silver-indium-cadmium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Control rods are used in
Control rods are used in
 Control rods are inserted into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted in order to
Control rods are inserted into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted in order to
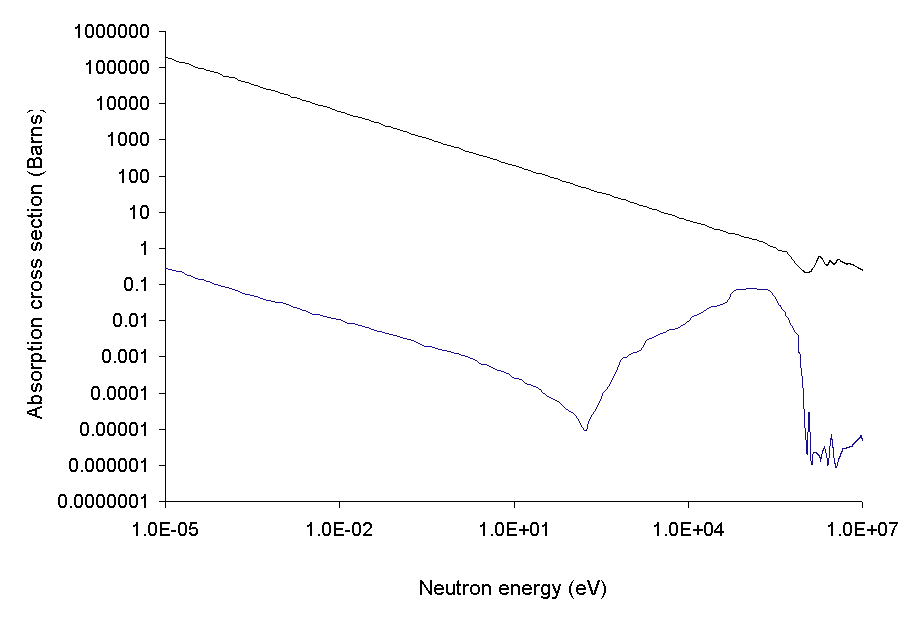 Chemical elements with usefully high neutron capture cross-sections include
Chemical elements with usefully high neutron capture cross-sections include
 Control rods are used in
Control rods are used in nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nu ...
s to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
or plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
. Their compositions include chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s such as boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has th ...
, cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
, or indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts p ...
, that are capable of absorbing many neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
s without themselves decaying. These elements have different neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, ...
cross sections for neutrons of various energies
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat ...
. Boiling water reactor
A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is a design different from a Soviet graphite-moderated RBMK. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nu ...
s (BWR), pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water reactor, light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan and Canada). In a PWR, the primary ...
s (PWR), and heavy-water reactor
A pressurized heavy-water reactor (PHWR) is a nuclear reactor that uses heavy water ( deuterium oxide D2O) as its coolant and neutron moderator. PHWRs frequently use natural uranium as fuel, but sometimes also use very low enriched uranium. T ...
s (HWR) operate with thermal neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with ...
s, while breeder reactor
A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor that generates more fissile material than it consumes. Breeder reactors achieve this because their neutron economy is high enough to create more fissile fuel than they use, by irradiation of a fertile mate ...
s operate with fast neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with ...
s. Each reactor design can use different control rod materials based on the energy spectrum of its neutrons. Control rods have been used in nuclear aircraft engines like Project Pluto
Project Pluto was a United States government program to develop nuclear-powered ramjet engines for use in cruise missiles. Two experimental engines were tested at the Nevada Test Site (NTS) in 1961 and 1964 respectively.
On 1 January 1957, t ...
as a method of control.
Operating principle
 Control rods are inserted into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted in order to
Control rods are inserted into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted in order to control
Control may refer to:
Basic meanings Economics and business
* Control (management), an element of management
* Control, an element of management accounting
* Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization
* Controllin ...
the rate of the nuclear chain reaction
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions. The specific nu ...
and, thereby, the thermal power
A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary ...
output of the reactor, the rate of steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization ...
production, and the electrical power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions of ...
output of the power station.
The number of control rods inserted, and the distance to which they are inserted, strongly influence the ''reactivity'' of the reactor. When reactivity (as effective neutron multiplication factor
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions. The specific nu ...
