Septimius Severus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day
 Severus sought a public career in
Severus sought a public career in
 About 175, Septimius Severus, in his early thirties at the time, contracted his first marriage, to
About 175, Septimius Severus, in his early thirties at the time, contracted his first marriage, to
LXXIX.30
Bassianus accepted Severus' marriage proposal in early 187, and in the summer the couple married in Lugdunum (modern-day
 In 191, on the advice of Quintus Aemilius Laetus, prefect of the Praetorian Guard,
In 191, on the advice of Quintus Aemilius Laetus, prefect of the Praetorian Guard,
Roman History
', LXXV.1.1–2Birley (1999), p. 113. The legions of

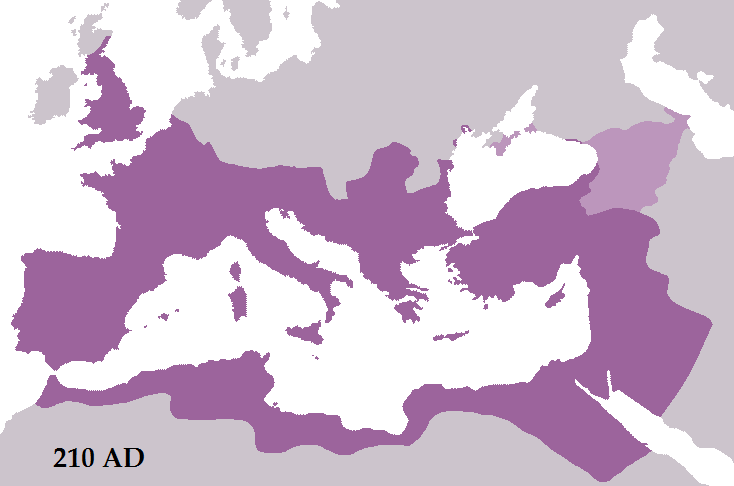
 In early 197 Severus left Rome and sailed to the east. He embarked at Brundisium and probably landed at the port of Aegeae in
In early 197 Severus left Rome and sailed to the east. He embarked at Brundisium and probably landed at the port of Aegeae in
Handbook to Life in Ancient Rome
', p. 68 Around 197 he increased the number of legions from 30 to 33, with the introduction of the three new legions: I, II and III ''Parthica''. He garrisoned
Historia Augusta
', Septimius Severus, 17.1 that punished conversion to Judaism and Christianity. A number of
 In late 202 Severus launched a campaign in the province of Africa. The '' legatus legionis'' or commander of Legio III Augusta, Quintus Anicius Faustus, had been fighting against the Garamantes along the '' Limes Tripolitanus'' for five years. He captured several settlements such as Cydamus, Gholaia, Garbia and their capital Garama—over south of Leptis Magna. The province of
In late 202 Severus launched a campaign in the province of Africa. The '' legatus legionis'' or commander of Legio III Augusta, Quintus Anicius Faustus, had been fighting against the Garamantes along the '' Limes Tripolitanus'' for five years. He captured several settlements such as Cydamus, Gholaia, Garbia and their capital Garama—over south of Leptis Magna. The province of


 The Roman Empire reached its greatest extent under his reign—over million square kilometres. David L. Kennedy, Derrick Riley (2012)
The Roman Empire reached its greatest extent under his reign—over million square kilometres. David L. Kennedy, Derrick Riley (2012)
''Rome's Desert Frontiers'', page 13
,
''An Introduction to the Ancient World'', page 272
,
Life of Septimius Severus
(''Historia Augusta'' at LacusCurtius: Latin text and English translation)
an
of
Septimius Severus on Ancient History Encyclopedia
Online encyclopaedia of Roman emperors
Septimius Severus in Scotland
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Severus, Septimius 145 births 211 deaths 2nd-century Roman emperors 3rd-century Roman emperors 2nd-century Punic people 3rd-century Punic people Imperial Roman consuls Roman governors of Gallia Lugdunensis Severan dynasty Ancient Romans in Britain Septimii Deified Roman emperors Romans from Africa Ancient Libyans People of the Roman–Parthian Wars Burials at the Castel Sant'Angelo Roman pharaohs
Al-Khums
Al-Khums or Khoms ( ar, الخمس) is a city, port and the de jure capital of the Murqub District on the Mediterranean coast of Libya with an estimated population of around 202,000. The population at the 1984 census was 38,174. Between 1983 an ...
