Singing Technique on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of
 Within Western culture, the study of vocal pedagogy began in
Within Western culture, the study of vocal pedagogy began in  Voice teachers in the 19th century continued to train singers for careers in opera.
Voice teachers in the 19th century continued to train singers for careers in opera.  The field of voice pedagogy became more fully developed in the middle of the 20th century. A few American voice teachers began to study the science, anatomy, and physiology of singing, especially
The field of voice pedagogy became more fully developed in the middle of the 20th century. A few American voice teachers began to study the science, anatomy, and physiology of singing, especially
 There are four physical processes involved in producing vocal sound:
There are four physical processes involved in producing vocal sound:
 In its most basic sense, respiration is the process of moving air in and out of the body—inhalation and exhalation. Sound is produced in the larynx. But producing the sound would not be possible without a power source: the flow of air from the lungs. This flow sets the vocal folds into motion to produce sound. Breathing for singing and speaking is a more controlled process than is the ordinary breathing used for sustaining life. The controls applied to exhalation are particularly important in good vocal technique.
In its most basic sense, respiration is the process of moving air in and out of the body—inhalation and exhalation. Sound is produced in the larynx. But producing the sound would not be possible without a power source: the flow of air from the lungs. This flow sets the vocal folds into motion to produce sound. Breathing for singing and speaking is a more controlled process than is the ordinary breathing used for sustaining life. The controls applied to exhalation are particularly important in good vocal technique.
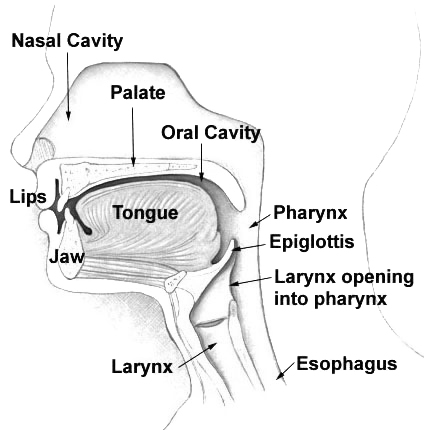 Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air. Various terms related to the resonation process include amplification, enrichment, enlargement, improvement, intensification, and prolongation, although in strictly scientific usage acoustic authorities would question most of them. The main point to be drawn from these terms by a singer or speaker is that the end result of resonation is, or should be, to make a better sound.
There are seven areas that may be listed as possible vocal resonators. In sequence from the lowest within the body to the highest, these areas are the
Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air. Various terms related to the resonation process include amplification, enrichment, enlargement, improvement, intensification, and prolongation, although in strictly scientific usage acoustic authorities would question most of them. The main point to be drawn from these terms by a singer or speaker is that the end result of resonation is, or should be, to make a better sound.
There are seven areas that may be listed as possible vocal resonators. In sequence from the lowest within the body to the highest, these areas are the
 Articulation is the process by which the joint product of the vibrator and the resonators is shaped into recognizable speech sounds through the muscular adjustments and movements of the speech organs. These adjustments and movements of the articulators result in verbal communication and thus form the essential difference between the human voice and other musical instruments. Singing without understandable words limits the voice to nonverbal communication. In relation to the physical process of singing, vocal instructors tend to focus more on active articulation as opposed to passive articulation. There are five basic active articulators: the lip ("
Articulation is the process by which the joint product of the vibrator and the resonators is shaped into recognizable speech sounds through the muscular adjustments and movements of the speech organs. These adjustments and movements of the articulators result in verbal communication and thus form the essential difference between the human voice and other musical instruments. Singing without understandable words limits the voice to nonverbal communication. In relation to the physical process of singing, vocal instructors tend to focus more on active articulation as opposed to passive articulation. There are five basic active articulators: the lip ("
National Association of Teachers of SingingVocapedia, NATS-sponsored comprehensive database on singing and vocal pedagogy
{{Authority control Human voice Singing Opera terminology * Vocal skills
voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in ...
instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing
Singing is the act of creating musical sounds with the voice. A person who sings is called a singer, artist or vocalist (in jazz and/or popular music). Singers perform music (arias, recitatives, songs, etc.) that can be sung with or without ...
and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how proper singing technique is accomplished.
Vocal pedagogy covers a broad range of aspects of singing, ranging from the physiological process of vocal production to the artistic aspects of interpretation of songs from different genres or historical eras. Typical areas of study include:
:
* Human anatomy
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
It comprises a he ...
and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
as it relates to the physical process of singing.
* Breathing and air support for singing
* Posture
Posture or posturing may refer to:
Medicine
* Human position
** Abnormal posturing, in neurotrauma
** Spinal posture
** List of human positions
* Posturography Posturography is the technique used to quantify postural control in upright stance in ...
for singing
* Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
* Vocal resonation Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, various ...
or voice projection
Voice projection is the strength of speaking or singing whereby the human voice is used powerfully and clearly. It is a technique employed to command respect and attention, as when a teacher talks to a class, or simply to be heard clearly, as used ...
* Diction, vowels and articulation
* Vocal registration
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in la ...
* Sostenuto
Piano pedals are foot-operated levers at the base of a piano that change the instrument's sound in various ways. Modern pianos usually have three pedals, from left to right, the soft pedal (or una corda), the sostenuto pedal, and the sustainin ...
and legato
In music performance and notation, legato (; Italian for "tied together"; French ''lié''; German ''gebunden'') indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly and connected. That is, the player makes a transition from note to note wit ...
for singing
* Other singing elements, such as range extension, tone quality, vibrato
Vibrato (Italian language, Italian, from past participle of "wikt:vibrare, vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch (music), pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. ...
