Smithian (regional geological stage) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the
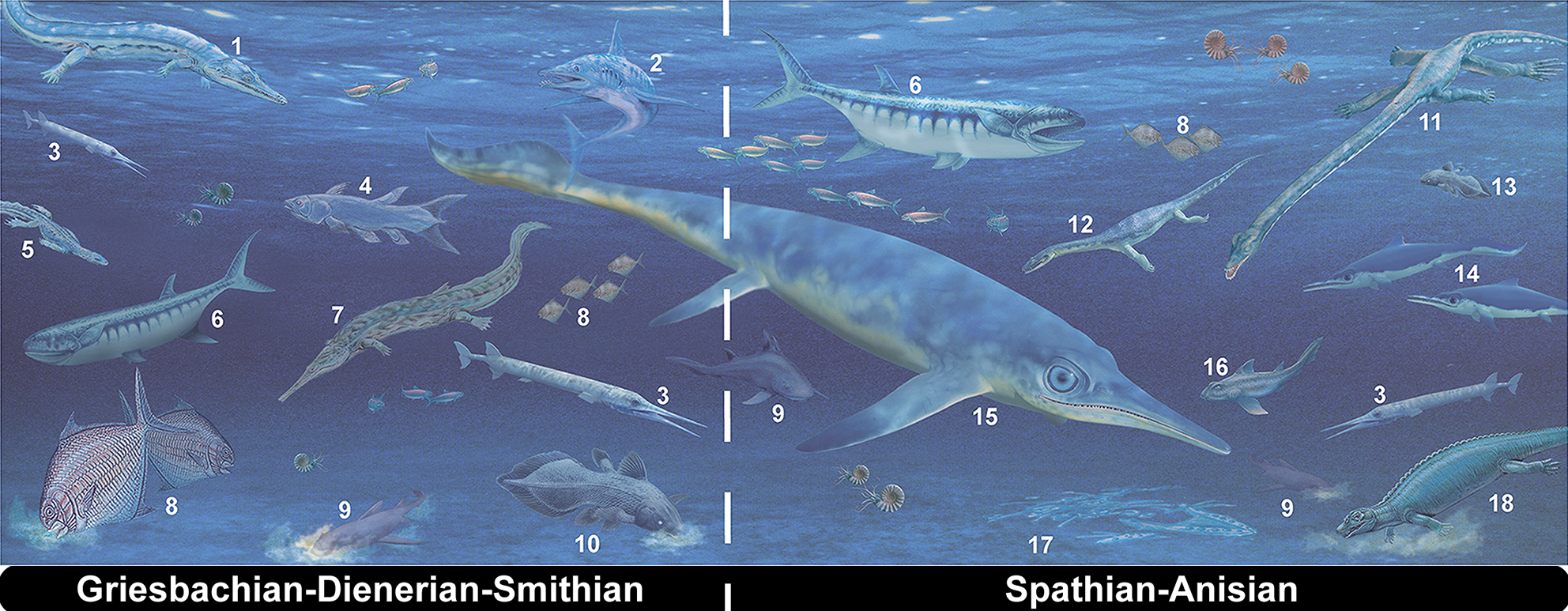 An important extinction event occurred during the Olenekian age of the Early Triassic, near the Smithian and Spathian subage boundary. The main victims of this Smithian–Spathian boundary event, often called the Smithian–Spathian extinction, were 'disaster taxa': Palaeozoic species that survived the
An important extinction event occurred during the Olenekian age of the Early Triassic, near the Smithian and Spathian subage boundary. The main victims of this Smithian–Spathian boundary event, often called the Smithian–Spathian extinction, were 'disaster taxa': Palaeozoic species that survived the
GeoWhen Database - OlenekianLower Triassic timescale
at the website of the subcommission for stratigraphic information of the ICS
Lower Triassic timescale
at the website of Norges Network of offshore records of geology and stratigraphy. {{coord, 31.9653, N, 78.0247, E, source:wikidata, display=title *02 Geological ages Triassic geochronology Geology of Siberia Olenyok basin
geologic timescale
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochr ...
, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a un ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
; in chronostratigraphy
Chronostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy that studies the ages of rock strata in relation to time.
The ultimate aim of chronostratigraphy is to arrange the sequence of deposition and the time of deposition of all rocks within a geologic ...
, it is a stage
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* Sta ...
in the Lower Triassic series
Series may refer to:
People with the name
* Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series
* George Series (1920–1995), English physicist
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Series, the ordered sets used in ...
. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometime ...
and is followed by the Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage or earliest age of the Middle Triassic series or epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ago. The Anisian Age succeeds the Olenekian Age (part of the Lower Triassic ...
(Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and ...
).
The Olenekian saw the deposition of a large part of the Buntsandstein
The Buntsandstein (German for ''coloured'' or ''colourful sandstone'') or Bunter sandstone is a lithostratigraphic and allostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Buntsandst ...
in Europe. The Olenekian is roughly coeval with the regional Yongningzhenian Stage used in China.
