Shunt (electrical) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
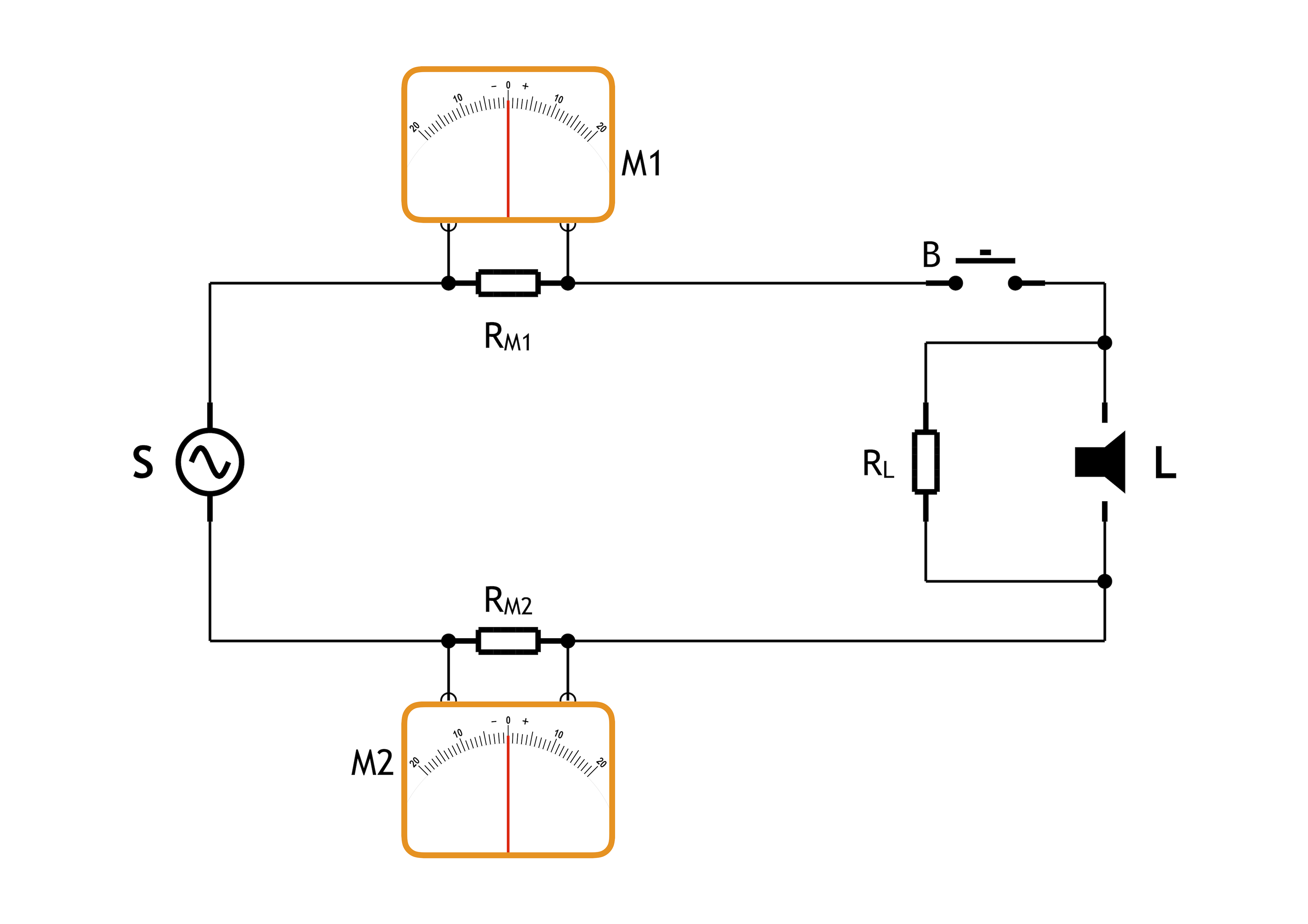 As an introduction to the next chapter, this figure shows that the term "shunt resistor" should be understood in the context of what it shunts.
In this example the resistor RL would be understood as "the shunt resistor" (to the load L), because this resistor would pass current around the load L. RL is connected in parallel with the load L.
However, the series resistors RM1 and RM2 are low Ohmic resistors (like in the photo) meant to pass current around the instruments M1 and M2, and function as shunt resistors to those instruments. RM1 and RM2 are connected in parallel with M1 and M2. If seen without the instruments these two resistors would be considered series resistors in this circuit.
As an introduction to the next chapter, this figure shows that the term "shunt resistor" should be understood in the context of what it shunts.
In this example the resistor RL would be understood as "the shunt resistor" (to the load L), because this resistor would pass current around the load L. RL is connected in parallel with the load L.
However, the series resistors RM1 and RM2 are low Ohmic resistors (like in the photo) meant to pass current around the instruments M1 and M2, and function as shunt resistors to those instruments. RM1 and RM2 are connected in parallel with M1 and M2. If seen without the instruments these two resistors would be considered series resistors in this circuit.
