Shkodër on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shkodër ( , ; sq-definite, Shkodra) is the fifth-most-populous city of the
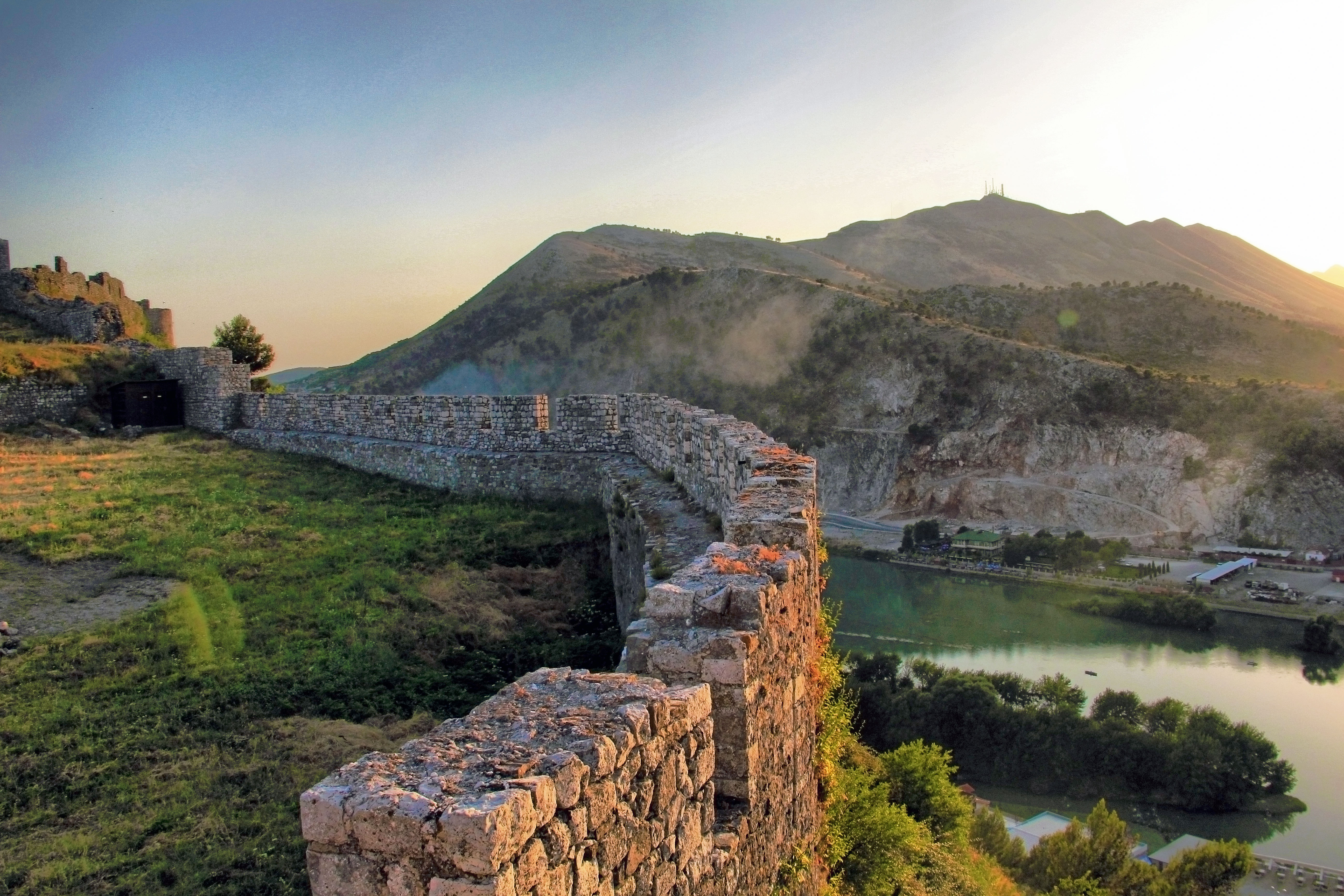 The earliest signs of human activity in the lands of Shkodër can be traced back to the
The earliest signs of human activity in the lands of Shkodër can be traced back to the
 With two
With two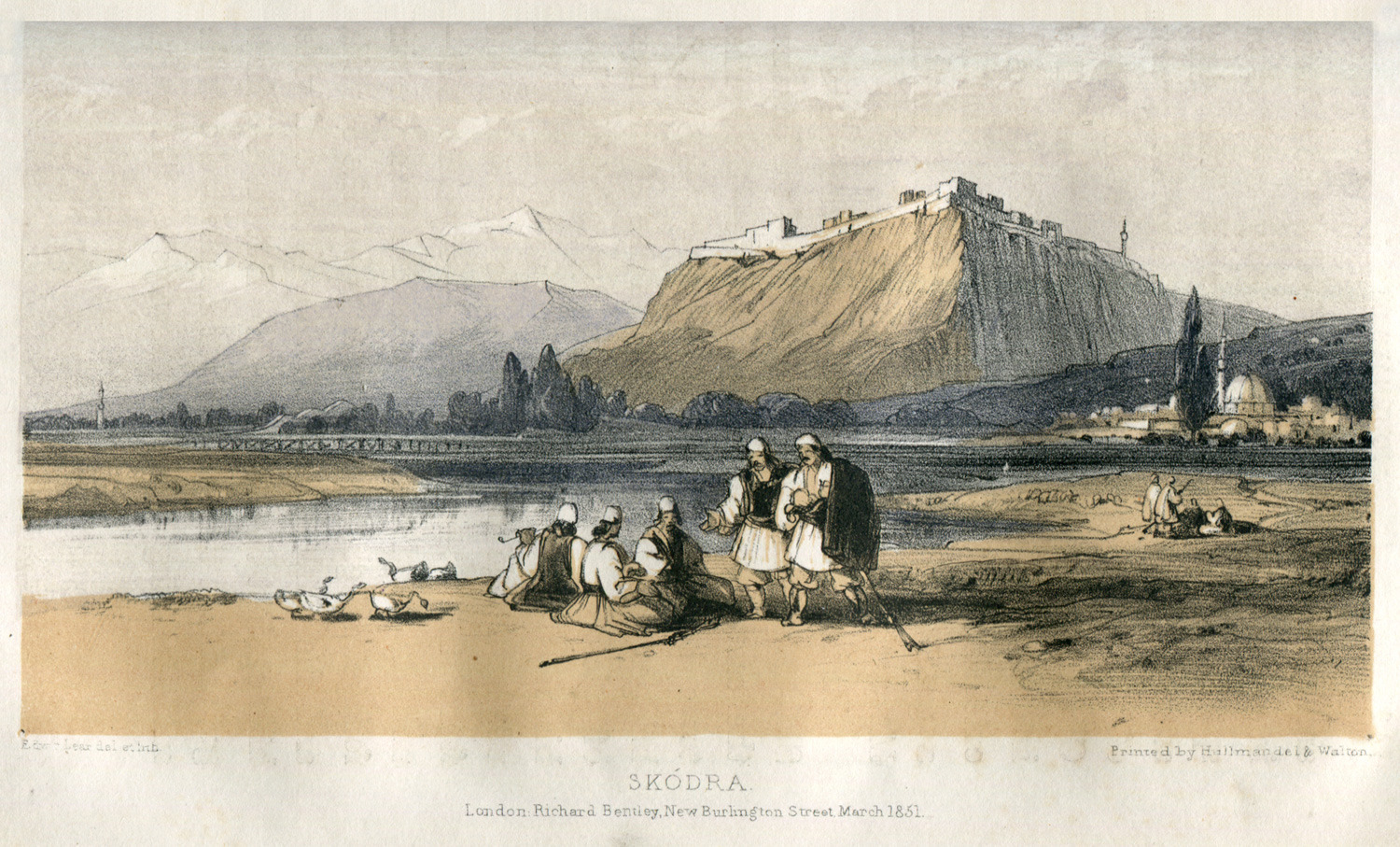  After Ottoman domination was secure, much of the population fled. Around the 17th century, the city began to prosper as the centre of the
After Ottoman domination was secure, much of the population fled. Around the 17th century, the city began to prosper as the centre of the  Shkodër was a major city under Ottoman rule in southeast Europe. It retained its importance up until the end of the empire's rule in the Balkans in the early 20th century. This is due to its geo-strategic position that connects it directly with the
Shkodër was a major city under Ottoman rule in southeast Europe. It retained its importance up until the end of the empire's rule in the Balkans in the early 20th century. This is due to its geo-strategic position that connects it directly with the
 Shkodër played an important role during the
Shkodër played an important role during the
 Shkodër extends strategically on the Mbishkodra Plain between the
Shkodër extends strategically on the Mbishkodra Plain between the
 The main activities of the processing industry in Shkodra were the processing of tobacco and manufacture of cigarettes, production of preserved foods, sugar-based foods, soft and alcoholic drinks, and pasta, bread, rice and vegetable oil. The main activities of the textile industry were focused on garments and silk products. The city also had a wood-processing and paper-production plant. The most important mechanical engineering industries concerned wire manufacturing, elevator manufacturing, bus assembly and the Drini Plant.
According to the World Bank, Shkodër has had significant steps of improving the economy in recent years. In 2016, Shkodër ranked 8 among 22 cities in southeastern Europe.
As the largest city in northern
The main activities of the processing industry in Shkodra were the processing of tobacco and manufacture of cigarettes, production of preserved foods, sugar-based foods, soft and alcoholic drinks, and pasta, bread, rice and vegetable oil. The main activities of the textile industry were focused on garments and silk products. The city also had a wood-processing and paper-production plant. The most important mechanical engineering industries concerned wire manufacturing, elevator manufacturing, bus assembly and the Drini Plant.
According to the World Bank, Shkodër has had significant steps of improving the economy in recent years. In 2016, Shkodër ranked 8 among 22 cities in southeastern Europe.
As the largest city in northern
 Shkodër is referred to as the capital and cultural cradle of
Shkodër is referred to as the capital and cultural cradle of
