Saturn IB on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Saturn IB (also known as the uprated Saturn I) was an American
 The S-IB stage was built by the
The S-IB stage was built by the
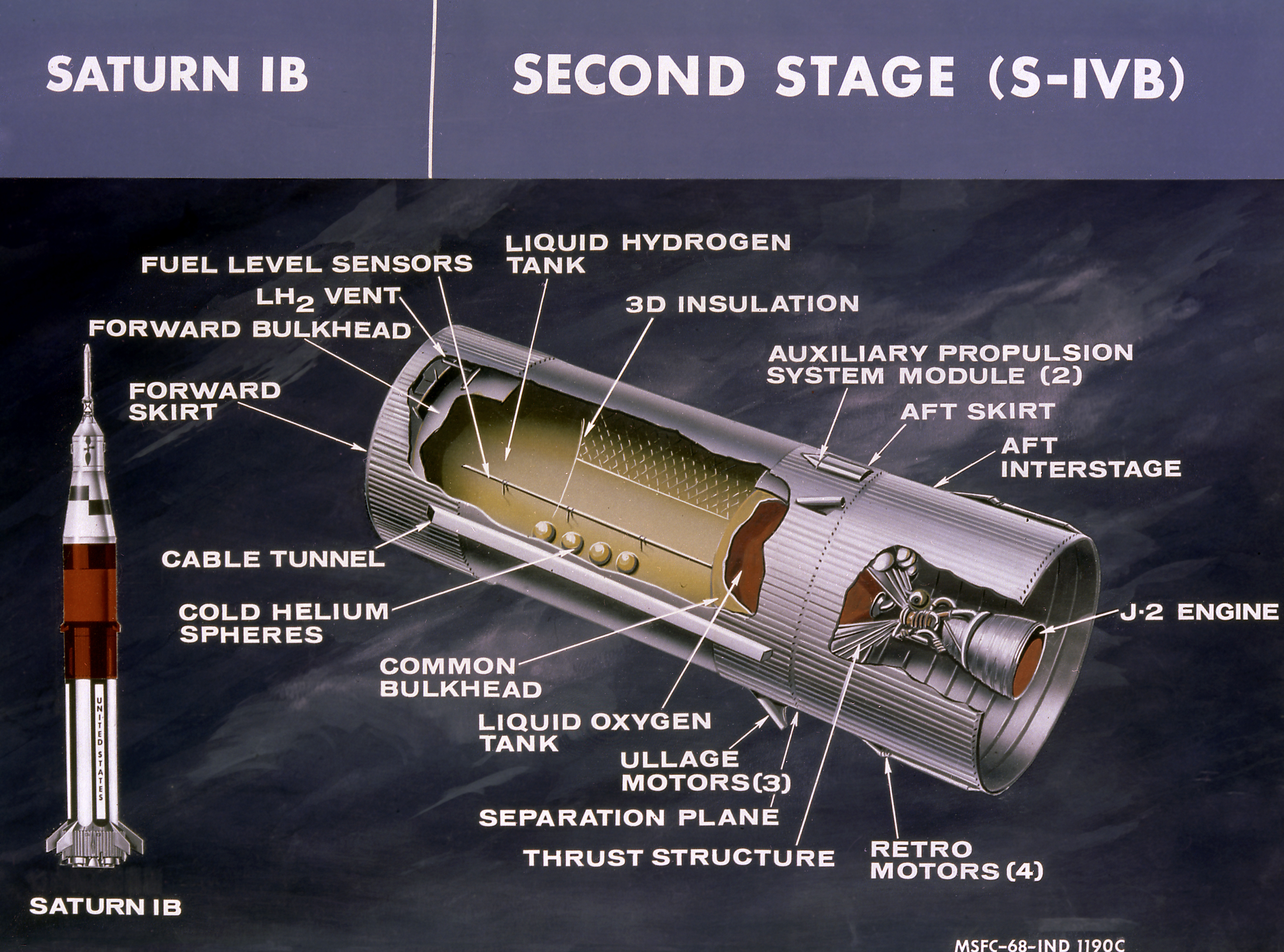 The S-IVB was built by the
The S-IVB was built by the
 IBM built the instrument unit at the Space Systems Center in
IBM built the instrument unit at the Space Systems Center in
 The first five Saturn IB launches for the Apollo program were made from LC-34 and LC-37,
The first five Saturn IB launches for the Apollo program were made from LC-34 and LC-37, 
 For earlier launches of vehicles in the Saturn I series, see the list in the
For earlier launches of vehicles in the Saturn I series, see the list in the
 As of 2019 there are three locations where Saturn IB vehicles (or parts thereof) are on display:
*SA-209 is on display at the
As of 2019 there are three locations where Saturn IB vehicles (or parts thereof) are on display:
*SA-209 is on display at the
 In 1972, the cost of a Saturn IB including launch was .