) is above 1, the rate of the nuclear chain reaction
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions. The specific nu ...
increases exponentially over time. When reactivity is below 1, the rate of the reaction decreases exponentially over time. When all control rods are fully inserted, they keep reactivity barely above 0, which quickly slows a running reactor to a stop and keeps it stopped (in shutdown
Shutdown or shut down may refer to:
* Government shutdowns in the United States
* Shutdown (computing)
* Shutdown (economics)
* Shutdown (nuclear reactor)
Arts and entertainment Music
* "Shut Down" (The Beach Boys song), 1963
* ''Shut Down Volu ...
). If all control rods are fully removed, reactivity is significantly above 1, and the reactor quickly runs hotter and hotter, until some other factor (such as temperature reactivity feedback) slows the reaction rate. Maintaining a constant power output requires keeping the long-term average neutron multiplication factor close to 1.
A new reactor is assembled with its control rods fully inserted. Control rods are partially removed from the core to allow the nuclear chain reaction
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions. The specific nu ...
to start up and increase to the desired power level. Neutron flux
The neutron flux, φ, is a scalar quantity used in nuclear physics and nuclear reactor physics. It is the total length travelled by all free neutrons per unit time and volume. Equivalently, it can be defined as the number of neutrons travelling ...
can be measured, and is roughly proportional to reaction rate and power level. To increase power output, some control rods are pulled out a small distance for a while. To decrease power output, some control rods are pushed in a small distance for a while. Several other factors affect the reactivity; to compensate for them, an automatic control system adjusts the control rods small amounts in or out, as-needed in some reactors. Each control rod influences some part of the reactor more than others; calculated adjustments to fuel distribution can be made to maintain similar reaction rates and temperatures in different parts of the core.
Typical shutdown
Shutdown or shut down may refer to:
* Government shutdowns in the United States
* Shutdown (computing)
* Shutdown (economics)
* Shutdown (nuclear reactor)
Arts and entertainment Music
* "Shut Down" (The Beach Boys song), 1963
* ''Shut Down Volu ...
time for modern reactors such as the European Pressurized Reactor
The EPR is a Generation III reactor, third generation pressurised water reactor design. It has been designed and developed mainly by Framatome (part of Areva between 2001 and 2017) and Électricité de France (EDF) in France, and Siemens in Germ ...
or Advanced CANDU reactor is 2 seconds for 90% reduction, limited by decay heat
Decay heat is the heat released as a result of radioactive decay. This heat is produced as an effect of radiation on materials: the energy of the alpha, beta or gamma radiation is converted into the thermal movement of atoms.
Decay heat occurs na ...
.
Control rods are usually used in control rod assemblies (typically 20 rods for a commercial PWR assembly) and inserted into guide tubes within the fuel elements. Control rods often stand vertically within the core. In PWRs they are inserted from above, with the control rod drive mechanisms mounted on the reactor pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.
Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size o ...
head. In BWRs, due to the necessity of a steam dryer above the core, this design requires insertion of the control rods from beneath.
Materials
 Chemical elements with usefully high neutron capture cross-sections include
Chemical elements with usefully high neutron capture cross-sections include silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts p ...
, and cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
. Other candidate elements include boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has th ...
, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, pr ...
, hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
, samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samar ...
, europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lanth ...
, gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
, terbium
Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with wa ...
, dysprosium
Dysprosium is the chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare-earth element in the lanthanide series with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though, like other lanthanides, it ...
, holmium
Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like a lot of othe ...
, erbium
Erbium is a chemical element with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare-earth element
...
, thulium
Thulium is a chemical element with the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is the thirteenth and third-last element in the lanthanide series. Like the other lanthanides, the most common oxidation state is +3, seen in its oxide, halides and other c ...
, ytterbium
Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. However, like the othe ...
, and lutetium
Lutetium is a chemical element with the symbol Lu and atomic number 71. It is a silvery white metal, which resists corrosion in dry air, but not in moist air. Lutetium is the last element in the lanthanide series, and it is traditionally counted am ...
. Alloys or compounds may also be used, such as high-boron steel
Boron steel refers to steel alloyed with a small amount of boron, usually less than 1%. The addition of boron to steel greatly increases the hardenability of the resulting alloy.
Description
Boron is added to steel as ferroboron (~12-24% B). As ...
, silver-indium-cadmium alloy, boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers hard ...
