Siege of Stralsund (1628) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The siege of Stralsund was a siege laid on

 The following night, on 28 and 29 June, Wallenstein succeeded in taking the outer works of the fortifications. Rosladin was wounded and governor Seaton took over his command.
On 29 June, Bogislaw XIV, Duke of Pomerania sent two of his high-ranking nobles, the count von Putbus and his chancellor von Horn, to persuade Stralsund to adhere to the Capitulation of Franzburg and surrender to Wallenstein. On 30 June, Rosladin persuaded the city not to enter into negotiations with Wallenstein, who had resorted to bombardment again. The same day, ten Swedish vessels reinforced Stralsund with 600 troops, while under heavy fire by Wallenstein's forces. Soon after, Christian ordered another Scottish regiment, that of
The following night, on 28 and 29 June, Wallenstein succeeded in taking the outer works of the fortifications. Rosladin was wounded and governor Seaton took over his command.
On 29 June, Bogislaw XIV, Duke of Pomerania sent two of his high-ranking nobles, the count von Putbus and his chancellor von Horn, to persuade Stralsund to adhere to the Capitulation of Franzburg and surrender to Wallenstein. On 30 June, Rosladin persuaded the city not to enter into negotiations with Wallenstein, who had resorted to bombardment again. The same day, ten Swedish vessels reinforced Stralsund with 600 troops, while under heavy fire by Wallenstein's forces. Soon after, Christian ordered another Scottish regiment, that of
 Also in August, Swedish chancellor
Also in August, Swedish chancellor
File:Kaiser Ferdinand II. 1614.jpg,
File:Gustaf-ii-adolf-stralsund.jpg,
''An Unofficial Alliance: Scotland and Sweden, 1569-1654''
(Leiden, 2003) * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Riis, Thomas, ''Should Auld Acquaintance Be Forgot'' (2 vols., Odense, 1988) * * * *
Digitalized collection of primary sources about the siege by Johann Albert Dinnies from the Stralsund archivesKonze, M. and R. Samariter ‘Momentaufnahme aus dem Dreißigjährigen Krieg: Das Stralsunder Söldnergrab von 1628’
{{Authority control 1628 in Europe Stralsund 1628 Stralsund 1628 Stralsund 1628 Stralsund 1628 Conflicts in 1628 History of Pomerania Stralsund Albrecht von Wallenstein Battles in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
Stralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish: ''Strålsund''), officially the Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rostock, Schwerin, N ...
by Albrecht von Wallenstein's Imperial Army during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
, from 13 May 1628 to 4 August 1628. Stralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish: ''Strålsund''), officially the Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rostock, Schwerin, N ...
was aided by Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, with considerable Scottish participation. The lifting of the siege ended Wallenstein's series of victories, and contributed to his downfall. The Swedish garrison in Stralsund was the first on German soil in history. The battle marked the ''de facto'' entrance of Sweden into the war.
Prelude
Belligerents
Christian IV of Denmark
Christian IV (12 April 1577 – 28 February 1648) was King of Denmark and Norway and Duke of Holstein and Schleswig from 1588 until his death in 1648. His reign of 59 years, 330 days is the longest of Danish monarchs and Scandinavian mona ...
had declared war on the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
in 1625. He then invaded the empire with an army commanded by Ernst von Mansfeld to oppose the Catholic League's army commanded by Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly
Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly ( nl, Johan t'Serclaes Graaf van Tilly; german: Johann t'Serclaes Graf von Tilly; french: Jean t'Serclaes de Tilly ; February 1559 – 30 April 1632) was a field marshal who commanded the Catholic League's ...
. In response, Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria of Bavaria. His parents were dev ...
, had Albrecht von Wallenstein raise an additional army to support Tilly. Wallenstein defeated Mansfeld in the Battle of Dessau Bridge
The Battle of Dessau Bridge () was a significant battle of the Thirty Years' War between Danish Protestants and the Imperial German Catholic forces on the Elbe River outside Dessau, Germany on 25 April 1626.
