Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and
largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
of
North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.
The territory of Skopje has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC; remains of
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
settlements have been found within the old
Kale Fortress that overlooks the modern city centre. Originally a
Paeonian
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia ( grc, Παιονία, Paionía) was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians ( grc, Παίονες, Paíones).
The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, a ...
city,
Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
became the capital of
Dardania in the second century BC. On the eve of the 1st century AD, the settlement was seized by the Romans and became a military camp. When the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
was divided into eastern and western halves in 395 AD, Scupi came under
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
rule from
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. During much of the
early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
period, the town was contested between the
Byzantines and the
Bulgarian Empire, whose capital it was between 972 and 992.
From 1282, the town was part of the
Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
, and acted as its capital city from 1346 to 1371. In 1392, Skopje was conquered by the
Ottoman Turk
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
s, who called it (). The town stayed under Ottoman control for over 500 years, serving as the capital of the
pashasanjak of and later the
Vilayet of Kosovo. In 1912, it was annexed by the
Kingdom of Serbia during the
Balkan Wars. During the First World War the city was seized by the
Kingdom of Bulgaria
The Tsardom of Bulgaria ( bg, Царство България, translit=Tsarstvo Balgariya), also referred to as the Third Bulgarian Tsardom ( bg, Трето Българско Царство, translit=Treto Balgarsko Tsarstvo, links=no), someti ...
, and, after the war, it became part of the newly formed
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
as the capital of
Vardarska Banovina
The Vardar Banovina, or Vardar Banate ( mk, Вардарска бановина, Vardarska banovina; sr, Вардарска бановина, translit=Vardarska Banovina; al, Banovina e Vardarit, italics=no), was a province (banate) of the King ...
. In the Second World War the city was again captured by Bulgaria and in 1945 became the capital of
SR Macedonia, a
federated state
A federated state (which may also be referred to as a state, a province, a region, a canton, a land, a governorate, an oblast, an emirate or a country) is a territorial and constitutional community forming part of a federation. Such states d ...
within the
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
. The city developed rapidly, but this was interrupted in 1963 when it was hit by
a disastrous earthquake.
Skopje is on the upper course of the
Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
River, and is on a major north–south
Balkan route between
Belgrade and
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
. It is a centre for metal-processing, chemical, timber, textile, leather, and printing industries. Industrial development of the city has been accompanied by development of the trade, logistics, and banking sectors, as well as an emphasis on the fields of transportation, culture and sport. According to the last official census from 2021, Skopje had a population of 422,540 inhabitants in its urban area and 526,502 in ten municipalities that form the city and, beside Skopje, include many other less urbanized and rural settlements some of which are away from the city itself or even border the neighbouring
Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
.
Name

The name of the city comes from
Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
, which was the name of early
Paeonian
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia ( grc, Παιονία, Paionía) was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians ( grc, Παίονες, Paíones).
The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, a ...
settlement (later capital of
Dardania and subsequently
Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Character ...
) nearby. The meaning of that name is unknown, but there is a hypothesis, it derives from the Greek , (lit. "watcher, observer"), referring to its position on a high place, from which the whole place could be observed.
After
Antiquity, Scupi was occupied by various people and consequently its name was translated several times in several languages. Thus Scupi became "Skopje",
and later "Üsküb" ( ota, اسكوب) for the
Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
. This name was adapted in Western languages in "Uskub" or "Uskup", and these two appellations were used in the Western world until 1912. Some Western sources also cite "Scopia" and "Skopia".
is in fact the name of the city in
Aromanian. Nowadays, the local Albanian population call the city "Shkup" and "Shkupi", the latter being the definite form.
When
Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia (Macedonian and sr, Вардарска Македонија, ''Vardarska Makedonija'') was the name given to the territory of the Kingdom of Serbia (1912–1918) and Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918–1941) roughly corresponding to to ...
was annexed by the
Kingdom of Serbia in 1912, the city officially became "Skoplje" () and this name was adopted by many languages. To reflect local pronunciation, the city's name was eventually spelled as "Skopje" ( mk, Скопје) after the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, when standard
Macedonian became the official language of the new
Socialist Republic of Macedonia.
Geography
Topography
Skopje is in the north of the country, in the centre of the
Balkan peninsula, and halfway between
Belgrade and
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
. The city was built in the Skopje valley, oriented on a west–east axis, along the course of the
Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
river, which flows into the
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
in Greece. The valley is approximately wide
and it is limited by several mountain ranges to the north and south. These ranges limit the urban expansion of Skopje, which spreads along the Vardar and the Serava, a small river which comes from the North. In its administrative boundaries, the City of Skopje stretches for more than ,
but it is only wide.

Skopje is approximately 245 m above sea level and covers 571.46 km
2.
The urbanized area only covers 337 km
2, with a density of 65 inhabitants per hectare.
Skopje, in its administrative limits, encompasses many villages and other settlements, including
Dračevo,
Gorno Nerezi
Gorno Nerezi (, sq, Nerez i Epërm) is a village in the municipality of Karpoš, North Macedonia. The settlement is situated at an altitude of 771 meters (2532 feet). It is located on the wooded slopes of Mt. Vodno, covers a 7 km radius ...
and Bardovci. According to the 2021 census, the City of Skopje itself comprised 422,540 inhabitants and 526,502 within administrative limits.
The City of Skopje reaches the
Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
border to the north-east. Clockwise, it is also bordered by the municipalities of
Čučer-Sandevo
Čučer-Sandevo ( mk, ) is a village in Republic of North Macedonia. It is a seat of the Čučer-Sandevo Municipality.
Geography
The village is located in the northern part of the Skopje Valley, in the central part of the territory of the Muni ...
,
Lipkovo
Lipkovo ( mk, , sq, Likovë) is a village in North Macedonia. It is the seat of Lipkovo Municipality.
History
Lipkovo was a central strategic village during the 2001 armed conflict between the Albanian National Liberation Army and the Maced ...
,
Aračinovo
Aračinovo ( mk, Арачиново , sq, Haraçinë) is a village and seat of the municipality of Aračinovo, North Macedonia.
History
During the 2001 Macedonia conflict, it was occupied by ethnic Albanian insurgents. Later, during violence ...
,
Ilinden,
Studeničani,
Sopište,
Želino
Želino ( mk, , sq, Zhelinë) is a village and seat of the municipality of Želino, North Macedonia.
History
According to the 1467-68 Ottoman defter, Želino appears as being largely inhabited by an Orthodox Christian Albanian population. Due ...
and
Jegunovce.

Hydrography

The
Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
river, which flows through Skopje, is at approximately from its source near
Gostivar
Gostivar ( mk, Гостивар , Albanian and Turkish: ''Gostivar''), is a city in North Macedonia, located in the upper Polog valley region. It is one of the largest municipalities in the country with a population of 81,042, and the town also ...
. In Skopje, its average discharge is 51 m
3/s, with a wide amplitude depending on seasons, between 99.6 m
3/s in May and 18.7 m
3/s in July. The water temperature is comprised between 4.6 °C in January and 18.1 °C in July.

Several rivers meet the Vardar within the city boundaries. The largest is the
Treska
Treska ( mk, Треска, ) is a river in the western part of North Macedonia, a right tributary to Vardar. It is long, and its basin is 2350 km2.''Opća enciklopedija Jugoslavenskog leksikografskog zavoda - Zagreb, 1982. (2. izdanje)''
...
, which is long. It crosses the
Matka Canyon before reaching the Vardar on the western extremity of the City of Skopje. The
Lepenac
The Lepenac ( sq, Lepenci ; mk, ; sr, Лепенац, ) is a river in southern Kosovo and northern North Macedonia, a long left tributary to the Vardar river.
Sirinić
The Lepenac springs out on the Kodža Balkan mountain, east of the ci ...
, coming from
Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, flows into the Vardar on the northwestern end of the urban area. The Serava, also coming from the North, had flowed through the
Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
until the 1960s, when it was diverted towards the West because its waters were very polluted. Originally, it met the Vardar close to the seat of the
Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts
The Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts ( mk, Македонска Академија на Науките и Уметностите, МАНУ) is an academic institution in North Macedonia.
History
The Academy of Sciences and Arts was establ ...
. Nowadays, it flows into the Vardar near the ruins of
Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
. Finally, the Markova Reka, the source of which is on Mount
Vodno
Vodno ( mk, Водно) is a mountain in North Macedonia. It is located in the northern part of the country, to the southwest of the capital city Skopje. The highest point of the mountain is at ''Krstovar peak'', on 1066 meters and the submontane ...
, meets the Vardar at the eastern extremity of the city. These three rivers are less than long.
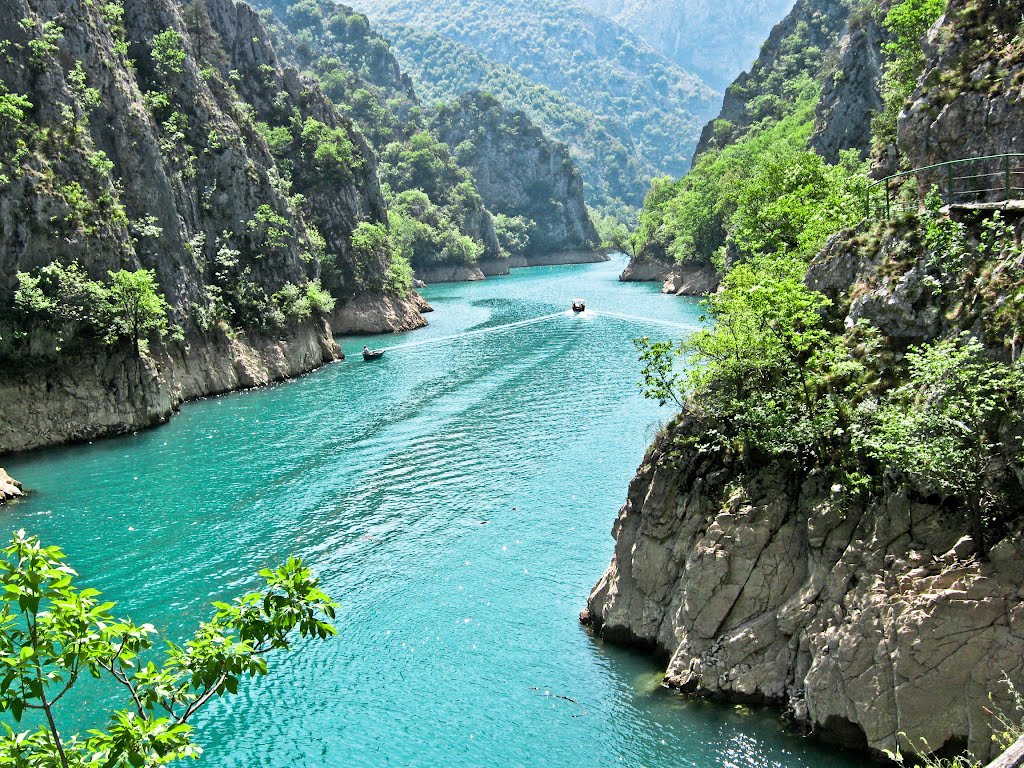

The City of Skopje incorporates two artificial lakes, on the Treska. The lake Matka is the result of the construction of a dam in the Matka Canyon in the 1930s, and the Treska lake was dug for leisure purpose in 1978.
Three small natural lakes can be found near Smiljkovci, on the northeastern edge of the urban area.
The river
Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
historically caused many floods, such as in 1962, when its outflow reached 1110 m
3/s
−1.
Several works have been carried since Byzantine times to limit the risks, and since the construction of the Kozjak dam on the Treska in 1994, the flood risk is close to zero.
The subsoil contains a large
water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
which is alimented by the Vardar river and functions as an underground river. Under the table lies an
aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteris ...
contained in
marl. The water table is 4 to 12 m under the ground and 4 to 144 m deep. Several wells collect its waters but most of the drinking water used in Skopje comes from a
karstic spring in Rašče, west of the city.
Geology


The Skopje valley is bordered on the West by the
Šar Mountains
The Šar Mountains (Serbian and mk, Шар Планина, Šar Planina, colloquially also ) or Sharr Mountains ( sq, Malet e Sharrit), form a mountain range in the Balkans that extends from Kosovo and the northwest of North Macedonia to north ...
, on the South by the
Jakupica range, on the East by hills belonging to the
Osogovo
Osogovo ( Bulgarian/Macedonian: ), or Osogovska Planina or Osogovski Planini (Осоговска Планина or Осоговски Планини), is a mountain range and ski resort between the south-western part of Bulgaria (Kyustendil Provi ...
range, and on the North by the
Skopska Crna Gora
tr, Karadağ, italics=no
, photo = Skopska Crna Gora-MKD.JPG
, photo_caption =
, photo_size = 250
, highest = Ramno
, elevation_m = 1651
, elevation_ref =
, prominence_m =
, prominence_ref =
, listing =
, location = North Macedonia ...
. Mount
Vodno
Vodno ( mk, Водно) is a mountain in North Macedonia. It is located in the northern part of the country, to the southwest of the capital city Skopje. The highest point of the mountain is at ''Krstovar peak'', on 1066 meters and the submontane ...
, the highest point inside the city limits, is 1066 m high and is part of the
Jakupica range.
Although Skopje is built on the foot of Mount Vodno, the urban area is mostly flat. It comprises several minor hills, generally covered with woods and parks, such as Gazi Baba hill (325 m), Zajčev Rid (327 m), the foothills of Mount Vodno (the smallest are between 350 and 400 m high) and the promontory on which
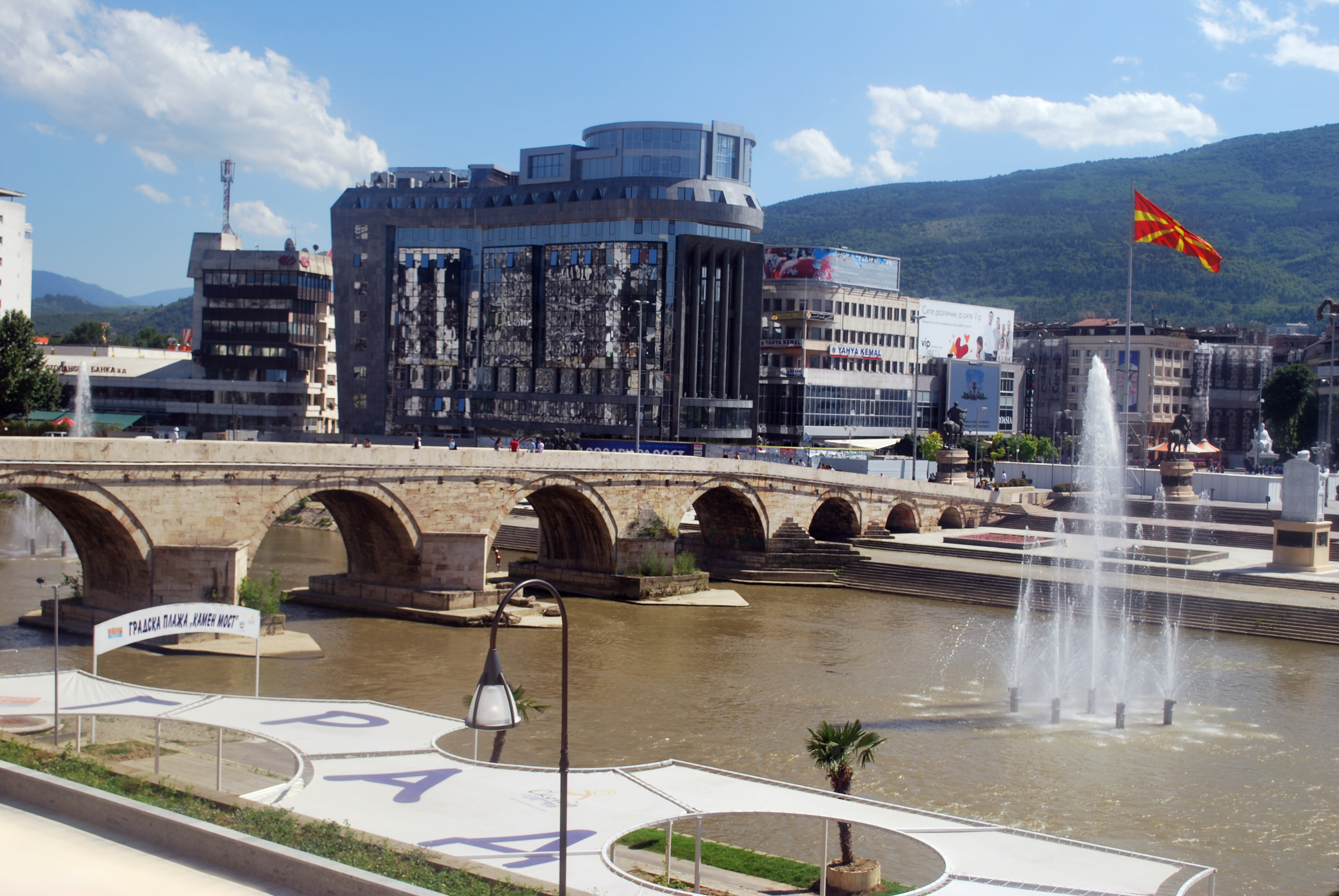
Skopje Fortress is built.