bashkiashkoder.gov.al
fficial Website {{DEFAULTSORT:Shkoder Shkodër, Cities in Albania Municipalities in Shkodër County Administrative units of Shkodër Gegëri Illyrian Albania Cities in ancient Illyria Territories of the Republic of Venice Former capitals of Montenegro Populated places established in the 4th century BC
Republic of Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares l ...
and the seat of Shkodër County
Shkodër County ( sq, Qarku i Shkodrës) is a county in northwestern Albania, with the capital in Shkodër. The county spans and had a total population of 197,177 people as of 2021. The county borders on the counties of Lezhë, Kukës and the co ...
and Shkodër Municipality. The city sprawls across the Plain of Mbishkodra between the southern part of Lake Shkodër
Lake Skadar ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, Скадарско језеро, Skadarsko jezero, ; sq, Liqeni i Shkodrës, ) also called Lake Scutari, Lake Shkodër and Lake Shkodra lies on the border of Albania and Montenegro, and is the largest lake in Southern ...
and the foothills of the Albanian Alps
The Accursed Mountains ( sq, Bjeshkët e Nemuna; sh-Cyrl-Latn, Проклетије, Prokletije, ; both translated as "Cursed Mountains"), also known as the Albanian Alps ( sq, Alpet Shqiptare), are a mountain group in the western part of the B ...
on the banks of Buna, Drin and Kir. Due to its proximity to the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, Shkodër is affected by a seasonal Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
with continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
influences.
One of the oldest continuously inhabited cities
This is a list of present-day cities by the time period over which they have been continuously inhabited as a city. The age claims listed are generally disputed. Differences in opinion can result from different definitions of "city" as well as "c ...
in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, Shkodër was founded under the name ''Scodra'' upon the traditional lands of the Illyrian tribes of the Ardiaei
The Ardiaei were an Illyrian people who resided in the territory of present-day Albania, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia between the Adriatic coast on the south, Konjic on the north, along the Neretva river and its right ...
and Labeates
The Labeatae, Labeatai or Labeates ( grc, Λαβεᾶται; la, Labeatae) were an Illyrian people that lived on the Adriatic coast of southern Illyria, between modern Albania and Montenegro, around Lake Scodra (the ancient ''Lacus Labeatis' ...
in the 4th century BCE. It has historically developed on a hill strategically located in the outflow of Lake Shkodër into the Buna River
The Bojana ( cnr, Бојана), also known as the Buna ( sq, Bunë), is a river in Albania and Montenegro which flows into the Adriatic Sea. An outflow of Lake Skadar, measured from the source of the lake's longest tributary, the Morača, t ...
