school belonging on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The most commonly used definition of school belonging comes from a 1993 academic article by researchers Carol Goodenow and Kathleen Grady, who describe school belonging as "the extent to which students feel personally accepted,
The most commonly used definition of school belonging comes from a 1993 academic article by researchers Carol Goodenow and Kathleen Grady, who describe school belonging as "the extent to which students feel personally accepted,
 Peer relations have been identified as a direct contributor to students' development of school belonging. Positive social relations with peers involve feelings of acceptance, connection, encouragement, academic and social support,
Peer relations have been identified as a direct contributor to students' development of school belonging. Positive social relations with peers involve feelings of acceptance, connection, encouragement, academic and social support,

 Research has shown that being involved in
Research has shown that being involved in
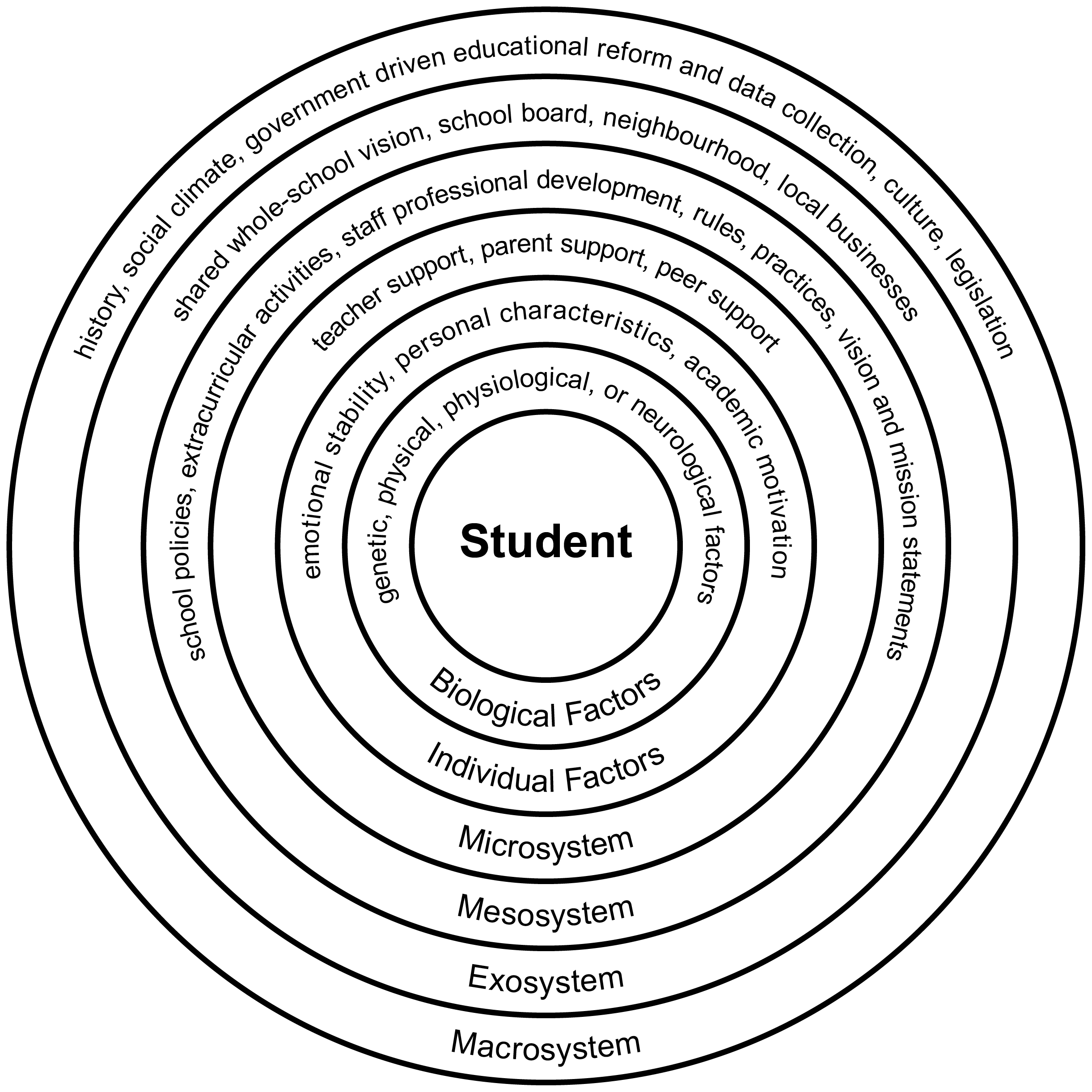 The many determinants of school belonging can be conceptualised in a socio-ecological model. The ''Socio-ecological Model of School Belonging'' developed by Allen and Colleagues (2016), adapted from Bronfenbrenner's Socio-ecological systems theory (1979) is used to describe the school system as whole and the multiple and dynamic influencers of school belonging. The model depicts students at the centre of their school environment. The inner circles describe biological and individual level characteristics that influence school belonging. These factors include biological traits and personal characteristics such as emotional stability and academic motivation. The microsystem is represented by relationships with others, specifically, teachers, peers, and parents. The mesosystem represents the school policy and practices that occur within the day-to-day operations of the school and the exosystem represents a broader level that may include the wider school community. The macro-system describes the cultural context of a school that may be influenced by where a school is geographically located, the external social climate, and other factors such as history, legislation, and government driven priorities.
