Smuggling in Iran on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Taxation in Iran is levied and collected by the Iranian National Tax Administration under the Ministry of Finance and Economic Affairs of the
 There are five categories of income earned by individuals. Each category is taxed separately and has its own computational rules.
*Salaries (tax rate for public sector employees: 10%; other sectors: 10-35%);A Review of the Iranian Tax System -2014
There are five categories of income earned by individuals. Each category is taxed separately and has its own computational rules.
*Salaries (tax rate for public sector employees: 10%; other sectors: 10-35%);A Review of the Iranian Tax System -2014
. Organization for Investment Economic and Technical Assistance of Iran. Retrieved March 14, 2014. *Income from professions, trades, and miscellaneous sources;
More info here
According to the Iranian direct tax rolls article no 84. all employees salary tax rate from the beginning of the 1396 fiscal year is as below: Every year annual salary exemption from tax will be announce by Iranian tax organization up to this level the salary tax rate is zero. Up to the 5 times more than annual exemption salary tax rate is 10%. In excess of above level salary tax rate is 20%. *Incidental or windfall earnings;
More info here
*Real estate income (see also under "Real estate tax" section below) *Income derived from agriculture (see also under "Tax exemptions" section below) For taxable income consisting of salary and benefits, employers are required to make the necessary tax deductions from their employees’ payroll and submit them to the tax authorities. However, when calculating taxable income, exemptions and deductions are allowed. As of 2009, only government employees were paying their fair share of income taxes. Individuals of Iranian nationality resident in
. Retrieved July 31, 2010 * Share transfers: the ''Tax Amendment'' has changed the regulations regarding calculation of tax on transfer of shares and their rights in Iranian corporate entities. **In the case of shares listed on the Tehran Stock Exchange (TSE) the tax on transfer of such shares and other rights is 0.5 per cent of the sales price. **In the case of transfer of the shares and their rights to other corporate entities (i.e. those not listed on the TSE) a flat rate of four per cent of value of the shares and rights transferred applies. No other taxes will be charged. The Amendment has removed the requirement to value the shares in this category.
various taxes and exemptions are applicable
including profit tax,
Algeria, Austria, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Belarus, Bulgaria, China, Croatia, France, Georgia, Germany, Indonesia, India, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Malaysia, Norway, Oman, Pakistan, Poland, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Serbia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Switzerland, Syria, Tajikistan, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Venezuela. Vietnam
Direct Taxation Law
*j) Banking and credit services rendered by banks, credit institutes and cooperatives, authorized interest-free loan funds and cooperative funds; *k) Public transportation services and urban and inter-city roads, railway, air and sea passenger transport services; *l) Hand woven carpets; *m) All types of research and training services, as stipulated in a By-Law to be approved by the Council of Ministers; *n) Animal and poultry feed; *o) Export of goods and services from official exit points. Any tax paid on account of such exports shall be reimbursed (as regards commodities) upon submitting a certification of the customs certifying the export of goods.

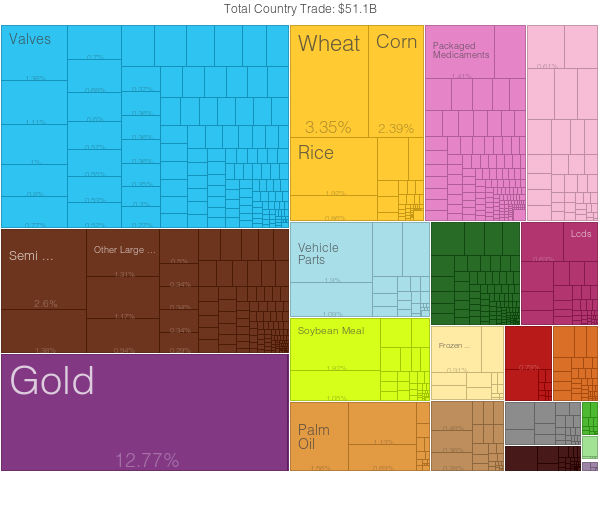
 As of 2015, there are a variety of items which are exempt from taxes being imported into Iran, such as:
*unprocessed agricultural products
*flour, bread, sugar, rice, milk, cheese
*machinery
*livestock and animals
*feedstock and pesticides.
As of 2015, there are a variety of items which are exempt from taxes being imported into Iran, such as:
*unprocessed agricultural products
*flour, bread, sugar, rice, milk, cheese
*machinery
*livestock and animals
*feedstock and pesticides.
the Islamic Republic of Iran Customs Administration
(IRICA),
Export-Import Regulations Act
the pre-exportation entry (temporary importation) of materials and goods to be used in producing, finishing, processing and packaging of exported goods are exempted from all import duties.
Government of Iran
The Government of the Islamic Republic of Iran ( fa, نظام جمهوری اسلامی ایران, Neẓām-e jomhūrī-e eslāmi-e Irān, known simply as ''Neẓām'' ( fa, نظام, lit=the system) among its supporters) is the ruling state ...
. In 2008, about 55% of the government's budget came from oil and natural gas revenues, the rest from taxes and fees. An estimated 50% of Iran's GDP was exempt from taxes in FY 2004. There are virtually millions of people who do not pay taxes in Iran and hence operate outside the formal economy. The fiscal year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many ...
begins on March 21 and ends on March 20 of the next year.
As part of the Iranian Economic Reform Plan
The economy of Iran is a mixed economy with a large state-owned sector and is the largest in the Middle East in terms of nominal GDP. It is the world's 21st largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). Some 60% of Iran's economy is centrally ...
, the government has proposed income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Ta ...
increases on traders in gold, steel, fabrics and other sectors, prompting several work stoppages by merchants. In 2011, the government announced that during the second phase of the economic reform plan, it aims to increase tax revenues, simplify tax calculation method, introduce double taxation, mechanize tax system, regulate tax exemptions and prevent tax evasion.
Government's budget
The government can increase its tax revenues 2.5 times by enacting tax reforms. As at 2012, taxes account for 43% of the government's revenues and 7% of Iran's GDP. The Expediency Council's report recommended increasing that share to 15% of the GDP. As of 2014, the share of direct taxes from the total tax revenues was around 70%. Top ten percent earners in Iranian society pay 3% of all income taxes, while in the United States the top 10% pay more than 70% of the totalincome tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Ta ...
es. Contradicting this, the head of the Majlis
( ar, المجلس, pl. ') is an Arabic term meaning "sitting room", used to describe various types of special gatherings among common interest groups of administrative, social or religious nature in countries with linguistic or cultural conne ...