Stratigraphic definitions
The Olenekian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by Russian stratigraphers in 1956. The stage is named afterOlenëk
The Olenyok (russian: Оленёк, sometimes spelled ''Оленек'', ''Olenek''; sah, Өлөөн, Ölöön) is a major river in northern Siberian Russia, west of the lower Lena and east of the Anabar. It is long, of which around is navigable ...
in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
. Before the subdivision in Olenekian and Induan became established, both stages formed the Scythian Stage, which has since disappeared from the official timescale.
The base of the Olenekian is at the lowest occurrence of the ammonoids
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
'' Hedenstroemia'' or '' Meekoceras gracilitatis'', and of the conodont '' Neospathodus waageni''. It is defined as ending near the lowest occurrences of genera '' Japonites'', '' Paradanubites'', and '' Paracrochordiceras''; and of the conodont '' Chiosella timorensis''. A GSSP
A Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) is an internationally agreed upon reference point on a stratigraphic section which defines the lower boundary of a stage on the geologic time scale. The effort to define GSSPs is conducted ...
(global reference profile for the base) has not been established as of December 2020.
Olenekian life
Life was still recovering from the severe end-Permian mass extinction. During the Olenekian, theflora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' ...
changed from lycopod
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching s ...
dominated (e.g. '' Pleuromeia'') to gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
and pteridophyte dominated. These vegetation changes are due to global changes in temperature and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
. Conifers ( gymnosperms) were the dominant plants during most of the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
. Among land vertebrates, the archosaurs
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avia ...
- a group of diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years a ...
reptiles encompassing crocodiles
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant memb ...
, pterosaurs, dinosaurs, and ultimately birds - first evolved from archosauriform ancestors during the Olenekian. This group includes ferocious predators like ''Erythrosuchus
''Erythrosuchus'' (from el, ἐρυθρός , 'red' and el, σοῦχος , 'crocodile') is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile from the Triassic of South Africa. Remains have been found from the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Bea ...
''.
In the oceans, microbial reefs were common during the Early Triassic, possibly due to lack of competition with metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
reef builders as a result of the extinction. However, transient metazoan reefs reoccurred during the Olenekian wherever permitted by environmental conditions. Ammonoids
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
and conodonts
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which ...
diversified, but both suffered losses during the Smithian-Spathian boundary extinction
In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Olenekian is sometimes divided i ...
at the end of the Smithian subage.
Ray-finned fishes
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or hor ...
largely remained unaffected by the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Many genera show a cosmopolitan (worldwide) distribution during the Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometime ...
and Olenekian (e.g. '' Australosomus'', '' Birgeria'', Parasemionotidae, '' Pteronisculus'', Ptycholepidae, '' Saurichthys''). This is well exemplified in the Griesbachian (early Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometime ...
) aged fish assemblages of the Wordie Creek Formation (East Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
), the Dienerian (late Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometime ...
) aged assemblages of the Sakamena Formation Sakamena is a village near Betroka in the region of Anosy in Madagascar.
Sakamena is also the name of a Permian sedimentary geological formation that has yielded many vertebrate fossil, including Triadobatrachus (the first lissamphibian), Claudios ...
(Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
), Candelaria Formation (Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
), and Mikin Formation (Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
), and the Smithian aged assemblages of the Vikinghøgda Formation ( Spitsbergen, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
), Thaynes Formation (western United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
), and Helongshan Formation (Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River ...
, China). Ray-finned fishes
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or hor ...
diversified during the Triassic and reached peak diversity during the Middle Triassic. This diversification is, however, obscured by a taphonomic megabias during the late Olenekian and early middle Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage or earliest age of the Middle Triassic series or epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ago. The Anisian Age succeeds the Olenekian Age (part of the Lower Triassic ...
.
Marine temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carbo ...
amphibians, such as the superficially crocodile-shaped trematosaurids '' Aphaneramma'' and ''Wantzosaurus
''Wantzosaurus'' was a genus of temnospondyl amphibian of the Trematosauridae family. Fossils have been found in the Early Triassic Middle Sakamena Formation (Sakamena Group) of what is now Madagascar. It showed adaptations for an almost complete ...
'', show wide geographic ranges during the Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometime ...
and Olenekian ages. Their fossils are found in Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
, Spitsbergen, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
and Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
. Others, such as '' Trematosaurus'', inhabited freshwater environments and were less widespread.
The first marine reptiles appeared during the Olenekian. Hupehsuchia, Ichthyopterygia
Ichthyopterygia ("fish flippers") was a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the Jurassic ichthyosaurs that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitiv ...
and Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became ...
are among the first marine reptiles to enter the scene (e.g. '' Cartorhynchus'', '' Chaohusaurus'', '' Utatsusaurus'', '' Hupehsuchus'', '' Grippia'', '' Omphalosaurus'', '' Corosaurus''). Sauropterygians and ichthyosaurs ruled the oceans during the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
Era
An era is a span of time defined for the purposes of chronology or historiography, as in the regnal eras in the history of a given monarchy, a calendar era used for a given calendar, or the geological eras defined for the history of Earth.
Comp ...
.