The many determinants of school belonging can be conceptualised in a socio-ecological model. The ''Socio-ecological Model of School Belonging'' developed by Allen and Colleagues (2016), adapted from Bronfenbrenner's Socio-ecological systems theory (1979) is used to describe the school system as whole and the multiple and dynamic influencers of school belonging. The model depicts students at the centre of their school environment. The inner circles describe biological and individual level characteristics that influence school belonging. These factors include biological traits and personal characteristics such as emotional stability and academic motivation. The microsystem is represented by relationships with others, specifically, teachers, peers, and parents. The mesosystem represents the school policy and practices that occur within the day-to-day operations of the school and the exosystem represents a broader level that may include the wider school community. The macro-system describes the cultural context of a school that may be influenced by where a school is geographically located, the external social climate, and other factors such as history, legislation, and government driven priorities.
 Feelings of school belonging can have a significant influence on academic development and outcomes for students. School belonging is related to students' expectancy of success, effort in school, and perceived value of school and education. Greater feelings of school belonging has been shown to increase engagement and participation both inside school and within extracurricular activities. Similarly, school belonging is associated with a greater commitment to school. Strong feelings of school belonging have also been shown to improve overall academic performance and achievement, as shown by increases in grade point averages. A sense of belonging at school can also improve academic self-efficacy, or in other words, students' belief in their ability to succeed in school.
Research has suggested that school belonging can also alleviate the prevalence of negative academic outcomes. Greater feelings of school belonging are associated with decreased misbehavior and misconduct, such as
Feelings of school belonging can have a significant influence on academic development and outcomes for students. School belonging is related to students' expectancy of success, effort in school, and perceived value of school and education. Greater feelings of school belonging has been shown to increase engagement and participation both inside school and within extracurricular activities. Similarly, school belonging is associated with a greater commitment to school. Strong feelings of school belonging have also been shown to improve overall academic performance and achievement, as shown by increases in grade point averages. A sense of belonging at school can also improve academic self-efficacy, or in other words, students' belief in their ability to succeed in school.
Research has suggested that school belonging can also alleviate the prevalence of negative academic outcomes. Greater feelings of school belonging are associated with decreased misbehavior and misconduct, such as
School belonging measure
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210124181752/https://www.thebelonginglab.com/belonging-tools , date=2021-01-24 s are found on th
International Belonging Research Laboratory
Developmental psychology Educational assessment and evaluation Educational environment Education and health Educational research Teaching
 The most commonly used definition of school belonging comes from a 1993 academic article by researchers Carol Goodenow and Kathleen Grady, who describe school belonging as "the extent to which students feel personally accepted,
The most commonly used definition of school belonging comes from a 1993 academic article by researchers Carol Goodenow and Kathleen Grady, who describe school belonging as "the extent to which students feel personally accepted, respect
Respect, also called esteem, is a positive feeling or action shown towards someone or something considered important or held in high esteem or regard. It conveys a sense of admiration for good or valuable qualities. It is also the process of ...
ed, included, and supported by others in the school social environment." The construct of school belonging involves feeling connected with and attached to one's school. It also encompasses involvement and affiliation with one's school community. Conversely, students who do not feel a strong sense of belonging within their school environment are frequently described as being alienated or disaffected. There are a number of terms within educational research that are used interchangeably with school belonging, including school connectedness, school attachment, and school engagement.