. The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
annexed the city after the third Illyrian War
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the ''First Illyrian War'', which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the ...
in 168 BCE, when Gentius
Gentius ( grc, Γένθιος, "Génthios"; 181168 BC) was an Illyrian king who belonged to the Labeatan dynasty. He ruled in 181–168 BC, being the last attested Illyrian king. He was the son of Pleuratus III, a king who kept positive relati ...
was defeated by the Roman force of Anicius Gallus. In the 3rd century CE, Shkodër became the capital of Praevalitana
Praevalitana (also ''Prevalitana'', ''Prevaliana'', ''Praevaliana'' or ''Prevalis'') was a Late Roman province that existed between c. 284 and c. 600. It included parts of present-day Montenegro, northern Albania, and part of present-day Kosovo. ...
, due to the administrative reform of the Roman Emperor Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
. With the spread of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
in the 4th century CE, the Archdiocese of Scodra was founded and was assumed in 535 by Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
.
Shkodër is regarded as the traditional capital of northern Albania
Northern Albania ( sq, Shqipëria Veriore) is one of the three NUTS-2 Regions of Albania. This ethnographical territory is sometimes referred to as ''Ghegeria'' ( sq, Gegëria) which also includes parts of the Albanian-inhabited territories of ...
, also referred to as Gegëria, and is noted for its arts, culture, religious diversity and turbulent history among the Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Se ...
. The architecture of Shkodër is particularly dominated by mosques and churches reflecting the city's high degree of religious diversity and tolerance. Shkodër was home to many influential personalities, who among others, helped to shape the Albanian Renaissance
The Albanian National Awakening ( sq, Rilindja or ), commonly known as the Albanian Renaissance or Albanian Revival, is a period throughout the 19th and 20th century of a cultural, political and social movement in the Albanian history where th ...
.
Name
The city was first attested in calassical sources as ''Skodra'' (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
: ''Σκόδρα''; genitive "of the Skodrians", appearing on 2nd c. BC coins) and ''Scodra'' (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
form).
Although the ultimate origin of the toponym is uncertain,; Albanian translation: . the name is certainly pre-Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
. A Paleo-Balkan origin has been suggested, relating it to the sq, kodër
Kodër ( sq-definite, Kodra, el, Καλύβια Πασά) is a village in the former commune of Livadhe, Vlorë County, southern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality of Finiq. A 1993 study by Le ...
(definite
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases, distinguishing between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those which are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical d ...
form: ) 'hill', and ro, codru '(wooded) mountain, forest', with the same root as the ancient toponym '' Codrio/Kodrion''.
The further development of the name has been a subject of discussion among linguists over the exact location of Albanian-speakers in classical antiquity. Linguists Eqrem Çabej and Shaban Demiraj
Shaban Demiraj (1920–2014) was an Albanian albanologist, linguist, professor at the University of Tirana from 1972–1990, and chairman of the Academy of Sciences of Albania during the period of 1993-1997.
Life
Demiraj was born on 1 January ...
treat the development from ''Skodra'' to modern ''Shkodra/Shkodër'' as evidence of regular development within the Albanian language. Other linguists have argued that ''Shkodra/Shkodër'' fails to display certain known phonological changes that would have to have happened if the name had been continually in use in Proto-Albanian
The Proto-Albanian language is the unattested language from which Albanian later developed. Albanian evolved from an ancient Paleo-Balkan language, traditionally thought to be Illyrian, or otherwise a totally unattested Balkan Indo-European ...
since pre-Roman times.
In modern times, the term was adapted to Italian as ''Scodra'' () and ''Scutari'' (); in this form it was also in wide use in English until the 20th century.Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
, 11th edition (1911), "Scutari" article. In Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and ...
, Shkodër is known as ''Skadar'' (), and in Turkish as ''İşkodra''.
History
Early history
 The earliest signs of human activity in the lands of Shkodër can be traced back to the
The earliest signs of human activity in the lands of Shkodër can be traced back to the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
. The favorable conditions on the fertile plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
, around the lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
, have brought people here from early antiquity. Artefacts and inscriptions, discovered in the Rozafa Castle, are assumed to be the earliest examples of symbolic behaviour in humans in the city. Although, it was known under the name Scodra and was inhabited by the Illyrian tribe
This is a list of ancient tribes in the ancient territory of Illyria ( grc-gre, Ἰλλυρία; la, Illyria). The name ''Illyrians'' seems to be the name of a single Illyrian tribe that was the first to come into contact with the ancient Greeks ...
s of the Labeates
The Labeatae, Labeatai or Labeates ( grc, Λαβεᾶται; la, Labeatae) were an Illyrian people that lived on the Adriatic coast of southern Illyria, between modern Albania and Montenegro, around Lake Scodra (the ancient ''Lacus Labeatis' ...
and Ardiaei
The Ardiaei were an Illyrian people who resided in the territory of present-day Albania, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia between the Adriatic coast on the south, Konjic on the north, along the Neretva river and its right ...
, which ruled over a large territory between modern Albania up to Croatia. King Agron, Queen Teuta
Teuta (Illyrian languages, Illyrian: *''Teutana'', 'mistress of the people, queen'; grc, Τεύτα; lat, Teuta) was the queen regent of the Ardiaei tribe in Illyria, who reigned approximately from 231 BC to 228/227 BC.
Following the death ...
and King Gentius
Gentius ( grc, Γένθιος, "Génthios"; 181168 BC) was an Illyrian king who belonged to the Labeatan dynasty. He ruled in 181–168 BC, being the last attested Illyrian king. He was the son of Pleuratus III, a king who kept positive relati ...
, were among the most famous personalities of the Ardiaei
The Ardiaei were an Illyrian people who resided in the territory of present-day Albania, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia between the Adriatic coast on the south, Konjic on the north, along the Neretva river and its right ...
.
The city was first mentioned during antiquity as the site of the Illyrian Labeates in which they minted coins and that of Queen Teuta. In 168 BCE, the city was captured by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and became an important trade and military route. The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
colonized the town. Scodra remained in the province of Illyricum and, later, Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
. By it 395 CE, it was part of the Diocese of Dacia, within Praevalitana
Praevalitana (also ''Prevalitana'', ''Prevaliana'', ''Praevaliana'' or ''Prevalis'') was a Late Roman province that existed between c. 284 and c. 600. It included parts of present-day Montenegro, northern Albania, and part of present-day Kosovo. ...
.