, zirconium diboride
Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) is a highly covalent refractory ceramic material with a hexagonal crystal structure. ZrB2 is an ultra high temperature ceramic (UHTC) with a melting point of 3246 °C. This along with its relatively low density of ...
, titanium diboride
Titanium diboride (TiB2) is an extremely hard ceramic which has excellent heat conductivity, oxidation stability and wear resistance. TiB2 is also a reasonable electrical conductor,J. Schmidt et al. "Preparation of titanium diboride TiB2 by spark ...
, hafnium diboride
Hafnium diboride belongs to the class of ultra-high-temperature ceramics, a type of ceramic composed of hafnium and boron. It has a melting temperature of about 3250 °C. It is an unusual ceramic, having relatively high thermal and electrical ...
, gadolinium nitrate, gadolinium titanate, dysprosium titanate
Dysprosium titanate ( Dy2 Ti2 O7) is an inorganic compound, a ceramic of the titanate family, with pyrochlore structure.
Dysprosium titanate, like holmium titanate and holmium stannate, is a spin ice material. In 2009, quasiparticles resembli ...
, and boron carbide–europium hexaboride composite.
The material choice is influenced by the neutron energy in the reactor, their resistance to neutron-induced swelling
Neutron-induced swelling is the increase of volume and decrease of density of materials subjected to intense neutron radiation. Neutrons impacting the material's lattice rearrange its atoms, causing buildup of dislocations, voids, and Wigner ener ...
, and the required mechanical and lifespan properties. The rods may have the form of tubes filled with neutron-absorbing pellets or powder. The tubes can be made of stainless steel or other "neutron window" materials such as zirconium, chromium, silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal sin ...
, or cubic (cubic boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal ...
).
The burnup of "burnable poison
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable eff ...
" isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
s also limits lifespan of a control rod. They may be reduced by using an element such as hafnium, a "non-burnable poison" which captures multiple neutrons before losing effectiveness, or by not using neutron absorbers for trimming. For example, in pebble bed reactor
The pebble-bed reactor (PBR) is a design for a graphite-moderated, gas-cooled nuclear reactor. It is a type of very-high-temperature reactor (VHTR), one of the six classes of nuclear reactors in the Generation IV initiative.
The basic desig ...
s or in possible new type lithium-7
Naturally occurring lithium (3Li) is composed of two stable isotopes, lithium-6 and lithium-7, with the latter being far more abundant on Earth. Both of the natural isotopes have an unexpectedly low nuclear binding energy per nucleon ( for lit ...
-moderated and -cooled reactors that use fuel and absorber pebbles.
Some rare-earth element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silve ...
s are excellent neutron absorbers and are more common than silver (reserves of about 500,000t). For example, ytterbium (reserves about 1 M tons) and yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with the symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a "rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in com ...
, 400 times more common, with middle capturing values, can be found and used together without separation inside minerals like xenotime
Xenotime is a rare-earth phosphate mineral, the major component of which is yttrium orthophosphate ( Y P O4). It forms a solid solution series with chernovite-(Y) ( Y As O4) and therefore may contain trace impurities of arsenic, as well as sili ...
(Yb) (Yb0.40Y0.27Lu0.12Er0.12Dy0.05Tm0.04Ho0.01)PO4, or keiviite (Yb) (Yb1.43Lu0.23Er0.17Tm0.08Y0.05Dy0.03Ho0.02)2Si2O7, lowering the cost. Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
is also a strong neutron absorber as a gas, and can be used for controlling and (emergency) stopping helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
-cooled reactors, but does not function in cases of pressure loss, or as a burning protection gas together with argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
around the vessel part especially in case of core catching reactors or if filled with sodium or lithium. Fission-produced xenon can be used after waiting for caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
to precipitate, when practically no radioactivity is left. Cobalt-59 is also used as an absorber for winning of cobalt-60 for X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
production. Control rods can also be constructed as thick turnable rods with a tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolat ...
reflector and absorber side turned to stop by a spring in less than 1 second.
Silver-indium-cadmium alloys, generally 80% Ag, 15% In, and 5% Cd, are a common control rod material for pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water reactor, light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan and Canada). In a PWR, the primary ...
s. The somewhat different energy absorption regions of the materials make the alloy an excellent neutron absorber
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable eff ...
. It has good mechanical strength and can be easily fabricated. It must be encased in stainless steel to prevent corrosion in hot water. Although indium is less rare than silver, it is more expensive.