School belonging is determined by a myriad of factors, including academic achievement and motivation, personal characteristics, social relation
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
ships, demographic
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as edu ...
characteristics, school climate, and participation in extracurricular activities
An extracurricular activity (ECA) or extra academic activity (EAA) or cultural activities is an activity, performed by students, that falls outside the realm of the normal curriculum of school, college or university education. Such activities a ...
. Research indicates that school belonging has significant implications for students, as it has been consistently linked with academic outcomes, psychological adjustment, well-being
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
, identity formation
Identity formation, also called identity development or identity construction, is a complex process in which humans develop a clear and unique view of themselves and of their Identity (social science), identity.
Self-concept, personality developme ...
, mental health, and physical health—it is considered a fundamental aspect of students' development. A sense of belonging to one's school is considered particularly important for adolescents
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with the te ...
because they are within a period of transition and identity formation, and research has found that school belonging significantly declines during this period.
Psychological Sense of School Membership (PSSM), developed in 1993, is one of the measures to ascertain the degree to which students feel a sense of school belonging. Students rate the extent to which they agree or disagree with statements, such as "People here notice when I'm good at something." In 2003, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
held an international convention where the Wingspread Declaration on School Connections was developed as a group of tactics to increase students' sense of belonging and connection with their school.
Prevalence and trajectory
Research indicates that many students have deficient feelings of school belonging. TheProgramme for International Student Assessment
The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) is a worldwide study by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in member and non-member nations intended to evaluate educational systems by measuring 15-yea ...
(PISA) has an investigated school belonging and disaffection in students around the world since 2003. Their most recent collection of data occurred in 2018. Approximately 600,000 students representing 32 million 15 years olds (aged between 15 years 3 months and 16 years 2 months) from 79 countries and economies participated in PISA
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the cit ...
2018. Their analyses revealed that a significant proportion of students around the world are lacking strong feelings of belongingness to school. On average, a third of all students surveyed felt they did not belong to their school. In addition, they found that one in five students feels like an outsider at school and one in six reports feeling lonely. In most of the education systems, students who were socio-economically felt less belonging to school. On average student belonging to school declined by 2% between 2015 and 2018. The portion of students who do not feel like they belong to school has increased since 2003 indicating a trend in the deterioration of school belonging globally.
School belonging tends to decrease as students grow older, as indicated in several different research studies. In one study involving students from Latin America, Asia, and Europe, researchers Cari Gillen-O'Neel and Andrew Fuligni found that in childhood, students generally report high levels of school belonging. However, once students transition into middle school and adolescence, their perceptions of school belonging drop significantly. Similarly, a separate study found that students' school belonging decreased in the transition from middle to high school; these students also displayed an increase in depressive symptoms
Depression is a mental state of low Mood (psychology), mood and aversion to activity, which affects more than 280 million people of all ages (about 3.5% of the global population). Classified medically as a mental disorder, mental and Abnor ...
and a decline in social support
Social support is the perception and actuality that one is cared for, has assistance available from other people, and most popularly, that one is part of a supportive social network. These supportive resources can be emotional (e.g., nurturance), ...
, which could be considered either causes or consequences of the decline in school belonging. This trend has been replicated in many other studies, suggesting that school belonging declines once students reach adolescence.
Determinants
A meta-analysis of 51 studies (N = 67,378) by K. Allen and colleagues (2018) identified that there are multiple individual and social level factors that influence school belonging. These core themes include academic factors, personal characteristics, social relationships, demographic characteristics, school climate and extra-curricular activities. For many of the determinants of school belonging, it is likely that each of them have a reciprocal relationship with a student's sense of belonging. That is, they operate as both an antecedents or consequences.Academic factors
Research has documented the influence of academic factors (i.e. achievement,motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-dire ...
