Shasu on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
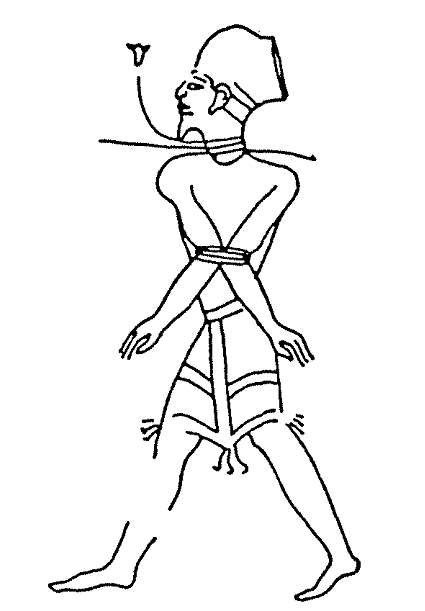 The Shasu ( from Egyptian ''šꜣsw'', probably pronounced ''Shaswe'') were Semitic-speaking cattle nomads in the
The Shasu ( from Egyptian ''šꜣsw'', probably pronounced ''Shaswe'') were Semitic-speaking cattle nomads in the
 Two Egyptian texts, one dated to the period of
Two Egyptian texts, one dated to the period of tA-M8-M23-w-i-i-h-V4-w
Regarding the name , Michael Astour observed that the "hieroglyphic rendering corresponds very precisely to the
 The Shasu ( from Egyptian ''šꜣsw'', probably pronounced ''Shaswe'') were Semitic-speaking cattle nomads in the
The Shasu ( from Egyptian ''šꜣsw'', probably pronounced ''Shaswe'') were Semitic-speaking cattle nomads in the Southern Levant
The Southern Levant is a Region, geographical region encompassing the southern half of the Levant. It corresponds approximately to modern-day Israel, State of Palestine, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southe ...
from the late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
to the Early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
or the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt
The Third Intermediate Period of ancient Egypt began with the death of Pharaoh Ramesses XI in 1077 BC, which ended the New Kingdom, and was eventually followed by the Late Period. Various points are offered as the beginning for the latt ...
. They were organized in clans under a tribal chieftain, and were described as brigands active from the Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, עמק יזרעאל, translit. ''ʿĒmeq Yīzrəʿēʿl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, مرج ابن عامر), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
to Ashkelon
Ashkelon or Ashqelon (; Hebrew: , , ; Philistine: ), also known as Ascalon (; Ancient Greek: , ; Arabic: , ), is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border with ...
and the Sinai
Sinai commonly refers to:
* Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Biblical Mount Sinai, the site in the Bible where Moses received the Law of God
Sinai may also refer to:
* Sinai, South Dakota, a place ...
.
Some scholars link the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
and YHWH
The Tetragrammaton (; ), or Tetragram, is the four-letter Hebrew theonym (transliterated as YHWH), the name of God in the Hebrew Bible. The four letters, written and read from right to left (in Hebrew), are ''yodh'', '' he'', ''waw'', and '' ...
with the Shasu.
Etymology
The name's etymon may be Egyptian ''šꜣsw'', which originally meant "those who move on foot". Levy, Adams, and Muniz report similar possibilities: an Egyptian word that means "to wander", and an alternative Semitic one with the meaning "to plunder".History
The earliest known reference to the Shasu occurs in a 15th-century BCE list of peoples in the Transjordan region. The name appears in a list of Egypt's enemies inscribed on column bases at the temple ofSoleb
Soleb is an ancient town in Nubia, in present-day Sudan. The site is located north of the third
cataract of the Nile, on the western side of the Nile. It was discovered and described by
Karl Richard Lepsius in 1844.
Necropolis
Soleb is also t ...
built by Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(.w), ''Amānəḥūtpū'' , "Amun is Satisfied"; Hellenized as Amenophis III), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different ...
. Copied later in the 13th century BCE either by Seti I
Menmaatre Seti I (or Sethos I in Greek) was the second pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the New Kingdom period, ruling c.1294 or 1290 BC to 1279 BC. He was the son of Ramesses I and Sitre, and the father of Ramesses II.