, coloratura
Coloratura is an elaborate melody with runs, trills, wide leaps, or similar virtuoso-like material,''Oxford American Dictionaries''.Apel (1969), p. 184. or a passage of such music. Operatic roles in which such music plays a prominent part, an ...
* Vocal health and voice disorders Voice disordersTitze, I.R. (1994). Principles of Voice Production, Prentice Hall, . are medical conditions involving abnormal pitch, loudness or quality of the sound produced by the larynx and thereby affecting speech production. These include:
*
...
related to singing
* Vocal styles, such as learning to sing opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
, belt
Belt may refer to:
Apparel
* Belt (clothing), a leather or fabric band worn around the waist
* Championship belt, a type of trophy used primarily in combat sports
* Colored belts, such as a black belt or red belt, worn by martial arts practit ...
, or art song
An art song is a Western vocal music composition, usually written for one voice with piano accompaniment, and usually in the classical art music tradition. By extension, the term "art song" is used to refer to the collective genre of such songs ...
* Phonetics
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. ...
* Voice classification
A voice type is a group of voices with similar vocal ranges, capable of singing in a similar tessitura, and with similar vocal transition points ('' passaggi''). Voice classification is most strongly associated with European classical music, t ...
All of these different concepts are a part of developing proper vocal technique. Not all voice teacher
A voice teacher or singing teacher is a musical instructor who assists adults and children in the development of their abilities in singing.
Typical work
A voice teacher works with a student singer to improve the various skills involved in singi ...
s have the same opinions within every topic of study which causes variations in pedagogical approaches and vocal technique.
History
 Within Western culture, the study of vocal pedagogy began in
Within Western culture, the study of vocal pedagogy began in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
. Scholars such as Alypius and Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samos, Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionians, Ionian Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher and the eponymou ...
studied and made observations on the art of singing. It is unclear, however, whether the Greeks ever developed a systematic approach to teaching singing as little writing on the subject survives today.''The New Grove Dictionary of Music & Musicians
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language ''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and theo ...
''. Edited by Stanley Sadie
Stanley John Sadie (; 30 October 1930 – 21 March 2005) was an influential and prolific British musicologist, music critic, and editor. He was editor of the sixth edition of the '' Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' (1980), which was publ ...
, ''Volume 6. Edmund to Fryklund''. , Copyright Macmillan 1980.
The first surviving record of a systematized approach to teaching singing was developed in the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
sometime near the beginning of the 13th century. As with other fields of study, the monasteries were the center of musical intellectual life during the medieval period and many men within the monasteries devoted their time to the study of music and the art of singing. Highly influential in the development of a vocal pedagogical system were monks Johannes de Garlandia and Jerome of Moravia
Jerome of Moravia (or Hieronymus de Moravia) (died after 1271) was a medieval music theorist. He was a Dominican friar. His origin is unknown, but he is believed to have worked in Paris at the Dominican convent on the Rue Saint-Jacques. He most l ...
who were the first to develop a concept of vocal registers
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in ...
. These men identified three registers: chest voice
Chest voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regard to this term. Chest voice can be used in ...
, throat voice, and head voice
Head voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regard to this term. Head voice can be used in re ...
(pectoris, guttoris, and capitis). Their concept of head voice, however, is much more similar to the modern pedagogists understanding of the falsetto register. Other concepts discussed in the monastic system included vocal resonance Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, various ...
, voice classification
A voice type is a group of voices with similar vocal ranges, capable of singing in a similar tessitura, and with similar vocal transition points ('' passaggi''). Voice classification is most strongly associated with European classical music, t ...
, breath support, diction, and tone quality to name a few. The ideas developed within the monastic system highly influenced the development of vocal pedagogy over the next several centuries including the Bel Canto
Bel canto (Italian for "beautiful singing" or "beautiful song", )—with several similar constructions (''bellezze del canto'', ''bell'arte del canto'')—is a term with several meanings that relate to Italian singing.
The phrase was not associat ...
style of singing.
With the onset of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
in the 15th century, the study of singing began to move outside of the church. The courts of rich patrons, such as the Dukes of Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
who supported the Burgundian School
The Burgundian School was a group of composers active in the 15th century in what is now northern and eastern France, Belgium, and the Netherlands, centered on the court of the Dukes of Burgundy. The school inaugurated the music of Burgundy.
The ...
and the Franco-Flemish School
The designation Franco-Flemish School, also called Netherlandish School, Burgundian School, Low Countries School, Flemish School, Dutch School, or Northern School, refers, somewhat imprecisely, to the style of polyphonic vocal music composition or ...
, became secular centers of study for singing and all other areas of musical study. The vocal pedagogical methods taught in these schools, however, were based on the concepts developed within the monastic system. Many of the teachers within these schools had their initial musical training from singing in church choirs as children. The church also remained at the forefront of musical composition at this time and remained highly influential in shaping musical tastes and practices both in and outside the church. It was the Catholic Church that first popularized the use of castrato
A castrato (Italian, plural: ''castrati'') is a type of classical male singing voice equivalent to that of a soprano, mezzo-soprano, or contralto. The voice is produced by castration of the singer before puberty, or it occurs in one who, due to ...
singers in the 16th century, which ultimately led to the popularity of castrato voices in Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
and Classical operas
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a libretti ...
