Saint Lawrence River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from
 With the draining of the Champlain Sea, due to a rebounding continent from the Last Glacial Maximum, the St. Lawrence River was formed. The Champlain Sea lasted from about 13,000 years ago to about 10,000 years ago and was continuously shrinking during that time, a process that continues today.
Today, the St. Lawrence River begins at the outflow of
With the draining of the Champlain Sea, due to a rebounding continent from the Last Glacial Maximum, the St. Lawrence River was formed. The Champlain Sea lasted from about 13,000 years ago to about 10,000 years ago and was continuously shrinking during that time, a process that continues today.
Today, the St. Lawrence River begins at the outflow of
 Flowing through and adjacent to numerous
Flowing through and adjacent to numerous

Regional Geography of the St. Lawrence RiverInformation about Juniper Island (Ontario)Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway System
– Historical essay, illustrated with drawings and photographs
Annotated Bibliography on St. Lawrence County and Northern New York region.International St. Lawrence River Board of Control
Saint Lawrence River from ''The Canadian Encyclopedia''St. Lawrence River CamWatch the Jacques Cousteau documentary, ''St. Lawrence: Stairway to the Sea''The Steamboats ''Sir James Kemp'' and ''Lord Dalhousie'' on the River St. Lawrence, Upper Canada in 1833 by D.J. Kennedy, Historical Society of Pennsylvania
{{Authority control Physiographic provinces International rivers of North America Rivers of New York (state) Rivers of Ontario Canada–United States border Rivers of Montérégie Rivers of Capitale-Nationale Rivers of St. Lawrence County, New York Regions of New York (state) Rivers of Quebec
Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border ...
in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting the American Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, and forming the primary drainage outflow of the Great Lakes Basin
The Great Lakes Basin consists of the Great Lakes and the surrounding lands of the states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin in the United States, and the province of Ontario in Canada, whose dir ...
. The river traverses the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, as well as the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of New York, and demarcates part of the international boundary between Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. It also provides the foundation for the commercial St. Lawrence Seaway.