Economic Commission says that 85% of Iran's tax revenues “come from barely 3% of taxpayers”.
Tax evasion
According to theExpediency Council
The Expediency Discernment Council of the System ( fa, مجمع تشخیص مصلحت نظام ''Majma'-e Taškhīs-e Maslahat-e Nezām'') is an administrative assembly appointed by the Supreme Leader and was created upon the revision to the Co ...
, more than 60% of economic activity in Iran avoids or evades taxation: 40% of the economic activity falls under an exemption and the remaining 21% are conducted off-the-books (2012). Iran is losing between $12–20 billion a year through tax avoidance and evasion. However the Iranian National Tax Administration only identified and collected through audit unpaid taxes worth 184 trillion rials ($1.5 billion) in FY 2018. Starting in 2015, Iran's parliament decided to tax Setad and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC; fa, سپاه پاسداران انقلاب اسلامی, Sepāh-e Pāsdārān-e Enghelāb-e Eslāmi, lit=Army of Guardians of the Islamic Revolution also Sepāh or Pasdaran for short) is a branch o ...
.
Tax evaders typically are either involved in activities in the gray sector of economy or in the underground market which they do not divulge. Others are engaged in smuggling and the black market. The loses are equivalent to 20% to 25% of the country's gross domestic product revenue. In 2014, international medias reported Iranian nationals and companies to be listed among the tax evaders in Switzerland and other offshore centers.
In 2019, Iranian tax revenues increased by 35% because of reported taxation evasion crackdown. As of 2021, tax authorities estimated tax cheats are costing the country $4.5 billion a year.
Income tax
 There are five categories of income earned by individuals. Each category is taxed separately and has its own computational rules.
*Salaries (tax rate for public sector employees: 10%; other sectors: 10-35%);A Review of the Iranian Tax System -2014
There are five categories of income earned by individuals. Each category is taxed separately and has its own computational rules.
*Salaries (tax rate for public sector employees: 10%; other sectors: 10-35%);A Review of the Iranian Tax System -2014. Organization for Investment Economic and Technical Assistance of Iran. Retrieved March 14, 2014. *Income from professions, trades, and miscellaneous sources;
More info here
According to the Iranian direct tax rolls article no 84. all employees salary tax rate from the beginning of the 1396 fiscal year is as below: Every year annual salary exemption from tax will be announce by Iranian tax organization up to this level the salary tax rate is zero. Up to the 5 times more than annual exemption salary tax rate is 10%. In excess of above level salary tax rate is 20%. *Incidental or windfall earnings;
More info here
*Real estate income (see also under "Real estate tax" section below) *Income derived from agriculture (see also under "Tax exemptions" section below) For taxable income consisting of salary and benefits, employers are required to make the necessary tax deductions from their employees’ payroll and submit them to the tax authorities. However, when calculating taxable income, exemptions and deductions are allowed. As of 2009, only government employees were paying their fair share of income taxes. Individuals of Iranian nationality resident in
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
are subject to tax on all their income whether earned in Iran or abroad. Foreign nationals working in Iran are also subject to the same income tax based on their salary. Non-resident individuals are liable to pay tax only on their Iranian-sourced income. Foreign employees cannot obtain an exit visa from Iran unless they provide proof that they have paid their due taxes, and since they need to obtain an exit permit when their presence in Iran is based on a work permit, the government can easily enforce this rule. The government assumes a certain salary for employees depending on their position and country of origin. The assumed minimum monthly salaries in 2004 range from US$2,500 for unskilled European workers to US$7,000 for European managing director
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a central executive officer (CEO), chief administrator officer (CAO) or just chief executive (CE), is one of a number of corporate executives charged with the management of an organization especiall ...
s.
According to the 131 note of Iranian tax rolls, from the beginning of the 1395 Iranian year tax rates of the individual business income have changed:
up to 500.000.000 IRR is 15%
500.000.000 to 1.000.000.000 IRR is 20%
In excess of 1.000.000.000 IRR is 25%
Islamic taxes
In addition to these mandatory taxes, as of 2007, Islamic taxes were collected on a ''voluntary
Voluntary may refer to:
* Voluntary (music)
* Voluntary or volunteer, person participating via volunteering/volunteerism
* Voluntary muscle contraction
See also
* Voluntary action
* Voluntariness, in law and philosophy
* Voluntaryism, reje ...
'' basis. These included an individual's income tax (Arabic khums
In Islam, khums ( ar, خُمْس , literally 'one fifth') refers to the required religious obligation of any Muslims to pay 20% of their acquired wealth from certain sources toward specified causes. It is treated differently in Shia and Su ...
, “one-fifth”); an alms-tax (zakat
Zakat ( ar, زكاة; , "that which purifies", also Zakat al-mal , "zakat on wealth", or Zakah) is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam as a religious obligation, and by Quranic ranking, is ...
), which has a variable rate and benefits charitable causes; and a land tax (kharaj
Kharāj ( ar, خراج) is a type of individual Islamic tax on agricultural land and its produce, developed under Islamic law.
With the first Muslim conquests in the 7th century, the ''kharaj'' initially denoted a lump-sum duty levied upon the ...
), the rate of which is based on the principle of one-tenth ( ushr) of the value of crops, unless the land is tax-exempt.
''Al Khums'' or the Fifth of excess income paid as a form of ''Zakat'' (alms-giving), which is usually reserved for Aal-Al-Bayt, Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mon ...
’s Household. The black turban of Khamenei signifies that he belongs to Imam Ali Ibn Abi Talib
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam. ...
and Fatima
Fāṭima bint Muḥammad ( ar, فَاطِمَة ٱبْنَت مُحَمَّد}, 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fāṭima al-Zahrāʾ (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, ...
’s household and being Al Wali Al Faqeeh (guardian of Islamic jurists with full control of the society's affairs) gives him the majority share of the Fifth, as was the case with Ayatollah Khomeini
Ruhollah Khomeini, Ayatollah Khomeini, Imam Khomeini ( , ; ; 17 May 1900 – 3 June 1989) was an Iranian political and religious leader who served as the first supreme leader of Iran from 1979 until his death in 1989. He was the founder of ...
. The amount is worth hundreds of millions of dollars accrued annually and added to Setad’s revenues.
