Solanum dulcamara on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Solanum dulcamara'' is a
 It is native to northern Africa, Europe, and Asia, but has spread throughout the world. The plant is relatively important in the diet of some species of birds such as European
It is native to northern Africa, Europe, and Asia, but has spread throughout the world. The plant is relatively important in the diet of some species of birds such as European
File:Bitterweet Nightshade 2.jpg, Flowers,
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselv ...
in the genus ''Solanum
''Solanum'' is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, which include three food crops of high economic importance: the potato, the tomato and the eggplant (aubergine, brinjal). It is the largest genus in the nightshade family Solanaceae ...
'' (which also includes the potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
and the tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
) of the family Solanaceae
The Solanaceae , or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and orn ...
. Common names include bittersweet, bittersweet nightshade, bitter nightshade, blue bindweed, Amara Dulcis, climbing nightshade, felonwort, fellenwort, felonwood, poisonberry, poisonflower, scarlet berry, snakeberry, trailing bittersweet, trailing nightshade, violet bloom, and woody nightshade.
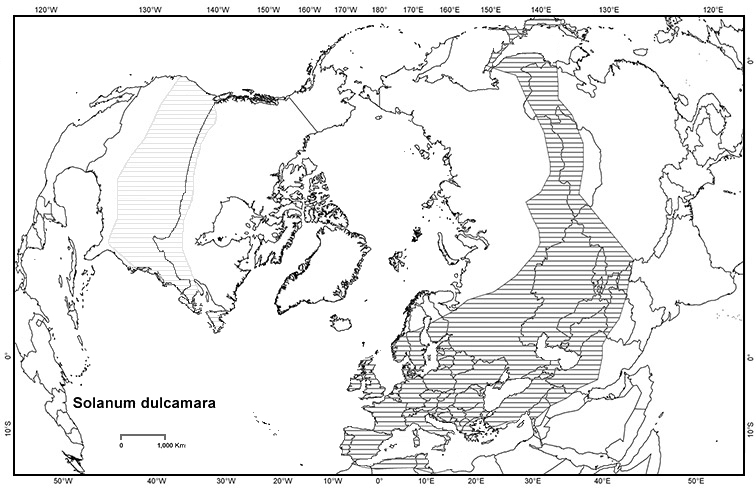
It is native to Europe and Asia, and widely naturalised elsewhere, including North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
.
Overview
It occurs in a very wide range ofhabitats
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
, from woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
s to scrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominance (ecology), dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, Herbaceous plant, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or ...
, hedge
A hedge or hedgerow is a line of closely spaced shrubs and sometimes trees, planted and trained to form a barrier or to mark the boundary of an area, such as between neighbouring properties. Hedges that are used to separate a road from adjoini ...
s and marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
es.
''Solanum dulcamara'' is a very woody herbaceous
Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials.
Definitions of "herb" and "herbaceous"
The fourth edition of t ...
perennial
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also wide ...
vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselv ...
, which scrambles over other plants, capable of reaching a height of 4 m where suitable support is available, but more often 1–2 m high. The leaves are 4–12 cm long, roughly arrowhead-shaped, and often lobed at the base. The flowers are in loose clusters of 3–20, 1–1.5 cm across, star-shaped, with five purple petals and yellow stamens and style pointing forward. The fruit is an ovoid red berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, raspb ...
about 1 cm long, soft and juicy, with the aspect and odour of a tiny tomato, and edible for some birds, which disperse the seeds widely. However, the berry is poisonous to humans and livestock, and the berry's attractive and familiar look make it dangerous for children.
 It is native to northern Africa, Europe, and Asia, but has spread throughout the world. The plant is relatively important in the diet of some species of birds such as European
It is native to northern Africa, Europe, and Asia, but has spread throughout the world. The plant is relatively important in the diet of some species of birds such as European thrushes
The thrushes are a passerine bird family, Turdidae, with a worldwide distribution. The family was once much larger before biologists reclassified the former subfamily Saxicolinae, which includes the chats and European robins, as Old World flycat ...