Boron is another common neutron absorber. Due to the different cross sections of 10B and 11B, materials containing boron enriched in 10B by isotopic separation
Isotope separation is the process of concentrating specific isotopes of a chemical element by removing other isotopes. The use of the nuclides produced is varied. The largest variety is used in research (e.g. in chemistry where atoms of "marker" n ...
are frequently used. The wide absorption spectrum of boron also makes it suitable as a neutron shield. The mechanical properties of boron in its elementary form are unsuitable, and therefore alloys or compounds have to be used instead. Common choices are high-boron steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
and boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers hard ...
. The latter is used as a control rod material in both PWRs and BWRs. 10B/11B separation is done commercially with gas centrifuge
A gas centrifuge is a device that performs isotope separation of gases. A centrifuge relies on the principles of centrifugal force accelerating molecules so that particles of different masses are physically separated in a gradient along the radiu ...
s over BF3, but can also be done over BH3 from borane
Trihydridoboron, also known as borane or borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula . The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated ...
production or directly with an energy optimized melting centrifuge, using the heat of freshly separated boron for preheating.
Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
has excellent properties for reactors using water for both moderation and cooling. It has good mechanical strength, can be easily fabricated, and is resistant to corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
in hot water. Hafnium can be alloyed with other elements, e.g. with tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
to increase tensile and creep strength, with iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
, and niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
for corrosion resistance, and with molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lea ...
for wear resistance, hardness, and machineability. Such alloys are designated as Hafaloy, Hafaloy-M, Hafaloy-N, and Hafaloy-NM. The high cost and low availability of hafnium limit its use in civilian reactors, although it is used in some US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of ...
reactors. Hafnium carbide can also be used as an insoluble material with a high melting point of 3890 °C and density higher than that of uranium dioxide for sinking, unmelted, through corium.
Dysprosium titanate
Dysprosium titanate ( Dy2 Ti2 O7) is an inorganic compound, a ceramic of the titanate family, with pyrochlore structure.
Dysprosium titanate, like holmium titanate and holmium stannate, is a spin ice material. In 2009, quasiparticles resembli ...
was undergoing evaluation for pressurized water control rods. Dysprosium titanate is a promising replacement for Ag-In-Cd alloys because it has a much higher melting point, does not tend to react with cladding materials, is easy to produce, does not produce radioactive waste, does not swell and does not outgas
Outgassing (sometimes called offgassing, particularly when in reference to indoor air quality) is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen, or absorbed in some material. Outgassing can include sublimation and evaporation (which ...
. It was developed in Russia and is recommended by some for VVER
The water-water energetic reactor (WWER), or VVER (from russian: водо-водяной энергетический реактор; transliterates as ; ''water-water power reactor'') is a series of pressurized water reactor designs originally de ...
and RBMK
The RBMK (russian: реактор большой мощности канальный, РБМК; ''reaktor bolshoy moshchnosti kanalnyy'', "high-power channel-type reactor") is a class of graphite-moderated nuclear power reactor designed and buil ...
reactors. A disadvantage is less titanium and oxide absorption, that other neutron absorbing elements do not react with the already high-melting point cladding materials and that just using the unseparated content with dysprosium inside of minerals like Keiviit Yb inside chromium, SiC or c11B15N tubes deliver superior price and absorption without swelling and outgassing.
Hafnium diboride
Hafnium diboride belongs to the class of ultra-high-temperature ceramics, a type of ceramic composed of hafnium and boron. It has a melting temperature of about 3250 °C. It is an unusual ceramic, having relatively high thermal and electrical ...
is another such material. It can be used alone or in a sintered mixture of hafnium and boron carbide powders.
Many other compounds of rare-earth elements can be used, such as samarium with boron-like europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lanth ...
and samarium boride
Samarium is a chemical element with chemical symbol, symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. C ...
, which is already used in the colour industry. Less absorptive compounds of boron similar to titanium, but inexpensive, such as molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lea ...
as Mo2B5. Since they all swell with boron, in practice other compounds are better, such as carbides, etc., or compounds with two or more neutron-absorbing elements together. It is important that tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolat ...
, and probably also other elements like tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is ...
