segmented regression on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Segmented regression, also known as piecewise regression or broken-stick regression, is a method in
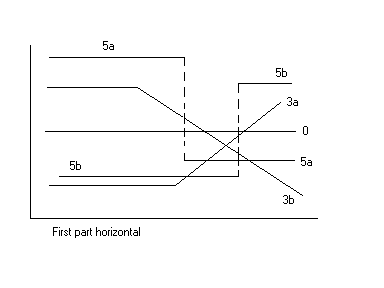

 Segmented linear regression with two segments separated by a ''breakpoint'' can be useful to quantify an abrupt change of the response function (Yr) of a varying influential factor (x). The breakpoint can be interpreted as a ''critical'', ''safe'', or ''threshold'' value beyond or below which (un)desired effects occur. The breakpoint can be important in decision making
The figures illustrate some of the results and regression types obtainable.
A segmented regression analysis is based on the presence of a set of ( y, x ) data, in which y is the
Segmented linear regression with two segments separated by a ''breakpoint'' can be useful to quantify an abrupt change of the response function (Yr) of a varying influential factor (x). The breakpoint can be interpreted as a ''critical'', ''safe'', or ''threshold'' value beyond or below which (un)desired effects occur. The breakpoint can be important in decision making
The figures illustrate some of the results and regression types obtainable.
A segmented regression analysis is based on the presence of a set of ( y, x ) data, in which y is the
:Yr is the expected (predicted) value of y for a certain value of x; :A1 and A2 are regression coefficients (indicating the slope of the line segments); :K1 and K2 are ''regression constants'' (indicating the intercept at the y-axis). The data may show many types or trends, see the figures. The method also yields two correlation coefficients (R): * for x < BP (breakpoint) and * for x > BP (breakpoint) where:
: is the minimized SSD per segment and :Ya1 and Ya2 are the average values of y in the respective segments. In the determination of the most suitable trend,
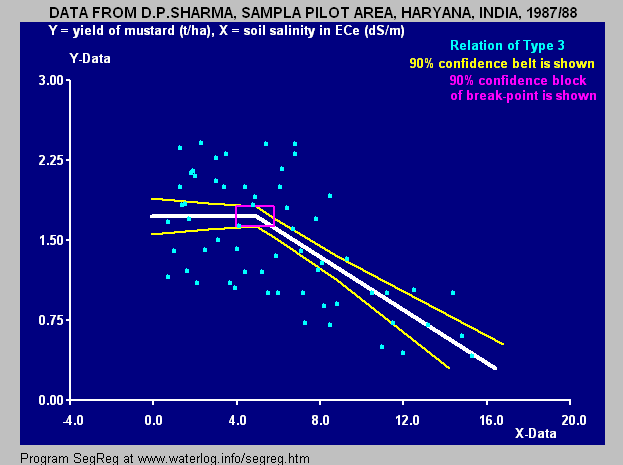 For the blue figure at the right that gives the relation between yield of mustard (Yr = Ym, t/ha) and
For the blue figure at the right that gives the relation between yield of mustard (Yr = Ym, t/ha) and

 The following ''statistical tests'' are used to determine the type of trend:
# significance of the breakpoint (BP) by expressing BP as a function of ''regression coefficients'' A1 and A2 and the means Y1 and Y2 of the y-data and the means X1 and X2 of the x data (left and right of BP), using the laws of propagation of errors in additions and multiplications to compute the
The following ''statistical tests'' are used to determine the type of trend:
# significance of the breakpoint (BP) by expressing BP as a function of ''regression coefficients'' A1 and A2 and the means Y1 and Y2 of the y-data and the means X1 and X2 of the x data (left and right of BP), using the laws of propagation of errors in additions and multiplications to compute the
In a pure, unsegmented, linear regression, the values of Cd and Ra2 are equal. In a segmented regression, Cd needs to be significantly larger than Ra2 to justify the segmentation. The
 Segmented regression is often used to detect over which range an explanatory variable (X) has no effect on the dependent variable (Y), while beyond the reach there is a clear response, be it positive or negative.
The reach of no effect may be found at the initial part of X domain or conversely at its last part. For the "no effect" analysis, application of the
Segmented regression is often used to detect over which range an explanatory variable (X) has no effect on the dependent variable (Y), while beyond the reach there is a clear response, be it positive or negative.
