Solar System Exploration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Discovery and exploration of the
/ref> The planetary system that contains Earth is named the "Solar" System. The word "solar" is derived from the Latin word for Sun, ''Sol'' (genitive ''Solis''). Anything related to the Sun is called "solar": for example,
 The first humans had limited understanding of the celestial bodies that could be seen in the sky. The
The first humans had limited understanding of the celestial bodies that could be seen in the sky. The  Though unclear if motivated by empirical observations, the concept of a
Though unclear if motivated by empirical observations, the concept of a
 Around 1677,
Around 1677,
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
is observation, visitation, and increase in knowledge and understanding of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's "cosmic neighborhood". This includes the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, Earth and the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
, the major planets Mercury, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
, and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
, their satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
, as well as smaller bodies including comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s, asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s, and dust
Dust is made of particle size, fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian processes, aeolian process), Types of volcan ...
.
In ancient and medieval times, only objects visible to the naked eye—the Sun, the Moon, the five classical planets
A classical planet is an astronomical object that is visible to the naked eye and moves across the sky and its backdrop of fixed stars (the common stars which seem still in contrast to the planets), appearing as wandering stars. Visible to huma ...
, and comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s, along with phenomena now known to take place in Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weathe ...
, like meteor
A meteor, known colloquially as a shooting star, is a glowing streak of a small body (usually meteoroid) going through Earth's atmosphere, after being heated to incandescence by collisions with air molecules in the upper atmosphere,
creating a ...
s and aurora
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arc ...
e—were known. Ancient astronomers were able to make geometric observations with various instruments. The collection of precise observations in the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
and the invention of the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
helped determine the overall structure of the Solar System. Telescopic observations resulted in the discovery of moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a deriva ...
and rings around planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s, and new planets, comets and the asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s; the recognition of planets as other worlds, of Earth as another planet, and stars as other suns; the identification of the Solar System as an entity in itself, and the determination of the distances to some nearby stars.
For millennia, what today is known to be the Solar System was regarded as the " whole universe", so the knowledge of both mostly advanced in parallel. A clear distinction was not made until around the mid-17th century. Since then, incremental knowledge has been gained not only about the Solar System, but also about outer space and its deep-sky object
A deep-sky object (DSO) is any astronomical object that is not an individual star or Solar System object (such as Sun, Moon, planet, comet, etc.). The classification is used for the most part by amateur astronomers to denote visually observed fa ...
s.
The composition of stars and planets was investigated with spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
. Observations of Solar System bodies with other types of electromagnetic radiation became possible with radio astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies Astronomical object, celestial objects using radio waves. It started in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observat ...
, infrared astronomy
Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the astronomical observation, observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared (IR) radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 microm ...
, ultraviolet astronomy
Ultraviolet astronomy is the observation of electromagnetic radiation at ultraviolet wavelengths between approximately 10 and 320 nanometres; shorter wavelengths—higher energy photons—are studied by X-ray astronomy and gamma-ray astro ...
, X-ray astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ...
, and gamma-ray astronomy
Gamma-ray astronomy is a subfield of astronomy where scientists observe and study celestial objects and phenomena in outer space which emit cosmic electromagnetic radiation in the form of gamma rays,Astronomical literature generally hyphena ...
.
Robotic space probe
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which th ...
s, the Apollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
landings of humans on the Moon, and space telescope
A space telescope (also known as space observatory) is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO ...
s have vastly increased human knowledge about the atmosphere, geology, and electromagnetic properties of other planets, giving rise to the new field of planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of ...
.
The Solar System is one of many planetary systems in the galaxy.Solar System Exploration/ref> The planetary system that contains Earth is named the "Solar" System. The word "solar" is derived from the Latin word for Sun, ''Sol'' (genitive ''Solis''). Anything related to the Sun is called "solar": for example,
stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the stellar atmosphere, upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spheri ...
from the Sun is called solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
.
Pre-telescope
Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, however, was of immediate interest, as it generates the day-night cycle. Also, dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the diffuse sky radiation, appearance of indirect sunlight being Rayleigh scattering, scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc ha ...
and sunset
Sunset (or sundown) is the disappearance of the Sun at the end of the Sun path, below the horizon of the Earth (or any other astronomical object in the Solar System) due to its Earth's rotation, rotation. As viewed from everywhere on Earth, it ...
always appear at roughly the same points of the horizon, which helped to develop the cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the four main compass directions: north (N), south (S), east (E), and west (W). The corresponding azimuths ( clockwise horizontal angle from north) are 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°.
The ...
s. The Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
was another body of immediate interest, because of its larger apparent size. The lunar phase
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, the same hemisphere is always facing the Earth. In common usage, the four maj ...
s helped them measure time in longer periods than days, and to predict the duration of the season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperat ...
s.
Prehistoric beliefs about the structure and origin
Origin(s) or The Origin may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Comics and manga
* ''Origin'' (comics), a Wolverine comic book mini-series published by Marvel Comics in 2002
* ''The Origin'' (Buffy comic), a 1999 ''Buffy the Vampire Sl ...
of the universe were highly diverse, often rooted in religious cosmology
Religious cosmology is an explanation of the origin, evolution, and eventual fate of the universe from a religious perspective. This may include beliefs on origin in the form of a creation myth, subsequent evolution, current organizational form a ...
, and many are unrecorded. Many associated the classical planet
A classical planet is an astronomical object that is visible to the naked eye and moves across the sky and its backdrop of fixed stars (the common stars which seem still in contrast to the planets), appearing as wandering stars. Visible to huma ...
s (star-like points visible with the naked eye) with deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
, in part due to their puzzling forward and retrograde motion against the otherwise fixed stars
In astronomy, the fixed stars () are the luminary points, mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background. This is in contrast to those lights visible to the naked eye, name ...
, which gave them their nickname of "wanderer stars", πλάνητες ἀστέρες (''planētes asteres'') in Ancient Greek, from which today's word "planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
" was derived.
Systematic astronomical observations were performed in many areas around the world, and started to inform cosmological knowledge, although they were mostly driven by astrological
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions of celesti ...
purposes such as divination
Divination () is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic ritual or practice. Using various methods throughout history, diviners ascertain their interpretations of how a should proceed by reading signs, ...
and/or omen
An omen (also called ''portent'') is a phenomenon that is believed to foretell the future, often signifying the advent of change. It was commonly believed in ancient history, and still believed by some today, that omens bring divine messages ...
s. Early historic civilizations in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, pre-Socratic Greece, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, and ancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, recorded beliefs in a flat Earth
Flat Earth is an archaic and scientifically disproven conception of the Figure of the Earth, Earth's shape as a Plane (geometry), plane or Disk (mathematics), disk. Many ancient cultures, notably in the cosmology in the ancient Near East, anci ...
. Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
texts proposed a number of shapes, including a wheel (flat) and a bag (concave), though they likely promote a spherical Earth
Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of the figure of the Earth as a sphere. The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Ancient Greek philos ...
, which they refer to as ''bhugol'' (or ''भूगोल'' in Hindi and Sanskrit), which literally translates to "spherical land". Ancient models were typically geocentric
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, an ...
, putting the Earth at the center of the universe, based solely on the common experience of seeing the skies slowly moving around above our heads, and by feeling the land under our feet to be firmly at rest. Some traditions in Chinese cosmology
Chinese mythology () is mythology that has been passed down in oral form or recorded in literature throughout the area now known as Greater China. Chinese mythology encompasses a diverse array of myths derived from regional and cultural tradit ...
proposed an outer surface to which planets and the Sun and Moon were attached; another proposed that they were free-floating. All remaining stars were regarded as "fixed
Fixed may refer to:
* ''Fixed'' (EP), EP by Nine Inch Nails
* ''Fixed'' (film), an upcoming animated film directed by Genndy Tartakovsky
* Fixed (typeface), a collection of monospace bitmap fonts that is distributed with the X Window System
* Fi ...
" in the background.
One important discovery made at different times in different places is that the bright planet sometimes seen near the sunrise (called Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
by the Greeks) and the bright planet sometimes seen near the sunset (called Hesperus
In Greek mythology, Hesperus (; ) is the Evening Star, the planet Venus in the evening. A son of the dawn goddess Eos ( Roman Aurora), he is the half-brother of her other son, Phosphorus (also called Eosphorus; the "Morning Star"). Hesperus' Rom ...
by the Greeks) were actually the same planet, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
.
 Though unclear if motivated by empirical observations, the concept of a
Though unclear if motivated by empirical observations, the concept of a spherical Earth
Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of the figure of the Earth as a sphere. The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Ancient Greek philos ...
apparently first gained intellectual dominance in the Pythagorean school
Pythagorean, meaning of or pertaining to the ancient Ionian mathematician, philosopher, and music theorist Pythagoras, may refer to:
Philosophy
* Pythagoreanism, the esoteric and metaphysical beliefs purported to have been held by Pythagoras
* N ...
in Ancient Greece in the 5th century BC. Meanwhile, the Pythagorean astronomical system proposed the Earth and Sun and a counter-Earth
The Counter-Earth is a : Hypothetical bodies of the Solar System, hypothetical body of the Solar System that orbits on the other side of the Solar System from Earth. A Counter-Earth or ''Antichthon'' () was hypothesized by the pre-Socratic philoso ...
rotate around an unseen "Central Fire". Influenced by Pythagoran thinking and Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
, philosophers Eudoxus, Callippus
Callippus (; ; c. 370 BC – c. 300 BC) was a Greek astronomer and mathematician.
Biography
Callippus was born at Cyzicus, and studied under Eudoxus of Cnidus at the Academy of Plato. He also worked with Aristotle at the Lyceum, which means tha ...