Real estate tax
Rental income is subject to real estate income tax in Iran. A fixed deduction of 25% of the gross income is extended to all taxpayers to account for income-generating expenses. The net income, which is 75% of the gross rent, is then subject to the same rates as in the above table (max. 35%). Rental income is exempted from real estate tax if the property is a residential property leased as such and measures up to 150 sq. m. if it is located inTehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
(up to 200 sq. m. if it is located in other parts of the country).
According to the presented above rate for individual business tax rate:
-If the landlord is a company the rental income after deducting 25% as exemption will be-multiply 25% because the income tax rate for companies is 25%
-If the landlord is a person rate of calculating tax on rent is as below ''from the beginning of the 1395 fiscal year'':
up to 500.000.000 IRR is 15%
500.000.000 to 1.000.000.000 IRR is 20%
In excess of 1.000.000.000 IRR is 25%
In Iran the transfer of land, not the land itself, is subject to taxation. Transfer of properties: 5% of the transaction value (15% for new buildings).
Capital gains tax
As of 2020, Iran has nocapital gains tax
A capital gains tax (CGT) is the tax on profits realized on the sale of a non-inventory asset. The most common capital gains are realized from the sale of stocks, bonds, precious metals, real estate, and property.
Not all countries impose a c ...
on the sale of real estate
Real estate is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this (also) an item of real property, (more genera ...
assets.
Capital markets
Starting April 2014, all companies have to report their short term investments atfair value
In accounting and in most schools of economic thought, fair value is a rational and unbiased estimate of the potential market price of a good, service, or asset. The derivation takes into account such objective factors as the costs associated wi ...
instead of cost. As of July 2010, taxes on TSE transactions were as follows:
* Cash dividend: none (22.5% at source from Company).Tehran Stock Exchange: FACT BOOK. Retrieved July 31, 2010 * Share transfers: the ''Tax Amendment'' has changed the regulations regarding calculation of tax on transfer of shares and their rights in Iranian corporate entities. **In the case of shares listed on the Tehran Stock Exchange (TSE) the tax on transfer of such shares and other rights is 0.5 per cent of the sales price. **In the case of transfer of the shares and their rights to other corporate entities (i.e. those not listed on the TSE) a flat rate of four per cent of value of the shares and rights transferred applies. No other taxes will be charged. The Amendment has removed the requirement to value the shares in this category.
Exemptions
*Capital gain
Capital gain is an economic concept defined as the profit earned on the sale of an asset which has increased in value over the holding period. An asset may include tangible property, a car, a business, or intangible property such as shares.
A ...
: no tax (bonds or equities).
*Interest income
Passive income is unearned income that is acquired automatically with minimal labor to earn or maintain. It is often combined with another source of income, such as a side job. In the United States, the IRS divides income into three categories ...
: no tax.
* Participation papers: Profit and awards accrued are tax exempt.
* Listed companies: 10% tax exemption, companies holding 20% free loat shares are provided 20% tax exemption.
* Foreign investors: Foreign investors in TSE are tax-exempt.
Inheritance tax
Inheritance tax
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an e ...
es are levied at progressive rates depending on the relationship between the deceased and the heir.
*Category I: (first degree heirs) parents, spouse, children, grandchildren
*Category II: (second degree heirs) grandparents, siblings, nieces, nephews
*Category III: (third degree heirs) uncles, aunts, children of uncles and aunts
According to Article (17) has approved 2015 ,any estate or property left from an individual, because of his death, whether actual or presumptive, shall be subject to taxation as follows:
(1) In respect of bank deposits, partnership bonds and any other negotiable papers, excluding those mentioned under Paragraph (2) of this Article, and their allocated interests, as well as dividends and partners’ shares till the date of registration of transfer to the name of the heirs and or the date when the same is paid and delivered to them, at the rate of 3%;
(2) In respect of shares and partners’ shares and their priority rights, at a rate which is 1.5 times higher than the rates stipulated in Note (1) under Articles
(143) and (143 bis) of the present Act, as per relevant provisions at the date of registration of transfer to the name of the heirs;
(3) In respect of royalties and other properties, as well as financial rights not stipulated in the aforementioned paragraphs, at the rate of 10% of their market value at the date of delivery or registration of transfer to the name of the
heirs;
1 In view of Article (2) of the Act Partially Amending the Direct Taxes Act, approved on February 16, 2002, the provisions related to the collection of the Annual Tax on Real estates (subject to the previous text of Articles (3-9), Tax on Unoccupied Residential Immovable Properties (subject to the previous text of Articles (10-11) and Tax on Undeveloped Lands (subject to the previous text of Articles (12-16) were deleted.
2 In view of Paragraph (12) of the Single Article Amending Direct Taxes Act approved on July 22,
2015, provisions concerning the taxation of unoccupied residential units were stipulated through Article (54 bis) annexed to the present Act.
3 Refer to the footnote (1) above.
4 In view of Article (15) of the Act on the Organization and Support of the Production and Supply of Housing, approved on May 14, 2008, a 12 percent tax shall be applied to the transactional value of the undeveloped lands with residential use. 5 Refer to the footnote (1) above.
(4) In respect of different types of motor vehicles, whether ground, marine or aerial ones, at a rate of 2% of the price declared by the Iranian National Tax Administration at the date of registration of transfer to the name of the heirs;
(5) In respect of real estates and goodwill, at a rate 1.5 times higher than the rates stipulated in Article (59) of this Act, applicable to the transactional value of the real estates for tax purposes, or the market value of the goodwill at the date of registration of transfer to the name of the heirs, as the case may be;
Corporate income tax
A new flat rate corporation tax of 25 per cent payable on the profits of corporate commercial entities has been introduced. This rate replaces the old corporation tax of 10 per cent and progressive rates of income tax (12-54 per cent) on reserves and distributable income. Apart from the 25 per cent corporation tax and the 0.3 per centChamber of Commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to ...
tax no more taxes will be payable by the corporate entity or the shareholders.
The new rate of corporation tax will also apply to joint venture
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four reasons: to acces ...
corporate entities registered in Iran. The tax incidence
In economics, tax incidence or tax burden is the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Economists distinguish between the entities who ultimately bear the tax burden and those on whom tax is initially imposed. The ta ...
will therefore be on the corporate entity and not on the shareholder. The calculation of the tax has been simplified.
