founder of the Welland Canal Company. Until 1858, Merritton was n ...
and the town of Port Dalhousie
Port Dalhousie is a community in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. Known for its waterfront appeal, it is home to the Royal Canadian Henley Regatta and is historically significant as the terminus for the first three (19th century) routes of the ...
existed as separate municipalities to the south and north of the city, each slowly growing their own residential base.
Along with the rest of Ontario, St. Catharines experienced explosive growth after World War II. St. Catharines continued to annex Grantham Township as development continued, including the large swaths of land to the north known now as " The North End". St. Catharines would also absorb Merritton and Port Dalhousie in 1961, making them part of the city. During this time, St. Catharines nearly tripled in population.
With the formation of the Regional Municipality of Niagara
The Regional Municipality of Niagara, also colloquially known as the Niagara Region or Region of Niagara, is a regional municipality comprising twelve municipalities of Southern Ontario, Canada. The regional seat is in Thorold. It is the souther ...
in 1970, the portion of Louth Township east of Fifteen Mile Creek was transferred to the City of St. Catharines. This included the eastern portion of the Hamlet of Rockway, as well as the Hamlet of Power Glen. The few remaining portions of Grantham Township in the Northeast corner of the area, including Port Weller, were also transferred to the city. With the new Louth Township lands belonging to the city, St. Catharines would begin two developments in the west end — Martindale Road in 1983, and Vansickle Road in 1987. These developments are nearing completion. There was also a push to continue further expansion to the west in the late 1990s, but this has since been halted by Ontario Greenbelt legislation.
The following distinct communities exist within St. Catharines:
Downtown
 Numerous efforts have been made to improve the downtown; the restructuring of manufacturing resulted in a loss of jobs and retail businesses. In the early 21st century, city, university, and private developers undertook several initiatives to revive downtown, related to urban design, clustering activities to attract people to the area as a destination from day through evening events.
In 2006, city council approved converting one-way arteries through the city centre to allow for two-way traffic, to make it easier for people to make their way around the city to explore it. In terms of urban planning and use, two-way traffic improves circulation within the area. The city wanted to improve downtown as a destination, rather than a place to pass through. The council also want to have downtown St. Catharines on the Wine Route, a driving tour of Niagara wineries and an Ontario Wine Council initiative to boost the number of visitors to the region's many wineries. The Wine Route was modified to officially redirect winery goers through the downtown starting in 2012. The first phase of two-way traffic was completed in 2009, with St. Paul and King streets being converted. The cost of the conversion was $3.5 million and was shared with Niagara Region. In 2012, most observers concluded that the change had achieved its goals; it garnered national media attention.
In 2009, $54 million in joint federal, provincial and municipal funding was announced for the construction of a performing arts centre in the city's core, officially opened in September 2015 as the FirstOntario Performing Arts Centre. Complementing the centre, which features concert, dance and film venues, is
Numerous efforts have been made to improve the downtown; the restructuring of manufacturing resulted in a loss of jobs and retail businesses. In the early 21st century, city, university, and private developers undertook several initiatives to revive downtown, related to urban design, clustering activities to attract people to the area as a destination from day through evening events.
In 2006, city council approved converting one-way arteries through the city centre to allow for two-way traffic, to make it easier for people to make their way around the city to explore it. In terms of urban planning and use, two-way traffic improves circulation within the area. The city wanted to improve downtown as a destination, rather than a place to pass through. The council also want to have downtown St. Catharines on the Wine Route, a driving tour of Niagara wineries and an Ontario Wine Council initiative to boost the number of visitors to the region's many wineries. The Wine Route was modified to officially redirect winery goers through the downtown starting in 2012. The first phase of two-way traffic was completed in 2009, with St. Paul and King streets being converted. The cost of the conversion was $3.5 million and was shared with Niagara Region. In 2012, most observers concluded that the change had achieved its goals; it garnered national media attention.
In 2009, $54 million in joint federal, provincial and municipal funding was announced for the construction of a performing arts centre in the city's core, officially opened in September 2015 as the FirstOntario Performing Arts Centre. Complementing the centre, which features concert, dance and film venues, is Brock University
Brock University is a public research university in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It is the only university in Canada in a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, at the centre of Canada's Niagara Peninsula on the Niagara Escarpment. The university bears t ...
's Marilyn I. Walker School of Fine and Performing Arts. The university renovated the former Canada Hair Cloth Building to use for the school. This former industrial building is behind St. Paul Street and next to the municipal performing arts centre.
In late 2011, city council approved moving forward with the construction of a new spectator facility to replace the crumbling Garden City Arena Complex
The Garden City Arena Complex (formerly the "Gatorade Garden City Complex") is a sports complex in St. Catharines, Ontario. It was the main arena facility in that city from its construction in 1938 until the opening of the Meridian Centre in 2 ...
, built in 1938. Council voted to build a U-shaped facility, which will be home to the Niagara IceDogs, an Ontario Hockey League team, and be able to host other events, such as concerts. It would have room for 4,500 to 5,300 spectators. The goal is to keep the cost of the facility at or below $50 million and to build it on a swath of land known locally as the lower-level parking lot, behind St. Paul Street and abutting Highway 406. Council's commitment to build the facility resulted in IceDogs' owner Bill Burke promising to sign a 20-year lease with the city after he threatened to move his team if the city chose not to build a new arena.
The city has made other infrastructure improvements to the downtown. In January 2012, a new edition of the Carlisle Street Parking Garage opened. It was built to Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design standards and was certified for its environmentally friendly features, including a green roof
A green roof or living roof is a roof of a building that is partially or completely covered with vegetation and a growing medium, planted over a waterproofing membrane. It may also include additional layers such as a root barrier and draina ...
, preferred carpool and hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.
The basic princi ...
parking, greywater collection, permeable interlocking brick pavement, and several bike racks for users. A mixed-use development, the structure was planned for retail space at street level on Carlisle Street, in order to promote activity and business on the street. The project cost $27.9 million, with funding split three ways between the federal, provincial and municipal governments. Starting in 2019, certain streets located in downtown St. Catharines have been closed during weekends to vehicle traffic. These pedestrian zone
Pedestrian zones (also known as auto-free zones and car-free zones, as pedestrian precincts in British English, and as pedestrian malls in the United States and Australia) are areas of a city or town reserved for pedestrian-only use and in whi ...
s have expanded over time. $214,500 was allocated in the cities budget in 2021 for these road closures.
Demographics
In the2021 Census of Population
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, which is sli ...
conducted by Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and cultu ...
, St. Catharines had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
At the census metropolitan area
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of stat ...
(CMA) level in the 2021 census, the St. Catharines - Niagara CMA had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
As of the 2021 Census, 16.5% of residents were visible minorities, 3.5% had Indigenous ancestry, and the remaining 80.0% were White. The largest visible minority groups were Black (4.1%), South Asian (2.5%), Latin American (2.3%), Chinese (1.6%), Filipino (1.5%) and Arab (1.3%)
In 2021, 58.3% of residents were Christians, down from 71.8% in 2011. 25.8% of residents were Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, 17.8% were Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
, 9.4% were Christians of unspecified denomination, 1.3% were Christian Orthodox, and 3.9 were other Christian/Christian related traditions. 35.9% of the population had were irreligious or secular, up from 24.5% in 2011. All other religions/spiritual traditions made up 5.8% of the population. The largest non-Christian religions were Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
(3.4%), Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
(0.6%), and Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
(0.6%).