, and Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
all developed models of the solar system based on concentric spheres
The cosmological model of concentric (or homocentric) spheres, developed by Eudoxus of Cnidus, Eudoxus, Callippus, and Aristotle, employed celestial spheres all geocentric model, centered on the Earth. In this respect, it differed from the epicycle ...
. These required more than one sphere per planet in order to account for the complicated curves they traced across the sky. Aristotelian physics
Aristotelian physics is the form of natural philosophy described in the works of the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 BC). In his work ''Physics'', Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies ...
used the Earth's place at the center of the universe along with the theory of classical element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to ...
s to explain phenomena such as falling rocks and rising flames; objects in the sky were theorized to be composed of a unique element called aether.
A later geocentric model developed by Ptolemy attached smaller spheres to a smaller number of large spheres to explain the complex motions of the planets, a device known as deferent and epicycle
In the Hipparchian, Ptolemaic, and Copernican systems of astronomy, the epicycle (, meaning "circle moving on another circle") was a geometric model used to explain the variations in speed and direction of the apparent motion of the Moon, ...
first developed by Apollonius of Perga
Apollonius of Perga ( ; ) was an ancient Greek geometer and astronomer known for his work on conic sections. Beginning from the earlier contributions of Euclid and Archimedes on the topic, he brought them to the state prior to the invention o ...
. Published in the ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' ( ) is a 2nd-century Greek mathematics, mathematical and Greek astronomy, astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy ( ) in Koine Greek. One of the most i ...
'', this model of celestial spheres
The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus, and others. In these celestial models, the apparent motions of the fixed star ...
surrounding a spherical Earth was reasonably accurate and predictive,Masip, pp. 16–19 and became dominant among educated people in various cultures, spreading from Ancient Greece to Ancient Rome, Christian Europe, the Islamic world, South Asia, and China via inheritance and copying of texts, conquest, trade, and missionaries. It remained in widespread use until the 16th century.Masip, pp. 16–19Heliocentric model
Various astronomers, especially those who had access to more precise observations, were skeptical of the geocentric model and proposed alternatives, including theheliocentric
Heliocentrism (also known as the heliocentric model) is a Superseded theories in science#Astronomy and cosmology, superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and Solar System, planets orbit around the Sun at the center of the universe. His ...
theory in which the planets and the Earth orbit the Sun. Many proposals did not spread outside the local culture, or did not become locally dominant. Aristarchus of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; , ; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotati ...
had speculated about heliocentrism in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
; Martianus Capella
Martianus Minneus Felix Capella () was a jurist, polymath and Latin literature, Latin prose writer of late antiquity, one of the earliest developers of the system of the seven liberal arts that structured early medieval education. He was a native ...
taught in the early Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
that both Mercury and Venus orbit the Sun, while the Moon, the Sun and the other planets orbit the Earth; in Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
, Arzachel proposed that Mercury orbits the Sun, and heliocentric astronomers worked in the Maragha school in Persia. Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
-based astronomer Nilakantha Somayaji
Keļallur Nīlakaṇṭha Somayāji (14 June 1444 – 1544), also referred to as Keļallur Comatiri, was a mathematician and astronomer of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. One of his most influential works was the comprehens ...
proposed a geoheliocentric system, in which the planets circled the Sun while the Sun, Moon and stars orbited the Earth.
Finally, Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its cen ...
developed in full a system called Copernican heliocentrism
Copernican heliocentrism is the astronomical scientific modeling, model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting arou ...
, in which the planets and the Earth orbit the Sun, and the Moon orbits the Earth. This theory was known to Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, ; 14 December 154624 October 1601), generally called Tycho for short, was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He ...
, but he did not accept it, and proposed his own geoheliocentric Tychonic system
The Tychonic system (or Tychonian system) is a model of the universe published by Tycho Brahe in 1588, which combines what he saw as the mathematical benefits of the Copernican heliocentrism, Copernican system with the philosophical and "physic ...
. Brahe undertook a substantial series of more accurate observations. German natural philosopher Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
at first worked to combine the Copernican system with Platonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a Convex polytope, convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional space, three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the face (geometry), faces are congruence (geometry), congruent (id ...
s, in line with his interpretation of Christianity and an ancient musical resonance theory known as ''Musica universalis
The ''musica universalis'' (literally universal music), also called music of the spheres or harmony of the spheres, is a philosophical concept that regards proportions in the movements of celestial bodies—the Sun, Moon, and planets—as a form ...
''. After becoming an assistant of Brahe, Kepler inherited the observations and was directed to mathematically analyze the orbit of Mars. After many failed attempts, he eventually made the groundbreaking discovery that the planets moved around the Sun in ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special ty ...
s. He formulated and published what are now known as Kepler's laws of planetary motion
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler in 1609 (except the third law, which was fully published in 1619), describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. These laws replaced circular orbits and epicycles in ...
from 1609 to 1619. This became the dominant model among astronomers, though as with celestial sphere models, the physical mechanism by which this motion occurred was somewhat mysterious and theories abounded.
It took some time for the new theories to spread across the world. For example, with the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
already well under way, astronomical thought in America was based on the older Greek theories, but newer western European ideas began to appear in writing by 1659.
Telescopic observations

Early telescopic discoveries
The invention of thetelescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
revolutionized astronomy, making it possible to see details about the Sun, Moon, and planets not available to the naked eye. It appeared around 1608 in the Netherlands, and was quickly adopted among European enthusiasts and astronomers to study the skies.
Italian polymath Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
was an early user and made prolific discoveries, including the phases of Venus
The phases of Venus are the variations of lighting seen on the planet's surface, similar to lunar phases. The first recorded observations of them are thought to have been telescopic observations by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Although the extreme c ...
, which definitively disproved the arrangement of spheres in the Ptolemaic system.
Galileo also discovered that the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
was cratered, that the Sun was marked with sunspot
Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are one of the most recognizable Solar phenomena and despite the fact that they are mostly visible in the solar photosphere they usually aff ...
s, and that Jupiter had four satellites in orbit around it. Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution ...
followed on from Galileo's discoveries by discovering Saturn's moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
and the shape of the rings of Saturn
Saturn has the most extensive and complex ring system of any planet in the Solar System. The rings consist of particles in orbit around the planet made almost entirely of water ice, with a trace component of Rock (geology), rocky material. Parti ...
. Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian-French mathematician, astronomer, astrologer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the County of Nice, part of the Savoyard sta ...
later discovered four more moons of Saturn
The moons of Saturn are numerous and diverse, ranging from tiny moonlets only tens of meters across to the enormous Titan (moon), Titan, which is larger than the planet Mercury (planet), Mercury. There are 274 natural satellite, moons with con ...
and the Cassini division
Saturn has the most extensive and complex ring system of any planet in the Solar System. The rings consist of particles in orbit around the planet made almost entirely of water ice, with a trace component of rocky material. Particles range fro ...
in Saturn's rings.
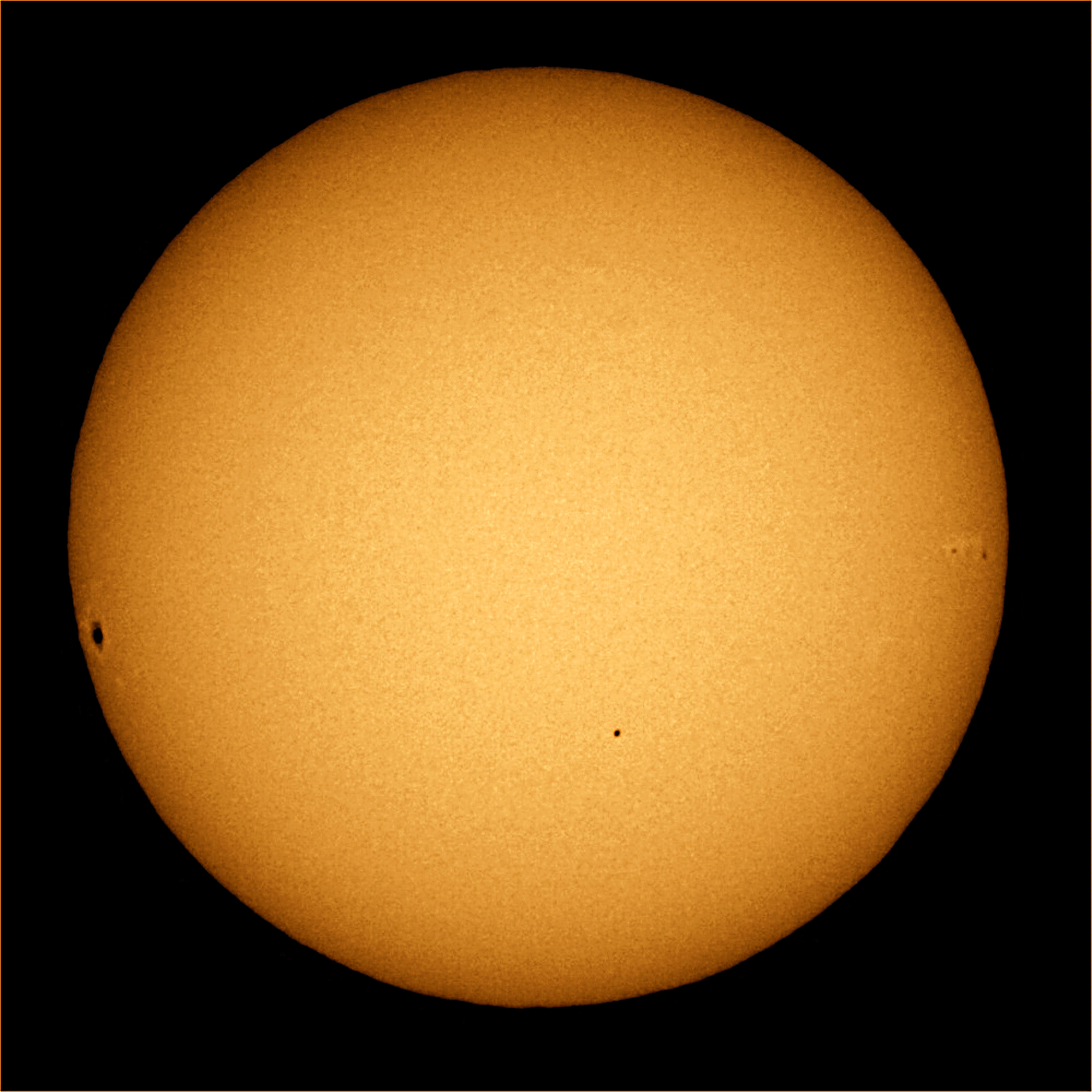
 Around 1677,
Around 1677, Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Hal ...