All contracting work performed by foreign contractors, whether or not the company is registered in Iran, is taxed. For contracts signed before March 21, 2003, gross taxable income is calculated as gross contract receipts less the cost of imported material. Income is then taxed at 12% of gross taxable income less contract retention. For contracts signed after March 21, 2003, taxable income is the gross contract receipts less contract expenses. Income is taxed at 25 per cent less 5 per cent taxes withheld at source.
Taxation of foreign companies
Taxation in Iran generates particular unease among foreign firms because they appear to be arbitrarily enforced – tax bills are initially based on 'assumed earnings' calculated by the Finance and Economy Ministry according to the size of the company and the sector in which it operates. Factors such as the quality and location of a company's offices are also widely believed to affect tax assessment. All foreign investors doing business in Iran or deriving income from sources inIran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
are subject to taxation
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, o ...
. Depending on the type of activity the foreign investor is engaged invarious taxes and exemptions are applicable
including profit tax,
income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Ta ...
, property tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inher ...
, etc.
Generally speaking, Iran has two types of laws concerning foreign companies. The first are laws that address issues concerning foreign companies directly such as the '' Foreign Investment Promotion and Protection Act'' (FIPPA) and the second are general laws of which certain articles or by-laws address foreign companies, for instance the Taxation Law and the Labor Law
Labour laws (also known as labor laws or employment laws) are those that mediate the relationship between workers, employing entities, trade unions, and the government. Collective labour law relates to the tripartite relationship between employee ...
. The Tax Act had divided the source of income earned by foreign companies either direct or through their branches in Iran into three main categories:
*Income earned in Iran by way of contracting operations
*Income earned from Iran by way of royalties and licensing fees
*Other activities - trading operations, etc.
ote: ''The Amendment'' has introduced certain changes in the tax treatment of the above activities.
Foreign legal entities must pay taxes on all taxable income earned through investments in mainland Iran or from direct or indirect (through agents, branch offices, etc.) activities in mainland Iran, at the flat rate of 25% as mentioned in Article 47 of ''the Amendment'' law.
Income from royalty and licensing
A license (or licence) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another party (licensee) as an element of an agreeme ...
fees received from industrial and mining companies, government ministries and municipalities, and income from film-screening rights are subject to a deemed taxable coefficient on income of 20 per cent. All other income from royalties and licences from foreign companies is subject to a deemed taxable coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves ...
on income of 30 per cent. The coefficients are based on the standard corporate tax rate of 25 per cent, so that the effective tax rate
In a tax system, the tax rate is the ratio (usually expressed as a percentage) at which a business or person is taxed. There are several methods used to present a tax rate: statutory, average, marginal, and effective. These rates can also be p ...
is either 5 per cent or 7.5 per cent.
[Note: ''The Amendment'' has removed the confusion surrounding 'technical assistance contracting' by including 'technical assistance' and 'transfer of technology' in contracting operations subject to tax on the basis of 12 per cent of annual fees.]
Tax on liaison, representative and branch Offices
The same corporate and profit taxes will be applied to the taxable income of branches of foreign companies (contractors, consultant engineers, et al.) Other income earning activities of foreign branches will be subject to taxation on an actual basis, i.e. based on their income tax return as filed and supported by their statutory accounting books. Expenses incurred in Iran by Iranian registered branches and representative offices of foreign companies that are not authorized by their head offices to engage in any trading activity but are only authorized to conduct marketing and market research in Iran are tax deductible upon presentation of receipts from their head office.Tax advantages & exemptions
Article 132 The income declared for producing and mining activities, which is derived by non-government legal persons in producing or mining enterprises, for whom exploitation licenses are issued, or with whom extraction and sale contracts are concluded by relevant ministries as of the date of entry into force of the present Act, as well as the income derived from services delivered by hospitals, hotels and touristy residential centers, namely, non-government legal persons, for whom exploitation licenses or permits are issued by relevant legal authorities as of the aforementioned date, shall be subject to a zero tax rate for a period of 5 years beginning from the date of exploitation or extraction or activity start up. As regards the less-developed regions, the provision shall apply to a period of 10 years.1 A) Zero-rate taxation refers to a method whereby the taxpayers in question are obliged to file returns and submit their statutory books or their accounting documents, if any, to the Iranian National Tax Administration in accordance with the arrangements and deadlines required by this Act with regards to their incomes. The Iranian National Tax Administration shall be obliged to investigate such tax returns and assess the taxable income of such taxpayers based on the supporting documents and the tax returns information and shall apply a zero tax rate to the resulting taxable income. B) As for producing or service-oriented enterprises and other centers mentioned in the present Article, if, during the period of exemption, they have more than 50 employees, the term of application of the aforementioned exemption shall increase, providing that they raise the number of employees at least for 50% annually. Consequently, there will 1 In view of Article (31) of the Law for Removing Obstacles to Competitive Production and Promoting the Country’s Financial System approved on 21/04/2015, this text and its Paragraphs and Notes substituted the former text of Article (132) of the Act and its Notes. be an increase of one further year of tax exemption for each annual increase of at least 50% of their employees. The number of employees working in such enterprises, as well as the rate of increase in the number of employees shall be determined upon the confirmation of the Ministry of Cooperatives, Labor and Social Welfare based on documents relevant to the lists of employees’ social security insurance. In case the minimum rate of increase in the number of employees is lowered down in the subsequent year for which the tax incentive prescribed in this Paragraph has been granted, then, the tax amount exempted for that particular year shall be claimed and collected. Cases of retirement, redemption or resign are not regarded as decrease. C) The term of application of the zero rate taxation for enterprises mentioned in the present Article shall increase for 2 further years, if they are located in special economic zones, and for 3 further years, if they are located in industrial towns or special economic zones of less-developed regions. D) The requirement for entitlement to any tax exemptions by real and legal persons engaged in free zones and other regions of the Country is filing tax returns within the due deadline. The legal persons’ tax returns include the balance sheet, as well as profit and loss account in accordance with samples prepared by the Iranian National Tax Administration. E) In order to promote and increase the levels of economic investments in entities subject to the present Article, in addition to the protection period for zero-rate taxation, investments in less-developed regions and other regions shall also be supported in other ways as follows: 1) For less-developed regions: In the computation of taxes relevant to the subsequent years following the zero-rate taxation period pursuant to provisions prescribed in the present Article, as long as the aggregate taxable income is twice the registered and paid-up capital, the zero rate shall still apply but beyond that level, the due taxes shall be