The Skopje valley is near a seismic fault between the African and Eurasian
tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
s and experiences regular seismic activity.
This activity in enhanced by the porous structure of the subsoil. Large earthquakes occurred in Skopje in 518, 1555 and 1963.
The Skopje valley belongs to the Vardar geotectonic region, the subsoil of which is formed of
Neogene and
Quaternary deposits. The substratum is made of
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58[sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...](_blank)
,
marl and various conglomerates. It is covered by a first layer of Quaternary sands and silt, which is between 70 and 90 m deep. The layer is topped by a much smaller layer of clay, sand, silt and gravel, carried by the
Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
river. It is between 1.5 and 5.2 m deep.
In some areas, the subsoil is
karstic. It led to the formation of canyons, such as the
Matka Canyon, which is surrounded by ten caves. They are between 20 and 176 m deep.
Climate
Skopje has a borderline
humid subtropical climate (''Cfa'' in the
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
) and cold
semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of sem ...
(''BSk''). with a mean annual temperature of . Precipitation is relatively low due to the pronounced
rain shadow of the
Prokletije
The Accursed Mountains ( sq, Bjeshkët e Nemuna; sh-Cyrl-Latn, Проклетије, Prokletije, ; both translated as "Cursed Mountains"), also known as the Albanian Alps ( sq, Alpet Shqiptare), are a mountain group in the western part of the B ...
mountains to the northwest, being significantly less than what is received on the Adriatic Sea coast at the same latitude. The summers are long, hot and relatively dry with low humidity. Skopje's average July high is . On average Skopje sees 88 days above each year, and 10.2 days above every year. Winters are short, relatively cold and wet. Snowfalls are common in the winter period, but heavy snow accumulation is rare and the snowcover lasts only for a few hours or a few days if heavy. In summer, temperatures are usually above and sometimes above . In spring and autumn, the temperatures range from . In winter, the day temperatures are roughly in the range from , but at nights they often fall below and sometimes below . Typically, temperatures throughout one year range from −13 °C to 39 °C. Occurrences of precipitation are evenly distributed throughout the year, being heaviest from October to December, and from April to June.
Environment

The City of Skopje encompasses various natural environments and its fauna and flora are rich. However, it is threatened by the intensification of agriculture and the urban extension. The largest protected area within the city limits is Mount Vodno, which is a popular leisure destination. A cable car connects its peak to the downtown, and many pedestrian paths run through its woods. Other large natural spots include the
Matka Canyon.
The city itself comprises several parks and gardens amounting to 4,361 hectares. Among these are the City Park (Gradski Park), built by the Ottoman Turks at the beginning of the 20th century; Žena Borec Park, in front of the Parliament; the university arboretum; and Gazi Baba forest. Many streets and boulevards are planted with trees.
Skopje experiences many environmental issues which are often overshadowed by the economic poverty of the country. However, alignment of North Macedonian law on European law has brought progress in some fields, such as water and waste treatment, and industrial emissions.
Skopje remains one of the most polluted cities in the world, topping the ranks in December 2017.
Steel processing, which a crucial activity for the local economy, is responsible for soil pollution with heavy metals such as lead,
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
and
cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
, and air pollution with
nitrogen oxide and
carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
.
Vehicle traffic and
district heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating a ...
plants are also responsible for air pollution. The highest pollution levels usually occur in autumn and winter.
Water treatment plants are being built, but much polluted water is still discharged untreated into the
Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
.
Waste is disposed of in the open-air municipal landfill site, north of the city. Every day, it receives 1,500 m
3 of domestic waste and 400 m
3 of industrial waste. Health levels are better in Skopje than in the rest of North Macedonia, and no link has been found between the low environmental quality and the health of the residents.
Urbanism
Urban morphology

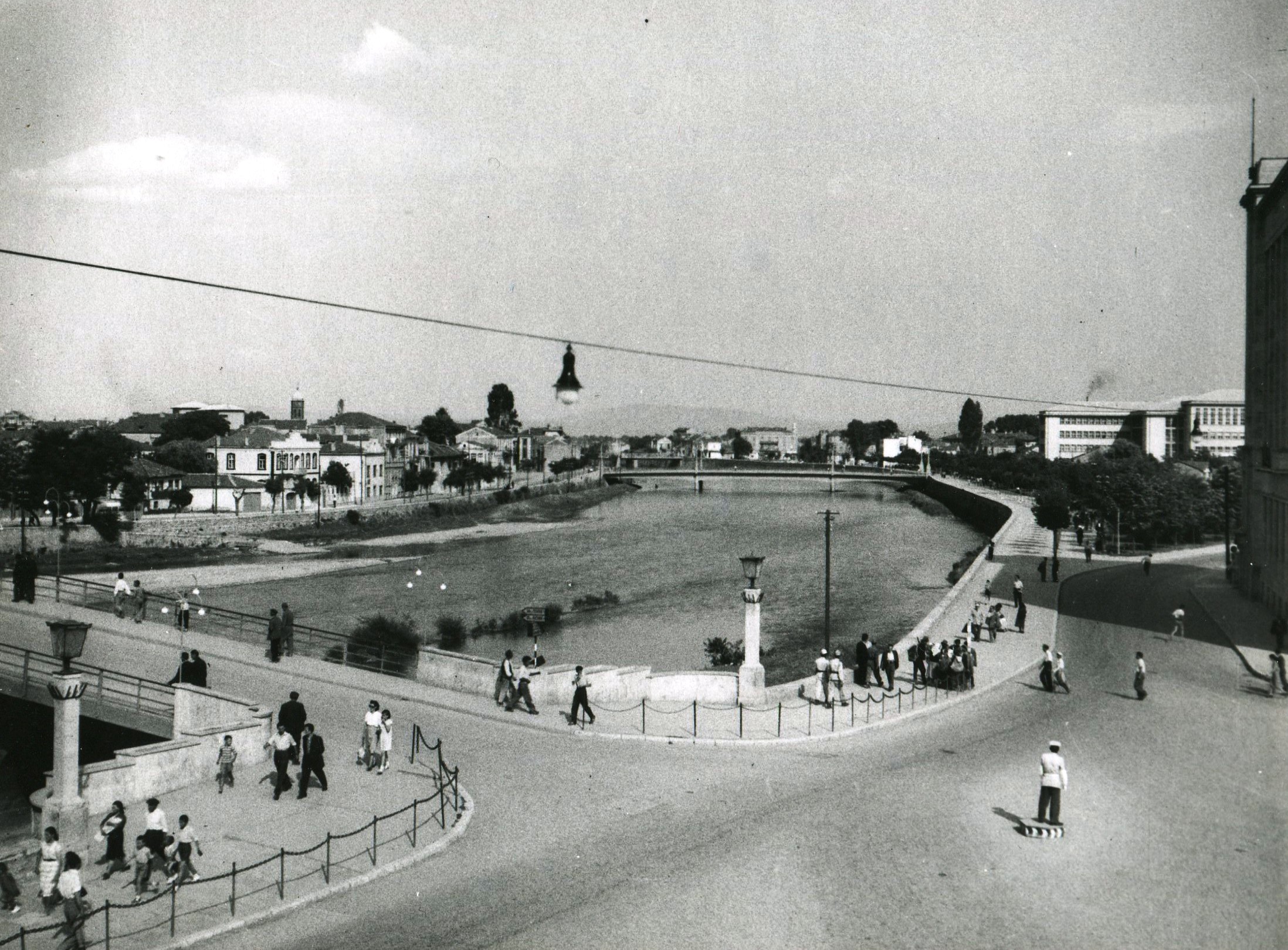
The urban morphology of Skopje was deeply impacted by the
26 July 1963 earthquake, which destroyed 80% of the city, and by the reconstruction that followed.
[ For instance, neighbourhoods were rebuilt in such a way that the demographic density remains low to limit the impact of potential future earthquakes.][
Reconstruction following the 1963 earthquake was mainly conducted by the Polish architect Adolf Ciborowski, who had already planned the reconstruction of ]Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Ciborowski divided the city in blocks dedicated to specific activities. The banks of the Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
river became natural areas and parks, areas between the main boulevards were built with highrise housing and shopping centres, and the suburbs were left to individual housing and industry. The south bank of the Vardar river generally comprises highrise tower blocks, including the vast Karpoš neighbourhood which was built in the 1970s west of the centre. Towards the East, the new municipality of Aerodrom was planned in the 1980s to house 80,000 inhabitants on the site of the old airport. Between Karpoš and Aerodrom lies the city centre, rebuilt according to plans by Japanese architect
The south bank of the Vardar river generally comprises highrise tower blocks, including the vast Karpoš neighbourhood which was built in the 1970s west of the centre. Towards the East, the new municipality of Aerodrom was planned in the 1980s to house 80,000 inhabitants on the site of the old airport. Between Karpoš and Aerodrom lies the city centre, rebuilt according to plans by Japanese architect Kenzo Tange
is a common masculine Japanese given name.
Possible writings
Kenzō can be written using different kanji characters and can mean:
*賢三, "wise, three"
*健三, "healthy, three"
*謙三, "humble, three"
*健想, "healthy, concept"
*建造, "bu ...
. The centre is surrounded by a row of long buildings suggesting a wall ("Gradski Zid").[
On the north bank, where the most ancient parts of the city lie, the ]Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
was restored and its surroundings were rebuilt with low-rise buildings, so as not to spoil views of the Skopje Fortress. Several institutions, including the university and the Macedonian academy, were also relocated on the north bank to reduce borders between the ethnic communities. Indeed, the north bank is mostly inhabited by Muslim Albanians, Turks and Roma, whereas Christian ethnic Macedonians predominantly reside on the south bank.[
The earthquake left the city with few historical monuments, apart from the Ottoman ]Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
, and the reconstruction, conducted between the 1960s and 1980s, turned Skopje into a modernist
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
but grey city. At the end of the 2000s, the city centre experienced profound changes. A highly controversial urban project, "Skopje 2014
Skopje 2014 ( mk, Скопје 2014) was a project financed by the Macedonian government of the then-ruling nationalist party VMRO-DPMNE, with the official purpose of giving the capital Skopje a more classical appeal. The project, officially anno ...
", was adopted by the municipal authorities to give the city a more monumental and historical aspect, and thus to transform it into a proper national capital. Several neoclassical buildings destroyed in the 1963 earthquake were rebuilt, including the national theatre, and streets and squares were refurbished. Many other elements were also built, including fountains, statues, hotels, government buildings and bridges. The project has been criticized because of its cost and its historicist aesthetics.Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
.
Some areas of Skopje suffer from a certain anarchy because many houses and buildings were built without consent from the local authorities.Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
.
File:Towers Karpos4 Skopje.jpg, Highrise housing in Karpoš.
File:Park Aerodrom vo Novo Lisiče 03.JPG, The newly developed neighbourhood of Novo Lisiče, in Aerodrom.
File:Skopje 2014 - Archeological Museum of Macedonia (by Pudelek).JPG, The archeological museum, one of the elements of "Skopje 2014
Skopje 2014 ( mk, Скопје 2014) was a project financed by the Macedonian government of the then-ruling nationalist party VMRO-DPMNE, with the official purpose of giving the capital Skopje a more classical appeal. The project, officially anno ...
".
Urban sociology
 Skopje is an ethnically diverse city, and its urban sociology primarily depends on ethnic and religious belonging. Macedonians form 66% of the city population, while Albanians and Roma account respectively for 20% and 6%.
Skopje is an ethnically diverse city, and its urban sociology primarily depends on ethnic and religious belonging. Macedonians form 66% of the city population, while Albanians and Roma account respectively for 20% and 6%.Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
, in areas massively rebuilt after 1963, and Muslims live on the northern side, in the oldest neighbourhoods of the city. These neighbourhoods are considered more traditional, whereas the south side evokes to Macedonians modernity and rupture from rural life.Čair municipality
Čair ( mk, , sq, Komuna e Çairit) is one of the ten municipalities that make up the Skopje, the capital of the North Macedonia. The municipal administration consists of a council and mayor. Skopje's old town is located in Čair. The municip ...
, and for Šuto Orizari municipality
Šuto Orizari ( mk, ; Balkan Romani: ''Shuto Orizari''; sq, Shutkë), often shortened as ''Šutka'' (Шутка), is one of the ten municipalities that make up the City of Skopje, the capital of the Republic of North Macedonia. ''Šuto Orizari' ...
, which are the two main Roma neighbourhoods. They are made of many illegal constructions not connected to electricity and water supply, which are passed from a generation to the other. Topaana, close to the Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
, is a very old area: it was first mentioned as a Roma neighbourhood in the beginning of the 14th century. It has between 3,000 and 5,000 inhabitants. Šuto Orizari, on the northern edge of the city, is a municipality of its own, with Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
as its local official language. It was developed after the 1963 earthquake to accommodate Roma who had lost their house.
Localities and villages
 Outside of the urban area, the City of Skopje encompasses many small settlements. Some of them are becoming outer suburbs, such as
Outside of the urban area, the City of Skopje encompasses many small settlements. Some of them are becoming outer suburbs, such as Čento
Čento ( mk, Ченто; sq, Hasanbeg)''Таков е примерот со мухаирите што дошле од Гацко од Босна , кои што биле привремено сместени во Хасанбегово ( дене� ...
, on the road to Belgrade, which has more than 23,000 inhabitants, and Dračevo, which has almost 20,000 inhabitants.Saraj municipality
Saraj ( mk, , sq, Saraj) is one of the ten municipalities that make up the city of Skopje, the capital of the Republic of North Macedonia.
* '' Saraj'', which means "palace" in Turkish, is also the name of the village where the municipal seat ...
, which is the most rural of the ten municipalities that form the City of Skopje.Petrovec municipality
The Municipality of Petrovec ( mk, Петровец, ''Petrovec''; sq, Ibrahimovë) is a municipality in northern North Macedonia, near the capital Skopje. '' Petrovec'' is also the name of the village where the municipal seat is found. It is lo ...
. They benefit from the presence of major roads, railways and the airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surfa ...
, in Petrovec.
