Seismic Experiment For Interior Structure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) is a
 While two seismometers were landed on Mars during the ''Viking'' missions in 1976, results were limited. SEIS/INSIGHT: One year prior launch for Seismic Discovery on Mars. Lognonne, Philippe; Banerdt, W. Bruce; Giardini, Domenico; Pike, W. Tom; Christensen, Ulli; Knapmeyer-Endrun, Brigitte; de Raucourt, Sebastien; Umland, Jeff; Hurst, Ken; Zweifel, Peter; Calcutt, Simon; Bierwirth, Marco; Mimoun, David; Pont, Gabriel; Verdier, Nicolas; Laudet, Philippe; Smrekar, Sue; Hoffman, Tom. 19th EGU General Assembly, EGU2017, proceedings from the conference held 23–28 April 2017 in Vienna, Austria., p.9978 Seismometers on both ''Viking'' spacecraft were mounted on the lander, which meant that it also picked up vibrations from various operations of the lander and caused by the wind. In addition, the ''
While two seismometers were landed on Mars during the ''Viking'' missions in 1976, results were limited. SEIS/INSIGHT: One year prior launch for Seismic Discovery on Mars. Lognonne, Philippe; Banerdt, W. Bruce; Giardini, Domenico; Pike, W. Tom; Christensen, Ulli; Knapmeyer-Endrun, Brigitte; de Raucourt, Sebastien; Umland, Jeff; Hurst, Ken; Zweifel, Peter; Calcutt, Simon; Bierwirth, Marco; Mimoun, David; Pont, Gabriel; Verdier, Nicolas; Laudet, Philippe; Smrekar, Sue; Hoffman, Tom. 19th EGU General Assembly, EGU2017, proceedings from the conference held 23–28 April 2017 in Vienna, Austria., p.9978 Seismometers on both ''Viking'' spacecraft were mounted on the lander, which meant that it also picked up vibrations from various operations of the lander and caused by the wind. In addition, the ''
(PDF). Mark P. Panning, Philippe Lognonne, W. Bruce Banerdt, Raphael Garcia, Matthew Golombek, et al. ''Space Science Reviews'' 16 November 2016. The SEIS instrument is deployed by the Instrument Deployment System, a robotic arm that can position the sensor directly on the surface. The instrument is supported by a suite of meteorological sensors (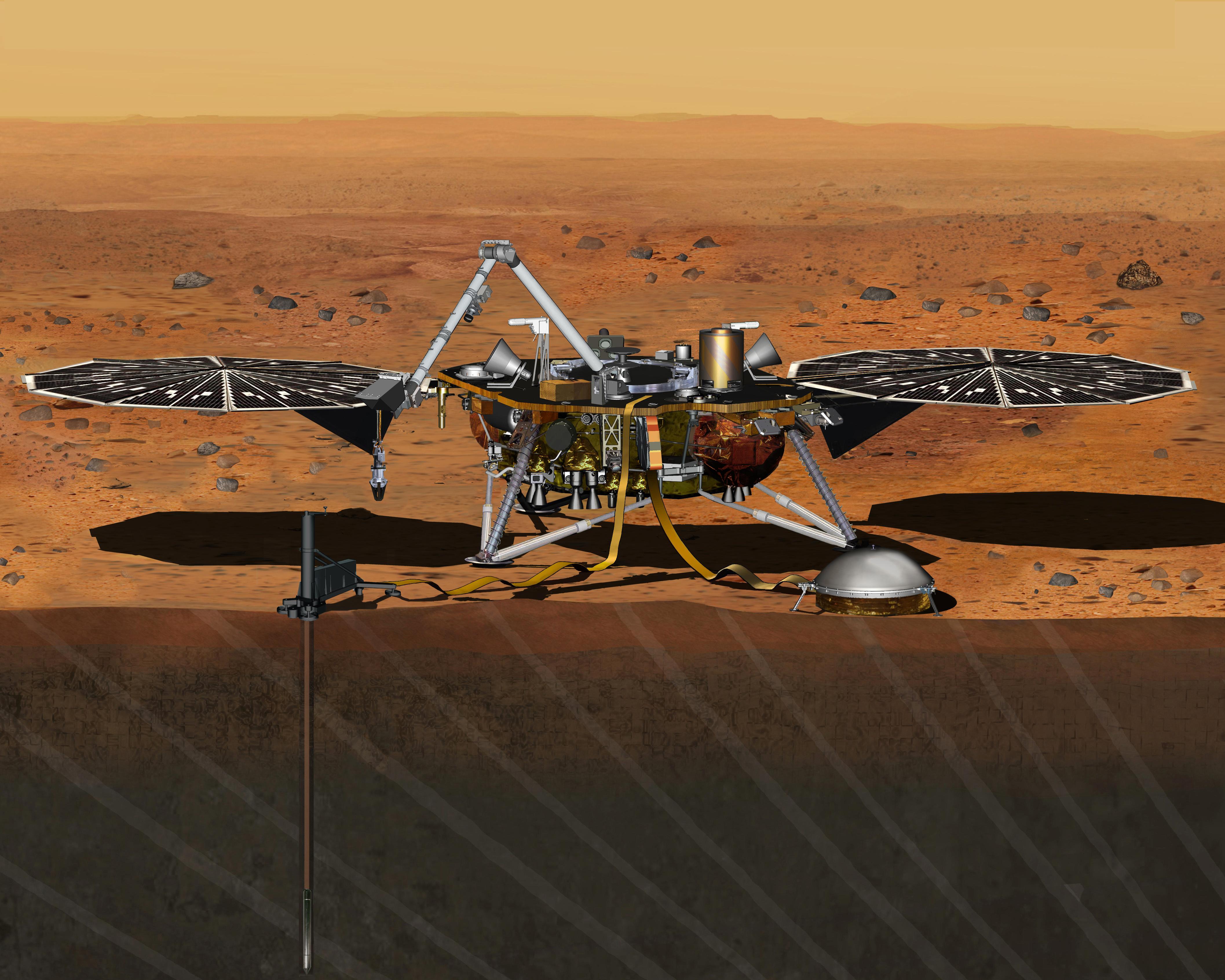 During the final integration of SEIS, several small leaks were found in the vacuum thermal enclosure. This forced the postponement of the ''InSight'' launch from 2016 to 2018, and the redesign of a new enclosure under the supervision of JPL. The cost of the delay was estimated to be .