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Su ...
) in the Roman province of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. As a young man he advanced through the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
and Commodus. Severus seized power after the death of the emperor Pertinax in 193 during the Year of the Five Emperors.
After deposing and killing the incumbent emperor Didius Julianus
Marcus Didius Julianus (; 29 January 133 or 137 – 2 June 193) was Roman emperor for nine weeks from March to June 193, during the Year of the Five Emperors. Julianus had a promising political career, governing several provinces, including Da ...
, Severus fought his rival claimants, the Roman generals Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was Roman Emperor from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a riva ...
and Clodius Albinus. Niger was defeated in 194 at the Battle of Issus in Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian language, Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from th ...
. Later that year Severus waged a short punitive campaign beyond the eastern frontier, annexing the Kingdom of Osroene as a new province. Severus defeated Albinus three years later at the Battle of Lugdunum in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
. Following the consolidation of his rule over the western provinces, Severus waged another brief, more successful war in the east against the Parthian Empire, sacking their capital Ctesiphon in 197 and expanding the eastern frontier to the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
. He then enlarged and fortified the ''Limes Arabicus
The ''Limes Arabicus'' was a desert frontier of the Roman Empire, running north from its start in the province of Arabia Petraea. It ran northeast from the Gulf of Aqaba for about at its greatest extent, reaching northern Syria and forming part ...
'' in Arabia Petraea. In 202, he campaigned in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, ...
against the Garamantes, capturing their capital Garama and expanding the '' Limes Tripolitanus'' along the southern desert frontier of the empire.
He proclaimed as ''augusti
''Augustus'' (plural ''Augusti''; , ; "majestic", "great" or "venerable") was an ancient Roman title given as both name and title to Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus (often referred to simply as Augustus), Rome's first Emperor. On his death, it ...
'' (co-emperors) his elder son Caracalla in 198 and his younger son Geta in 209, both born of his second wife Julia Domna. Severus travelled to Britain in 208, strengthening Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. ...
and reoccupying the Antonine Wall. In 209 he invaded Caledonia (modern Scotland) with an army of 50,000 men but his ambitions were cut short when he fell fatally ill of an infectious disease in late 210. He died in early 211 at Eboracum (today York, England), and was succeeded by his sons, who were advised by their mother and his powerful widow, Julia Domna, thus founding the Severan dynasty. It was the last dynasty of the Roman Empire before the Crisis of the Third Century.
Early life
Family and education
Born on 11 April 145 at Leptis Magna (in present-dayLibya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Su ...
) as the son of Publius Septimius Geta and Fulvia Pia
Publius Septimius Geta (fl. 2nd century, c. 110 – 171) was the father of the emperor Lucius Septimius Severus, father-in-law of the Roman empress Julia Domna and the paternal grandfather of the Roman emperors Caracalla and Geta. Besides mention ...
, Septimius Severus came from a wealthy and distinguished family of equestrian rank. Severus had Italic and Punic ancestry; the Roman ancestry came from his mother's side, while his Punic ancestry came from his father's side.Birley (1999), pp. 212–213. Due to his family background on his father's side he is considered the first provincial emperor as he was the first emperor not only born in the provinces but also into a provincial family of non-Italian origin. Severus' father, an obscure provincial, held no major political status, but he had two cousins, Publius Septimius Aper and Gaius Septimius Severus, who served as consuls under the emperor Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
. His mother's ancestors had moved from Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
to North Africa; they belonged to the ''gens'' Fulvia, an Italian patrician family that originated in Tusculum.