computed and collected at the rates prescribed in Article (105) of this Act and the Notes under it. 2) For other regions: In the computation of taxes relevant to the years following the zero- rate taxation period pursuant to provisions prescribed in the preamble of the present Article, 50% of the taxes shall still be zero rated and the remaining 50% shall be computed and collected at the rates prescribed in Article (105) of this Act and the Notes under it. This provision will persist unless the aggregate taxable income of the enterprise in question equals its registered and paid-up capital, but beyond that level, 100% of the due tax shall be computed at the rates prescribed in Article (105) of the present Act and the Notes under it. The tax incentives mentioned in Sections (1) and (2) of the present Paragraph shall also apply to the income derived from transportation activities by non-government legal persons. If such non-government legal persons have been established prior to the present amendment, they shall be entitled to the tax incentive mentioned in this Article, if they have any reinvestment. Any investments authorized by receiving legal licenses from relevant legal authorities for the establishment, development, reconstruction and renovation of the enterprises in question to create fixed assets, except for lands, shall also be subject to the rule of this Paragraph. F) The exception stipulated for lands at the end of Paragraph (E) is not applicable in cases of investment by non-government legal persons on enterprises of transportation, hospitals, hotels and touristy residential centers, but merely to the extent prescribed in legal licenses issued by relevant authorities. G) In cases of decrease in the registered or paid-up capitals of the abovementioned persons who have already taken benefits from the tax incentive granted by the present Article for increasing their capital, the tax due and the fines thereof shall be claimed and collected. H) If the investments subject to the provisions of the present Article have been made in partnership with foreign investors under the license of the Organization for Investment, Economic and Technical Assistance of Iran, then for any 5% of foreign investment partnership, there will be a 10% increase in the tax incentive prescribed by this Article, which shall not exceed 50% of the registered and paid-in capital. I) Foreign companies that produce well-known brand products in Iran by exploiting capabilities of domestic producing enterprises, shall be subject to the provisions of the present Article as of the date of conclusion of their cooperation contract with the Iranian producing enterprise all throughout the zero-rate taxation period granted to that producing enterprise, provided that they manage to export at least 20% of their products. Moreover, after the expiry of the zero-rate taxation period, such foreign companies shall still be subject to the 50% relief in the tax rate with regard to the profits derived from the sale of their products during the period stipulated in this Article. J) The zero-rate taxation and incentives provisioned in this Article shall not apply to the income of producing and mining entities established within a 120-kilometer radius from the center of Tehran Province or within 50kilometer radius from the center of Isfahan and within a 30-kilometers radius from the administrative centers of provinces and cities with a population exceeding 300,000, according to the latest population and housing census. However, producing enterprises involved in the area of information technology, upon the confirmation of relevant ministries and the VicePresidency for Science and Technology shall be entitled to the privileges provided by this Article. Moreover, producing and mining enterprises established in all special economic zones and industrial townships, except for special economic zones and industrial townships established within the 120-kilometer radius from the center of Tehran Province shall be zero-rated and shall be entitled to the tax incentives provided by this Article. As regards the special economic zones and industrial townships or producing enterprises located within the territory of two or more provinces or cities, the criterion for making decision on the territory to which such zones or townships belong shall be stipulated in a bylaw to be approved by the Council of Ministers, within three months from the approval of the present Act, upon the joint proposal of the Ministry of Industry, Mine and Trade, the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Finance, the State Organization of Management and Planning and the Department of Environment of the Islamic Republic of Iran. K) The list of less-developed regions, including the names of provinces, townships, counties and rural districts, shall be prepared, within the first three months of the 5-year term of each development plan by the State Organization of Management and Planning in collaboration with the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Finance and will be approved by the Council of Ministers to be applicable until a new list is approved. The date of activity start up, as verified by relevant competent authorities, will be the basis for granting tax incentives for less-developed regions. L) All enterprises for internal and international tourism that have, prior to the entry into force of the present Article, received their exploitation licenses from relevant legal authorities shall be exempt from the payment of 50% of the tax on their declared income up to 6 years after the date of entry into force of this Article. This provision, however, does not apply to incomes derived from sending tourists abroad. M) One hundred percent (100%) of the income declared by tourism and pilgrimage travel agents that have received their licenses from relevant authorities shall be zero rated, provided that such income has been derived from foreign tourists or from sending pilgrims to Saudi Arabia, Iraq or Syria. N) Zero-rate treatment as provisioned by the present Law shall only apply to the income declared by taxpayers and does not apply to hidden incomes. This exclusion shall be applicable in regard with all cases of zerorate taxation provisioned in the present Act or in any other relevant laws. O) Study and research costs of legal persons from the private and cooperative sectors engaged in producing and industrial enterprises, holding exploitation licenses from relevant ministries shall be exempt from the payment of a maximum of 10% of such persons’ declared tax in the year of accrual, provided that such study and research activities have been carried out through contracts concluded with universities or other research and higher education centers holding finalized licenses from the Ministries of “Science, Research and Technology” or “Health and Medical Education”, within the framework of the State Comprehensive Scientific Map. The latter mentioned contracts shall be eligible for the concerned purpose, only if research councils of the universities or research centers involved have already approved the annual progress reports of the contracts. Moreover, for the entitlement to the exemption, the income declared by such enterprises for producing and industrial activities shall not be less than IRR 5,000,000,000. The study and research costs, which are taken into account as the tax paid by such persons, shall not be accepted as allowable expenses for tax purposes. The administrative bylaw of this Paragraph will be approved by the Ministers of “Economic Affairs and Finance”, “Industry, Mine and Trade”, “Science, Research and Technology” and “Health and Medical Education” upon the proposal of the Iranian National Tax Administration. Note (1) All tax exemptions and zero-rate privileges provisioned by existing laws, other than laws and regulations mentioned in the present Article shall lsobe applicable as of the beginning of the year 1395 (i.e. as of March 20, 2016). Note (2) The administrative bylaw of the present Article and the paragraphs under it, will be prepared, within 6 months of the date of entry into force of this Act, by the Ministries of “Economic Affairs and Finance” and “Industry, Mine and Trade” in collaboration with the Iranian National Tax Administration to be approved by the Council of Ministers.Foreign Investment Promotion and Protection Act (FIPPA)
Location requirement for tax-exemption: #If investment located out of a 120-kilometer radius from the center ofTehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
,
#If investment located out of a 50-kilometer radius from the center of Isfahan
Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Region, Isfahan Province, Iran. It is lo ...