Image:Low side current shunt.svg, Low-side insertion can eliminate common-mode voltage, but not without drawbacks.
Image:High side current shunt diagram.svg, High-side insertion resolves low-side drawbacks but guarantees common-mode voltage.
Image:isolation amp current shunt.gif, Isolated amplifiers resolve all the difficulties and limitations with high- or low-side current shunt measurements.
electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
, a shunt is a device that creates a low- resistance path for electric current, to allow it to pass around another point in the circuit.Rudolf F. Graf, ''Modern dictionary of Electronics'', Mc-Graw Hill, 1968 Library of Congress 68-13873 ''Shunt'' page 454. The origin of the term is in the verb 'to shunt' meaning to turn away or follow a different path.
Defective device bypass
One example is in miniatureChristmas lights
Christmas lights (also known as fairy lights, festive lights or string lights) are lights often used for decoration in celebration of Christmas, often on display throughout the Christmas season including Advent and Christmastide. The custom g ...
which are wired in series. When the filament burns out in one of the incandescent light bulbs, the full line voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
appears across the burnt out bulb. A shunt resistor, which has been connected in parallel across the filament before it burnt out, will then short out to bypass the burnt filament and allow the rest of the string to light. If too many lights burn out however, a shunt will also burn out, requiring the use of a multimeter to find the point of failure.
Photovoltaics
In photovoltaics, the term is widely used to describe an ''unwanted'' short circuit between the front and back surface contacts of a solar cell, usually caused bywafer
A wafer is a crisp, often sweet, very thin, flat, light and dry biscuit, often used to decorate ice cream, and also used as a garnish on some sweet dishes. Wafers can also be made into cookies with cream flavoring sandwiched between them. They ...
damage.
Lightning arrester
Agas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
-filled tube can also be used as a shunt, particularly in a lightning arrester. Neon and other noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
es have a high breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to experience electrical breakdown and become electrically conductive.
For diodes, the breakdown voltage is the minimum reverse voltage that mak ...
, so that normally current will not flow across it. However, a direct lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an avera ...
strike (such as on a radio tower
Radio masts and towers are typically tall structures designed to support antennas for telecommunications and broadcasting, including television. There are two main types: guyed and self-supporting structures. They are among the tallest human-made ...
antenna) will cause the shunt to arc and conduct the massive amount of electricity to ground, protecting transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the ...
s and other equipment.
Another older form of lightning arrester employs a simple narrow spark gap, over which an arc will jump when a high voltage is present. While this is a low cost solution, its high triggering voltage offers almost no protection for modern solid-state electronic devices powered by the protected circuit.
Electrical noise bypass
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
s are used as shunts to redirect high-frequency noise to ground before it can propagate to the load or other circuit components.
Use in electronic filter circuits
The term shunt is used infilter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
and similar circuits with a ladder topology
Electronic filter topology defines electronic filter circuits without taking note of the values of the components used but only the manner in which those components are connected.
Filter design characterises filter circuits primarily by their ...
to refer to the components connected between the line and common. The term is used in this context to distinguish the shunt components connected between the signal and return lines from the components connected in series along the signal line. More generally, the term shunt can be used for a component connected in parallel with another. For instance, ''shunt m-derived half section'' is a common filter section from the image impedance Image impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term ''image impedance'' applies to the impedance seen looking into a Port (circuit theory), port of a network. Usually a two-port ...
method of filter design.
Diodes as shunts
Where devices are vulnerable to reverse polarity of a signal or power supply, a diode may be used to protect the circuit. If connected in series with the circuit it simply prevents reversed current, but if connected in parallel it can shunt the reversed supply, causing a fuse or other current limiting circuit to open. All semiconductor diodes have a threshold voltage – typically between volt and 1 volt – that must be exceeded before significant current will flow through the diode in the normally allowed direction. Two anti-parallel shunt diodes (one to conduct current in each direction) can be used to limit the signal flowing past them to no more than their threshold voltages, in order to protect later components from overload.Shunts as circuit protection
When a circuit must be protected from overvoltage and there are failure modes in the power supply that can produce such overvoltages, the circuit may be protected by a device commonly called a crowbar circuit. When this device detects an overvoltage it causes a short circuit between the power supply and its return. This will cause both an immediate drop in voltage (protecting the device) and an instantaneous high current which is expected to open a current sensitive device (such as a fuse orcircuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by an overcurrent or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent the ris ...
). This device is called a ''crowbar'' as it is likened to dropping an actual crowbar across a set of bus bars (exposed electrical conductors).
Battle short
On warships, it is common to install battle short shunts across fuses for essential equipment before entering combat. This disablesovercurrent protection
Power system protection is a branch of electrical power engineering that deals with the protection of electrical power systems from faults through the disconnection of faulted parts from the rest of the electrical network. The objective of a prot ...
at a time when removing power to the equipment is not a safe reaction.
Shunting an instrument but series connected in circuit
 As an introduction to the next chapter, this figure shows that the term "shunt resistor" should be understood in the context of what it shunts.