During the final integration of SEIS, several small leaks were found in the vacuum thermal enclosure. This forced the postponement of the ''InSight'' launch from 2016 to 2018, and the redesign of a new enclosure under the supervision of JPL. The cost of the delay was estimated to be .

 During development, the power of multiple sites was noted, but one site offers a tremendous insight to the interior. With a single site, the location of a marsquake event can be constrained to the surface of a sphere, by measuring what are known as P-waves and S-waves.Geophysical Network Mission for MARS 2009
During development, the power of multiple sites was noted, but one site offers a tremendous insight to the interior. With a single site, the location of a marsquake event can be constrained to the surface of a sphere, by measuring what are known as P-waves and S-waves.Geophysical Network Mission for MARS 2009
/ref> There is a variety of single-site seismology techniques that can yield data, for example, the detection of an impact on the surface by a meteorite for which the location is identified. If Mars has large marsquakes, they may allow the deep interior to be determined. As the vibrations pass through the planet they are affected by the properties of the materials and its configuration. For example, the effect of tidal forces on Mars by Phobos, which should be about 10 mm, would be noticeably affected by a liquid Mars core. Even without any marsquake, it should be possible after about six months of observation to use this method to increase or decrease the likelihood Mars has a liquid core.
seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The outpu ...
and the primary scientific instrument on board the ''InSight
Insight is the understanding of a specific cause and effect within a particular context. The term insight can have several related meanings:
*a piece of information
*the act or result of understanding the inner nature of things or of seeing intui ...