Pollution
Air pollution is a serious problem in Skopje, especially in winter. Concentrations of certain types of particulate matter (PM2 and PM10) are regularly over twelve times the WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
recommended maximum levels. In winter, smoke regularly obscures vision and can lead to problems for drivers. Together with India and Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
is one of the most polluted places in the world.
Skopje's high levels of pollution are caused by a combination of smoke from houses, emissions from the industry, from buses and other forms of public transport, as well as from cars, and a lack of interest in caring for the environment. Central heating is often not affordable, and so households often burn firewood, as well as used car tyres, various plastic garbage, petroleum and other possible flammable waste, which emits toxic chemicals harmful to the population, especially to children and the elderly.
The city's smog has reduced its air quality and affected the health of many of its citizens, many of which have died from pollution-related illnesses.
An application called ''AirCare'' ('MojVozduh') has been launched by local eco activist Gorjan Jovanovski to help citizens track pollution levels. It uses a Traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – known also as robots in South Africa are signalling devices positioned at road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order to control flows of traffic.
Traffic light ...
system, with purple for heavily polluted air, red for high levels detected, amber for moderate levels detected, and green for when the air is safe to inhale. The application relies on both government and volunteer sensors to track hourly air pollution. Unfortunately, government sensors are frequently inoperable and malfunctioning, causing the need for more low-cost, but less accurate, volunteer sensors to be put up by citizens. Faults on government sensors are especially frequent when the pollution is measured is extremely high, according to the AQILHC (Air Quality Index Levels of Health Concern).
On 29 November 2019, a march, organized by the Skopje Smog Alarm activist community, attracted thousands of people who opposed the government's lack of action in dealing with the city's pollution, which has worsened since 2017, contributing to around 1300 deaths annually.
History
Origins
The rocky promontory on which stands the Fortress was the first site to be settled in Skopje. The earliest vestiges of human occupation found on this site date from the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
(4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
).Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
. Archeological research suggest that the settlement always belonged to a same culture, which progressively evolved thanks to contacts with Balkan and Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
cultures, and later with the Aegean. The locality eventually disappeared during the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
emerged. It was on Zajčev Rid hill, some west of the fortress promontory. at the centre of the Balkan peninsula and on the road between Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
and Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
,Triballi
The Triballi ( grc, Τριβαλλοί, Triballoí, lat, Triballi) were an ancient people who lived in northern Bulgaria in the region of Roman Oescus up to southeastern Serbia, possibly near the territory of the Morava Valley in the late Iron A ...
. Later the area was populated by the Paionians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
. Scupi was originally a Paionian settlement, but it became afterwards Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
an town.Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
ans, who lived in present-day Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, invaded the region around Skopje during the 3rd century BC. ''Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
'', the ancient name for Skopje, became the capital of Dardania, which extended from Naissus to Bylazora
Bylazora or Vilazora ( grc, Βυλάζωρα) was a Paeonian city from the period of early classic antiquity. It is located near the village of Knezhje, which is part of the municipality of Sveti Nikole in North Macedonia.
History
Polybius te ...
in the second century BC. The Dardanians had remained independent after the Roman conquest of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an Classical antiquity, ancient monarchy, kingdom on the periphery of Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. Th ...
, and it seems most likely that Dardania lost independence in 28 BC.
Roman Scupi
 Roman expansion east brought Scupi under Roman rule as a colony of legionnaires, mainly veterans of the
Roman expansion east brought Scupi under Roman rule as a colony of legionnaires, mainly veterans of the Legio VII Claudia
Legio VII Claudia (Claudius' Seventh Legion) was a legion of the Imperial Roman army.
History
According to H.M.D. Parker, the first legion Julius Caesar raised for his campaigns in Cisalpine Gaul was the Seventh; the numbers 1-4 were omitted ...
in the time of Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
(81–96 AD). However, several legions from the Roman province of Macedonia
Macedonia ( grc-gre, Μακεδονία) was a province of the Roman Empire, encompassing the territory of the former Antigonid Kingdom of Macedonia, which had been conquered by Rome in 168 BC at the conclusion of the Third Macedonian War. The pr ...
of Crassus' army may already have been stationed in there around 29–28 BC, before the official imperial command was instituted. The first mention of the city was made at that period by Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
, who died in 17 AD.Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
's rule. After the division of the province by Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
in 86 AD, Scupi was elevated to colonial status, and became a seat of government within the new province of Moesia Superior. The district called Dardania (within Moesia Superior) was formed into a special province by Diocletian, with the capital at Naissus. In Roman times the eastern part of Dardania, from Scupi to Naissus, remained inhabited mostly by a local population, mainly from Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
origin.
The city population was very diverse. Engravings on tombstones suggest that only a minority of the population came from Italy, while many veterans were from Dalmatia, South Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
and Syria. Because of the ethnic diversity of the population, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
maintained itself as the main language in the city at the expense of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, which was spoken in most of the Moesian and Macedonian cities. During the following centuries, Scupi experienced prosperity. The period from the end of the 3rd century to the end of the 4th century was particularly flourishing.Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
and Scupi became the seat of a diocese. In 395, following the division of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in two, Scupi became part of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
.Albanoi
The Albanoi ( grc, Ἀλβανοί, ''Albanoi''; la, Albani) were an Illyrian tribe. They were possibly first mentioned by Hecataeus of Miletus (550-476 BCE) under the name ''Abroi''. Ptolemy (200-118 BCE) is the first authors who mentions them u ...
was found in Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
.
In its heyday, Scupi covered 40 hectares and was closed by a wide wall. It had many monuments, including four necropoles, a theatre, thermae,
Middle Ages

 In 518, Scupi was destroyed by a violent earthquake,
In 518, Scupi was destroyed by a violent earthquake,[ possibly the most devastating the town experienced. At that time, the region was threatened by the Barbarian invasions, and the city inhabitants had already fled in forests and mountains before the disaster occurred. The city was eventually rebuilt by ]Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renova ...
. During his reign, many Byzantine towns were relocated on hills and other easily defendable places to face invasions. It was thus transferred on another site: the promontory on which stands the fortress. However, Scupi was sacked by Slavs at the end of the 6th century and the city seems to have fallen under Slavic rule in 595. The Slavic tribe which sacked Scupi were probably the Berziti,Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
valley. However the Slavs did not settle permanently in the region that had been already plundered and depopulated, but continued south to the Mediterranean coast. After the Slavic invasion it was deserted for some time and is not mentioned during the following centuries.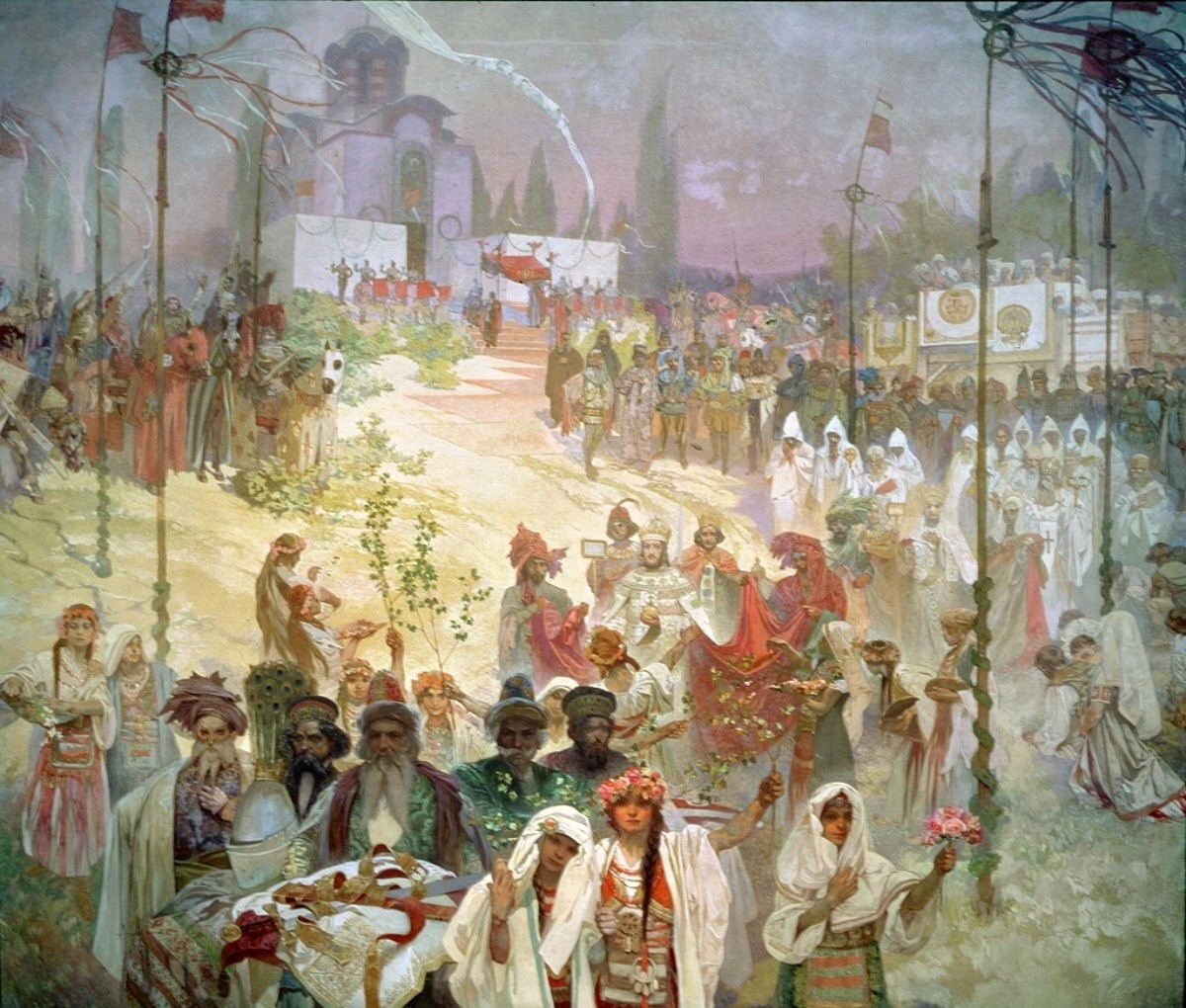 Starting from the end of the 10th century Skopje experienced a period of wars and political troubles. It served as Bulgarian capital from 972 to 992, and
Starting from the end of the 10th century Skopje experienced a period of wars and political troubles. It served as Bulgarian capital from 972 to 992, and Samuil
Samuel (also Samuil; bg, Самуил, ; mk, Самоил/Самуил, ; Old Church Slavonic: Самоилъ; died October 6, 1014) was the Tsar (''Emperor'') of the First Bulgarian Empire from 997 to 6 October 1014. From 977 to 997, he was ...
ruled it from 976province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
called Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
. Later Skopje was briefly seized twice by Slavic insurgents who wanted to restore the Bulgarian state. At first in 1040 under Peter Delyan
Petar II Delyan (reigned 1040–1041) ( bg, Петър II Делян, Greek: Πέτρος Δελεάνος) was the leader of an uprising against Byzantine rule in the Theme of Bulgaria during the summer of 1040. He was proclaimed Tsar of Bulgari ...
's command, and in 1072 under the orders of Georgi Voyteh Georgi Voyteh ( bg, Георги Войтех) was an 11th-century Bulgarian aristocrat from Skopje who started a major uprising in Byzantine Bulgaria against the Byzantine rule.Dennis P. Hupchick, The Bulgarian-Byzantine Wars for Early Medieval B ...
. In 1081, Skopje was captured by Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
troops led by Robert Guiscard and the city remained in their hands until 1088. Skopje was subsequently conquered by the Serbian Grand Prince Vukan in 1093, and again by the Normans four years later. However, because of epidemics and food shortage, Normans quickly surrendered to the Byzantines.
During the 12th and 13th centuries, Bulgarians and Serbs took advantage of Byzantine decline to create large kingdoms stretching from Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
to the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
. Kaloyan
Kaloyan or Kalojan, also known as Ioannitsa or Johannitsa ( bg, Калоян, Йоаница; 1170 – October 1207), was emperor or tsar of Bulgaria from 1196 to 1207. He was the younger brother of Theodor and Asen, who led the anti-Byzant ...
brought Skopje back into reestablished Bulgaria in 1203Boril of Bulgaria
Boril ( bg, Борил) was the emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria from 1207 to 1218. He was the son of an unnamed sister of his predecessor, Kaloyan and Kaloyan's brothers, Peter II and Ivan Asen I, who had restored the independent Bulga ...
with whom he led a successful joint campaign against Serbia's first internationally recognized king Stefan Nemanjić
Stefan Nemanja II ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Немања II, ), or Stephen the First-Crowned ( sr, / , ; – 24 September 1228), was the Grand Prince of Serbia from 1196 and the King of Serbia from 1217 until his death in 1228. He was the first ...
.Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinri ...
before recaptured by Ivan Asen II
Ivan Asen II, also known as John Asen II ( bg, Иван Асен II, ; 1190s – May/June 1241), was Emperor (Tsar) of Bulgaria from 1218 to 1241. He was still a child when his father Ivan Asen I one of the founders of the Second Bulgarian Empir ...
and held by Bulgaria until 1246 when the Upper Vardar valley was incorporated once more into a Byzantine state – the Empire of Nicaea. Byzantine conquest was briefly reversed in 1255 by the regents of the young Michael Asen I of Bulgaria
Michael II Asen ( bg, Михаил II Асен; 1239 – December 1256/January 1257) was emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria from 1246 to 1256 or 1257. He was the son of Ivan Asen II and Irene Komnene Doukaina. He succeeded his half-brother, Kaliman I ...
. Meanwhile, in the parallel civil war for the Crown in Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
Skopje boyar and grandson to Stefan Nemanja
Stefan Nemanja (Serbian Cyrillic: , ; – 13 February 1199) was the Grand Prince ( Veliki Župan) of the Serbian Grand Principality (also known as Raška, lat. ) from 1166 to 1196. A member of the Vukanović dynasty, Nemanja founded the Nema ...
Constantine Tikh gained the upper hand and ruled until Europe's only successful peasant revolt the Uprising of Ivaylo
The Uprising of Ivaylo ( bg, Въстанието на Ивайло) was a rebellion of the Bulgarian peasantry against the incompetent rule of Emperor Constantine Tikh and the Bulgarian nobility. The revolt was fuelled mainly by the failure ...
deposed him.
In 1282 Skopje was captured by Serbian king Stefan Milutin. Under the political stability of the Nemanjić rule, settlement has spread outside the walls of the fortress, towards Gazi Baba hill.Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
and Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterran ...
opened shops. The town greatly benefited from its location near European, Middle Eastern, and African market. In the 14th century, Skopje became such an important city that king Stefan Dušan
Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан, ), known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr, / ; circa 1308 – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Tsar (or Emperor) and autocrat of the Serbs, Gre ...
made it the capital of the Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
. In 1346, he was crowned "Emperor of the Serbs and Greeks" in Skopje.Vuk Branković
Vuk Branković ( sr-cyr, Вук Бранковић, , 1345 – 6 October 1397) was a Serbian medieval nobleman who, during the Fall of the Serbian Empire, inherited a province that extended over present-day southern and southwestern Serbia, enti ...
in the wake of the Battle of Maritsa (1371) before becoming part of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in 1392.Stefan Dečanski
Stefan Uroš III ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош III, ), known as Stefan Dečanski ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Дечански, ; 1276 – 11 November 1331), was the King of Serbia from 6 January 1322 to 8 September 1331. Dečanski was the son of ...
mentioned Albanians as being in the district of Skopje and regularly going to the Fair of Saint George
Saint George (Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
which convened near the city.