.
It was not until the development of opera in the 17th century that vocal pedagogy began to break away from some of the established thinking of the monastic writers and develop deeper understandings of the physical process of singing and its relation to key concepts like vocal registration
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in la ...
and vocal resonation Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, various ...
. It was also during this time that noted voice teacher
A voice teacher or singing teacher is a musical instructor who assists adults and children in the development of their abilities in singing.
Typical work
A voice teacher works with a student singer to improve the various skills involved in singi ...
s began to emerge. Giulio Caccini
Giulio Romolo Caccini (also Giulio Romano) (8 October 1551 – buried 10 December 1618) was an Italian composer, teacher, singer, instrumentalist and writer of the late Renaissance and early Baroque eras. He was one of the founders of the genre ...
is an example of an important early Italian voice teacher. In the late 17th century, the bel canto
Bel canto (Italian for "beautiful singing" or "beautiful song", )—with several similar constructions (''bellezze del canto'', ''bell'arte del canto'')—is a term with several meanings that relate to Italian singing.
The phrase was not associat ...
method of singing began to develop in Italy. This style of singing had a huge impact on the development of opera and the development of vocal pedagogy during the Classical and Romantic periods. It was during this time that teachers and composers first began to identify singers by and write roles for more specific voice types
A voice type is a group of voices with similar vocal ranges, capable of singing in a similar tessitura, and with similar vocal transition points ('' passaggi''). Voice classification is most strongly associated with European classical music, ...
. However, it was not until the 19th century that more clearly defined voice classification systems like the German Fach
The German system (; literally "compartment" or "subject of study", here in the sense of "vocal specialization") is a method of classifying singers, primarily opera singers, according to the range, weight, and color of their voices. It is used w ...
system emerged. Within these systems, more descriptive terms were used in classifying voices such as coloratura soprano
A coloratura soprano is a type of operatic soprano voice that specializes in music that is distinguished by agile runs, leaps and trills.
The term '' coloratura'' refers to the elaborate ornamentation of a melody, which is a typical component o ...
and lyric soprano
A lyric soprano is a type of operatic soprano voice that has a warm quality with a bright, full timbre that can be heard over an orchestra. The lyric soprano voice generally has a higher tessitura than a soubrette and usually plays ingenues and ot ...
.
 Voice teachers in the 19th century continued to train singers for careers in opera.
Voice teachers in the 19th century continued to train singers for careers in opera. Manuel Patricio Rodríguez García
Manuel may refer to:
People
* Manuel (name)
* Manuel (Fawlty Towers), a fictional character from the sitcom ''Fawlty Towers''
* Charlie Manuel, manager of the Philadelphia Phillies
* Manuel I Komnenos, emperor of the Byzantine Empire
* Manu ...
is often considered one of the most important voice teachers of the 19th century, and is credited with the development of the laryngoscope
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ge ...
and the beginning of modern voice pedagogy.
 The field of voice pedagogy became more fully developed in the middle of the 20th century. A few American voice teachers began to study the science, anatomy, and physiology of singing, especially
The field of voice pedagogy became more fully developed in the middle of the 20th century. A few American voice teachers began to study the science, anatomy, and physiology of singing, especially Ralph Appelman
Ralph (pronounced ; or ,) is a male given name of English, Scottish and Irish origin, derived from the Old English ''Rædwulf'' and Radulf, cognate with the Old Norse ''Raðulfr'' (''rað'' "counsel" and ''ulfr'' "wolf").
The most common forms ...
at Indiana University
Indiana University (IU) is a system of public universities in the U.S. state of Indiana.
Campuses
Indiana University has two core campuses, five regional campuses, and two regional centers under the administration of IUPUI.
*Indiana Universit ...
, Oren Brown
Oren Brown (April 13, 1909 – March 6, 2004) was a well-known and highly successful American vocal pedagogue and voice teacher.
Born in Somerville, Massachusetts, Brown attended Boston University, where he earned a Bachelor of Music with an emp ...
at the Washington University School of Medicine
Washington University School of Medicine (WUSM) is the medical school of Washington University in St. Louis in St. Louis, Missouri. Founded in 1891, the School of Medicine has 1,260 students, 604 of which are pursuing a medical degree with or ...
and later the Juilliard School
The Juilliard School ( ) is a private performing arts conservatory in New York City. Established in 1905, the school trains about 850 undergraduate and graduate students in dance, drama, and music. It is widely regarded as one of the most el ...
, and William Vennard
William Vennard (January 31, 1909 Normal, Illinois – January 10, 1971, Los Angeles, California) was a famous American vocal pedagogist who devoted his life to researching the human voice and its use in singing. He was one of the driving fo ...
at the University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in C ...
. This shift in approach to the study of singing led to the rejection of many of the assertions of the bel canto
Bel canto (Italian for "beautiful singing" or "beautiful song", )—with several similar constructions (''bellezze del canto'', ''bell'arte del canto'')—is a term with several meanings that relate to Italian singing.
The phrase was not associat ...
singing method, most particularly in the areas of vocal registration
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in la ...
and vocal resonation Vocal resonance may be defined as "the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air." Throughout the vocal literature, various ...
. As a result, there are currently two predominating schools of thought among voice teachers today, those who maintain the historical positions of the bel canto method and those who choose to embrace more contemporary understandings based in current knowledge of human anatomy and physiology. There are also those teachers who borrow ideas from both perspectives, creating a hybrid of the two.