This battle was an attempt by Ernst ...
in 1626.Press (1991), p.203 The remnants of Mansfeld's army left Central Germany, and turned to Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
to regroup with Gabriel Bethlen's forces.
After Tilly had defeated Christian IV in the Battle of Lutter am Barenberge
The Battle of Lutter ( German: '' Lutter am Barenberge'') took place on 27 August 1626 during the Thirty Years' War, south of Salzgitter, in Lower Saxony. A combined Danish-German force led by Christian IV of Denmark was defeated by Johan Tzerc ...
in August 1626, and Bethlen was neutralized in the (third) Peace of Pressburg in December, Tilly and Wallenstein were able to subsequently expel Christian IV from the North German plain, organized in the Lower Saxon and Upper Saxon
Upper Saxon (german: Obersächsisch, ; ) is an East Central German language spoken in much of the modern German state of Saxony and in adjacent parts of southeastern Saxony-Anhalt and eastern Thuringia. As of the early 21st century, it's mo ...
imperial circles, and pressure him even in Danish Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
. The internally divided Upper Saxon circle, to which the Duchy of Pomerania with Stralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish: ''Strålsund''), officially the Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rostock, Schwerin, N ...
belonged, was incapable of self-defence and had formally declared neutrality.
Christian IV's army staff heavily relied on Scottish expertise: with 300 Scottish officers in his service, Scottish officers outnumbered Danish and Norwegian officers combined by 3:1.Murdoch in Mackillop & Murdoch (2003), p.13 Also, Christian IV had issued patents to raise 9,000 Scottish troops in 1627, adding to 2,000-3,000 Scottish troops raised by Donald Mackay for Ernst von Mansfeld's army, but who had been deployed to Denmark instead.
Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">N.S_19_December.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/now ...
was since 1626 involved in the Polish-Swedish War, with Poland allied to the Holy Roman Empire.Murdoch in Mackillop & Murdoch(2003), p.59 In this war, Scotsman Alexander Leslie
Alexander Leslie, 1st Earl of Leven (15804 April 1661) was a Scottish soldier in Swedish and Scottish service. Born illegitimate and raised as a foster child, he subsequently advanced to the rank of a Swedish Field Marshal, and in Scotland bec ...
started his career in Swedish service as commandant and governor of Pillau in East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
. Gustavus Adolphus had made plans to intervene in the Holy Roman Empire, of which the Riksdag
The Riksdag (, ; also sv, riksdagen or ''Sveriges riksdag'' ) is the legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (), elected proportionally and se ...
commission approved in the winter of 1627/28.Theologische Realenzyklopädie I (1993), p.172
Situation in Pomerania
In November 1627, the Duchy of Pomerania had capitulated to the forces of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
.Langer (2003), p.402 Bogislaw XIV, Duke of Pomerania, on 10 November signed the Capitulation of Franzburg with Hans Georg von Arnim, who on behalf of Albrecht von Wallenstein commanded the imperial occupation forces in Pomerania. With the occupation, Wallenstein sought to secure the southern coastline of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
for Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria of Bavaria. His parents were dev ...
against Christian IV of Denmark
Christian IV (12 April 1577 – 28 February 1648) was King of Denmark and Norway and Duke of Holstein and Schleswig from 1588 until his death in 1648. His reign of 59 years, 330 days is the longest of Danish monarchs and Scandinavian mona ...
.
The Capitulation of Franzburg required all towns except for ducal residences to take in imperial troops, and Wallenstein had ordered Arnim to occupy the Pomeranian ports and seize their vessels already in October.Heitz (1995), p.218 Stralsund however was unwilling to give in,Theologische Realenzyklopädie II (1993), p.45 as its status as a Hanseatic town had provided for considerable self-determination and independence from the Pomeranian dukes
This is a list of the duchies and dukes of Pomerania.