In the early 11th century, Jovan Vladimir
Jovan Vladimir or John Vladimir ( sr-cyr, Јован Владимир; c. 990 – 22 May 1016) was the ruler of Duklja, the most powerful Serbian principality of the time, from around 1000 to 1016. He ruled during the protracted war between t ...
ruled Duklja
Duklja ( sh-Cyrl, Дукља; el, Διόκλεια, Diokleia; la, Dioclea) was a medieval South Slavic state which roughly encompassed the territories of modern-day southeastern Montenegro, from the Bay of Kotor in the west to the Bojana Ri ...
amidst the war between Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
and Samuel. Vladimir allegedly retreated into Koplik
Koplik (also known as Koplik i Poshtëm) is a town and former municipality in the northwestern tip of Albania. At the 2015 local government reform, it became a subdivision, and the seat of the municipality Malësi e Madhe. It was the seat of the ...
when Samuel invaded Duklja and was subsequently forced to accept Bulgarian vassalage. He was later slain by the Bulgarians. Shingjon (feast of Jovan Vladimir) has since been celebrated by Albanian Orthodox Christians.
In the 1030s, Stefan Vojislav
Stefan Vojislav ( sr-cyr, Стефан Војислав; gr, Στέφανος Βοϊσθλάβος; 1034–d. 1043) was the Prince of Duklja from 1040 to 1043. Beginning in the year 1018, he served as a Byzantine governor, until 1034 when he led ...
from Travunija
Travunia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Travunija, Травунија; el, Τερβουνία, Tervounía; grc, Τερβουνία, Terbounía; la, Tribunia) was a South Slavic medieval principality that was part of Medieval Serbia (850–13 ...
expelled the last strategos
''Strategos'', plural ''strategoi'', Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized ''strategus'', ( el, στρατηγός, pl. στρατηγοί; Doric Greek: στραταγός, ''stratagos''; meaning "army leader") is used in Greek language, Greek to ...
and successfully defeated the Byzantines by 1042. Stefan Vojislav set up Shkodër, as his capital. Constantine Bodin
Constantine Bodin ( Bulgarian and sr, italic=no, Константин Бодин, ''Konstantin Bodin''; 1072–1101) was a medieval king and the ruler of Duklja, the most powerful Serbian principality of the time, from 1081 to 1101, succee ...
accepted the crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
of the Crusade of 1101
The Crusade of 1101 was a minor crusade of three separate movements, organized in 1100 and 1101 in the successful aftermath of the First Crusade. It is also called the Crusade of the Faint-Hearted due to the number of participants who joined this ...
in Shkodër. After the dynastic struggles in the 12th century, Shkodër became an integral part of the Serbian Nemanjić Zeta
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; grc, ζῆτα, el, ζήτα, label= Demotic Greek, classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived f ...
province. In 1214 the city was briefly annexed to Despotate of Epirus under Michael I Komnenos Doukas. In 1330, Stefan Dečanski
Stefan Uroš III ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош III, ), known as Stefan Dečanski ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Дечански, ; 1276 – 11 November 1331), was the King of Serbia from 6 January 1322 to 8 September 1331. Dečanski was the son of ...
, King of Serbia, appointed his son Stefan Dušan
Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан, ), known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr, / ; circa 1308 – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Tsar (or Emperor) and autocrat of the Serbs, Gre ...
as the governor of Zeta with its seat in Shkodër. In the same year Dušan and his father entered the conflict which resulted with campaign of Dečanski who destroyed Dušan's court on Drin River
The Drin (; sq, Drin or ; mk, Дрим, Drim ) is a river in Southern and Southeastern Europe with two distributaries one discharging into the Adriatic Sea and the other one into the Buna River. Its catchment area extends across Albania, ...
near Shkodër in January 1331. In April 1331, they made a truce, but in August 1331 Dušan went from Shkodër to Nerodimlje and overthrew his father.
During the disintegration of the Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
, Shkodër was taken by the Balšić family of Zeta, who surrendered the city to the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
in 1396, in order to form a protection zone from the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. During the Venetian rule the city adopted the Statutes of Scutari
The Statutes of Scutari ( it, Statuti di Scutari, sq, Statutet e Shkodrës) were the highest form of expression of the self-government of Scutari (Shkodër) during Venetian rule. There were other cities in Albania which had statutes but only thos ...
, a civic law written in Venetian. The Statutes of Scutari
The Statutes of Scutari ( it, Statuti di Scutari, sq, Statutet e Shkodrës) were the highest form of expression of the self-government of Scutari (Shkodër) during Venetian rule. There were other cities in Albania which had statutes but only thos ...
mention Albanian and Slavic presence in the city, but under Venetian rule many Dalmatians were brought to Shkodra and as such formed the majority there. After the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
killed most of the inhabitants Albanians and Slavs formed the majority in the city. Venetians built the ''St. Stephen's Church'' (later converted into the Fatih Sultan Mehmet Mosque
The Fatih Sultan Mehmet Mosque ( sq, Xhamia e Sulltan Mehmet Fatihut), also known as the Fatih Mosque ( sq, Xhamia e Fatihut), is a 13th-century building. It is within the Rozafa Castle near Shkodër, Albania. It was built by the Ottoman Empir ...
by the Ottomans) and the Rozafa Castle. In 1478-79 Mehmed the conqueror laid siege on Shkodër. In 1479 the city fell to the Ottomans and the defenders of the citadel emigrated to Venice, while many Albanians from the region retreated into the mountains. The city then became a seat of a newly established Ottoman sanjak, the Sanjak of Scutari.
Ottoman Period
 With two
With two siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity con ...
s, Shkodër became secure as an Ottoman territory. It became the centre of the sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
and by 1485 there were 27 Muslim and 70 Christian hearths, although by the end of the next century there were more than 200 Muslim ones compared to the 27 Christian ones, respectively.
Military manoeuvres in 1478 by the Ottomans meant that the city was again entirely surrounded by Ottoman forces. Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
personally laid the siege
''The Siege'' is a 1998 American action thriller film directed by Edward Zwick. The film is about a fictional situation in which terrorist cells have made several attacks in New York City. The film stars Denzel Washington, Annette Bening, Tony Sh ...
. About ten heavy cannons were cast on site. Balls as heavy as were fired on the citadel (such balls are still on display on the castle museum). Nevertheless, the city resisted. Mehmed left the field and had his commanders continue the siege. By the winter the Ottomans had captured one after the other all adjacent castles: Lezhë
Lezhë (, sq-definite, Lezha) is a city in the Republic of Albania and seat of Lezhë County and Lezhë Municipality.
One of the main strongholds of the Labeatai, the earliest of the fortification walls of Lezhë are of typical Illyrian cons ...