In 1972, the cost of a Saturn IB including launch was .
launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch contro ...
commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding th ...
(NASA) for the Apollo program. It uprated the Saturn I
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to low Earth orbit payloads.Terminology has changed since the 1960s; back then, 20,000 pounds was considered "heavy lift". The rocket's first stag ...
by replacing the S-IV
The S-IV was the second stage of the Saturn I rocket used by NASA for early flights in the Apollo program.
The S-IV was manufactured by the Douglas Aircraft Company and later modified by them to the S-IVB, a similar but distinct stage used on t ...
second stage (, 43,380,000 lb-sec total impulse), with the S-IVB
The S-IVB (pronounced "S-four-B") was the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB launch vehicles. Built by the Douglas Aircraft Company, it had one J-2 (rocket engine), J-2 rocket engine. For lunar missions it was fired twi ...
(, 96,000,000 lb-sec total impulse). The S-IB first stage also increased the S-I
The S-I was the first stage of the Saturn I rocket used by NASA for the Apollo program.
Design
The S-I stage was powered by eight H-1 rocket engines burning RP-1 fuel with liquid oxygen (LOX) as oxidizer. The design of the S-I was based on J ...
baseline's thrust from to and propellant load by 3.1%. This increased the Saturn I's low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
payload capability from to , enough for early flight tests of a half-fueled Apollo command and service module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship ...
(CSM) or a fully fueled Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed ...
(LM), before the larger Saturn V
Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, with multistage rocket, three stages, and powered with liquid-propellant r ...
needed for lunar flight was ready.
By sharing the S-IVB upper stage, the Saturn IB and Saturn V provided a common interface to the Apollo spacecraft. The only major difference was that the S-IVB on the Saturn V burned only part of its propellant to achieve Earth orbit, so it could be restarted for trans-lunar injection
A trans-lunar injection (TLI) is a propulsive maneuver used to set a spacecraft on a trajectory that will cause it to arrive at the Moon.
History
The first space probe to attempt TLI was the Soviet Union's Luna 1 on January 2, 1959 which wa ...
. The S-IVB on the Saturn IB needed all of its propellant to achieve Earth orbit.
The Saturn IB launched two uncrewed CSM suborbital flights to a height of 162 km, one uncrewed LM orbital flight, and the first crewed CSM orbital mission (first planned as Apollo 1
Apollo 1, initially designated AS-204, was intended to be the first crewed mission of the Apollo program, the American undertaking to land the first man on the Moon. It was planned to launch on February 21, 1967, as the first low Earth orbita ...
, later flown as Apollo 7
Apollo 7 (October 1122, 1968) was the first crewed flight in NASA's Apollo program, and saw the resumption of human spaceflight by the agency after the fire that killed the three Apollo 1 astronauts during a launch rehearsal test on Ja ...
). It also launched one orbital mission, AS-203
AS-203 (or SA-203) was an uncrewed flight of the Saturn IB rocket on July 5, 1966. It carried no command and service module, as its purpose was to verify the design of the S-IVB rocket stage restart capability that would later be used in the A ...
, without a payload so the S-IVB would have residual liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully li ...
fuel. This mission supported the design of the restartable version of the S-IVB used in the Saturn V, by observing the behavior of the liquid hydrogen in weightlessness
Weightlessness is the complete or near-complete absence of the sensation of weight. It is also termed zero gravity, zero G-force, or zero-G.
Weight is a measurement of the force on an object at rest in a relatively strong gravitational fi ...
.
In 1973, the year after the Apollo lunar program ended, three Apollo CSM/Saturn IBs ferried crews to the Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations in ...
space station. In 1975, one last Apollo/Saturn IB launched the Apollo portion of the joint US-USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
Apollo–Soyuz Test Project
Apollo–Soyuz was the first crewed international space mission, carried out jointly by the United States and the Soviet Union in July 1975. Millions of people around the world watched on television as a United States Apollo spacecraft docked ...
(ASTP). A backup Apollo CSM/Saturn IB was assembled and made ready for a Skylab rescue mission, but never flown.