,
#If investment located out of a 30-kilometers radius from the centers of provinces (except for the Industrial Estates within this radius)
Tax exemption – major changes
The exemptions on exports of manufactured andagricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
goods remain in force, but an ambiguity has occurred in the amendment regarding exemptions extended to the public sector (Iranian Government owned entities). Government owned enterprises and their shares in the private sector entities were excluded from all exemptions granted under the Tax Act.
This exclusion has been removed from the relevant texts in the amendment. Until clarification is provided, it is not certain whether or not the government minority shares in the private sector manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
, mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
and exports activities would enjoy the exemptions granted.
The 50 per cent tax exemption previously granted to tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
enterprises has been extended to include five-star hotels. Since 2014, foreign companies who set up business in Iran will receive corporate tax breaks of up to 50%, if they export at least 30% of their products.
Losses
Losses sustained by all taxpayers engaged in trading and other activities, who are required to keep proper books of account, provided they are accepted by the tax authorities; will be carried forward and written off against future profits for a period of three years.Double taxation
List of countries that have adouble-taxation
Double taxation is the levying of tax by two or more jurisdictions on the same income (in the case of income taxes), asset (in the case of capital taxes), or financial transaction (in the case of sales taxes).
Double liability may be mitigated i ...
avoidance agreement with Iran (as of 2014):Algeria, Austria, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Belarus, Bulgaria, China, Croatia, France, Georgia, Germany, Indonesia, India, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Malaysia, Norway, Oman, Pakistan, Poland, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Serbia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Switzerland, Syria, Tajikistan, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Venezuela. Vietnam
Appeals procedure
It is noteworthy to point out that ''the Amendment'' has removed the second stage of appeal process. Appeals to the High Council of Taxation could only be made on questions of non-compliance with the provisions of the Tax Act rather than questions of fact.Accounting standards
''The Amendment'' has for the first time after 1979 reintroduced the concept of thetax audit
In the United States of America, an income tax audit is the examination of a business or individual tax return by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or state tax authority. The IRS and various state revenue departments use the terms audit, examin ...
to be undertaken by 'official accountants' and their designated firms. The taxpayer or the tax administration can choose to appoint an official accountant or a designated firm of official accountants to examine his records and report to the tax authorities.
The accounting profession is not particularly organized in Iran. However, the influence of the foreign accounting practices implies an evolution and a relation between the Iranian accountants training and the American one. Thus, an increasing number of accountants and Iranian auditors receives an American training and apply it in Iran. This will contribute to strengthen the harmonization of Iranian book-keeping
Bookkeeping is the recording of financial transactions, and is part of the process of accounting in business and other organizations. It involves preparing source documents for all transactions, operations, and other events of a business. Tr ...
systems with international standards
international standard is a technical standard developed by one or more international standards organizations. International standards are available for consideration and use worldwide. The most prominent such organization is the International Org ...
. Iranian banks use interest-based transactions and retain the accounting standards
Publicly traded companies typically are subject to rigorous standards. Small and midsized businesses often follow more simplified standards, plus any specific disclosures required by their specific lenders and shareholders. Some firms operate on th ...
of conventional banking. Following international sanctions
International sanctions are political and economic decisions that are part of diplomatic efforts by countries, multilateral or regional organizations against states or organizations either to protect national security interests, or to protect i ...
, KPMG
KPMG International Limited (or simply KPMG) is a multinational professional services network, and one of the Big Four accounting organizations.
Headquartered in Amstelveen, Netherlands, although incorporated in London, England, KPMG is a net ...
, PriceWaterhouseCoopers
PricewaterhouseCoopers is an international professional services brand of firms, operating as partnerships under the PwC brand. It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is considered one of the Big Four accounti ...
, RSM, Crowe Horwath
Crowe Global, commonly referred to as Crowe, previously Crowe Horwath International, is a multinational professional services network. It is the 9th largest global accounting network in the world by revenue. The network consists of more than 220 ...
and Grant Thornton have suspended their activities in Iran in recent years. The main professionals and representative organization in Iran is the Iranian Institute of Certified Accountants.
Starting in FY 2017, all Iranian companies are required to prepare their financial statements based on International Financial Reporting Standards
International Financial Reporting Standards, commonly called IFRS, are accounting standards issued by the IFRS Foundation and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). They constitute a standardised way of describing the company's f ...
(IFRS).
Indirect taxes
Value added tax (VAT)
in 2008,sales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a gove ...
rate in Iran was 3%.but changed to 9% from 2011 ''Value Added Tax Act (VATA)'' was put into effect since mid-year 1387 (2008). Its implementation was suspended following 10 days of widespread demonstrations across Iran in October 2008. This Act has substituted all previous laws and regulations dealing with indirect taxes (including sales tax). According to the VATA, supply of commodities and services, as well as their imports and exports, shall be subject to the provisions of this Law.
According to article 16 of this Act, the VAT rate is 9%, but the VAT rates of certain goods such as "cigarettes and tobacco products" and "gasoline and jet fuel" are respectively 12 and 20%. In addition to the VAT rates just mentioned, article 38 of VATA levies the following duties on goods and services which are subject to this Act:
The fifth development plan stipulates that VAT is to be increased by 1% each year, in order that it reaches 8% by the end of the plan (by 2015). As of 2010, VAT for goods and services (except oil and tobacco products) was 3%.
VAT tax exemption
VAT will not apply to free trade zones in Iran. However, goods and services entering Iran's customs territory will be subject to payment of VAT according to the law. Articles 12 and 13 stipulate that supply and importation of some commodities and services including the following shall be exempt from the VATA: *a) Unprocessed agricultural products; *b) Livestock and live poultry, aquatic products, honey bees and silkworms; *c) All types of fertilizers, pesticides, seeds and saplings; *d) Bakery flour, bread, meat, sugar, rice, cereals and soya, milk, cheese, shortening and baby formula; *e) Books, press, notebooks and all types of printing papers, writing pads and papers and press papers; *f) Passenger goods for personal use, as exempted under the Export-Import Regulations ; *g) Immovable property; *h) All types of medicine, medical consumables, medical services (human, animal or plant) as well as rehabilitation and other supportive services; *i) Services subject to payment of salary taxes envisaged in thDirect Taxation Law
*j) Banking and credit services rendered by banks, credit institutes and cooperatives, authorized interest-free loan funds and cooperative funds; *k) Public transportation services and urban and inter-city roads, railway, air and sea passenger transport services; *l) Hand woven carpets; *m) All types of research and training services, as stipulated in a By-Law to be approved by the Council of Ministers; *n) Animal and poultry feed; *o) Export of goods and services from official exit points. Any tax paid on account of such exports shall be reimbursed (as regards commodities) upon submitting a certification of the customs certifying the export of goods.