Names
Originally known by a variety of names by localFirst Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
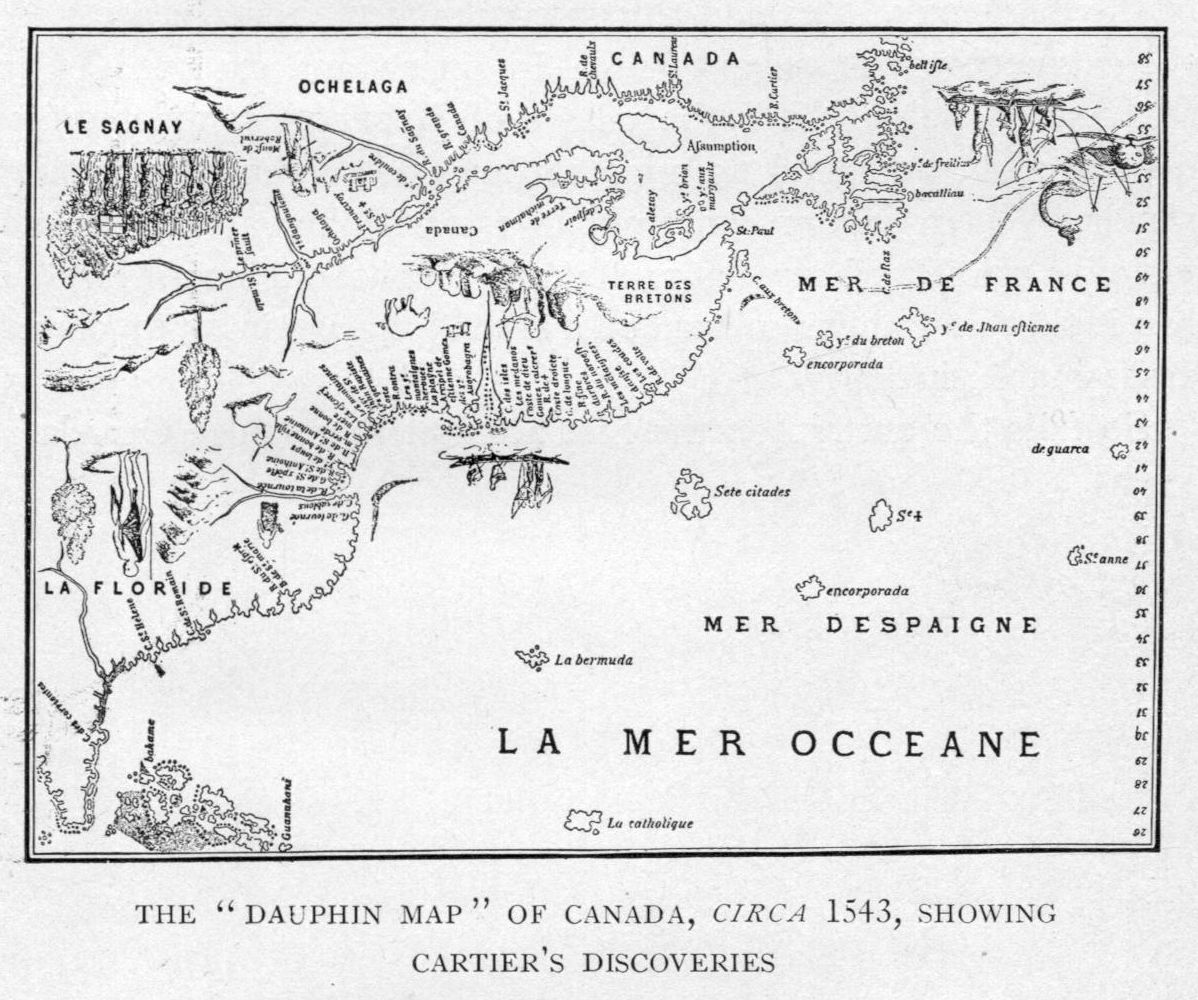
, the St. Lawrence became known in French as ''le fleuve Saint-Laurent'' (also spelled ''St-Laurent'') in 1604 by Samuel de Champlain. Opting for the ''grande riviere de sainct Laurens'' and ''fleuve sainct Laurens'' in his writings and on his maps, de Champlain supplanted previous French names for the river including the ''Grand fleuve de Hochelaga'' and the ''Grande rivière de Canada'', which was the more popular name of the river in the 16th century. The name ''Saint-Laurent'' (Saint Lawrence) was originally applied to the eponymous bay by Jacques Cartier upon his arrival into the region on the 10th of August feast day for Saint Lawrence in 1535.
Today, the river is still known by Indigenous nations by a number of distinct names. Innu-aimun, the language of Nitassinan
Nitassinan ( moe, script=Cans, i=no, ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) is the ancestral homeland of the Innu, an indigenous people of Eastern Quebec and Labrador, Canada. Nitassinan means "our land" in the Innu language. The territory covers the eastern por ...
, refers to it as ''Wepistukujaw Sipo''/''Wepìstùkwiyaht sīpu''; the Abenaki call it ''Moliantegok''/''Moliantekw'' ("Montréal River"), ''Kchitegw''/''Ktsitekw''/''Gicitegw'' ("Great River"), or ''Oss8genaizibo''/''Ws8genaisibo''/''Wsogenaisibo'' ("River of the Algonquins"); the Mohawk Mohawk may refer to:
Related to Native Americans
* Mohawk people, an indigenous people of North America (Canada and New York)
*Mohawk language, the language spoken by the Mohawk people
* Mohawk hairstyle, from a hairstyle once thought to have been ...
refer to it in Kanienʼkéha as ''Roiatatokenti'', ''Raoteniateara'', ''Ken’tarókwen'', or ''Kaniatarowanénhne''; the Tuscarora call it ''Kahnawáˀkye'' or ''Kaniatarowanenneh'' ("Big Water Current"); the Algonquins (or Omàmiwininiwak) call it "the Walking Path" or ''Magtogoek'' or ''Kitcikanii sipi'', the "Large Water River"; the Huron-Wendats refer to it as ''Lada8anna'' or ''Laooendaooena''; and, the Atikamekw of Nitaskinan
Nitaskinan is the ancestral homeland of the Atikamekw people. It is located in the valley of the Saint-Maurice River in Quebec, Canada. It covers an area of 80,000 km2 (30,000 sq. mi.) On 8 September 2014, the Conseil de la Nation Atikamek ...
refer to it as '' Micta sipi'' ("Huge River").