, hardiness, interest in school) on students' school belonging. Academic achievement, or one's skills and competencies in school, has been identified as a substantial predictor of school belonging. For example, research has demonstrated that students' grade point averages (GPAs), a common measure of academic achievement, are positively associated with school belonging. This means that students who have higher GPAs have higher levels of school belonging. Studies have also found several measures of academic motivation to be determinants of students' school belonging. Academic motivation encompasses behaviors such as homework completion, setting goals, expectancy of success, and effort and engagement within the classroom. Carol Goodenow and Kathleen Grady found each of these sub-sects of academic motivation to be significant predictors of students' perceptions of school belonging. More recent research has replicated these findings, suggesting that academic motivation plays an important role in developing feelings of school belonging. In addition, students' perceived value of school influences their school belonging: when they perceive their assignments and education as instructive, meaningful, and valuable, they are more likely to report greater school belonging.
Personal characteristics
Personal characteristics refer to students' distinctive qualities, traits,personality
Personality is the characteristic sets of behaviors, cognitions, and emotional patterns that are formed from biological and environmental factors, and which change over time. While there is no generally agreed-upon definition of personality, mos ...
, emotion
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure. There is currently no scientific consensus on a definition. ...
s, and attributes, and have been consistently identified as a substantial determinant of school belonging. Personal characteristics can be classified as either positive or negative. Positive personal characteristics such as self-esteem
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth or abilities. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Mackie (2007) d ...
, self-efficacy
In psychology, self-efficacy is an individual's belief in their capacity to act in the ways necessary to reach specific goals. The concept was originally proposed by the psychologist Albert Bandura.
Self-efficacy affects every area of human endea ...
, positive affect
Positive affectivity (PA) is a human characteristic that describes how much people experience positive affects (sensations, emotions, sentiments); and as a consequence how they interact with others and with their surroundings.
People with high po ...
, and effective emotional regulation
Emotional self-regulation
or emotion regulation is the ability to respond to the ongoing demands of experience with the range of emotions in a manner that is socially tolerable and sufficiently flexible to permit spontaneous reactions as well as ...
have been shown to help foster students' sense of school belonging. A study by Xin Ma found that students' self-esteem had the greatest impact on school belonging compared to all other personal factors. Conversely, negative personal characteristics like anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, depressive symptoms
Depression is a mental state of low Mood (psychology), mood and aversion to activity, which affects more than 280 million people of all ages (about 3.5% of the global population). Classified medically as a mental disorder, mental and Abnor ...
, heightened stress, negative affect
Negative affectivity (NA), or negative affect, is a personality variable that involves the experience of negative emotions and poor self-concept. Negative affectivity subsumes a variety of negative emotions, including anger, contempt, disgust, gui ...
, and mental illness
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
can lower students' perceptions of school belonging. Emotional instability can further influence school belonging by negatively affecting students' educational experiences.
Social relationships
Social relation
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
ships are involved in developing students' feelings of belonging within a school. There are large, positive correlations between school belonging and positive social relations with peers, teachers, and parents. Support, acceptance, and encouragement from these sources can help students develop the feeling that they connect and identify with their school.
Peers
 Peer relations have been identified as a direct contributor to students' development of school belonging. Positive social relations with peers involve feelings of acceptance, connection, encouragement, academic and social support,
Peer relations have been identified as a direct contributor to students' development of school belonging. Positive social relations with peers involve feelings of acceptance, connection, encouragement, academic and social support, trust
Trust often refers to:
* Trust (social science), confidence in or dependence on a person or quality
It may also refer to:
Business and law
* Trust law, a body of law under which one person holds property for the benefit of another
* Trust (bus ...
, closeness, and caring. Such qualities within a peer relationship can significantly facilitate students' feelings of school belonging. When students are rejected or unsupported by their peers, they may experience anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, stress, and alienation. This alters their perceptions of belonging at school because the school environment now seems unwelcome and distressing, making it harder to identify and connect with the school.
Parents
Relationships with one's parents can have significant implications for students' feelings of school belonging, given that parents typically provide students' first social relationships. Positive parental relations include parents providing academic andsocial support
Social support is the perception and actuality that one is cared for, has assistance available from other people, and most popularly, that one is part of a supportive social network. These supportive resources can be emotional (e.g., nurturance), ...