Since 1998, St. Catharines has had one of the highest obesity rates of any centre in Canada. A 2001 analysis by Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and cultu ...
showed that 57.3 percent of its residents were overweight. This has caused some elements of the media, including CTV
CTV may refer to:
Television
* Connected TV, or Smart TV, a TV set with integrated internet
North America and South America
* CTV Television Network, a Canadian television network owned by Bell Media
** CTV 2, a secondary Canadian televisio ...
, the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (french: Société Radio-Canada), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is a Canadian public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a federal Crown corporation that receives funding from the governmen ...
and ''The Globe and Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of approximately 2 million in 2015, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on weekdays and Saturdays, although it ...
'' to dub St. Catharines as Canada's "fattest" city. In 2008, new statistics were released that show that the percentage obese or obese/overweight residents of Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
(74.3%), Kingston (70.1%), and St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador
St. John's is the capital and largest city of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, located on the eastern tip of the Avalon Peninsula on the island of Newfoundland.
The city spans and is the easternmost city in North America ...
(70%) is now higher than St. Catharines-Niagara (69.3%), though the obesity rate in St. Catharines was higher in 2008 than in 1998.
23% of children in St. Catharines were estimated to be living in poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse
as of 2015, which was above Canada's average rate of child poverty
Child poverty refers to the state of children living in poverty and applies to children from poor families and orphans being raised with limited or no state resources. UNICEF estimates that 356 million children live in extreme poverty. It's es ...
. In 2022, the municipality itself as an employer became the largest in Ontario to offer a living wage
A living wage is defined as the minimum income necessary for a worker to meet their basic needs. This is not the same as a subsistence wage, which refers to a biological minimum, or a solidarity wage, which refers to a minimum wage tracking lab ...
, an action praised by the Niagara Poverty Reduction Network.
Economy
 Tourism was considered to be an influential factor in
Tourism was considered to be an influential factor in Conference Board of Canada
The Conference Board of Canada is a Canadian not-for-profit think tank dedicated to researching and analyzing economic trends, as well as organizational performance and public policy issues.
Describing itself as "objective" and "non-partisan", th ...
's projected GDP growth for St. Catharines. The city is approximately 20 km from the U.S.–Canada border. Its economy is affected by the millions of tonnes of cargo shipped through the Welland Canal, with the locks for the canal being considered a tourist attraction by itself. St. Catharines was the location of a transmission plant for General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
. The 20 hectare property where the factory once operated is now classified as a contaminated brownfield
In urban planning, brownfield land is any previously developed land that is not currently in use. It may be potentially contaminated, but this is not required for the area to be considered brownfield. The term is also used to describe land pre ...
.
Arts and culture
Theatre
St. Catharines is also home to a variety of theatre companies. These companies include Garden City Productions (formerly the Operatic Society of Grantham United Church 1956–1962), Carousel Players (in the Old Courthouse), Mirror Theatre, Essential Collectives Theatre, and the Empty Box Theatre Company. In 2015, the FirstOntario Performing Arts Centre opened. In 2016, the ''Film House'' launched within the space, featuring cinema screenings with themed or genre-specific nights.Events
The Grape and Wine Festival Parade is held annually each September. More than 100,000 people were anticipated for the 2022 event. The International Chicken Chucking Championships takes place every January in the St. Catharines neighbourhood of Port Dalhousie and attracts hundreds of participants and observers.Walter, Karena (17 January 2009)Time for a poultry-pitching party"
The St. Catharines Standard. Retrieved 27 December 2009. Chicken Chucking consists of pitching or sliding frozen chickens along the ice-covered Martindale Pond and is hosted by the
Kilt and Clover
The Kilt and Clover is a restaurant and bar located at 17 Lock Street in Port Dalhousie, Ontario, a district within the City of St. Catharines, Ontario on the shores of Lake Ontario. It is known for its annual frozen chicken chucking competition ...
. Animal rights groups such as Niagara Action for Animals have protested the event. Proceeds from the event are donated to Community Care, a local food bank.
St. Catharines was one of the cities that hosted the 2022 Canada Summer Games
The 2022 Canada Summer Games or informally as Niagara 2022 is the summer season portion of the Canada Games and a multi-sport event for amateur athletes.
The games took place from August 6–21, 2022 in the Niagara Region of Ontario,, Canada, wi ...
. More than 5,000 athletes and coaches arrived for the games, which took place from August 6 to August 21, 2022. The opening ceremony was held at the Meridian Centre
The Meridian Centre is a 5,300 seat arena in downtown St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada, located at 1 David S. Howes Way. The arena is the home of the Niagara IceDogs of the Ontario Hockey League and the Niagara River Lions of the Canadian Elite Ba ...
.
Attractions
 * Burgoyne Bridge – a bridge in downtown St. Catharines
*
* Burgoyne Bridge – a bridge in downtown St. Catharines
* Garden City Skyway
The Garden City Skyway is a major high-level bridge located in St. Catharines and Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada, that allows the Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) to cross the Welland Canal without the interruption of a lift bridge. Six lanes of ...
– QEW crossing over the Welland Canal
* Lakeside Park Carousel
The Lakeside Park Carousel is a historic carousel located in Port Dalhousie, Ontario, Canada, a community in the city of St. Catharines.
History
The Lakeside Park Carousel was carved by Charles I.D. Looff between 1898 and 1905 in Brooklyn, New Yo ...
– historic carousel located in Port Dahousie
* Merritton Tunnel
* Morningstar Mill
Morningstar Mill is a heritage site located in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. The site includes the Morningstar Mill, a sawmill, the home of the Morningstar family, a barn used for blacksmith demonstrations, and the Decew Falls gorge along the ...
– heritage site and mill
* Pen Centre
The Pen Centre (originally Niagara Peninsula Shopping Centre) is the largest shopping mall in the Niagara Region, located in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada.
History
The Pen Centre was built in 1957 as the Niagara Peninsula Centre, a single ...
– a regional shopping centre
* The St. Catharines Armoury
The St. Catharines Armoury is a Recognized Federal Heritage Building in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. The building is currently used by the Canadian Armed Forces as a drill hall. It was built in 1905 to replace a previous drill-shed that was de ...
is a recognized Federal Heritage building, #1991 on the Register of the Government of Canada Heritage Buildings.
* The St. Catharines Museum is at Lock 3 on the Welland Canal, off the Welland Canals Parkway. An elevated viewing platform at the museum allows visitors to get a close-up look at international ships crossing this section of the St. Lawrence Seaway. Along with its exhibits dedicated to the city's history and the canals, the museum is home to the Ontario Lacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensiv ...
Hall of Fame and Museum.
Parks
*Montebello Park
Montebello Park is a public park in downtown St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada, designed by Frederick Law Olmsted. It features a commemorative rose garden with over 1,300 bushes in 25 varieties is the city's largest rose collection and an ornamenta ...
: Designed by Frederick Law Olmsted
Frederick Law Olmsted (April 26, 1822August 28, 1903) was an American landscape architect, journalist, social critic, and public administrator. He is considered to be the father of landscape architecture in the USA. Olmsted was famous for co- ...
in 1887, who was renowned for designing and developing New York City's Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban park in the United States, with an estimated ...
in 1853. A commemorative rose garden, with over 1,300 bushes in 25 varieties, is the city's largest rose collection; it features an ornamental fountain. The focal point of the park is a band shell and pavilion built in 1888. The park is designated under the ''Ontario Heritage Act
The ''Ontario Heritage Act'', (the ''Act'') first enacted on March 5, 1975, allows municipalities and the provincial government to designate individual properties and districts in the Province of Ontario, Canada, as being of cultural heritage ...