'' Mars lander launched on 5 May 2018 for a landing on 26 November 2018; the instrument was deployed to the surface of Mars on 19 December. SEIS is expected to provide seismic measurements of marsquake
A marsquake is a quake which, much like an earthquake, would be a shaking of the surface or interior of the planet Mars as a result of the sudden release of energy in the planet's interior, such as the result of plate tectonics, which most quakes ...
s, enabling researchers to develop 3D structure maps of the deep interior. Better understanding the internal structure of Mars will lead to better understanding of the Earth, Moon, and rocky planetary bodies in general.
SEIS detected marsquakes in Cerberus Fossae in 2019.
On 24 December 2021, the seismometer for the InSight mission on Mars detected a large seismic event with a distinct signature. The event was caused by a meteor impact on the surface of Mars, which was confirmed by satellite observations of a newly formed 150-kilometer crater.
Overview
Mars flybys and landings to gather scientific data have been conducted since the 1960s, but quality seismological studies – which would provide detailed information about the interior of Mars – have yet to be performed in the 21st century. Only two astronomical bodies – the Earth and theMoon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
– have been studied in this way, and learning about Mars is hoped to contribute to understanding the geology of all rocky planetary bodies.
Other onboard instruments working in synergy with SEIS are the Temperature and Winds for InSight
Temperature and Winds for InSight (TWINS) is a NASA meteorological suite of instruments on board the ''InSight'' lander that landed on Mars on 26 November 2018. TWINS provides continuous wind and air temperature measurements to help understand t ...
module, the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package, and the Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment
Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment (RISE) is a radio science experiment onboard ''InSight'' Mars lander that will use the spacecraft communication system to provide precise measurements of Mars' rotation and wobble. RISE precisely tracks t ...
.
Earlier missions
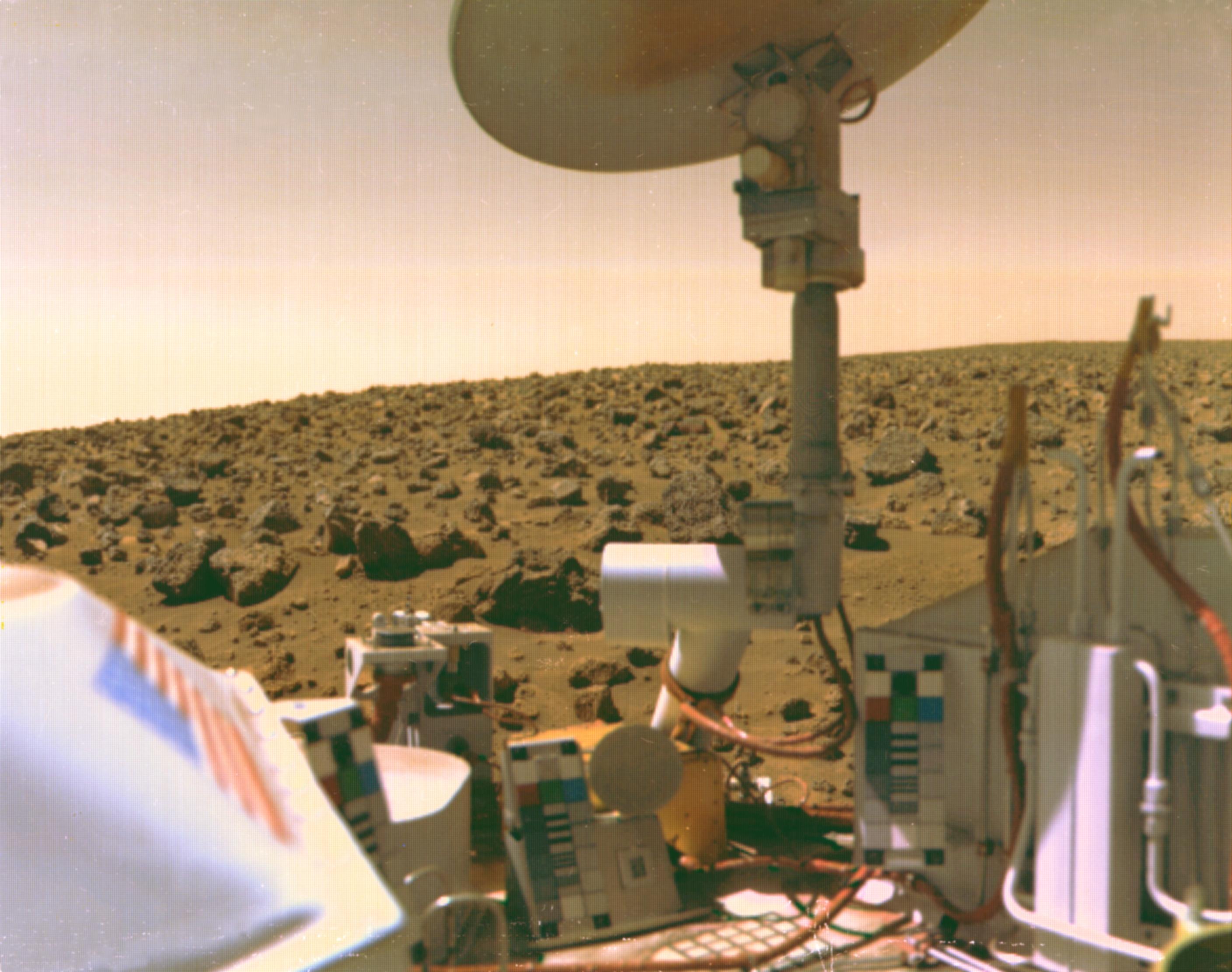
 While two seismometers were landed on Mars during the ''Viking'' missions in 1976, results were limited. SEIS/INSIGHT: One year prior launch for Seismic Discovery on Mars. Lognonne, Philippe; Banerdt, W. Bruce; Giardini, Domenico; Pike, W. Tom; Christensen, Ulli; Knapmeyer-Endrun, Brigitte; de Raucourt, Sebastien; Umland, Jeff; Hurst, Ken; Zweifel, Peter; Calcutt, Simon; Bierwirth, Marco; Mimoun, David; Pont, Gabriel; Verdier, Nicolas; Laudet, Philippe; Smrekar, Sue; Hoffman, Tom. 19th EGU General Assembly, EGU2017, proceedings from the conference held 23–28 April 2017 in Vienna, Austria., p.9978 Seismometers on both ''Viking'' spacecraft were mounted on the lander, which meant that it also picked up vibrations from various operations of the lander and caused by the wind. In addition, the ''
While two seismometers were landed on Mars during the ''Viking'' missions in 1976, results were limited. SEIS/INSIGHT: One year prior launch for Seismic Discovery on Mars. Lognonne, Philippe; Banerdt, W. Bruce; Giardini, Domenico; Pike, W. Tom; Christensen, Ulli; Knapmeyer-Endrun, Brigitte; de Raucourt, Sebastien; Umland, Jeff; Hurst, Ken; Zweifel, Peter; Calcutt, Simon; Bierwirth, Marco; Mimoun, David; Pont, Gabriel; Verdier, Nicolas; Laudet, Philippe; Smrekar, Sue; Hoffman, Tom. 19th EGU General Assembly, EGU2017, proceedings from the conference held 23–28 April 2017 in Vienna, Austria., p.9978 Seismometers on both ''Viking'' spacecraft were mounted on the lander, which meant that it also picked up vibrations from various operations of the lander and caused by the wind. In addition, the ''Viking 1
''Viking 1'' was the first of two spacecraft, along with '' Viking 2'', each consisting of an orbiter and a lander, sent to Mars as part of NASA's Viking program. The lander touched down on Mars on July 20, 1976, the first successful Mars la ...
'' lander's seismometer did not deploy properly.
The seismometer readings were used to estimate a Martian geological crust thickness between at the ''Viking 2
The ''Viking 2'' mission was part of the American Viking program to Mars, and consisted of an orbiter and a lander essentially identical to that of the ''Viking 1'' mission. ''Viking 2'' was operational on Mars for sols ( days; '). The ''Vi ...
'' lander site. Unexpectedly, the seismometer also detected pressure from the Mars winds, complementing the meteorology results. A single possible candidate for a marsquake
A marsquake is a quake which, much like an earthquake, would be a shaking of the surface or interior of the planet Mars as a result of the sudden release of energy in the planet's interior, such as the result of plate tectonics, which most quakes ...
was recorded, although it was not confirmed due to the limitations of the design, and interference from other sources of vibration such as wind. Despite these limitations, it was clear that widespread and large marsquakes were not detected.