Dukes of the Slavic Pomeranian tribes (All Pomerania)
The lands of Pomerania were firstly ruled by local tribes, who settled in Pomerania around the 10th and 11th centuries.
Non-dynastic
...
. Thus, Stralsund ignored Bogislaw's order to adhere to the capitulation, issued since February 1628, and instead turned first to Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
and then to Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
for support.
Siege
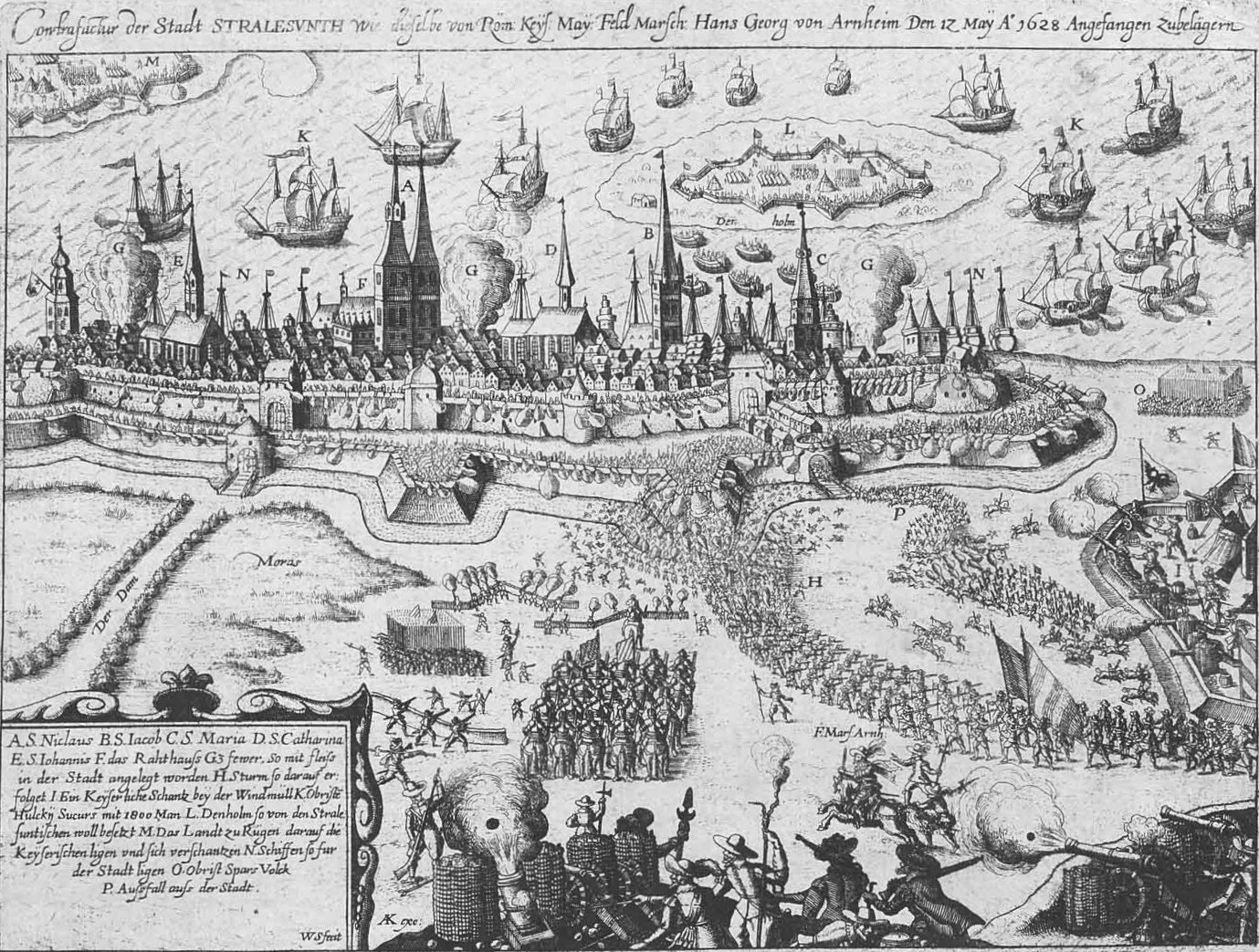
Starting in May 1628, siege was laid onStralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish: ''Strålsund''), officially the Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rostock, Schwerin, N ...