Septimius Severus had two siblings: an elder brother, Publius Septimius Geta; and a younger sister, Septimia Octavilla. Severus' maternal cousin was the praetorian prefect
The praetorian prefect ( la, praefectus praetorio, el, ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders be ...
and consul Gaius Fulvius Plautianus.Birley (1999), pp. 216–217. Septimius Severus grew up in Leptis Magna. He spoke the local Punic language fluently, but he was also educated in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
and Greek, which he spoke with a slight accent. Little else is known of the young Severus' education but, according to Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, the boy had been eager for more education than he actually received. Presumably, Severus received lessons in oratory: at the age of 17, he gave his first public speech.
Public service
 Severus sought a public career in
Severus sought a public career in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
in around 162. At the recommendation of his relative Gaius Septimius Severus, the emperor Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
() granted him entry into the senatorial ranks. Membership in the senatorial order was a prerequisite to attain positions within the '' cursus honorum'' and to gain entry into the Roman Senate. Nevertheless, it appears that Severus' career during the 160s met with some difficulties.Birley (1999), p. 40.
It is likely that he served as a '' vigintivir'' in Rome, overseeing road maintenance in or near the city, and he may have appeared in court as an advocate. At the time of Marcus Aurelius, he was the State Attorney (''Advocatus fisci''). However, he omitted the military tribunate from the ''cursus honorum'' and had to delay his quaestor
A ( , , ; "investigator") was a public official in Ancient Rome. There were various types of quaestors, with the title used to describe greatly different offices at different times.
In the Roman Republic, quaestors were elected officials who ...
ship until he had reached the required minimum age of 25. To make matters worse, the Antonine Plague swept through the capital in 166.Birley (1999), p. 45.
With his career at a halt, Severus decided to temporarily return to Leptis, where the climate was healthier. According to the ''Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the sim ...
'', a usually unreliable source, he was prosecuted for adultery
Adultery (from Latin ''adulterium'') is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and leg ...
during this time but the case was ultimately dismissed. At the end of 169, Severus was of the required age to become a quaestor and journeyed back to Rome. On 5December, he took office and was officially enrolled in the Roman Senate. Between 170 and 180 his activities went largely unrecorded, in spite of the fact that he occupied an impressive number of posts in quick succession. The Antonine Plague had thinned the senatorial ranks and, with capable men now in short supply, Severus' career advanced more steadily than it otherwise might have.
The sudden death of his father necessitated another return to Leptis Magna to settle family affairs. Before he was able to leave Africa, Mauri tribesmen invaded southern Spain. Control of the province was handed over to the emperor, while the Senate gained temporary control of Sardinia as compensation. Thus, Septimius Severus spent the remainder of his second term as quaestor on the island of Sardinia.
In 173, Severus' kinsman Gaius Septimius Severus was appointed proconsul of the Province of Africa. The elder Severus chose his cousin as one of his two '' legati pro praetore'', a senior military appointment. Following the end of this term, Septimius Severus returned to Rome, taking up office as tribune of the plebs, a senior legislative position, with the distinction of being the ''candidatus'' of the emperor.Birley (1999), p. 52.
Marriages
 About 175, Septimius Severus, in his early thirties at the time, contracted his first marriage, to
About 175, Septimius Severus, in his early thirties at the time, contracted his first marriage, to Paccia Marciana
Paccia Marciana was the first wife of Septimius Severus, who later became Roman emperor. They married around 175 and she died of natural causes around 186.
Name and marriage
Her name shows her links to two Roman gentes, the Paccia and the Mar ...
, a woman from Leptis Magna. He probably met her during his tenure as legate under his uncle. Marciana's name suggests Punic or Libyan origin, but nothing else is known of her. Septimius Severus does not mention her in his autobiography, though he commemorated her with statues when he became emperor. The unreliable ''Historia Augusta'' claims that Marciana and Severus had two daughters, but no other attestation of them has survived. It appears that the marriage produced no surviving children, despite lasting for more than ten years.