An example of an exceptionally diverse Early Triassic assemblage is the Paris Biota, fossils of which were discovered near Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyomi ...
and other nearby sites in Idaho and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
. The Paris Biota was deposited in the wake of the SSBM and it features at least 7 phyla and 20 distinct metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
orders, including leptomitid protomonaxonid sponges (previously only known from the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
), thylacocephala
The Thylacocephala (from the Greek language, Greek or ', meaning "Bag, pouch", and or ' meaning "head") are a unique grouping of extinct probable Mandibulata, mandibulate arthropods, that have been considered by some researchers as having possi ...
ns, crustaceans
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
, nautiloid
Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods (Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living ''Nautilus'' and '' Allonautilus''. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded specie ...
s, ammonoids
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
, coleoid
Subclass Coleoidea,
or Dibranchiata, is the grouping of cephalopods containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less" (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish). Unlike its extant sister group, Nautiloidea, whose ...
s, ophiuroid
Brittle stars, serpent stars, or ophiuroids (; ; referring to the serpent-like arms of the brittle star) are echinoderms in the class Ophiuroidea, closely related to starfish. They crawl across the sea floor using their flexible arms for locomot ...
s, crinoids
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are ...
, and vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
. Such diverse assemblages show that organisms diversified wherever and whenever climatic an environmental conditions ameliorated.
Smithian–Spathian boundary event
 An important extinction event occurred during the Olenekian age of the Early Triassic, near the Smithian and Spathian subage boundary. The main victims of this Smithian–Spathian boundary event, often called the Smithian–Spathian extinction, were 'disaster taxa': Palaeozoic species that survived the
An important extinction event occurred during the Olenekian age of the Early Triassic, near the Smithian and Spathian subage boundary. The main victims of this Smithian–Spathian boundary event, often called the Smithian–Spathian extinction, were 'disaster taxa': Palaeozoic species that survived the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as ...
and flourished in the immediate aftermath of the extinction; ammonoids, conodonts, and radiolarians in particular suffered drastic biodiversity losses. Marine reptiles, such as ichthyopterygians and sauropterygians, diversified after the extinction.
The flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' ...
was also affected significantly. It changed from lycopod
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching s ...
dominated (e.g. '' Pleuromeia'') during the Dienerian and Smithian subages to gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
and pteridophyte dominated in the Spathian. These vegetation changes are due to global changes in temperature and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
. Conifers ( gymnosperms) were the dominant plants during most of the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
. Until recently the existence of this extinction event about 249.4 Ma ago was not recognised.
The Smithian–Spathian boundary extinction was linked to late eruptions of the Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
, which released warming greenhouse gases
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
, resulting in climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
and acidification, both on land and in the ocean. A large spike in mercury concentrations relative to total organic carbon, much like during the Permian-Triassic extinction, has been suggested as another contributor to the extinction, although this is controversial and has been disputed by other research that suggests elevated mercury levels already existed by the middle Spathian. Prior to the SSBM extinction event, a flat gradient of latitudinal species richness is observed, suggesting that warmer temperatures extended into higher latitudes
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north–south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole ...
, allowing extension of geographic ranges of species adapted to warmer temperatures, and displacement or extinctions of species adapted to cooler temperatures. Oxygen isotope studies on conodonts have revealed that temperatures rose in the first 2 million years of the Triassic, ultimately reaching sea surface temperatures of up to in the tropics during the Smithian. The extinction itself occurred during a subsequent drop in global temperatures (ca. 8°C over a geologically short period) in the latest Smithian; however, temperature alone cannot account for the Smithian-Spathian boundary extinction, because several factors were at play.
In the ocean, many large and mobile species moved away from the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referr ...
, but large fish remained, and amongst the immobile species such as molluscs
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ...
, only the ones that could cope with the heat survived; half the bivalves disappeared. Conodonts decreased in average size as a result of the extinction. On land, the tropics were nearly devoid of life, with exceptionally arid conditions recorded in Iberia and other parts of Europe then at low latitude. Many big, active animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
returned to the tropics, and plants recolonised on land, only when temperatures returned to normal.
There is evidence that life had recovered rapidly, at least locally. This is indicated by sites that show exceptionally high biodiversity (e.g. the earliest Spathian Paris Biota), which suggest that food webs were complex and comprised several trophic levels
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it i ...
.
References
Notes
Literature
* *; 2004: ''A Geologic Time Scale 2004'',Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pre ...
.
*; 1956: ''Расчленение нижнего отдела триасовой системы на ярусы (Subdivision of the lower series of the Triassic System into stages)'', Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR
The ''Proceedings of the USSR Academy of Sciences'' (russian: Доклады Академии Наук СССР, ''Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR'' (''DAN SSSR''), french: Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences de l'URSS) was a Soviet journal that ...
109(4), pp 842–845 .
External links
GeoWhen Database - Olenekian
at the website of the subcommission for stratigraphic information of the ICS
Lower Triassic timescale
at the website of Norges Network of offshore records of geology and stratigraphy. {{coord, 31.9653, N, 78.0247, E, source:wikidata, display=title *02 Geological ages Triassic geochronology Geology of Siberia Olenyok basin