Design
SEIS is the primary instrument of the ''InSight'' mission, and it was designed and produced by the French Space Agency (CNES
The (CNES; French: ''Centre national d'études spatiales'') is the French government space agency (administratively, a "public administration with industrial and commercial purpose"). Its headquarters are located in central Paris and it is und ...
), with the participation of the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris ( IPGP), the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH
(colloquially)
, former_name = eidgenössische polytechnische Schule
, image = ETHZ.JPG
, image_size =
, established =
, type = Public
, budget = CHF 1.896 billion (2021)
, rector = Günther Dissertori
, president = Joël Mesot
, a ...
), the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research ( MPS), Imperial College, Institut supérieur de l'aéronautique et de l'espace ( ISAE) and JPL. The Principal Investigator is Philippe Lognonné from the Institute of Earth Physics of Paris (''Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris''), in the E.U.crust and mantle respond to the effects of meteorite impacts, which gives clues to the planet's inner structure. The seismometer will also detect sources including atmospheric waves and gravimetric signals (tidal forces
The tidal force is a gravitational effect that stretches a body along the line towards the center of mass of another body due to a gradient (difference in strength) in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenomen ...
) from Mars' moon Phobos, up to high-frequency seismic waves at 50 Hz.Planned products of the Mars Structure Service for the InSight mission to Mars(PDF). Mark P. Panning, Philippe Lognonne, W. Bruce Banerdt, Raphael Garcia, Matthew Golombek, et al. ''Space Science Reviews'' 16 November 2016. The SEIS instrument is deployed by the Instrument Deployment System, a robotic arm that can position the sensor directly on the surface. The instrument is supported by a suite of meteorological sensors (
TWINS
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
) to characterize atmospheric disturbances that might affect the measurements. These include a vector magnetometer provided by UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California ...
that will measure magnetic disturbances such as those caused by the Martian ionosphere; a suite of air temperature, wind speed and wind direction sensors based on the Spanish/Finnish Rover Environmental Monitoring Station; and a barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis ...
from JPL.
 During the final integration of SEIS, several small leaks were found in the vacuum thermal enclosure. This forced the postponement of the ''InSight'' launch from 2016 to 2018, and the redesign of a new enclosure under the supervision of JPL. The cost of the delay was estimated to be .
During the final integration of SEIS, several small leaks were found in the vacuum thermal enclosure. This forced the postponement of the ''InSight'' launch from 2016 to 2018, and the redesign of a new enclosure under the supervision of JPL. The cost of the delay was estimated to be .

Operations
Routine operations will be split into two services, the Mars Structure Service (MSS) and Marsquake Service (MQS), which will be responsible, respectively, for defining the structure models and seismic activity. Combination of data with results from the ''InSight'' radio science and orbital observations will allow for constraint of the deeper structure. Possible observations include: *P waves
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic Body wave (seismology), body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an eart ...
and S waves
* Meteor strikes (see also :Meteorites found on Mars)
* Marsquake
A marsquake is a quake which, much like an earthquake, would be a shaking of the surface or interior of the planet Mars as a result of the sudden release of energy in the planet's interior, such as the result of plate tectonics, which most quakes ...
s
* Impact by other manmade objects
* Tidal force
The tidal force is a gravitational effect that stretches a body along the line towards the center of mass of another body due to a gradient (difference in strength) in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenomen ...