In this example the resistor RL would be understood as "the shunt resistor" (to the load L), because this resistor would pass current around the load L. RL is connected in parallel with the load L.
However, the series resistors RM1 and RM2 are low Ohmic resistors (like in the photo) meant to pass current around the instruments M1 and M2, and function as shunt resistors to those instruments. RM1 and RM2 are connected in parallel with M1 and M2. If seen without the instruments these two resistors would be considered series resistors in this circuit.
As an introduction to the next chapter, this figure shows that the term "shunt resistor" should be understood in the context of what it shunts.
In this example the resistor RL would be understood as "the shunt resistor" (to the load L), because this resistor would pass current around the load L. RL is connected in parallel with the load L.
However, the series resistors RM1 and RM2 are low Ohmic resistors (like in the photo) meant to pass current around the instruments M1 and M2, and function as shunt resistors to those instruments. RM1 and RM2 are connected in parallel with M1 and M2. If seen without the instruments these two resistors would be considered series resistors in this circuit.
Use in current measuring
Anammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''Ampere meter'') is an instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit ...
shunt allows the measurement of current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
values too large to be directly measured by a particular ammeter. In this case, a separate shunt, a resistor of very low but accurately known resistance, is placed in parallel with a voltmeter, so that virtually all of the current to be measured will flow through the shunt (provided the internal resistance of the voltmeter takes such a low portion of the current that it is negligible). The resistance is chosen so that the resultant voltage drop
Voltage drop is the decrease of electrical potential along the path of a current flowing in an electrical circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are undesirab ...
is measurable but low enough not to disrupt the circuit. The voltage across the shunt is proportional to the current flowing through it, and so the measured voltage can be scaled to directly display the current value.''Manual of Electric Instruments'', General Electric, 1949, pages 8–9Terrell Croft, ''American Electricians' Handbook'', McGraw-Hill, 1948 p. 70
Shunts are rated by maximum current and voltage drop at that current. For example, a 500 A, 75 mV shunt would have a resistance of , a maximum allowable current of 500 amps and at that current the voltage drop would be 75 millivolt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defini ...
s. By convention, most shunts are designed to drop 50 mV, 75 mV or 100 mV when operating at their full rated current and most ammeters consist of a shunt and a voltmeter with full-scale deflections of 50, 75, or 100 mV. All shunts have a derating factor for continuous (more than 2 minutes) use, 66% being the most common, so the example shunt should not be operated above 330 A (and 50 mV drop) longer than that.
This limitation is due to thermal limits at which a shunt will no longer operate correctly. For manganin, a common shunt material, at 80 °C thermal drift begins to occur, at 120 °C thermal drift is a significant problem where error, depending on the design of the shunt, can be several percent and at 140 °C the manganin alloy becomes permanently damaged due to annealing resulting in the resistance value drifting up or down.
If the current being measured is also at a high voltage potential this voltage will be present in the connecting leads too and in the reading instrument itself. Sometimes, the shunt is inserted in the return leg ( grounded side) to avoid this problem. Some alternatives to shunts can provide isolation from the high voltage by not directly connecting the meter to the high voltage circuit. Examples of devices that can provide this isolation are Hall effect
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was dis ...
current sensors and current transformer
A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary.
Current transformers, along with volt ...
s (see clamp meters). Current shunts are considered more accurate and cheaper than Hall effect devices. Common accuracy specifications of such devices are ±0.1%, ±0.25% or ±0.5%.
The Thomas-type double manganin walled shunt and MI type (improved Thomas-type design) were used by NIST and other standards laboratories as the legal reference of an ohm until superseded in 1990 by the quantum Hall effect
The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect which is observed in two-dimensional electron systems subjected to low temperatures and strong magnetic fields, in which the Hall resistance exh ...
. Thomas-type shunts are still used as secondary standards to take very accurate current measurements, as using quantum Hall effect is a time-consuming process. The accuracy of these types of shunts is measured in the ppm and sub-ppm scale of drift per year of set resistance.
Where the circuit is grounded (earthed) on one side, a current measuring shunt can be inserted either in the ungrounded conductor or in the grounded conductor. A shunt in the ungrounded conductor must be insulated for the full circuit voltage to ground; the measuring instrument must be inherently isolated from ground or must include a resistive voltage divider or an isolation amplifier
Isolation amplifiers are a form of differential amplifier that allow measurement of small signals in the presence of a high common mode voltage by providing electrical isolation and an electrical safety barrier. They protect data acquisition compo ...
between the relatively high common-mode voltage and lower voltages inside the instrument. A shunt in the grounded conductor may not detect leakage current that bypasses the shunt, but it will not experience high common-mode voltage to ground. The load is removed from a direct path to ground, which may create problems for control circuitry, result in unwanted emissions, or both.
See also
*Shunt generator
A shunt generator is a type of electric generator in which field winding and Armature (electrical engineering), armature winding are connected in Series and parallel circuits, parallel, and in which the armature supplies both the load current and ...
* Shunt wound motor
* Shunt jumper
* Zero-ohm link
* Fuse (electrical)
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows thr ...
References
External links
{{Authority control Electrical engineering