Marciana died of natural causes around 186.Birley (1999), p. 75. Septimius Severus, now in his forties, childless and eager to remarry, began enquiring into the horoscopes of prospective brides. The ''Historia Augusta'' relates that he heard of a woman in Syria of whom it had been foretold that she would marry a king, and so Severus sought her as his wife.Birley (1999), p. 71. This woman was an Emesene Syrian
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indi ...
named Julia Domna. Her father, Julius Bassianus, descended from the Arab Emesene dynasty
The Emesene (or Emesan) dynasty, also called the Sampsigeramids or the Sampsigerami or the House of Sampsigeramus ( ar, آل شمسيغرام, translit=ʾĀl Šamsīġirām), were a Roman client dynasty of Arab priest-kings known to have ruled by ...
and served as a high priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious caste.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many gods rever ...
to the local cult of the sun god Elagabal
Elagabalus (), Aelagabalus, Heliogabalus, () or simply Elagabal (Aramaic: 𐡁𐡋𐡄𐡂𐡀𐡋 ''ʾĕlāhgabāl'' or 𐡁𐡋𐡄𐡀𐡂𐡀𐡋 ''ʾĕlāhaʾgabāl''; Arabic: إله الجبل ''Ilah al-Jabal'', "mountain god") ...
.Birley (1999), p. 72. Domna's older sister, Julia Maesa, would become the grandmother of the future emperors Elagabalus and Alexander Severus.Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'LXXIX.30
Bassianus accepted Severus' marriage proposal in early 187, and in the summer the couple married in Lugdunum (modern-day
Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of ...
, France), of which Severus was the governor. The marriage proved happy, and Severus cherished Julia and her political opinions. Julia built "the most splendid reputation" by applying herself to letters and philosophy. They had two sons, Lucius Septimius Bassianus (later nicknamed Caracalla, born 4April 188 in Lugdunum) and Publius Septimius Geta (born 7March 189 in Rome).Birley (1999), pp. 76–77.
Rise to power
emperor Commodus
Commodus (; 31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was a Roman emperor who ruled from 177 to 192. He served jointly with his father Marcus Aurelius from 176 until the latter's death in 180, and thereafter he reigned alone until his assassination. ...
appointed Severus as governor of Pannonia Superior. At around this time he is described by the classicist Kyle Harper as being "a middling senator of modest physical stature and unacceptional accomlishment". Commodus was assassinated the following year. Pertinax was acclaimed emperor, but he was then killed by the Praetorian Guard in early 193. In response to the murder of Pertinax, Severus' legion ''XIV Gemina'' acclaimed him emperor at Carnuntum
Carnuntum ( according to Ptolemy) was a Roman legionary fortress ( la, castra legionis) and headquarters of the Pannonian fleet from 50 AD. After the 1st century, it was capital of the Pannonia Superior province. It also became a large ...
. Nearby legions, such as ''X Gemina'' at Vindobona, soon followed suit. Having assembled an army, Severus hurried to Italy.
Pertinax's successor in Rome, Didius Julianus
Marcus Didius Julianus (; 29 January 133 or 137 – 2 June 193) was Roman emperor for nine weeks from March to June 193, during the Year of the Five Emperors. Julianus had a promising political career, governing several provinces, including Da ...
, had bought the emperorship in an auction. Julianus was condemned to death by the Senate and killed. Severus took possession of Rome without opposition. He executed Pertinax's murderers and dismissed the rest of the Praetorian Guard, filling its ranks with loyal troops from his own legions.Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, Roman History
', LXXV.1.1–2Birley (1999), p. 113. The legions of
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
had proclaimed Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was Roman Emperor from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a riva ...
emperor. At the same time Severus felt it reasonable to offer Clodius Albinus, the powerful governor of Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Gr ...
, who had probably supported Didius against him, the rank of Caesar, which implied some claim to the succession. With his rear safe, he moved to the East and crushed Niger's forces at the Battle of Issus (194). While campaigning against Byzantium, he ordered that the tomb of his fellow-Carthaginian Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
be covered with fine marble.