, Drisht
Drisht ( sq-definite, Drishti) is a village, former bishopric and Latin titular see with an Ancient and notable medieval history (Latin ''Drivastum,'' Italian ''Drivasto'') in Albania, 6 km from Mes Bridge (Albanian: ''Ura e Mesit''). It is l ...
and Žabljak Crnojevića
Žabljak Crnojevića ( sr-cyrl, Жабљак Црнојевића, ), commonly referred to as Žabljak, is an abandoned medieval fortified town (fortress) in Montenegro. The fortress is located on the confluence of the Morača river in Lake Skada ...
. This, together with famine and constant bombardment lowered the morale of defenders. On the other hand, the Ottomans were already frustrated by the stubborn resistance. The castle is situated on a naturally protected hill and every attempted assault resulted in considerable casualties for the attackers. A truce became an option for both parties. On January 25 an agreement between the Venetians and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
ended the siege, permitting the citizens to leave unharmed, and the Ottomans to take over the deserted city.
 After Ottoman domination was secure, much of the population fled. Around the 17th century, the city began to prosper as the centre of the
After Ottoman domination was secure, much of the population fled. Around the 17th century, the city began to prosper as the centre of the Sanjak of Scutari
The Sanjak of Scutari or Sanjak of Shkodra ( sq, Sanxhaku i Shkodrës; sr, Скадарски санџак; tr, İskenderiye Sancağı or ''İşkodra Sancağı'') was one of the sanjaks of the Ottoman Empire. It was established after the Otto ...
(sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
was an Ottoman administrative unit smaller than a vilayet
A vilayet ( ota, , "province"), also known by various other names, was a first-order administrative division of the later Ottoman Empire. It was introduced in the Vilayet Law of 21 January 1867, part of the Tanzimat reform movement initiated ...
). It became the economic centre of northern Albania, its craftsmen producing fabric, silk, arms and silver artifacts. Construction included two-storey stone houses, the bazaar, and the Central or Middle Bridge (''Ura e Mesit'') over the Kir river, built during the second half of the 18th century, over long, with 13 arcs of stone, the largest one being wide and tall.
 Shkodër was a major city under Ottoman rule in southeast Europe. It retained its importance up until the end of the empire's rule in the Balkans in the early 20th century. This is due to its geo-strategic position that connects it directly with the
Shkodër was a major city under Ottoman rule in southeast Europe. It retained its importance up until the end of the empire's rule in the Balkans in the early 20th century. This is due to its geo-strategic position that connects it directly with the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
and with the Italian ports, but also with land-routes to the other important Ottoman centre, namely Prizren
)
, settlement_type = Municipality and city
, image_skyline = Prizren Collage.jpg
, imagesize = 290px
, image_caption = View of Prizren
, image_alt = View of Prizren
, image_flag ...
. The city was an important meeting place of diverse cultures from other parts of the Empire, as well as influences coming westwards, by Italian merchants. It was a centre of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
in the region, producing many ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
, poets and administrators, particularly from the Bushati
The Bushati family ( sq, Bushatllinjtë) was a prominent Ottoman Albanian family that ruled the Pashalik of Scutari from 1757 to 1831.
Origins
They are descendants of the medieval Bushati tribe, a pastoralist tribe (''fis'') in northern Albani ...
family.
In the 18th century Shkodër became the centre of the (pashaluk
Eyalets (Ottoman Turkish: ایالت, , English: State), also known as beylerbeyliks or pashaliks, were a primary administrative division of the Ottoman Empire.
From 1453 to the beginning of the nineteenth century the Ottoman local government ...
) of Shkodër, under the rule of the Bushati
The Bushati family ( sq, Bushatllinjtë) was a prominent Ottoman Albanian family that ruled the Pashalik of Scutari from 1757 to 1831.
Origins
They are descendants of the medieval Bushati tribe, a pastoralist tribe (''fis'') in northern Albani ...
family, which ruled from 1757 to 1831. Shkodër's importance as a trade centre in the second half of the 19th century was owed to the fact that it was the centre of the vilayet of Shkodër, and an important trading centre for the entire Balkan peninsula. It had over 3,500 shops, and clothing, leather, tobacco and gunpowder were some of the major products of Shkodër. A special administration was established to handle trade, a trade court, and a directorate of postage services with other countries. Other countries had opened consulates in Shkodër ever since 1718. Obot and Ulcinj
Ulcinj ( cyrl, Улцињ, ; ) is a town on the southern coast of Montenegro and the capital of Ulcinj Municipality. It has an urban population of 10,707 (2011), the majority being Albanians.
As one of the oldest settlements in the Adriatic co ...
served as ports for Shkodër, and, later on, Shëngjin
Shëngjin is a coastal town and a former municipality in Lezhë County, northwestern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality of Lezhë. The population at the 2011 census was 8,091.
(''San Giovanni di Medua''). The Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
seminary and the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include t ...
committee were opened in the 19th century.
Following the rebellion of Mustafa Pasha Bushatlliu Shkodër was sieged by the Ottomans for more than 6 months who finally managed to break the Albanian resistance in 10 November 1831. In 1833 around 4,000 Albanian rebels seized the town again holding off the Ottoman forces between April and December and even sending a delegation to Istanbul until the Ottoman government finally gave in to their terms giving an end to the rebellion.
Before 1867 Shkodër (İşkodra) was a sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
of Rumelia Eyalet
The Eyalet of Rumeli, or Eyalet of Rumelia ( ota, ایالت روم ایلی, ), known as the Beylerbeylik of Rumeli until 1591, was a first-level province ('' beylerbeylik'' or ''eyalet'') of the Ottoman Empire encompassing most of the Balkans (" ...
in Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. In 1867, Shkodër sanjak merged with Skopje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.
The territory of Skopje has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC; r ...