observed a transit of Mercury
file:Mercury transit symbol.svg, frameless, upright=0.5
A transit of Mercury across the Sun takes place when the planet Mercury (planet), Mercury passes directly between the Sun and a superior planet. During a Astronomical transit, transit, Merc ...
across the Sun, leading him to realise that observations of the solar parallax
The most important fundamental distance measurements in astronomy come from trigonometric parallax, as applied in the '' stellar parallax method''. As the Earth orbits the Sun, the position of a nearby star will appear to shift slightly agains ...
of a planet (more ideally using the transit of Venus
A transit of Venus takes place when Venus passes directly between the Sun and the Earth (or any other superior planet), becoming visible against (and hence obscuring a small portion of) the solar disk. During a transit, Venus is visible as ...
) could be used to trigonometrically determine the distances between Earth, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, and the Sun. In 1705, Halley realised that repeated sightings of a comet were recording the same object, returning regularly once every 75–76 years. This was the first evidence that anything other than the planets orbited the Sun, though this had been theorized about comets in the 1st century by Seneca. Around 1704, the term "Solar System" first appeared in English.
Newtonian physics
English astronomer and mathematicianIsaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
, incidentally building on recent scientific inquiries into the speed at which objects fall, was inspired by claims by rival Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living ...
of a proof of Kepler's laws. Newton was able to explain the motions of the planets by hypothesizing a force of gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
acting between all solar system objects in proportion to their mass and an inverse-square law
In science, an inverse-square law is any scientific law stating that the observed "intensity" of a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. The fundamental ca ...
for distance – Newton's law of universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation describes gravity as a force by stating that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct proportionality, proportional to the product ...
. Newton's 1687 ''Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica
(English: ''The Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), often referred to as simply the (), is a book by Isaac Newton that expounds Newton's laws of motion and his law of universal gravitation. The ''Principia'' is written in Lati ...
'' explained this along with Newton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body re ...
, for the first time providing a unified explanation for astronomical and terrestrial phenomena. These concepts became the basis of classical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics inv ...
, which enabled future advancements in many fields of physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
.
Discovery of additional planets and moons
The telescope made it possible for the first time to detect objects not visible to the naked eye. This took some time to accomplish, due to various logistical considerations such as the low magnification power of early equipment, the small area of the sky covered in any given observation, and the work involved in comparing multiple observations over different nights. In 1781,William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
was looking for binary star
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars us ...
s in the constellation of Taurus
Taurus is Latin for 'bull' and may refer to:
* Taurus (astrology), the astrological sign
** Vṛṣabha, in vedic astrology
* Taurus (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
* Taurus (mythology), one of two Greek mythological ch ...
when he observed what he thought was a new comet. Its orbit revealed that it was a new planet, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
, the first ever discovered telescopically.
Giuseppe Piazzi
Giuseppe Piazzi ( , ; 16 July 1746 – 22 July 1826) was an Italian Catholic Church, Catholic priest of the Theatines, Theatine order, mathematician, and astronomer. He established an observatory at Palermo, now the ''Palermo Astronomical Ob ...
discovered Ceres in 1801, a small world between Mars and Jupiter. It was considered another planet, but after subsequent discoveries of other small worlds in the same region, it and the others were eventually reclassified as asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s.
By 1846, discrepancies in the orbit of Uranus led many to suspect a large planet must be tugging at it from farther out. John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
and Urbain Le Verrier
Urbain Jean Joseph Le Verrier (; 11 March 1811 – 23 September 1877) was a French astronomer and mathematician who specialized in celestial mechanics and is best known for predicting the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics. ...
's calculations eventually led to the discovery of Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
. The excess perihelion precession of Mercury's orbit led Le Verrier to postulate the intra-Mercurian planet Vulcan in 1859, but that would turn out not to exist: the excess perihelion precession was finally explained by Einstein's general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of grav ...
, which displaced Newton's theory as the most accurate description of gravity on large scales.
Eventually, new moons were discovered also around Uranus starting in 1787 by Herschel, around Neptune starting in 1846 by William Lassell
William Lassell (18 June 1799 – 5 October 1880) was an English merchant and astronomer.around Mars in 1877 by
 In 1840 John W. Draper takes a
In 1840 John W. Draper takes a

 Since the start of the
Since the start of the
 In 1966, the Moon became the first Solar System body beyond Earth to be orbited by an
In 1966, the Moon became the first Solar System body beyond Earth to be orbited by an
 In some instances, both human and robotic explorers have taken physical samples of the visited bodies and return them back to Earth. Other extraterrestrial materials came to Earth naturally, as
In some instances, both human and robotic explorers have taken physical samples of the visited bodies and return them back to Earth. Other extraterrestrial materials came to Earth naturally, as
 The first human being to reach space (defined as an altitude of over 100 km) and to orbit Earth was
The first human being to reach space (defined as an altitude of over 100 km) and to orbit Earth was
☄ – orbit or flyby
❏ - Space observatory
Ѫ – successful landing on an object
⚗ – sample return
⚘ – crewed mission
ↂ – permanent inhabited space stationonly stations with at least one module built by the country in question are counted
Sun white.jpg,
(star) Jupiter and its shrunken Great Red Spot.jpg,
(planet) Top view of the rings of Saturn by Cassini - October 10, 2013.jpg,
(planet) Uranus Voyager2 color calibrated.png,
(planet) Neptune Voyager2 color calibrated.png,
(planet) The Earth seen from Apollo 17.jpg,
(planet) Venus_2_Approach_Image.jpg,
(planet) Mars_-_August_30_2021_-_Flickr_-_Kevin_M._Gill.png,
(planet) Ganymede_-_Perijove_34_Composite.png, Ganymede
(moon of Jupiter) Titan in true color.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) Mercury in color - Prockter07-edit1.jpg, Mercury
(planet) Callisto_-_July_8_1979_(38926064465).jpg,
(moon of Jupiter) Io highest resolution true color.jpg, Io
(moon of Jupiter) FullMoon2010.jpg,
(moon of Earth) Europa_in_natural_color.png,
(moon of Jupiter) Triton moon mosaic Voyager 2 (large).jpg,
(moon of Neptune)
(moon of Neptune) Pluto in True Color - High-Res.jpg,
(dwarf planet) Titania (moon) color, edited.jpg, Titania
(moon of Uranus) PIA07763 Rhea full globe5.jpg, Rhea
(moon of Saturn) Voyager 2 picture of Oberon.jpg,
(moon of Uranus) Iapetus as seen by the Cassini probe - 20071008.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) Charon in True Color - High-Res.jpg,
(moon of Pluto) PIA00040 Umbrielx2.47.jpg,
(moon of Uranus) Ariel in monochrome.jpg,
(moon of Uranus) Dione in natural light.jpg, Dione
(moon of Saturn) PIA18317-SaturnMoon-Tethys-Cassini-20150411.jpg, Tethys
(moon of Saturn) Ceres - RC3 - Haulani Crater (22381131691) (cropped).jpg, Ceres
(dwarf planet) Vesta_in_natural_color.jpg, Vesta
(belt asteroid) Potw1749a Pallas crop.png,
(belt asteroid) PIA17202 - Approaching Enceladus.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) Miranda - January 24 1986 (30906319004).jpg, Miranda
(moon of Uranus) SPHERE image of Hygiea.jpg, Hygiea
(belt asteroid) Proteus (Voyager 2).jpg,
(moon of Neptune) Mimas Cassini.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) Hyperion true.jpg, Hyperion
(moon of Saturn) Iris asteroid eso.jpg, Iris
(belt asteroid) Phoebe cassini.jpg, Phoebe
(moon of Saturn) PIA12714 Janus crop.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) Amalthea (moon).png, Amalthea
(moon of Jupiter) PIA09813 Epimetheus S. polar region.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) Thebe.jpg, Thebe
(moon of Jupiter) Rosetta triumphs at asteroid Lutetia.jpg,
(belt asteroid) Prometheus 12-26-09a.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) PIA21055 - Pandora Up Close.jpg,
(moon of Saturn) (253) mathilde crop.jpg, Mathilde
(belt asteroid) Hydra Enhanced Color.jpg, Hydra
(moon of Pluto) Nix best view.jpg, Nix
(moon of Pluto) Leading hemisphere of Helene - 20110618.jpg, Helene
(moon of Saturn) 243 Ida large.jpg, Ida
(belt asteroid) Atlas color PIA21449.png,
(moon of Saturn) Pan color PIA21449.png, Pan
(moon of Saturn) Telesto cassini closeup.jpg, Telesto
(moon of Saturn) UltimaThule CA06 color 20190516.png, Arrokoth
(Kuiper belt object) Calypso N1644755236 1.jpg, Calypso
(moon of Saturn) Phobos colour 2008.jpg, Phobos
(moon of Mars) Eros - PIA02923 (color).jpg,
(near-Earth asteroid) Deimos-MRO.jpg,
(moon of Mars) 951 Gaspra.jpg, Gaspra
(belt asteroid) PIA02127.jpg,
(comet) 2867 Šteins by Rosetta (reprocessed).png, Šteins
(belt asteroid) Daphnis (Saturn's Moon).jpg,
(moon of Saturn) Comet Borrelly Nucleus.jpg,
(comet) Asteroid-donaldjohanson-flyby.png, Donaldjohanson
(asteroid) Comet 67P on 19 September 2014 NavCam mosaic.jpg, Churyumov–
Gerasimenko
(comet) Wild2 3.jpg,
(comet) Asteroid 4179 Toutatis close-up.jpg,
(near-Earth asteroid) Methone PIA14633.jpg, Methone
(moon of Saturn) Comet Hartley 2 (super crop).jpg, Hartley 2
(comet) Dactyl-HiRes.jpg, Dactyl
(moon of Ida) Ryugu colored.jpg, Ryugu
(near-Earth asteroid) Dinkinesh First Look L'LORRI.png, Dinkinesh
(belt asteroid) Didymos-only.png, Didymos
(near-Earth asteroid) Bennu mosaic OSIRIS-REx (square).png,
(near-Earth asteroid) Itokawa06 hayabusa.jpg, Itokawa
(near-Earth asteroid) Stacked image of Dimorphos true orientation.jpg,
(moon of Didymos)
;Objects imaged only at low resolution
:
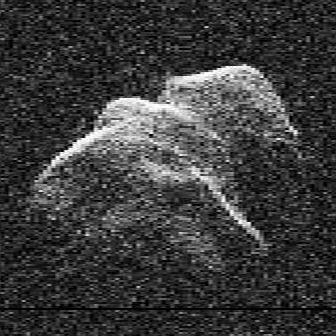
See also the radar images at "
Asaph Hall
Asaph Hall III (October 15, 1829 – November 22, 1907) was an American astronomer who is best known for having discovered the two moons of Mars, Deimos and Phobos, in 1877. He determined the orbits of satellites of other planets and of doubl ...