The ...
or by Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, wikt:rꜥ-ms-sw, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is oft ...
at Amarah-West, the list mentions six groups of Shasu: the Shasu of '' S'rr'', the Shasu of ''Rbn'', the Shasu of ''Sm't'', the Shasu of ''Wrbr'', the Shasu of ''Yhw'', and the Shasu of ''Pysps''.
Shasu of Yhw
 Two Egyptian texts, one dated to the period of
Two Egyptian texts, one dated to the period of Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(.w), ''Amānəḥūtpū'' , "Amun is Satisfied"; Hellenized as Amenophis III), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different ...
(14th century BCE), the other to the age of Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, wikt:rꜥ-ms-sw, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is oft ...
(13th century BCE), refer to , i.e. "''yhwꜣw'' in the land of the Shasu", in which ' (also rendered as ' or ') or ''Yahu'', is a toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
.
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
tetragrammaton YHWH
The Tetragrammaton (; ), or Tetragram, is the four-letter Hebrew theonym (transliterated as YHWH), the name of God in the Hebrew Bible. The four letters, written and read from right to left (in Hebrew), are ''yodh'', '' he'', ''waw'', and '' ...
, or Yahweh
Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he posse ...
, and antedates the hitherto oldest occurrence of that divine name – on the Moabite Stone – by over five hundred years." K. Van Der Toorn concludes: "By the 14th century BC, before the cult of Yahweh had reached Israel, groups of Edom
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ...
ites and Midian
Midian (; he, מִדְיָן ''Mīḏyān'' ; ar, مَدْيَن, Madyan; grc-gre, Μαδιάμ, ''Madiam'') is a geographical place mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and Quran. William G. Dever states that biblical Midian was in the "northwest Ar ...
ites worshipped Yahweh as their god."
Donald B. Redford
Donald Bruce Redford (born September 2, 1934) is a Canadian Egyptologist and archaeologist, currently Professor of Classics and Ancient Mediterranean Studies at Pennsylvania State University. He is married to Susan Redford, who is also an Egyptolo ...
has argued that the earliest Israelites, semi-nomadic highlanders in central Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
mentioned on the Merneptah Stele
The Merneptah Stele, also known as the Israel Stele or the Victory Stele of Merneptah, is an inscription by Merneptah, a pharaoh in ancient Egypt who reigned from 1213–1203 BCE. Discovered by Flinders Petrie at Thebes in 1896, it is now hous ...
at the end of the 13th century BCE, are to be identified as a Shasu enclave. Since later Biblical tradition portrays Yahweh "coming forth from Seʿir",Book of Judges
The Book of Judges (, ') is the seventh book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. In the narrative of the Hebrew Bible, it covers the time between the conquest described in the Book of Joshua and the establishment of a kingdom i ...
, 5:4 and Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy ( grc, Δευτερονόμιον, Deuteronómion, second law) is the fifth and last book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called (Hebrew: hbo, , Dəḇārīm, hewords Moses.html"_;"title="f_Moses">f_Moseslabel=none)_and_th ...
, 33:2 the Shasu, originally from Moab
Moab ''Mōáb''; Assyrian: 𒈬𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Mu'abâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀
''Ma'bâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒀊 ''Ma'ab''; Egyptian: 𓈗𓇋𓃀𓅱𓈉 ''Mū'ībū'', name=, group= () is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territo ...
and northern Edom/Seʿir, went on to form one major element in the amalgam that would constitute the "Israel" which later established the Kingdom of Israel. Per his own analysis of the el-Amarna letters, Anson Rainey
Anson Frank Rainey (January 11, 1930 – February 19, 2011) was professor emeritus of ancient Near Eastern cultures and Semitic linguistics at Tel Aviv University. He is known in particular for contributions to the study of the Amarna table ...
concluded that the description of the Shasu best fits that of the early Israelites. If this identification is correct, these Israelites/Shasu would have settled in the uplands in small villages with buildings similar to contemporary Canaanite structures towards the end of the 13th century BCE.