''.
* Lakeside Park: Located in the North end, along the shores of Lake Ontario in the community known as Port Dalhousie. Hosts yearly fireworks displays on 1 July (Canada Day). Has picnic areas, a pavilion, snack bar, change rooms, washrooms, playground equipment, boardwalk, the Lakeside Park Carousel, and public docks for visiting boaters. The beach offers magnificent sunset views over Lake Ontario. Lakeside Park inspired a song
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetiti ...
by the rock band Rush which describes the park itself and drummer/lyricist Neil Peart
Neil Ellwood Peart OC (; September 12, 1952 – January 7, 2020) was a Canadian-American musician, best known as the drummer and primary lyricist of the rock band Rush. Peart earned numerous awards for his musical performances, including an ...
's memories there.
* Burgoyne Woods: A 50-hectare (0.5 km2) wooded area and recreational park near the Downtown core. It also contains a dog park and is the host of annual cross country races within the District School Board of Niagara
The District School Board of Niagara (DSBN, known as English-language Public District School Board No. 22 prior to 1999) is a school board in the public school system of Ontario, Canada, in the Regional Municipality of Niagara. Its head office ...
(DSBN) and the Niagara Catholic District School Board
The Niagara Catholic District School Board (Niagara Catholic or NCDSB, previously known as English-language Separate District School Board No. 50 prior to 1999) is the publicly funded Catholic school board in the Regional Municipality of Niagara ...
(NCDSB).
* Happy Rolph's Bird Sanctuary: A 6-hectare (0.06 km2) park on the shores of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
in the community of Port Weller. It is home to hundreds of native and migratory birds and features an exotic collection of flowering rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; from Ancient Greek ''rhódon'' "rose" and ''déndron'' "tree") is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are nati ...
s. An onsite petting farm (containing horses, pigs, sheep, goats and llamas, as well as a donkey named 'Hoti'—'Don Quixote') is operated by the city from Victoria Day
Victoria Day (french: Fête de la Reine, lit=Celebration of the Queen) is a federal Canadian public holiday celebrated on the last Monday preceding May 25. Initially in honour of Queen Victoria's birthday, it has since been celebrated as the off ...
to Thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden ...
weekend. A trail running throughout the park leads to a peaceful waterfront memorial to Canadian victims of the 9/11
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commerci ...
terrorist attacks.
* Ontario Jaycee Gardens: Overlooking the Henley Rowing Course, this is the city's largest horticultural park, with more than 8 hectares (0.08 km2) of meticulously landscaped gardens and flower displays. Among the displays is a memorial site dedicated to Kristen French. The park exists on land that once featured the Third Welland Canal. The former entrance to the canal can still be seen at the north-west end of the park.
* Walker Arboretum: Located along the hillside of Rodman Hall and the Twelve Mile Creek below, the original owner of this estate was Thomas Rodman Merritt
Thomas Rodman Merritt (October 17, 1824 – January 11, 1906) was a Canadian businessman and political figure in Upper Canada, later Ontario, Canada. He represented Lincoln in the House of Commons of Canada as a Liberal member from 1868 t ...
, son of William Hamilton Merritt
William Hamilton Merritt (July 3, 1793July 5, 1862) was a businessman and politician in the Niagara Peninsula of Upper Canada in the early 19th century. Although he was born in the United States, his family was Loyalist and eventually settled ...
. In the late 19th century, an English landscape design
Landscape design is an independent profession and a design and art tradition, practiced by landscape designers, combining nature and culture. In contemporary practice, landscape design bridges the space between landscape architecture and ga ...
er named Samuel Richardson was hired by Merritt to tend the grounds. As a result, the arboretum
An arboretum (plural: arboreta) in a general sense is a botanical collection composed exclusively of trees of a variety of species. Originally mostly created as a section in a larger garden or park for specimens of mostly non-local species, man ...
is an extensive, rambling garden with rare conifers
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All ext ...
which benefit from an exceptional micro-climate. It boasts one of the largest Chinese Empress trees in Canada.
* Woodgale Park: Located along Glendale Avenue between Glenridge Avenue and the Pen Centre. Features wide open spaces, flowing fruit trees, rare birds, a soccer field and tennis courts. Also features a memorial to the original farm building on the north end of the park near Denis Morris Catholic High School
Denis Morris Catholic High School is a Catholic high school located in St. Catharines, Ontario. The school is administered by the Niagara Catholic District School Board.
Denis Morris provides educational programs and services for students with ...
. Locally known as Doug Hill Park, after a nearby resident who coached a number of baseball and tug of war teams in this area.
Trail system
 The city's trail system offers over 90 kilometres (55 mi) of accessible pathways that are suitable for walking, jogging, cycling, hiking and cross-country skiing.
*
The city's trail system offers over 90 kilometres (55 mi) of accessible pathways that are suitable for walking, jogging, cycling, hiking and cross-country skiing.
* Bruce Trail
The Bruce Trail is a hiking trail in southern Ontario, Canada, from the Niagara River to the tip of Tobermory, Ontario. The main trail is more than long and there are over of associated side trails. The trail mostly follows the edge of the Niag ...
: Canada's oldest and longest hiking trail, following the Niagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that runs predominantly east–west from New York through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and into Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff ove ...
(designated as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
World Biosphere Reserve site) from Niagara-on-the-Lake
Niagara-on-the-Lake is a town in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the Niagara Peninsula at the point where the Niagara River meets Lake Ontario, across the river from New York, United States. Niagara-on-the-Lake is in the Niagara Region of O ...
to Tobermory. A 20-kilometre (12 mi) section with associated side trails winds through St. Catharines passing by places such as the Morningstar Mill
Morningstar Mill is a heritage site located in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. The site includes the Morningstar Mill, a sawmill, the home of the Morningstar family, a barn used for blacksmith demonstrations, and the Decew Falls gorge along the ...
.
* Merritt Trail: a segmented 11 km (6.8 mi) trail that passes many of the old sections of the second Welland Canal and remnants of its locks.
* Laura Secord Legacy Trail
Laura Secord Legacy Trail is a 32-kilometer (20 mile) trail as a monument to Laura Secord's journey and legacy. It includes the Laura Secord Commemorative Walk that was established in 2013. Secord embarked on a journey in June 1813 during the War o ...
– a trail that was established to commemorate Laura Secord
Laura Secord ( Ingersoll; 13 September 1775 – 17 October 1868) was a Canadian heroine of the War of 1812. She is known for having walked out of American-occupied territory in 1813 to warn British forces of an impending American atta ...
's 32 km walk to warn of an upcoming American attack during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
.
* Terry Fox
Terrance Stanley Fox (July 28, 1958 June 28, 1981) was a Canadian athlete, humanitarian, and cancer research activist. In 1980, with one leg having been amputated due to cancer, he embarked on an east-to-west cross-Canada run to raise money ...
Trail: a 1.5 km trail that runs along Carlon Street and Geneva Street. Six exercise stations are placed throughout it.
* Waterfront Trail
Stretching over 3600 km (2236 miles) from Prince Township, west of Sault Ste. Marie, to the Quebec border, the Great Lakes Waterfront Trail is a signed route of interconnecting roads and off-road trails joining over 150 communities and First Na ...