Value Added Tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the en ...
(VAT) does not apply to free trade zones (FTZ) in Iran. However, goods and services entering Iran's customs territory from FTZs will be subject to payment of VAT according to the law.
Municipal tax
This tax only applies to companies, which are subject to a municipal tax at the rate of three per cent of their taxable income (2006).E-commerce
Neither the Electronic Commerce Law of 2004 nor any other Iranian legislation deals specifically with taxation arising from e-commerce.Customs
As of 2006, imports to Iran valued at more than IR500,000 ($50,000) must undergo pre-shipment quantity and quality inspection in their country of origin by an internationally recognised inspection organisation (such as SGS S.A.). Goods exported to Iran must be subject to invoices authenticated by the Iranian Embassy and by a nominated Chamber of Commerce operating in the supplier's country.Tariff rates


 As of 2015, there are a variety of items which are exempt from taxes being imported into Iran, such as:
*unprocessed agricultural products
*flour, bread, sugar, rice, milk, cheese
*machinery
*livestock and animals
*feedstock and pesticides.
As of 2015, there are a variety of items which are exempt from taxes being imported into Iran, such as:
*unprocessed agricultural products
*flour, bread, sugar, rice, milk, cheese
*machinery
*livestock and animals
*feedstock and pesticides.
Protectionism and dumping
As much as 70% of Iran's imports could be substituted by domestically produced products. Iran has passed a law that bans the import of foreign goods and services when similar products or capacities already exist in Iran. The government says that 200 thousand new jobs are created with every one billion dollar reduction in imports. Reported issues are increasing the quality of domestic products, moreresearch and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existi ...
needed, adaptation by domestic suppliers to the Iranian consumer tastes and marketing
Marketing is the process of exploring, creating, and delivering value to meet the needs of a target market in terms of goods and services; potentially including selection of a target audience; selection of certain attributes or themes to emph ...
. As part of the resistive economy, the Supreme Leader of Iran
The Supreme Leader of Iran ( fa, رهبر ایران, rahbar-e irān) is the head of state of the Islamic Republic of Iran. The Supreme Leader directs the executive system and judicial system of the Islamic theocratic government and is the co ...
has urged Iranians to consume more domestic products over imported ones.
In 2019, Iranian media reported that foreign firms were dumping their medicines in order to hinder the development of competing domestic pharmaceutical firms.
Modernization
In an effort to streamline and harmonize the customs procedure with other governmental and private partners, theGovernment of Iran
The Government of the Islamic Republic of Iran ( fa, نظام جمهوری اسلامی ایران, Neẓām-e jomhūrī-e eslāmi-e Irān, known simply as ''Neẓām'' ( fa, نظام, lit=the system) among its supporters) is the ruling state ...
has selected ASYCUDAWORLD as a tool for its customs administration in order to move toward e-commerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the activity of electronically buying or selling of products on online services or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain manag ...
and e-customs. This project is a technical cooperation project betweethe Islamic Republic of Iran Customs Administration
(IRICA),
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the ...
and UNDP
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
.
As of March 21, 2010, all imported goods must have barcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or o ...
stickers '' Irancode'' that meet the national and international standards.
Free trade zones and re-export
Value added tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the en ...
(VAT) will not apply to free trade zones in Iran. However, goods and services entering Iran's customs territory will be subject to payment of VAT according to the law. In accordance with Article 12 of thExport-Import Regulations Act
the pre-exportation entry (temporary importation) of materials and goods to be used in producing, finishing, processing and packaging of exported goods are exempted from all import duties.
Smuggling
One third of the imported goods in Iran are delivered through theblack market
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the ...
, underground economy
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the ...
, and illegal jetties. Iran is modernizing the customs to prevent the smuggling of contraband
Contraband (from Medieval French ''contrebande'' "smuggling") refers to any item that, relating to its nature, is illegal to be possessed or sold. It is used for goods that by their nature are considered too dangerous or offensive in the eyes o ...
''in'' and ''out'' of the country worth $12 billion annually. Other estimates put the value of smuggled goods ''into'' Iran alone at $5.5 billion-$6 billion annually. In 2010, Police in Iran estimated about $16 billion worth of goods is smuggled into Iran each year. $12 billion worth of goods are illegal to have or own in Iran, with the remaining $4 billion being legal goods that are legal to own in Iran. In 2013, smugglers imported $17 billion of goods. Nearly $3 billion of goods were also imported, using tariff exemptions, while the total import reached $50 billion in value. Less than 1% of smuggled goods are intercepted by the authorities.
Largest black markets in Iran are those of:
*Drug smuggling
The illegal drug trade or drug trafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs through ...
($8.5 billion),
* Petroleum smuggling (over $3 billion); 20 million liters of fuel per day as of 2014,
*Alcohol smuggling
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.
There are variou ...
($912.5 million),
*Cigarette smuggling
The illicit cigarette trade is defined as “the production, import, export, purchase, sale, or possession of tobacco goods which fail to comply with legislation” (FATF 2012). Illicit cigarette trade activities fall under 3 categories:
# Con ...
($2 billion),
*Prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
,
*Arms trafficking
Arms trafficking or gunrunning is the illicit trade of contraband small arms and ammunition, which constitutes part of a broad range of illegal activities often associated with transnational criminal organizations. The illegal trade of small arm ...
,
*Corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
,
* Unlicensed imported films and software packages,
*Cash
In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.
In bookkeeping and financial accounting, cash is current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-im ...
($1 billion).
One Majlis
( ar, المجلس, pl. ') is an Arabic term meaning "sitting room", used to describe various types of special gatherings among common interest groups of administrative, social or religious nature in countries with linguistic or cultural conne ...
member recently stated that IRGC black-market activities alone might account for $12 billion per year. Iranian commander Mohammadreza Yazdi has stated that all IRGC economic activities are legitimate. Besides the IRGC, rogue elements within the Government of Iran
The Government of the Islamic Republic of Iran ( fa, نظام جمهوری اسلامی ایران, Neẓām-e jomhūrī-e eslāmi-e Irān, known simply as ''Neẓām'' ( fa, نظام, lit=the system) among its supporters) is the ruling state ...