by Albrecht von Wallenstein's troops, commanded by Hans Georg von Arnim.Berg (1962), p.38 By then, the town with its 20,000 inhabitants was defended by a citizen force of 2,500, a levy of 1,500, and another 1,000 enlisted men. The first major imperial assault on the city took place between 16 and 24 May.

Christian IV of Denmark
Christian IV (12 April 1577 – 28 February 1648) was King of Denmark and Norway and Duke of Holstein and Schleswig from 1588 until his death in 1648. His reign of 59 years, 330 days is the longest of Danish monarchs and Scandinavian mona ...
had reacted positively to Stralsund's call and deployed a force including 900Parker (1997, p.180 of Mackay's Scotsmen, organized in seven companies, and a company of Germans in her defence. Though dispatched already on 8 May, they only landed on 24 May. Initially, the Danish-German mercenary Heinrich Holk
Heinrich Holk (also Holke or Henrik Holck;Olesen (2003), p. 390 18 April 1599 – 9 September 1633) was a Danish-German mercenary in both Christian IV of Denmark's and Albrecht von Wallenstein's service during the Thirty Years' War.Keegan ...
was appointed governor.Murdoch in Mackillop & Murdoch (2003), p.16Keegan (1996), p.137 When Holk retired to seek reinforcements, he was succeeded by Scotsman Lieutenant Colonel Alexander Seaton of Mackay's Regiment.
The Imperial army renewed its assault on 26 and 27 May. When checked, Arnim resorted to bombardment awaiting Wallenstein's personal appearance.
On 20 June, a Swedish auxiliary expedition, dispatched already on 2 June, arrived with 600 men commanded by Colonel Fretz, Colonel James MacDougall, and Major Semple.
On 23Olesen (2003), p.390 or 25Heitz (1995), p.219 June, Stralsund concluded an alliance with Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">N.S_19_December.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/now ...
, scheduled to last twenty years. Gustavus Adolphus then stationed a garrison in the town, the first such on German soil in history. This event marked the starting point of Swedish engagement in the Thirty Years' War.Heckel (1983), p.143; Groesjean (2003), pp.68-69 Robert Monro recorded that Semple was killed almost upon arrival and Macdougall temporarily captured. However he noted that this Swedish contingent "did come voluntarily come to succour and help our Nation" indicating the sheer number of Scots from both the standing Danish garrison and the Swedish relief force.
On 27 June, Wallenstein took command of the besieging forces, and renewed the assaults starting the very same night. The Scottish troops, entrusted with the defence of a crucial section of Stralsund's fortifications, distinguished themselves by an extremely fierce way of fighting. The main assault was on the eastern district of Franken, commanded by major Robert Monro. Of 900 Scots, 500 were killed and 300 wounded, including Monro. Rosladin was able to relieve Monro's force and re-take lost ground. An overall 2,000 defenders were killed and captured in this assault. Monro later recalled that "''we were not suffered to come off our posts for our ordinary recreation, nor yet to sleepe''" - for a period of six weeks.
 The following night, on 28 and 29 June, Wallenstein succeeded in taking the outer works of the fortifications. Rosladin was wounded and governor Seaton took over his command.