s from Mars' moons
* Interior revelations, such as the presence of a solid or liquid core and its size
Single-site seismology
 During development, the power of multiple sites was noted, but one site offers a tremendous insight to the interior. With a single site, the location of a marsquake event can be constrained to the surface of a sphere, by measuring what are known as P-waves and S-waves.Geophysical Network Mission for MARS 2009
During development, the power of multiple sites was noted, but one site offers a tremendous insight to the interior. With a single site, the location of a marsquake event can be constrained to the surface of a sphere, by measuring what are known as P-waves and S-waves.Geophysical Network Mission for MARS 2009/ref> There is a variety of single-site seismology techniques that can yield data, for example, the detection of an impact on the surface by a meteorite for which the location is identified. If Mars has large marsquakes, they may allow the deep interior to be determined. As the vibrations pass through the planet they are affected by the properties of the materials and its configuration. For example, the effect of tidal forces on Mars by Phobos, which should be about 10 mm, would be noticeably affected by a liquid Mars core. Even without any marsquake, it should be possible after about six months of observation to use this method to increase or decrease the likelihood Mars has a liquid core.
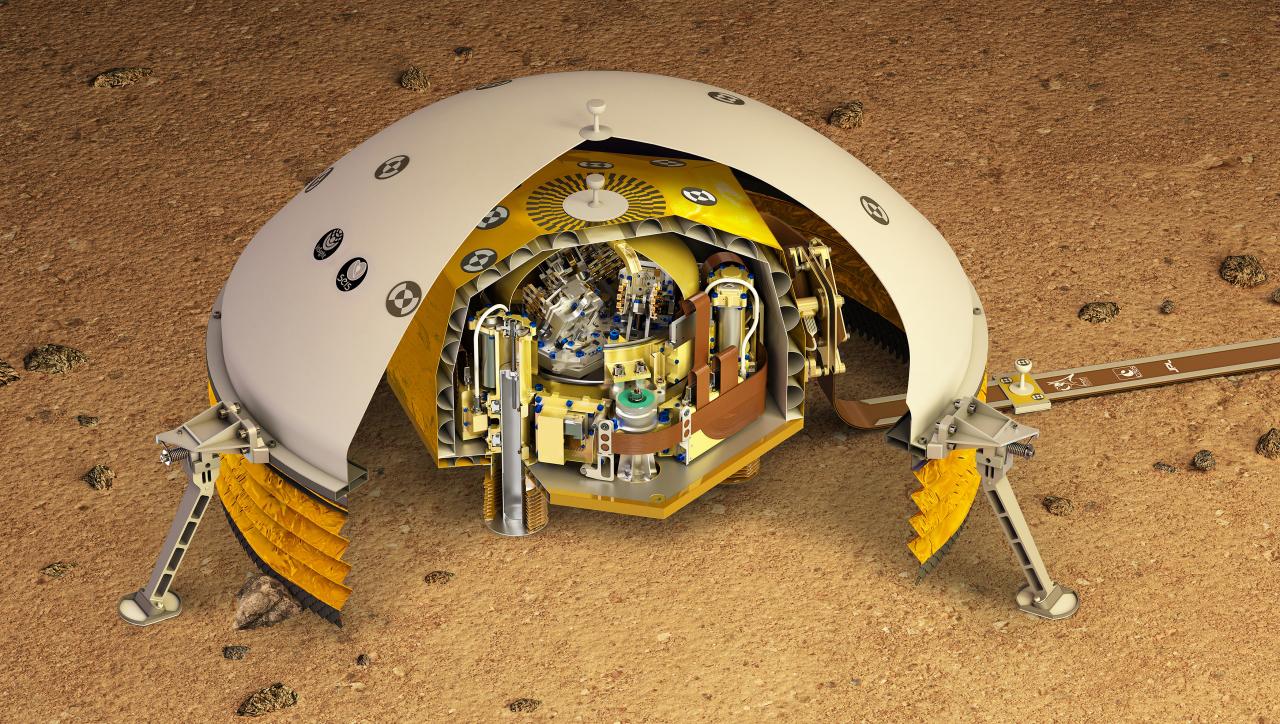
Cutaway illustration

Placement on the surface
On 19 December 2018, the SEIS instrument was deployed to the surface of Mars next to the lander by its robotic arm.See also
*Composition of Mars
The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.
Elemental composition
Mars is differentiated, which—for a terrestrial planet—implies that it has a central core made up of me ...
*Geology of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geo ...
*Volcanology of Mars
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features in ...
References
{{authority control Geology of Mars Spacecraft instruments InSight CNES