The remaining Saturn IBs in NASA's inventory were scrapped after the ASTP mission, as no use could be found for them and all heavy lift needs of the US space program could be serviced by the cheaper and more versatile Titan III family and also the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
.
History
In 1959, NASA'sSilverstein Committee The Saturn Vehicle Evaluation Committee, better known as the Silverstein Committee, was a US government commission assembled in 1959 to recommend specific directions that NASA could take with the Saturn rocket program. The committee was chaired by ...
issued recommendations to develop the Saturn class launch vehicles, growing from the C-1. When the Apollo program was started in 1961 with the goal of landing men on the Moon, NASA chose the Saturn I for Earth orbital test missions. However, the Saturn I's payload limit of to 162 km would allow testing of only the command module with a smaller propulsion module attached, as the command and service module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship ...
would have a dry weight of at least , in addition to service propulsion and reaction control fuel. In July 1962, NASA announced selection of the C-5 for the lunar landing mission, and decided to develop another launch vehicle by upgrading the Saturn I, replacing its S-IV
The S-IV was the second stage of the Saturn I rocket used by NASA for early flights in the Apollo program.
The S-IV was manufactured by the Douglas Aircraft Company and later modified by them to the S-IVB, a similar but distinct stage used on t ...
second stage with the S-IVB
The S-IVB (pronounced "S-four-B") was the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB launch vehicles. Built by the Douglas Aircraft Company, it had one J-2 (rocket engine), J-2 rocket engine. For lunar missions it was fired twi ...
, which would also be modified for use as the Saturn V third stage. The S-I
The S-I was the first stage of the Saturn I rocket used by NASA for the Apollo program.
Design
The S-I stage was powered by eight H-1 rocket engines burning RP-1 fuel with liquid oxygen (LOX) as oxidizer. The design of the S-I was based on J ...
first stage would also be upgraded to the S-IB by improving the thrust of its engines and removing some weight. The new Saturn IB, with a payload capability of at least , would replace the Saturn I for Earth orbit testing, allowing the command and service module to be flown with a partial fuel load. It would also allow launching the lunar excursion module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed s ...
separately for uncrewed and crewed Earth orbital testing, before the Saturn V was ready to be flown. It would also give early development to the third stage.
On May 12, 1966, NASA announced the vehicle would be called the "uprated Saturn I", at the same time the "lunar excursion module" was renamed the lunar module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed ...
. However, the "uprated Saturn I" terminology was reverted to Saturn IB on December 2, 1967.
By the time it was developed, the Saturn IB payload capability had increased to . By 1973, when it was used to launch three Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations in ...
missions, the first-stage engine had been upgraded further, raising the payload capability to .
Specifications
Launch vehicle
Payload configurations
S-IB stage
 The S-IB stage was built by the
The S-IB stage was built by the Chrysler
Stellantis North America (officially FCA US and formerly Chrysler ()) is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automoti ...
corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility
The Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) is an manufacturing complex owned by NASA in New Orleans East, a district within New Orleans, Louisiana, in the United States. Organizationally it is part of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, and is currentl ...
, New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
. It was powered by eight Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
Rocketdyne H-1
The Rocketdyne H-1 was a thrust liquid-propellant rocket engine burning LOX and RP-1. The H-1 was developed for use in the S-I and S-IB first stages of the Saturn I and Saturn IB rockets, respectively, where it was used in clusters of eight e ...
rocket engines burning RP-1
RP-1 (alternatively, Rocket Propellant-1 or Refined Petroleum-1) is a highly refined form of kerosene outwardly similar to jet fuel, used as rocket fuel. RP-1 provides a lower specific impulse than liquid hydrogen (LH2), but is cheaper, is st ...
fuel with liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an applica ...
(LOX). Eight Redstone tanks (four holding fuel and four holding LOX) were clustered around a Jupiter rocket LOX tank, which earned the rocket the nickname "Cluster's Last Stand". The four outboard engines were mounted on gimbal
A gimbal is a pivoted support that permits rotation of an object about an axis. A set of three gimbals, one mounted on the other with orthogonal pivot axes, may be used to allow an object mounted on the innermost gimbal to remain independent of ...
s, allowing them to be steered to control the rocket. Eight fins surrounding the base thrust structure provided aerodynamic stability and control.