Appelman and Vennard were also part of a group of voice instructors who developed courses of study for beginning voice teachers, adding these scientific ideas to the standard exercises and empirical ways to improve vocal technique, and by 1980 the subject of voice pedagogy was beginning to be included in many college music degree programs for singers and vocal music educators.
More recent works by authors such as Richard Miller and Johan Sundberg have increased the general knowledge of voice teachers, and scientific and practical aspects of voice pedagogy continue to be studied and discussed by professionals. In addition, the creation of organisations such as the National Association of Teachers of Singing
The National Association of Teachers of Singing (NATS) is a professional organization for singing teachers, and it is the largest association of its kind in the world. There are more than 6,500 members, mostly from the United States. Additional m ...
(now an international organization of Vocal Instructors) has enabled voice teachers to establish more of a consensus about their work, and has expanded the understanding of what singing teachers do.
Topics of study
Pedagogical philosophy
There are basically three major approaches to vocal pedagogy. They're all related to how the mechanistic and psychological controls are employed while singing. Some voice instructors advocate an extreme mechanistic approach that believes that singing is largely a matter of getting the right physical parts in the right places at the right time, and that correcting vocal faults is accomplished by calling direct attention to the parts which are not working well. On the other extreme, is the school of thought that believes that attention should never be directed to any part of the vocal mechanism—that singing is a matter of producing the right mental images of the desired tone, and that correcting vocal faults is achieved by learning to think the right thoughts and by releasing the emotions through interpretation of the music. Most voice teachers, however, believe that the truth lies somewhere in between the two extremes and adopt a composite of those two approaches.The nature of vocal sounds
Physiology of vocal sound production
 There are four physical processes involved in producing vocal sound:
There are four physical processes involved in producing vocal sound: respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellula ...
, phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
, resonation, and articulation. These processes occur in the following sequence:
#Breath is taken
#Sound is initiated in the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
#The vocal resonators receive the sound and influence it
#The articulators shape the sound into recognizable units
Although these four processes are to be considered separately, in actual practice they merge into one coordinated function. With an effective singer or speaker, one should rarely be reminded of the process involved as their mind and body are so coordinated that one only perceives the resulting unified function. Many vocal problems result from a lack of coordination within this process.
=Respiration
= In its most basic sense, respiration is the process of moving air in and out of the body—inhalation and exhalation. Sound is produced in the larynx. But producing the sound would not be possible without a power source: the flow of air from the lungs. This flow sets the vocal folds into motion to produce sound. Breathing for singing and speaking is a more controlled process than is the ordinary breathing used for sustaining life. The controls applied to exhalation are particularly important in good vocal technique.
In its most basic sense, respiration is the process of moving air in and out of the body—inhalation and exhalation. Sound is produced in the larynx. But producing the sound would not be possible without a power source: the flow of air from the lungs. This flow sets the vocal folds into motion to produce sound. Breathing for singing and speaking is a more controlled process than is the ordinary breathing used for sustaining life. The controls applied to exhalation are particularly important in good vocal technique.
=Phonation
=Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
is the process of producing vocal sound by the vibration of the vocal folds
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech ...
that is in turn modified by the resonance of the vocal tract
The vocal tract is the cavity in human bodies and in animals where the sound produced at the sound source (larynx in mammals; syrinx (biology), syrinx in birds) is filtered.
In birds it consists of the Vertebrate trachea, trachea, the Syrinx (bio ...
. It takes place in the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
when the vocal folds
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech ...
are brought together and breath pressure is applied to them in such a way that vibration ensues causing an audible source of acoustic energy, i.e., sound, which can then be modified by the articulatory actions of the rest of the vocal apparatus
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articula ...
. The vocal folds are brought together primarily by the action of the interarytenoid muscles, which pull the arytenoid cartilages
The arytenoid cartilages () are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx. They are the site of attachment of the vocal cords. Each is pyramidal or ladle-shaped and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex. The arytenoid ...
together.
=Resonation
= Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air. Various terms related to the resonation process include amplification, enrichment, enlargement, improvement, intensification, and prolongation, although in strictly scientific usage acoustic authorities would question most of them. The main point to be drawn from these terms by a singer or speaker is that the end result of resonation is, or should be, to make a better sound.
There are seven areas that may be listed as possible vocal resonators. In sequence from the lowest within the body to the highest, these areas are the
Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air. Various terms related to the resonation process include amplification, enrichment, enlargement, improvement, intensification, and prolongation, although in strictly scientific usage acoustic authorities would question most of them. The main point to be drawn from these terms by a singer or speaker is that the end result of resonation is, or should be, to make a better sound.
There are seven areas that may be listed as possible vocal resonators. In sequence from the lowest within the body to the highest, these areas are the chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
, the tracheal tree, the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
itself, the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
, the oral cavity
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
, the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal c ...
, and the sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
.
Research has shown that the larynx, the pharynx and the oral cavity are the main resonators of vocal sound, with the nasal cavity only coming into play in nasal consonants, or nasal vowels, such as those found in French. This main resonating space, from above the vocal folds to the lips is known as the vocal tract
The vocal tract is the cavity in human bodies and in animals where the sound produced at the sound source (larynx in mammals; syrinx (biology), syrinx in birds) is filtered.
In birds it consists of the Vertebrate trachea, trachea, the Syrinx (bio ...