On 29 June, Bogislaw XIV, Duke of Pomerania sent two of his high-ranking nobles, the count von Putbus and his chancellor von Horn, to persuade Stralsund to adhere to the Capitulation of Franzburg and surrender to Wallenstein. On 30 June, Rosladin persuaded the city not to enter into negotiations with Wallenstein, who had resorted to bombardment again. The same day, ten Swedish vessels reinforced Stralsund with 600 troops, while under heavy fire by Wallenstein's forces. Soon after, Christian ordered another Scottish regiment, that of
The following night, on 28 and 29 June, Wallenstein succeeded in taking the outer works of the fortifications. Rosladin was wounded and governor Seaton took over his command.
On 29 June, Bogislaw XIV, Duke of Pomerania sent two of his high-ranking nobles, the count von Putbus and his chancellor von Horn, to persuade Stralsund to adhere to the Capitulation of Franzburg and surrender to Wallenstein. On 30 June, Rosladin persuaded the city not to enter into negotiations with Wallenstein, who had resorted to bombardment again. The same day, ten Swedish vessels reinforced Stralsund with 600 troops, while under heavy fire by Wallenstein's forces. Soon after, Christian ordered another Scottish regiment, that of Alexander Lindsay, 2nd Lord Spynie
Alexander Lindsay, 2nd Lord Spynie (died March 1646) was a Scottish nobleman and soldier of fortune.
Life
He was the eldest son of Alexander Lindsay, 1st Lord Spynie, by his wife Jean Lyon, and was still a minor at the time of his father's murde ...
, to help with the defence of the town. These troops arrived around 4 July and suffered huge casualties (being reduced from a regiment to four companies) in the ensuing assaults, many led by Wallenstein in person.Heckel (1983), p.143 On 10 July, Wallenstein and Stralsund negotiated a treaty in the ''Hainholz'' woods northwest of the town, requiring Stralsund to take in Pomeranian troops. The treaty was signed by Wallenstein and Bogislaw XIV on 21 July, but not by Stralsund. Though Bogislaw vouched for the town, the treaty did not come into effect.
Already on 2 July, Stralsund had been reinforced by 400 Danish troops, and by 1,100 troops of the Danish-Scottish regiments of Donald Mackay and Alexander Lindsay, 2nd Lord Spynie
Alexander Lindsay, 2nd Lord Spynie (died March 1646) was a Scottish nobleman and soldier of fortune.
Life
He was the eldest son of Alexander Lindsay, 1st Lord Spynie, by his wife Jean Lyon, and was still a minor at the time of his father's murde ...
in the following week. By the 17 July Scotsman Alexander Leslie
Alexander Leslie, 1st Earl of Leven (15804 April 1661) was a Scottish soldier in Swedish and Scottish service. Born illegitimate and raised as a foster child, he subsequently advanced to the rank of a Swedish Field Marshal, and in Scotland bec ...
, arrived with 1,100 troops, including more Scottish volunteers, and succeeded Seaton as Stralsund's governor.Salmon (2003), p.32 Leslie commanded a total of 4,000 to 5,000 troops.Murdoch in Mackillop & Murdoch (2003), p.62; Grosjean (2003), p.70 The Danish support amounted to 2,650 troops deployed during the siege. One of Leslie's first actions was an audacious all-out assault on the besieging troops which Robert Monro described as follows:
''Sir Alexander Leslie being made governour, he resolved for the credit of his countrymen to make an out-fall upon the Enemy, and desirous to conferre the credit on his own Nation alone, being his first Essay in that Citie''
Heavy rainfall between 21 and 24 July turned the battlefield into a marsh. On 4 August, Wallenstein lifted the siege, acknowledging his first misfortune in the Thirty Years' War.
Aftermath
After the unsuccessful siege, Wallenstein headed to nearbyWolgast
Wolgast (; csb, Wòłogòszcz) is a town in the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the bank of the river (or strait) Peenestrom, vis-a-vis the island of Usedom on the Baltic coast that can b ...
, to fight a final battle with Christian IV: Danish troops had landed in the area and occupied the island of Usedom
Usedom (german: Usedom , pl, Uznam ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It is north of the Szczeci ...
, and had taken the town of Wolgast on 14 August without fighting. On 22 August, Wallenstein retook the town.