(Üsküp) sanjak and became Shkodër vilayet. Shkodër vilayet was split into Shkodër, Prizren
)
, settlement_type = Municipality and city
, image_skyline = Prizren Collage.jpg
, imagesize = 290px
, image_caption = View of Prizren
, image_alt = View of Prizren
, image_flag ...
and Dibra Dibra is an Albanian surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Abdurrahman Dibra (1885–1961), Albanian politician
* Arenc Dibra (born 1990), Albanian footballer
* Dino Dibra (1975–2000), Australian suspected murderer
* Fuad Dibra (18 ...
sanjaks. In 1877, Prizren passed to Kosovo vilayet and Debar
Debar ( mk, Дебaр ; Albanian: ''Dibër''/''Dibra'' or ''Dibra e Madhe;'' ) is a city in the western part of North Macedonia, near the border with Albania, off the road from Struga to Gostivar. It is the seat of Debar Municipality. Debar has ...
passed to Monastir vilayet, while Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
township became a sanjak. In 1878 Bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
and Podgorica
Podgorica (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Подгорица, ; Literal translation, lit. 'under the hill') is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Montenegro, largest city of Montenegro. The city was formerly known as Titograd ...
townships belonged to Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. Ottoman-Albanian intellectual Sami Frashëri
Sami bey Frashëri ( tr, Şemseddin Sami Bey; June 1, 1850 – June 18, 1904) or Şemseddin Sâmi was an Ottoman Albanian writer, philosopher, playwright and a p ...
during the 1880s estimated the population of Shkodër as numbering 37,000 inhabitants that consisted of three quarters being Muslims and the rest Christians made up of mostly Catholics and a few hundred Orthodox. In 1900, Shkodër vilayet was split into Shkodër and Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
sanjaks.
Modern
 Shkodër played an important role during the
Shkodër played an important role during the League of Prizren
The League of Prizren ( sq, Besëlidhja e Prizrenit), officially the League for the Defense of the Rights of the Albanian Nation ( sq, Lidhja për mbrojtjen e të drejtave te kombit Shqiptar), was an Albanian political organization which was offi ...
, the Albanian liberation movement. The people of Shkodër participated in battles to protect Albanian land. The branch of the League of Prizren for Shkodër, which had its own armed unit, fought for the protection of Plav, Gusinje
Gusinje ( cyrl, Гусиње, ; sq, Gucia) is a small town in north-eastern Montenegro. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 1,673 and is the administrative center of Gusinje Municipality.
Name
Two alternative etymologies ...
, Hoti and Gruda, and the war for the protection of Ulcinj. The Bushati Library, built during the 1840s, served as a centre for the League of Prizren's branch for Shkodër. Many books were collected in libraries of Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
missionaries working in Shkodër. Literary, cultural and sports associations were formed, such as ''Bashkimi'' ("The Union") and ''Agimi'' ("The Dawn"). The first Albanian newspapers and publications printed in Albania came out of the printing press of Shkodër. The Marubi family of photographers began working in Shkodër, which left behind over 150,000 negatives from the period of the Albanian liberation movement, the rise of the Albanian flag in Vlorë
Vlorë ( , ; sq-definite, Vlora) is the third most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Vlorë County and Vlorë Municipality. Located in southwestern Albania, Vlorë sprawls on the Bay of Vlorë and is surrounded by the foo ...
, and life in Albanian towns during the end of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century.
During the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defe ...
, Shkodër went from one occupation to another, when the Ottomans were defeated by the Kingdom of Montenegro
The Kingdom of Montenegro ( sr, Краљевина Црна Горa, Kraljevina Crna Gora) was a monarchy in southeastern Europe, present-day Montenegro, during the tumultuous period of time on the Balkan Peninsula leading up to and during World ...
. The Ottoman forces led by Hasan Riza Pasha and Esad Pasha had resisted for seven months the surrounding of the town by Montenegrin forces and their Serbian allies. Esad (Hasan had previously been mysteriously killed by Esad Pasha Toptani in an ambush inside the town) finally surrendered to Montenegro in April 1913, after Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
suffered a high death toll with more than 10,000 casualties. Edith Durham
Edith Durham, (8 December 1863 – 15 November 1944) was a British artist, anthropologist and writer who is best known for her anthropological accounts of life in Albania in the early 20th century. Her advocacy on behalf of the Albanian cause a ...
also notes the cruelties suffered at the hand of Montenegrins in the wake of October 1913: "Thousands of refugees arriving from Djakovo and neighbourhood. Victims of Montenegro. My position was indescribably painful, for I had no funds left, and women came to me crying: 'If you will not feed my child, throw it in the river. I cannot see it starve.'" Montenegro was compelled to leave the city to the new country of Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
in May 1913, in accordance with the London Conference of Ambassadors.
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Montenegrin forces again occupied Shkodër on 27 June 1915. In January 1916, Shkodër was taken over by Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
and was the centre of the zone of their occupation. When the war ended on 11 November 1918, French forces occupied Shkodër as well as other regions with sizable Albanian populations. After World War I, the international military administration of Albania was temporarily located in Shkodër, and in March 1920, Shkodër was put under the administration of the national government of Tirana. In the second half of 1920, Shkodër resisted another threat, the military intervention of the forces of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
.
Shkodër was the centre of democratic movements of the years 1921–1924. The democratic opposition won the majority of votes for the Constitutional Assembly, and on 31 May 1924, the democratic forces took over the town and from Shkodër headed to Tirana. From 1924 to 1939, Shkodër had a slow industrial development, small factories that produced food, textile and cement were opened. From 43 of such in 1924, the number rose to 70 in 1938. In 1924, Shkodër had 20,000 inhabitants, the number grew to 29,000 in 1938. During September 1928, Albania was proclaimed a monarchy by King Zog I
Zog I ( sq, Naltmadhnija e tij Zogu I, Mbreti i Shqiptarëve, ; 8 October 18959 April 1961), born Ahmed Muhtar bey Zogolli, taking the name Ahmet Zogu in 1922, was the leader of Albania from 1922 to 1939. At age 27, he first served as Albania's ...
. He was a self-made Muslim monarch and the king of all Albanians until 1939. After 1939, Zog went into exile and Victor Emmanuel III
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to:
* Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname
Arts and entertainment
Film
* ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film
* ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French shor ...
became the king of the Albanians. Shortly after World War II, Emmanuel was formally abdicated in 1946. In 1945, Enver Hoxha established communism in Albania.
Shkodër was the seat of a Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
archbishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associa ...
and had a number of religious schools. The first laic school was opened here in 1913, and the State Gymnasium was opened in 1922. It was the centre of many cultural associations. In sports Shkodër was the first city in Albania to constitute a sports association, the "Vllaznia" (brotherhood). Vllaznia Shkodër is the oldest sport club in Albania.