''Data from:''
S-IVB-200 stage
 The S-IVB was built by the
The S-IVB was built by the Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer based in Southern California. It was founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. and later merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas; it then operated as ...
at Huntington Beach, California
Huntington Beach is a seaside city in Orange County, California, Orange County in Southern California, located southeast of Downtown Los Angeles. The city is named after American businessman Henry E. Huntington. The population was 198,711 duri ...
. The S-IVB-200 model was similar to the S-IVB-500 third stage used on the Saturn V
Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, with multistage rocket, three stages, and powered with liquid-propellant r ...
, with the exception of the interstage adapter, smaller auxiliary propulsion control modules, and lack of on-orbit engine restart capability. It was powered by a single Rocketdyne J-2
The J-2 is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine used on NASA's Saturn IB and Saturn V launch vehicles. Built in the U.S. by Rocketdyne, the J-2 burned cryogenic liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, with each engine producin ...
engine. The fuel and oxidizer tanks shared a common bulkhead, which saved about ten tons of weight and reduced vehicle length over ten feet.
Instrument unit
 IBM built the instrument unit at the Space Systems Center in
IBM built the instrument unit at the Space Systems Center in Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is a city in Madison County, Limestone County, and Morgan County, Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Madison County. Located in the Appalachian region of northern Alabama, Huntsville is the most populous city in t ...
. Located at the top of the S-IVB stage, it consisted of a Launch Vehicle Digital Computer (LVDC), an inertial platform, accelerometers, a tracking, telemetry and command system and associated environmental controls. It controlled the entire rocket from just before liftoff until battery depletion. Like other rocket guidance systems, it maintained its state vector (position and velocity estimates) by integrating accelerometer measurements, sent firing and steering commands to the main engines and auxiliary thrusters, and fired the appropriate ordnance and solid rocket motors during staging and payload separation events.
As with other rockets, a completely independent and redundant range safety
In the field of rocketry, range safety may be assured by a system which is intended to protect people and assets on both the rocket range and downrange in cases when a launch vehicle might endanger them. For a rocket deemed to be ''off course'' ...
system could be invoked by ground radio command to terminate thrust and to destroy the vehicle should it malfunction and threaten people or property on the ground. In the Saturn IB and V, the range safety system was permanently disabled by ground command after safely reaching orbit. This was done to ensure that the S-IVB stage would not inadvertently rupture and create a cloud of debris in orbit that could endanger the crew of the Apollo CSM.
Launch sequence events
Acceleration of the Saturn IB increased from 1.24G at liftoff to a maximum of 4.35G at the end of the S-IB stage burn, and increased again from 0G to 2.85G from stage separation to the end of the S-IVB burn. AS-206, 207, and 208 inserted theCommand and Service Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship ...
in a elliptical orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. In a stricter sense, it ...
which was co-planar with the Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations in ...
one. The SPS engine of the Command and Service Module was used at orbit apogee to achieve a Hohmann transfer
In astronautics, the Hohmann transfer orbit () is an orbital maneuver used to transfer a spacecraft between two orbits of different altitudes around a central body. Examples would be used for travel between low Earth orbit and Moon, the Moon, ...
to the Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations in ...
orbit at .
Saturn IB vehicles and launches
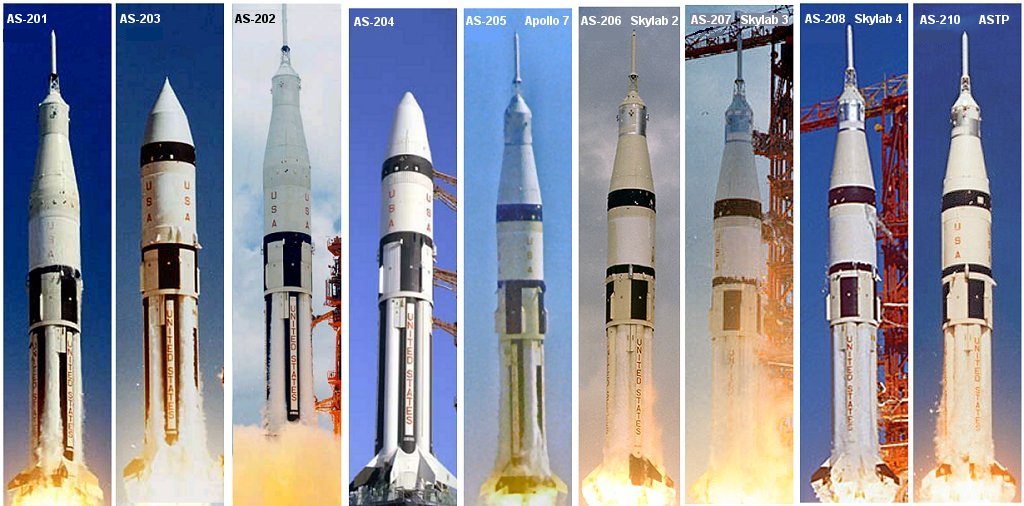
 The first five Saturn IB launches for the Apollo program were made from LC-34 and LC-37,
The first five Saturn IB launches for the Apollo program were made from LC-34 and LC-37, Cape Kennedy Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station ...