, healthy communication, encouragement, compassion
Compassion motivates people to go out of their way to relieve the physical, mental or emotional pains of others and themselves. Compassion is often regarded as being sensitive to the emotional aspects of the suffering of others. When based on n ...
, acceptance, and safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to risk management, the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are ...
. Such qualities within parent-child relationships have been shown to foster students' sense of school belonging by influencing their perceived connection with their school environment.
Teachers

Teacher
A teacher, also called a schoolteacher or formally an educator, is a person who helps students to acquire knowledge, competence, or virtue, via the practice of teaching.
''Informally'' the role of teacher may be taken on by anyone (e.g. whe ...
s have been identified as being noteworthy contributors to students' feelings of belonging at school. Several academic studies have identified teacher support as the strongest predictor of school belonging compared to support from peers or parents. Teachers can help instil school belonging by developing a safe and healthy classroom climate, providing academic and social support, fostering respect
Respect, also called esteem, is a positive feeling or action shown towards someone or something considered important or held in high esteem or regard. It conveys a sense of admiration for good or valuable qualities. It is also the process of ...
amongst peers, and treating students fairly. Teachers can also promote feelings of school belonging by being friendly, approachable, and making an effort to connect with their students. Teaching practices that seem to promote students' school belonging include scaffolding
Scaffolding, also called scaffold or staging, is a temporary structure used to support a work crew and materials to aid in the construction, maintenance and repair of buildings, bridges and all other man-made structures. Scaffolds are widely use ...
learning, commending positive behaviors and performance, allowing students autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
within the classroom, and using academic pressure, such as holding high expectations of students.
Demographic characteristics
Gender
The relationship between gender and school belonging is largely inconclusive because research has produced conflicting results. Several studies have foundgender differences
Sex differences in humans have been studied in a variety of fields. Sex determination occurs by the presence or absence of a Y in the 23rd pair of chromosomes in the human genome. Phenotypic sex refers to an individual's sex as determined by the ...
in perceptions of school belonging: some research indicates that females possess a higher sense of school belonging compared to males, while other studies have found the opposite effect and conclude that males have higher school belonging than females. Other research has demonstrated that school belonging is not at all influenced by gender.
Race and ethnicity
Similar to gender, some research on the effect ofrace and ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
on school belonging has found a significant relationship between the two, while other research contradicts these findings. For example, one study found that Black students experience lower feelings of school belonging compared to white students, however, other research has found the opposite pattern or has found no significant influence of race on school belonging at all.
School climate
A school's climate can have significant consequences for students feeling like they belong at school. School climate broadly refers to the feelings associated with a school's environment and quality; it is considered to have physical (e.g. adequacy of buildings), social (e.g. interpersonal relationships), and academic dimensions (e.g. teaching quality). School climate influences school belonging through its support (or lack thereof) of students' feelings of connection with and attachment to their school. One important facet of school climate is school safety, which is how safe students feel at school. It includes variables such as a school's safety policies, use of discipline,bullying
Bullying is the use of force, coercion, hurtful teasing or threat, to abuse, aggressively dominate or intimidate. The behavior is often repeated and habitual. One essential prerequisite is the perception (by the bully or by others) of an imba ...
prevalence, and fairness. School safety is regarded as an important determinant of school belonging. Higher perceptions of school safety is associated with students holding greater feelings of school belonging.
Extracurricular activities
 Research has shown that being involved in
Research has shown that being involved in extracurricular activities
An extracurricular activity (ECA) or extra academic activity (EAA) or cultural activities is an activity, performed by students, that falls outside the realm of the normal curriculum of school, college or university education. Such activities a ...
can positively influence students' perceptions of school belonging. For example, researchers Casey Knifsend and Sandra Graham found that students who participated in two extracurricular activities reported greater feelings of school belonging compared to those students who participated in fewer than two. Other studies have replicated this relationship, highlighting the importance of participating in extracurricular activities for developing school belonging. Extracurricular activities may influence school belonging by providing collaborative and long-term interactions between students and their peers.