: follows the shore of Lake Ontario, connecting communities from Niagara-on-the-Lake to Brockville
Brockville, formerly Elizabethtown, is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada, in the Thousand Islands region. Although it is the seat of the United Counties of Leeds and Grenville, it is politically independent of the county. It is included with Le ...
. The Port Dalhousie
Port Dalhousie is a community in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. Known for its waterfront appeal, it is home to the Royal Canadian Henley Regatta and is historically significant as the terminus for the first three (19th century) routes of the ...
portion of the trail is a major highlight.
* Welland Canals Parkway Trail – The trail in its entirety is 45 km, stretching from St. Catharines to Port Colborne
Port Colborne is a city in Ontario, Canada that is located on Lake Erie, at the southern end of the Welland Canal, in the Niagara Region of Southern Ontario. The original settlement, known as Gravelly Bay, dates from 1832 and was renamed afte ...
.
Sports
Ice hockey
St. Catharines entered into theOntario Hockey Association
The Ontario Hockey Association (OHA) is the governing body for the majority of junior and senior level ice hockey teams in the Province of Ontario. The OHA is sanctioned by the Ontario Hockey Federation along with the Northern Ontario Hockey As ...
Junior 'A' Hockey in 1943 as the St. Catharines Falcons. In 1947, they became the Teepees and were affiliated with the American Hockey League
The American Hockey League (AHL) is a professional ice hockey league based in the United States and Canada that serves as the primary developmental league for the National Hockey League (NHL). Since the 2010–11 season, every team in the lea ...
's Buffalo Bisons
The Buffalo Bisons (known colloquially as the Herd) are a Minor League Baseball team of the International League and the Triple-A affiliate of the Toronto Blue Jays. Located in Buffalo, New York, the team plays their home games at Sahlen F ...
. When the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey sports league, league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranke ...
's (NHL) Chicago Blackhawks
The Chicago Blackhawks (spelled Black Hawks until 1986, and known colloquially as the Hawks) are a professional ice hockey team based in Chicago. The Blackhawks compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Central Divisio ...
made the Bisons their number one farm team, they inherited the Teepees. In the 1960s, the Jr. 'A' team went deeply into debt to the Chicago Black Hawks, but continued as a successful franchise and were named the St. Catharines Black Hawks. The Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
Fincups moved to St. Catharines in 1976 and played here for one year before moving back to Hamilton. The AHL St. Catharines Saints
The St. Catharines Saints was a minor league ice hockey team in St. Catharines, Ontario. It played in the American Hockey League from 1982 to 1986 as the farm team of the Toronto Maple Leafs.
History
The Moncton-based New Brunswick Hawks had bee ...
played in St. Catharines between 1982 and 1986, before being forced to re-locate to Newmarket due to protests from the NHL Buffalo Sabres
The Buffalo Sabres are a professional ice hockey team based in Buffalo, New York. The Sabres compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Atlantic Division in the Eastern Conference. The team was established in 1970, alon ...
. The St. Catharines Saints served as the farm team
In sports, a farm team, farm system, feeder team, feeder club, or nursery club is generally a team or club whose role is to provide experience and training for young players, with an agreement that any successful players can move on to a higher ...
for the Toronto Maple Leafs
The Toronto Maple Leafs (officially the Toronto Maple Leaf Hockey Club and often referred to as the Leafs) are a professional ice hockey team based in Toronto. They compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Atlantic Div ...
, and today are known as the Toronto Marlies
The Toronto Marlies are a professional ice hockey team based in Toronto. They compete in the American Hockey League (AHL) as a member of the North Division of the Eastern Conference. The Marlies is owned by Maple Leafs Sports & Entertainment, a c ...
.
In 2007, the OHL's Mississauga IceDogs relocated to St. Catharines and became the Niagara IceDogs
The Niagara IceDogs are a major junior ice hockey team in the Ontario Hockey League based in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. The franchise was originally known as the Mississauga IceDogs and founded in 1996. The team was relocated to St. Cathar ...
. The IceDogs played out of the Jack Gatecliff Arena
The Garden City Arena Complex (formerly the "Gatorade Garden City Complex") is a sports complex in St. Catharines, Ontario. It was the main arena facility in that city from its construction in 1938 until the opening of the Meridian Centre in 2 ...
, which was renamed the Gatorade Garden City Complex (since renamed Garden City Arena Complex
The Garden City Arena Complex (formerly the "Gatorade Garden City Complex") is a sports complex in St. Catharines, Ontario. It was the main arena facility in that city from its construction in 1938 until the opening of the Meridian Centre in 2 ...
). In 2014, the IceDogs moved to the newly built Meridian Centre
The Meridian Centre is a 5,300 seat arena in downtown St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada, located at 1 David S. Howes Way. The arena is the home of the Niagara IceDogs of the Ontario Hockey League and the Niagara River Lions of the Canadian Elite Ba ...
.
Since starting out the team has won the Emms Trophy in 2010–2011 & 2018–2019. They have also won the Bobby Orr Trophy
The Bobby Orr Trophy is awarded annually to the champion of the Eastern conference playoffs in the Ontario Hockey League. It was first awarded in 1999. The winning team competes for the J. Ross Robertson Cup in the OHL finals versus the Wayne Gret ...
during 2011–2012 season and 2015–2016 season, qualifying for the OHL Finals. They would be beaten both times by the London Knights. The team has had numerous NHL alumni including Alex Pietrangelo
Alexander Pietrangelo (born January 18, 1990) is a Canadian professional ice hockey defenceman and alternate captain for the Vegas Golden Knights of the National Hockey League (NHL). He previously played for the St. Louis Blues for parts of twe ...
, Dougie Hamilton
Douglas Jonathan Hamilton Jr. (born June 17, 1993) is a Canadian professional ice hockey defenceman for the New Jersey Devils of the National Hockey League (NHL). He previously played in the NHL for the Boston Bruins, Calgary Flames, and Ca ...
, Vince Dunn
Vince Dunn (born October 29, 1996) is a Canadian professional ice hockey defenceman currently playing for the Seattle Kraken of the National Hockey League (NHL).
A native of Mississauga, Ontario, Dunn began his minor hockey career with the Ce ...
, Ryan Strome
Ryan Edward Gaston Strome (born July 11, 1993) is a Canadian ice hockey centre for the Anaheim Ducks of the National Hockey League (NHL). He was selected fifth overall in the 2011 NHL Entry Draft by the New York Islanders and began playing with ...
, Akil Thomas
Akil Thomas (born January 2, 2000) is a Canadian-American professional ice hockey centre currently playing for the Ontario Reign in the American Hockey League (AHL) as a prospect to the Los Angeles Kings. Prior to the 2018 NHL Entry Draft, Tho ...
and Mark Visentin
Mark Visentin (born August 7, 1992) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey goaltender. He was selected in the first round, 27th overall, by the Phoenix Coyotes in the 2010 NHL Entry Draft.
Visentin represented Canada at the 2011 World J ...
.
The St. Catharines Falcons play in the Golden Horseshoe Division of the Greater Ontario Junior Hockey League
The Greater Ontario Junior Hockey League (GOJHL) is a Canadian junior ice hockey league based in Southern Ontario, Canada. The league is sanctioned by the Ontario Hockey Association, Ontario Hockey Federation, and Hockey Canada. The league is ...