He devoted the following year to suppressing Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
and other Parthian vassals who had backed Niger. Afterwards, Severus declared his son Caracalla as his successor, which caused Albinus to be hailed emperor by his troops and to invade Gaul. After a short stay in Rome, Severus moved north to meet him. On 19February 197 at the Battle of Lugdunum, with an army of about 75,000 men, mostly composed of Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
n, Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
n and Dacian legions and a large number of auxiliaries, Severus defeated and killed Clodius Albinus, securing his full control over the empire.
Emperor

War against Parthia

 In early 197 Severus left Rome and sailed to the east. He embarked at Brundisium and probably landed at the port of Aegeae in
In early 197 Severus left Rome and sailed to the east. He embarked at Brundisium and probably landed at the port of Aegeae in Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian language, Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from th ...
, travelling on to Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
by land. He immediately gathered his army and crossed the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the ...
. Abgar IX, titular King of Osroene but essentially only the ruler of Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene ...
since the annexation of his kingdom as a Roman province, handed over his children as hostages and assisted Severus' expedition by providing archers. King Khosrov I of Armenia also sent hostages, money and gifts.
Severus travelled on to Nisibis, which his general Julius Laetus
The gens Julia (''gēns Iūlia'', ) was one of the most prominent patrician families in ancient Rome. Members of the gens attained the highest dignities of the state in the earliest times of the Republic. The first of the family to obtain the c ...
had prevented from falling into Parthian hands. Afterwards Severus returned to Syria to plan a more ambitious campaign. The following year he led another, more successful campaign against the Parthian Empire, reportedly in retaliation for the support it had given to Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was Roman Emperor from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a riva ...
. His legions sacked the Parthian royal city of Ctesiphon and he annexed the northern half of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
to the empire;Birley (1999), p. 153. Severus took the title ', following the example of Trajan. However, he was unable to capture the fortress of Hatra, even after two lengthy sieges—just like Trajan, who had tried nearly a century before. During his time in the east, though, Severus also expanded the ''Limes Arabicus
The ''Limes Arabicus'' was a desert frontier of the Roman Empire, running north from its start in the province of Arabia Petraea. It ran northeast from the Gulf of Aqaba for about at its greatest extent, reaching northern Syria and forming part ...
'', building new fortifications in the Arabian Desert from Basie to Dumatha.
Birley (1999), p. 134.
Relations with the Senate and People
Severus' relations with theSenate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
were never good. He was unpopular with them from the outset, having seized power with the help of the military, and he returned the sentiment. Severus ordered the execution of a large number of Senators on charges of corruption or conspiracy against him and replaced them with his favourites. Although his actions turned Rome more into a military dictatorship
A dictatorship is a form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, which holds governmental powers with few to no limitations on them. The leader of a dictatorship is called a dictator. Politics in a dictatorship a ...
, he was popular with the citizens of Rome, having stamped out the rampant corruption of Commodus' reign. When he returned from his victory over the Parthians, he erected the Arch of Septimius Severus in Rome.
According to Cassius Dio, however, after 197 Severus fell heavily under the influence of his Praetorian prefect, Gaius Fulvius Plautianus, who came to have almost total control of the imperial administration. At the same time, a bloody power crisis erupted between Plautianus and Julia Domna, Severus' influential and powerful wife, which had a relatively destructive effect on the centre of power. Plautianus' daughter, Fulvia Plautilla
Publia Fulvia Plautilla (c. 185/around 188/189 – 211) was the wife of the Roman emperor Caracalla, her paternal second cousin. After her father was condemned for treason, she was exiled and eventually killed, possibly on Caracalla's orders. ...
, was married to Severus' son, Caracalla. Plautianus' excessive power came to an end in 204, when he was denounced by the emperor's dying brother. In January 205 Julia Domna and Caracalla accused Plautianus of plotting to kill him and Severus. The powerful prefect was executed while he was trying to defend his case in front of the two emperors. One of the two following ''praefecti'' was the famous jurist Papinian
Aemilius Papinianus (; grc, Αἰμίλιος Παπινιανός; 142 CE–212 CE), simply rendered as Papinian () in English, was a celebrated Roman jurist, ''magister libellorum'', attorney general (''advocatus fisci'') and, after the dea ...