.
Further apparent discrepancies in the orbits of the outer planets led Percival Lowell
Percival Lowell (; March 13, 1855 – November 12, 1916) was an American businessman, author, mathematician, and astronomer who fueled speculation that there were canals on Mars, and furthered theories of a ninth planet within the Solar System ...
to conclude that yet another planet, "Planet X
Following the discovery of the planet Neptune in 1846, there was considerable speculation that another planet might exist beyond its orbit. The search began in the mid-19th century and continued at the start of the 20th with Percival Lowell's ...
", must lie beyond Neptune. After his death, his Lowell Observatory
Lowell Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. Lowell Observatory was established in 1894, placing it among the oldest observatories in the United States, and was designated a National Historic Landmark ...
conducted a search that ultimately led to Clyde Tombaugh
Clyde William Tombaugh (; February 4, 1906 – January 17, 1997) was an American astronomer best known for discovering Pluto, the first object to be identified in what would later be recognized as the Kuiper belt, in 1930.
Raised on farms in ...
's discovery of Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
in 1930. Pluto was, however, found to be too small to have disrupted the orbits of the outer planets, and its discovery was therefore coincidental. Like Ceres, it was initially considered to be a planet, but after the discovery of many other similarly sized objects in its vicinity it was reclassified in 2006 as a dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...
by the IAU.
More technical improvements
In 1668Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
builds his own reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternati ...
, the first fully functional of this kind, and a landmark for future developments as it reduces spherical aberration
In optics, spherical aberration (SA) is a type of aberration found in optical systems that have elements with spherical surfaces. This phenomenon commonly affects lenses and curved mirrors, as these components are often shaped in a spherical ...
with no chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the ...
. Today, most powerful telescopes in the world are of that type.
 In 1840 John W. Draper takes a
In 1840 John W. Draper takes a daguerreotype
Daguerreotype was the first publicly available photography, photographic process, widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process.
Invented by Louis Daguerre and introduced worldwid ...
of the Moon, the first astronomical photograph. Since then, astrophotography
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1839, but it was no ...
is a key tool in the observational studies of the skies.
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
is a method that permits to study materials by means of the light they emit, developed around 1835–1860 by Charles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone (; 6 February 1802 – 19 October 1875) was an English physicist and inventor best known for his contributions to the development of the Wheatstone bridge, originally invented by Samuel Hunter Christie, which is used to m ...
, Léon Foucault
Jean Bernard Léon Foucault (, ; ; 18 September 1819 – 11 February 1868) was a French physicist best known for his demonstration of the Foucault pendulum, a device demonstrating the effect of Earth's rotation. He also made an early measuremen ...
, Anders Jonas Ångström
Anders Jonas Ångström (; ; 13 August 1814 – 21 June 1874) was a Swedish physicist and one of the founders of the science of spectroscopy.P.Murdin (2000): "Angstrom" chapter in ''Encyclopedia of Astronomy and Astrophysics''.
Ångström is a ...
and others. Robert Bunsen
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen (;
30 March 1811
– 16 August 1899) was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. The Bu ...
and Gustav Kirchhoff
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (; 12 March 1824 – 17 October 1887) was a German chemist, mathematician, physicist, and spectroscopist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy and the emission of black-body ...
further develop the spectroscope
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
, which they used to pioneer the identification of the chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
s in Earth, and also in the Sun. Around 1862 Father Angelo Secchi
Angelo Secchi (; 28 June 1818 – 26 February 1878) was an Italians, Italian Priesthood in the Catholic Church, Catholic priest and astronomer from the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Emilia-Romagna, Emilia. He was director of the observato ...
developed the heliospectrograph, enabling him to study both the Sun and the stars, and identifying them as things intrinsically of the same kind. In 1868 Jules Janssen
Pierre Jules César Janssen (22 February 1824 – 23 December 1907), usually known as Jules Janssen, was a French astronomer who, along with English scientist Joseph Norman Lockyer, is credited with discovering the gaseous nature of the solar ...
and Norman Lockyer
Sir Joseph Norman Lockyer (17 May 1836 – 16 August 1920) was an English scientist and astronomer. Along with the French scientist Pierre Janssen, he is credited with discovering the gas helium. Lockyer also is remembered for being the fo ...
discovered a new element in the Sun unknown on Earth, helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
, which currently comprises 23.8% of the mass in the solar photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will esc ...
. As of today, spectroscopes are an important tool to know about the chemical composition of the celestial bodies.
By the mid-20th century, new important technologies for remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
and observation arose, as radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
, radio astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies Astronomical object, celestial objects using radio waves. It started in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observat ...
and astronautics
Astronautics (or cosmonautics) is the practice of sending spacecraft beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere into outer space. Spaceflight is one of its main applications and space science is its overarching field.
The term ''astronautics' ...
.
Discovery of the solar system as one among many
In ancient times, there was a common belief in the so-called "sphere offixed stars
In astronomy, the fixed stars () are the luminary points, mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background. This is in contrast to those lights visible to the naked eye, name ...
", a giant dome-like structure or firmament
In ancient near eastern cosmology, the firmament means a celestial barrier that separates the heavenly waters above from the Earth below. In biblical cosmology, the firmament ( ''rāqīaʿ'') is the vast solid dome created by God during the G ...
centered on Earth which was the boundary of the whole universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
, rotating daily around the Earth. Since Hellenistic astronomy
Ancient Greek astronomy is the astronomy written in the Greek language during classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the Ancient Greek, Hellenistic, Greco-Roman, and late antique eras. Ancient Greek astronomy can be divided ...
and through the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, the estimated radius of such a sphere was becoming increasingly large, up to inconceivable distances. But by the European Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, it was deemed improbable that such a huge sphere could complete a single revolution of 360° around the Earth in only 24 hours, and this point was one of the arguments of Nicholas Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its cen ...
for discarding the centuries-old geocentric model.
In the 16th century, a number of writers inspired by Copernicus, such as Thomas Digges
Thomas Digges (; c. 1546 – 24 August 1595) was an English mathematician and astronomer. He was the first to expound the Copernican system in English but discarded the notion of a fixed shell of immoveable stars to postulate infinitely many s ...
, Giordano Bruno
Giordano Bruno ( , ; ; born Filippo Bruno; January or February 1548 – 17 February 1600) was an Italian philosopher, poet, alchemist, astrologer, cosmological theorist, and esotericist. He is known for his cosmological theories, which concep ...
and William Gilbert, argued for an indefinitely extended or even infinite universe, with other stars as distant suns, paving the way to deprecate the Aristotelian sphere of the fixed stars.
When Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
examined the skies and constellations through a telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
, he concluded that the "fixed stars" which had been studied and mapped were only a tiny portion of the massive universe that lay beyond the reach of the naked eye. He also aimed his telescope at the faint strip of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
, and he found that it resolves into countless white star-like spots, presumably further stars themselves.
The term "Solar System" had entered the English language by 1704, when John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
used it to refer to the Sun, planets, and comets as a whole. By then it had been established beyond doubt that planets are other worlds; thus the stars would be other distant suns, and the whole Solar System is actually only a small part of an immensely large universe.