Objections exist to this proposed link between the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
and the Shasu, given that the group in the Merneptah reliefs identified with the Israelites are not described or depicted as Shasu (see Merneptah Stele § Karnak reliefs). The Shasu are usually depicted hieroglyphically with a determinative
A determinative, also known as a taxogram or semagram, is an ideogram used to mark semantic categories of words in logographic scripts which helps to disambiguate interpretation. They have no direct counterpart in spoken language, though they may ...
indicating a land, not a people; the most frequent designation for the "foes of Shasu" is the hill-country determinative. Thus they are differentiated from the Canaanites, who are defending the fortified cities of Ashkelon, Gezer
Gezer, or Tel Gezer ( he, גֶּזֶר), in ar, تل الجزر – Tell Jezar or Tell el-Jezari is an archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (eithe ...
, and Yenoam; and from Israel, which is determined as a people, though not necessarily as a socio-ethnic group. Scholars point out that Egyptian scribes tended to bundle up "rather disparate groups of people within a single artificially unifying rubric."
Frank J. Yurco
Frank J. Yurco (July 31, 1944 – February 6, 2004) was an Egyptologist from Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, ...
and Michael G. Hasel would distinguish the Shasu in Merneptah's Karnak reliefs from the people of Israel since they wear different clothing and hairstyles, and are determined differently by Egyptian scribes. Lawrence Stager
Lawrence E. "Larry" Stager (January 5, 1943 – December 29, 2017) was an American archaeologist and academic, specialising in Syro-Palestinian archaeology and Biblical archaeology. He was the Dorot Professor of the Archaeology of Israel in ...
also objected to identifying Merneptah's Shasu with Israelites, since the Shasu are shown dressed differently from the Israelites, who are dressed and hairstyled like the Canaanites.
The usefulness of the determinatives has been called into question, though, as in Egyptian writings, including the Merneptah Stele, determinatives are used arbitrarily. Gösta Werner Ahlström countered Stager's objection by arguing that the contrasting depictions are because the Shasu were the nomads, while the Israelites were sedentary, and added: "The Shasu that later settled in the hills became known as Israelites because they settled in the territory of Israel".
Moreover, the hill-country determinative is not always used for Shasu, with the Egyptologist Thomas Schneider connecting references to "Yah", believed to be an abbreviated form of the Tetragrammaton, with the writings in the Shasu-sequence at Soleb and Amarah-West.
In an Egyptian Book of the Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom ...
papyrus from the late 18th or 19th dynasty, Schneider identifies a Northwest Semitic
Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic language, Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite ...
theophoric name
A theophoric name (from Greek: , ''theophoros'', literally "bearing or carrying a god") embeds the word equivalent of 'god' or God's name in a person's name, reflecting something about the character of the person so named in relation to that deit ...
''‘adōnī-rō‘ē-yāh'', meaning “My lord is the shepherd of Yah”, which would be the first documented occurrence of the god Yahweh in his function as a shepherd of Yah.
See also
*Habiru
Habiru (sometimes written as Hapiru, and more accurately as ʿApiru, meaning "dusty, dirty"; Sumerian: 𒊓𒄤, ''sagaz''; Akkadian: 𒄩𒁉𒊒, ''ḫabiru'' or ''ʿaperu'') is a term used in 2nd-millennium BCE texts throughout the Fertile C ...
* Shutu
Shutu or Sutu is the name given in ancient Akkadian language sources to certain nomadic groups of the Trans-Jordanian highlands, extending deep into Mesopotamia and Southern Iraq. Many scholars have speculated that "Shutu" may be a variant of ...
* Irsu
Irsu ( egy, jr- sw, "he who made himself"; alternatively Su) is the name used in Papyrus Harris I to designate a Khasu who became overlord of a group of local rulers nominally under Egyptian control, at a time of unrest between the Nineteenth a ...
* Iah
Iah ( Egyptian: ''jꜥḥ'', Coptic ) is a lunar deity in ancient Egyptian religion. The word ''jꜥḥ'' simply means "Moon". It is also transcribed as ''Yah'', ''Jah'', or ''Aah''.
Worship
By the New Kingdom (16th century to 11th century ...
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Refend Foreign contacts of ancient Egypt Semitic-speaking peoples Ancient peoples of the Near East Ancient Levant Nomadic groups in Eurasia Third Intermediate Period of Egypt