The reach of no effect may be found at the initial part of X domain or conversely at its last part. For the "no effect" analysis, application of the
/ref> over the range, extending the range with small steps until the regression coefficient gets significantly different from zero. In the next figure the break point is found at X=7.9 while for the same data (see blue figure above for mustard yield), the least squares method yields a break point only at X=4.9. The latter value is lower, but the fit of the data beyond the break point is better. Hence, it will depend on the purpose of the analysis which method needs to be employed.
regression analysis
In statistical modeling, regression analysis is a set of statistical processes for estimating the relationships between a dependent variable (often called the 'outcome' or 'response' variable, or a 'label' in machine learning parlance) and one ...
in which the independent variable
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or dema ...
is partitioned into intervals and a separate line segment is fit to each interval. Segmented regression analysis can also be performed on multivariate data by partitioning the various independent variables. Segmented regression is useful when the independent variables, clustered into different groups, exhibit different relationships between the variables in these regions. The boundaries between the segments are ''breakpoints''.
Segmented linear regression is segmented regression whereby the relations in the intervals are obtained by linear regression
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is cal ...
.
Segmented linear regression, two segments


 Segmented linear regression with two segments separated by a ''breakpoint'' can be useful to quantify an abrupt change of the response function (Yr) of a varying influential factor (x). The breakpoint can be interpreted as a ''critical'', ''safe'', or ''threshold'' value beyond or below which (un)desired effects occur. The breakpoint can be important in decision making
The figures illustrate some of the results and regression types obtainable.
A segmented regression analysis is based on the presence of a set of ( y, x ) data, in which y is the
Segmented linear regression with two segments separated by a ''breakpoint'' can be useful to quantify an abrupt change of the response function (Yr) of a varying influential factor (x). The breakpoint can be interpreted as a ''critical'', ''safe'', or ''threshold'' value beyond or below which (un)desired effects occur. The breakpoint can be important in decision making
The figures illustrate some of the results and regression types obtainable.
A segmented regression analysis is based on the presence of a set of ( y, x ) data, in which y is the dependent variable
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or dema ...
and x the independent variable
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or dema ...
.
The least squares
The method of least squares is a standard approach in regression analysis to approximate the solution of overdetermined systems (sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns) by minimizing the sum of the squares of the re ...
method applied separately to each segment, by which the two regression lines are made to fit the data set as closely as possible while minimizing the ''sum of squares of the differences'' (SSD) between observed (y) and calculated (Yr) values of the dependent variable, results in the following two equations:
* Yr = A1.x + K1 for x < BP (breakpoint)
* Yr = A2.x + K2 for x > BP (breakpoint)
where::Yr is the expected (predicted) value of y for a certain value of x; :A1 and A2 are regression coefficients (indicating the slope of the line segments); :K1 and K2 are ''regression constants'' (indicating the intercept at the y-axis). The data may show many types or trends, see the figures. The method also yields two correlation coefficients (R): * for x < BP (breakpoint) and * for x > BP (breakpoint) where:
: is the minimized SSD per segment and :Ya1 and Ya2 are the average values of y in the respective segments. In the determination of the most suitable trend,
statistical tests
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis.
Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters.
...
must be performed to ensure that this trend is reliable (significant).
When no significant breakpoint can be detected, one must fall back on a regression without breakpoint.
Example
 For the blue figure at the right that gives the relation between yield of mustard (Yr = Ym, t/ha) and
For the blue figure at the right that gives the relation between yield of mustard (Yr = Ym, t/ha) and soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt (chemistry), salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral wea ...
(x = Ss, expressed as electric conductivity of the soil solution EC in dS/m) it is found that:
BP = 4.93, A1 = 0, K1 = 1.74, A2 = −0.129, K2 = 2.38, R12 = 0.0035 (insignificant), R22 = 0.395 (significant) and:
* Ym = 1.74 t/ha for Ss < 4.93 (breakpoint)
* Ym = −0.129 Ss + 2.38 t/ha for Ss > 4.93 (breakpoint)
indicating that soil salinities < 4.93 dS/m are safe and soil salinities > 4.93 dS/m reduce the yield @ 0.129 t/ha per unit increase of soil salinity.
The figure also shows confidence intervals and uncertainty as elaborated hereunder.
Test procedures

 The following ''statistical tests'' are used to determine the type of trend:
# significance of the breakpoint (BP) by expressing BP as a function of ''regression coefficients'' A1 and A2 and the means Y1 and Y2 of the y-data and the means X1 and X2 of the x data (left and right of BP), using the laws of propagation of errors in additions and multiplications to compute the
The following ''statistical tests'' are used to determine the type of trend:
# significance of the breakpoint (BP) by expressing BP as a function of ''regression coefficients'' A1 and A2 and the means Y1 and Y2 of the y-data and the means X1 and X2 of the x data (left and right of BP), using the laws of propagation of errors in additions and multiplications to compute the standard error
The standard error (SE) of a statistic (usually an estimate of a parameter) is the standard deviation of its sampling distribution or an estimate of that standard deviation. If the statistic is the sample mean, it is called the standard error o ...
(SE) of BP, and applying Student's t-test
A ''t''-test is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's ''t''-distribution under the null hypothesis. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of ...