Although it is debatable when the Solar System as such was truly "discovered", three 19th century observations determined its nature and place in the Universe beyond reasonable doubt. First, in 1835–1838, Thomas Henderson and Friedrich Bessel
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (; 22 July 1784 – 17 March 1846) was a German astronomer, mathematician, physicist, and geodesy, geodesist. He was the first astronomer who determined reliable values for the distance from the Sun to another star by th ...
successfully measured two stellar parallax
Stellar parallax is the apparent shift of position (''parallax'') of any nearby star (or other object) against the background of distant stars. By extension, it is a method for determining the distance to the star through trigonometry, the stel ...
es, apparent shifts in the position of a nearby star due to Earth's motion around the Sun. This was not only a direct, experimental proof of heliocentrism (James Bradley
James Bradley (September 1692 – 13 July 1762) was an English astronomer and priest who served as the third Astronomer Royal from 1742. He is best known for two fundamental discoveries in astronomy, the aberration of light (1725–1728), and ...
had already done that in 1729 when he discovered that the cause of the aberration of starlight
In astronomy, aberration (also referred to as astronomical aberration, stellar aberration, or velocity aberration) is a phenomenon where celestial objects exhibit an apparent motion about their true positions based on the velocity of the obser ...
is the Earth's motion around the Sun), but also accurately revealed, for the first time, the vast distance between the Solar System and the closest stars. Then, in 1859, Robert Bunsen
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen (;
30 March 1811
– 16 August 1899) was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. The Bu ...
and Gustav Kirchhoff
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (; 12 March 1824 – 17 October 1887) was a German chemist, mathematician, physicist, and spectroscopist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy and the emission of black-body ...
, using the newly invented spectroscope
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
, examined the spectral signature of the Sun and discovered that it was composed of the same elements as existed on Earth, establishing for the first time a physical similarity between Earth and the other bodies visible from Earth. Then, Father Angelo Secchi
Angelo Secchi (; 28 June 1818 – 26 February 1878) was an Italians, Italian Priesthood in the Catholic Church, Catholic priest and astronomer from the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Emilia-Romagna, Emilia. He was director of the observato ...
compared the spectral signature of the Sun with those of other stars, and found them virtually identical. The realisation that the Sun is a star led to a scientifically updated hypothesis that other stars could have planetary systems of their own, though this was not to be proven for nearly 140 years.
Observational cosmology
Observational cosmology is the study of the structure, the evolution and the origin of the universe through observation, using instruments such as telescopes and cosmic ray detectors.
Early observations
The science of physical cosmology as it is ...
began with attempts by William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
to describe the shape of the then known universe. In 1785, he proposed the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
was a disk, but assumed the Sun was at the center. This heliocentric theory was overturned by galactocentrism in the 1910s, after more observations by Harlow Shapley
Harlow Shapley (November 2, 1885 – October 20, 1972) was an American astronomer, who served as head of the Harvard College Observatory from 1921–1952, and political activist during the latter New Deal and Fair Deal.
Shapley used Cepheid var ...
placed the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a ...
relatively far away.
Extrasolar planets and the Kuiper belt
In 1992, the first evidence of aplanetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravity, gravitationally bound non-stellar Astronomical object, bodies in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although ...
other than our own was discovered, orbiting the pulsar
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its Poles of astronomical bodies#Magnetic poles, magnetic poles. This radiation can be obse ...
PSR B1257+12
PSR B1257+12, alternatively designated PSR J1300+1240, is a millisecond pulsar, from the Sun, in the constellation Virgo, rotating at about 161 times per second (faster than the blade of a blender). It is also named Lich, after a powerf ...
. Three years later, 51 Pegasi b
51 Pegasi b, officially named Dimidium (), is an extrasolar planet approximately away in the constellation of Pegasus. It was the first exoplanet to be discovered orbiting a main-sequence star, the Sun-like 51 Pegasi, and marked a breakthr ...
, the first extrasolar planet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first detect ...
around a Sunlike star, was discovered. NASA announced in March 2022 that the number of discovered exoplanets reached 5,000, of several types and sizes.
Also in 1992, astronomers David C. Jewitt of the University of Hawaii
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
and Jane Luu
Jane X. Luu (; born July 1963) is a Vietnamese-American astronomer and defense systems engineer. She was awarded the Kavli Prize (shared with David C. Jewitt and Michael Brown) for 2012 "for discovering and characterizing the Kuiper Belt and ...
of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
discovered Albion
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than "Britain" today. The name for Scot ...
. This object proved to be the first of a new population, which became known as the Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt ( ) is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
; an icy analogue to the asteroid belt of which such objects as Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
and Charon
In Greek mythology, Charon or Kharon ( ; ) is a psychopomp, the ferryman of the Greek underworld. He carries the souls of those who have been given funeral rites across the rivers Acheron and Styx, which separate the worlds of the living and ...
were deemed a part, the Kuiper belt objects (KBO).
Teams by Mike Brown, Chad Trujillo and David Rabinowitz
David Lincoln Rabinowitz (born 1960) is an American astronomer, discoverer of minor planets and researcher at Yale University.
Career
David Rabinowitz has built CCD cameras and software for the detection of near-Earth and Kuiper belt obje ...
discovered the trans-Neptunian object
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has an orbital semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (AU).
...
s (TNO) Quaoar
Quaoar (minor-planet designation: 50000 Quaoar) is a ringed dwarf planet in the Kuiper Belt, a ring of many icy planetesimals beyond Neptune. It has an elongated ellipsoidal shape with an average diameter of , about half the size of the dwarf ...
in 2002, Sedna in 2003, Orcus
Orcus was a god of the underworld, punisher of broken oaths in Etruscan and Roman mythology. As with Hades, the name of the god was also used for the underworld itself. Eventually, he was conflated with Dis Pater and Pluto.
A temple to Orcus ma ...
and Haumea
Haumea ( minor-planet designation: 136108 Haumea) is a dwarf planet located beyond Neptune's orbit. It was discovered in 2004 by a team headed by Mike Brown of Caltech at the Palomar Observatory, and formally announced in 2005 by a team heade ...
in 2004 and Makemake
Makemake ( minor-planet designation: 136472 Makemake) is a dwarf planet and the largest of what is known as the classical population of Kuiper belt objects, with a diameter approximately that of Saturn's moon Iapetus, or 60% that of Pluto. It ...
in 2005, part of the most notable KBOs, some now regarded as dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...
s. Also in 2005 they announced the discovery of Eris, a scattered disc
The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small Solar System bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc obj ...
object initially thought to be larger than Pluto, which would make it the largest object discovered in orbit around the Sun since Neptune. ''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institut ...
'' fly-by of Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
in July 2015 resulted in more-accurate measurements of Pluto, which is slightly larger, though less massive, than Eris.
Observations by radar


Radar astronomy
Radar astronomy is a technique of observing nearby astronomical objects by reflecting radio waves or microwaves off target objects and analyzing their reflections. Radar astronomy differs from ''radio astronomy'' in that the latter is a passive ob ...
is the technique for observing nearby astronomical object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are of ...
s by reflecting radio wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths g ...
s or microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
s off target objects and analyzing their reflections, which provide information about the shapes and surface properties of solid bodies, unavailable by other means. Radar can also accurately measure the position and track the movement of such bodies, specially when they are small, as comets and asteroids, as well as to determine distances between objects in the Solar System. In certain cases radar imaging
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), direction (geometry), direction (azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to det ...
has produced images with up to 7.5-meter resolution.
The Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
is comparatively close and was studied by radar soon after the invention of the technique in 1946, mainly precise measurements of its distance and its surface roughness.
Other bodies that have been observed by this means include:
* Mercury – Improved value for the distance from the Earth observed (test of theory of General relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of grav ...
). Rotational period, libration
In lunar astronomy, libration is the cyclic variation in the apparent position of the Moon that is perceived by observers on the Earth and caused by changes between the orbital and rotational planes of the moon. It causes an observer to see ...
, surface mapping, study of polar regions.
* Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
– First radar detection in 1961. Measurement of the size of the astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its m ...
. Rotation period, gross surface properties. The '' Magellan'' mission mapped the entire planet using a radar altimeter
A radar altimeter (RA), also called a radio altimeter (RALT), electronic altimeter, reflection altimeter, or low-range radio altimeter (LRRA), measures altitude above the terrain presently beneath an aircraft or spacecraft by timing how long it t ...
, a task that cannot be made by optical means due to the opaque atmosphere of this planet.
* Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
– Numerous airborne and spacecraft radars have mapped the entire planet, for various purposes. One example is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission
The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort that obtained digital elevation models on a near-global scale from 56th parallel south, 56°S to 60th parallel north, 60°N, to generate the most complete high-resol ...
, which mapped large parts of the surface of Earth at 30 m resolution.
* Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
– Mapping of surface roughness from Arecibo Observatory
The Arecibo Observatory, also known as the National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center (NAIC) and formerly known as the Arecibo Ionosphere Observatory, is an observatory in Barrio Esperanza, Arecibo, Puerto Rico owned by the US National Science F ...
. The ''Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission by the European Space Agency, European Space Agency (ESA) exploring the planet Mars and its moons since 2003, and the first planetary mission attempted by ESA.
''Mars Express'' consisted of two ...
'' mission carries a ground-penetrating radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, asphalt, metals, pipes, cables ...
.
* Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
system – Survey of moon Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliffs, Alexan ...
.
* Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
system – Rings and Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
from Arecibo Observatory
The Arecibo Observatory, also known as the National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center (NAIC) and formerly known as the Arecibo Ionosphere Observatory, is an observatory in Barrio Esperanza, Arecibo, Puerto Rico owned by the US National Science F ...
. Mapping of Titan's surface and observations of other moons from the Cassini spacecraft. As Venus, Titan also possesses an opaque atmosphere.
By 2018, there have been radar observations of 138 main belt asteroids, 789 near-Earth asteroid
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit aro ...
s, and 20 comets, including 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann.
Observations by spacecraft
 Since the start of the
Since the start of the Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the space race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the launch of Sputnik 1 on October 4, 1957, and co ...
, a great deal of exploration has been performed by robotic spacecraft
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which t ...
missions that have been organized and executed by various space agencies.
All planets in the Solar System, plus their major moons along some asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s and comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s, have now been visited to varying degrees by spacecraft launched from Earth. Through these uncrewed missions, humans have been able to get close-up photographs of all the planets and, in the case of landers, perform tests of the soils and atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
s of some.
The first artificial object sent into space was the Soviet satellite ''Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (, , ''Satellite 1''), sometimes referred to as simply Sputnik, was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program ...
