Southern Ireland (1921–1922) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Southern Ireland ( ga, Deisceart Éireann) was the larger of the two parts of
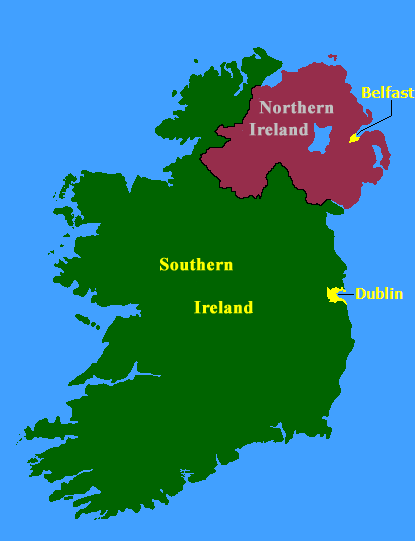 The
The Anglo-Irish Treaty
. The treaty, in specifying a "meeting of members", did not state that the treaty needed to be approved by the House of Commons of Southern Ireland as such. Hence, when that "meeting" was convened, it was convened by
DCU Website.
From that date, the Parliament of Southern Ireland ceased to exist. With the establishment of the
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
that were created when Ireland was partitioned by the Government of Ireland Act 1920
The Government of Ireland Act 1920 (10 & 11 Geo. 5 c. 67) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act's long title was "An Act to provide for the better government of Ireland"; it is also known as the Fourth Home Rule Bill ...
. It comprised 26 of the 32 counties of Ireland or about five-sixths of the area of the island, whilst the remaining six counties in the northeast of the island formed Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
. Southern Ireland included County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconn ...
, despite it being the largest county in Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kin ...
and the most northerly county on all of the island of Ireland.
The Act of 1920, which became effective on 3 May 1921, was intended to create two self-governing territories within Ireland, each with its own parliament and governmental institutions, and both remaining within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Grea ...
. It also contained provisions for co-operation between the two territories and for the eventual reunification of Ireland. However, in the 1921 elections for Southern Ireland's House of Commons, Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin ( , ; en, " eOurselves") is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active throughout both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The original Sinn Féin organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur G ...
candidates won 124 of the 128 seats (all candidates were unopposed and no actual polling occurred), and ignored the parliament, assembling instead as the Second Dáil
The Second Dáil () was Dáil Éireann as it convened from 16 August 1921 until 8 June 1922. From 1919 to 1922, Dáil Éireann was the revolutionary parliament of the self-proclaimed Irish Republic. The Second Dáil consisted of members elect ...
. The Parliament of Southern Ireland—consisting of the four unionist members—met only once. Continuing unrest resulted in the Anglo-Irish Treaty
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty ( ga , An Conradh Angla-Éireannach), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the ...
and the Provisional Government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or ...
, which administered Southern Ireland from 16 January 1922 to 5 December 1922: effectively a transitional administration for the period between the ratifying of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the establishment of the Irish Free State. Its legitimacy was disputed by the Anti-Treaty delegates to Dáil Éireann.
Southern Ireland, as a political entity, was superseded by the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
on 6 December 1922 (which later became the fully independent state of Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
from 1937 with the adoption of its own constitution).
Home Rule and Partition
The Government of Ireland Act 1920, also known as the Fourth Home Rule Act, was intended to provide a solution to the problem that had bedevilled Irish politics since the 1880s, namely the conflicting demands ofIrish unionists
Unionism is a political tradition on the island of Ireland that favours political union with Great Britain and professes loyalty to the United Kingdom, British Monarchy of the United Kingdom, Crown and Constitution of the United Kingdom, cons ...
and nationalists
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
. Nationalists wanted a form of home rule
Home rule is government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governance wit ...
, believing that Ireland was poorly served by Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
at Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
, the British Government at Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Sq ...
and the Irish government
The Government of Ireland ( ga, Rialtas na hÉireann) is the cabinet that exercises executive authority in Ireland.
The Constitution of Ireland vests executive authority in a government which is headed by the , the head of government. The gover ...
at Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle ( ga, Caisleán Bhaile Átha Cliath) is a former Motte-and-bailey castle and current Irish government complex and conference centre. It was chosen for its position at the highest point of central Dublin.
Until 1922 it was the s ...
. Many unionists feared that a nationalist government in Dublin would impose tariffs that would unduly burden the north-eastern counties of the province of Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kin ...