Geography
 With the draining of the Champlain Sea, due to a rebounding continent from the Last Glacial Maximum, the St. Lawrence River was formed. The Champlain Sea lasted from about 13,000 years ago to about 10,000 years ago and was continuously shrinking during that time, a process that continues today.
Today, the St. Lawrence River begins at the outflow of
With the draining of the Champlain Sea, due to a rebounding continent from the Last Glacial Maximum, the St. Lawrence River was formed. The Champlain Sea lasted from about 13,000 years ago to about 10,000 years ago and was continuously shrinking during that time, a process that continues today.
Today, the St. Lawrence River begins at the outflow of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border ...
and flows adjacent to Gananoque
Gananoque ( )
is a town in the Leeds and Grenville area of Ontario, Canada. The town had a population of 5,383 year-round residents in the 2021 Canadian Census, as well as summer residents sometimes referred to as "Islanders" because of the Tho ...
, Brockville
Brockville, formerly Elizabethtown, is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada, in the Thousand Islands region. Although it is the seat of the United Counties of Leeds and Grenville, it is politically independent of the county. It is included with Le ...
, Morristown, Ogdensburg, Massena, Cornwall, Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, Trois-Rivières, and Quebec City before draining into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, one of the largest estuaries in the world. The estuary begins at the eastern tip of Île d'Orléans
Île d'Orléans (; en, Island of Orleans) is an island located in the Saint Lawrence River about east of downtown Quebec City, Quebec, Canada. It was one of the first parts of the province to be colonized by the French, and a large percentage ...
, just downstream from Quebec City. The river becomes tidal around Quebec City.
The St. Lawrence River runs from the farthest headwater to the mouth and from the outflow of Lake Ontario. These numbers include the estuary; without the estuary the length from Lake Ontario is c. 500 km (c. 300 mi). The farthest headwater is the North River in the Mesabi Range at Hibbing
Hibbing is a city in Saint Louis County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 16,214 at the 2020 census. The city was built on mining the rich iron ore of the Mesabi Iron Range and still relies on that industrial activity today. At th ...
, Minnesota. Its drainage area, which includes the Great Lakes, the world's largest system of freshwater lakes, is , of which is in Canada and is in the United States. The basin covers parts of Ontario and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
in Canada, parts of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, New York, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
, and nearly the entirety of the state of Michigan in the United States. The average discharge below the Saguenay River
__NOTOC__
The Saguenay River () is a major river of Quebec, Canada.
It drains Lac Saint-Jean in the Laurentian Highlands, leaving at Alma and running east; the city of Saguenay is located on the river. It drains into the Saint Lawrence River. ...
is . At Quebec City, it is . The average discharge at the river's source, the outflow of Lake Ontario, is .
The St. Lawrence River includes Lake Saint-Louis
Lake Saint-Louis is a lake in southwestern Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa Rivers. The Saint Lawrence Seaway passes through the lake.
Lake St. Louis is a widening of the St. Lawrence River in the Hochelaga Arch ...
south of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, Lake Saint Francis at Salaberry-de-Valleyfield and Lac Saint-Pierre east of Montreal. It encompasses four archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
es: the Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (french: Mille-Îles) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for abo ...
chain near Alexandria Bay, New York
Alexandria Bay is a village in Jefferson County, New York, United States, within the town of Alexandria. It is located in the Thousand Islands region of northern New York. The population of the village was 1,078 at the 2010 United States Census. I ...
and Kingston, Ontario
Kingston is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the north-eastern end of Lake Ontario, at the beginning of the St. Lawrence River and at the mouth of the Cataraqui River (south end of the Rideau Canal). The city is midway between To ...
