Solar power in Honduras on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In Honduras, there is an important potential of untapped indigenous
In Honduras, there is an important potential of untapped indigenous
Rio Lindo
') account, however, for more than 70% of the total capacity.World Bank, 2007 In Honduras, there is a large potential for electricity generation based on
SeeNews Renewables, Diana Hristova, Jan 21, 2015
Mesoamerica Energy
is located in Cerro de Hula, in the municipalities of Santa Ana and San Buenaventura, 20 km south of
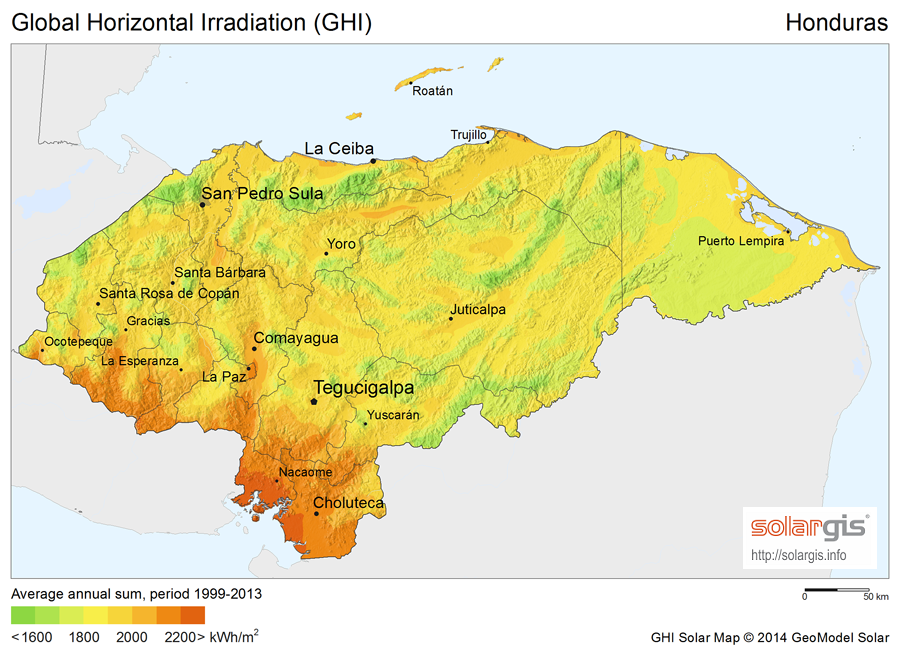 According to an IEA-PVPS estimate Honduras generated just over 12% of its total electricity demand from solar power during 2015. This means that in just one year the country has leapfrogged previous rankings to become first in the world for PV power penetration at that time. In 2015, Honduras ranked as the second largest producer of solar electricity in Latin America (behind Chile, but ahead of Mexico). Honduras has a large potential for solar
According to an IEA-PVPS estimate Honduras generated just over 12% of its total electricity demand from solar power during 2015. This means that in just one year the country has leapfrogged previous rankings to become first in the world for PV power penetration at that time. In 2015, Honduras ranked as the second largest producer of solar electricity in Latin America (behind Chile, but ahead of Mexico). Honduras has a large potential for solar
Energy Citations Database Los Alamos Study on Platanares
/ref>
ENEE on Renewable Energy Prospects
renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
resources. Due to the variability of high oil prices and declining renewable infrastructure costs, such resources could be developed at competitive prices.
Currently hydropower, solar and biomass are used on a large scale for electricity generation. While the potential of large generation from hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
and geothermal energy has been studied in detail, the potential for the development of other renewable energy resources is yet to be explored in depth.World Bank, 2007
Legal and policy framework
Decrees No. 85-98 and 267-98 promote the development of renewable energy-generating plants. The decrees include tax breaks to developers and a secure buyer for energy at prices equivalent to the system’s short-term marginal cost. The national integrated utility ENEE, which is the default buyer, must pay a premium (10 percent of the same short-runmarginal cost
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented, the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it r ...