. Many voice users experience sensations in the sinuses that may be misconstrued as resonance. However, these sensations are caused by sympathetic vibrations, and are a result, rather than a cause, of efficient vocal resonance.
=Articulation
=labial consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. The two common labial articulations are bilabials, articulated using both lips, and labiodentals, articulated with the lower lip against the upper teeth, bot ...
s"), the flexible front of the tongue ("coronal consonant
Coronals are consonants articulated with the flexible front part of the tongue. Among places of articulation, only the coronal consonants can be divided into as many articulation types: apical (using the tip of the tongue), laminal (using the bla ...
s"), the middle/back of the tongue ("dorsal consonant
Dorsal consonants are consonants articulated with the back of the tongue (the dorsum). They include the palatal, velar and, in some cases, alveolo-palatal and uvular consonants. They contrast with coronal consonants, articulated with the flexibl ...
s"), the root of the tongue together with the epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food int ...
("pharyngeal consonant
A pharyngeal consonant is a consonant that is articulated primarily in the pharynx. Some phoneticians distinguish upper pharyngeal consonants, or "high" pharyngeals, pronounced by retracting the root of the tongue in the mid to upper pharynx, ...
s"), and the glottis
The glottis is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing vowels and voiced consonants.
Etymology
From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), va ...
("glottal consonant
Glottal consonants are consonants using the glottis as their primary articulation. Many phoneticians consider them, or at least the glottal fricative, to be transitional states of the glottis without a point of articulation as other consonants ...
s"). These articulators can act independently of each other, and two or more may work together in what is called ''coarticulation''.
Unlike active articulation, passive articulation is a continuum without many clear-cut boundaries. The places linguolabial and interdental, interdental and dental, dental and alveolar, alveolar and palatal, palatal and velar, velar and uvular merge into one another, and a consonant may be pronounced somewhere between the named places.
In addition, when the front of the tongue is used, it may be the upper surface or ''blade'' of the tongue that makes contact ("laminal consonant
A laminal consonant is a phone (speech sound) produced by obstructing the air passage with the blade of the tongue, the flat top front surface just behind the tip of the tongue in contact
with upper lip, teeth, alveolar ridge, to possibly, as ...
s"), the tip of the tongue ("apical consonant
An apical consonant is a phone (speech sound) produced by obstructing the air passage with the tip of the tongue (apex) in conjunction with upper articulators from lips to postalveolar, and possibly prepalatal. It contrasts with laminal cons ...
s"), or the under surface (" sub-apical consonants"). These articulations also merge into one another without clear boundaries.
=Interpretation
= Interpretation is sometimes listed by voice teachers as a fifth physical process even though strictly speaking it is not a physical process. The reason for this is that interpretation does influence the kind of sound a singer makes which is ultimately achieved through a physical action the singer is doing. Although teachers may acquaint their students with musical styles and performance practices and suggest certain interpretive effects, most voice teachers agree that interpretation can not be taught. Students who lack a natural creative imagination and aesthetic sensibility can not learn it from someone else. Failure to interpret well is not a vocal fault, even though it may affect vocal sound significantly.Classification of vocal sounds
Vocal sounds are divided into two basic categories—vowels
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (leng ...
and consonants
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced wit ...
—with a wide variety of sub-classifications. Voice teachers and serious voice students spend a great deal of time studying how the voice forms vowels and consonants, and studying the problems that certain consonants or vowels may cause while singing. The International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic transcription, phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standa ...
is used frequently by voice teachers and their students.
Problems in describing vocal sounds
Describing vocal sound is an inexact science largely because thehuman voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production ...
is a self-contained instrument. Since the vocal instrument is internal, the singer's ability to monitor the sound produced is complicated by the vibrations carried to the ear through the Eustachean (auditory) tube and the bony structures of the head and neck. In other words, most singers hear something different in their ears/head than what a person listening to them hears. As a result, voice teachers often focus less on how it "sounds" and more on how it "feels". Vibratory sensations resulting from the closely related processes of phonation and resonation, and kinesthetic ones arising from muscle tension, movement, body position, and weight serve as a guide to the singer on correct vocal production.
Another problem in describing vocal sound lies in the vocal vocabulary itself. There are many schools of thought within vocal pedagogy and different schools have adopted different terms, sometimes from other artistic disciplines. This has led to the use of a plethora of descriptive terms applied to the voice which are not always understood to mean the same thing. Some terms sometimes used to describe a quality of a voice's sound are: warm, white, dark, light, round, reedy, spread, focused, covered, swallowed, forward, ringing, hooty, bleaty, plummy, mellow, pear-shaped, and so forth.
Body alignment
The singing process functions best when certain physical conditions of the body exist. The ability to move air in and out of the body freely and to obtain the needed quantity of air can be seriously affected by the body alignment of the various parts of the breathing mechanism. A sunken chest position will limit the capacity of the lungs, and a tense abdominal wall will inhibit the downward travel of the diaphragm. Good body alignment allows the breathing mechanism to fulfill its basic function efficiently without any undue expenditure of energy. Good body alignment also makes it easier to initiate phonation and to tune the resonators as proper alignment prevents unnecessary tension in the body. Voice Instructors have also noted that when singers assume good body alignment it often provides them with a greater sense of self-assurance and poise while performing. Audiences also tend to respond better to singers with good body alignment. Habitual good body alignment also ultimately improves the overall health of the body by enabling better blood circulation and preventing fatigue and stress on the body.Breathing and breath support
All singing begins with breath. All vocal sounds are created byvibrations
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin ''vibrationem'' ("shaking, brandishing"). The oscillations may be periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, such ...
in the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
caused by air from the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of th ...
. Breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular ...
in everyday life is a subconscious
In psychology, the subconscious is the part of the mind that is not currently of focal awareness.
Scholarly use of the term
The word ''subconscious'' represents an anglicized version of the French ''subconscient'' as coined in 1889 by the psycho ...
bodily function which occurs naturally; however, the singer
Singing is the act of creating musical sounds with the voice. A person who sings is called a singer, artist or vocalist (in jazz and/or popular music). Singers perform music (arias, recitatives, songs, etc.) that can be sung with or without ...
must have control of the intake and exhalation of breath to achieve maximum results from their voice.
Natural breathing has three stages: a breathing-in period, a breathing-out period, and a resting or recovery period; these stages are not usually consciously controlled. Within singing there are four stages of breathing:
# breathing-in period (inhalation)
# setting up controls period (suspension)
# controlled exhalation period (phonation)
# recovery period
These stages must be under conscious control by the singer until they become conditioned reflexes. Many singers abandon conscious controls before their reflexes are fully conditioned which ultimately leads to chronic vocal problems.
Voice classification
In Europeanclassical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" also ...
and opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
, voices are treated like musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
s. Composers
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Classical music, Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
E ...
who write vocal music must have an understanding of the skills, talents, and vocal properties of singers. Voice classification is the process by which human singing voices are evaluated and are thereby designated into voice types
A voice type is a group of voices with similar vocal ranges, capable of singing in a similar tessitura, and with similar vocal transition points ('' passaggi''). Voice classification is most strongly associated with European classical music, ...
. These qualities include but are not limited to: vocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
, vocal weight Vocal weight refers to the perceived "lightness" or "heaviness" of a singing voice. This quality of the voice is one of the major determining factors in voice classification within classical music. Lighter voices are often associated with the term ...
, vocal tessitura
In music, tessitura (, pl. ''tessiture'', "texture"; ) is the most acceptable and comfortable vocal range for a given singer or less frequently, musical instrument, the range in which a given type of voice presents its best-sounding (or characte ...
, vocal timbre
In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or musical tone, tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voice ...
, and vocal transition points
Passaggio () is a term used in classical singing to describe the transition area between the vocal registers. The ''passaggi'' (plural) of the voice lie between the different vocal registers, such as the chest voice, where any singer can produce ...
such as breaks and lifts within the voice. Other considerations are physical characteristics, speech level, scientific testing, and vocal registration
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register.
Registers originate in la ...
.
The science behind voice classification developed within European classical music and has been slow in adapting to more modern forms of singing. Voice classification is often used within opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
to associate possible roles with potential voices. There are currently several different systems in use within classical music including: the German ''Fach
The German system (; literally "compartment" or "subject of study", here in the sense of "vocal specialization") is a method of classifying singers, primarily opera singers, according to the range, weight, and color of their voices. It is used w ...
'' system and the choral music system among many others. No system is universally applied or accepted.
However, most classical music systems acknowledge seven different major voice categories. Women are typically divided into three groups: soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical female singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hz to "high A" (A5) = 880&n ...
, mezzo-soprano
A mezzo-soprano or mezzo (; ; meaning "half soprano") is a type of classical female singing voice whose vocal range lies between the soprano and the contralto voice types. The mezzo-soprano's vocal range usually extends from the A below middle C ...
, and contralto
A contralto () is a type of classical female singing voice whose vocal range is the lowest female voice type.
The contralto's vocal range is fairly rare; similar to the mezzo-soprano, and almost identical to that of a countertenor, typically b ...
. Men are usually divided into four groups: countertenor
A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a s ...
, tenor
A tenor is a type of classical music, classical male singing human voice, voice whose vocal range lies between the countertenor and baritone voice types. It is the highest male chest voice type. The tenor's vocal range extends up to C5. The lo ...
, baritone
A baritone is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the bass and the tenor voice-types. The term originates from the Greek (), meaning "heavy sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the r ...
, and bass. When considering children's voices, an eighth term, treble
Treble may refer to:
In music:
*Treble (sound), tones of high frequency or range, the counterpart of bass
*Treble voice, a choirboy or choirgirl singing in the soprano range
*Treble (musical group), a three-piece girl group from the Netherlands
*T ...
, can be applied. Within each of these major categories there are several sub-categories that identify specific vocal qualities like coloratura
Coloratura is an elaborate melody with runs, trills, wide leaps, or similar virtuoso-like material,''Oxford American Dictionaries''.Apel (1969), p. 184. or a passage of such music. Operatic roles in which such music plays a prominent part, an ...
facility and vocal weight to differentiate between voices.
Within choral music
A choir ( ; also known as a chorale or chorus) is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform. Choirs may perform music from the classical music repertoire, which sp ...
, singers voices are divided solely on the basis of vocal range. Choral music most commonly divides vocal parts into high and low voices within each sex (SATB). As a result, the typical choral situation affords many opportunities for misclassification to occur. Since most people have medium voices, they must be assigned to a part that is either too high or too low for them; the mezzo-soprano must sing soprano or alto and the baritone must sing tenor or bass. Either option can present problems for the singer, but for most singers there are fewer dangers in singing too low than in singing too high.