Ottoman period
Skopje economic life greatly benefited from its position in the middle of Rumelia, the European province of the Ottomans. The Stone Bridge, "one of the most imposing stone bridges to be found in Yugoslavia", was reconstructed under the patronage of Sultan Mehmed II the Conqueror between 1451 and 1469.Mustafa Pasha Mosque
Mustafa Pasha Mosque ( mk, Мустафа-пашина џамија; ; tr, Mustafa Paşa Camii) is an Ottoman-era mosque located in the Old Bazaar of Skopje, North Macedonia.
History
The structure stands on a plateau above the old bazaar, built ...
, built in 1492, is reputed to be "undoubtedly one of the most resplendent sacral Islamic buildings in the Balkans."Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, together with Belgrade and Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo ...
. At that time, Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterran ...
, which was a busy harbour, had not even 7,000 inhabitants. Following the Ottoman conquest, the city population changed. Christians were forcibly converted to Islam or were replaced by Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
and Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
. At that time, Christians of Skopje were mostly non-converted Slavs and Albanians, but also Ragusan Ragusan may refer to:
* citizen of the Republic of Ragusa
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world"
, population_estimate ...
and Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
tradesmen.Modified Mercalli intensity scale
The Modified Mercalli intensity scale (MM, MMI, or MCS), developed from Giuseppe Mercalli's Mercalli intensity scale of 1902, is a seismic intensity scale used for measuring the intensity of shaking produced by an earthquake. It measures the eff ...
, although others believe this is an overestimate.Hapsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
seized Skopje which was already weakened by a cholera epidemic. The same day, general Silvio Piccolomini set fire to the city to end the epidemic.Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
in 1683. Skopje burned during two days but the general himself perished of the plague and his leaderless army was routed.Hajduk
A hajduk ( hu, hajdúk, plural of ) is a type of irregular infantry found in Central and parts of Southeast Europe from the late 16th to mid 19th centuries. They have reputations ranging from bandits to freedom fighters depending on time, p ...
s, leaders of the uprisings, had to follow them in their retreat north of the Balkans.plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pe ...
and cholera epidemics and many inhabitants emigrated.Hajduk
A hajduk ( hu, hajdúk, plural of ) is a type of irregular infantry found in Central and parts of Southeast Europe from the late 16th to mid 19th centuries. They have reputations ranging from bandits to freedom fighters depending on time, p ...
s.Štip
Štip ( mk, Штип ) is the largest urban agglomeration in the eastern part of North Macedonia, serving as the economic, industrial, entertainment and educational focal point for the surrounding municipalities.
As of the 2002 census, the city ...
(15–20,000).Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, which were gaining autonomy and independence from the Empire at that time.nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
arose in the Empire and in 1870 a new Bulgarian Church was established and its separate diocese was created, based on ethnic identity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, rather than religious principles. The Slavic population of the bishopric of Skopje voted in 1874 overwhelmingly, by 91% in favour of joining the Exarchate and became part of the Bulgarian Millet. Economic growth was permitted by the construction of the Skopje-Salonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
railway in 1873.Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
and this contributed to the relocation of economic activities on this side of the river, which had never been urbanized before.Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO; bg, Вътрешна Македонска Революционна Организация (ВМРО), translit=Vatrešna Makedonska Revoljucionna Organizacija (VMRO); mk, Внатр� ...
when it organized the 1903 Ilinden uprising Ilinden ( Bulgarian/Macedonian Cyrillic: Илинден) or Ilindan (Serbian Cyrillic: Илиндан), meaning "Saint Elijah
Elijah ( ; he, אֵלִיָּהוּ, ʾĒlīyyāhū, meaning "My God is Yahweh/YHWH"; Greek form: Elias, ''Elías'' ...
. Its revolutionary network in Skopje region was not well-developed and the lack of weapons was a serious problem. At the outbreak of the uprising the rebel forces derailed a military train. On 3 and 5 August respectively, they attacked an Ottoman unit guarding the bridge on the Vardar river and gave a battle in the "St. Jovan" monastery. In the next few days the band was pursued by numerous Bashibozuks and moved to Bulgaria.
In 1877, Skopje was chosen as the capital city of the new Kosovo Vilayet, which encompassed present-day Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, northwestern Macedonia and the Sanjak of Novi Pazar
The Sanjak of Novi Pazar ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Novopazarski sandžak, Новопазарски санџак; tr, Yeni Pazar sancağı) was an Ottoman sanjak (second-level administrative unit) that was created in 1865. It was reorganized in 1880 and ...
. In 1905, the city had 32,000 inhabitants, making it the largest of the vilayet, although closely followed by Prizren with its 30,000 inhabitants.Gustav Weigand
Gustav Weigand (1 February 1860 – 8 July 1930), was a German linguist and specialist in Balkan languages, especially Romanian and Aromanian. He is known for his seminal contributions to the dialectology of the Romance languages of the Balkans ...
described that the Skopje Muslim population of "Turks" or Ottomans (Osmanli) during the late Ottoman period were mainly Albanians that spoke Turkish in public and Albanian at home.[ "Aarbakke notes that Weigand says of Skopje that the "Turks" are mostly Albanians who speak Turkish in public and Albanian at home, "but should be regarded as Osmanli" (Aarbakke 1992:10)."] At the beginning of the 20th century, local economy was focused on dyeing
Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular c ...
, weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal ...
, tanning
Tanning may refer to:
*Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather
*Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin
**Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun
**Sunless tanning, application of a stain or dye t ...
, ironworks and wine and flour processing.Young Turk Revolution
The Young Turk Revolution (July 1908) was a constitutionalist revolution in the Ottoman Empire. The Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), an organization of the Young Turks movement, forced Sultan Abdul Hamid II to restore the Ottoman Consti ...
in 1908, the Ottoman Empire experienced democracy and several political parties were created.Mustafa Pasha Mosque
Mustafa Pasha Mosque ( mk, Мустафа-пашина џамија; ; tr, Mustafa Paşa Camii) is an Ottoman-era mosque located in the Old Bazaar of Skopje, North Macedonia.
History
The structure stands on a plateau above the old bazaar, built ...
.
File:Shkup1912.jpg, Skopje after being captured by Albanian revolutionaries in August 1912 after defeating the Ottoman forces holding the city
File:Ottoman Postcard of Huriet in Skopie2.jpg, Bulgarian manifestation in support of the Young Turk Revolution
The Young Turk Revolution (July 1908) was a constitutionalist revolution in the Ottoman Empire. The Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), an organization of the Young Turks movement, forced Sultan Abdul Hamid II to restore the Ottoman Consti ...
File:Sv. Bogorodica Skopje 01.jpg, The Church of the Nativity of the Theotokos, seat of the Bulgarian Orthodox Diocese of Skopje, built in the 19th century.
File:Skopje-couteliers 1919.jpg, Cutlers in the Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
around 1900.
Balkan Wars to present day
 Following an alliance contracted in 1912,
Following an alliance contracted in 1912, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
declared war on the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. Their goal was to definitively expel the Ottomans from Europe. The First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
started on 8 October 1912 and lasted six weeks. Serbians reached Skopje on 26 October. Ottoman forces had left the city the day before.
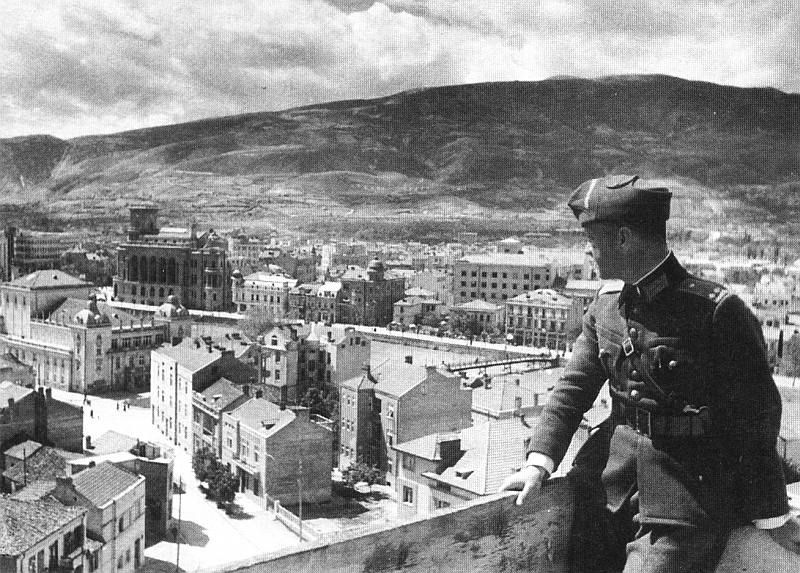 In 1915, during the
In 1915, during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Serbian Macedonia was invaded by Bulgaria, which captured Skopje on 22 October 1915. Serbia, allied to the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French '' entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well a ...
, was helped by France, Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, and Italy, which formed the Macedonian front. Following a great Allied offensive in 1918, the Armée française d'Orient reached Skopje 29 September and took the city by surprise. After the end of the World War, Vardar Macedonia became part of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
, which became "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" in 1929.Vardar Banovina
The Vardar Banovina, or Vardar Banate ( mk, Вардарска бановина, Vardarska banovina; sr, Вардарска бановина, translit=Vardarska Banovina; al, Banovina e Vardarit, italics=no), was a province ( banate) of the Kin ...
of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
. Until the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, Skopje experienced strong economic growth, and its population increased. The city had 41,066 inhabitants in 1921, 64,807 in 1931, and 80,000 in 1941. In 1941, during the Second World War, Yugoslavia was invaded by
In 1941, during the Second World War, Yugoslavia was invaded by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. Germans seized Skopje 8 AprilTreblinka
Treblinka () was an extermination camp, built and operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland during World War II. It was in a forest north-east of Warsaw, south of the village of Treblinka in what is now the Masovian Voivodeship. The cam ...
where almost all of them died.Bulgarian People's Army
The Bulgarian People's Army ( bg, Българска народна армия, БНА, translit=Balgarska narodna armiya, BNA) was the army of the People's Republic of Bulgaria. It comprised the Bulgarian Land Forces, Air Force and Air Defence, ...
(Bulgaria having switched sides in the war in September) aided by Yugoslav Partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovene: , or the National Liberation Army, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska (NOV), Народноослободилачка војска (НОВ); mk, Народноослобод� ...
of the Macedonian National Liberation Army
The Macedonian Partisans, officially the National Liberation Army and Partisan Detachments of Macedonia, sh, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska i partizanski odredi Makedonije was a communist and anti-fascist resistance movement formed in occupied Y ...
.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Skopje greatly benefited from Socialist Yugoslav policies which encouraged industry and the development of Macedonian cultural institutions. Consequently, Skopje became home to a national library, a national philharmonic orchestra, a university and the Macedonian Academy. However, its post-war development was altered by the 1963 earthquake which occurred 26 July. Although relatively weak in magnitude, it caused enormous damage in the city and can be compared to the 1960 Agadir earthquake
The 1960 Agadir earthquake occurred 29 February at 23:40 Western European Time near the city of Agadir, located in western Morocco on the shore of the Atlantic Ocean. Despite the earthquake's moderate scale magnitude of 5.8, its relatively shal ...
. The disaster killed 1,070 people, injuring 3,300 others. 16,000 people were buried alive in ruins and 70% of the population lost their home. After the
After the earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
, reconstruction was quick. It had a deep psychological impact on the population because neighbourhoods were split and people were relocated to new houses and buildings they were not familiar with.modernist architecture
Modern architecture, or modernist architecture, was an architectural movement or architectural style based upon new and innovative technologies of construction, particularly the use of glass, steel, and reinforced concrete; the idea that form ...
. Demographic growth was very important after 1963, and Skopje had 408,100 inhabitants in 1981. After 1963, rural youth migrated to Skopje and were involved in the reconstruction process resulting in a large growth of the urban Macedonian population.Skopje 2014
Skopje 2014 ( mk, Скопје 2014) was a project financed by the Macedonian government of the then-ruling nationalist party VMRO-DPMNE, with the official purpose of giving the capital Skopje a more classical appeal. The project, officially anno ...
" project renewed the appearance of the city centre.
Emblems
The Flag of Skopje
The flag of Skopje (in mk, Знаме на Скопје) is a red vertical banner in proportions 1:2 with the coat of arms of the city in golden-yellow placed in its left upper quarter. The coat of arms has the form of a shield and on it are p ...
is a red banner in proportions 1:2 with a gold-coloured coat of arms of the city positioned in the upper-left corner. It is either vertical or horizontal, but the vertical version was the first to be used.Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
river, the Kale Fortress and the snow-capped peaks of the Šar mountains
The Šar Mountains (Serbian and mk, Шар Планина, Šar Planina, colloquially also ) or Sharr Mountains ( sq, Malet e Sharrit), form a mountain range in the Balkans that extends from Kosovo and the northwest of North Macedonia to north ...
.
Administration
Status
 Being the capital and largest city of North Macedonia, Skopje enjoys a particular status granted by law. The last revision of its status was made in 2004. Since then, the City of Skopje has been divided into 10 municipalities which all have a council and a mayor, like all of the country's municipalities. Municipalities only deal with matters specific of their territory, and the City of Skopje deals with matters that concern all of them, or that cannot be divided between two or more municipalities.
Being the capital and largest city of North Macedonia, Skopje enjoys a particular status granted by law. The last revision of its status was made in 2004. Since then, the City of Skopje has been divided into 10 municipalities which all have a council and a mayor, like all of the country's municipalities. Municipalities only deal with matters specific of their territory, and the City of Skopje deals with matters that concern all of them, or that cannot be divided between two or more municipalities.Skopje Statistical Region
The Skopje Statistical Region ( mk, Скопски Регион; Albanian: Rajoni i Shkupit) is one of eight Statistical regions of North Macedonia. Skopje, located in the north of the country, borders Kosovo to the north. Internally, it border ...
, which has no political or administrative power.
City Council
The City Council consists of 45 members who serve a four-year term. It primarily deals with budget, global orientations and relations between the city and the government. Several commissions exist to treat more specific topics, such as urbanism, finances, environment of local development.SDSM
The Social Democratic Union of Macedonia ( mk, Социјалдемократски сојуз на Македонија – СДСМ, ''Socijaldemokratski Sojuz na Makedonija'' – SDSM, sq, Lidhja socialdemokrate e Maqedonisë – LSDM) is a ...
.
Mayor
The Mayor of Skopje is elected every four years.
The mayor represents the City of Skopje and can submit ideas to the council, manages the administrative bodies and their officials.
Municipalities
Skopje was first divided into administrative units in 1945, but the first municipalities were created in 1976. They were five: Centar, Čair, Karpoš, Gazi Baba and Kisela Voda. After the independence of the Republic of Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
, power was centralized and municipalities lost much of their competences. A 1996 law restored them and created two new municipalities: Ǵorče Petrov and Šuto Orizari. After the insurgency between Albanian rebels and Macedonian forces in 2001, a new law was enacted in 2004 to incorporate Saraj Municipality
Saraj ( mk, , sq, Saraj) is one of the ten municipalities that make up the city of Skopje, the capital of the Republic of North Macedonia.
* '' Saraj'', which means "palace" in Turkish, is also the name of the village where the municipal seat ...
into the City of Skopje. Saraj is mostly populated by Albanians and, since then, Albanians represent more than 20% of the city population. Thus Albanian became the second official language of the city administration, something which was one of the claims of the Albanian rebels. The same year, Aerodrom Municipality separated itself from Kisela Voda, and Butel Municipality
Butel Municipality ( mk, ; sq, Butel) is one of the ten municipalities that make up the City of Skopje, the capital of North Macedonia. The municipality administration consists of a council and mayor. "Skopje encompasses ten municipalities (A ...
from Čair.