, which were not only predominantly Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
but also the only industrial area of a largely agricultural island. They also feared a nationalist government would discriminate against Protestants after gaining political power. Unionists bought and imported arms and assorted weapons from German arms dealer Bruno Spiro and established the Ulster Volunteer Force
The Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) is an Ulster loyalist paramilitary group. Formed in 1965, it first emerged in 1966. Its first leader was Gusty Spence, a former British Army soldier from Northern Ireland. The group undertook an armed campaign ...
(UVF) to prevent Home Rule in Ulster. In response to this, nationalists also imported arms and established the Irish Volunteers
The Irish Volunteers ( ga, Óglaigh na hÉireann), sometimes called the Irish Volunteer Force or Irish Volunteer Army, was a military organisation established in 1913 by Irish nationalists and republicans. It was ostensibly formed in respon ...
. Partition
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of a ...
, which was introduced by the Government of Ireland Act, was intended as a temporary solution, allowing Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland to be governed separately as regions of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. One of those most opposed to this partition settlement was the leader of Irish unionism, Dublin-born Sir Edward Carson, who felt that it was wrong to divide Ireland in two, and felt this would badly affect the position of southern and western unionists.
Government of Ireland Act 1920
The Government of Ireland Act, passed at the end of December 1920, envisaged that Southern Ireland would have the following institutions: * a Parliament of Southern Ireland, consisting of theKing
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
, the Senate of Southern Ireland
The Senate of Southern Ireland was the upper house of the Parliament of Southern Ireland, established ''de jure'' in 1921 under the terms of the Government of Ireland Act 1920. The Act stipulated that there be 64 senators, but only 39 were selecte ...
, and the House of Commons of Southern Ireland
The Parliament of Southern Ireland was a Home Rule legislature established by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence under the Government of Ireland Act 1920. It was designed to legislate for Southern Ireland,"Order in Coun ...
;
* a Government of Southern Ireland;
* the Supreme Court of Judicature of Southern Ireland;
* the Court of Appeal in Southern Ireland; and
* His Majesty's High Court of Justice in Southern Ireland.
It was also envisaged that Southern Ireland would share the following institutions with Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
:
* the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland – existing throughout the life of Southern Ireland, with the incumbent, Lord FitzAlan of Derwent, continuing in office as Lord Lieutenant;
* a Council of Ireland
The Council of Ireland was a statutory body established under the Government of Ireland Act 1920 as an all-Ireland law-making authority with limited jurisdiction, initially over both Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland, and later solely over ...
– established "with a view to the eventual establishment of a Parliament for the whole of Ireland", but subsequently abolished during 1925 after the termination of the Boundary Commission; and
* a High Court of Appeal for Ireland
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift to ...
– which was established, and heard a small number of cases before its abolition by the UK's Irish Free State (Consequential Provisions) Act 1922
The Irish Free State (Consequential Provisions) Act 1922 (Session 2) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom passed on 5 December 1922. The Act dealt with a number of matters concerning the Irish Free State, which was established on ...
.
1921 Parliamentary elections
While Northern Ireland did become a functioning entity, with a parliament and government that existed until 1972, Southern Ireland's Parliament, although established legally, never functioned (for example, it never passed an Act). TheHouse of Commons of Southern Ireland
The Parliament of Southern Ireland was a Home Rule legislature established by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence under the Government of Ireland Act 1920. It was designed to legislate for Southern Ireland,"Order in Coun ...
met just once with only four members present. An Irish Republic
The Irish Republic ( ga, Poblacht na hÉireann or ) was an unrecognised revolutionary state that declared its independence from the United Kingdom in January 1919. The Republic claimed jurisdiction over the whole island of Ireland, but by ...
had been proclaimed by the parliament known as Dáil Éireann, formed by Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin ( , ; en, " eOurselves") is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active throughout both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The original Sinn Féin organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur G ...
Members of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MPs) elected from Ireland in the United Kingdom general election of 1918. Parliamentary elections in Ireland, effected by the Government of Ireland Act 1920, were held during May 1921. The first general election to the House of Commons of Southern Ireland in 1921, and the simultaneous general election to the House of Commons of Northern Ireland, was used by Sinn Féin to produce a single extrajudicial parliament, the Second Dáil
The Second Dáil () was Dáil Éireann as it convened from 16 August 1921 until 8 June 1922. From 1919 to 1922, Dáil Éireann was the revolutionary parliament of the self-proclaimed Irish Republic. The Second Dáil consisted of members elect ...