. The team has played since 1968 and plays all home games out of the Jack Gatecliff Arena. The team were runners up for the Sutherland Cup in 1979, 1990, 1994, 1997, 2000 and 2014, but won the cup in 2012.
Basketball
In 2015, theNational Basketball League of Canada
The National Basketball League of Canada (NBL Canada; french: Ligue nationale de basketball du Canada) is a Canadian professional men's minor league basketball organization. The NBL Canada was founded in 2011, when three existing Premier Basketb ...
announced that Niagara had been awarded a new franchise to play in the Meridian Centre. The team, named the Niagara River Lions
The Niagara River Lions are a Canadian professional basketball team based in St. Catharines, Ontario, that competes in the Canadian Elite Basketball League. From 2015 to 2018, they were members of the National Basketball League of Canada. The Riv ...
, began play in 2015
File:2015 Events Collage new.png, From top left, clockwise: Civil service in remembrance of November 2015 Paris attacks; Germanwings Flight 9525 was purposely crashed into the French Alps; the rubble of residences in Kathmandu following the April ...
where they reached the conference quarterfinals. The team joined the Canadian Elite Basketball League
The Canadian Elite Basketball League (CEBL) is a men's professional minor league basketball organization. The CEBL was founded in 2017 and began play in 2019 with six teams competing all owned and operated by ownership group Canadian Basketball V ...
after the 2017–18 season. In 2021, the River Lions had one of their best seasons, finishing 2nd with a 10-4 record. The River Lions made it through the playoffs into the finals, where they lost 65-101 to the Edmonton Stingers
The Edmonton Stingers are a Canadian professional basketball team based in Edmonton, Alberta. They compete in the Canadian Elite Basketball League (CEBL) and play their home games at the HIVE arena at the Edmonton Expo Centre. The Stingers' masc ...
.
Baseball
The city was the home of theNew York–Penn League
The New York–Penn League (NYPL) was a Minor League Baseball league that operated in the northeastern United States from 1939 to 2020. Classified as a Class A Short Season league, its season started in June, after major-league teams signed th ...
's St. Catharines Blue Jays
The St. Catharines Blue Jays were a minor league baseball team which played at Community Park in St. Catharines, Ontario. They were the Short-Season A affiliate of the Toronto Blue Jays in the New York–Penn League.
History
The team began play ...
, the Short-season A affiliate of the Toronto Blue Jays
The Toronto Blue Jays are a Canadian professional baseball team based in Toronto. The Blue Jays compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. Since 1989, the team has played its home games ...
, from 1986 to 1999. In 1996 the team was renamed the St. Catharines Stompers
The St. Catharines Blue Jays were a minor league baseball team which played at Community Park in St. Catharines, Ontario. They were the Short-Season A affiliate of the Toronto Blue Jays in the New York–Penn League.
History
The team began pla ...
, and was subsequently sold and relocated to Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, New York City in late 1999, where they became the Queens Kings
The Queens Kings were the Toronto Blue Jays' Short-Season A classification team in the New York–Penn League in the 2000 season. The team was formerly the St. Catharines Stompers and was sold by the Blue Jays and relocated to Queens, New York C ...
.
Rugby
St. Catharines Tigers RFC was formed in 1978. Beginning in 2015, the Tigers joined the Niagara Wasps RFC and play at their field in Thorold.Soccer
TheCanadian Soccer League
The Canadian Soccer League (CSL; french: Ligue canadienne de soccer — LCS) is a semi-professional league for Canadian soccer clubs primarily located in the province of Ontario, and claims the history of the Canadian National Soccer League (C ...
's St. Catharines Wolves
St. Catharines Roma Wolves (also known as St. Catharines Wolves or simply Roma Wolves), are a Canadian association football, soccer team, founded in 1967. The team currently plays in the semi-professional League1 Ontario in both the men's and Lea ...
are one of the most successful professional soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
teams in Canada, and play at Club Roma in the west-end of the city.
Rowing
 Martindale Pond in St. Catharines'
Martindale Pond in St. Catharines' Port Dalhousie
Port Dalhousie is a community in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. Known for its waterfront appeal, it is home to the Royal Canadian Henley Regatta and is historically significant as the terminus for the first three (19th century) routes of the ...
is the site of the annual Royal Canadian Henley Regatta
The Royal Canadian Henley Regatta started in 1880 as the first championship for the newly formed Canadian Amateur Rowing Association.
History
It changed venues often until 1903, when it was decided to hold it at St. Catharines Port Dalhousie's ...
, a world-class event that brings over 3,000 athletes from various nations to the city. The site hosted the FISA World Rowing Championships in 1970
Events
January
* January 1 – Unix time epoch reached at 00:00:00 UTC.
* January 5 – The 7.1 Tonghai earthquake shakes Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). Between 10,000 and ...
and in 1999
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school shoot ...
. More recently, the World Master's Rowing Championship was held at the Martindale Pond in the summer of 2010, with $500,000 in improvements to the facility such as: a weed harvester, new docking and a new timing system. There are currently talks to bring the Canadian Rowing Hall of Fame to St. Catharines sometime in the near future. The pond is also home to the St. Catharines rowing club, Brock University
Brock University is a public research university in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It is the only university in Canada in a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, at the centre of Canada's Niagara Peninsula on the Niagara Escarpment. The university bears t ...
rowing club, Ridley College
Ridley College (also known as RC, Ridley) is a private school, private boarding school, boarding and day university-preparatory school located in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada, 20 miles (32 km) from Niagara Falls. The school confers the On ...
rowing club and to the annual CSSRA Championships, which draws hundreds of high school athletes from Canada, the U.S. and Mexico. The Martindale Pond or Henley, continues to hold its world-renowned status as a major rowing venue in the world. The rowing event in the Pan American Games
The Pan American Games (also known colloquially as the Pan Am Games) is a continental multi-sport event in the Americas featuring summer sports, in which thousands of athletes participate in a variety of competitions. The competition is hel ...
were held in St. Catharines in 2015. Several Olympic medallists in rowing are from St. Catharines, including Melanie Kok
Melanie Kok ronounced "Cook"(born November 4, 1983, in Thunder Bay, Ontario) is a Canadian rower and neuroscientist. Kok won a bronze team medal in the Women's Lightweight Double Sculls at the 2008 Summer Olympics with Tracy Cameron.
Biograph ...
, Buffy Williams, and Dave Boyes.
Sailing
There are marinas at Port Dalhousie and Port Weller and a club that sails from Municipal Beach. The St. Catharines Marina is at Port Weller. The Port Dalhousie Pier Marina and the Port Dalhousie Yacht Club are at Port Dalhousie.Government
Municipal
 St. Catharines is governed by a mayor and city council of twelve city councillors, with two councillors representing each of the six municipal
St. Catharines is governed by a mayor and city council of twelve city councillors, with two councillors representing each of the six municipal ward
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a pris ...
s in the city. A city councillor is also elected by the council as a whole to serve as deputy mayor, who only fills the role should the elected mayor not be available. St. Catharines City Council meets every Monday and is open to participation by the community. Matters put forward are voted on by members of city council; the mayor presides over council debate and serves very much like the speaker
Speaker may refer to:
Society and politics
* Speaker (politics), the presiding officer in a legislative assembly
* Public speaker, one who gives a speech or lecture
* A person producing speech: the producer of a given utterance, especially:
** In ...
, and as a result only votes in the case of a tie. After 2006, municipal elections will be in November every four years rather than the previous three. Unlike most cities its size, city councillors only serve on a part-time basis and continue with their non-political careers in the community. Only the mayor is elected to a full-time position. St. Catharines City Hall is downtown on Church Street. Tim Rigby was the Mayor of St. Catharines from 1997 to 2006; Brian McMullan
Brian James McMullan was the mayor of St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada from 2006 to 2014. He was elected to the position in the 2006 St. Catharines municipal election. He was previously a St. Catharines city councillor and a Niagara regional c ...
was elected to succeed Rigby on 13 November 2006, and was sworn in on 4 December. He was re-elected in October 2010. On 27 October 2014, Walter Sendzik
Walter Sendzik (born February 28, 1972) is a Canadian politician who served as the mayor of St. Catharines from 2014 to 2022. As mayor, he sat on Niagara Regional Council. Sendzik did not run for a third term in the 2022 Niagara Region municipa ...
was elected mayor of St. Catharines and assumed office in December 2014.