A Socio-ecological perspective
 The many determinants of school belonging can be conceptualised in a socio-ecological model. The ''Socio-ecological Model of School Belonging'' developed by Allen and Colleagues (2016), adapted from Bronfenbrenner's Socio-ecological systems theory (1979) is used to describe the school system as whole and the multiple and dynamic influencers of school belonging. The model depicts students at the centre of their school environment. The inner circles describe biological and individual level characteristics that influence school belonging. These factors include biological traits and personal characteristics such as emotional stability and academic motivation. The microsystem is represented by relationships with others, specifically, teachers, peers, and parents. The mesosystem represents the school policy and practices that occur within the day-to-day operations of the school and the exosystem represents a broader level that may include the wider school community. The macro-system describes the cultural context of a school that may be influenced by where a school is geographically located, the external social climate, and other factors such as history, legislation, and government driven priorities.
The many determinants of school belonging can be conceptualised in a socio-ecological model. The ''Socio-ecological Model of School Belonging'' developed by Allen and Colleagues (2016), adapted from Bronfenbrenner's Socio-ecological systems theory (1979) is used to describe the school system as whole and the multiple and dynamic influencers of school belonging. The model depicts students at the centre of their school environment. The inner circles describe biological and individual level characteristics that influence school belonging. These factors include biological traits and personal characteristics such as emotional stability and academic motivation. The microsystem is represented by relationships with others, specifically, teachers, peers, and parents. The mesosystem represents the school policy and practices that occur within the day-to-day operations of the school and the exosystem represents a broader level that may include the wider school community. The macro-system describes the cultural context of a school that may be influenced by where a school is geographically located, the external social climate, and other factors such as history, legislation, and government driven priorities.
Consequences
Psychological health and adjustment
School belonging has numerous consequences for students'psychological health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental health ...
and adjustment. Research has shown that when students feel a greater sense of school belonging, their mental health and well-being is improved: they exhibit greater levels of emotional stability
Equanimity (Latin: ''æquanimitas'', having an even mind; ''aequus'' even; ''animus'' mind/soul) is a state of psychological stability and composure which is undisturbed by experience of or exposure to emotions, pain, or other phenomena that may ...
, lower levels of depression, reduced stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
, and an increase in positive emotions, such as happiness
Happiness, in the context of Mental health, mental or emotional states, is positive or Pleasure, pleasant emotions ranging from contentment to intense joy. Other forms include life satisfaction, well-being, subjective well-being, flourishin ...
and pride
Pride is defined by Merriam-Webster as "reasonable self-esteem" or "confidence and satisfaction in oneself". A healthy amount of pride is good, however, pride sometimes is used interchangeably with "conceit" or "arrogance" (among other words) wh ...
. Feelings of school belonging have also been shown to predict self-esteem
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth or abilities. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Mackie (2007) d ...
, self-concept
In the psychology of self, one's self-concept (also called self-construction, self-identity, self-perspective or self-structure) is a collection of beliefs about oneself. Generally, self-concept embodies the answer to the question ''"Who am I? ...
, and self-worth
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth or abilities. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Mackie (2007) d ...
. Students who possess school belonging experience more positive life transitions as well, which can have important implications for psychological health and adjustment.
On the other hand, students who do not have a strong sense of school belonging are at risk for a number of disadvantageous psychological and mental health outcomes. Students who lack a sense of belonging at school are at significantly greater risk for exhibiting anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, depression, negative affect, suicidal ideation
Suicidal ideation, or suicidal thoughts, means having thoughts, ideas, or ruminations about the possibility of ending one's own life.World Health Organization, ''ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics'', ver. 09/2020MB26.A Suicidal ideatio ...
, and overall developing mental illness
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
. It may also increase their feelings of social rejection
Social rejection occurs when an individual is deliberately excluded from a social relationship or social interaction. The topic includes ''interpersonal rejection'' (or peer rejection), ''romantic rejection'' and ''familial estrangement''. A pers ...
and alienation.
Academic development and outcomes
 Feelings of school belonging can have a significant influence on academic development and outcomes for students. School belonging is related to students' expectancy of success, effort in school, and perceived value of school and education. Greater feelings of school belonging has been shown to increase engagement and participation both inside school and within extracurricular activities. Similarly, school belonging is associated with a greater commitment to school. Strong feelings of school belonging have also been shown to improve overall academic performance and achievement, as shown by increases in grade point averages. A sense of belonging at school can also improve academic self-efficacy, or in other words, students' belief in their ability to succeed in school.