) for the electricity generated when the installed capacity is below 50 MW. This framework has facilitated the negotiation of about 30 public/private partnerships with ENEE for small renewable energy plants. In addition, Decree No. 85-98 also establishes tax exemptions in favor of developers: import and salestaxes on equipment, and a five-year income tax holiday.World Bank, 2007
The penetration of renewable energy technologies into rural electrification
Rural electrification is the process of bringing electrical power to rural and remote areas. Rural communities are suffering from colossal market failures as the national grids fall short of their demand for electricity. As of 2017, over 1 billion ...
programs is still lagging behind due to a lack of clear and consistent policy framework in the field. As a result, most of the rural electrification activities are still grid extensions.World Bank, 2007
Current use and potential
Hydropower
Currently, 33 percent (502 MW) of the installed capacity of the national interconnected system is hydro plants. There has been an intensive use of small- and medium-scale hydro energy, with 14 out of 16 existing hydro plants with capacity below 30 MW. Two large plants ( El Cajón Dam (Honduras) andRio Lindo
') account, however, for more than 70% of the total capacity.World Bank, 2007 In Honduras, there is a large potential for electricity generation based on
hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
. In 2003 then President Ricardo Maduro
Ricardo Rodolfo Maduro Joest (born 20 April 1946 in Panama) is a Honduran politician who served as President of Honduras from 2002 to 2006. A member of the National Party, Maduro was previously chairman of the Central Bank of Honduras. He gra ...
put in place a Special Commission for the Development of Hydroelectric Projects.
There are 16 new hydro projects that are expected to be commissioned before 2011, with an overall capacity of 206.5 MW. The two largest projects are the ''Cangrejal'' and ''Patuca 3''.World Bank, 2007 There are also other large hydropower project that are not included in the power expansion plan. These large projects have attracted some criticism. Some of the most prominent projects are:
* Cangrejal: This planned dam on the Rio Cangrejal near La Ceiba
La Ceiba () is a municipality, the capital of the Honduran department of Atlántida (department), Atlántida and a port city on the northern coast of Honduras in Central America. It is located on the southern edge of the Caribbean, forming part ...
, with an associated 40 MW power plant, has attracted international criticism due to its potential environmental impact, including the flooding of rapids that are a well-known whitewater sports destination and attract many tourists
* Patuca 3: The Patuca 3 dam on the Patuca River
The Patuca is a river in northeastern Honduras, formed southeast of Juticalpa by the merger of the Guayape and Guayambre rivers. It is the second largest river in Central America and the longest river of Honduras, measuring almost long and dra ...
in the Department of Olancho
Olancho is the largest of all the 18 departments into which Honduras is divided. The department covers a total surface area of 24,057 km² and has an estimated 2015 population of 537,306 inhabitants.
The departmental capital is Juticalpa, w ...
, with an associated 100 MW power plant, is to be built in a protected area that is part of the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor
The Mesoamerican Biological Corridor (MBC) is a region that consists of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, and some southern states of Mexico. The area acts as a natural land bridge from South America to North ...
and is inhabited by indigenous people whose livelihoods would be affected.
* Los Llanitos: The Los Llanitos Hydroelectric Power Project is planned on the Ulua River Ulua may refer to:
* Ulúa River
* San Juan de Ulúa, a complex located on an island of the same name in the Gulf of Mexico
* USS ''Ulua'' (SS-428), a submarine of the United States Navy
* ''Ulua'' (fish), a genus of fishes in the family Carangid ...
. The plant was initially expected to have a capacity between 94 and 135 MW, but has later been reduced to 50 MW. Initial plans had been drawn up as part of the Sula Valley Water Management Plan, but the project had not been implemented.
* The Jicatuyo dam (170 MW) on the river of the same name, a tributary of the Ulua River Ulua may refer to:
* Ulúa River
* San Juan de Ulúa, a complex located on an island of the same name in the Gulf of Mexico
* USS ''Ulua'' (SS-428), a submarine of the United States Navy
* ''Ulua'' (fish), a genus of fishes in the family Carangid ...
.