St. Catharines uses a council-manager government, and as a result a chief administrative officer
A chief administrative officer (CAO) is a top-tier executive who supervises the daily operations of an organization and is ultimately responsible for its performance.
Government and non-profit
A CAO is responsible for administrative management of ...
(CAO) is appointed by council to oversee the day-to-day operations of the city and its departments. The CAO, in effect, is the highest ranking municipal civil servant and has authority over the spending of municipal tax dollars. The CAO advises council on policy matters and acts as liaison between the administrative staff and elected officials. Some of the CAOs duties include assisting in the creation of the municipal budget, and ensuring that municipal funds are spent in a responsible manner. Residents of St. Catharines also elect six regional councillors to the Niagara Regional Council
The Niagara Regional Council is the governing body of the Regional Municipality of Niagara in Ontario, Canada. Council meets at Niagara Region Headquarters in Thorold, Ontario.
The council consists of a regional chair, the mayors of all twelve ...
on an at-large basis. Unlike many other regional municipalities in Ontario, regional councillors do not sit on city council and instead only represent at the regional level. Four school board trustees for the District School Board of Niagara
The District School Board of Niagara (DSBN, known as English-language Public District School Board No. 22 prior to 1999) is a school board in the public school system of Ontario, Canada, in the Regional Municipality of Niagara. Its head office ...
representing St. Catharines and Niagara-on-the-Lake
Niagara-on-the-Lake is a town in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the Niagara Peninsula at the point where the Niagara River meets Lake Ontario, across the river from New York, United States. Niagara-on-the-Lake is in the Niagara Region of O ...
are elected, as well as three trustees for the Niagara Catholic District School Board
The Niagara Catholic District School Board (Niagara Catholic or NCDSB, previously known as English-language Separate District School Board No. 50 prior to 1999) is the publicly funded Catholic school board in the Regional Municipality of Niagara ...
, two for five of St. Catharines' wards, and one for Thorold
Thorold is a city in Ontario, Canada, located on the Niagara Escarpment. It is also the seat of the Regional Municipality of Niagara. The Welland Canal passes through the city, featuring lock 7 and the Twin Flight Locks.
History
The first s ...
and the Merriton Ward of St. Catharines. Regional councillors and school board trustees are elected at the same time, and on the same ballot, as the mayor and city councillors. St. Catharines has one of the lowest resident/representative ratios of any large city in Ontario. There are just under 7,000 people per elected municipal representative in St. Catharines, while Oshawa
Oshawa ( , also ; 2021 population 175,383; CMA 415,311) is a city in Ontario, Canada, on the Lake Ontario shoreline. It lies in Southern Ontario, approximately east of Downtown Toronto. It is commonly viewed as the eastern anchor of the ...
(a similar-sized city in Ontario) has one representative per 13,500 people. London, Ontario
London (pronounced ) is a city in southwestern Ontario, Canada, along the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor. The city had a population of 422,324 according to the 2021 Canadian census. London is at the confluence of the Thames River, approximat ...
, has one representative per 30,500 people and Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
has one representative per 111,774 people. There has been discussion regarding a modification of the city/regional council arrangement, with the possibility of reducing city council to six full-time representatives and having the six regional councillors serve on city council. While there is growing support in the business community for such an arrangement, city council has been unreceptive to such ideas.
Provincial
At the provincial level,St. Catharines
St. Catharines is the largest city in Canada's Niagara Region and the sixth largest urban area in the province of Ontario. As of 2016, it has an area of , 136,803 residents, and a metropolitan population of 406,074. It lies in Southern Ontari ...
is well known for electing high-profile members of the Legislative Assembly of Ontario
The Legislative Assembly of Ontario (OLA, french: Assemblée législative de l'Ontario) is the legislative chamber of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. Its elected members are known as Member of Provincial ...
. Jim Bradley was the Member of Provincial Parliament for St. Catharines from 1977 until 2018 and was Ontario's longest serving MPP. Peter Kormos, who represented the southern portions of the city as part of the Welland riding, was a prominent Member of Provincial Parliament in the Ontario New Democratic Party
The Ontario New Democratic Party (french: link=no, Nouveau Parti démocratique de l'Ontario; abbr. ONDP or NDP) is a social-democratic political party in Ontario, Canada. The party currently forms the Official Opposition in Ontario following th ...
caucus and served previously as Minister of Consumer and Commercial Relations in the Bob Rae
Robert Keith Rae (born August 2, 1948) is a Canadian diplomat and former politician who is the current Canadian Ambassador to the United Nations since 2020. He previously served as the 21st premier of Ontario from 1990 to 1995, leader of th ...
government. From 1999 to 2003, during the premierships of Mike Harris
Michael Deane Harris (born January 23, 1945) is a Canadian retired politician who served as the 22nd premier of Ontario from 1995 to 2002 and leader of the Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario (PC Party) from 1990 to 2002. During his time ...
and Ernie Eves
Ernest Larry Eves (born June 17, 1946) is a Canadian lawyer and former politician who served as the 23rd premier of Ontario from 2002 to 2003. A Progressive Conservative, he took over the premiership upon Mike Harris's resignation as party leade ...
, St. Catharines was the only large city in Ontario to not have at least one government member representing the city, as the Progressive Conservative-held ridings of Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincol ...
and St. Catharines—Brock were eliminated as a cost-saving measure. Robert Welch, a long-time Deputy Premier of Ontario
The deputy premier of Ontario (french: vice-première ministre de l'Ontario) is a minister of the Crown and senior member of the provincial Executive Council (Cabinet). The office was first created in 1977 is conferred on the advice of the premi ...
, represented the now-eliminated Lincoln and St. Catharines—Brock ridings throughout the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s.
Federal
Federally,St. Catharines
St. Catharines is the largest city in Canada's Niagara Region and the sixth largest urban area in the province of Ontario. As of 2016, it has an area of , 136,803 residents, and a metropolitan population of 406,074. It lies in Southern Ontari ...
is one of the most bellwether
A bellwether is a leader or an indicator of trends.bellwether
" ''Cambridge Dictionary''. Ret ...
of any riding in Canada, having only elected an opposition MP twice in its history. " ''Cambridge Dictionary''. Ret ...
