Second Maccabees on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
2 Maccabees, el, Μακκαβαίων Β´, translit=Makkabaíōn 2 also known as the Second Book of Maccabees, Second Maccabees, and abbreviated as 2 Macc., is a deuterocanonical book which recounts the persecution of Jews under King
Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his de ...
and the Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended ...
against him. It concludes with the defeat of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
general Nicanor in 161 BC by Judas Maccabeus
Judah Maccabee (or Judas Maccabeus, also spelled Machabeus, or Maccabæus, Hebrew: יהודה המכבי, ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') was a Jewish priest ('' kohen'') and a son of the priest Mattathias. He led the Maccabean Revolt against the Se ...
, the leader of the Maccabees.
2 Maccabees was originally written in Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
by an unknown diaspora Jew
The negation of the Diaspora ( he, שלילת הגלות, ''shlilat ha' galut'', or he, שלילת הגולה, ''shlilat ha' golah'') is a central assumption in many currents of Zionism. The concept encourages the dedication to Zionism and it is u ...
living in Hellenistic Egypt. It was likely written some time between 150 and 120 BC. Together with the book 1 Maccabees
The First Book of Maccabees, also known as First Maccabees (written in shorthand as 1 Maccabees or 1 Macc.), is a book written in Hebrew by an anonymousRappaport, U., ''47. 1 Maccabees'' in Barton, J. and Muddiman, J. (2001)The Oxford Bible Comme ...
, it is one of the most important sources on the Maccabean Revolt. The work is not a sequel to 1 Maccabees but rather its own independent rendition of the historical events of the Maccabean Revolt. It both starts and ends its history earlier than 1 Maccabees, starting with an incident with the Seleucid official Heliodorus attempting to tax the Second Temple in 178 BC, and ending with the Battle of Adasa
The Battle of Adasa was fought during the Maccabean revolt on the 13th of the month Adar (late winter, equivalent to March), 161 BC at Adasa ( he, חדשה), near Beth-horon. It was a battle between the rebel Maccabees of Judas Maccabeus (Judah ...
in 161 BC. Some scholars believe the book to be influenced by the Pharisaic
The Pharisees (; he, פְּרוּשִׁים, Pərūšīm) were a Jewish social movement and a school of thought in the Levant during the time of Second Temple Judaism. After the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE, Pharisaic beliefs ...
tradition, with sections that include an endorsement of prayer for the dead
Religions with the belief in a future judgment, a resurrection of the dead or a purgatory often offer prayers on behalf of the dead to God.
Buddhism
For most funerals that follow the tradition of Chinese Buddhism, common practices include chant ...
and a resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead ( Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died ...
.
The book, like the other Books of the Maccabees
The Books of the Maccabees or the Sefer HaMakabim (the ''Book of the Maccabees'') recount the history of the Maccabees, the leaders of the Jewish rebellion against the Seleucid dynasty.
List of books
The Books of the Maccabees refers to a series o ...
, was included in the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond t ...
, a prominent Greek collection of Jewish scripture. It was not promptly translated to Hebrew nor included in the Masoretic Hebrew canon, the Tanakh
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Greek-speaking Jews in the two centuries after its creation, later
 The
The
 In the
In the
 2 Maccabees was in a position of being an official part of the canon, but as a deuterocanonical work and thus subtly lesser than the older scriptures during the early 1500s.
2 Maccabees was in a position of being an official part of the canon, but as a deuterocanonical work and thus subtly lesser than the older scriptures during the early 1500s.
 The most influential part of 2 Maccabees was its stories of the martyrdom of Eleazar and the woman with seven sons; various works expanded the story to add more details such as the woman's name (variously called Hannah, Miriam, Shmouni, and other names) and their story. A prominent early example is the book of
The most influential part of 2 Maccabees was its stories of the martyrdom of Eleazar and the woman with seven sons; various works expanded the story to add more details such as the woman's name (variously called Hannah, Miriam, Shmouni, and other names) and their story. A prominent early example is the book of
'' Greek-speaking Jews in the two centuries after its creation, later
Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites"" ...
s did not consider the work canonical nor important. Early Christians did honor the work, and it was included as a deuterocanonical
The deuterocanonical books (from the Greek meaning "belonging to the second canon") are books and passages considered by the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox Churches, and the Assyrian Church of the East to be ...
work of the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. T ...
. Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonica ...
, and Oriental Orthodox
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent o ...
Christians still consider the work deuterocanonical; Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
Christians do not regard 2 Maccabees as canonical, although many include 2 Maccabees as part of the biblical apocrypha
The biblical apocrypha (from the grc, ἀπόκρυφος, translit=apókruphos, lit=hidden) denotes the collection of apocryphal ancient books thought to have been written some time between 200 BC and AD 400. The Roman Catholic, Eastern O ...
, noncanonical books useful for the purpose of edification.
Authorship and composition date
The author of 2 Maccabees is not identified, but he claims to be abridging a 5-volume work by Jason of Cyrene.Since 2 Maccabees is largely an abridgment of another's work, the person who wrote 2 Maccabees is often referred to as " epitomist" or "epitomator" rather than "author". This longer work is not preserved, and it is uncertain how much of the present text of 2 Maccabees is copied from Jason's work. The author wrote in Greek, as there is no particular evidence of an earlier Hebrew version. A few sections of the book, such as the Preface, Epilogue, and some reflections on morality are generally assumed to come from the author, not from Jason. Scholars disagree on both when Jason's work was written and when 2 Maccabees was written. Many scholars argue that Jason's work was likely published by a contemporary of the Maccabean Revolt, around 160–140 BCE, although all that is known for sure is that it was before 2 Maccabees. Scholars suggest 2 Maccabees was composed at some point from 150–100 BC. It is generally considered that the work must have been written no later than the 70s BC, given that the author seems unaware thatPompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
would defeat the Hasmonean kingdom
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, an ...
and make Judea a Roman protectorate in 63 BC. The work was possibly modified some after creation, but reached its final form in the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond t ...
, the Greek Jewish scriptures. The Septuagint version also gave the work its title of "2 Maccabees" to distinguish it from the other books of the Maccabees
The Books of the Maccabees or the Sefer HaMakabim (the ''Book of the Maccabees'') recount the history of the Maccabees, the leaders of the Jewish rebellion against the Seleucid dynasty.
List of books
The Books of the Maccabees refers to a series o ...
in it; the original title of the work, if any, is unknown.
The author appears to be an Egyptian Jew, possibly writing from the capital in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, addressing other diaspora Jews. The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
style of the writer is educated and erudite, and he is familiar with the forms of rhetoric and argument of the era. The beginning of the book includes two letters sent by Jews in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
to Jews of the diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews aft ...
in Hellenistic Egypt concerning the feast day set up to celebrate the purification of the temple (Hanukkah
or English translation: 'Establishing' or 'Dedication' (of the Temple in Jerusalem)
, nickname =
, observedby = Jews
, begins = 25 Kislev
, ends = 2 Tevet or 3 Tevet
, celebrations = Lighting candles each night ...
) and the feast to celebrate the defeat of Nicanor. If the author of the book inserted these letters, the book would have to have been written after 188 SE (~124 BC), the date of the second letter. Some commentators hold that these letters were a later addition, while others consider them the basis for the work.
Contents

Summary
2 Maccabees both starts and ends its history earlier than1 Maccabees
The First Book of Maccabees, also known as First Maccabees (written in shorthand as 1 Maccabees or 1 Macc.), is a book written in Hebrew by an anonymousRappaport, U., ''47. 1 Maccabees'' in Barton, J. and Muddiman, J. (2001)The Oxford Bible Comme ...
does, instead covering the period from the high priest Onias III
Onias III ( he, חוֹנִיּוֹ ''Ḥōnīyyō''), son of Simon II, was Jewish High Priest during the Second Temple period. He is described in scriptures as a pious man who opposed the Hellenization of Judea. He was succeeded by his brother Ja ...
and King Seleucus IV (180 BC) to the defeat of Nicanor in 161. The exact focus of the work is debated. All agree that the work has a moralistic tenor, showing the triumph of Judaism, the supremacy of God, and the just punishment of villains. Some see it as a paean to Judas Maccabeus personally, describing the background of the Revolt to write a biography praising him; some see its focus as the Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inheri ...
, showing its gradual corruption by Antiochus IV and how it was saved and purified; others see the focus as the city of Jerusalem and how it was saved; and others disagree with all of the above, seeing it as written strictly for literary and entertainment value.
The author is interested in providing a theological interpretation of the events; in this book God's interventions direct the course of events, punishing the wicked and restoring the Temple to his people. Some events appear to be presented out of strict chronological order to make theological points, such as the occasional "flash forward
A flashforward (also spelled flash-forward, and more formally known as prolepsis) is a scene that temporarily takes the narrative forward in time from the current point of the story in literature, film, television and other media. Flashforwards ...
" to a villain's later death. The numbers cited for sizes of armies may also appear exaggerated, though not all of the manuscripts of this book agree.
After the introductory stories of the controversies at the Temple and the persecutions of Antiochus IV, the story switches to its narrative of the Revolt itself. After the death of Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his de ...
, the Feast of the Dedication of the Temple is instituted. The newly dedicated Temple is threatened by the Seleucid general Nicanor. After his death, the festivities for the dedication are concluded. A special day is dedicated to commemorate the Jewish victory in the month of Adar
Adar ( he, אֲדָר ; from Akkadian ''adaru'') is the sixth month of the civil year and the twelfth month of the religious year on the Hebrew calendar, roughly corresponding to the month of March in the Gregorian calendar. It is a month of 29 ...
, on the day before "Mordecai
Mordecai (; also Mordechai; , IPA: ) is one of the main personalities in the Book of Esther in the Hebrew Bible. He is described as being the son of Jair, of the tribe of Benjamin. He was promoted to Vizier after Haman was killed.
Biblical acco ...
's Day" (Purim
Purim (; , ; see Name below) is a Jewish holiday which commemorates the saving of the Jews, Jewish people from Haman, an official of the Achaemenid Empire who was planning to have all of Persia's Jewish subjects killed, as recounted in the Bo ...
). The work explicitly urges diaspora Jews to celebrate both Hanukkah and Nicanor's Day.
Structure
2 Maccabees consists of 15 chapters. *1:1–2:18: Two letters to the Jews of Egypt. *2:19–32: Epitomist's preface. *3: Heliodorus attempts to tax the Temple of Jerusalem's treasury, but is repelled. (~178 BC) *4: High PriestOnias III
Onias III ( he, חוֹנִיּוֹ ''Ḥōnīyyō''), son of Simon II, was Jewish High Priest during the Second Temple period. He is described in scriptures as a pious man who opposed the Hellenization of Judea. He was succeeded by his brother Ja ...
of the Temple of Jerusalem is succeeded by his brother Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He wa ...
; Jason is then succeeded by the corrupt Menelaus
In Greek mythology, Menelaus (; grc-gre, Μενέλαος , 'wrath of the people', ) was a king of Mycenaean (pre- Dorian) Sparta. According to the '' Iliad'', Menelaus was a central figure in the Trojan War, leading the Spartan contingent of ...
; Onias III is murdered. (~175–170 BC)
*5: Jason attempts to overthrow Menelaus. King Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his de ...
returns from the second expedition of the Sixth Syrian War
The Syrian Wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, successor states to Alexander the Great's empire, during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region then called Coele-Syria, one of t ...
in Egypt, defeats Jason's supporters, sacks Jerusalem, loots the Temple treasury, and kills and enslaves local Jews as retribution for the perceived revolt. Jason is forced into exile. (168 BC)
*6: The Temple is converted into syncretic Greek-Jewish worship site. Antiochus IV issues decrees forbidding traditional Jewish practices, such as circumcision, keeping kosher, and keeping the Sabbath. Eleazar
Eleazar (; ) or Elʽazar was a priest in the Hebrew Bible, the second High Priest, succeeding his father Aaron after he died. He was a nephew of Moses.
Biblical narrative
Eleazar played a number of roles during the course of the Exodus, fro ...
the scribe is tortured and killed after refusing to eat pork. (168–167 BC)
*7: Martyrdom of the woman and her seven sons after torture by Antiochus IV.
*8: Start of the Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended ...
. Judas Maccabeus
Judah Maccabee (or Judas Maccabeus, also spelled Machabeus, or Maccabæus, Hebrew: יהודה המכבי, ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') was a Jewish priest ('' kohen'') and a son of the priest Mattathias. He led the Maccabean Revolt against the Se ...
defeats Nicanor, Gorgias
Gorgias (; grc-gre, Γοργίας; 483–375 BC) was an ancient Greek sophist, pre-Socratic philosopher, and rhetorician who was a native of Leontinoi in Sicily. Along with Protagoras, he forms the first generation of Sophists. Several dox ...
, and Ptolemy son of Dorymenes at the Battle of Emmaus. (~166–165 BC)
*9:1–10:9: Antiochus IV is stricken with disease by God. He belatedly repents and writes a letter attempting to make peace before dying in Persia. Judas conquers Jerusalem, cleanses the Temple, and establishes the festival of Hanukkah
or English translation: 'Establishing' or 'Dedication' (of the Temple in Jerusalem)
, nickname =
, observedby = Jews
, begins = 25 Kislev
, ends = 2 Tevet or 3 Tevet
, celebrations = Lighting candles each night ...
. (~164 BC)
*10:10–38: Lysias
Lysias (; el, Λυσίας; c. 445 – c. 380 BC) was a logographer (speech writer) in Ancient Greece. He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian Canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrace ...
becomes regent. Governor Ptolemy Macron attempts to cement peace with the Jews, but is undermined by anti-Jewish nobles and commits suicide. The Maccabees campaign in outlying regions against Timothy of Ammon and others. (~163 BC)
*11: Lysias leads a military expedition to Judea. Judas defeats him at the Battle of Beth Zur
The Battle of Beth Zur was fought between the Maccabees led by Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) and a Seleucid Greek army led by Regent Lysias in October 164 BC at Beth Zur. According to the books of Maccabees, the rebels won the battle, altho ...
. Four documents detailing negotiations with Lysias and the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman K ...
. (~160s BC)
*12: More accounts of the campaigns in outlying regions against Timothy, Gorgias, and others. (~163 BC)
*13: Lysias orders the execution of unpopular High Priest Menelaus. Judas harries Lysias's expedition with minor victories. Lysias leaves and returns to the capital of Antioch to face the usurper Philip. (~163–162 BC, likely near in time to the Battle of Beth Zechariah
The Battle of Beth Zechariah was a battle around May 162 BC during the Maccabean revolt fought between Jewish rebels under the leadership of Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) against an army of the Seleucid Empire, the Greek successor state (diadoch ...
described in 1 Maccabees)
*14:1–15:36: Demetrius I becomes King. Alcimus
Alcimus (from grc-gre, Ἄλκιμος ''Alkimos'', "valiant" or Hebrew אליקום ''Elyaqum'', "God will rise"), also called Jakeimos, Jacimus, or Joachim (), was High Priest of Israel for three years from 162–159 BCE. He was a moderate Hell ...
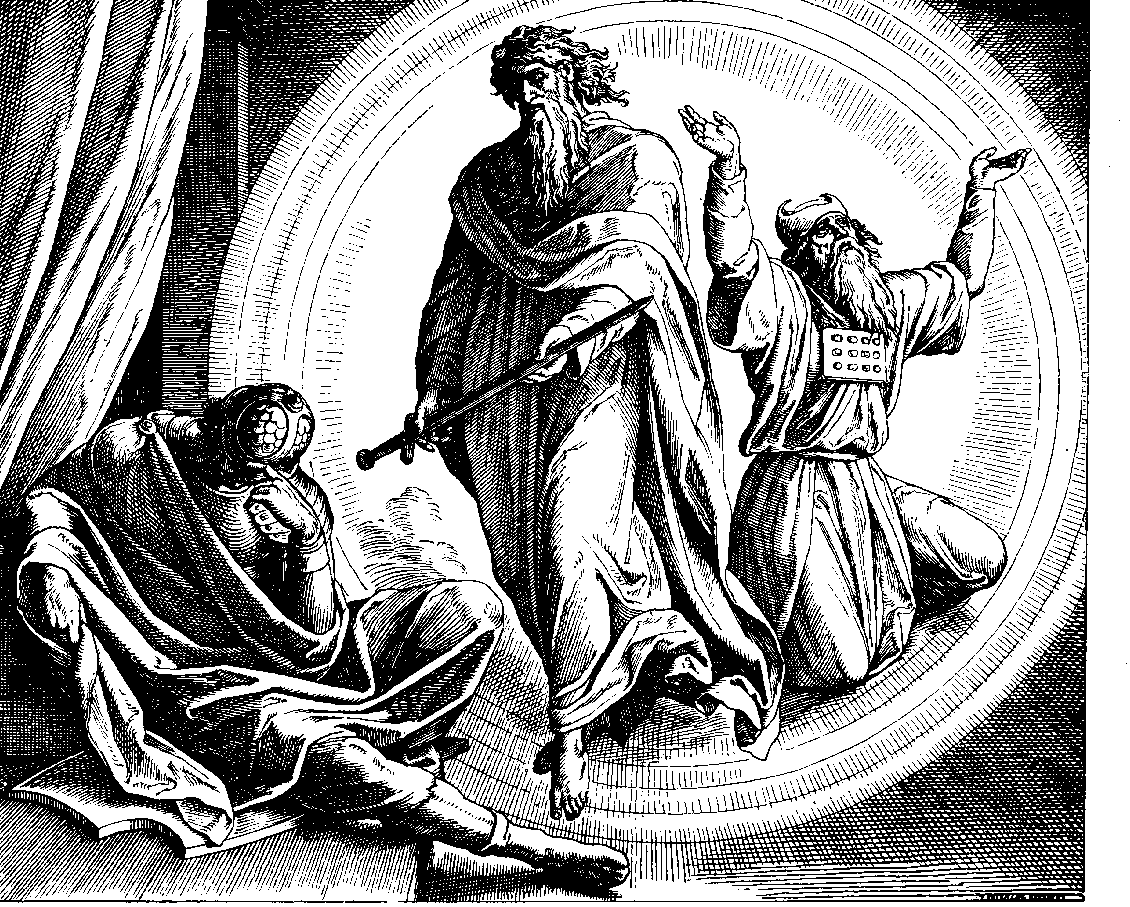
, who had replaced Menelaus as High Priest, is affirmed by Demetrius I. Nicanor is appointed governor of Judea. Nicanor and Judas enter negotiations for peace, but are subverted by Alcimus, who complains to the king; Judas's arrest is ordered. Nicanor threatens to destroy the Temple. In a dream vision, Onias III and the prophet Jeremiah
Jeremiah, Modern: , Tiberian: ; el, Ἰερεμίας, Ieremíās; meaning " Yah shall raise" (c. 650 – c. 570 BC), also called Jeremias or the "weeping prophet", was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewi ...
give Judas a divine golden sword. At the Battle of Adasa
The Battle of Adasa was fought during the Maccabean revolt on the 13th of the month Adar (late winter, equivalent to March), 161 BC at Adasa ( he, חדשה), near Beth-horon. It was a battle between the rebel Maccabees of Judas Maccabeus (Judah ...
, Judas defeats and kills Nicanor, preserving the sanctity of the Temple. The Day of Nicanor festival is established. (~161 BC)
*15:37–39: Epitomist's epilogue.
Canonicity and theology
 The
The Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
, and Oriental Orthodox Churches
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent ...
regard 2 Maccabees as canonical. Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites"" ...
and Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
s do not.
Hellenistic Judaism
Greek-speaking Jews were the original audience addressed by the work. Both 1 and 2 Maccabees appear in some manuscripts of theSeptuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond t ...
. Unlike most works in the Septuagint which were Greek translations of Hebrew originals, 2 Maccabees was a Greek work originally. While not a problem for Greek-speaking Hellenistic Jews
Hellenistic Judaism was a form of Judaism in classical antiquity that combined Jewish religious tradition with elements of Greek culture. Until the early Muslim conquests of the eastern Mediterranean, the main centers of Hellenistic Judaism were A ...
nor Christians (whose scriptures were written in Greek), other Jews who kept to the Hebrew version of the Jewish Scriptures never included it. Hellenistic Judaism slowly waned as many of its adherents either converted to Christianity or switched to other languages, and 2 Maccabees thus did not become part of the Jewish canon. Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
, the most famous Jewish writer of the first century whose work was preserved, does not appear to have read 2 Maccabees, for example; neither does Philo of Alexandria
Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
Philo's depl ...
. Neither book of the Maccabees were found among the Dead Sea Scrolls
The Dead Sea Scrolls (also the Qumran Caves Scrolls) are ancient Jewish and Hebrew religious manuscripts discovered between 1946 and 1956 at the Qumran Caves in what was then Mandatory Palestine, near Ein Feshkha in the West Bank, on the ...
of the Essene
The Essenes (; Hebrew: , ''Isiyim''; Greek: Ἐσσηνοί, Ἐσσαῖοι, or Ὀσσαῖοι, ''Essenoi, Essaioi, Ossaioi'') were a mystic Jewish sect during the Second Temple period that flourished from the 2nd century BCE to the 1st ce ...
s, a Jewish sect hostile to the Hasmoneans and their memory. Various works such as Seder Olam Rabbah
''Seder Olam Rabbah'' ( he, סדר עולם רבה, "The Great Order of the World") is a 2nd-century CE Hebrew language chronology detailing the dates of biblical events from creation to Alexander the Great's conquest of Persia. It adds no stori ...
(a 2nd century AD work) indicate that the age of prophecy ended with Alexander the Great, and 2 Maccabees, a work clearly written later, thus could not be prophetic.
Traditionally, it was hypothesized that the author of 2 Maccabees might have been influenced by the Pharasaic tradition. Harris, Stephen L., Understanding the Bible. Palo Alto: Mayfield. 1985. The Pharisees emphasized adherence to Jewish law and disputed with the rulers of the Hasmonean kingdom
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, an ...
. They criticized how the Hasmoneans took a dual role of both Chief Priest and King, and demanded that they cede one of the titles (usually the kingship, which was expected to be held by one of the family lineage of King David). Hasmonean King Alexander Jannaeus
Alexander Jannaeus ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξανδρος Ἰανναῖος ; he, ''Yannaʾy''; born Jonathan ) was the second king of the Hasmonean dynasty, who ruled over an expanding kingdom of Judea from 103 to 76 BCE. A son of John Hyrcanus, ...
is recorded as organizing a massacre of his political opponents, and many went into exile. The theory goes that 2 Maccabees praises Judas for saving the temple, but excludes mention of how his brothers and extended family later took the throne, and might have been written by a Pharisee from Judea writing in Egyptian exile. The work's emphasis on adherence to the Law even on pain of martyrdom, keeping the Sabbath, and the promise of a future resurrection seem to fit with the Pharisees' ideology. Still, other scholars disagree that the author shows any signs of such inclinations, and belief in a future resurrection of the dead was not limited to only Pharisees; scholars since the 1980s have tended to be skeptical of the proposed connection.
The theology of the work is an update to the "Deuteronomist
The Deuteronomist, abbreviated as either Dtr or simply D, may refer either to the source document underlying the core chapters (12–26) of the Book of Deuteronomy, or to the broader "school" that produced all of Deuteronomy as well as the Deutero ...
" history seen in older Jewish works. The classical Deuteronomist view had been that when Israel is faithful and upholds the covenant, the Jews prosper; when Israel neglects the covenant, God withdraws his favor, and Israel suffers. The persecution of Antiochus IV stood in direct contradiction to this tradition: the most faithful Jews were the ones who suffered the most, while those who abandoned Jewish practices became wealthy and powerful. The author of 2 Maccabees attempts to make sense of this in several ways: he explains that the suffering was a swift and merciful corrective to set the Jews back on the right path. While God had revoked his protection of the Temple in anger at the Hellenizing High Priests, his wrath turns to mercy upon seeing the suffering of the martyrs. The work also takes pains to ensure that when setbacks occur, some sort of sin or error was at fault. For those truly blameless, such as the martyrs, the author invokes life after death: that post-mortem rewards and punishments would accomplish what might have been lacking in the mortal world. These references to the resurrection of the dead despite suffering and torture were part of a new current in Judaism also seen in the Book of Daniel
The Book of Daniel is a 2nd-century BC biblical apocalypse with a 6th century BC setting. Ostensibly "an account of the activities and visions of Daniel, a noble Jew exiled at Babylon", it combines a prophecy of history with an eschatology (a ...
, a work the authors of 2 Maccabees were likely familiar with. This would prove especially influential among Roman-era Jews who converted to Christianity.
Christianity in the era of the Roman Empire
early Christian
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish d ...
tradition, the Septuagint was used as the basis for the Christian Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. T ...
. The inclusion of 2 Maccabees in some copies of the Septuagint saw it a part of various early canon lists and manuscripts, albeit sometimes as part of an appendix. The early manuscripts of the Septuagint were not uniform in their lists of books. The Codex Vaticanus
The Codex Vaticanus ( The Vatican, Bibl. Vat., Vat. gr. 1209), designated by siglum B or 03 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), δ 1 ( von Soden), is a fourth-century Christian manuscript of a Greek Bible, containing the majority of the Greek Old ...
lacks 1 and 2 Maccabees; the Codex Sinaiticus
The Codex Sinaiticus (Shelfmark: London, British Library, Add MS 43725), designated by siglum [Aleph] or 01 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 2 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts) ...
includes only 1 and 4 Maccabees; and only the Codex Alexandrinus
The Codex Alexandrinus (London, British Library, Royal MS 1. D. V-VIII), designated by the siglum A or 02 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 4 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts), is a man ...
includes all of 1, 2, 3, and 4 Maccabees. Pope Damasus I
Pope Damasus I (; c. 305 – 11 December 384) was the bishop of Rome from October 366 to his death. He presided over the Council of Rome of 382 that determined the canon or official list of sacred scripture. He spoke out against major heresies (i ...
's Council of Rome in 382, if the 6th century Gelasian Decree
The Gelasian Decree ( la, Decretum Gelasianum) is a Latin text traditionally thought to be a Decretal of the prolific Pope Gelasius I, bishop of Rome from 492–496. The work reached its final form in a five-chapter text written by an anonymous sc ...
is a correct guide to its decision, issued a biblical canon which included both 1 and 2 Maccabees (but not 3 and 4).
Pope Innocent I
Pope Innocent I ( la, Innocentius I) was the bishop of Rome from 401 to his death on 12 March 417. From the beginning of his papacy, he was seen as the general arbitrator of ecclesiastical disputes in both the East and the West. He confirmed the ...
(405 AD), the Synod of Hippo
The Synod of Hippo refers to the synod of 393 which was hosted in Hippo Regius in northern Africa during the early Christian Church. Additional synods were held in 394, 397, 401 and 426. Some were attended by Augustine of Hippo.
The synod of 393 ...
(393 AD), the Council of Carthage (397 AD), the Council of Carthage (419 AD), and the Apostolic Canons
The Apostolic Canons, also called Apostolic canons (Latin: ''Canones apostolorum'', "Canons of the Apostles"), Ecclesiastical Canons of the Same Holy Apostles, or Canons of the Holy Apostles, is a 4th-century Syrian Christian text. It is an Anc ...
all seemed to think that 2 Maccabees was canonical, either by explicitly saying so or citing it as scripture. Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is com ...
and Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
(c. 397 AD) had seemingly inconsistent positions: they directly excluded 2 Maccabees from canon, but did say that the book was useful; yet in other works, both cited 2 Maccabees as if it was scripture, or lists it among scriptural works.
Theologically, the major aspects of 2 Maccabees that resonated with Roman-era Christians and medieval Christians were its stories of martyrology
A martyrology is a catalogue or list of martyrs and other saints and beati arranged in the calendar order of their anniversaries or feasts. Local martyrologies record exclusively the custom of a particular Church. Local lists were enriched by na ...
and the resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead ( Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died ...
in its stories of Eleazar
Eleazar (; ) or Elʽazar was a priest in the Hebrew Bible, the second High Priest, succeeding his father Aaron after he died. He was a nephew of Moses.
Biblical narrative
Eleazar played a number of roles during the course of the Exodus, fro ...
and the woman with seven sons
The woman with seven sons was a Jewish martyr described in 2 Maccabees 7 and other sources, who had seven sons that were arrested (along with her) by Antiochus IV Epiphanes, who forced them to prove their respect to him by consuming pig meat. Whe ...
. Christians made sermons and comparisons of Christian martyrs to the Maccabean martyrs, along with the hope of an eventual salvation; Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christia ...
compared the persecuted Christians of Lyon to the Maccabean martyrs, for example. Several churches were dedicated to the "Maccabean martyrs", and they are among the few pre-Christian figures to appear on the calendar of saints' days. A cult to the Maccabean martyrs flourished in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
, the former capital of the Seleucids; Augustine of Hippo found it ironic and fitting that the city that named Antiochus IV now revered those he persecuted. The one awkward aspect was that the martyrs had died upholding Jewish Law in an era when many Christians felt that the Law of Moses was not merely obsolete, but actively harmful. Christian authors generally downplayed the Jewishness of the martyrs, treating them as proto-Christians instead.
Controversy in the Reformation era
 2 Maccabees was in a position of being an official part of the canon, but as a deuterocanonical work and thus subtly lesser than the older scriptures during the early 1500s.
2 Maccabees was in a position of being an official part of the canon, but as a deuterocanonical work and thus subtly lesser than the older scriptures during the early 1500s. Josse van Clichtove
Josse van Clichtove or Judocus Clichtoveus Neoportuensis ( Nieuwpoort, 1472/73 – Chartres 22 September 1543), was a Flemish theologian, priest and humanist.
Life
He received his education at Leuven and at Paris under Jacques Lefèvre d'Étaples ...
, in his work ''The Veneration of Saints'', cited 2 Maccabees as support for the idea of dead saints interceding for the salvation of the living; in Chapter 15, during a dream vision, both the earlier high priest Onias III and the prophet Jeremiah are said to pray for whole of the people. He also cited 2 Maccabees as support for prayers for the dead, the reverse case of the living praying for the salvation of souls suffering in purgatory.
The book became controversial due to opposition from Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
and other reformers during the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
of the 1500s. Luther had a very high opinion of scripture, but precisely because of this, he wished for the canon to be strict. He would eventually demote the deuterocanonical works to "apocrypha
Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered ...
"; still useful to read and part of the 1534 version of the Luther Bible
The Luther Bible (german: Lutherbibel) is a German language Bible translation from Latin sources by Martin Luther. The New Testament was first published in September 1522, and the complete Bible, containing the Old and New Testaments with Apocr ...
, but set aside in their own separate section and not accepted as a sound basis for Christian doctrine. Luther had several complaints. One was that it was an abridgment of another work, rather than a single divinely inspired author. Another was a general preference for using the Hebrew Bible as the basis for the Old Testament, rather than the Latin Vulgate or the Greek Septuagint. Another was with the prevailing Catholic interpretation and use of one story: that of Judas making a "sin offering
A sin offering ( he, קָרְבַּן חַטָּאת, ''korban ḥatat'', , lit: "purification offering") is a sacrificial offering described and commanded in the Torah (Lev. 4.1-35); it could be fine flour or a proper animal.Leviticus 5:11 A sin ...
" of silver after some of his troops were slain and found with idols, so that the dead might be delivered from their sin. This passage was used as an example of the efficacy of monetary indulgence
In the teaching of the Catholic Church, an indulgence (, from , 'permit') is "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins". The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' describes an indulgence as "a remission before God of ...
s paid to the Catholic Church to free souls from purgatory
Purgatory (, borrowed into English via Anglo-Norman and Old French) is, according to the belief of some Christian denominations (mostly Catholic), an intermediate state after physical death for expiatory purification. The process of purgator ...
by some Catholic authors of the period. Luther disagreed with both indulgences and the concept of purgatory, and in his 1530 work ''Disavowl of Purgatory'', he denied that 2 Maccabees was a valid source to cite. Luther was reported as having said: "I am so great an enemy to the second book of the Maccabees, and to Esther
Esther is the eponymous heroine of the Book of Esther. In the Achaemenid Empire, the Persian king Ahasuerus seeks a new wife after his queen, Vashti, is deposed for disobeying him. Hadassah, a Jewess who goes by the name of Esther, is chosen ...
, that I wish they had not come to us at all, for they have too many heathen unnaturalities." The reformer Jean Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the syste ...
agreed with Luther's criticism of 2 Maccabees, and added his own criticism as well. Calvin propounded predestination
Predestination, in theology, is the doctrine that all events have been willed by God, usually with reference to the eventual fate of the individual soul. Explanations of predestination often seek to address the paradox of free will, whereby Go ...
, the doctrine that God has chosen the elect, and nothing can change this. Thus, the arguments from Clichtove and other Catholics that cited 2 Maccabees for the doctrine of the intercession of saints
Intercession of the Saints is a Christian doctrine held by the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. The practice of praying through saints can be found in Christian writings from the 3rd century onward.
The 4th-century Apos ...
was suspect to him: for Calvin, salvation was strictly God's choice, and not a matter that dead saints could intervene on. Another issue Calvin and other Protestants raised was the self-effacing epilogue to 2 Maccabees, which Calvin took as an admission from the epitomist that he was not divinely inspired.
In response to this, the Catholic Church went the opposite direction. While earlier Church Fathers had considered the deuterocanonical books useful but lesser than the main scriptures, the Catholic Church now affirmed that 2 Maccabees (and other deuterocanonical works) were in fact fully reliable as scripture at the Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described as ...
in 1546.
Modern status
2 Maccabees is still used to endorse the doctrine of resurrection of the dead, intercession of saints, and prayers for the dead to be released from purgatory in the Catholic tradition. TheLatin Church
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
Lectionary
A lectionary ( la, lectionarium) is a book or listing that contains a collection of scripture readings appointed for Christian or Judaic worship on a given day or occasion. There are sub-types such as a "gospel lectionary" or evangeliary, and a ...
makes use of texts from 2 Maccabees 6 and 7, along with texts from 1 Maccabees 1 to 6, in the weekday readings for the 33rd week in Ordinary Time
Ordinary Time ( la, Tempus per annum) is the part of the liturgical year in the liturgy of the Roman Rite, which falls outside the two great seasons of Christmastide and Eastertide, or their respective preparatory seasons of Advent and Lent. O ...
, in year 1 of the two-year cycle of readings, always in November, and as one of the options available for readings during a Mass for the Dead
A Requiem or Requiem Mass, also known as Mass for the dead ( la, Missa pro defunctis) or Mass of the dead ( la, Missa defunctorum), is a Mass of the Catholic Church offered for the repose of the soul or souls of one or more deceased persons, ...
.
The Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox Churches consider the book canonical. As in antiquity, the most notable section remains the martyrs, who are celebrated as saints by a variety of feast days. They are especially honored in Syriac Christianity
Syriac Christianity ( syr, ܡܫܝܚܝܘܬܐ ܣܘܪܝܝܬܐ / ''Mšiḥoyuṯo Suryoyto'' or ''Mšiḥāyūṯā Suryāytā'') is a distinctive branch of Eastern Christianity, whose formative theological writings and traditional liturgies are exp ...
, perhaps due to suffering persecution themselves; the mother of seven sons is known as Marth Shmouni in that tradition.
In the Protestant tradition, the book remains non-canonical. Many Protestant Bibles stopped including the apocrypha, leading to a loss of relevance for 2 Maccabees. Still, the book is treated at least somewhat respectfully. The twentieth century evangelical author James B. Jordan, for example, argues that while 1 Maccabees "was written to try and show the Maccabean usurpers as true heirs of David and as true High Priests" and is a "wicked book", a "far more accurate picture of the situation is given in 2 Maccabees."
Article VI of the Thirty-nine Articles
The Thirty-nine Articles of Religion (commonly abbreviated as the Thirty-nine Articles or the XXXIX Articles) are the historically defining statements of doctrines and practices of the Church of England with respect to the controversies of th ...
of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church record ...
and the wider Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is the third largest Christian communion after the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. Founded in 1867 in London, the communion has more than 85 million members within the Church of England and other ...
defines 2 Maccabees as useful but not the basis of doctrine.
The texts regarding the martyrdoms under Antiochus IV in 2 Maccabees are held in high esteem by the Anabaptists
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
, who faced persecution in their history.
Literary influence
 The most influential part of 2 Maccabees was its stories of the martyrdom of Eleazar and the woman with seven sons; various works expanded the story to add more details such as the woman's name (variously called Hannah, Miriam, Shmouni, and other names) and their story. A prominent early example is the book of
The most influential part of 2 Maccabees was its stories of the martyrdom of Eleazar and the woman with seven sons; various works expanded the story to add more details such as the woman's name (variously called Hannah, Miriam, Shmouni, and other names) and their story. A prominent early example is the book of 4 Maccabees
4 Maccabees, el, Μακκαβαίων Δʹ, translit=Makkabaíōn 4 also called the Fourth Book of Maccabees and possibly originally known as On the Sovereignty of Reason, el, περί αύτοκράτορος λογισμού, translit=Perí áf ...
, written by a 1st-century Jewish author who used 2 Maccabees as a direct source (as well as the Book of Daniel
The Book of Daniel is a 2nd-century BC biblical apocalypse with a 6th century BC setting. Ostensibly "an account of the activities and visions of Daniel, a noble Jew exiled at Babylon", it combines a prophecy of history with an eschatology (a ...
). 4 Maccabees discusses in detail the martyrdoms described in 2 Maccabees, but provides a different interpretation of them. While 2 Maccabees attempts to arouse sympathy and emotions (''pathos''), 4 Maccabees was written by someone schooled in Stoic philosophy
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy founded by Zeno of Citium in Athens in the early 3rd century BCE. It is a philosophy of personal virtue ethics informed by its system of logic and its views on the natural world, asserting tha ...
. As such, in its depiction, the martyred woman and Eleazar calmly discuss matters with their oppressors; they use reason and intellectual argument to stay calm and defy Antiochus IV. 4 Maccabees takes the idea of the resurrection of the dead even more directly than 2 Maccabees and Daniel: if God will revive those who suffer for obeying God's law, then it makes perfect sense to obey the greater ruler rather than the lesser ruler.
To a lesser degree, the book 3 Maccabees
3 Maccabees, el, Μακκαβαίων Γ´, translit=Makkabaíōn 3 also called the Third Book of Maccabees, is a book written in Koine Greek, likely in the 1st century BC in Roman Egypt. Despite the title, the book has nothing to do with the Macc ...
evinces familiarity with 2 Maccabees; while the setting is different (it is set fifty years before the Maccabean Revolt in Egypt, not Judea), Eleazar the scribe appears in it, and the depictions of turmoil and suffering among Egyptian Jews are influenced by 2 Maccabees. The Christian Epistle to the Hebrews
The Epistle to the Hebrews ( grc, Πρὸς Ἑβραίους, Pros Hebraious, to the Hebrews) is one of the books of the New Testament.
The text does not mention the name of its author, but was traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle. Mos ...
possibly makes a reference to 2 Maccabees as well.
A later work that directly expanded 2 Maccabees was the ''Yosippon
''Josippon'' ( ''Sefer Yosipon'') is a chronicle of Jewish history from Adam to the age of Titus. It is named after its supposed author, Josephus Flavius, though it was actually composed in the 10th century in Southern Italy. The Ethiopic ve ...