During the early 1990s, Shkodër was once again a major centre, this time of the democratic movement that finally brought to an end the communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
regime established by Enver Hoxha. In the later 2000s (decade), the city experiences a rebirth as main streets are being paved, buildings painted and streets renamed. In December 2010, Shkodër and the surrounding region was hit by probably the worst flooding in the last 100 years. In 2011, a new swing bridge
A swing bridge (or swing span bridge) is a movable bridge that has as its primary structural support a vertical locating pin and support ring, usually at or near to its center of gravity, about which the swing span (turning span) can then pi ...
over the Buna River
The Bojana ( cnr, Бојана), also known as the Buna ( sq, Bunë), is a river in Albania and Montenegro which flows into the Adriatic Sea. An outflow of Lake Skadar, measured from the source of the lake's longest tributary, the Morača, t ...
was constructed, thus replacing the old bridge nearby.
Geography
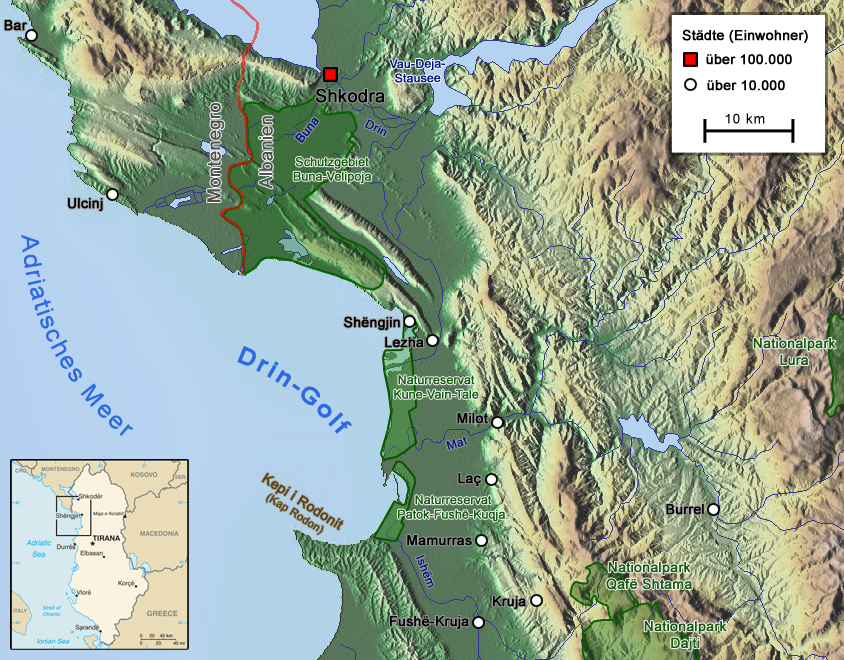
 Shkodër extends strategically on the Mbishkodra Plain between the
Shkodër extends strategically on the Mbishkodra Plain between the Lake of Shkodër
Lake Skadar ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, Скадарско језеро, Skadarsko jezero, ; sq, Liqeni i Shkodrës, ) also called Lake Scutari, Lake Shkodër and Lake Shkodra lies on the border of Albania and Montenegro, and is the largest lake in Southern ...
and the foothills of the Albanian Alps
The Accursed Mountains ( sq, Bjeshkët e Nemuna; sh-Cyrl-Latn, Проклетије, Prokletije, ; both translated as "Cursed Mountains"), also known as the Albanian Alps ( sq, Alpet Shqiptare), are a mountain group in the western part of the B ...
, which forms the southern continuation of the Dinaric Alps
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herz ...
. The northeast of the city is dominated by Mount Maranaj standing at above the Adriatic. Shkodër is trapped on three sides by Kir in the east, Drin in the south and Buna in the west. Rising from the Lake of Shkodër, Buna flows into the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, forming the border with Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. The river joins the Drin for approximately southwest of the city. In the east, Shkodër is bordered by Kir, which originates from the north flowing also into the Drin, that surrounds Shkodër in the south. The area of the municipality of Shkodër is ; the area of the municipal unit of Shkodër (the city proper) is .
Lake Shkodër
Lake Skadar ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, Скадарско језеро, Skadarsko jezero, ; sq, Liqeni i Shkodrës, ) also called Lake Scutari, Lake Shkodër and Lake Shkodra lies on the border of Albania and Montenegro, and is the largest lake in Southern ...
lies in the west of the city and forms the frontier of Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. The lake became the symbol of the stable and consistent economic and social divide of the city. Although, the lake is the largest lake in Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern regions of Europe, region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countrie ...
and an important habitat for various animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
and plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
species. Further, the Albanian section has been designated as a nature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
. In 1996, it also has been recognised as a wetland of international importance by designation under the Ramsar Convention. River Buna connects the lake with the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, while the Drin provides a link with Lake Ohrid in the southeast of Albania.Pešić V. & Glöer P. (2013). "A new freshwater snail genus (Hydrobiidae, Gastropoda) from Montenegro, with a discussion on gastropod diversity and endemism in Skadar Lake". ''ZooKeys'' 281: 69-90. It is a cryptodepression, filled by the river Morača and drained into the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
by the Buna.
Climate
Shköder has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (''Csa'') under the Köppen climate classification, that is almost wet enough in July to be a humid subtropical climate withcontinental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
influences. The average yearly temperature varies from to . Although, mean monthly temperature ranges between to in January and to in August. The average yearly precipitation is about , which makes the area one of the wettest in Europe.
Governance
Shkodër is a Municipalities of Albania, municipality governed by a Mayor–council government, mayor–council system with the mayor of Shkodër and the members of Shkodër Municipal Council responsible for the administration of Shkodër Municipality. The municipality is encompassed inShkodër County
Shkodër County ( sq, Qarku i Shkodrës) is a county in northwestern Albania, with the capital in Shkodër. The county spans and had a total population of 197,177 people as of 2021. The county borders on the counties of Lezhë, Kukës and the co ...
within the Northern Albania, Northern Region of Albania and consists of the administrative units of Ana e Malit, Bërdicë, Dajç, Shkodër, Dajç, Guri i Zi, Shkodër, Guri i Zi, Postribë, Pult, Rrethinat, Shalë, Albania, Shalë, Shosh, Albania, Shosh, Velipojë and Shkodër as its seat.
International relations
Shkodër is Sister city, twinned with: * Cetinje Municipality, Cetinje, Montenegro * Knin, Croatia * Pécs, Hungary * Üsküdar, Turkey * Zeytinburnu, TurkeyEconomy
 The main activities of the processing industry in Shkodra were the processing of tobacco and manufacture of cigarettes, production of preserved foods, sugar-based foods, soft and alcoholic drinks, and pasta, bread, rice and vegetable oil. The main activities of the textile industry were focused on garments and silk products. The city also had a wood-processing and paper-production plant. The most important mechanical engineering industries concerned wire manufacturing, elevator manufacturing, bus assembly and the Drini Plant.