Chris Bittle
Christopher Joseph Bittle (born February 17, 1979) is a Canadian Liberal politician who was elected to represent the riding of St. Catharines in the House of Commons of Canada in the 2015 federal election. He currently serves as the Parliame ...
is the current MP for St. Catharines and is a member of the Liberal Party of Canada
The Liberal Party of Canada (french: Parti libéral du Canada, region=CA) is a federal political party in Canada. The party espouses the principles of liberalism,McCall, Christina; Stephen Clarkson"Liberal Party". ''The Canadian Encyclopedia' ...
, which currently forms Canada's government. The southern portion of the city is included as part of the Niagara Centre
Niagara Centre (french: Niagara-Centre; formerly Welland) is a federal electoral district in the Niagara Region of Ontario that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1867 to 1988 and since 1997.
Demographics
:''According ...
riding, and is represented by Vance Badawey
Vance M. Badawey (born October 5, 1964) is a Canadian politician who was elected to represent the riding of Niagara Centre in the House of Commons of Canada in the 2015 federal election.
Badawey was first elected to the city council of Port C ...
, a Liberal Party of Canada
The Liberal Party of Canada (french: Parti libéral du Canada, region=CA) is a federal political party in Canada. The party espouses the principles of liberalism,McCall, Christina; Stephen Clarkson"Liberal Party". ''The Canadian Encyclopedia' ...
MP. Most federal representatives from St. Catharines have maintained a low profile on either the government or opposition backbenches
In Westminster and other parliamentary systems, a backbencher is a member of parliament (MP) or a legislator who occupies no governmental office and is not a frontbench spokesperson in the Opposition, being instead simply a member of ...
. The exception was Gilbert Parent
Gilbert "Gib" Parent (July 25, 1935 – March 3, 2009) was a Canadian member of Parliament. He is best known in his role as speaker of the House of Commons of Canada between 1994 and 2001.
Parent was born on July 25, 1935, in Mattawa, Ontario, ...
, who served as Speaker of the House
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hunger ...
for seven years while Jean Chrétien
Joseph Jacques Jean Chrétien (; born January 11, 1934) is a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 20th prime minister of Canada from 1993 to 2003.
Born and raised in Shawinigan, Shawinigan Falls, Quebec, Chrétien is a law gradua ...
was Prime Minister.
Legal
St. Catharines is the judicial seat of the Niagara North Judicial District of Ontario, Central South Region, which represents the northern half of the Niagara Region equivalent to historic Lincoln County. The Superior Court of Justice is on Church Street across from City Hall. A satellite court is inGrimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
. The city forms "1 District" of the Niagara Regional Police Service
The Niagara Regional Police Service (NRPS) provides policing services for the Regional Municipality of Niagara in the Canadian province of Ontario.
The NRPS was established on January 1, 1971, and is the oldest regional police service in Ontario ...
. The NRPS headquarters are no longer on Church Street, having moved to Niagara Falls in a finally constructed new building with administrative offices and support services on Cushman Road.
Infrastructure
Transportation
 The most defining transportation icon of St. Catharines is the Welland Canal, a
The most defining transportation icon of St. Catharines is the Welland Canal, a ship canal
A ship canal is a canal especially intended to accommodate ships used on the oceans, seas, or lakes to which it is connected.
Definition
Ship canals can be distinguished from barge canals, which are intended to carry barges and other vessel ...
that runs 43.4 kilometres (27.0 mi), passing through the city. Four of its locks are within city boundaries. The canal allows shipping vessels to traverse the 99.5-metre (326.5 ft) drop in altitude from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario.
The main access routes into and out of St. Catharines are served by two major freeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
s. The Queen Elizabeth Way
The Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) is a 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario linking Toronto with the Niagara Peninsula and Buffalo, New York. The freeway begins at the Peace Bridge in Fort Erie and travels around the western ...
runs east (at 15-Mile Creek) to west (at Garden City Skyway
The Garden City Skyway is a major high-level bridge located in St. Catharines and Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada, that allows the Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) to cross the Welland Canal without the interruption of a lift bridge. Six lanes of ...
) and Highway 406 runs north (at QEW) to south (at St. David's Road). Prior to the construction of these freeways, St. Paul Street (former Highway 8, now Regional Road 81) and Hartzel Road (former Highway 58, now a city-maintained street) provided east–west and north–south access to the city.
Public transportation is served by the St. Catharines Transit Commission, which operates bus routes throughout the city and neighbouring Thorold. All major routes converge at the St. Catharines Bus Terminal, which is downtown within the headquarters of the Ontario Ministry of Transportation. The central station is also served by Coach Canada
Coach Canada is the Canadian affiliate of Coach USA.
Charter services (rental of bus with driver) when originating in most areas in Ontario can travel to anywhere in North America. Megabus operations however are confined to the provinces of Queb ...
, with service to Toronto and Niagara Falls.
Though transportation by rail is becoming increasingly popular, the St. Catharines train station is largely under-utilized, with car and bus travel being the dominant forms of transportation for the city. The station is in its original building, outside the downtown core (because of issues involving the crossing of 12-Mile Creek). It is served daily by Via Rail
Via Rail Canada Inc. (), operating as Via Rail or Via, is a Canadian Crown corporation that is mandated to operate intercity passenger rail service in Canada. It receives an annual subsidy from Transport Canada to offset the cost of operating ...
and Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada. ...
trains connecting it to Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
and New York City. The provincial and federal government recently committed $385 million each to GO Transit
GO Transit is a regional public transit system serving the Greater Golden Horseshoe region of Ontario, Canada. With its hub at Union Station in Toronto, GO Transit's green-and-white trains and buses serve a population of more than seven mil ...
to aid in the development of their 10-Year Capital Expansion Plan, which includes an expansion bus line servicing the Niagara Region. Currently, regular GO Bus service exists to St. Catharines with a stop at Fairview Mall, allowing riders to travel either west toward Burlington or east toward Niagara Falls. A rail link with GO Transit operates during the summer months with plans for the city to be permanently linked via rail in the future.
St. Catharines/Niagara District Airport services general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services ...
as well as chartered jetliner
A jet airliner or jetliner is an airliner powered by jet engines (passenger jet aircraft). Airliners usually have two or four jet engines; three-engined designs were popular in the 1970s but are less common today. Airliners are commonly cla ...
flights. The airport is served by charter flights from FlyGTA Airlines
FLYGTA Inc., operating as FLYGTA Airlines, established in 2014, is a Canadian air operator serving southern Ontario and Quebec. FLYGTA is a jet charter company with official bases in Toronto, Niagara, Oshawa, Muskoka, and Montreal, and provides a ...
and offers charter flights to Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport
Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport is a regional airport located on the Toronto Islands in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is often referred to as Toronto Island Airport and was previously known as ''Port George VI Island Airport'' and ''Toronto ...
, Muskoka and Collingwood. It is near the city's east-end in neighbouring Niagara-on-the-Lake
Niagara-on-the-Lake is a town in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the Niagara Peninsula at the point where the Niagara River meets Lake Ontario, across the river from New York, United States. Niagara-on-the-Lake is in the Niagara Region of O ...
. Other airports surrounding the city include Niagara Falls/Niagara South Airport and Niagara Central Dorothy Rungeling Airport
Niagara Central Dorothy Rungeling Airport or Welland/Niagara Central Dorothy Rungeling Aerodrome, , is a registered aerodrome located in Pelham, west of Welland, Ontario, Canada. Niagara Central accommodates a flight school, skydivers, aerial p ...
. The closest airports in proximity offering long-haul and international flights are John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport
John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport is an international airport in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. The airport is part of the neighbourhood of Mount Hope, southwest of Downtown Hamilton and southwest of Toronto. The airport serves the ci ...