Economy
Economic weight
 Skopje is a medium city at European level. Being the capital and largest city of North Macedonia, Skopje concentrates a large share of the national economy. The
Skopje is a medium city at European level. Being the capital and largest city of North Macedonia, Skopje concentrates a large share of the national economy. The Skopje Statistical Region
The Skopje Statistical Region ( mk, Скопски Регион; Albanian: Rajoni i Shkupit) is one of eight Statistical regions of North Macedonia. Skopje, located in the north of the country, borders Kosovo to the north. Internally, it border ...
, which encompasses the City of Skopje and some neighbouring municipalities, produces 45.5% of the Macedonian GDP. In 2009, the regional GDP per capita amounted to US$6,565, or 155% of the Macedonian GDP per capita. This figure is, however, smaller than the one of neighboring Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
(US$10,106), Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo ...
(US$10,048) or Belgrade (US$7,983), but higher than the one of Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
(US$4,126).
Because there are no other large cities in the country, and because of political and economical centralization, a large number of Macedonians living outside of Skopje work in the capital city. The dynamism of the city also encourages rural exodus
Rural flight (or rural exodus) is the migratory pattern of peoples from rural areas into urban areas. It is urbanization seen from the rural perspective.
In industrializing economies like Britain in the eighteenth century or East Asia in the ...
, not only from North Macedonia, but also from Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and Southern Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
.
Firms and activities
In 2009, Skopje had 26,056 firms but only 145 of them had a large size. The large majority of them are either small (12,017) or very small (13,625). A large share of the firms deal with trade of goods (9,758), 3,839 are specialized in business and real estate, and 2,849 are manufacturers. Although few in number, large firms account for 51% of the local production outside finance. The city industry is dominated by food processing, textile, printing and metal processing. In 2012, it accounted for 30% of the city GDP.
The city industry is dominated by food processing, textile, printing and metal processing. In 2012, it accounted for 30% of the city GDP.Gazi Baba municipality
Gazi Baba ( mk, , sq, Gazi Babë) is one of the ten municipalities that make up the City of Skopje, the capital of North Macedonia. The municipality administration consists of a council and mayor. "Skopje encompasses ten municipalities (Aerodr ...
, on the major routes and rail lines to Belgrade and Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
. Notably, the ArcelorMittal
ArcelorMittal S.A. is a Luxembourgian multinational steel manufacturing corporation headquartered in Luxembourg City. It was formed in 2006 from the takeover and merger of Arcelor by Indian-owned Mittal Steel. ArcelorMittal is the second la ...
and Makstil steel plants are there, and also the Skopje Brewery. Other zones are between Aerodrom and Kisela Voda, along the railway to Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
. These zones comprise Alkaloid Skopje (pharmaceuticals), Rade Končar (electrical supplies), Imperial Tobacco
Imperial Brands plc (formerly Imperial Tobacco Group plc), is a British multinational tobacco company headquartered in Bristol, England. It is the world's fourth-largest international cigarette company measured by market share after Philip Mo ...
, and Ohis (fertilizers). Two special economic zone
A special economic zone (SEZ) is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country's national borders, and their aims include increasing trade balance, employment, increas ...
s also exist, around the airport and the Okta refinery. They have attracted several foreign companies, such as Johnson Controls
Johnson Controls International is an American
Irish-domiciled multinational conglomerate headquartered in Cork, Ireland, that produces fire, HVAC, and security equipment for buildings. As of mid-2019, it employed 105,000 people in around 2,00 ...
, Johnson Matthey
Johnson Matthey is a British multinational speciality chemicals and sustainable technologies company headquartered in London, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.
History Early years
Jo ...
and Van Hool
Van Hool NV () is a Belgium, Belgian family-owned coachbuilder and manufacturer of buses, Coach (bus), coaches, trolleybuses, and Semi-trailer, trailers.
Most of the buses and coaches are built entirely by Van Hool, with engines and axle ...
.
As the country's financial capital, Skopje is the seat of the Macedonian Stock Exchange
The Macedonian Stock Exchange (MSE; Macedonian: Македонска берза, ''Makedonska berza'') is the principal stock exchange in the Republic of North Macedonia, located in the capital city of Skopje. It was established in 1995 and the ...
, of the National Bank
In banking, the term national bank carries several meanings:
* a bank owned by the state
* an ordinary private bank which operates nationally (as opposed to regionally or locally or even internationally)
* in the United States, an ordinary p ...
and of most of the country's banking, insurance and telecommunication companies, such as Makedonski Telekom
Makedonski Telekom AD ( mk, Македонски Телеком АД, lit=Macedonian Telekom PLC) is a telecommunications company in North Macedonia with headquarters in Skopje. It is part of the Magyar Telekom Group, which is a fully consolida ...
, Komercijalna banka Skopje
Komercijalna banka Skopje ( mk, Комерцијална банка Скопје; abbr. KBS) is a commercial bank with headquarters in Skopje, North Macedonia.
History
It was established in 1955 as Komunalna Banka (business bank for city of Skop ...
and Stopanska Banka. The services sector produces 60% of the city GDP. Besides many small traditional shops, Skopje has two large markets, the "Zelen Pazar" (green market) and the "Bit Pazar" (flea market). They are both considered as local institutions.
Besides many small traditional shops, Skopje has two large markets, the "Zelen Pazar" (green market) and the "Bit Pazar" (flea market). They are both considered as local institutions.Carrefour
Carrefour () is a French multinational retail and wholesaling corporation headquartered in Massy, France. The eighth-largest retailer in the world by revenue, it operates a chain of hypermarkets, groceries stores and convenience stores, whic ...
hypermarket, 130 shops and a cinema, and employs 2,000 people.

Employment
51% of the Skopje active population is employed in small firms. 52% of the population work in the services sector, 34% in industry, and the remaining is mainly employed in administration.Skopje Statistical Region
The Skopje Statistical Region ( mk, Скопски Регион; Albanian: Rajoni i Shkupit) is one of eight Statistical regions of North Macedonia. Skopje, located in the north of the country, borders Kosovo to the north. Internally, it border ...
was at 27% in 2009, three points under the national rate (30%). The neighbouring Polog Region had a similar rate, but the less affected region was the South-West
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
, with 22%. Unemployment in Skopje mainly affects men, who represent 56% of job-seekers, people between 25 and 44 years old (45% of job-seekers), and non-qualified people (43%).Roma people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sign ...
, who represent 4.63% of the city population but affects 70% of the active population in the community.Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo ...
(€522), Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
(€436), and in Belgrade (€440).
Demographics
Population
 According to the results of the 2002 census, the City of Skopje itself had 428,988 in its urban area and 506,926 inhabitants within administrative limits that encompass many villages and other settlements, including Dračevo, Bardovci, Kondovo, Radišani,
According to the results of the 2002 census, the City of Skopje itself had 428,988 in its urban area and 506,926 inhabitants within administrative limits that encompass many villages and other settlements, including Dračevo, Bardovci, Kondovo, Radišani, Gorno Nerezi
Gorno Nerezi (, sq, Nerez i Epërm) is a village in the municipality of Karpoš, North Macedonia. The settlement is situated at an altitude of 771 meters (2532 feet). It is located on the wooded slopes of Mt. Vodno, covers a 7 km radius ...
etc.Kumanovo
Kumanovo ( mk, Куманово ; also known by other alternative names) is a city in North Macedonia and the seat of Kumanovo Municipality, the largest municipality in the country. Kumanovo lies above sea level and is surrounded by the K ...
and Tetovo
Tetovo ( mk, Тетово, , sq, Tetovë/Tetova) is a city in the northwestern part of North Macedonia, built on the foothills of Šar Mountain and divided by the Pena River. The municipality of Tetovo covers an area of at above sea level, w ...
, and totaling more than one million inhabitants.Kumanovo
Kumanovo ( mk, Куманово ; also known by other alternative names) is a city in North Macedonia and the seat of Kumanovo Municipality, the largest municipality in the country. Kumanovo lies above sea level and is surrounded by the K ...
, had 107,632 inhabitants in 2011,urban unit
In France, an urban unit (''fr: "unité urbaine"'') is a statistical area defined by INSEE, the French national statistics office, for the measurement of contiguously built-up areas. According to the INSEE definition , an "unité urbaine" is a ...
of 76,272 inhabitants in 2002.Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, with a population estimated between 30,000 and 60,000 inhabitants.Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, and it had 448,200 inhabitants in 1971. Since then, the demographic growth has continued at a steady pace.
Ethnic groups
Skopje, just like North Macedonia as a whole, is characterized by a large ethnic diversity. The city is in a region where Macedonians and Albanians meet, and it welcomed Romani, Turks, Jews and Serbs throughout its history. Skopje was mainly a Muslim city until the 19th century, when large numbers of Christians started to settle there. According to the 2002 census, Macedonians were the largest ethnic group in Skopje, with 338,358 inhabitants, or 66.75% of the population. Then came Albanians with 103,891 inhabitants (20.49%), Roma people with 23,475 (4.63%), Serbs (14,298 inhabitants), Turks (8,595), Bosniaks (7,585) and Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armãnji, Rrãmãnji) are an ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and ...
(also known as "Vlachs", 2,557). 8,167 people did not belong to any of these groups.Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
.Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
, and in Saraj.
Religion
 Religious affiliation is diverse: Macedonians, Serbs, and Aromanians are mainly Orthodox, with the majority affiliated to the
Religious affiliation is diverse: Macedonians, Serbs, and Aromanians are mainly Orthodox, with the majority affiliated to the Macedonian Orthodox Church
The Macedonian Orthodox Church – Archdiocese of Ohrid (MOC-AO; mk, Македонска православна црква – Охридска архиепископија), or simply the Macedonian Orthodox Church (MOC) or the Archdiocese o ...
; Turks are almost entirely Muslim; those of Albanian ethnicity are largely Muslim, although Skopje also has a sizeable Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
Albanian minority, into which Mother Teresa
Mary Teresa Bojaxhiu, MC (; 26 August 1910 – 5 September 1997), better known as Mother Teresa ( sq, Nënë Tereza), was an Indian-Albanian Catholic nun who, in 1950, founded the Missionaries of Charity. Anjezë Gonxhe Bojaxhiu () was ...
was born; the Roma (Gypsies) represent a mixture (in almost equal numbers) of Muslim and Orthodox religious heritage.
According to the 2002 census, 68.5% of the population of Skopje belonged to the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
, while 28.6% of it belonged to Islam. The city also had Catholic (0.5%) and Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
(0.04%) minorities. The Catholics are served by the Latin bishopric of Skopje, in which is also vested the Byzantine Catholic Apostolic Exarchate of Macedonia.
Until World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Skopje had a significant Jewish minority which mainly descended from Spanish Sephardis who had escaped the Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
. The community comprised 2,424 members in 1939 (representing about 3% of the city population), but most of them were deported and killed by Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
. After the war, most of the survivors settled in Israel.Macedonian Orthodox Church
The Macedonian Orthodox Church – Archdiocese of Ohrid (MOC-AO; mk, Македонска православна црква – Охридска архиепископија), or simply the Macedonian Orthodox Church (MOC) or the Archdiocese o ...
and the Islamic Religious Union of Macedonia. It has an Orthodox cathedral and seminary, several madrasahs, a Roman Catholic cathedral and a synagogue.
Health
Skopje has several public and private hospitals and specialized medical institutions, such as the Filip II Hospital, a psychiatric hospital, two obstetric hospitals, a gerontology hospital and institutes for respiratory and ocular diseases. In 2012, Skopje had a ratio of one physician per 251.6 inhabitants, a figure higher than the national ratio (one per 370.9). The ratio of medical specialists was also higher than in the rest of the country. However, the ratio of hospital beds, pharmacists and dentists was lower in Skopje.
Education
 Skopje's citizenry is generally more educated than the rest of the country. For one, 16% of Skopjans have graduated from university in contrast to 10% for the rest of the country. The number of people with a complete lack of education or ones who received a partial education is lower in Skopje at 9% compared to the provincial average of 17%. 80% of Macedonian citizens who hold a PhD take up residence in Skopje.
Skopje's citizenry is generally more educated than the rest of the country. For one, 16% of Skopjans have graduated from university in contrast to 10% for the rest of the country. The number of people with a complete lack of education or ones who received a partial education is lower in Skopje at 9% compared to the provincial average of 17%. 80% of Macedonian citizens who hold a PhD take up residence in Skopje.
Media
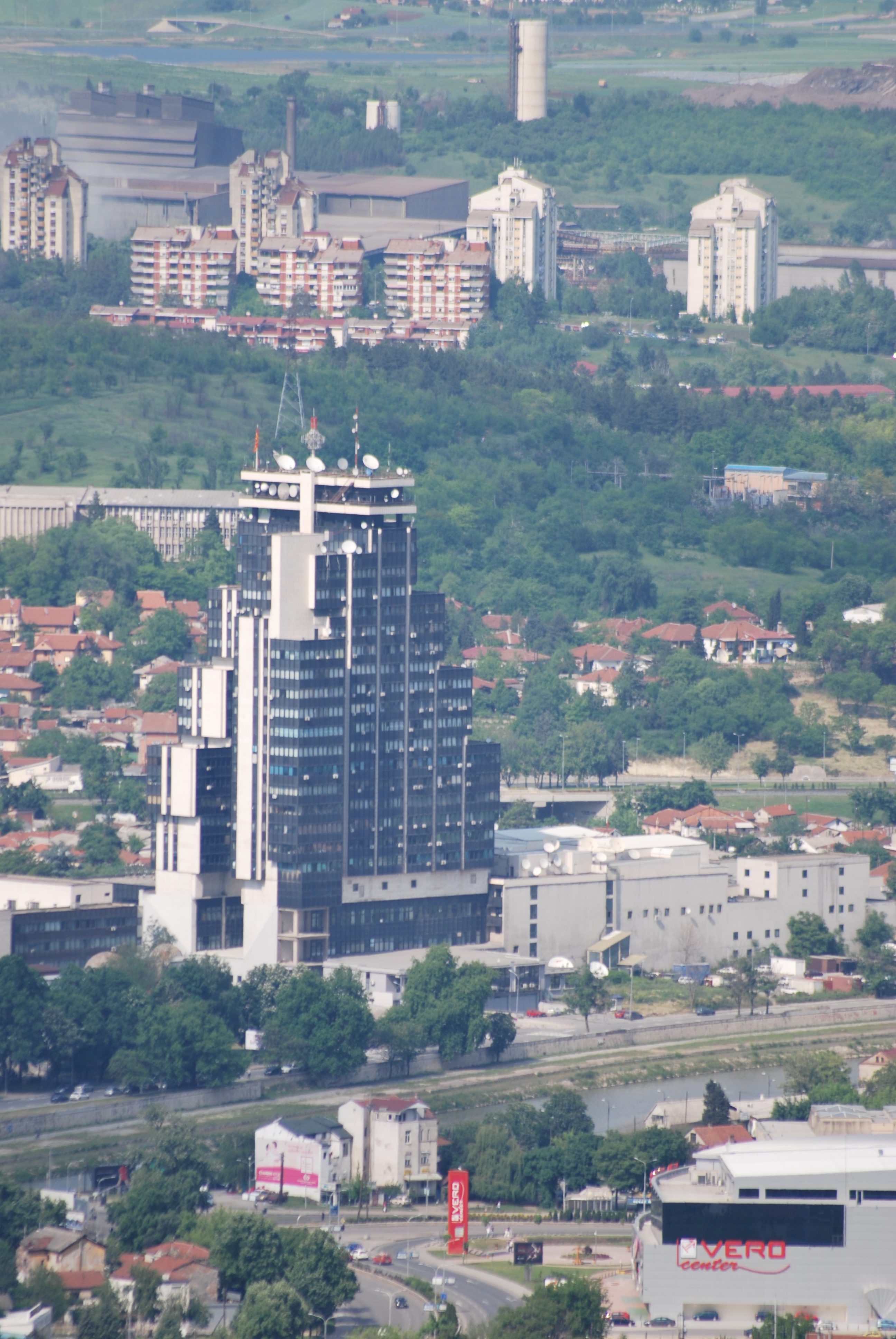 Skopje is the largest media centre in North Macedonia. Of the 818 newspapers surveyed in 2000 by the Ministry of Information, over 600 had their headquarters in Skopje. The daily Dnevnik, founded in 1996, with 60 000 runs per day is the most printed in the country. Also based in Skopje, Večer is pulled 50,000 copies and the state owns one third of its capital, as well as
Skopje is the largest media centre in North Macedonia. Of the 818 newspapers surveyed in 2000 by the Ministry of Information, over 600 had their headquarters in Skopje. The daily Dnevnik, founded in 1996, with 60 000 runs per day is the most printed in the country. Also based in Skopje, Večer is pulled 50,000 copies and the state owns one third of its capital, as well as Nova Makedonija
''Nova Makedonija'' ( mk, Нова Македонија, "New Macedonia") is the oldest daily newspaper in the Republic of North Macedonia. It was established with decision of the presidium of ASNOM and published by NIP Nova Makedonija.