Within contemporary forms of music (sometimes referred to as Contemporary Commercial Music), singers are classified by the style of music they sing, such as jazz, pop, blues, soul, country, folk, and rock styles. There is currently no authoritative voice classification system within non-classical music. Attempts have been made to adopt classical voice type
A voice type is a group of voices with similar vocal ranges, capable of singing in a similar tessitura, and with similar vocal transition points ('' passaggi''). Voice classification is most strongly associated with European classical music, t ...
terms to other forms of singing but such attempts have been met with controversy. The development of voice categorizations were made with the understanding that the singer would be using classical vocal technique within a specified range using unamplified (no microphones) vocal production. Since contemporary musicians use different vocal techniques, microphones, and are not forced to fit into a specific vocal role, applying such terms as soprano, tenor, baritone, etc. can be misleading or even inaccurate.
Dangers of quick identification
Many voice teachers warn of the dangers of quick identification. Premature concern with classification can result in misclassification, with all its attendant dangers. Vennard says: "I never feel any urgency about classifying a beginning student. So many premature diagnoses have been proved wrong, and it can be harmful to the student and embarrassing to the teacher to keep striving for an ill-chosen goal. It is best to begin in the middle part of the voice and work upward and downward until the voice classifies itself." Most voice teachers believe that it is essential to establish good vocal habits within a limited and comfortable range before attempting to classify the voice. When techniques of posture, breathing,phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
, resonation, and articulation have become established in this comfortable area, the true quality of the voice will emerge and the upper and lower limits of the range can be explored safely. Only then can a tentative classification be arrived at, and it may be adjusted as the voice continues to develop. Many acclaimed voice instructors suggest that teachers begin by assuming that a voice is of a medium classification until it proves otherwise. The reason for this is that the majority of individuals possess medium voices and therefore this approach is less likely to misclassify or damage the voice.
Vocal registration
Vocal registration refers to the system of vocal registers within the human voice. A register in the human voice is a particular series of tones, produced in the same vibratory pattern of thevocal fold
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedality, bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and compl ...
s, and possessing the same quality. Registers originate in laryngeal function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches and produces certain characteristic sounds.
The term register can be somewhat confusing as it encompasses several aspects of the human voice. The term register can be used to refer to any of the following:
* A particular part of the vocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
such as the upper, middle, or lower registers.
* A resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillatin ...
area such as chest voice
Chest voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regard to this term. Chest voice can be used in ...
or head voice
Head voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regard to this term. Head voice can be used in re ...
.
* A phonatory
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
process
* A certain vocal timbre
In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or musical tone, tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voice ...
* A region of the voice which is defined or delimited by vocal breaks.
* A subset of a language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
used for a particular purpose or in a particular social setting.
In linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
, a register language is a language which combines tone and vowel phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
into a single phonological
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
system.
Within speech pathology
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
the term vocal register has three constituent elements: a certain vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, a certain series of pitches, and a certain type of sound. Speech pathologists identify four vocal registers based on the physiology of laryngeal function: the vocal fry register
The vocal fry register (also known as pulse register, laryngealization, pulse phonation, creaky voice, creak, croak, popcorning, glottal fry, glottal rattle, glottal scrape) is the lowest vocal register and is produced through a loose glottal clos ...
, the modal register
Modal voice is the vocal register used most frequently in speech and singing in most languages. It is also the term used in linguistics for the most common phonation of vowels. The term "modal" refers to the resonant mode of vocal folds; that is ...
, the falsetto register, and the whistle register
The whistle register (also called the flute register or flageolet register) is the highest register of the human voice, lying above the modal register and falsetto register. This register has a specific physiological production that is different ...
. This view is also adopted by many teachers of singing.
Some voice teachers, however, organize registers differently. There are over a dozen different constructs of vocal registers in use within the field. The confusion which exists concerning what a register is, and how many registers there are, is due in part to what takes place in the modal register when a person sings from the lowest pitches of that register to the highest pitches. The frequency of vibration of the vocal folds is determined by their length, tension, and mass. As pitch rises, the vocal folds are lengthened, tension increases, and their thickness decreases. In other words, all three of these factors are in a state of flux in the transition from the lowest to the highest tones.
If a singer holds any of these factors constant and interferes with their progressive state of change, his laryngeal function tends to become static and eventually breaks occur with obvious changes of tone quality. These breaks are often identified as register boundaries or as transition areas between registers. The distinct change or break between registers is called a passaggio
Passaggio () is a term used in classical singing to describe the transition area between the vocal registers. The ''passaggi'' (plural) of the voice lie between the different vocal registers, such as the chest voice, where any singer can produce ...
or a ponticello
A variety of musical terms are likely to be encountered in printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms Italian musical terms used in English, are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical co ...
.John Warrack, Ewan West. ‘’The Oxford Dictionary of Opera’’, Vocal instructors teach that with study a singer can move effortlessly from one register to the other with ease and consistent tone. Registers can even overlap while singing. Teachers who like to use this theory of "blending registers" usually help students through the "passage" from one register to another by hiding their "lift" (where the voice changes).
However, many voice instructors disagree with this distinction of boundaries blaming such breaks on vocal problems which have been created by a static laryngeal adjustment that does not permit the necessary changes to take place. This difference of opinion has effected the different views on vocal registration.