'', launched on 4 October 1957, which successfully orbited Earth until 4 January the following year. The American probe ''Explorer 6
Explorer 6, or S-2, was a NASA satellite, launched on 7 August 1959, at 14:24:20 GMT. It was a small, spherical satellite designed to study trapped radiation of various energies, galactic cosmic rays, geomagnetism, radio propagation in the ...
'', launched in 1959, was the first satellite to image Earth from space.
Flybys
The first successful probe to fly by another Solar System body was ''Luna 1
''Luna 1'', also known as ''Mechta'' ( , ''Literal translation, lit.'': ''Dream''), ''E-1 No.4'' and ''First Lunar Rover'', was the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of Earth's Moon, the first spacecraft to leave Earth's orbit, and the fi ...
'', which sped past the Moon in 1959. Originally meant to impact with the Moon, it instead missed its target and became the first artificial object to orbit the Sun. ''Mariner 2
Mariner 2 (Mariner-Venus 1962), an American space probe to Venus, was the first robotic space probe to report successfully from a planetary encounter. The first successful spacecraft in the NASA Mariner program, it was a simplified version of t ...
'' was the first planetary flyby
A planetary flyby is the act of sending a space probe past a planet or a dwarf planet close enough to record scientific data. This is a subset of the overall concept of a flyby in spaceflight.
The first flyby of another planet with a functionin ...
, passing Venus in 1962. The first successful flyby of Mars was made by ''Mariner 4
Mariner 4 (Mariner C-3, together with Mariner 3 known as Mariner-Mars 1964) was the Mariner program, fourth in a series of spacecraft intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode. It was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations ...
'' in 1965. ''Mariner 10
''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets.
''Marin ...
'' first passed Mercury in 1974.
The first probe to explore the outer planets was ''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is a NASA space probe launched in 1972 that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to achieve the escape velocity needed ...
'', which flew by Jupiter in 1973. ''Pioneer 11
''Pioneer 11'' (also known as ''Pioneer G'') is a NASA robotic space probe launched on April 5, 1973, to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, the solar wind, and cosmic rays. It was the first probe to Exploration ...
'' was the first to visit Saturn, in 1979. The Voyager
Voyager may refer to:
Computing and communications
* LG Voyager, a mobile phone model manufactured by LG Electronics
* NCR Voyager, a computer platform produced by NCR Corporation
* Voyager (computer worm), a computer worm affecting Oracle ...
probes performed a Grand Tour of the outer planets following their launch in 1977, with both probes passing Jupiter in 1979 and Saturn in 1980–1981. ''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, as a part of the Voyager program. It was launched on a trajectory towards the gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn) and enabled further encounters with the ice giants (Uranus and ...
'' then went on to make close approaches to Uranus in 1986 and Neptune in 1989. The two Voyager probes are now far beyond Neptune's orbit, and are on course to find and study the termination shock
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere, and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, tailed bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding in ...
, heliosheath, and heliopause. According to NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
, both Voyager probes have encountered the termination shock at a distance of approximately 93 AU from the Sun.
The first flyby of a comet occurred in 1985, when the ''International Cometary Explorer
The International Cometary Explorer (ICE) spacecraft, designed and launched as the International Sun-Earth Explorer-3 (ISEE-3) satellite, was launched on 12 August 1978 into a heliocentric orbit. It was one of three spacecraft, along with the m ...
'' (ICE) passed by the comet Giacobini–Zinner, whereas the first flybys of asteroids were conducted by the ''Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
'' space probe, which imaged both 951 Gaspra
951 Gaspra is an S-type asteroid, S-type asteroid that orbits very close to the inner edge of the asteroid belt. Gaspra was discovered by Russian astronomer G. N. Neujmin in 1916. Neujmin named it after Gaspra, a Black Sea retreat that was visite ...
(in 1991) and 243 Ida
243 Ida is an asteroid in the Koronis family of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 29 September 1884 by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at Vienna Observatory and named after Ida (nurse of Zeus), a nymph from Greek mythology. Later telesc ...
(in 1993) on its way to Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
.
Launched on January 19, 2006, the ''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institut ...
'' probe is the first human-made spacecraft to explore the Kuiper belt. This uncrewed mission flew by Pluto in July 2015. The mission was extended to observe a number of other Kuiper belt objects, including a close flyby of 486958 Arrokoth
486958 Arrokoth (Provisional designation in astronomy, provisional designation ; formerly nicknamed Ultima Thule) is a trans-Neptunian object located in the Kuiper belt. Arrokoth became the farthest and most primitive List of minor planet ...
on New Year's Day, 2019.
As of 2011, American scientists are concerned that exploration beyond the Asteroid Belt will hampered by a shortage of Plutonium-238
Plutonium-238 ( or Pu-238) is a radioactive isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 87.7 years.
Plutonium-238 is a very powerful alpha emitter; as alpha particles are easily blocked, this makes the plutonium-238 isotope suitable for usage ...
.
Orbiters, landers, rovers and flying probes
 In 1966, the Moon became the first Solar System body beyond Earth to be orbited by an
In 1966, the Moon became the first Solar System body beyond Earth to be orbited by an artificial satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scienti ...
(''Luna 10
Luna 10 (or Lunik 10) was a 1966 Soviet lunar robotic spacecraft mission in the Luna program. It was the first artificial satellite of the Moon, and any other body other than Earth and the Sun (in heliocentric orbit).
Luna 10 conducted extens ...
''), followed by Mars in 1971 (''Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from Spaceport Florida Launch Comp ...
''), Venus in 1975 (''Venera 9
Venera 9 (), manufacturer's designation: 4V-1 No. 660, was a Soviet uncrewed space mission to Venus. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. It was launched on June 8, 1975, at 02:38:00 UTC and had a mass of . The orbiter was the first sp ...
''), Jupiter in 1995 (''Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
''), the asteroid Eros
Eros (, ; ) is the Greek god of love and sex. The Romans referred to him as Cupid or Amor. In the earliest account, he is a primordial god, while in later accounts he is the child of Aphrodite.
He is usually presented as a handsome young ma ...
in 2000 (''NEAR Shoemaker
''Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous – Shoemaker'' (''NEAR Shoemaker''), renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene Merle Shoemaker, Eugene Shoemaker, was a Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe designed by the Johns ...
''), Saturn in 2004 (''Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, i ...
''), and Mercury and Vesta in 2011 (''MESSENGER
Messenger, Messengers, The Messenger or The Messengers may refer to:
People
* Courier, a person or company that delivers messages, packages, or mail
* Messenger (surname)
* Bicycle messenger, a bicyclist who transports packages through cities
* M ...
'' and ''Dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the diffuse sky radiation, appearance of indirect sunlight being Rayleigh scattering, scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc ha ...
'' respectively). ''Dawn'' was orbiting the asteroid–dwarf planet Ceres since 2015 and it is still there as of 2023, but it became inactive since 2018. In 2014 ''Rosetta
Rosetta ( ) or Rashid (, ; ) is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Rosetta Stone was discovered there in 1799.
Founded around the 9th century on the site of the ancient town of Bolbitine, R ...
'' spacecraft becomes the first comet orbiter, around Churyumov–Gerasimenko.
The first probe to land on another Solar System body was the Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
''Luna 2
''Luna 2'' (), originally named the Second Soviet Cosmic Rocket and nicknamed Lunik 2 in contemporaneous media, was the sixth of the Soviet Union's Luna programme spacecraft launched to the Moon, E-1 No.7. It was the first spacecraft Moon landi ...
'' probe, which impacted the Moon in 1959. Since then, increasingly distant planets have been reached, with probes landing on or impacting the surfaces of Venus in 1966 (''Venera 3
Venera 3 ( meaning ''Venus 3'') was a Venera program space probe that was built and launched by the Soviet Union to explore the surface of Venus. It was launched on 16 November 1965 at 04:19 UTC from Baikonur, Kazakhstan, USSR. The probe comp ...
''), Mars in 1971 (''Mars 3
Mars 3 was a robotic space probe of the Soviet Mars program, launched May 28, 1971, nine days after its twin spacecraft Mars 2. The probes were identical robotic spacecraft launched by Proton-K rockets with a Blok D upper stage, each consisti ...
'', although a fully successful landing didn't occur until ''Viking 1
''Viking 1'' was the first of two spacecraft, along with '' Viking 2'', each consisting of an orbiter and a lander, sent to Mars as part of NASA's Viking program. The lander touched down on Mars on July 20, 1976, the first successful Mars lan ...
'' in 1976), the asteroid Eros
Eros (, ; ) is the Greek god of love and sex. The Romans referred to him as Cupid or Amor. In the earliest account, he is a primordial god, while in later accounts he is the child of Aphrodite.
He is usually presented as a handsome young ma ...
in 2001 (''NEAR Shoemaker
''Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous – Shoemaker'' (''NEAR Shoemaker''), renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene Merle Shoemaker, Eugene Shoemaker, was a Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe designed by the Johns ...
''), Saturn's moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
in 2004 ('' Huygens''), the comets Tempel 1
Tempel 1 (official designation: 9P/Tempel) is a periodic Jupiter-family comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.6 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the ''Deep Impact'' space mission, which photogr ...
('' Deep Impact'') in 2005, and Churyumov–Gerasimenko (''Philae
The Philae temple complex (; , , Egyptian: ''p3-jw-rķ' or 'pA-jw-rq''; , ) is an island-based temple complex in the reservoir of the Aswan Low Dam, downstream of the Aswan Dam and Lake Nasser, Egypt.
Originally, the temple complex was ...
'') in 2014. The ''Galileo'' orbiter also dropped a probe into Jupiter's atmosphere in 1995, this was intended to descend as far as possible into the gas giant before being destroyed by heat and pressure.