.
The Saturn IB was used between 1973 and 1975 for three crewed Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations in ...
flights, and one Apollo-Soyuz Test Project flight. This final production run did not have alternating black and white S-IB stage tanks, or vertical stripes on the S-IVB aft tank skirt, which were present on the earlier vehicles. Since LC-34 and 37 were inactive by then, these launches utilized Kennedy Space Center's LC-39B. Mobile Launcher Platform
A mobile launcher platform (MLP), also known as mobile launch platform, is a structure used to support a large multistage space vehicle which is assembled (stacked) vertically in an integration facility (e.g. the Vehicle Assembly Building) and t ...
No. 1 was modified, adding an elevated platform known as the "milkstool" to accommodate the height differential between the Saturn IB and the much larger Saturn V. This enabled alignment of the Launch Umbilical Tower's access arms to accommodate crew access, fueling, and ground electrical connections for the Apollo spacecraft and S-IVB upper stage. The tower's second stage access arms were modified to service the S-IB first stage.

 For earlier launches of vehicles in the Saturn I series, see the list in the
For earlier launches of vehicles in the Saturn I series, see the list in the Saturn I
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to low Earth orbit payloads.Terminology has changed since the 1960s; back then, 20,000 pounds was considered "heavy lift". The rocket's first stag ...
article.
Saturn IB rockets on display
 As of 2019 there are three locations where Saturn IB vehicles (or parts thereof) are on display:
*SA-209 is on display at the
As of 2019 there are three locations where Saturn IB vehicles (or parts thereof) are on display:
*SA-209 is on display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex
The Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is the visitor center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island, Florida. It features exhibits and displays, historic spacecraft and memorabilia, shows, two IMAX theaters, and a range of bus to ...
, with the Apollo Facilities Verification Vehicle. Due to severe corrosion, the first stage engines and service module were replaced with fabricated duplicates in 1993–1994.
*The SA-211 first stage is on display with a mockup S-IVB
The S-IVB (pronounced "S-four-B") was the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB launch vehicles. Built by the Douglas Aircraft Company, it had one J-2 (rocket engine), J-2 rocket engine. For lunar missions it was fired twi ...
stage stacked in a launch-ready condition at the Alabama Welcome Center on Interstate 65
Interstate 65 (I-65) is a major north–south Interstate Highway in the central United States. As with most primary Interstates ending in 5, it is a major crosscountry, north–south route, connecting between the Great Lakes and the Gulf ...
in Ardmore, Alabama
Ardmore is a town in Limestone County, Alabama, Limestone County, Alabama, United States, and is included in the Huntsville-Decatur Metro Area. It is home to the Saturn IB rocket at the Alabama Welcome Center, just south of the Tennessee border, ...
.
*The SA-211 S-IVB stage was mated with the Skylab underwater training docking adapter and Apollo Telescope Mount and is on display in the Rocket Garden of the U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
Cost
 In 1972, the cost of a Saturn IB including launch was .
In 1972, the cost of a Saturn IB including launch was .
See also
*Comparison of orbital launchers families
This article compares different orbital launcher families (although many launchers that are significantly different from other members of the same 'family' have their own separate entries). The article is organized into two tables: the first tabl ...
* Comparison of orbital launch systems
This comparison of orbital launch systems lists the attributes of all individual rocket configurations designed to reach orbit. A first list contains rockets that are operational or in development as of 2022; a second list includes all retired roc ...
Notes
References
External links
* http://www.apollosaturn.com/ * http://www.spaceline.org/rocketsum/saturn-Ib.html * NASA Marshall Spaceflight Center, '' '', 30 September 1972 * {{Saturn rockets 1966 in spaceflight 1968 in spaceflight 1973 in spaceflight 1975 in spaceflight Apollo program Apollo 7 IB Vehicles introduced in 1966