Coordination
Singing is an integrated and coordinated act and it is difficult to discuss any of the individual technical areas and processes without relating them to the others. For example, phonation only comes into perspective when it is connected with respiration; the articulators affect resonance; the resonators affect the vocal folds; the vocal folds affect breath control; and so forth. Vocal problems are often a result of a breakdown in one part of this coordinated process which causes voice teachers to frequently focus in, intensively, on one area of the process with their student until that issue is resolved. However, some areas of the art of singing are so much the result of coordinated functions that it is hard to discuss them under a traditional heading like phonation, resonation, articulation, or respiration. Once the voice student has become aware of the physical processes that make up the act of singing and of how those processes function, the student begins the task of trying to coordinate them. Inevitably, students and teachers will become more concerned with one area of the technique than another. The various processes may progress at different rates, with a resulting imbalance or lack of coordination. The areas of vocal technique which seem to depend most strongly on the student's ability to coordinate various functions are: # Extending thevocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
to its maximum potential
# Developing consistent vocal production with a consistent tone quality
# Developing flexibility and agility
# Achieving a balanced vibrato
Vibrato (Italian language, Italian, from past participle of "wikt:vibrare, vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch (music), pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. ...
Developing the singing voice
Some consider that singing is not a natural process but is a skill that requires highly developed muscle reflexes, but others consider that some ways of singing can be considered as natural. ''For thousands of years all over the world people have sung—to express joy, celebration and grief, to aid healing, to accompany work, devotion and the rituals of life—without worrying about having a ‘good’ voice or ‘getting it right’''. Singing does not require much muscle strength but it does require a high degree of muscle coordination. Individuals can develop their voices further through the careful and systematic practice of both songs and vocal exercises. Voice teachers instruct their students to exercise their voices in an intelligent manner. Singers should be thinking constantly about the kind of sound they are making and the kind of sensations they are feeling while they are singing.=Exercising the singing voice
= There are several purposes for vocal exercises, including: # Warming up the voice # Extending the vocal range # "Lining up" the voice horizontally and vertically # Acquiring vocal techniques such as legato, staccato, control of dynamics, rapid figurations, learning to comfortably sing wide intervals, and correcting vocal faults.=Extending the vocal range
= An important goal of vocal development is to learn to sing to the natural limits of one's vocal range without any obvious or distracting changes of quality or technique. Voice instructors teach that a singer can only achieve this goal when all of the physical processes involved in singing (such as laryngeal action, breath support, resonance adjustment, and articulatory movement) are effectively working together. Most voice teachers believe that the first step in coordinating these processes is by establishing good vocal habits in the most comfortable tessitura of the voice first before slowly expanding the range beyond that. There are three factors which significantly affect the ability to sing higher or lower: #The Energy Factor – In this usage the word energy has several connotations. It refers to the total response of the body to the making of sound. It refers to a dynamic relationship between the breathing-in muscles and the breathing-out muscles known as the breath support mechanism. It also refers to the amount of breath pressure delivered to the vocal folds and their resistance that pressure, and it refers to the dynamic level of the sound. #The Space Factor – Space refers to the amount of space created by the moving of the mouth and the position of the palate and larynx. Generally speaking, a singer's mouth should be opened wider the higher they sing. The internal space or position of the soft palate and larynx can be widened by the relaxing of the throat. Voice teachers often describe this as feeling like the "beginning of a yawn". #The Depth Factor – In this usage the word depth has two connotations. It refers to the actual physical sensations of depth in the body and vocal mechanism and it refers to mental concepts of depth as related to tone quality. McKinney says, "These three factors can be expressed in three basic rules: (1) As you sing higher, you must use more energy; as you sing lower, you must use less. (2) As you sing higher, you must use more space; as you sing lower, you must use less. (3) As you sing higher, you must use more depth; as you sing lower, you must use less."General music studies
Some voice teachers will spend time working with their students on general music knowledge and skills, particularlymusic theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
, music history
Music history, sometimes called historical musicology, is a highly diverse subfield of the broader discipline of musicology that studies music from a historical point of view.
In theory, "music history" could refer to the study of the history o ...
, and musical styles and practices as it relates to the vocal literature being studied. If required they may also spend time helping their students become better sight readers, often adopting solfège
In music, solfège (, ) or solfeggio (; ), also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a music education method used to teach aural skills, Pitch (music), pitch and sight-reading of Western classical music, Western music. Solfège is ...
, which assigns certain syllables to the notes of the scale.
Performance skills and practices
Since singing is a performing art, voice teachers spend some of their time preparing their students for performance. This includes teaching their students etiquette of behavior on stage such as bowing, learning to manage stage fright, addressing problems like nervous tics, and the use of equipment such as microphones. Some students may also be preparing for careers in the fields ofopera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
or musical theater
Musical theatre is a form of theatrical performance that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance. The story and emotional content of a musical – humor, pathos, love, anger – are communicated through words, music, movement ...
where acting skills are required. Many voice instructors will spend time on acting techniques and audience communication with students in these fields of interest. Students of opera also spend a great deal of time with their voice teachers learning foreign language pronunciations.
See also
*Human voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production ...
* Voice teacher
A voice teacher or singing teacher is a musical instructor who assists adults and children in the development of their abilities in singing.
Typical work
A voice teacher works with a student singer to improve the various skills involved in singi ...
*Throat singing
Throat singing refers to several vocal practices found in different cultures around the world. The most distinctive feature of such vocal practices is to be associated to some type of guttural voice, that contrasts with the most common types of voi ...
Notes
References
*External links
National Association of Teachers of Singing
{{Authority control Human voice Singing Opera terminology * Vocal skills