, three bodies in the Solar System, the Moon, Mars and Ryugu have been visited by mobile rovers. The first robotic rover to visit another celestial body was the Soviet ''Lunokhod 1
''Lunokhod 1'' (Russian language, Russian: Луноход-1 "Moonwalker 1"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 203 ("Device 8EL No. 203") was the first rover (space exploration), robotic rover lunar rover, on the Moon and the first to freel ...
'', which landed on the Moon in 1970. The first to visit another planet was ''Sojourner
A sojourner is a person who resides temporarily in a place.
Sojourner may also refer to:
People
* Sojourner Truth (1797–1883), abolitionist and women's rights activist
* Albert Sojourner (1872–1951), member of the Mississippi House of Rep ...
'', which travelled 500 metres across the surface of Mars in 1997. The first flying probe on in Solar System was the Vega balloons in 1985, while first powered flight was undertook by '' Ingenuity'' in 2020. The only crewed rover to visit another world was NASA's Lunar Roving Vehicle
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is a Battery electric vehicle, battery-powered four-wheeled Rover (space exploration), rover used on the Moon in the last three missions of the American Apollo program (Apollo 15, 15, Apollo 16, 16, and Apollo 17 ...
, which traveled with Apollos 15, 16 and 17 between 1971 and 1972.
In 2022, the DART impactor crashed into Dimorphos
Dimorphos (formal designation (65803) Didymos I; provisional designation S/2003 (65803) 1) is a natural satellite or minor-planet moon, moon of the near-Earth object, near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a Binary asteroid, bina ...
, the minor-planet moon
A minor-planet moon is an astronomical object that orbits a minor planet as its natural satellite. , there are 457 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons (and binary objects, in general) are important ...
of the asteroid Didymos, with the explicit purpose of intentionally deviate (slightly) the orbit of a Solar System body for the first time ever, which it accomplished.
Sample return
 In some instances, both human and robotic explorers have taken physical samples of the visited bodies and return them back to Earth. Other extraterrestrial materials came to Earth naturally, as
In some instances, both human and robotic explorers have taken physical samples of the visited bodies and return them back to Earth. Other extraterrestrial materials came to Earth naturally, as meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
s, or became stuck to artificial satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation (GPS), broadcasting, scientifi ...
; they are specimens which also allows studying Solar System matter.
*Moon (various missions including Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
, Luna
Luna commonly refers to:
* Earth's Moon, named "Luna" in Latin, Spanish and other languages
* Luna (goddess)
In Sabine and ancient Roman religion and myth, Luna is the divine embodiment of the Moon (Latin ''Lūna'' ). She is often presented as t ...
and Chang'e
Chang'e ( ; ), originally known as Heng'e (), is the goddess of the Moon and wife of Hou Yi, the great archer. Renowned for her beauty, Chang'e is also known for her ascending to the Moon with her pet Yu Tu, the Moon Rabbit and living in the Mo ...
).
*Asteroid (''Hayabusa
was a robotic spacecraft developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to return a sample of material from a small near-Earth asteroid named 25143 Itokawa to Earth for further analysis.
''Hayabusa'', formerly known as MUSES-C ...
, Osiris Rex, Tianwen-2
''Tianwen-2'' () is a Chinese asteroid sample return and comet exploration mission that launched on 28 May 2025. China National Space Agency (CNSA) plans for the probe to return samples from asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa in 2027. After the ...
and Hayabusa2
is an asteroid sample-return mission operated by the Japanese state space agency JAXA. It is a successor to the ''Hayabusa'' mission, which returned asteroid samples for the first time in June 2010. ''Hayabusa2'' was launched on 3 December 2 ...
'').
*Comet dust ('' Stardust'').
*Solar wind (''Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of humankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Bo ...
'').
Spacecraft exploration
See also the categories for missions tocomets
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or coma surrounding the nucleus, an ...
, asteroids
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
, the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It orbits around Earth at an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth's diameter). The Moon rotates, with a rotation period ( lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period ( lunar ...
, and the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot Plasma (physics), plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as ...
.
Crewed exploration
 The first human being to reach space (defined as an altitude of over 100 km) and to orbit Earth was
The first human being to reach space (defined as an altitude of over 100 km) and to orbit Earth was Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed sp ...
, a Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
cosmonaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spa ...
who was launched in Vostok 1
Vostok 1 (, ) was the first spaceflight of the Vostok programme and the first human spaceflight, human orbital spaceflight in history. The Vostok 3KA space capsule was launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome on 12 April 1961, with Soviet astronaut, c ...
on April 12, 1961. The first human to walk on the surface of another Solar System body was Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aerospace engineering, aeronautical engineer who, in 1969, became the Apollo 11#Lunar surface operations, first person to walk on the Moon. He was al ...
, who stepped onto the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
on July 21, 1969 during the Apollo 11
Apollo 11 was a spaceflight conducted from July 16 to 24, 1969, by the United States and launched by NASA. It marked the first time that humans Moon landing, landed on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and Lunar Module pilot Buzz Aldrin l ...
mission. From then until 1972, there were five more Moon landings. The United States' reusable Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
flew 135 missions between 1981 and 2011. Two of the five shuttles were destroyed in accidents.
The first orbital space station
A space station (or orbital station) is a spacecraft which remains orbital spaceflight, in orbit and human spaceflight, hosts humans for extended periods of time. It therefore is an artificial satellite featuring space habitat (facility), habitat ...
to host more than one crew was NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructe ...
, which successfully held three crews from 1973 to 1974. True human settlement in space began with the Soviet space station Mir
''Mir'' (, ; ) was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, first by the Soviet Union and later by the Russia, Russian Federation. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to ...
, which was continuously occupied for close to ten years, from 1989 to 1999. Its successor, the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
, has maintained a continuous human presence in space since 2001. In 2004, U.S. President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he i ...
announced the Vision for Space Exploration
The Vision for Space Exploration (VSE) was a plan for space exploration announced on January 14, 2004 by President George W. Bush. It was conceived as a response to the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster, the state of human spaceflight at NASA, ...
, which called for a replacement for the aging Shuttle, a return to the Moon and, ultimately, a crewed mission to Mars.
Exploration by country
Legend☄ – orbit or flyby
❏ - Space observatory
Ѫ – successful landing on an object
⚗ – sample return
⚘ – crewed mission
ↂ – permanent inhabited space stationonly stations with at least one module built by the country in question are counted
Exploration survey
;Bodies imaged up closeSun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
(star) Jupiter and its shrunken Great Red Spot.jpg,
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
(planet) Top view of the rings of Saturn by Cassini - October 10, 2013.jpg,
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
(planet) Uranus Voyager2 color calibrated.png,
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
(planet) Neptune Voyager2 color calibrated.png,
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
(planet) The Earth seen from Apollo 17.jpg,
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
(planet) Venus_2_Approach_Image.jpg,
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
(planet) Mars_-_August_30_2021_-_Flickr_-_Kevin_M._Gill.png,
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
(planet) Ganymede_-_Perijove_34_Composite.png, Ganymede
(moon of Jupiter) Titan in true color.jpg,
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
(moon of Saturn) Mercury in color - Prockter07-edit1.jpg, Mercury
(planet) Callisto_-_July_8_1979_(38926064465).jpg,
Callisto
CALLISTO (''Cooperative Action Leading to Launcher Innovation in Stage Toss-back Operations'') is a reusable VTVL Prototype, demonstrator propelled by a small 40 kN Japanese LOX-LH2 rocket engine. It is being developed jointly by the CNES, French ...
(moon of Jupiter) Io highest resolution true color.jpg, Io
(moon of Jupiter) FullMoon2010.jpg,
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
(moon of Earth) Europa_in_natural_color.png,
Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliffs, Alexan ...
(moon of Jupiter) Triton moon mosaic Voyager 2 (large).jpg,
Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus' ...
(moon of Neptune)
Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus' ...
(moon of Neptune) Pluto in True Color - High-Res.jpg,
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
(dwarf planet) Titania (moon) color, edited.jpg, Titania
(moon of Uranus) PIA07763 Rhea full globe5.jpg, Rhea
(moon of Saturn) Voyager 2 picture of Oberon.jpg,
Oberon
Oberon () is a king of the fairy, fairies in Middle Ages, medieval and Renaissance literature. He is best known as a character in William Shakespeare's play ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'', in which he is King of the Fairies and spouse of Titania ...
(moon of Uranus) Iapetus as seen by the Cassini probe - 20071008.jpg,
Iapetus
In Greek mythology, Iapetus (; ; ), also Japetus, is a Titan, the son of Uranus and Gaia and father of Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus, and Menoetius. He was also called the father of Buphagus and Anchiale in other sources.
Iapetus was linked ...
(moon of Saturn) Charon in True Color - High-Res.jpg,
Charon
In Greek mythology, Charon or Kharon ( ; ) is a psychopomp, the ferryman of the Greek underworld. He carries the souls of those who have been given funeral rites across the rivers Acheron and Styx, which separate the worlds of the living and ...
(moon of Pluto) PIA00040 Umbrielx2.47.jpg,
Umbriel
Umbriel () is the third-largest moon of Uranus. It was discovered on October 24, 1851, by William Lassell at the same time as neighboring moon Ariel. It was named after a character in Alexander Pope's 1712 poem '' The Rape of the Lock''. Umb ...
(moon of Uranus) Ariel in monochrome.jpg,
Ariel
Ariel may refer to:
Film and television
*Ariel Award, a Mexican Academy of Film award
* ''Ariel'' (film), a 1988 Finnish film by Aki Kaurismäki
*, a Russian film directed by Yevgeni Kotov
* ''ARIEL Visual'' and ''ARIEL Deluxe'', a 1989 and 1991 ...