History ...
, reprinted 20,000 copies. Other major newspapers in Skopje, totally private, are Utrinski Vesnik (30,000 copies), Vest (25,000 copies) and Vreme
''Vreme'' (Serbian for ''Time'') is a weekly news magazine based in Belgrade, Serbia.
History
Launch
In 1990, dissatisfied with the media climate in SR Serbia, SFR Yugoslavia's largest constituent unit, a group of liberal Serbian intellectuals, i ...
(15,000 copies). Magazines Fokus (12,000 copies), Start (10,000 copies), and Denes (7,500 copies) also have their headquarters in Skopje.Macedonian Radio-Television
Macedonian Radio Television (MRT; mk, Македонска радио-телевизија (МРТ), Makedonska radio-televizija (MRT)), officially National Radio-Television ( mk, Национална Радиотелевизија, Nacionalna ...
(MRT), the country's public radio and television. Founded in 1966, it operates with three national broadcast channels, twenty-four hours at day. The most popular private television stations are Sitel
Sitel Group is a privately owned contact center company headquartered in Miami, Florida. It provides outsourced sales, technical support, customer service, and other business processes for large companies. The company has 160,000 employees an ...
, Kanal 5, Telma, Alfa TV and AlsatM are another major private television companies. MRT also operates radio stations with national coverage, the private station Skopje's Kanal 77 is the only one to have such a span. Radio Antenna 5 and Metropolis are two other major private stations that have their headquarters in Skopje.
Also, the city boasts big news agencies in the country, both public, as the Media Information Agency, and private, such as the Makfax.
Sports
As the capital and largest city of North Macedonia, Skopje has many major sporting facilities. The city has three large swimming pools, two of which feature Olympic pools. These pools are particularly relevant to coaching water polo teams. Skopje also boasts many football stadiums, like Ilinden in Čair and Železarnica, which can accommodate between 4,000 and 4,500 spectators. The basketball court Kale can accommodate 2,200 people and the court of Jane Sandanski has a 6,000 seat capacity.
 The largest stadium remains
The largest stadium remains Toše Proeski Arena
Toše Proeski National Arena ( mk, Национална арена "Тоше Проески") is a sports stadium in Skopje, North Macedonia. It is currently used mostly for football matches, but sometimes also for music concerts or athletics. I ...
. The stadium, built in 1947 and named until 2008, City Stadium Skopje experienced a total renovation, begun in 2009 to meet the standards of FIFA. Fully renovated the stadium contains 33,460 seats, and a health spa and fitness area. The Boris Trajkovski Sports Center
The Boris Trajkovski Sports Center ( mk, Спортски центар Борис Трајковски, Sportski centar Boris Trajkovski) in Skopje is a multi-functional indoor sports arena. It is located in the Karpoš Municipality of Skopje, No ...
is the largest sports complex in the country. It was opened in 2008 and named after former president Boris Trajkovski
Boris Trajkovski ( GCMG) ( mk, Борис Трајковски, pronounced ; 25 June 1956 – 26 February 2004) was a Macedonian politician who served as the second President of Macedonia from 1999 until his death in 2004 in a plane crash.
Tra ...
, who died in 2004. It includes rooms dedicated to handball, basketball and volleyball and host 6,250 seats, a bowling alley, a fitness area and an ice hockey court. Its main hall, which regularly hosts concerts, holds around 10,000 people.
FK Vardar and FK Rabotnički
FK Rabotnichki ( mk, ФК Работнички) or more commonly Rabotnički (old transliteration) and Rabotnicki is a football club that plays at the Toshe Proeski Arena in Skopje, North Macedonia. They currently compete in the Macedonian First ...
are the two most popular football teams in the city, Vardar plays in the second division
In sport, the Second Division, also called Division 2 or Division II is usually the second highest division of a league, and will often have promotion and relegation with divisions above and below. Following the rise of Premier League style compet ...
, while Rabotnicki plays in the first division. Their games are held at Toše Proeski Arena, like those of the national team. The city is also home to many smaller football clubs, such as: FK Makedonija Ǵorče Petrov, FK Gorno Lisiče
FK Gorno Lisiče ( mk, ФК Горно Лисиче) is a football club from Gorno Lisiče in Skopje, Republic of Macedonia. They currently play in the 3.MFL (North).
History
The club played its first match in 1940 under the name ''Lisiče'' aga ...
, FK Lokomotiva Skopje
FK Lokomotiva Skopje ( mk, ФК Локомотива Скопје) is a football club based in the Karpoš neighborhood of Skopje, North Macedonia. They are currently competing in the Macedonian Second League.
History
The club was founded in 195 ...
, FK Metalurg Skopje, FK Madžari Solidarnost
FK Madžari Solidarnost Junior ( mk, ФК Маџари Солидарност Јуниор ) is a football club from Madžari neighborhood, Skopje, Republic of North Macedonia. They are currently competing in the Macedonian Third League (North ...
and FK Skopje
FK Skopje ( mk, ФК Скопје) is a football club from Skopje, the capital of the North Macedonia. They are currently competing in the Macedonian First League.
History
The club was created in 1960, by uniting ''FK Metalec'' and ''FK Indus ...
, who play in first, second or third national league. Another popular sport in North Macedonia is basketball, represented in particular by the teams MZT Skopje and Rabotnički. Handball is illustrated by RK Vardar
RK Vardar 1961 ( mk, РК Вардар 1961) is a professional handball club from Skopje, Republic of Macedonia. Vardar is the most successful handball team in the country, having won fifteen national League and Cup titles. Also, Vardar is the ...
PRO and RK Metalurg Skopje
RK Metalurg Skopje ( mk, РК Металург Скопје) is a Macedonian handball club based in Skopje. They compete in the domestic Macedonian Handball Super League and EHF European League.
History
The club was founded in 1971 under patron ...
, also the women's team ŽRK Metalurg
WHC Metalurg ( mk, ЖРК Металург) is a women's handball club from Skopje, North Macedonia. The team currently competes in the Macedonian women's First League of Handball.
History
The club was established in 1964 under the name MIK and p ...
and ŽRK Vardar
ŽRK Vardar ( mk, ЖРК Вардар) is a Macedonian women's handball club from Skopje, North Macedonia. The team currently competes in the Macedonian women's First League of Handball, Women’s Regional Handball League and used to be a top ...
. The city co-hosted the 2008 European Women's Handball Championship together with Ohrid
Ohrid ( mk, Охрид ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the List of cities in North Macedonia, eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording ...
, and hosted the 2017 UEFA Super Cup
The 2017 UEFA Super Cup was the 42nd edition of the UEFA Super Cup, an annual football match organised by UEFA and contested by the reigning champions of the two main European club competitions, the UEFA Champions League and the UEFA Europa League ...
, the match between the two giants of the European football Real Madrid and Manchester United
Transport
Main connections
 Skopje is near three other capital cities,
Skopje is near three other capital cities, Prishtina
Pristina, ; sr, / (, ) is the capital and largest city of Kosovo. The city's municipal boundaries in Pristina District form the largest urban center in Kosovo. After Tirana, Pristina has the second largest population of ethnic Albanians and ...
( away), Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
(291 km) and Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
(245 km). Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
is south and Belgrade is north.Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, and Corridor VIII, which runs from the Adriatic in Albania to the Black sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
in Bulgaria. Corridor X links Skopje to Thessaloniki, Belgrade and Western Europe, while Corridor VIII links it with Tirana and Sofia.
Corridor X locally corresponds to the M-1 motorway ( E75), which is the longest highway in North Macedonia. It also corresponds to the Tabanovce
Tabanovce ( mk, Табановце; ) is a village located in the north of North Macedonia, at the border with Serbia, situated 8 km from the nearest town, Kumanovo.
Geography
It is located in the north of North Macedonia, at the border with ...
-Gevgelija
Gevgelija ( mk, Гевгелија; ) is a town with a population of 15,685 located in the very southeast of the North Macedonia along the banks of the Vardar River, situated at the country's main border with Greece (Bogorodica-Evzoni), the point ...
railway. Corridor VIII, less developed, corresponds to the M-4 motorway and the Kičevo-Beljakovce railway. Skopje is not quite on the Corridor X and the M-1 does not pass on the city territory. Thus the junction between the M-1 and M-4 is some east, close to the airport. Although Skopje is geographically close to other major cities, movement of people and goods is not optimized, especially with Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
. This is mainly due to poor infrastructure. As a result, 61.8% of Skopjans have never been to Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
, while only 6.7% have never been to Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
and 0% to Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
. Furthermore, 26% of Thessalonians, 33% of Sofians and 37% of Tiranans have never been to Skopje.Brotherhood and Unity Highway
The Brotherhood and Unity Highway (; ; or , ), officially classed as the M-1 highway, was a highway that stretched over across Yugoslavia, from the Austrian border at Jesenice in the northwest via Ljubljana, Zagreb, Belgrade and Skopje to Gevgel ...
to, what was then, Yugoslav capital Belgrade to North, and Greek border to South.
Rail and coach stations
 The main railway station in Skopje is serviced by the Belgrade-
The main railway station in Skopje is serviced by the Belgrade-Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
and Skopje-Prishtina
Pristina, ; sr, / (, ) is the capital and largest city of Kosovo. The city's municipal boundaries in Pristina District form the largest urban center in Kosovo. After Tirana, Pristina has the second largest population of ethnic Albanians and ...
international lines.Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
and Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
. Daily trains also link Skopje with other towns of North Macedonia, such as Kumanovo
Kumanovo ( mk, Куманово ; also known by other alternative names) is a city in North Macedonia and the seat of Kumanovo Municipality, the largest municipality in the country. Kumanovo lies above sea level and is surrounded by the K ...
, Kičevo, Štip
Štip ( mk, Штип ) is the largest urban agglomeration in the eastern part of North Macedonia, serving as the economic, industrial, entertainment and educational focal point for the surrounding municipalities.
As of the 2002 census, the city ...
, Bitola or Veles.Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
, Prague, Hamburg and Stockholm.
Public transport
 Skopje has a bus network managed by the city and operated by three companies. The oldest and largest is JSP Skopje, a public company founded in 1948. JSP lost its monopoly on public transport in 1990 and two new companies, Sloboda Prevoz and Mak Ekspres, obtained several lines. However, most of the network is still in the hands of JSP which operates 67 lines out of 80. Only 24 lines are urban, the others serving localities around the city.
Skopje has a bus network managed by the city and operated by three companies. The oldest and largest is JSP Skopje, a public company founded in 1948. JSP lost its monopoly on public transport in 1990 and two new companies, Sloboda Prevoz and Mak Ekspres, obtained several lines. However, most of the network is still in the hands of JSP which operates 67 lines out of 80. Only 24 lines are urban, the others serving localities around the city.Yutong
Yutong (officially Zhengzhou Yutong Group Co., Ltd.) is a Chinese manufacturer of commercial vehicles, especially electric buses, headquartered in Zhengzhou, Henan. Yutong also covers areas of construction machinery, real estate, and other inve ...
and designed to resemble the classic British AEC Routemaster
The AEC Routemaster is a front-engined double-decker bus that was designed by London Transport and built by the Associated Equipment Company (AEC) and Park Royal Vehicles. The first prototype was completed in September 1954 and the last one ...
.
A tram network has long been planned in Skopje and the idea was first proposed in the 1980s. The project became real in 2006 when the mayor Trifun Kostovski asked for feasibility studies. His successor Koce Trajanovski launched a call for tenders in 2010 and the first line is scheduled for 2019.
A new network for small buses started to operate in June 2014, not to replace but to decrease the number of big buses in the city centre.
Airport
The airport was built in 1928. The first commercial flights in Skopje were introduced in 1929 when the Yugoslav carrier Aeroput
Aeroput () was an airline and flag carrier of Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia from 1927 until 1948.
Society for Air traffic List of legal entity types by country#Serbia, AD Aeroput was the first Serbian company for civil air traffic, which was ...
introduced a route linking the city with the capital, Belgrade.[Drustvo za Vazdusni Saobracaj A D – Aeroput (1927–1948)](_blank)
at europeanairlines.no A year later the route was extended to Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
in Greece, and further extended to Greek capital Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
in 1933.Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while ...
, and also operated a longer international route linking Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
and Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
through Zagreb, Belgrade and Skopje.Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, Vienna, Bratislava, Zürich, Brussels, Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, London and Rome. It also maintains a direct connection with Dubai and Doha, Qatar.
Culture
Cultural institutions
 Skopje is home to the largest cultural institutions of the country, such as the National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", the
Skopje is home to the largest cultural institutions of the country, such as the National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", the Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts
The Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts ( mk, Македонска Академија на Науките и Уметностите, МАНУ) is an academic institution in North Macedonia.
History
The Academy of Sciences and Arts was establ ...
, the National Theatre, the National Philharmonic Orchestra and the Macedonian Opera and Ballet. Among the local institutions are the Brothers Miladinov Library which has more than a million documents, the Cultural Information Centre which manages festivals, exhibitions and concerts, and the House of Culture Kočo Racin which is dedicated to contemporary art and young talents.
Skopje has also several foreign cultural centres, such as a Goethe-Institut, a British Council, an Alliance française, an American Corner.
The city has several theatres and concert halls. The Univerzalna Sala, seating 1,570, was built in 1966 and is used for concerts, fashion shows and congresses. The Metropolis Arena, designed for large concerts, has 3,546 seats. Other large halls include the Macedonian Opera and Ballet (800 seats), the National Theatre (724), and the Drama Theatre (333). Other smaller venues exist, such as the Albanian Theatre and the Youth Theatre. A Turkish Theatre and a Philharmonic hall are under construction.
Museums
 The largest museum in Skopje is the Museum of the Republic of North Macedonia which details the history of the country. Its icons and lapidary collections are particularly rich. The Macedonian Archeological Museum, opened in 2014, keeps some of the best archeological finds in North Macedonia, dating from Prehistory to the Ottoman period. The National Gallery of Macedonia exhibits paintings dating from the 14th to the 20th century in two former Turkish baths of the
The largest museum in Skopje is the Museum of the Republic of North Macedonia which details the history of the country. Its icons and lapidary collections are particularly rich. The Macedonian Archeological Museum, opened in 2014, keeps some of the best archeological finds in North Macedonia, dating from Prehistory to the Ottoman period. The National Gallery of Macedonia exhibits paintings dating from the 14th to the 20th century in two former Turkish baths of the Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
. The Contemporary Art Museum (North Macedonia), Contemporary Art Museum was built after the 1963 earthquake thanks to international assistance. Its collections include Macedonian and foreign art, with works by Fernand Léger, André Masson, Pablo Picasso, Hans Hartung, Victor Vasarely, Alexander Calder, Pierre Soulages, Alberto Burri and Christo.