. Executions of senators did not stop: Cassius Dio records that many of them were put to death, some after being formally tried. After the assassination of Gaius Fulvius Plautianus in the rest of his reign, he relied more on the advice of his clever and educated wife, Julia Domna, in the administration of the empire.
Military reforms
Upon his arrival at Rome in 193, Severus discharged the Praetorian Guard, which had murdered Pertinax and had then auctioned the Roman Empire to Didius Julianus. Its members were stripped of their ceremonial armour and forbidden to come within miles of the city on pain of death. Severus replaced the old guard with 10 new cohorts recruited from veterans of his Danubian legions.Lesley Adkins and Roy A. Adkins, Both ProfessionalHandbook to Life in Ancient Rome
', p. 68 Around 197 he increased the number of legions from 30 to 33, with the introduction of the three new legions: I, II and III ''Parthica''. He garrisoned
Legio II Parthica
Legio II Parthica ("Parthian-conquering Second Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 197 by the emperor Septimius Severus (r. 193–211), for his campaign against the Parthian Empire, hence the '' cognomen'' ''Parthica ...
at Albanum, only from Rome. He gave his soldiers a donative of a thousand ''sesterces
The ''sestertius'' (plural ''sestertii''), or sesterce (plural sesterces), was an ancient Roman coin. During the Roman Republic it was a small, silver coin issued only on rare occasions. During the Roman Empire it was a large brass coin.
The na ...
'' (250 '' denarii'') each, and raised the annual wage for a soldier in the legions from 300 to 400 ''denarii''.
Severus was the first Roman emperor to station some of the imperial army in Italy. He realized that Rome needed a military central reserve with the capability to be sent anywhere.
Reputed persecution of Christians
At the beginning of Severus' reign, Trajan's policy toward the Christians was still in force. That is, Christians were only to be punished if they refused to worship the emperor and the gods, but they were not to be sought out. Therefore, persecution was inconsistent, local and sporadic. Faced with internal dissidence and external threats, Severus felt the need to promote religious harmony by promotingsyncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in t ...
. He, possibly, issued an edictHistoria Augusta
', Septimius Severus, 17.1 that punished conversion to Judaism and Christianity. A number of
persecution
Persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or group by another individual or group. The most common forms are religious persecution, racism, and political persecution, though there is naturally some overlap between these term ...
s of Christians occurred in the Roman Empire during his reign and are traditionally attributed to Severus by the early Christian community. This is based on the decree mentioned in the ''Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the sim ...
'', an unreliable mix of fact and fiction. Early church historian Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christ ...
described Severus as a persecutor. The Christian apologist Tertullian stated that Severus was well disposed towards Christians, employed a Christian as his personal physician and had personally intervened to save several high-born Christians known to him from the mob. Eusebius' description of Severus as a persecutor likely derives merely from the fact that numerous persecutions occurred during his reign, including those known in the '' Roman Martyrology'' as the martyrs of Madauros, Charalambos and Perpetua and Felicity in Roman-ruled Africa. These were probably the result of local persecutions rather than empire-wide actions or decrees by Severus.