(moon of Uranus) Dione in natural light.jpg, Dione
(moon of Saturn) PIA18317-SaturnMoon-Tethys-Cassini-20150411.jpg, Tethys
(moon of Saturn) Ceres - RC3 - Haulani Crater (22381131691) (cropped).jpg, Ceres
(dwarf planet) Vesta_in_natural_color.jpg, Vesta
(belt asteroid) Potw1749a Pallas crop.png,
Pallas
Pallas may refer to:
Astronomy
* 2 Pallas asteroid
** Pallas family, a group of asteroids that includes 2 Pallas
* Pallas (crater), a crater on Earth's moon
Mythology
* Pallas (Giant), a son of Uranus and Gaia, killed and flayed by Athena
* Pa ...
(belt asteroid) PIA17202 - Approaching Enceladus.jpg,
Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn and the 18th-largest in the Solar System. It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. It is covered by clean, freshly deposited snow hundreds of meters thick, ...
(moon of Saturn) Miranda - January 24 1986 (30906319004).jpg, Miranda
(moon of Uranus) SPHERE image of Hygiea.jpg, Hygiea
(belt asteroid) Proteus (Voyager 2).jpg,
Proteus
In Greek mythology, Proteus ( ; ) is an early prophetic sea god or god of rivers and oceanic bodies of water, one of several deities whom Homer calls the "Old Man of the Sea" (''hálios gérôn''). Some who ascribe a specific domain to Prote ...
(moon of Neptune) Mimas Cassini.jpg,
Mimas
Mimas, also designated Saturn I, is the seventh-largest natural satellite of Saturn. With a mean diameter of , Mimas is the smallest astronomical body known to be roughly rounded in shape due to its own gravity. Mimas's low density, 1.15 ...
(moon of Saturn) Hyperion true.jpg, Hyperion
(moon of Saturn) Iris asteroid eso.jpg, Iris
(belt asteroid) Phoebe cassini.jpg, Phoebe
(moon of Saturn) PIA12714 Janus crop.jpg,
Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janus (''Ianu ...
(moon of Saturn) Amalthea (moon).png, Amalthea
(moon of Jupiter) PIA09813 Epimetheus S. polar region.jpg,
Epimetheus
In Greek mythology, Epimetheus (; ) is the brother of Prometheus, the pair serving "as representatives of mankind". Both sons of the Titan Iapetus, while Prometheus ("foresight") is ingeniously clever, Epimetheus ("hindsight") is inept and fool ...
(moon of Saturn) Thebe.jpg, Thebe
(moon of Jupiter) Rosetta triumphs at asteroid Lutetia.jpg,
Lutetia
Lutetia, ( , ; ) also known as and ( ; ; ), was a Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo–Roman town and the predecessor of modern-day Paris. Traces of an earlier Neolithic settlement () have been found nearby, and a larger settlement was established ...
(belt asteroid) Prometheus 12-26-09a.jpg,
Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titans, Titan. He is best known for defying the Olympian gods by taking theft of fire, fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technol ...
(moon of Saturn) PIA21055 - Pandora Up Close.jpg,
Pandora
In Greek mythology, Pandora was the first human woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus. As Hesiod related it, each god cooperated by giving her unique gifts. Her other name—inscribed against her figure on a white-ground '' ky ...
(moon of Saturn) (253) mathilde crop.jpg, Mathilde
(belt asteroid) Hydra Enhanced Color.jpg, Hydra
(moon of Pluto) Nix best view.jpg, Nix
(moon of Pluto) Leading hemisphere of Helene - 20110618.jpg, Helene
(moon of Saturn) 243 Ida large.jpg, Ida
(belt asteroid) Atlas color PIA21449.png,
Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
(moon of Saturn) Pan color PIA21449.png, Pan
(moon of Saturn) Telesto cassini closeup.jpg, Telesto
(moon of Saturn) UltimaThule CA06 color 20190516.png, Arrokoth
(Kuiper belt object) Calypso N1644755236 1.jpg, Calypso
(moon of Saturn) Phobos colour 2008.jpg, Phobos
(moon of Mars) Eros - PIA02923 (color).jpg,
Eros
Eros (, ; ) is the Greek god of love and sex. The Romans referred to him as Cupid or Amor. In the earliest account, he is a primordial god, while in later accounts he is the child of Aphrodite.
He is usually presented as a handsome young ma ...
(near-Earth asteroid) Deimos-MRO.jpg,
Deimos
Deimos, a Greek word for ''dread'', may refer to:
In general
* Deimos (deity), one of the sons of Ares and Aphrodite in Greek mythology
* Deimos (moon), the smaller and outermost of Mars' two natural satellites
Fictional characters
* Deimos (comi ...
(moon of Mars) 951 Gaspra.jpg, Gaspra
(belt asteroid) PIA02127.jpg,
Tempel 1
Tempel 1 (official designation: 9P/Tempel) is a periodic Jupiter-family comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.6 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the ''Deep Impact'' space mission, which photogr ...
(comet) 2867 Šteins by Rosetta (reprocessed).png, Šteins
(belt asteroid) Daphnis (Saturn's Moon).jpg,
Daphnis
In Greek mythology, Daphnis (; , from , ''daphne'', "Bay Laurel") was a legendary Sicilian cowherd who was said to be the inventor of pastoral poetry. According to Diodorus the Sicilian (1st century BC), Daphnis was born in the Heraean Mountai ...
(moon of Saturn) Comet Borrelly Nucleus.jpg,
Borrelly
Alphonse Louis Nicolas Borrelly (December 8, 1842 – February 28, 1926) was a French astronomer born in Roquemaure, Gard.
He joined the Marseille Observatory in 1864. In the course of his career, he discovered a number of asteroids and comets, ...
(comet) Asteroid-donaldjohanson-flyby.png, Donaldjohanson
(asteroid) Comet 67P on 19 September 2014 NavCam mosaic.jpg, Churyumov–
Gerasimenko
(comet) Wild2 3.jpg,
Wild 2
Comet 81P/Wild, also known as Wild 2 (pronounced "vilt two") ( ), is a comet with a period of 6.4 years named after Swiss astronomer Paul Wild, who discovered it on January 6, 1978, using a 40-cm Schmidt telescope at Zimmerwald, Switzerland.
F ...
(comet) Asteroid 4179 Toutatis close-up.jpg,
Toutatis
Teutates (spelled variously Toutatis, Totatis, Totates) is a Celtic god attested in literary and epigraphic sources. His name, which is derived from a proto-Celtic word meaning "tribe", suggests he was a national god, tribal deity.
The Roman po ...
(near-Earth asteroid) Methone PIA14633.jpg, Methone
(moon of Saturn) Comet Hartley 2 (super crop).jpg, Hartley 2
(comet) Dactyl-HiRes.jpg, Dactyl
(moon of Ida) Ryugu colored.jpg, Ryugu
(near-Earth asteroid) Dinkinesh First Look L'LORRI.png, Dinkinesh
(belt asteroid) Didymos-only.png, Didymos
(near-Earth asteroid) Bennu mosaic OSIRIS-REx (square).png,
Bennu
Bennu () is an ancient Egyptian deity linked with the Sun, creation, and rebirth. He may have been the original inspiration for the phoenix legends that developed in Greek mythology.
Roles
According to Egyptian mythology, Bennu was a self-crea ...
(near-Earth asteroid) Itokawa06 hayabusa.jpg, Itokawa
(near-Earth asteroid) Stacked image of Dimorphos true orientation.jpg,
Dimorphos
Dimorphos (formal designation (65803) Didymos I; provisional designation S/2003 (65803) 1) is a natural satellite or minor-planet moon, moon of the near-Earth object, near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a Binary asteroid, bina ...
(moon of Didymos)
Near-Earth object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun ( perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit a ...
".
See also
* Astronomy ** Timeline of Solar System astronomy **Timeline of discovery of Solar System planets and their moons
The timeline of discovery of Solar System planets and their natural satellites charts the progress of the discovery of new bodies over history. Each object is listed in chronological order of its discovery (multiple dates occur when the moments o ...
**List of former planets
This is a list of astronomical objects formerly widely considered ''planets'' under any of the various definitions of this word in the history of astronomy. As the definition of planet, definition of ''planet'' has evolved, the wikt:en:de facto#Eng ...
**List of hypothetical Solar System objects
A hypothetical Solar System object is a planet, natural satellite, subsatellite or similar body in the Solar System whose existence is not known, but has been inferred from observational scientific evidence. Over the years a number of hypothetic ...
in astronomy
**Fixed stars
In astronomy, the fixed stars () are the luminary points, mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background. This is in contrast to those lights visible to the naked eye, name ...
** Historical models of the Solar System
* Exploration
**Timeline of spaceflight
This is a timeline of known spaceflights, both crewed and uncrewed, sorted chronologically by launch date. Due to its large size, the timeline has been split into smaller articles, one for each year since 1951. There is a separate list for ...
**Timeline of space exploration
This is a timeline of space exploration which includes notable achievements, first accomplishments and milestones in humanity's exploration of outer space.
This timeline generally does not distinguish achievements by a specific country or privat ...
**Timeline of Solar System exploration
This is a timeline of Solar System exploration ordering events in the exploration of the Solar System by date of spacecraft launch.
It includes:
*All spacecraft that have left Earth orbit for the purposes of Solar System exploration (or were l ...
**Timeline of first images of Earth from space
Photography and other imagery of planet Earth from outer space started in the 1940s, first from rockets in suborbital flight, subsequently from satellites around Earth, and then from spacecraft beyond Earth's orbit.
Timeline
See also
* L ...
**List of Solar System probes
This is a list of space probes that have left Earth orbit (or were launched with that intention but failed), organized by their planned destination. It includes planetary probes, solar probes, and probes to asteroids and comets. Flybys (such as ...
References
Bibliography
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Discovery And Exploration Of The Solar System Solar System