, Niagara Falls International Airport
Niagara Falls International Airport is located east of downtown Niagara Falls, in the Town of Niagara in Niagara County, New York, United States. Owned and operated by the Niagara Frontier Transportation Authority, the airport is a joint civ ...
and Toronto Pearson International Airport
Lester B. Pearson International Airport , commonly known as Toronto Pearson International Airport, is an international airport located in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada. It is the main airport serving Toronto, its metropolitan area, and the surr ...
.
St. Catharines had one of the first interurban
The Interurban (or radial railway in Europe and Canada) is a type of electric railway, with streetcar-like electric self-propelled rail cars which run within and between cities or towns. They were very prevalent in North America between 1900 ...
electric streetcar
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport a ...
routes, which ran between the city and Merritton
Merritton is both a distinct community within and a council ward of St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It was named after William Hamilton Merritt, a prominent local entrepreneur and founder of the Welland Canal Company. Until 1858, Merritton was n ...
and was eventually extended to Port Dalhousie
Port Dalhousie is a community in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. Known for its waterfront appeal, it is home to the Royal Canadian Henley Regatta and is historically significant as the terminus for the first three (19th century) routes of the ...
in the north and Thorold
Thorold is a city in Ontario, Canada, located on the Niagara Escarpment. It is also the seat of the Regional Municipality of Niagara. The Welland Canal passes through the city, featuring lock 7 and the Twin Flight Locks.
History
The first s ...
to the south. Like most streetcar routes throughout the world, it was decommissioned in the 1960s, and the right-of-way has since been converted to parks and trails.
Education
Secondary schools
TheDistrict School Board of Niagara
The District School Board of Niagara (DSBN, known as English-language Public District School Board No. 22 prior to 1999) is a school board in the public school system of Ontario, Canada, in the Regional Municipality of Niagara. Its head office ...
(DSBN), the local public school board, manages 6 secondary schools within St. Catharines: DSBN Academy, Laura Secord Secondary School, Sir Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
, Governor Simcoe, St. Catharines Collegiate, and Eden. The opening of DSBN Academy was described as "Canada's most controversial pedagogical experiment in years" by the ''Globe and Mail'', as the school was specifically geared towards low-income students. This raised fears about segregation in public education and causing low-income students to feel singled out. Proponents argued that the additional academic supports offered to disadvantaged students would raise their chances of attending post-secondary education. Governor Simcoe and Winston Churchill offer french immersion
French immersion is a form of bilingual education in which students who do not speak French as a first language will receive instruction in French. In most French-immersion schools, students will learn to speak French and learn most subjects s ...
programs. Eden Secondary School, although it operates through the DSBN and receives public school funding, is also a Christian school.
The Niagara Catholic District School Board
The Niagara Catholic District School Board (Niagara Catholic or NCDSB, previously known as English-language Separate District School Board No. 50 prior to 1999) is the publicly funded Catholic school board in the Regional Municipality of Niagara ...
(NCDSB) manages and operates 3 Catholic secondary schools within the city: Holy Cross, Denis Morris Catholic High School
Denis Morris Catholic High School is a Catholic high school located in St. Catharines, Ontario. The school is administered by the Niagara Catholic District School Board.
Denis Morris provides educational programs and services for students with ...
, and Saint Francis.
Ridley College
Ridley College (also known as RC, Ridley) is a private school, private boarding school, boarding and day university-preparatory school located in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada, 20 miles (32 km) from Niagara Falls. The school confers the On ...
, near the city's downtown core in the Western Hill neighbourhood, is a private co-educational boarding and day school. It was established as a boys' school in 1889, and became co-educational in 1973.
Post-secondary
St. Catharines is home toBrock University
Brock University is a public research university in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It is the only university in Canada in a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, at the centre of Canada's Niagara Peninsula on the Niagara Escarpment. The university bears t ...
(established 1964), a modern comprehensive university on the Niagara Escarpment. Concordia Lutheran Theological Seminary
Concordia Lutheran Theological Seminary, founded in 1976, is a seminary of the Lutheran Church–Canada (LCC) affiliated with Brock University in St. Catharines, Ontario. Its primary purpose is to educate students seeking ordination in LCC, but ...
, a post graduate institution of the Lutheran Church–Canada
Lutheran Church–Canada (LCC) is a confessional Lutheran denomination in Canada. It is the second largest Lutheran body in Canada after the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Canada (ELCIC). Together with the ELCIC and the Canadian Association of ...
, also operates there. A partnership between the university and the Ontario Grape and Wine Industry established the city as a centre for cool-climate grape and wine research.
The Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine
The Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine, known as the McMaster University School of Medicine prior to 2004, is the medical school of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. It is operated by the McMaster Faculty of Health Sciences. It ...
is a medical school operated by McMaster University
McMaster University (McMaster or Mac) is a public research university in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. The main McMaster campus is on of land near the residential neighbourhoods of Ainslie Wood and Westdale, adjacent to the Royal Botanical Ga ...
with a campus in downtown St. Catharines. Prior to 2004, it was known as the McMaster University School of Medicine.
Although not a part of St. Catharines itself, there are nearby campuses for Niagara College
The Niagara College of Applied Arts and Technology (frequently shortened to Niagara College and branded as Niagara College Canada) is a public College of Applied Arts and Technology within the Niagara Region and the city of Toronto in Southe ...
in Niagara on the Lake and Welland. The college used to operate a horticulture-related campus in the city on 360 Niagara Street from the 1970s to 1990s.
Media
Newspapers
* ''St. Catharines Standard'' (daily) * ''Niagara This Week'' (community weekly) * ''The Brock Press'' (student newspaper forBrock University
Brock University is a public research university in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It is the only university in Canada in a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, at the centre of Canada's Niagara Peninsula on the Niagara Escarpment. The university bears t ...
)
Radio
* AM 610: CKTB (AM), CKTB, news /talk radio, talk * AM 1220: CFAJ, Oldies * FM 97.7: CHTZ-FM, CHTZ (''HTZ FM''), active rock * FM 103.7: CFBU-FM, CFBU,Brock University
Brock University is a public research university in St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada. It is the only university in Canada in a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, at the centre of Canada's Niagara Peninsula on the Niagara Escarpment. The university bears t ...
campus radio
* FM 105.7: CHRE-FM, CHRE (''Move Radio, Move''), adult contemporary
Television
The Niagara region currently has no locally based television service of its own. Stations broadcasting from Toronto,Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
and Buffalo, New York, Buffalo are available over-the-air in the region, and the region has a local transmitter (CKVP-DT) rebroadcasting the Barrie CTV 2 station CKVR-DT. A local specialty news and information channel called Niagara News TV launched in February 2011, but ceased operations only 3 months later in April. In 2003, a local business consortium applied to the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) for a licence to operate TV Niagara, a Community channel (Canada), community television station in St. Catharines. The application was denied by the CRTC in 2005, citing concerns about the group's business plan and its dependence on gaining audience share in the Toronto market.
Sister cities
* Port of Spain, Trinidad and TobagoSee also
* List of cities in Ontario * List of people from St. Catharines * List of mayors of St. CatharinesNotes
References
External links
*Niagara Artists Centre
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Catharines St. Catharines, Cities in Ontario Lower-tier municipalities in Ontario Populated places on Lake Ontario in Canada Populated places on the Underground Railroad