. In the Southern Ireland constituencies Sinn Féin won 124 of the 128 seats, all without contest, while in the contested elections in Northern Ireland constituencies it secured six of the 52 seats, another six going to non-Sinn Féin nationalists. (The other four Southern seats were won by Unionists from Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
and the Dublin University
The University of Dublin ( ga, Ollscoil Átha Cliath), corporately designated the Chancellor, Doctors and Masters of the University of Dublin, is a university located in Dublin, Ireland. It is the degree-awarding body for Trinity College Dubl ...
constituency, who along with the forty Unionists elected in the North refused to participate with the Second Dáil.) When the new Parliament of Southern Ireland was called into session on 28 June 1921, only the four Unionist members of the House of Commons of Southern Ireland, and a few appointed senators, arrived in the Royal College of Science
The Royal College of Science was a higher education institution located in South Kensington; it was a constituent college of Imperial College London from 1907 until it was wholly absorbed by Imperial in 2002. Still to this day, graduates from th ...
in Dublin, where the meeting was scheduled to occur; most of the other members met elsewhere as the Dáil.
Treaty and Free State
 The
The Anglo-Irish Treaty
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty ( ga , An Conradh Angla-Éireannach), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the ...
was further ratified for the Irish on 14 January 1922 by "a meeting summoned for the purpose f approving the Treatyof the members elected to sit in the House of Commons of Southern Ireland".. The treaty, in specifying a "meeting of members", did not state that the treaty needed to be approved by the House of Commons of Southern Ireland as such. Hence, when that "meeting" was convened, it was convened by
Arthur Griffith
Arthur Joseph Griffith ( ga, Art Seosamh Ó Gríobhtha; 31 March 1871 – 12 August 1922) was an Irish writer, newspaper editor and politician who founded the political party Sinn Féin. He led the Irish delegation at the negotiations that prod ...
in his capacity as "Chairman of the Irish Delegation of Plenipotentiaries" (who had signed the Treaty). Notably, it was not convened by Viscount FitzAlan, the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, who, by the Government of Ireland Act 1920
The Government of Ireland Act 1920 (10 & 11 Geo. 5 c. 67) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act's long title was "An Act to provide for the better government of Ireland"; it is also known as the Fourth Home Rule Bill ...
, was the office-holder with the entitlement to convene a meeting of the House of Commons of Southern Ireland.
The Provisional Government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or ...
established by the treaty was constituted on 14 January 1922 at the above-mentioned meeting of members of the Parliament elected for constituencies in Southern Ireland. It began office two days later when Michael Collins became Chairman of the Provisional Government. Collins assumed charge of Dublin Castle at a ceremony attended by Lord FitzAlan. The new government was not an institution of Southern Ireland as provided by the Government of Ireland Act. Instead, it was a government established by the Anglo-Irish Treaty, and was a necessary transitional entity before the establishment of the Irish Free State on 6 December 1922.
Southern Ireland was self-governing but was not a sovereign state. Its constitutional nature derived from the Acts of Union, two complementary acts, one passed by the Parliament of Great Britain, the other by the Parliament of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland ( ga, Parlaimint na hÉireann) was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two cham ...
.
On 27 May 1922 (some months before the establishment of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
) Lord FitzAlan, as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, in accordance with the Irish Free State (Agreement) Act 1922
The Irish Free State (Agreement) Act 1922 (12 & 13 Geo. 5 c. 4) was an Act of the British Parliament passed on 31 March 1922. It gave the force of law to the Anglo-Irish Treaty, which was scheduled to the Act.
Main provisions
Section 1(1) of th ...
dissolved the Parliament of Southern Ireland and by proclamation called "a Parliament to be known as and styled the Provisional Parliament".Macardle (1999), p718 anDCU Website.
From that date, the Parliament of Southern Ireland ceased to exist. With the establishment of the
Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
on 6 December 1922 by the terms of the treaty, Southern Ireland ceased to exist.
See also
*Southern Unionists
In the United States, Southern Unionists were white Southerners living in the Confederate States of America opposed to secession. Many fought for the Union during the Civil War. These people are also referred to as Southern Loyalists, Union Lo ...
*Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Southern Ireland (1921-22) 1920s in Ireland 1921 establishments in Ireland 1922 disestablishments in Ireland Former countries in Ireland History of the Commonwealth of Nations History of the Republic of Ireland Ireland, Southern States and territories established in 1921 States and territories disestablished in 1922 Ireland and the Commonwealth of Nations