# significance of A1 and A2 applying Student's t-distribution and the ''standard error'' SE of A1 and A2
# significance of the difference of A1 and A2 applying Student's t-distribution using the SE of their difference.
# significance of the difference of Y1 and Y2 applying Student's t-distribution using the SE of their difference.
#A more formal statistical approach to test for the existence of a breakpoint, is via the pseudo score test which does not require estimation of the segmented line.
In addition, use is made of the correlation coefficient
A correlation coefficient is a numerical measure of some type of correlation, meaning a statistical relationship between two variables. The variables may be two columns of a given data set of observations, often called a sample, or two components ...
of all data (Ra), the coefficient of determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted ''R''2 or ''r''2 and pronounced "R squared", is the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable(s).
It is a statistic used i ...
or coefficient of explanation, confidence interval
In frequentist statistics, a confidence interval (CI) is a range of estimates for an unknown parameter. A confidence interval is computed at a designated ''confidence level''; the 95% confidence level is most common, but other levels, such as 9 ...
s of the regression functions, and ANOVA
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statistician ...
analysis.
The coefficient of determination for all data (Cd), that is to be maximized under the conditions set by the significance tests, is found from:
*
where Yr is the expected (predicted) value of y according to the former regression equations and Ya is the average of all y values.
The Cd coefficient ranges between 0 (no explanation at all) to 1 (full explanation, perfect match). In a pure, unsegmented, linear regression, the values of Cd and Ra2 are equal. In a segmented regression, Cd needs to be significantly larger than Ra2 to justify the segmentation. The
optimal
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
value of the breakpoint may be found such that the Cd coefficient is maximum
In mathematical analysis, the maxima and minima (the respective plurals of maximum and minimum) of a function, known collectively as extrema (the plural of extremum), are the largest and smallest value of the function, either within a given r ...
.
No-effect range
 Segmented regression is often used to detect over which range an explanatory variable (X) has no effect on the dependent variable (Y), while beyond the reach there is a clear response, be it positive or negative.
The reach of no effect may be found at the initial part of X domain or conversely at its last part. For the "no effect" analysis, application of the
Segmented regression is often used to detect over which range an explanatory variable (X) has no effect on the dependent variable (Y), while beyond the reach there is a clear response, be it positive or negative.
The reach of no effect may be found at the initial part of X domain or conversely at its last part. For the "no effect" analysis, application of the least squares
The method of least squares is a standard approach in regression analysis to approximate the solution of overdetermined systems (sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns) by minimizing the sum of the squares of the re ...
method for the segmented regression analysis may not be the most appropriate technique because the aim is rather to find the longest stretch over which the Y-X relation can be considered to possess zero slope while beyond the reach the slope is significantly different from zero but knowledge about the best value of this slope is not material. The method to find the no-effect range is progressive partial regression Partial Regression Analysis, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. Free download from the webpag/ref> over the range, extending the range with small steps until the regression coefficient gets significantly different from zero. In the next figure the break point is found at X=7.9 while for the same data (see blue figure above for mustard yield), the least squares method yields a break point only at X=4.9. The latter value is lower, but the fit of the data beyond the break point is better. Hence, it will depend on the purpose of the analysis which method needs to be employed.
See also
*Chow test
The Chow test (), proposed by econometrician Gregory Chow in 1960, is a test of whether the true coefficients in two linear regressions on different data sets are equal. In econometrics, it is most commonly used in time series analysis to test fo ...
* Simple regression
In statistics, simple linear regression is a linear regression model with a single explanatory variable. That is, it concerns two-dimensional sample points with one independent variable and one dependent variable (conventionally, the ''x'' a ...
* Linear regression
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is cal ...
* Ordinary least squares
In statistics, ordinary least squares (OLS) is a type of linear least squares method for choosing the unknown parameters in a linear regression model (with fixed level-one effects of a linear function of a set of explanatory variables) by the ...
* Multivariate adaptive regression splines
In statistics, multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) is a form of regression analysis introduced by Jerome H. Friedman in 1991. It is a non-parametric regression technique and can be seen as an extension of linear models that automaticall ...
* Local regression
Local regression or local polynomial regression, also known as moving regression, is a generalization of the moving average and polynomial regression.
Its most common methods, initially developed for scatterplot smoothing, are LOESS (locally e ...
* Regression discontinuity design
In statistics, econometrics, political science, epidemiology, and related disciplines, a regression discontinuity design (RDD) is a quasi-experimental pretest-posttest design that aims to determine the causal effects of interventions by assigning a ...
* Stepwise regression
In statistics, stepwise regression is a method of fitting regression models in which the choice of predictive variables is carried out by an automatic procedure. In each step, a variable is considered for addition to or subtraction from the set of ...
* SegReg (software) for segmented regression
References