; the Hochelaga Archipelago, including the Island of Montreal and Île Jésus
Île Jésus (, '' Jesus Island'') is a river island in southwestern Quebec, separated from the mainland to the north by the Rivière des Mille Îles, and from the Island of Montreal to the south by the Rivière des Prairies. It is the second-l ...
( Laval); the Lake St. Pierre Archipelago (classified biosphere world reserve by the UNESCO in 2000) and the smaller Mingan Archipelago. Other islands include Île d'Orléans near Quebec City and Anticosti Island
; moe, Notiskuan; mic, Natigostec
, sobriquet =
, image_name = RiviereHuileAnticosti.jpg
, image_caption = Salmon fisherman on Rivière à l'Huile
, image_map ...
north of the Gaspé. It is the second longest river in Canada.
Lake Champlain and the Ottawa, Richelieu, Saint-Maurice, Saint-François, Chaudière and Saguenay rivers drain into the St. Lawrence.
The St. Lawrence River is in a seismically active zone where fault reactivation is believed to occur along late Proterozoic to early Paleozoic normal faults related to the opening of the Iapetus Ocean. The faults in the area are rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
-related and comprise the Saint Lawrence rift system.
According to the United States Geological Survey, the St. Lawrence Valley is a physiographic province
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific characte ...
of the larger Appalachian division, containing the Champlain and Northern physiographic section. However, in Canada, where most of the valley is, it is instead considered part of a distinct St. Lawrence Lowlands physiographic division, and not part of the Appalachian division at all.
History

 Flowing through and adjacent to numerous
Flowing through and adjacent to numerous Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
homelands, the large river was always and remains to this day a primary thoroughfare for many peoples. Beginning in Dawnland at the Gulf of St. Lawrence, the river borders Mi'kma'ki in the South (what is today known as the Canadian Maritimes), and Nitassinan
Nitassinan ( moe, script=Cans, i=no, ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) is the ancestral homeland of the Innu, an indigenous people of Eastern Quebec and Labrador, Canada. Nitassinan means "our land" in the Innu language. The territory covers the eastern por ...
in the North, the national territory of the Innu people. On the south shore beyond the Mi'kmaw
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the nort ...
district of Gespe'gewa'ki, the river passes Wolastokuk (the Maliseet homeland), Pαnawαhpskewahki (the Penobscot
The Penobscot (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic ...
homeland), and Ndakinna (the Abenaki homeland). Continuing, the river passes through the former country of the St. Lawrence Iroquois and then three of the six homelands of the Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
: the Mohawk or Kanienʼkehá꞉ka, the Oneida or Onyota'a:ka, and the Onondaga or Onöñda’gaga’.
In the early 17th century, the Huron-Wendat Nation migrated from their original country of Huronia to what is now known as Nionwentsïo centred around Wendake. Nionwentsïo occupies both the north and south shores of the river, overlapping with Nitassinan and the more western Wabanaki or Dawnland countries. Adjacent on the north shore is the Atikamekw territorial homeland of Nitaskinan
Nitaskinan is the ancestral homeland of the Atikamekw people. It is located in the valley of the Saint-Maurice River in Quebec, Canada. It covers an area of 80,000 km2 (30,000 sq. mi.) On 8 September 2014, the Conseil de la Nation Atikamek ...
and, upstream, the further reaches of Anishinaabewaki, specifically the homelands of the Algonquin
Algonquin or Algonquian—and the variation Algonki(a)n—may refer to:
Languages and peoples
*Algonquian languages, a large subfamily of Native American languages in a wide swath of eastern North America from Canada to Virginia
**Algonquin la ...
and Mississauga Nations.
The Norse explored the Gulf of St. Lawrence in the 11th century and were followed by fifteenth- and early sixteenth-century European mariners, such as John Cabot, and the brothers Gaspar and Miguel Corte-Real
Miguel Corte-Real (; – 1502?) was a Portuguese explorer who charted about 600 miles of the coast of Labrador. In 1502, he disappeared while on an expedition and was believed to be lost at sea.