Outfit
The choice of colours and attributes worn by the emperor is not trivial. The clothes are staged and have a very precise symbolism, easily understood by the Roman people. Purple and red are the main colours. Purple is a very expensive colour because it is very difficult to manufacture. It is also the colour associated with the God Jupiter. Red is the colour of the God of War, Mars, who is also worn by the Roman military. The Greek-inspired shoes are a symbol of tradition and preservation worn on special occasions. The shoes are adorned with a lion's head, a representation of Hercules, as if the emperor was supported by this popular hero in the eyes of the Romans. The emperor is thus a continuator of Roman history, a guarantor of traditions. The subarmalis is a gold and purple support for the cuirass, and protects against the rubbing of the metal. The belt set with tiles represents several things: the institutions that the emperor leads, the homage to the gods, the character traits of the emperor. The cuirass worn by the emperor is magnified with gold details. We see Jupiter, who symbolizes the Roman power. Also shown is the winged Victory carrying two torches, a reminder of the stability of the empire. Another oft-repeated symbol is the jellyfish, which protects the wearer of the armour and ward off the evil eye. The paludamentum, folded over the shoulder, is a large rectangle of 5 to 7 metres, purple in colour, a mixture of silk and wool. A rare material because it was imported from the East, this makes it an exceptional outfit. This fabric is traditionally passed on from one emperor to another to enhance the legitimacy of one wearer to another. A bronze braided laurel wreath, overlaid with silver, the most common, as worn by generals during their triumphs. Those of the emperors are adorned with a rare rock crystal. No detail is left to chance.Military activity
Africa (202)
 In late 202 Severus launched a campaign in the province of Africa. The '' legatus legionis'' or commander of Legio III Augusta, Quintus Anicius Faustus, had been fighting against the Garamantes along the '' Limes Tripolitanus'' for five years. He captured several settlements such as Cydamus, Gholaia, Garbia and their capital Garama—over south of Leptis Magna. The province of
In late 202 Severus launched a campaign in the province of Africa. The '' legatus legionis'' or commander of Legio III Augusta, Quintus Anicius Faustus, had been fighting against the Garamantes along the '' Limes Tripolitanus'' for five years. He captured several settlements such as Cydamus, Gholaia, Garbia and their capital Garama—over south of Leptis Magna. The province of Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunis ...
was also enlarged: the empire annexed the settlements of Vescera, Castellum Dimmidi, Gemellae, Thabudeos and Thubunae. By 203 the entire southern frontier of Roman Africa had been dramatically expanded and re-fortified. Desert nomads could no longer safely raid the region's interior and escape back into the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
.
Britain (208)
In 208 Severus travelled to Britain with the intention of conquering Caledonia. Modern archaeological discoveries illuminate the scope and direction of his northern campaign.Birley, (1999) p. 180. Severus probably arrived in Britain with an army of over 40,000, considering some of the camps constructed during his campaign could house this number. He strengthenedHadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. ...
and reconquered the Southern Uplands up to the Antonine Wall, which was also enhanced. Severus built a camp south of the Antonine Wall at Trimontium, probably assembling his forces there. Supported and supplied by a strong naval force, Severus then thrust north with his army across the wall into Caledonian territory. Retracing the steps of Agricola of over a century before, Severus rebuilt and garrisoned many abandoned Roman forts along the east coast, such as Carpow.

Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
's account of the invasion reads:
By 210 Severus' campaigning had made significant gains, despite Caledonian guerrilla tactics and purportedly heavy Roman casualties. The Caledonians sued for peace, which Severus granted on condition they relinquish control of the Central Lowlands. This is evidenced by extensive Severan-era fortifications in the Central Lowlands. The Caledonians, short on supplies and feeling that their position was desperate, revolted later that year with the Maeatae. Severus prepared for another protracted campaign within Caledonia. He was now intent on exterminating the Caledonians, telling his soldiers: "Let no-one escape sheer destruction, no-one our hands, not even the babe in the womb of the mother, if it be male; let it nevertheless not escape sheer destruction."
Death (211)
Severus' campaign was cut short when he fell ill.Birley (1999), pp. 170–187. He withdrew to Eboracum (York) and died there in 211. Although his son Caracalla continued campaigning the following year, he soon settled for peace. The Romans never campaigned deep into Caledonia again. Shortly after this, the frontier was permanently withdrawn south to Hadrian's Wall. Severus is famously said to have given the advice to his sons: "Be harmonious, enrich the soldiers, scorn all others" before he died on 4 February 211. On his death, Severus was deified by the Senate and succeeded by his sons, Caracalla and Geta, who were advised by his wife Julia Domna. Severus was buried in theMausoleum of Hadrian
The Mausoleum of Hadrian, usually known as Castel Sant'Angelo (; English: ''Castle of the Holy Angel''), is a towering cylindrical building in Parco Adriano, Rome, Italy. It was initially commissioned by the Roman Emperor Hadrian as a mausoleum ...
in Rome.
