S8 (classification) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 S8, SB7, SM8 are disability swimming classifications used for categorizing swimmers based on their level of disability. This class includes a number of different disabilities including people with amputations and cerebral palsy. The classification is governed by the
S8, SB7, SM8 are disability swimming classifications used for categorizing swimmers based on their level of disability. This class includes a number of different disabilities including people with amputations and cerebral palsy. The classification is governed by the
/ref> The number following indicates degree of disability, with one being the most severely physically impaired to ten having the least amount of physical disability. According to the
File:ISOD A7 amputee sportperson profile.png, Visualization of an A6 classified swimmer competing in S8
File:ISOD A3 amputee sportperson profile.png, Visualization of an A3 classified swimmer competing in S8
File:ISOD A8 amputee sportperson profile.png, Visualization of an A8 classified swimmer competing in S8
File:ISOD A2 amputee sportperson profile.png, Visualization of an A2 classified swimmer competing in S8
File:ISOD A9 amputee sportperson profile.png, Visualization of an A9 classified swimmer competing in S8

 This class includes people with several disability types include
This class includes people with several disability types include
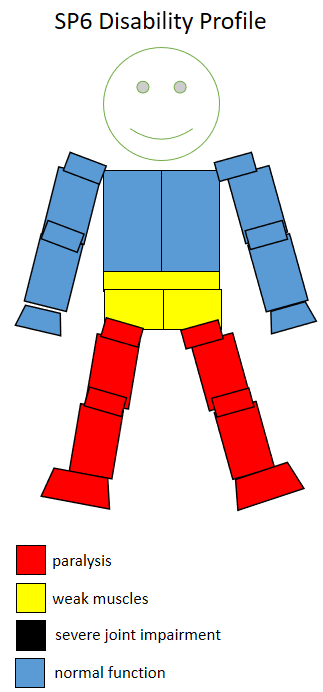 This is wheelchair sport classification that corresponds to the neurological level L2 - L5. Historically, this class has been known as Lower 4, Upper 5. People with lesions at L4 have issues with their lower back muscles, hip flexors and their quadriceps. People with lesions at the L4 to S2 who are complete paraplegics may have motor function issues in their gluts and hamstrings. Their quadriceps are likely to be unaffected. They may be absent sensation below the knees and in the groin area.
People in this class have good sitting balance. People with lesions at L4 have trunk stability, can lift a leg and can flex their hips. They can walk independently with the use of longer leg braces. They may use a wheelchair for the sake of convenience. Recommended sports include many standing related sports. People in this class have a total respiratory capacity of 88% compared to people without a disability.
S8 swimmers with spinal cord injuries tend to be complete paraplegics with lesions below L4 to L5. When swimming, they are able to kick but limited use of their ankles means that their propulsion from kicking can be limited. They normally do diving starts from the platform but are not able to get full power because of limited use of their legs. They do leg turns but have limited propulsion power off the wall.
A study of was done comparing the performance of athletics competitors at the 1984 Summer Paralympics. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m freestyle. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 14 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 50 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 4 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100 m freestyle.
This is wheelchair sport classification that corresponds to the neurological level L2 - L5. Historically, this class has been known as Lower 4, Upper 5. People with lesions at L4 have issues with their lower back muscles, hip flexors and their quadriceps. People with lesions at the L4 to S2 who are complete paraplegics may have motor function issues in their gluts and hamstrings. Their quadriceps are likely to be unaffected. They may be absent sensation below the knees and in the groin area.
People in this class have good sitting balance. People with lesions at L4 have trunk stability, can lift a leg and can flex their hips. They can walk independently with the use of longer leg braces. They may use a wheelchair for the sake of convenience. Recommended sports include many standing related sports. People in this class have a total respiratory capacity of 88% compared to people without a disability.
S8 swimmers with spinal cord injuries tend to be complete paraplegics with lesions below L4 to L5. When swimming, they are able to kick but limited use of their ankles means that their propulsion from kicking can be limited. They normally do diving starts from the platform but are not able to get full power because of limited use of their legs. They do leg turns but have limited propulsion power off the wall.
A study of was done comparing the performance of athletics competitors at the 1984 Summer Paralympics. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m freestyle. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 14 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 50 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 4 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100 m freestyle.

 F8 is standing wheelchair sport class. The level of spinal cord injury for this class involves people who have incomplete lesions at a slightly higher level. This means they can sometimes bear weight on their legs. In 2002, USA Track & Field defined this class as, "These are standing athletes with dynamic standing balance. Able to recover in standing when balance is challenged. Not more than 70 points in legs." In 2003, Disabled Sports USA defined this class as, "In a sitting class but not more than 70 points in the lower limbs. Are unable to recover balance in challenged standing position." In Australia, this class means combined lower plus upper limb functional problems. "Minimal disability." It can also mean in Australia that the athlete is "ambulant with moderately reduced function in one or both lower limbs." They have a normalized drag in the range of 0.6 to 0.7.
F8 is standing wheelchair sport class. The level of spinal cord injury for this class involves people who have incomplete lesions at a slightly higher level. This means they can sometimes bear weight on their legs. In 2002, USA Track & Field defined this class as, "These are standing athletes with dynamic standing balance. Able to recover in standing when balance is challenged. Not more than 70 points in legs." In 2003, Disabled Sports USA defined this class as, "In a sitting class but not more than 70 points in the lower limbs. Are unable to recover balance in challenged standing position." In Australia, this class means combined lower plus upper limb functional problems. "Minimal disability." It can also mean in Australia that the athlete is "ambulant with moderately reduced function in one or both lower limbs." They have a normalized drag in the range of 0.6 to 0.7.
 S8, SB7, SM8 are disability swimming classifications used for categorizing swimmers based on their level of disability. This class includes a number of different disabilities including people with amputations and cerebral palsy. The classification is governed by the
S8, SB7, SM8 are disability swimming classifications used for categorizing swimmers based on their level of disability. This class includes a number of different disabilities including people with amputations and cerebral palsy. The classification is governed by the International Paralympic Committee
The International Paralympic Committee (IPC; german: Internationales Paralympisches Komitee) is an international non-profit organisation and the global governing body for the Paralympic Movement. The IPC organizes the Paralympic Games and fun ...
, and competes at the Paralympic Games.
Definition
This classification is forswimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
. In the classification title, S represents Freestyle, Backstroke and Butterfly strokes. SB means breaststroke. SM means individual medley.IPC Swimming Classification/ref> The number following indicates degree of disability, with one being the most severely physically impaired to ten having the least amount of physical disability. According to the
International Paralympic Committee
The International Paralympic Committee (IPC; german: Internationales Paralympisches Komitee) is an international non-profit organisation and the global governing body for the Paralympic Movement. The IPC organizes the Paralympic Games and fun ...
, examples of those eligible for the S8, SB8 and SM8 classes include "Swimmers who have lost either both hands or one arm ..also, athletes with severe restrictions in the joints of the lower limbs." Jane Buckley, writing for the Sporting Wheelies
The Sporting Wheelies and Disabled Association is the peak body for sport, recreation and fitness for people with a physical disability or vision impairment in the Australian state of Queensland.
The not-for-profit organisation's mission was 'to ...
, an Australian disability association, describes the swimmers in this classification as having: "full use of their arms and trunk with some leg function; Swimmers with coordination problems mainly in the lower limbs; Both legs amputated just above or just below the knee; Single above elbow amputation."
Disability types
This class includes people with several disability types includecerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensa ...
and amputations.
Amputee
ISOD amputee A2, A3, A6, A8 and A9 swimmers may be found in this class. Prior to the 1990s, the A2, A3, A6, A8 and A9 classes were often grouped with other amputee classes in swimming competitions, including the Paralympic Games.Upper limb amputees
S8 and S9 amputee swimmers in this class have similar start times to people with legs amputations in S8 to S10 classes. S8 amputee swimmers in this class have much shorter points of entry into the water off the block. Compared to able bodied swimmers, amputee swimmers in this class have a shorter stroke length and increased stroke rate. Because their legs are their greatest strength, they modify their entry into the water to take advantage of this. The nature of a person's amputations in this class can effect their physiology and sports performance. Because they are missing a limb, amputees are more prone to overuse injuries in their remaining limbs. Common problems for intact upper limbs for people in this class include rotator cuffs tearing,shoulder impingement
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis (inflammation of tendons) of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of th ...
, epicondylitis Epicondylitis is a type of musculoskeletal disorder that refers to an inflammation of an epicondyle. It is caused by repetitive motion. In athletes, it is linked to poor technique. Nonsurgical treatment is effective in approximately 95% of cases.
T ...
and peripheral nerve entrapment.