, which feed on its fruits, being immune to its poisons, and scatter the seeds abroad. It grows in all types of terrain with a preference for wetlands and the understory
In forestry and ecology, understory (American English), or understorey (Commonwealth English), also known as underbrush or undergrowth, includes plant life growing beneath the forest canopy without penetrating it to any great extent, but abov ...
of riparian forests
A riparian forest or riparian woodland is a forested or wooded area of land adjacent to a body of water such as a river, stream, pond, lake, marshland, estuary, canal, sink or reservoir.
Etymology
The term riparian comes from the Latin word ' ...
. Along with other climbers, it creates a dark and impenetrable shelter for varied animals. The plant grows well in dark areas in places where it can receive the light of morning or afternoon. An area receiving bright light for many hours reduces their development. It grows more easily in rich wet soils with plenty of nitrogen. When grown for medicinal purposes, it is best grown in a dry, exposed environment.
It is a nonnative species in the United States.
History
''Solanum dulcamara'' has been valued byherbalists
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remed ...
since ancient Greek times. In the Middle Ages the plant was thought to be effective against witchcraft, and was sometimes hung around the neck of cattle to protect them from the "evil eye
The Evil Eye ( grc, ὀφθαλμὸς βάσκανος; grc-koi, ὀφθαλμὸς πονηρός; el, (κακό) μάτι; he, עַיִן הָרָע, ; Romanian: ''Deochi''; it, malocchio; es, mal de ojo; pt, mau-olhado, olho gordo; ar ...
".
John Gerard
John Gerard (also John Gerarde, c. 1545–1612) was an English herbalist with a large garden in Holborn, now part of London. His 1,484-page illustrated ''Herball, or Generall Historie of Plantes'', first published in 1597, became a popular gard ...
's ''Herball'' (1597) states that "the juice is good for those that have fallen from high places, and have been thereby bruised or beaten, for it is thought to dissolve blood congealed or cluttered anywhere in the intrals and to heale the hurt places."
Biological activity
This plant is one of the less poisonous members of the Solanaceae. Instances of poisoning in humans are very rare on account of the fruit's intensely bitter taste. Incidentally, the fruit has been reported to have a sweet aftertaste, hence the vernacular name ''bittersweet''. The poison in this species is believed to be solanine. The alkaloids,solanine
Solanine is a glycoalkaloid poison found in species of the nightshade family within the genus ''Solanum'', such as the potato (''Solanum tuberosum''), the tomato (''Solanum lycopersicum''), and the eggplant (''Solanum melongena''). It can occu ...
(from unripe fruits), solasodine
Solasodine is a poisonous alkaloid chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae such as potatoes and tomatoes. Solasonine and solamargine are glycoalkaloid derivatives of solasodine. Solasodine is teratogenic to hamster fetus ...
(from flowers) and beta-solamarine (from roots) have been found to inhibit the growth of '' E. coli'' and '' S. aureus''.
Solanine and solasodine extracted from ''Solanum dulcamara'' showed antidermatophytic activity against ''Chrysosporium indicum'', ''Trichophyton mentagrophytes
''Trichophyton mentagrophytes'' is a species in the fungal genus ''Trichophyton''. It is one of three common fungi which cause ringworm in companion animals. It is also the second-most commonly isolated fungus causing tinea infections in humans, ...
'' and ''T. simil'', thus it may cure ringworm
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple a ...
.
The stems are approved by the German Commission E for external use as supportive therapy in chronic eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the Human skin, skin, typically characterized by itchiness, erythema, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become lichenification, thick ...
.
Medicinal use
''Solanum dulcamara'' has a variety of documented medicinal uses, all of which are advised to be approached with proper caution as the entirety of the plant is considered to be poisonous. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally. There have only been records of medicinal use for adults (not children) and it is possible to be allergic to ''Solanum dulcamara;'' medicinal use is not advised in these cases.Use of stem
The stem of ''Solanum dulcamara'' is believed to be considerably less poisonous than the rest of the plant, and it has mostly been used in treatment for conditions of the skin. There are records of it being used to treat mild recurrenteczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the Human skin, skin, typically characterized by itchiness, erythema, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become lichenification, thick ...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete ...
, scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei''. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin ...
, and dermatomycosis
A dermatomycosis is a skin disease caused by a fungus.
The most frequent form is dermatophytosis (ringworm, tinea).
Another example is cutaneous candidiasis. These fungal infections impair superficial layers of the skin, hair and nails.
Litera ...
. Stems are harvested when they do not yet have leaves (or the leaves have already fallen) and are shredded into small pieces. They are mostly known to be applied in the form of liquid onto the skin, but infusing it into a drink is also possible, though not recommended. The stem has also been used in treatment for bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
, asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
, and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
.
Use of leaves, fruit, and root
The leaves of ''Solanum dulcamara'' have been known to treatwarts
Warts are typically small, rough, hard growths that are similar in color to the rest of the skin. They typically do not result in other symptoms, except when on the bottom of the feet, where they may be painful. While they usually occur on the ...
and tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
, while the fruit can treat conditions of the respiratory tract and joints. It has been documented that Indigenous people of North America used the roots for relief of fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
and nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
.
Symbolism
''Solanum dulcamara'' has been symbolized withfidelity
Fidelity is the quality of faithfulness or loyalty. Its original meaning regarded duty in a broader sense than the related concept of ''fealty''. Both derive from the Latin word ''fidēlis'', meaning "faithful or loyal". In the City of London f ...
. This is due to its distinct property of extreme bitterness to surprising sweetness, hence its common name "bittersweet." This symbolism is seen in Christian art from the Middle Ages as well as in bridal wreaths.
Bittersweet exists on a balance between sweet and bitter, medicine and poison, life and death; lending it to be a common metaphor. Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
has been known to employ this metaphor in dramas such as ''Macbeth
''Macbeth'' (, full title ''The Tragedie of Macbeth'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. It is thought to have been first performed in 1606. It dramatises the damaging physical and psychological effects of political ambition on those w ...
and'' ''The Winter's Tale
''The Winter's Tale'' is a play by William Shakespeare originally published in the First Folio of 1623. Although it was grouped among the comedies, many modern editors have relabelled the play as one of Shakespeare's late romances. Some criti ...
.''
Perhaps this parallelism has been used more directly by Italian composer Gaetano Donizetti
Domenico Gaetano Maria Donizetti (29 November 1797 – 8 April 1848) was an Italian composer, best known for his almost 70 operas. Along with Gioachino Rossini and Vincenzo Bellini, he was a leading composer of the '' bel canto'' opera style dur ...
in his opera ''L'Elisir d'Amore
''L'elisir d'amore'' (''The Elixir of Love'', ) is a ' (opera buffa) in two acts by the Italian composer Gaetano Donizetti. Felice Romani wrote the Italian libretto, after Eugène Scribe's libretto for Daniel Auber's ' (1831). The opera premiere ...
(Love Elixir''). Here, a Dr. Dulcamara sells the protagonist, Nemorino, a love elixir at the cost of his fortune. However, this "love elixir" is actually just cheap red wine. Under the illusion of a love elixir (and drunkenness), Nemorino, is confident to profess his love to an indifferent woman, Adina. Upon independently learning of Nemorino's fidelity by spending his fortune, Adina subsequently falls in love as well. Dr. Dulcamara has bitterly sold a fake elixir that had turned out to have sweet consequences anyway. This happy unexpectedness is at the heart of ''Solanum dulcamara''.
Gallery
Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
File:SolanumDulcamara-bloem-sm.jpg, Flowers
File:XN Solanum dulcamara 01.jpg, Fruits
File:Solanum dulcamara, Fogner, Oslo..JPG, Solanum dulcamara
File:Bittersweet Nightshade.JPG, Bittersweet Nightshade in Clark County, Ohio.
File:Solanum dulcamara; Boston, Massachusetts.jpg, Bittersweet after rain in Boston, Massachusetts
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q147707 dulcamara Plants described in 1753 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Flora of Europe Flora of Asia Garden plants of Europe Poisonous plants