 Also in August, Swedish chancellor
Also in August, Swedish chancellor Axel Oxenstierna
Axel Gustafsson Oxenstierna af Södermöre (; 1583–1654), Count of Södermöre, was a Swedish statesman. He became a member of the Swedish Privy Council in 1609 and served as Lord High Chancellor of Sweden from 1612 until his death. He was a c ...
came to Stralsund, and offered negotiations to Wallenstein.Ringmar (1996), p.113 The latter however refused. The inability to take Stralsund was to become one of the obstacles which led to Wallenstein's temporary dismissal in 1630.Lee (2002), p.25
When Gustavus Adolphus' invaded Pomerania in June 1630, he used his bridgehead in Stralsund to clear the flanks of his landing forces. Bogislaw XIV concluded an alliance with the Swedish king in the Treaty of Stettin in July. Wallenstein's forces were subsequently driven out of the Duchy of Pomerania, and Swedish forces had taken complete control of the duchy when Wallenstein's forces in Greifswald surrendered in June 1631.Heitz (1995), p.220
During the Swedish campaign, Alexander Leslie
Alexander Leslie, 1st Earl of Leven (15804 April 1661) was a Scottish soldier in Swedish and Scottish service. Born illegitimate and raised as a foster child, he subsequently advanced to the rank of a Swedish Field Marshal, and in Scotland bec ...
was succeeded as the governor of Stralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish: ''Strålsund''), officially the Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rostock, Schwerin, N ...
by another Scot in Swedish service, James MacDougal, in 1630. From 1679 to 1697, the position was to pass to yet another Scot, Peter Maclean.
Part of Wallenstein's forces were infected with the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
.Meier (2008), p.52 During the siege, the epidemics swept into the town, killing 2,000 in the months of August and September alone.
The battle of Stralsund entered Pomeranian folklore. The population of Stralsund commemorates the siege of 1628 with an annual festival, "''Wallensteintage''" ("Wallenstein Days").
Gallery
Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria of Bavaria. His parents were dev ...
File:Albrecht Wallenstein.jpeg, Albrecht von Wallenstein
File:Hans Georg von Arnim.jpg, Hans Georg von Arnim
Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">N.S_19_December.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/now ...
File:Alexleslie.jpg, Alexander Leslie
Alexander Leslie, 1st Earl of Leven (15804 April 1661) was a Scottish soldier in Swedish and Scottish service. Born illegitimate and raised as a foster child, he subsequently advanced to the rank of a Swedish Field Marshal, and in Scotland bec ...
File:Christian 4 som gammel.jpg, Christian IV of Denmark
Christian IV (12 April 1577 – 28 February 1648) was King of Denmark and Norway and Duke of Holstein and Schleswig from 1588 until his death in 1648. His reign of 59 years, 330 days is the longest of Danish monarchs and Scandinavian mona ...
See also
* Pomerania during the Early Modern Age *Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
* Capitulation of Franzburg
* Duchy of Pomerania
* Swedish Pomerania
*Scotland and the Thirty Years' War
There was a complicated involvement between Scotland and the Thirty Years' War of 1618–1648. Scotland and the Scots were heavily entangled in both the diplomatic and military events which centred on the Holy Roman Empire. There were a number of r ...
Notes
Sources
References
Bibliography
* * *Grosjean, Alexi''An Unofficial Alliance: Scotland and Sweden, 1569-1654''
(Leiden, 2003) * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Riis, Thomas, ''Should Auld Acquaintance Be Forgot'' (2 vols., Odense, 1988) * * * *
External links
Digitalized collection of primary sources about the siege by Johann Albert Dinnies from the Stralsund archives
{{Authority control 1628 in Europe Stralsund 1628 Stralsund 1628 Stralsund 1628 Stralsund 1628 Conflicts in 1628 History of Pomerania Stralsund Albrecht von Wallenstein Battles in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania