Schottky effect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Schottky effect or field enhanced thermionic emission is a phenomenon in
The Schottky effect or field enhanced thermionic emission is a phenomenon in  Electron emission that takes place in the field-and-temperature-regime where this modified equation applies is often called Schottky emission. This equation is relatively accurate for electric field strengths lower than about 108 V m−1. For electric field strengths higher than 108 V m−1, so-called Fowler–Nordheim (FN) tunneling begins to contribute significant emission current. In this regime, the combined effects of field-enhanced thermionic and field emission can be modeled by the Murphy–Good equation for thermo-field (T-F) emission. At even higher fields, FN tunneling becomes the dominant electron emission mechanism, and the emitter operates in the so-called "cold field electron emission (CFE)" regime.
Thermionic emission can also be enhanced by interaction with other forms of excitation such as light. For example, excited Cs-vapours in thermionic converters form clusters of Cs- Rydberg matter which yield a decrease of collector emitting work function from 1.5 eV to 1.0–0.7 eV. Due to long-lived nature of Rydberg matter this low work function remains low which essentially increases the low-temperature converter’s efficiency.
Electron emission that takes place in the field-and-temperature-regime where this modified equation applies is often called Schottky emission. This equation is relatively accurate for electric field strengths lower than about 108 V m−1. For electric field strengths higher than 108 V m−1, so-called Fowler–Nordheim (FN) tunneling begins to contribute significant emission current. In this regime, the combined effects of field-enhanced thermionic and field emission can be modeled by the Murphy–Good equation for thermo-field (T-F) emission. At even higher fields, FN tunneling becomes the dominant electron emission mechanism, and the emitter operates in the so-called "cold field electron emission (CFE)" regime.
Thermionic emission can also be enhanced by interaction with other forms of excitation such as light. For example, excited Cs-vapours in thermionic converters form clusters of Cs- Rydberg matter which yield a decrease of collector emitting work function from 1.5 eV to 1.0–0.7 eV. Due to long-lived nature of Rydberg matter this low work function remains low which essentially increases the low-temperature converter’s efficiency.
 The Schottky effect or field enhanced thermionic emission is a phenomenon in
The Schottky effect or field enhanced thermionic emission is a phenomenon in condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the ...
named after Walter H. Schottky. In electron emission devices, especially electron gun
An electron gun (also called electron emitter) is an electrical component in some vacuum tubes that produces a narrow, collimated electron beam that has a precise kinetic energy. The largest use is in cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), used in nearly ...
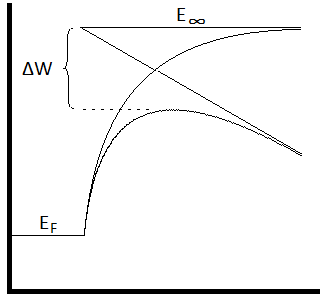
s, the thermionic electron emitter will be biased negative relative to its surroundings. This creates an electric field of magnitude ''F'' at the emitter surface. Without the field, the surface barrier seen by an escaping Fermi-level electron has height ''W'' equal to the local work-function. The electric field lowers the surface barrier by an amount Δ''W'', and increases the emission current. It can be modeled by a simple modification of the Richardson equation, by replacing ''W'' by (''W'' − Δ''W''). This gives the equation
:
:
where ''J'' is the emission current density
In electromagnetism, current density is the amount of charge per unit time that flows through a unit area of a chosen cross section. The current density vector is defined as a vector whose magnitude is the electric current per cross-sectional ar ...
, ''T'' is the temperature of the metal, ''W'' is the work function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelt workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately" m ...
of the metal, ''k'' is the Boltzmann constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constan ...
, ''q''e is the Elementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted by is the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 . This elementary charge is a fundame ...
, ''ε''0 is the vacuum permittivity
Vacuum permittivity, commonly denoted (pronounced "epsilon nought" or "epsilon zero"), is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It may also be referred to as the permittivity of free space, the electric const ...
, and ''A''G is the product of a universal constant ''A''0 multiplied by a material-specific correction factor ''λ''R which is typically of order 0.5.
 Electron emission that takes place in the field-and-temperature-regime where this modified equation applies is often called Schottky emission. This equation is relatively accurate for electric field strengths lower than about 108 V m−1. For electric field strengths higher than 108 V m−1, so-called Fowler–Nordheim (FN) tunneling begins to contribute significant emission current. In this regime, the combined effects of field-enhanced thermionic and field emission can be modeled by the Murphy–Good equation for thermo-field (T-F) emission. At even higher fields, FN tunneling becomes the dominant electron emission mechanism, and the emitter operates in the so-called "cold field electron emission (CFE)" regime.
Thermionic emission can also be enhanced by interaction with other forms of excitation such as light. For example, excited Cs-vapours in thermionic converters form clusters of Cs- Rydberg matter which yield a decrease of collector emitting work function from 1.5 eV to 1.0–0.7 eV. Due to long-lived nature of Rydberg matter this low work function remains low which essentially increases the low-temperature converter’s efficiency.
Electron emission that takes place in the field-and-temperature-regime where this modified equation applies is often called Schottky emission. This equation is relatively accurate for electric field strengths lower than about 108 V m−1. For electric field strengths higher than 108 V m−1, so-called Fowler–Nordheim (FN) tunneling begins to contribute significant emission current. In this regime, the combined effects of field-enhanced thermionic and field emission can be modeled by the Murphy–Good equation for thermo-field (T-F) emission. At even higher fields, FN tunneling becomes the dominant electron emission mechanism, and the emitter operates in the so-called "cold field electron emission (CFE)" regime.
Thermionic emission can also be enhanced by interaction with other forms of excitation such as light. For example, excited Cs-vapours in thermionic converters form clusters of Cs- Rydberg matter which yield a decrease of collector emitting work function from 1.5 eV to 1.0–0.7 eV. Due to long-lived nature of Rydberg matter this low work function remains low which essentially increases the low-temperature converter’s efficiency.
References
{{Reflist Condensed matter physics Electron beam