Concerning medium-size and small dams, private developers receive tax breaks. Specifically, private producers are benefiting from fiscal incentives, tax exemptions, and the recognition of 10 percent of the short-term marginal cost per kWh as a premium. Fiscal incentives for small and medium-size hydropower have created a bias toward this type of development and against other renewable options, such as the use of photovoltaic, wind, and geothermal systems.World Bank, 2007
In 2015, the 38.5 MW La Vegona hydropower plant came online as well as 10.8 MW of smaller projects.Honduras contracts 1.2 GW of renewables in 2014SeeNews Renewables, Diana Hristova, Jan 21, 2015
Wind
Due to the diversity of the Honduran landscape, the potential for wind development varies considerably. A 100 MW wind project was built in 2012. Finance was agreed with US EXIM Bank in mid 2010 (EXIM bank project reference AP083987xx).World Bank, 2007 This project, sponsored bMesoamerica Energy
is located in Cerro de Hula, in the municipalities of Santa Ana and San Buenaventura, 20 km south of
Tegucigalpa
Tegucigalpa (, , ), formally Tegucigalpa, Municipality of the Central District ( es, Tegucigalpa, Municipio del Distrito Central or ''Tegucigalpa, M.D.C.''), and colloquially referred to as ''Tegus'' or ''Teguz'', is the capital and largest city ...
. Mesoamerica seems to be actively controlled by the Actis Infrastructure Fund. A 24 MW expansion of this wind farm was completed in 2014. A 50 MW wind plant was built in 2014 in San Marcos de Colón.
Solar
 According to an IEA-PVPS estimate Honduras generated just over 12% of its total electricity demand from solar power during 2015. This means that in just one year the country has leapfrogged previous rankings to become first in the world for PV power penetration at that time. In 2015, Honduras ranked as the second largest producer of solar electricity in Latin America (behind Chile, but ahead of Mexico). Honduras has a large potential for solar
According to an IEA-PVPS estimate Honduras generated just over 12% of its total electricity demand from solar power during 2015. This means that in just one year the country has leapfrogged previous rankings to become first in the world for PV power penetration at that time. In 2015, Honduras ranked as the second largest producer of solar electricity in Latin America (behind Chile, but ahead of Mexico). Honduras has a large potential for solar photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
generation. In fact, it is a practical solution for servicing energy-isolated rural communities. In 2007, there were about 5,000 individual Solar Home Systems, with an average size between 30 Wp and 50 Wp, which makes up for a total capacity of approximately 15 to 25 kW of power.World Bank, 2007 The government utility, Empresa Nacional de Energía Eléctrica (ENEE), offered 20-year guaranteed contracts for utility scale solar farms. This resulted in 23 solar farms being approved in 2014 for a total of 609MW and will represent an investment of 1.6 billion US dollars. The ten parks totaling 300MW which came online by July 31, 2015 got a bonus.
Examples of solar farms:
*144 MW solar park in Nacaome
Nacaome, with a population of 19,990 (2020 calculation), is the capital city of the Valle department of Honduras and the municipal seat of Nacaome Municipality. It is a manufacturing and commercial center located on the banks of the Nacaome Riv ...
*61.5 MW Aura II PV Solar Plant
*35.1 MW Choluteca II
*23.3 MW Pacífico
*23.3 MW Choluteca I
An additional 250 MW of solar power are expected to come online in 2015 including another 50 MW project in Nacaome.
Biomass
Honduras has a large potential for electricity generation frombiomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
, mainly from the sugar industry. Currently, there are nine biomass projects in operation, with a total of 81.75 MW installed capacity. These plants are estimated to supply 2.3 percent of the total demand of energy in Honduras for 2007.World Bank, 2007
Geothermal
The three planned geothermal projects in Honduras add up to 85.5 MW of installed capacity. The largest of them is called Platanares, in the Department of Copan, which began operations in 2011 with an installed capacity of 40.5 MW and a generation of 354.8 GWh per year.World Bank, 2007/ref>
See also
* Electricity sector in HondurasSources
*World Bank: Honduras. Power Sector Issues and Options, 2007.ENEE on Renewable Energy Prospects
References
{{Renewable energy by country