The Skopje City Museum is inside the remains of the old railway station, destroyed by the 1963 earthquake. It is dedicated to local history and it has four departments: archeology, ethnology, history, and art history. The Memorial House of Mother Teresa was built in 2009 on the original site of the church in which the saint had been baptized. The Museum of the Macedonian Struggle (Skopje), Museum of the Macedonian Struggle is dedicated to the modern national history and the struggle of Macedonians for their independence. Nearby is the Holocaust Memorial Center for the Jews of Macedonia. The Macedonian Museum of Natural History showcases some 4,000 items while the 12-ha Skopje Zoo is home to 300 animals.
Architecture
 Although Skopje has been destroyed many times through its history, it still has many historical landmarks which reflect the successive occupations of the city. Skopje has one of the biggest Ottoman urban complexes in Europe, with many Ottoman monuments still serving their original purpose. It was also a ground for Modernist architecture, modernist experiments in the 20th century, following the 1963 earthquake. In the beginning of the 21st century, it is again the subject of massive building campaigns, thanks to the "
Although Skopje has been destroyed many times through its history, it still has many historical landmarks which reflect the successive occupations of the city. Skopje has one of the biggest Ottoman urban complexes in Europe, with many Ottoman monuments still serving their original purpose. It was also a ground for Modernist architecture, modernist experiments in the 20th century, following the 1963 earthquake. In the beginning of the 21st century, it is again the subject of massive building campaigns, thanks to the "Skopje 2014
Skopje 2014 ( mk, Скопје 2014) was a project financed by the Macedonian government of the then-ruling nationalist party VMRO-DPMNE, with the official purpose of giving the capital Skopje a more classical appeal. The project, officially anno ...
" project. Skopje is thus an environment where old, new, progressist, reactionary, eastern and western perspectives coexist.Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
, with ruins of a theatre, thermae and a basilica. Skopje Fortress was rebuilt several times before it was destroyed by the 1963 earthquake. Since then, it has been restored to its medieval appearance. It is the only medieval monument in Skopje, but several churches around the city illustrate the Serbo-Byzantine architecture, Vardar architectural school which flourished around 1300. Among these churches are the ones around Matka Canyon (St Nicholas, St Andrew and Matka churches). The church of St. Panteleimon (Gorno Nerezi), church of St. Panteleimon in
Skopje Fortress was rebuilt several times before it was destroyed by the 1963 earthquake. Since then, it has been restored to its medieval appearance. It is the only medieval monument in Skopje, but several churches around the city illustrate the Serbo-Byzantine architecture, Vardar architectural school which flourished around 1300. Among these churches are the ones around Matka Canyon (St Nicholas, St Andrew and Matka churches). The church of St. Panteleimon (Gorno Nerezi), church of St. Panteleimon in Gorno Nerezi
Gorno Nerezi (, sq, Nerez i Epërm) is a village in the municipality of Karpoš, North Macedonia. The settlement is situated at an altitude of 771 meters (2532 feet). It is located on the wooded slopes of Mt. Vodno, covers a 7 km radius ...
dates from the 12th century. Its expressive frescoes anticipate the Italian primitives.
 Examples of Ottoman architecture, Ottoman Turkish architecture are in the
Examples of Ottoman architecture, Ottoman Turkish architecture are in the Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
. Mosques in Skopje are usually simple in design, with a square base and a single dome and minaret. There entrance is usually emphasized by a portico, as on Mustafa Pasha Mosque
Mustafa Pasha Mosque ( mk, Мустафа-пашина џамија; ; tr, Mustafa Paşa Camii) is an Ottoman-era mosque located in the Old Bazaar of Skopje, North Macedonia.
History
The structure stands on a plateau above the old bazaar, built ...
, dating from the 15th century. Some mosques show some originality in their appearance: Sultan Murad Mosque, Sultan Murad and Yahya Pasha mosques have lost their dome and have a pyramidal roof, while Isa Bey mosque has a rectangular base, two domes and two side wings. The Aladža Mosque was originally covered with blue faience, but it disappeared in the 1689 Great Fire. However, some tiles are still visible on the adjoining türbe. Other Turkish public monuments include the 16th-century clock tower, a bedesten, three caravanserais, two Turkish baths and the Stone Bridge, first mentioned in 1469. After 1912, when Skopje was annexed by Serbia, the city was drastically westernized. Wealthy Serbs built mansions and town houses such as the 1926 Ristiḱ Palace. Architecture of that time is very similar to the one of Central Europe, but some buildings are more creative, such as the Moorish Revival architecture, Neo-Moorish Arab House and the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo-Byzantine train station, both built in 1938.
After 1912, when Skopje was annexed by Serbia, the city was drastically westernized. Wealthy Serbs built mansions and town houses such as the 1926 Ristiḱ Palace. Architecture of that time is very similar to the one of Central Europe, but some buildings are more creative, such as the Moorish Revival architecture, Neo-Moorish Arab House and the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo-Byzantine train station, both built in 1938.Kenzo Tange
is a common masculine Japanese given name.
Possible writings
Kenzō can be written using different kanji characters and can mean:
*賢三, "wise, three"
*健三, "healthy, three"
*謙三, "humble, three"
*健想, "healthy, concept"
*建造, "bu ...
who designed the new train station.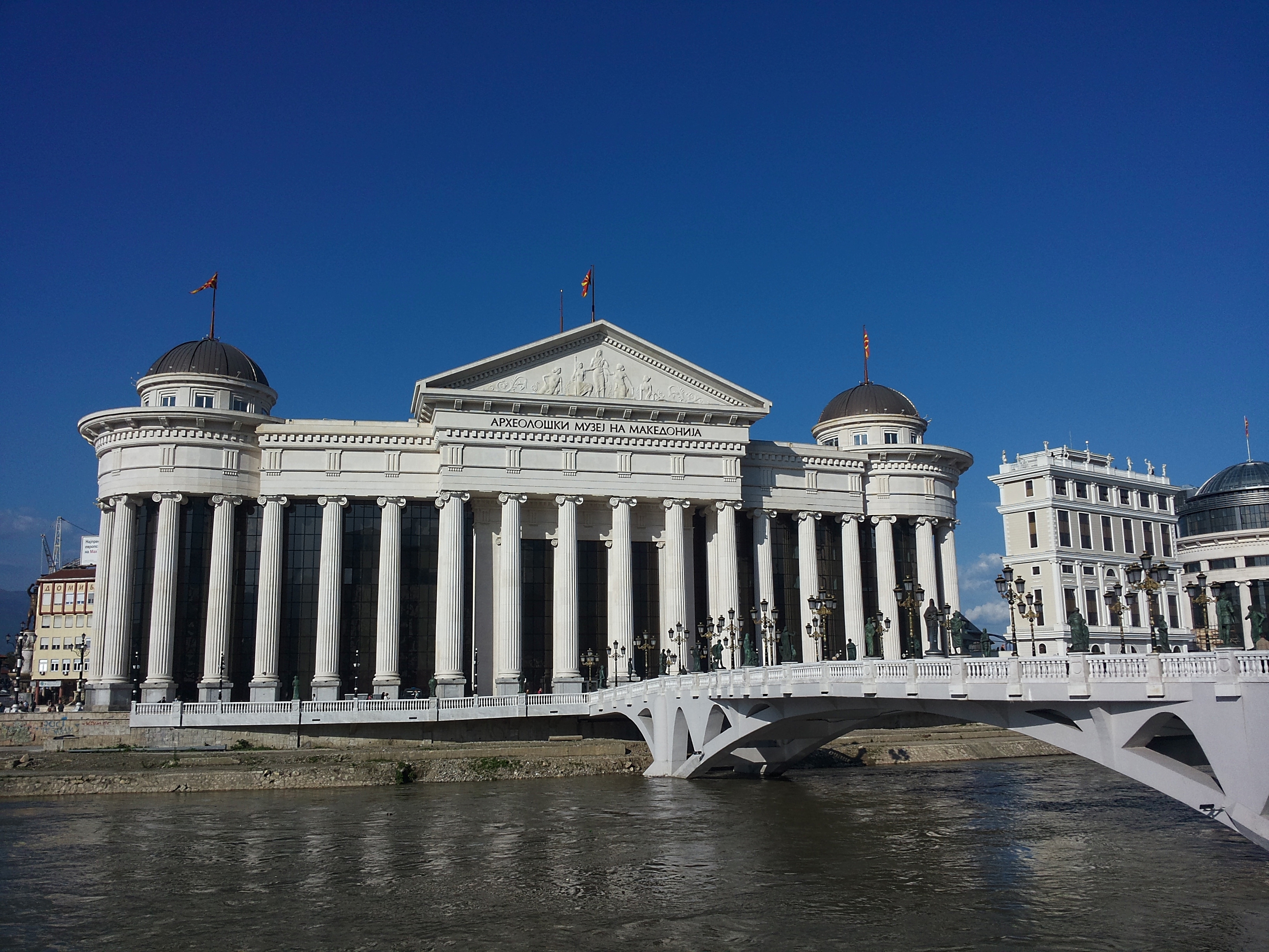 The reconstruction turned Skopje into a proper modernist city, with large blocks of flats, austere concrete buildings and scattered green spaces. The city centre was considered as a grey and unattractive place when local authorities unveiled the "
The reconstruction turned Skopje into a proper modernist city, with large blocks of flats, austere concrete buildings and scattered green spaces. The city centre was considered as a grey and unattractive place when local authorities unveiled the "Skopje 2014
Skopje 2014 ( mk, Скопје 2014) was a project financed by the Macedonian government of the then-ruling nationalist party VMRO-DPMNE, with the official purpose of giving the capital Skopje a more classical appeal. The project, officially anno ...
" project in 2010. It made plans to erect a large number of statues, fountains, bridges, and museums at a cost of about €500 million.
The project has generated controversy: critics have described the new landmark buildings as signs of reactionary Historicism (art), historicist aesthetics.Mustafa Pasha Mosque
Mustafa Pasha Mosque ( mk, Мустафа-пашина џамија; ; tr, Mustafa Paşa Camii) is an Ottoman-era mosque located in the Old Bazaar of Skopje, North Macedonia.
History
The structure stands on a plateau above the old bazaar, built ...
.
File:Daut-pasin amam, Skopje.jpg, Daut Pasha Turkish bath.
File:Saat Kula-Sultan Muratova Dzamija -Skopje (27).JPG, The clock tower.
File:Skopje X8.JPG, The Arab House.
File:Porta Macedonia, Skopie, Macedonia, 2014-04-16, DD 105.JPG, Porta Macedonia.
Festivals
The Skopje Jazz Festival has been held annually in October since 1981. It is part of the European Jazz Network and the European Forum of World Wide Festivals. The artists' profiles include fusion, acid jazz, Latin jazz, smooth jazz, and avant-garde jazz. Ray Charles, Tito Puente, Gotan Project, Al Di Meola, Youssou N'Dour, among others, have performed at the festival. Another music festival in Skopje is the Blues and Soul Festival. It is a relatively new event in the Macedonian cultural scene that occurs every summer in early July. Past guests include Larry Coryell, Mick Taylor & the All-Stars Blues Band, Candy Dulfer & Funky Stuff, João Bosco, The Temptations, Tolo Marton Trio, Blues Wire, and Phil Guy.
The Skopje Cultural Summer Festival is a renowned cultural event that takes place in Skopje each year during the summer. The festival is a member of the International Festivals and Events Association (IFEA) and it includes musical concerts, operas, ballets, plays, art and photograph exhibitions, movies, and multimedia projects that gather 2,000 participants from around the world each year including the St Petersburg Theatre, the Chamber Orchestra of the Bolshoi Theatre, Irina Arkhipova, Viktor Tretiakov, The Theatre of Shadows, Michel Dalberto, and Dave Burgess (musician), David Burgess.
May Opera Evenings is a festival that has occurred annually in Skopje since 1972 and is dedicated to promoting opera among the general public. Over the years, it has evolved into a stage on which artists from some 50 countries have performed. There is one other major international theatre festival that takes place each year at the end of month September, the Young Open Theater Festival (MOT), which was organized for the first time in May 1976 by the Youth Cultural Center – Skopje. More than 700 theatrical performances have been presented at this festival so far, most of them being alternative, experimental theatre groups engaging young writers and actors. The MOT International theatre festival is also a member of the International Network for Contemporary Performing Arts or IETM. Within the framework of the MOT Festival, the Macedonian National Center of the International Theater Institute (ITI) was established, and at the 25th ITI World Congress in Munich in 1993, it became a regular member of this theatre association. The festival has an international character, always representing theatres from all over the world that present and enhance exchange and circulation of young-fresh-experimental-avant-garde theatrical energy and experience between its participants on one side and the audience on the other.
The Skopje Film Festival is an annual event held in the city every March. Over 50 films are shown at this five-day festival, mostly from North Macedonia and Europe, but also including some non-commercial film productions from all over the world.
Nightlife
 Skopje has a diverse nightlife. There is a large emphasis on casinos, many of which are associated with hotels, such as that of the Holiday Inn. Other casinos include Helios Metropol, Olympic, Bon Venon, and Sherry.
Skopje has a diverse nightlife. There is a large emphasis on casinos, many of which are associated with hotels, such as that of the Holiday Inn. Other casinos include Helios Metropol, Olympic, Bon Venon, and Sherry.Toše Proeski Arena
Toše Proeski National Arena ( mk, Национална арена "Тоше Проески") is a sports stadium in Skopje, North Macedonia. It is currently used mostly for football matches, but sometimes also for music concerts or athletics. I ...
and Boris Trajkovski Sports Center
The Boris Trajkovski Sports Center ( mk, Спортски центар Борис Трајковски, Sportski centar Boris Trajkovski) in Skopje is a multi-functional indoor sports arena. It is located in the Karpoš Municipality of Skopje, No ...
.Old Bazaar
The Old Bazaar ( mk, Стара чаршија, ''Stara čaršija''; ; tr, Eski Çarşı or Üsküp Türk Çarşısı) is a bazaar located in Skopje, North Macedonia, situated on the eastern bank of the Vardar River, stretching from the Stone Br ...
was a popular nightlife destination in the past. The Government of North Macedonia, national government has created a project to revive nightlife in the Old Bazaar. The closing time in shops, cafés and restaurants was extended due to the high attendances recorded. In the bazaar's restaurants, along with the traditional Macedonian wine and food, dishes of the Ottoman cuisine are also served.
People from Skopje
International relations

Twin towns – sister cities
Skopje is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:
* City of Bradford, Bradford, United Kingdom (since 1961)
* Dijon, France (since 1961)
* Dresden, Germany (since 1967)
* Tempe, Arizona, Tempe, United States (since 1971)
* Roubaix, France (since 1973)
* Waremme, Belgium (since 1974)
* Nuremberg, Germany (since 1982)
* Chlef, Algeria (since 1983)
* Nanchang, China (since 1985)
* Manisa, Turkey (since 1985)
* Suez, Egypt (since 1985)
* Pittsburgh, United States (since 2002)
* Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, Turkey (since 2003)
* Ljubljana, Slovenia (since 2007)
* Podgorica, Montenegro (since 2007)
* Zaragoza, Spain (since 2008)
* Zagreb, Croatia (since 2011)
* Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea ...
, Albania (since 2016)
* Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina (since 2017)
Partnerships
* Ankara, Turkey (since 1995)
* Belgrade, Serbia (since 2012)
See also
*History of Skopje
*List of honorary citizens of Skopje
*List of people from Skopje
*Old Bazaar, Skopje
*Sports in Skopje
Notes
Citations
General sources
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Discover SkopjeCity of Skopje Official Portal
picture gallery.
