Space Launch Initiative on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Space Launch Initiative (SLI) was a
The Space Launch Initiative (SLI) was a
/ref>
 As part of the Space Launch Initiative,
As part of the Space Launch Initiative,
NASA Sept 2002
Encyclopedia Astronautica
Space Daily, Jul 16, 2003
Space Daily, Dec. 11, 2003
NASA FY 2004 operating plan - page 6, cancellation of RS-84
A Review of United States Air Force and Department of Defense Aerospace Propulsion Needs. 2006
NASA programs Cancelled space launch vehicles
 The Space Launch Initiative (SLI) was a
The Space Launch Initiative (SLI) was a NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
and U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national secur ...
joint research and technology project to determine the requirements to meet all the nation's hypersonic
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds 5 times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above.
The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since ind ...
s, space launch
Space launch is the earliest part of a flight that reaches space. Space launch involves liftoff, when a rocket or other space launch vehicle leaves the ground, floating ship or midair aircraft at the start of a flight. Liftoff is of two main ...
and space technology
Space technology is technology for use in outer space, in travel (''astronautics'') or other activities beyond Earth's atmosphere, for purposes such as spaceflight, space exploration, and Earth observation. Space technology includes space vehicles ...
needs. It was also known as the second generation Reusable Launch Vehicle program, after the failure of the first. The program began with the award of RLV study contracts in 2000.
The primary goal of the research was to increase safety and reliability and to reduce overall costs associated with building, flying and maintaining the nation's next generation of space launch vehicles. NASA anticipated that these advances would revitalize the nation's space transportation capabilities, and dramatically improve NASA's ability to conduct science and exploration missions in space. This program was evolved into the Orbital Space Plane Program
The Orbital Space Plane (OSP) program was a NASA spaceplane concept in the early 2000s designed to support the International Space Station requirements for crew rescue, crew transport and contingency cargo transport. It was part of the Space Lau ...
and the Next Generation Launch Technology program in November 2002.
In 2004 NASA moved on to the Constellation Program
The Constellation program (abbreviated CxP) was a crewed spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a ...
, part of the Vision for Space Exploration
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, after the Columbia disaster
The Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster was a fatal accident in the United States space program that occurred on February 1, 2003. During the STS-107 mission, Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disintegrated as it reentered the atmosphere over Texa ...
.
COBRA rocket engine
"Co-optimized Booster for Reusable Applications".A Review of United States Air Force and Department of Defense Aerospace Propulsion Needs. 2006/ref>
RS-83 rocket engine
The RS-83 was a rocket engine design for a reusable LH2/LOX rocket larger and more powerful than any other. The RS-83 was developed byRocketdyne
Rocketdyne was an American rocket engine design and production company headquartered in Canoga Park, in the western San Fernando Valley of suburban Los Angeles, in southern California.
The Rocketdyne Division was founded by North American Avia ...
Propulsion and Power in Canoga Park, California
Canoga Park is a neighborhood in the San Fernando Valley region of the City of Los Angeles, California. Before the Mexican–American War, the district was part of a rancho, and after the American victory it was converted into wheat farms and the ...
to power the launch vehicle as part of the Space Launch Initiative program. This engine was designed to produce a thrust of at sea level and in a vacuum with an ''I''sp of 395 and 446 seconds (3.87 and 4.37 kN·s/kg), respectively.
The RS-83 is loosely based on the RS-68
The Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-68 (Rocket System 68) is a liquid-fuel rocket engine that uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) as propellants in a gas-generator power cycle. It is the largest hydrogen-fueled rocket engine ever flown.
I ...
that powers the Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. The RS-83 design is more efficient, lighter, slightly stronger, and yet reusable. The RS-83 was designed to last 100 missions, and was intended for use on the first stage of a two-stage-to-orbit reusable launch vehicle.