Research has suggested that school belonging can also alleviate the prevalence of negative academic outcomes. Greater feelings of school belonging are associated with decreased misbehavior and misconduct, such as
Feelings of school belonging can have a significant influence on academic development and outcomes for students. School belonging is related to students' expectancy of success, effort in school, and perceived value of school and education. Greater feelings of school belonging has been shown to increase engagement and participation both inside school and within extracurricular activities. Similarly, school belonging is associated with a greater commitment to school. Strong feelings of school belonging have also been shown to improve overall academic performance and achievement, as shown by increases in grade point averages. A sense of belonging at school can also improve academic self-efficacy, or in other words, students' belief in their ability to succeed in school.
Research has suggested that school belonging can also alleviate the prevalence of negative academic outcomes. Greater feelings of school belonging are associated with decreased misbehavior and misconduct, such as fighting
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or ...
, bullying
Bullying is the use of force, coercion, hurtful teasing or threat, to abuse, aggressively dominate or intimidate. The behavior is often repeated and habitual. One essential prerequisite is the perception (by the bully or by others) of an imba ...
, and vandalism
Vandalism is the action involving deliberate destruction of or damage to public or private property.
The term includes property damage, such as graffiti and defacement directed towards any property without permission of the owner. The term f ...
. It can improve school attendance by reducing the frequency of truancy
Truancy is any intentional, unjustified, unauthorised, or illegal absence from compulsory education. It is a deliberate absence by a student's own free will (though sometimes adults or parents will allow and/or ignore it) and usually does not refe ...
and absenteeism
Absenteeism is a habitual pattern of absence from a duty or obligation without good reason. Generally, absenteeism is unplanned absences. Absenteeism has been viewed as an indicator of poor individual performance, as well as a breach of an implici ...
. Having school belonging also reduces students' likelihood of dropping out of school, thus improving rates of school completion. Conversely, students who lack a sense of school belonging are at greater risk for disengagement from school and potentially dropping out.
Physical health
School belonging has several implications for students' physical health. Students who possess feelings of school belonging exhibit reduced risk of having astroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
or disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
. School belonging is also associated with lower mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
s for students. In addition, perceptions of school belonging have a significant inverse relationship with risk-taking behaviors, including substance and tobacco use and early sexualization
Sexualization (or sexualisation) is to make something sexual in character or quality or to become aware of sexuality, especially in relation to men and women. Sexualization is linked to sexual objectification. According to the American Psychologi ...
. In other words, students who have higher levels of school belonging are less likely to engage in risk-taking behaviors.
Measures
There are a number of measures used to assess school belonging. The most commonly used measures include:Psychological Sense of School Membership (PSSM)
The most commonly used measure of school belonging is the Psychological Sense of School Membership (PSSM) scale, which was developed by Carol Goodenow in 1993. This scale measures students' feelings of belonging and membership within a school setting by having students respond to 18 items regarding their personal feelings and experiences within school. It is designed to be used with students of all ages and nationalities. Students answer the items on a scale ranging from 1 to 5, where 1 indicates ''Not at all true'', and 5 indicates ''Completely true''. The items are intended to measure students' perceptions of acceptance, academic and social support, value, and contentment within their social relationships at school. The following are some examples of items that students respond to: "''People here notice when I'm good at something''," "''Other students take my opinions seriously''," and "''I feel like a real part of this school''." Research has found the PSSM to have high validity and reliability, attesting to its status as a valuable and functional measure of school belonging.Hemingway Measure of Adolescent Connectedness (HMAC)
The Hemingway Measure of Adolescent Connectedness (HMAC) was constructed by Michael Karcher in 1999 and has been used in research as a measure of school belonging for adolescents specifically. It contains 74 items on a scale ranging from 1 (''Not true at all'') to 5 (''Very true''). It examines adolescents' perceptions of connectedness, or in other words, their involvement with and valuation of both the specific and general social support they receive, across three sub-categories: social connectedness, academic connectedness, and family connectedness. The social connectedness component measures adolescents' feelings of connection towards their friends, neighborhood, and self. Academic connectedness evaluates adolescents' sense of connection towards their school, teachers, peers, and academic self. Finally, the family connectedness component assesses adolescents' feelings of connectedness to their parents, siblings, religion, and ancestry. Items measuring school belonging specifically include: "''I feel good about myself when I am at school''," "''I get along well with the other students in my classes''" and "''I enjoy being at school.''" This scale has been found to be generalizable to adolescents across the globe.School Connectedness Scale (SCS)