Early life
Miguel Corte-Real was a son of ...
. The first European explorer known to have sailed up the St. Lawrence River itself was Jacques Cartier. At that time, the land along the river described as "about two leagues, a mountain as tall as a heap of wheat" was inhabited by the St. Lawrence Iroquoians; at the time of Cartier's second voyage in 1535. Because Cartier arrived in the estuary on Saint Lawrence's feast day 10 August, he named it the ''Gulf of Saint Lawrence''.
The St. Lawrence River is partly within the U.S. and as such is that country's sixth oldest surviving European place-name.
The earliest regular Europeans in the area were the Basques, who came to the St Lawrence Gulf and River in pursuit of whales from the early 16th century. The Basque whalers and fishermen traded with indigenous Americans and set up settlements, leaving vestiges all over the coast of eastern Canada and deep into the St. Lawrence River. Basque commercial and fishing activity reached its peak before the '' Armada Invencibles disaster (1588), when the Spanish Basque whaling fleet was confiscated by King Philip II of Spain and largely destroyed. Initially, the whaling galleons from Labourd were not affected by the Spanish defeat.
Until the early 17th century, the French used the name ''Rivière du Canada'' to designate the St. Lawrence upstream to Montreal and the Ottawa River after Montreal. The St. Lawrence River served as the main route for European exploration of the North American interior, first pioneered by French explorer Samuel de Champlain.
Control of the river was crucial to British strategy to capture New France in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
. Having captured Louisbourg in 1758, the British sailed up to Quebec the following year thanks to charts drawn up by James Cook. British troops were ferried via the St. Lawrence to attack the city from the west, which they successfully did at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham
The Battle of the Plains of Abraham, also known as the Battle of Quebec (french: Bataille des Plaines d'Abraham, Première bataille de Québec), was a pivotal battle in the Seven Years' War (referred to as the French and Indian War to describe ...
. The river was used again by the British to defeat the French siege of Quebec under the Chevalier de Lévis in 1760.
In 1809, the first steamboat to ply its trade on the St. Lawrence was built and operated by John Molson
John Molson (December 28, 1763 – January 11, 1836) was an English-born brewer and entrepreneur in colonial Quebec, which during his lifetime became Lower Canada. In addition to founding Molson Brewery, he built the first steamship and the fir ...
and associates, a scant two years after Fulton's steam-powered navigation of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
. The '' Accommodation'' with ten passengers made her maiden voyage from Montreal to Quebec City in 66 hours, for 30 of which she was at anchor. She had a keel of 75 feet, and a length overall of 85 feet. The cost of a ticket was eight dollars upstream, and nine dollars down. She had berths that year for twenty passengers.
Within a decade, daily service was available in the hotly-contested Montreal-Quebec route.
Because of the virtually impassable Lachine Rapids
The Lachine Rapids (french: Rapides de Lachine) are a series of rapids on the Saint Lawrence River, between the Island of Montreal and the south shore. They are located near the former city of Lachine.
The Lachine Rapids contain large standing ...
, the St. Lawrence was once continuously navigable only as far as Montreal. Opened in 1825, the Lachine Canal
The Lachine Canal ( in French) is a canal passing through the southwestern part of the Island of Montreal, Quebec, Canada, running 14.5 kilometres (9 miles) from the Old Port of Montreal to Lake Saint-Louis, through the boroughs of Lachine, ...
was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids. An extensive system of canals and locks, known as the St. Lawrence Seaway, was officially opened on 26 June 1959 by Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
(representing Canada) and President Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
(representing the United States). The Seaway (including the Welland Canal
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines ...
) now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, the Battle of the St. Lawrence
The Battle of the St. Lawrence involved marine and anti-submarine actions throughout the lower St. Lawrence River and the entire Gulf of Saint Lawrence, Strait of Belle Isle, Anticosti Island and Cabot Strait from May–October 1942, September ...
involved submarine and anti-submarine actions throughout the lower St. Lawrence River and the entire Gulf of St. Lawrence, Strait of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle (; french: Détroit de Belle Isle ) is a waterway in eastern Canada that separates the Labrador Peninsula from the island of Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Location
The strait is the northern o ...
and Cabot Strait
Cabot Strait
(; french: détroit de Cabot, ) is a strait in eastern Canada approximately 110 kilometres wide between Cape Ray, Newfoundland and Cape North, Cape Breton Island.