'' of the 10th century, which includes a paraphrase of parts of the Latin translation of 2 Maccabees. Among Jews, there had been practically no interest in 2 Maccabees itself for a millennium; the ''Yosippon'' was a rare exception of medieval Jews rediscovering the work. Much like in Christian works, the story of the mother and her seven sons was the most retold and influential.
Reliability as history
2 Maccabees has traditionally been considered a somewhat lesser source on the history of the Maccabean Revolt than 1 Maccabees by secular historians, especially in the 19th century. This is for a number of reasons: it wears its religious moralizing openly; it skips around in time and place at parts, rather than the chronological approach in 1 Maccabees; and it includes a number of implausible claims directly in contention with 1 Maccabees. In general, most scholars continue to agree that 1 Maccabees is a superior source on the military history of the revolt: it was written by a Judean who names and describes locations accurately compared to the occasional geographic blunders of 2 Maccabees written by an Egyptian, includes far more details on maneuvers and tactics than the simple depictions of battle in 2 Maccabees, and its figures for elements such as troop counts and casualties are considered more reliable than the wildly inflated numbers in 2 Maccabees. (For example, 2 Maccabees implausibly claims that there were 35,000 Syrian casualties at the Battle of Adasa, a number likely far larger than the entire Seleucid force.) 2 Maccabees was also written in a "pathetic" in the sense of ''pathos
Pathos (, ; plural: ''pathea'' or ''pathê''; , for "suffering" or "experience") appeals to the emotions and ideals of the audience and elicits feelings that already reside in them. Pathos is a term used most often in rhetoric (in which it is c ...
'' style, appealing to emotions and sentiment. Skeptical historians considered this a sign that the epitomist was not interested in historical accuracy much, but merely telling a good story.
In the 20th century, there was a renewed interest in rehabilitating 2 Maccabees as a source on par with 1 Maccabees by scholars. In particular, there was a growing recognition that a politically slanted history, as 1 Maccabees is, could be just as biased and unreliable as the religiously slanted history that 2 Maccabees is. A deeply devout observer could still be describing true events, albeit with a religious interpretation of them. By the 1930s, historians generally came to the conclusion that the historical documents present in 2 Maccabees - while seemingly out of chronological order - were likely legitimate and matched what would be expected of such Seleucid negotiations. Archaeological evidence supported many of the references made to Seleucid leadership, causing historians to think that Jason and the epitomist must have had better knowledge of internal Seleucid affairs than the author of 1 Maccabees. As an example, 2 Maccabees appears to be more reliable and honest on the date of the death of Antiochus IV. Archaeological evidence supports the claim in 2 Maccabees he died before the cleansing of the Temple, while 1 Maccabees moves his death later to hide the fact that Lysias abandoned his campaign in Judea not due to the efforts of the Maccabees at the Battle of Beth Zur
The Battle of Beth Zur was fought between the Maccabees led by Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) and a Seleucid Greek army led by Regent Lysias in October 164 BC at Beth Zur. According to the books of Maccabees, the rebels won the battle, altho ...
, but rather to respond to political turmoil resulting from Antiochus's death. 2 Maccabees writes that Antiochus's decrees were targeted against Judea and Samaria, which historians find more likely than the claim in 1 Maccabees that he demanded religious standardization across the entire empire.
Even to the extent that 2 Maccabees is still distrusted as history to a degree, the fact that it is a genuinely independent source is considered invaluable to historians. Many events in the Hellenistic and Roman periods have only passing mentions that they occurred; those that do have a detailed source often only have a single such detailed source, leaving it difficult to determine that author's biases or errors. For example, the Great Revolt against the Romans in 64–73 AD is only closely recorded by Josephus's ''The Jewish War
''The Jewish War'' or ''Judean War'' (in full ''Flavius Josephus' Books of the History of the Jewish War against the Romans'', el, Φλαυίου Ἰωσήπου ἱστορία Ἰουδαϊκοῦ πολέμου πρὸς Ῥωμαίους ...
''. The Maccabean Revolt having two independent detailed contemporary histories is a rarity.
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * *Further reading
*Borchardt, Francis. 2016. "Reading Aid: 2 Maccabees and the History of Jason of Cyrene Reconsidered." ''Journal for the Study of Judaism'' 47, no. 1: 71–87. *Coetzer, Eugene. 2016. "Heroes and Villains in 2 Maccabees 8:1–36: A Rhetorical Analysis." ''Old Testament Essays'': 419–33. *Doran, Robert. 1981. ''Temple Propaganda: The Purpose and Character of 2 Maccabees.'' Catholic Biblical Quarterly Monograph Series 12. Washington, DC: Catholic Biblical Association. *Habicht, C. 1976. "Royal Documents in II Maccabees." ''Harvard Studies in Classical Philology'' 80: 1–18. *Janowitz, Naomi. 2017. ''The Family Romance of Martyrdom In Second Maccabees.'' New York: Routledge. *Kosmin, P. 2016. "Indigenous Revolts in 2 Maccabees: The Persian Version." ''Classical Philology'' 111, no. 1: 32–53. *Stewart, Tyler A. 2017. "Jewish Paideia: Greek Education in the Letter of Aristeas and 2 Maccabees." Journal for the Study of Judaism 48, no. 2: 182–202. *Trotter, Jonathan R. 2017. "2 Maccabees 10:1–8: Who Wrote It and Where Does It Belong?" ''Journal of Biblical Literature'' 136, no. 1: 117–30.External links
* NRSV text of 2 Maccabees: , , * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Maccabees, 2 2nd-century BC books 1st-century BC books Deuterocanonical books 2 Hasmonean dynasty Texts in Koine Greek Jewish apocrypha