Jill Hendrickson Lohmeier and Steven W. Lee created the School Connectedness Scale (SCS) in 2011 to assess students' peer, adult, and school relationships within three distinct categories: general support (belongingness), specific support (relatedness), and engagement (connectedness).The scale includes 54 self-report items presented on a scale ranging from 1 to 5, where 1 represents 'Not at all true' and 5 represents 'Completely true'. Some items include "Students at my school help each other", "I am very involved in activities at my school, like clubs or teams", "Teachers at my school care about their students", and "I like spending time with my classmates." The SCS has shown generalizability to students from diverse populations, including different ages and ethnicities.School Engagement Instrument (SEI)
The School Engagement Instrument (SEI) was designed by James Appleton, Sandra Christenson, Dongjin Kim, and Amy Reschly in 2006 and is commonly used to gauge perceptions of school belonging. It includes 35 items on a four-point scale ranging from ''Strongly agree'' to ''Strongly disagree'' that measure students' cognitive and affective engagement within the school environment. The items are categorized into six sub-domains: "future goals and aspirations, control and relevance of schoolwork, extrinsic motivation, family support for learning, peer support for learning, and teacher-student relationships." Items from the SEI include: "''Overall, my teachers are open and honest with me''," "''Students at my school are there for me when I need them''," "''When I have problems at school, my family/guardian(s) want to know about it,''" and "''What I'm learning in my classes will be important for my future''."Implications for practice
In 2003, theCenters for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
(CDC) held an international convention to develop tactics for bolstering students' perceptions of school belonging. They developed the Wingspread Declaration on School Connections which identified the following strategies for increasing students' belonging to and connection with their school:
#Implementing high standards and expectations, and providing academic support to all students.
#Applying fair and consistent disciplinary policies that are collectively agreed upon and fairly enforced.
# Creating trusting relationships among students, teachers, staff, administrators, and families.
# Hiring and supporting capable teachers skilled in content, teaching techniques, and classroom management to meet each learner's needs.
# Fostering high parent/family expectations for school performance and school completion.
# Ensuring that every student feels close to at least one supportive adult at school.
::::—"Wingspread Declaration on School Connections", ''Journal of School Health''
The CDC later advanced the work of the Wingspread Declaration in 2009 by conducting a comprehensive, systematic review of school belonging and connectedness using sources from expert researchers, the government, educators, and more. This work produced four additional strategies for enhancing students' perception of belonging within school:
# Adult Support: School staff members can dedicate their time, interest, attention, and emotional support to students.
# Belonging to a Positive Peer Group: A stable network of peers can improve student perceptions of school.
# Commitment to Education: Believing that school is important to their future and perceiving that the adults in school are investing in their education can help students engaged in their own learning and involved in school activities.
# School Environment: The physical environment and psychosocial climate can set the stage for positive student perceptions of school.
::::—"School Connectedness: Strategies for Increasing Protective Factors Among Youth", ''Centers for Disease Control and Prevention''
Student-level implications for practice
Student-level interventions may also increase a sense of school belonging. Research has indicated that social and emotional learning opportunities may also increase a sense of school belonging in students. Many individual characteristics found to enhance a student's sense of belonging can be taught to students and thus offer a preventative mechanism to support their sense of school belonging. For example, research suggests that teaching emotional regulation, coping skills, interpersonal skills, and skills related to academic motivation hold promise for supporting a students sense of school belonging.See also
*Education in the United States
Education in the United States is provided in public and private schools and by individuals through homeschooling. State governments set overall educational standards, often mandate standardized tests for K–12 public school systems and sup ...
References
External links
School belonging measure
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210124181752/https://www.thebelonginglab.com/belonging-tools , date=2021-01-24 s are found on th
International Belonging Research Laboratory
Developmental psychology Educational assessment and evaluation Educational environment Education and health Educational research Teaching