, Bonyad
Bonyads ( fa, بنیاد "Foundation") are charitable trusts in Iran that play a major role in Iran's non-petroleum economy, controlling an estimated 20% of Iran's GDP, and channeling revenues to groups supporting the Islamic Republic. Exempt f ...
s and the Bazaar
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace consisting of multiple small stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East, the Balkans, North Africa and India. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, such as in t ...
are allegedly involved in the smuggling activity.
Dubai
Dubai (, ; ar, wikt:دبي, دبي, translit=Dubayy, , ) is the List of cities in the United Arab Emirates#Major cities, most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, the most populated of the 7 ...
and Khasab
Khasab ( ar, خَصَب, Ḫaṣab) is a city and local capital of the Musandam Governorate which is an exclave of Oman bordering the United Arab Emirates at the tip of the Musandam Peninsula by the Strait of Hormuz. It has been dubbed the " Norw ...
in the Persian Gulf are important foreign centers of smuggling into Iran. These imports enter Iran through major ports such as Bandar-e Abbas
Bandar Abbas or Bandar-e ‘Abbās ( fa, , , ), is a port city and capital of Hormozgān Province on the southern coast of Iran, on the Persian Gulf. The city occupies a strategic position on the narrow Strait of Hormuz (just across from Musa ...
or free trade zones such as the islands of Kish and Qeshm. A total of 750,000 unlicensed small shops serve as conduit for the distribution of those goods throughout Iran.
Excessive import tariffs (for items such as clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natura ...
for example) also contributes to smuggling in Iran.
Damage to the economy
Up to 80% of the goods enter the country through unregistered ports and jetties in thePersian gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
, thus undermining the domestic industries in energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of ...
, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
, garment, textile, electronics, home appliances (which account for 13% of all the goods smuggled into Iran/or one third of all home appliances in Iran).http://www.nitc.co.ir/iran-daily/1388/3438/html/economy.htm#s389754 As of 2014, 75% of the cell phones in the market were smuggled into the country.
Effect on employment
As per 2010 Iranian customs report $14.43 billion worth of goods were smuggled in and out of Iran out of which $13.25 billion was the value of goods smuggled into Iran leading to loss of some 600,000 jobs.See also
*Iranian labor law Iranian labor law describes the rules of employment in Iran. As a still developing country, Iran is considerably behind by international standards. It has failed to ratify the two basic Conventions of the International Labour Organization on freedom ...
*List of major economic laws in Iran
The list of major laws and legal acts affecting trade in goods and services in Iran as of 2009:Economy of Iran
* International Rankings of Iran in Economy
* Tax rates around the world
*
A Review of the Iranian Tax System
- Organization for Investment Economic and Technical Assistance of Iran
The Taxation System for Foreign Investors in Iran
- Iran-U.K. Chamber of Commerce
Paying Taxes in Iran
-
Ministry of Finance in Iran
- Direct tax laws
Annual Reviews
- Reports by the
Corporate Income Tax in Iran
- Iran Trade Point
(Note: document has not been updated)
Tehran Chamber of Commerce
- Offers free tax consulting for companies intending to invest in Iran
Nur Law
- Database on Iranian laws and regulations
- Iran's entry (details on Iran's social security laws) ;Customs
Islamic Republic of Iran's Customs AdministrationIran's Export-Import Regulation Act (2002)
Export-Import Guide (2014)Market Access Map
an online database of customs tariffs and market requirements. * - Many practical information including importation procedure to Iran. ;Videos
How to Export Goods to Iran
(all procedures explained)
How to Import Goods to Iran
(all procedures explained) {{DEFAULTSORT:Labour And Tax Laws In Iran Law of Iran Economy of Iran Society of Iran
Constitution of Iran
The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran ( fa, قانون اساسی جمهوری اسلامی ایران, ''Qanun-e Asasi-ye Jomhuri-ye Eslâmi-ye Iran'') was adopted by referendum on 2 and 3 December 1979, and went into force replac ...
*Bonyad
Bonyads ( fa, بنیاد "Foundation") are charitable trusts in Iran that play a major role in Iran's non-petroleum economy, controlling an estimated 20% of Iran's GDP, and channeling revenues to groups supporting the Islamic Republic. Exempt f ...
- Iran's foundations which control 20% of Iran's GDP.
* Fiscal policy in Iran
*Ministry of Economic Affairs and Finance (Iran)
The Ministry of Economic Affairs and Finance's functions are:
*Manage the Iranian treasury department,
*Lending by the government to banks in Iran,
*Regulation of Iran's economy and its financial policy,
*implementing & enforcing tax polici ...
*Iranian calendar
The Iranian calendars or Iranian chronology ( fa, گاهشماری ایرانی, ) are a succession of calendars invented or used for over two millennia in Iran, also known as Persia. One of the longest chronological records in human history ...
* Social class in Iran
* Iranian National Tax Administration
References and notes
External links
;TaxationA Review of the Iranian Tax System
- Organization for Investment Economic and Technical Assistance of Iran
The Taxation System for Foreign Investors in Iran
- Iran-U.K. Chamber of Commerce
Paying Taxes in Iran
-
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
Ministry of Finance in Iran
- Direct tax laws
Annual Reviews
- Reports by the
Central Bank of Iran
The Central Bank of Iran (CBI), also known as ''Bank Markazi'', officially the Central Bank of the Islamic Republic of Iran ( fa, بانک مرکزی جمهوری اسلامی ايران, Bank Markazi-ye Jomhuri-ye Eslāmi-ye Irān; SWIFT Code: ...
, including macro-economic data, sectoral activity and labor statistics.Corporate Income Tax in Iran
- Iran Trade Point
(Note: document has not been updated)
Tehran Chamber of Commerce
- Offers free tax consulting for companies intending to invest in Iran
Nur Law
- Database on Iranian laws and regulations
- Iran's entry (details on Iran's social security laws) ;Customs
Islamic Republic of Iran's Customs Administration
Export-Import Guide (2014)
an online database of customs tariffs and market requirements. * - Many practical information including importation procedure to Iran. ;Videos
How to Export Goods to Iran
(all procedures explained)
How to Import Goods to Iran
(all procedures explained) {{DEFAULTSORT:Labour And Tax Laws In Iran Law of Iran Economy of Iran Society of Iran
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...