, have much the same high capture qualities as hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
, but with the opposite effect. This is not explainable by neutron reflection alone. An obvious explanation is resonance gamma rays increasing the fission and breeding ratio versus causing more capture of uranium, etc. over metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate Energy level, energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's ground state, state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of me ...
conditions like for isotope 235mU, which has a half-life of about 26 min.
Additional means of reactivity regulation
Other means of controlling reactivity include (for PWR) a soluble neutron absorber (boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves ...
) added to the reactor coolant, allowing the complete extraction of the control rods during stationary power operation, ensuring an even power and flux distribution over the entire core. This chemical shim
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large Neutron cross section, neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is norma ...
, along with the use of burnable neutron poisons within the fuel pellets, is used to assist regulation of the core's long term reactivity, while the control rods are used for rapid reactor power changes (e.g. shutdown and start up). Operators of BWRs use the coolant flow through the core to control reactivity by varying the speed of the reactor recirculation pumps (an increase in coolant flow through the core improves the removal of steam bubbles, thus increasing the density of the coolant/ moderator, increasing power).
Safety
In most reactor designs, as a safety measure, control rods are attached to the lifting machinery byelectromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the ...
s, rather than direct mechanical linkage. This means that in the event of power failure, or if manually invoked due to failure of the lifting machinery, the control rods fall automatically, under gravity, all the way into the pile to stop the reaction. A notable exception to this fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safe ...
mode of operation is the BWR, which requires hydraulic insertion in the event of an emergency shut-down, using water from a special tank under high pressure. Quickly shutting down a reactor in this way is called scram
A scram or SCRAM is an emergency shutdown of a nuclear reactor effected by immediately terminating the fission reaction. It is also the name that is given to the manually operated kill switch that initiates the shutdown. In commercial reactor ...
ming.
Criticality accident prevention
Mismanagement or control rod failure have often been blamed fornuclear accident
A nuclear and radiation accident is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "an event that has led to significant consequences to people, the environment or the facility. Examples include lethal effects to individuals, lar ...
s, including the SL-1
Stationary Low-Power Reactor Number One, also known as SL-1 or the Argonne Low Power Reactor (ALPR), was a United States Army experimental nuclear reactor in the western United States at the National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS), later the ...
explosion and the Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuc ...
.
''Homogeneous'' neutron absorbers have often been used to manage criticality accident
A criticality accident is an accidental uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reaction. It is sometimes referred to as a critical excursion, critical power excursion, or divergent chain reaction. Any such event involves the unintended accumulation ...
s which involve aqueous solutions of fissile
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction. By definition, fissile material can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of thermal energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typ ...
metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
s. In several such accidents, either borax
Borax is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula often written . It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution. It is commonly available in powder or granular form, ...
(sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
borate
A borate is any of several boron oxyanions, negative ions consisting of boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate , metaborate , or tetraborate ; or any salt with such anions, such as sodium metaborate, and disodium tetraborate . The name also refe ...
) or a cadmium compound has been added to the system. The cadmium can be added as a metal to nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
solutions of fissile material; the corrosion of the cadmium in the acid will then generate cadmium nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zer ...
''in situ''.
In carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
-cooled reactors such as the AGR, if the solid control rods fail to arrest the nuclear reaction, nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
gas can be injected into the primary coolant cycle. This is because nitrogen has a larger absorption cross-section for neutrons than carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
or oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
; hence, the core then becomes less reactive.
As the neutron energy increases, the neutron cross section of most isotopes decreases. The boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has th ...
isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
10B is responsible for the majority of the neutron absorption. Boron-containing materials can also be used as neutron shielding, to reduce the activation
Activation, in chemistry and biology, is the process whereby something is prepared or excited for a subsequent reaction.
Chemistry
In chemistry, "activation" refers to the reversible transition of a molecule into a nearly identical chemical or ...
of material close to a reactor core.
See also
*Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
*Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nu ...
*Nuclear safety
Nuclear safety is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The achievement of proper operating conditions, prevention of accidents or mitigation of accident consequences, resulting in protection of workers, the public and the ...
*Wigner effect
The Wigner effect (named for its discoverer, Eugene Wigner), also known as the discomposition effect or Wigner's disease, is the displacement of atoms in a solid caused by neutron radiation.
Any solid can display the Wigner effect. The effect is ...
References
External links
Further reading
* * * {{Authority control Alloys Nuclear power plant components Nuclear reactor safety Pressurized water reactors