Assessment and legacy

 The Roman Empire reached its greatest extent under his reign—over million square kilometres. David L. Kennedy, Derrick Riley (2012)
The Roman Empire reached its greatest extent under his reign—over million square kilometres. David L. Kennedy, Derrick Riley (2012)''Rome's Desert Frontiers'', page 13
,
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law, ...
R.J. van der Spek, Lukas De Blois (2008)''An Introduction to the Ancient World'', page 272
,
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law, ...
Edward Gibbon famously levelled a harsh indictment of Septimius Severus as a principal agent in the empire's decline. "The contemporaries of Severus, in the enjoyment of the peace and glory of his reign, forgave the cruelties by which it had been introduced. Posterity, who experienced the fatal effects of his maxims and example, justly considered him as the principal author of the decline of the Roman empire." According to Gibbon, "his daring ambition was never diverted from its steady course by the allurements of pleasure, the apprehension of danger, or the feelings of humanity." His enlargement of the Limes Tripolitanus secured Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, the agricultural base of the empire where he was born. His victory over the Parthian Empire was for a time decisive, securing Nisibis and Singara for the empire and establishing a ''status quo'' of Roman dominance in the region until 251. His policy of an expanded and better-rewarded army was criticised by his contemporaries Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
and Herodianus
Herodian or Herodianus ( el, Ἡρωδιανός) of Syria, sometimes referred to as "Herodian of Antioch" (c. 170 – c. 240), was a minor Roman civil servant who wrote a colourful history in Greek titled ''History of the Empire from the Death o ...
: in particular, they pointed out the increasing burden, in the form of taxes and services, the civilian population had to bear to maintain the new and better-paid army. The large and ongoing increase in military expenditure caused problems for all of his successors.
To maintain his enlarged military, he debased the Roman currency
Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction to the Republic, during the third century BC, well into Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, denomi ...
. Upon his accession he decreased the silver purity of the denarius
The denarius (, dēnāriī ) was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very ...
from 81.5% to 78.5%, although the silver weight actually increased, rising from 2.40 grams to 2.46 grams. Nevertheless, the following year he debased the denarius again because of rising military expenditures. The silver purity decreased from 78.5% to 64.5%—the silver weight dropping from 2.46 grams to 1.98 grams. In 196 he reduced the purity and silver weight of the denarius again, to 54% and 1.82 grams, respectively. Severus' currency debasement was the largest since the reign of Nero, compromising the long-term strength of the economy.
Severus was also distinguished for his buildings. Apart from the triumphal arch in the Roman Forum carrying his full name, he also built the Septizodium in Rome. He enriched his native city of Leptis Magna, including commissioning a triumphal arch on the occasion of his visit of 203.
Severan dynasty family tree
See also
* Bulla Felix * Septimia gens *Arcus Argentariorum
The Arcus Argentariorum (Latin: ''Arch of the Money-Changers''; in Italian: ''Arco degli Argentari''), is an ancient Roman arch that was partly incorporated in the seventh century into the western wall of the nearby church of San Giorgio al Velab ...
dedicated by the money changers of Rome to the Severan family.
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Mattingly, Harold & Edward A. Sydenham (1936) ''The Roman Imperial Coinage, vol. IV, part I, Pertinax to Geta'', London, Spink & Son. * *External links
Life of Septimius Severus
(''Historia Augusta'' at LacusCurtius: Latin text and English translation)
an
of
Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, covering the rise to power and reign of Septimius Severus
Septimius Severus on Ancient History Encyclopedia
Online encyclopaedia of Roman emperors
Septimius Severus in Scotland
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Severus, Septimius 145 births 211 deaths 2nd-century Roman emperors 3rd-century Roman emperors 2nd-century Punic people 3rd-century Punic people Imperial Roman consuls Roman governors of Gallia Lugdunensis Severan dynasty Ancient Romans in Britain Septimii Deified Roman emperors Romans from Africa Ancient Libyans People of the Roman–Parthian Wars Burials at the Castel Sant'Angelo Roman pharaohs