It is the widest of the three outlets for the Gulf of Saint L ...
from May to October 1942, September 1943, and again in October and November 1944. During this time, German U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
s sank several merchant marine ships and three Canadian warships.
In the late 1970s, the river was the subject of a successful ecological campaign (called "Save the River"), originally responding to planned development by the United States Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
. The campaign was organized, among others, by Abbie Hoffman.
Resident whales

Sources
The source of the North River in the Mesabi Range in Minnesota (Seven Beaver Lake) is considered to be the source of the St. Lawrence River. Because it crosses so many lakes, the water system frequently changes its name. From source to mouth, the names are: The St. Lawrence River also passes throughLake Saint-Louis
Lake Saint-Louis is a lake in southwestern Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa Rivers. The Saint Lawrence Seaway passes through the lake.
Lake St. Louis is a widening of the St. Lawrence River in the Hochelaga Arch ...
and Lake Saint-Pierre in Quebec.
Works
The St. Lawrence River is at the heart of many Quebec novels ( Anne Hébert's '' Kamouraska'', Réjean Ducharme's '' L'avalée des avalés''), poems (in works of Pierre Morency, Bernard Pozier), and songs (Leonard Cohen
Leonard Norman Cohen (September 21, 1934November 7, 2016) was a Canadian singer-songwriter, poet and novelist. His work explored religion, politics, isolation, depression, sexuality, loss, death, and romantic relationships. He was inducted in ...
's " Suzanne", Michel Rivard's "L'oubli", Joe Dassin
Joseph Ira Dassin (; 5 November 1938 – 20 August 1980) was an American–French singer-songwriter and actor. He was the son of film director Jules Dassin.
Early life
Dassin was born in New York City to American film director Jules Dassin (19 ...
's " Dans les yeux d'Émilie", and André Gagnon
André Gagnon (2 August 1936 – 3 December 2020) was a Canadian pianist, composer, conductor, arranger, and actor, known for his fusion of classical and pop styles,Jean-Pierre Thiollet, ''88 notes pour piano solo'', Neva Editions, 2015, p.16 ...
's "Le Saint-Laurent"). The river was the setting for the Canadian television drama series Seaway. The river has also been portrayed in paintings, notably by the Group of Seven
The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated member". It is officiall ...
. In addition, the river is the namesake of Saint-Laurent Herald at the Canadian Heraldic Authority
The Canadian Heraldic Authority (CHA; french: Autorité héraldique du Canada) is part of the Canadian honours system under the Canadian monarch, whose authority is exercised by the Governor General of Canada. The authority is responsible for t ...
.
In 1980 Jacques Cousteau traveled to Canada to make two films on the St. Lawrence River and the Great Lakes, ''Cries from the Deep
''Cries from the Deep'' (French: ''Les pièges de la mer'') is a 1982 documentary directed by Jacques Gagné about Jacques Cousteau's exploration of the Grand Banks of Newfoundland.
Filmed in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, Québec, Canada, Halifax, ...
'' and ''St. Lawrence: Stairway to the Sea''.
Musician David Usher released the song "St. Lawrence River" on his '' Little Songs'' album in 1998.
The novel and film '' Black Robe'' are set primarily on the St. Lawrence River during the 17th century.
See also
References
Bibliography
External links
Regional Geography of the St. Lawrence River
– Historical essay, illustrated with drawings and photographs
Annotated Bibliography on St. Lawrence County and Northern New York region.
Saint Lawrence River from ''The Canadian Encyclopedia''
{{Authority control Physiographic provinces International rivers of North America Rivers of New York (state) Rivers of Ontario Canada–United States border Rivers of Montérégie Rivers of Capitale-Nationale Rivers of St. Lawrence County, New York Regions of New York (state) Rivers of Quebec