Skopje , Between Byzantine and Ottomans
{{Authority control
Skopje,
Former capitals of Bulgaria
Former capitals of Serbia
Cities in ancient Illyria
Capitals in Europe
Cities in North Macedonia
 The name of the city comes from
The name of the city comes from  Skopje is approximately 245 m above sea level and covers 571.46 km2. The urbanized area only covers 337 km2, with a density of 65 inhabitants per hectare. Skopje, in its administrative limits, encompasses many villages and other settlements, including Dračevo,
Skopje is approximately 245 m above sea level and covers 571.46 km2. The urbanized area only covers 337 km2, with a density of 65 inhabitants per hectare. Skopje, in its administrative limits, encompasses many villages and other settlements, including Dračevo,  The
The  Several rivers meet the Vardar within the city boundaries. The largest is the
Several rivers meet the Vardar within the city boundaries. The largest is the  The City of Skopje incorporates two artificial lakes, on the Treska. The lake Matka is the result of the construction of a dam in the Matka Canyon in the 1930s, and the Treska lake was dug for leisure purpose in 1978. Three small natural lakes can be found near Smiljkovci, on the northeastern edge of the urban area.
The river
The City of Skopje incorporates two artificial lakes, on the Treska. The lake Matka is the result of the construction of a dam in the Matka Canyon in the 1930s, and the Treska lake was dug for leisure purpose in 1978. Three small natural lakes can be found near Smiljkovci, on the northeastern edge of the urban area.
The river  The Skopje valley is bordered on the West by the
The Skopje valley is bordered on the West by the  The City of Skopje encompasses various natural environments and its fauna and flora are rich. However, it is threatened by the intensification of agriculture and the urban extension. The largest protected area within the city limits is Mount Vodno, which is a popular leisure destination. A cable car connects its peak to the downtown, and many pedestrian paths run through its woods. Other large natural spots include the Matka Canyon.
The city itself comprises several parks and gardens amounting to 4,361 hectares. Among these are the City Park (Gradski Park), built by the Ottoman Turks at the beginning of the 20th century; Žena Borec Park, in front of the Parliament; the university arboretum; and Gazi Baba forest. Many streets and boulevards are planted with trees.
Skopje experiences many environmental issues which are often overshadowed by the economic poverty of the country. However, alignment of North Macedonian law on European law has brought progress in some fields, such as water and waste treatment, and industrial emissions. Skopje remains one of the most polluted cities in the world, topping the ranks in December 2017.
Steel processing, which a crucial activity for the local economy, is responsible for soil pollution with heavy metals such as lead,
The City of Skopje encompasses various natural environments and its fauna and flora are rich. However, it is threatened by the intensification of agriculture and the urban extension. The largest protected area within the city limits is Mount Vodno, which is a popular leisure destination. A cable car connects its peak to the downtown, and many pedestrian paths run through its woods. Other large natural spots include the Matka Canyon.
The city itself comprises several parks and gardens amounting to 4,361 hectares. Among these are the City Park (Gradski Park), built by the Ottoman Turks at the beginning of the 20th century; Žena Borec Park, in front of the Parliament; the university arboretum; and Gazi Baba forest. Many streets and boulevards are planted with trees.
Skopje experiences many environmental issues which are often overshadowed by the economic poverty of the country. However, alignment of North Macedonian law on European law has brought progress in some fields, such as water and waste treatment, and industrial emissions. Skopje remains one of the most polluted cities in the world, topping the ranks in December 2017.
Steel processing, which a crucial activity for the local economy, is responsible for soil pollution with heavy metals such as lead,  The urban morphology of Skopje was deeply impacted by the 26 July 1963 earthquake, which destroyed 80% of the city, and by the reconstruction that followed. For instance, neighbourhoods were rebuilt in such a way that the demographic density remains low to limit the impact of potential future earthquakes.
Reconstruction following the 1963 earthquake was mainly conducted by the Polish architect Adolf Ciborowski, who had already planned the reconstruction of
The urban morphology of Skopje was deeply impacted by the 26 July 1963 earthquake, which destroyed 80% of the city, and by the reconstruction that followed. For instance, neighbourhoods were rebuilt in such a way that the demographic density remains low to limit the impact of potential future earthquakes.
Reconstruction following the 1963 earthquake was mainly conducted by the Polish architect Adolf Ciborowski, who had already planned the reconstruction of  The south bank of the Vardar river generally comprises highrise tower blocks, including the vast Karpoš neighbourhood which was built in the 1970s west of the centre. Towards the East, the new municipality of Aerodrom was planned in the 1980s to house 80,000 inhabitants on the site of the old airport. Between Karpoš and Aerodrom lies the city centre, rebuilt according to plans by Japanese architect
The south bank of the Vardar river generally comprises highrise tower blocks, including the vast Karpoš neighbourhood which was built in the 1970s west of the centre. Towards the East, the new municipality of Aerodrom was planned in the 1980s to house 80,000 inhabitants on the site of the old airport. Between Karpoš and Aerodrom lies the city centre, rebuilt according to plans by Japanese architect  Skopje is an ethnically diverse city, and its urban sociology primarily depends on ethnic and religious belonging. Macedonians form 66% of the city population, while Albanians and Roma account respectively for 20% and 6%. Each ethnic group generally restrict itself to certain areas of the city. Macedonians live south of the
Skopje is an ethnically diverse city, and its urban sociology primarily depends on ethnic and religious belonging. Macedonians form 66% of the city population, while Albanians and Roma account respectively for 20% and 6%. Each ethnic group generally restrict itself to certain areas of the city. Macedonians live south of the  Roman expansion east brought Scupi under Roman rule as a colony of legionnaires, mainly veterans of the
Roman expansion east brought Scupi under Roman rule as a colony of legionnaires, mainly veterans of the  In 518, Scupi was destroyed by a violent earthquake, possibly the most devastating the town experienced. At that time, the region was threatened by the Barbarian invasions, and the city inhabitants had already fled in forests and mountains before the disaster occurred. The city was eventually rebuilt by
In 518, Scupi was destroyed by a violent earthquake, possibly the most devastating the town experienced. At that time, the region was threatened by the Barbarian invasions, and the city inhabitants had already fled in forests and mountains before the disaster occurred. The city was eventually rebuilt by  Starting from the end of the 10th century Skopje experienced a period of wars and political troubles. It served as Bulgarian capital from 972 to 992, and
Starting from the end of the 10th century Skopje experienced a period of wars and political troubles. It served as Bulgarian capital from 972 to 992, and  Following an alliance contracted in 1912,
Following an alliance contracted in 1912, 
 In 1915, during the
In 1915, during the  In 1941, during the Second World War, Yugoslavia was invaded by
In 1941, during the Second World War, Yugoslavia was invaded by  After the
After the  Being the capital and largest city of North Macedonia, Skopje enjoys a particular status granted by law. The last revision of its status was made in 2004. Since then, the City of Skopje has been divided into 10 municipalities which all have a council and a mayor, like all of the country's municipalities. Municipalities only deal with matters specific of their territory, and the City of Skopje deals with matters that concern all of them, or that cannot be divided between two or more municipalities.
The City of Skopje is part of the
Being the capital and largest city of North Macedonia, Skopje enjoys a particular status granted by law. The last revision of its status was made in 2004. Since then, the City of Skopje has been divided into 10 municipalities which all have a council and a mayor, like all of the country's municipalities. Municipalities only deal with matters specific of their territory, and the City of Skopje deals with matters that concern all of them, or that cannot be divided between two or more municipalities.
The City of Skopje is part of the  Besides many small traditional shops, Skopje has two large markets, the "Zelen Pazar" (green market) and the "Bit Pazar" (flea market). They are both considered as local institutions. However, since the 1970s, retailing has largely been modernized and Skopje now has many supermarkets and shopping centres. The largest, Skopje City Mall, opened in 2012. It comprises a
Besides many small traditional shops, Skopje has two large markets, the "Zelen Pazar" (green market) and the "Bit Pazar" (flea market). They are both considered as local institutions. However, since the 1970s, retailing has largely been modernized and Skopje now has many supermarkets and shopping centres. The largest, Skopje City Mall, opened in 2012. It comprises a 
 Skopje's citizenry is generally more educated than the rest of the country. For one, 16% of Skopjans have graduated from university in contrast to 10% for the rest of the country. The number of people with a complete lack of education or ones who received a partial education is lower in Skopje at 9% compared to the provincial average of 17%. 80% of Macedonian citizens who hold a PhD take up residence in Skopje.
Skopje has 21 secondary schools; 5 of which serve as general high-school gymnasiums and 16 vocational schools. The city is also host to several higher education institutions, the most notable of which is Ss. Cyril and Methodius University, founded in 1949. The university has 23 departments, 10 research institutes and is attended by an average of 50,000 students. After the country's declaration of independence in 1991, several private universities were brought to existence. The largest private universities in Skopje are European University with 7 departments and FON University with 9 departments respectively.
Skopje's citizenry is generally more educated than the rest of the country. For one, 16% of Skopjans have graduated from university in contrast to 10% for the rest of the country. The number of people with a complete lack of education or ones who received a partial education is lower in Skopje at 9% compared to the provincial average of 17%. 80% of Macedonian citizens who hold a PhD take up residence in Skopje.
Skopje has 21 secondary schools; 5 of which serve as general high-school gymnasiums and 16 vocational schools. The city is also host to several higher education institutions, the most notable of which is Ss. Cyril and Methodius University, founded in 1949. The university has 23 departments, 10 research institutes and is attended by an average of 50,000 students. After the country's declaration of independence in 1991, several private universities were brought to existence. The largest private universities in Skopje are European University with 7 departments and FON University with 9 departments respectively.
 Skopje is near three other capital cities,
Skopje is near three other capital cities,  Skopje has a bus network managed by the city and operated by three companies. The oldest and largest is JSP Skopje, a public company founded in 1948. JSP lost its monopoly on public transport in 1990 and two new companies, Sloboda Prevoz and Mak Ekspres, obtained several lines. However, most of the network is still in the hands of JSP which operates 67 lines out of 80. Only 24 lines are urban, the others serving localities around the city. Many of the JSP vehicles are red Yutong City Master double-decker buses built by Chinese bus manufacturer
Skopje has a bus network managed by the city and operated by three companies. The oldest and largest is JSP Skopje, a public company founded in 1948. JSP lost its monopoly on public transport in 1990 and two new companies, Sloboda Prevoz and Mak Ekspres, obtained several lines. However, most of the network is still in the hands of JSP which operates 67 lines out of 80. Only 24 lines are urban, the others serving localities around the city. Many of the JSP vehicles are red Yutong City Master double-decker buses built by Chinese bus manufacturer  Skopje is home to the largest cultural institutions of the country, such as the National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", the
Skopje is home to the largest cultural institutions of the country, such as the National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", the  The largest museum in Skopje is the Museum of the Republic of North Macedonia which details the history of the country. Its icons and lapidary collections are particularly rich. The Macedonian Archeological Museum, opened in 2014, keeps some of the best archeological finds in North Macedonia, dating from Prehistory to the Ottoman period. The National Gallery of Macedonia exhibits paintings dating from the 14th to the 20th century in two former Turkish baths of the
The largest museum in Skopje is the Museum of the Republic of North Macedonia which details the history of the country. Its icons and lapidary collections are particularly rich. The Macedonian Archeological Museum, opened in 2014, keeps some of the best archeological finds in North Macedonia, dating from Prehistory to the Ottoman period. The National Gallery of Macedonia exhibits paintings dating from the 14th to the 20th century in two former Turkish baths of the  Skopje Fortress was rebuilt several times before it was destroyed by the 1963 earthquake. Since then, it has been restored to its medieval appearance. It is the only medieval monument in Skopje, but several churches around the city illustrate the Serbo-Byzantine architecture, Vardar architectural school which flourished around 1300. Among these churches are the ones around Matka Canyon (St Nicholas, St Andrew and Matka churches). The church of St. Panteleimon (Gorno Nerezi), church of St. Panteleimon in
Skopje Fortress was rebuilt several times before it was destroyed by the 1963 earthquake. Since then, it has been restored to its medieval appearance. It is the only medieval monument in Skopje, but several churches around the city illustrate the Serbo-Byzantine architecture, Vardar architectural school which flourished around 1300. Among these churches are the ones around Matka Canyon (St Nicholas, St Andrew and Matka churches). The church of St. Panteleimon (Gorno Nerezi), church of St. Panteleimon in  After 1912, when Skopje was annexed by Serbia, the city was drastically westernized. Wealthy Serbs built mansions and town houses such as the 1926 Ristiḱ Palace. Architecture of that time is very similar to the one of Central Europe, but some buildings are more creative, such as the Moorish Revival architecture, Neo-Moorish Arab House and the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo-Byzantine train station, both built in 1938. Modernist architecture, Modernism appeared as early as 1933 with the former Ethnographic Museum (today the City Gallery), designed by Milan Zloković. However, modernist architecture only fully developed in Skopje after the 1963 earthquake. The reconstruction of city centre was partially planned by Japanese
After 1912, when Skopje was annexed by Serbia, the city was drastically westernized. Wealthy Serbs built mansions and town houses such as the 1926 Ristiḱ Palace. Architecture of that time is very similar to the one of Central Europe, but some buildings are more creative, such as the Moorish Revival architecture, Neo-Moorish Arab House and the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo-Byzantine train station, both built in 1938. Modernist architecture, Modernism appeared as early as 1933 with the former Ethnographic Museum (today the City Gallery), designed by Milan Zloković. However, modernist architecture only fully developed in Skopje after the 1963 earthquake. The reconstruction of city centre was partially planned by Japanese  The reconstruction turned Skopje into a proper modernist city, with large blocks of flats, austere concrete buildings and scattered green spaces. The city centre was considered as a grey and unattractive place when local authorities unveiled the "
The reconstruction turned Skopje into a proper modernist city, with large blocks of flats, austere concrete buildings and scattered green spaces. The city centre was considered as a grey and unattractive place when local authorities unveiled the " Skopje has a diverse nightlife. There is a large emphasis on casinos, many of which are associated with hotels, such as that of the Holiday Inn. Other casinos include Helios Metropol, Olympic, Bon Venon, and Sherry. Among young people the most popular destinations are bars, discos, and nightclubs which can be found in the centre and the City Park. Among the most popular nightclubs are The Loft, Club Epicentar, Stanica 26, Midnight, Maracana, Havana Summer Club, XL Summer Club (former Colosseum Summer Club) where world-famous disc jockeys and idiosyncratic local performances are frequent. In 2010, the Colosseum club was named fifth on a list of the best clubs in Southeastern Europe. Armin van Buuren, Above and Beyond (band), Above and Beyond, Shapeshifters (music act), The Shapeshifters are just some of the many musicians that have visited the club. Nighttime concerts in local, regional and global music are often held at the
Skopje has a diverse nightlife. There is a large emphasis on casinos, many of which are associated with hotels, such as that of the Holiday Inn. Other casinos include Helios Metropol, Olympic, Bon Venon, and Sherry. Among young people the most popular destinations are bars, discos, and nightclubs which can be found in the centre and the City Park. Among the most popular nightclubs are The Loft, Club Epicentar, Stanica 26, Midnight, Maracana, Havana Summer Club, XL Summer Club (former Colosseum Summer Club) where world-famous disc jockeys and idiosyncratic local performances are frequent. In 2010, the Colosseum club was named fifth on a list of the best clubs in Southeastern Europe. Armin van Buuren, Above and Beyond (band), Above and Beyond, Shapeshifters (music act), The Shapeshifters are just some of the many musicians that have visited the club. Nighttime concerts in local, regional and global music are often held at the