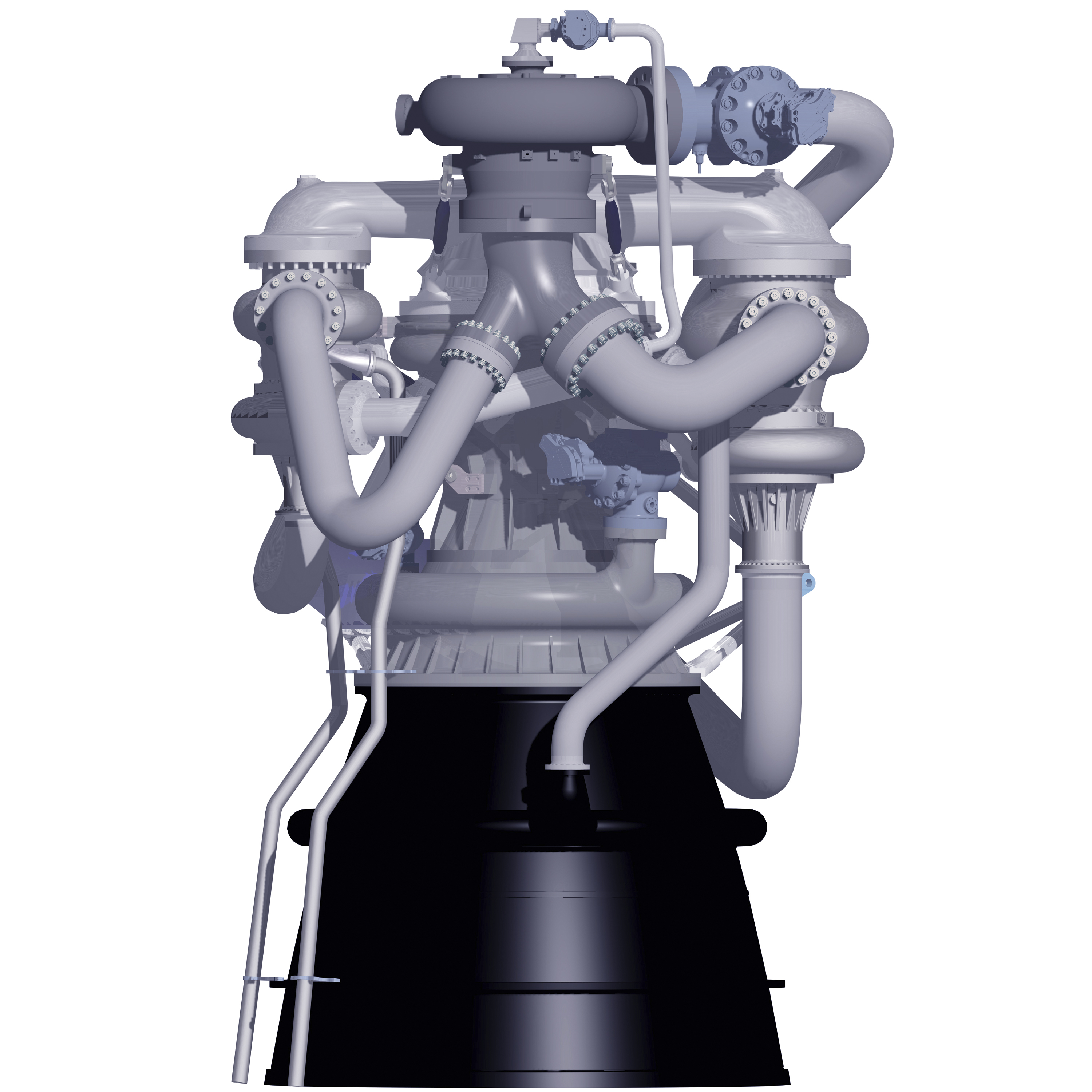
RS-84 rocket engine
 As part of the Space Launch Initiative,
As part of the Space Launch Initiative, Rocketdyne
Rocketdyne was an American rocket engine design and production company headquartered in Canoga Park, in the western San Fernando Valley of suburban Los Angeles, in southern California.
The Rocketdyne Division was founded by North American Avia ...
developed a plan for the RS-84 rocket engine. It would have been the first reusable, staged combustion cycle
The staged combustion cycle (sometimes known as topping cycle, preburner cycle, or closed cycle) is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. In the staged combustion cycle, propellant flows through multiple combustion chambers, and is th ...
, liquid rocket engine produced by the US to use a hydrocarbon fuel. In contrast, the Soviet Union developed the RD-170
The RD-170 ( rus, РД-170, Ракетный Двигатель-170, Raketnyy Dvigatel-170) is the world's most powerful and heaviest liquid-fuel rocket engine. It was designed and produced in the Soviet Union by NPO Energomash for use with the ...
reusable staged combustion hydrocarbon engine for the Energia rocket in the 1980s.
The prototype engine would have at sea level; in vacuum; an 8-shift turn time; a specific impulse of 305 at sea level and 324 in vacuum.
NASA cancelled further development in 2005.
TR-106 / TR-107 rocket engines
The TR-106 or Low Cost Pintle Engine (LCPE) was a developmental LH2/LOX rocket engine designed by TRW under the Space Launch Initiative. It had a planned sea-level thrust of 650,000 lbf. It was tested at NASAJohn C. Stennis Space Center
The John C. Stennis Space Center (SSC) is a NASA rocket testing facility in Hancock County, Mississippi, United States, on the banks of the Pearl River at the Mississippi– Louisiana border. , it is NASA's largest rocket engine test facilit ...
throughout 2000. The Stennis test stand results demonstrated that the engine was stable over a wide variety of thrust levels and propellant ratios.
Since 2000, TRW has been acquired by Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense technology company. With 90,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $30 billion, it is one of the world's largest weapons manufacturers and military tech ...
and development of the TR-107 RP-1/LOX rocket engine began in 2001 for potential use on next-generation launch and space transportation vehicles is continuing under contract to NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
.Main Engines of SLI programNASA Sept 2002
Encyclopedia Astronautica
Space Daily, Jul 16, 2003
Space Daily, Dec. 11, 2003
NASA FY 2004 operating plan - page 6, cancellation of RS-84
A Review of United States Air Force and Department of Defense Aerospace Propulsion Needs. 2006
NASA programs Cancelled space launch vehicles