According to the World Bank, Shkodër has had significant steps of improving the economy in recent years. In 2016, Shkodër ranked 8 among 22 cities in southeastern Europe.
As the largest city in northern
The main activities of the processing industry in Shkodra were the processing of tobacco and manufacture of cigarettes, production of preserved foods, sugar-based foods, soft and alcoholic drinks, and pasta, bread, rice and vegetable oil. The main activities of the textile industry were focused on garments and silk products. The city also had a wood-processing and paper-production plant. The most important mechanical engineering industries concerned wire manufacturing, elevator manufacturing, bus assembly and the Drini Plant.
According to the World Bank, Shkodër has had significant steps of improving the economy in recent years. In 2016, Shkodër ranked 8 among 22 cities in southeastern Europe.
As the largest city in northern Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, the city is the main road connection between the Albanian capital, Tirana and Montenegrin capital Podgorica
Podgorica (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Подгорица, ; Literal translation, lit. 'under the hill') is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Montenegro, largest city of Montenegro. The city was formerly known as Titograd ...
. The National Road 1 (Albania), SH1 leads to the Albanian–Montenegrin border at Han i Hotit border crossing. From Tirana at the Kamza Bypass northward, it passes through Fushë-Krujë, Fushë-Kruja, Milot, Lezhë, Lezha, Shkodra and Koplik. The road segment between Hani i Hotit at the Montenegrin border and Shkodra was completed in 2013 as a single carriageway standard. Shkodër Bypass started after the 2010 Albania floods. It was planned to incorporate a defensive dam against Shkodër Lake but works were abandoned a few years later. The road continues as a single carriageway down to Milot and contains some uncontrolled and dangerous entry and exit points. The SH5 starts from Shkodër to Morinë.
Demography
Shkodër is the List of cities and towns in Albania, fourth-most-populous city and Municipalities of Albania, fifth-most-populous municipality in Albania. As of the Demographics of Albania, 2011 census, the municipal unit of Shkodër had an estimated population of 77,075 of whom 37,630 were men and 39,445 women. The population of the municipality was 135,612 in 2011. The 20th century found Shkodër with a population of around 30,000 to 40,000. After Albanian Independence in 1912 the city numbered 23,000 inhabitants. Surveys in 1926–27 showed the city not to have experienced any relative growth, a figure of 23,784 inhabitants being given, which was the same figure as confirmed for the data of the population census of 1918, according to which Shkodër in 1918 had a population of 23,099. In 1918, the majority—two thirds—of the population was Muslim and one third was Catholic with a small community of Orthodox faith of Slavic and Vlah origin who immigrated to Shkodër during the 19th century. The city was divided into 12 mahallas, of which nine were inhabited by the Muslim and three by the Catholic population, and a separated bazaar. The Muslims were mostly to be found in the quarters on the west side of the city while the Catholics were living in the quarters on the east side of the city. The Orthodox population mostly lived within the Muslim quarters. The city of Shkodër was one of the most important centres for Islamic scholars and cultural and literary activity in Albania. Here stands the site of the only institution in Albania which provides high-level education in Arabic, Turkish and Islamic Studies. Shkodër is the centre of Roman Catholicism in Albania. The Christianity in Albania, Roman Catholic Church is represented in Shkodër by the episcopal seat of the Metropolitan Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Shkodër-Pult (Scutari-Pulati) in Shkodër Cathedral, with the current seat of the prelacy.Culture
 Shkodër is referred to as the capital and cultural cradle of
Shkodër is referred to as the capital and cultural cradle of northern Albania
Northern Albania ( sq, Shqipëria Veriore) is one of the three NUTS-2 Regions of Albania. This ethnographical territory is sometimes referred to as ''Ghegeria'' ( sq, Gegëria) which also includes parts of the Albanian-inhabited territories of ...
, also known as Gegëria, for having been the birthplace and home of List of people from Shkodër, notable individuals, who among others contributed to the Albanian Renaissance. Most of the inhabitants of Shkodër speak a distinctive dialect of northwestern Gheg Albanian that differs from other Albanian dialects. Shkodër has also a long tradition in the development of the urban music of Albania, marked by a characteristic use of instrumentation and a style of composition.
Rozafa Castle has played an instrumental role in Shkodër's history as the residence of Illyrians, Illyrian monarchs and a military stronghold. Located in the south of Shkodër, its foundations are associated with a legend about a woman who sacrificed herself so the castle could be constructed. Historical Museum of Shkodër is the most important museum in Shkodër and was founded to protect artefacts from all over the region of Shkodër, thus displaying their cultural and historical value. It is housed inside a monumental mansion from the 19th century, collectively known as the house of Oso Kuka. The expanded Marubi National Museum of Photography located on the Kolë Idromeno Street displays an extensive visual collection of Albanian social, cultural and political life beginning from 1850 on its galleries.
Shkodër's architecture and urban development are historically and culturally significant for northern Albania. It was and is inhabited by many people of different cultures and religions with many of them leaving mark of their cultural heritage. The Ebu Beker Mosque, Fatih Sultan Mehmet Mosque
The Fatih Sultan Mehmet Mosque ( sq, Xhamia e Sulltan Mehmet Fatihut), also known as the Fatih Mosque ( sq, Xhamia e Fatihut), is a 13th-century building. It is within the Rozafa Castle near Shkodër, Albania. It was built by the Ottoman Empir ...
, Franciscan Church of Shkodër, Franciscan Church, Lead Mosque, Shkodër, Lead Mosque, Nativity Cathedral, Shkodër, Nativity Cathedral and St. Stephen's Cathedral, Shkodër, St. Stephen's Cathedral are the most eminent religious buildings of Shkodër. Other major monuments include the Drisht Castle, Mesi Bridge and ruins of Shurdhah Island.
The KF Vllaznia Shkodër, Vllaznia club is a professional Albanian soccer team dedicated to Shkoder. It one of the most well-known teams in Albania.
See also
* List of settlements in Illyria * List of mayors of Shkodër * List of people from ShkodërNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
bashkiashkoder.gov.al
fficial Website {{DEFAULTSORT:Shkoder Shkodër, Cities in Albania Municipalities in Shkodër County Administrative units of Shkodër Gegëri Illyrian Albania Cities in ancient Illyria Territories of the Republic of Venice Former capitals of Montenegro Populated places established in the 4th century BC