Lower limb amputees
A3 swimmers in this class have a similar stroke length and stroke rate comparable to able bodied swimmers. A study of was done comparing the performance of swimming competitors at the 1984 Summer Paralympics. It found there was no significant difference in performance in times between men and women in A2 and A3 in the 50 meter breaststroke, men and women in A2 and A3 in the 50 meter freestyle, men and women in A2, A3 and A4 in the 25 meter butterfly, and men in A2 and A3 in the 50 meter backstroke. The nature of an A2 and A3 swimmers's amputations in this class can effect their physiology and sports performance. Because of the potential for balance issues related to having an amputation, during weight training, amputees are encouraged to use a spotter when lifting more than . Lower limb amputations effect a person's energy cost for being mobile. To keep their oxygen consumption rate similar to people without lower limb amputations, they need to walk slower. A3 swimmers use around 41% more oxygen to walk or run the same distance as some one without a lower limb amputation. A2 swimmers use around 87% more oxygen to walk or run the same distance as some one without a lower limb amputation.Upper and lower limb amputations
ISOD amputee A9 swimmers may be found in several classes. These include S2, S3, S4, S5 and S8. Prior to the 1990s, the A9 class was often grouped with other amputee classes in swimming competitions, including the Paralympic Games. Swimmers in this class have a similar stroke length and stroke rate to able bodied swimmers. The nature of a person's amputations in this class can effect their physiology and sports performance. Because of the potential for balance issues related to having an amputation, during weight training, amputees are encouraged to use a spotter when lifting more than . Lower limb amputations effect a person's energy cost for being mobile. To keep their oxygen consumption rate similar to people without lower limb amputations, they need to walk slower. Because they are missing a limb, amputees are more prone to overuse injuries in their remaining limbs. Common problems with intact upper limbs for people in this class include rotator cuffs tearing,shoulder impingement
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis (inflammation of tendons) of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of th ...
, epicondylitis Epicondylitis is a type of musculoskeletal disorder that refers to an inflammation of an epicondyle. It is caused by repetitive motion. In athletes, it is linked to poor technique. Nonsurgical treatment is effective in approximately 95% of cases.
T ...
and peripheral nerve entrapment.
Cerebral palsy

 This class includes people with several disability types include
This class includes people with several disability types include cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensa ...
. CP7 and CP8 class swimmers are sometimes found in this class. CP7 sportspeople are able to walk, but appear to do so while having a limp as one side of their body is more effected than the other. They may have involuntary muscles spasms on one side of their body. They have fine motor control on their dominant side of the body, which can present as asymmetry when they are in motion. People in this class tend to have energy expenditure similar to people without cerebral palsy.
Because of the neuromuscular nature of their disability, CP7 and CP8 swimmers have slower start times than other people in their classes. They are also more likely to interlock their hands when underwater in some strokes to prevent hand drift, which increases drag while swimming. For S8 classified swimmers with CP, they are able to record long distances underwater. The longest distances Paralympic S8 swimmers can measure are often half that of comparable Olympic counters. This is attributed to neuromuscular related drag issues. CP swimmers are more efficient at above water swimming than underwater swimming. CP8 swimmers experience swimmers shoulder, a swimming related injury, at rates similar to their able-bodied counterparts. When fatigued, asymmetry in their stroke becomes a problem for swimmers in this class. The integrated classification system used for swimming, where swimmers with CP compete against those with other disabilities, is subject to criticisms has been that the nature of CP is that greater exertion leads to decreased dexterity and fine motor movements. This puts competitors with CP at a disadvantage when competing against people with amputations who do not lose coordination as a result of exertion.
CP7 swimmers tend to have a passive normalized drag in the range of 0.6 to 0.8. This puts them into the passive drag band of PDB6, PDB8, and PDB9. CP8 swimmers tend to have a passive normalized drag in the range of 0.4 to 0.9. This puts them into the passive drag band of PDB6, PDB8, and PDB10.
Spinal cord injuries
People with spinal cord injuries compete in this class, including F6 and F8 sportspeople.F6
 This is wheelchair sport classification that corresponds to the neurological level L2 - L5. Historically, this class has been known as Lower 4, Upper 5. People with lesions at L4 have issues with their lower back muscles, hip flexors and their quadriceps. People with lesions at the L4 to S2 who are complete paraplegics may have motor function issues in their gluts and hamstrings. Their quadriceps are likely to be unaffected. They may be absent sensation below the knees and in the groin area.
People in this class have good sitting balance. People with lesions at L4 have trunk stability, can lift a leg and can flex their hips. They can walk independently with the use of longer leg braces. They may use a wheelchair for the sake of convenience. Recommended sports include many standing related sports. People in this class have a total respiratory capacity of 88% compared to people without a disability.
S8 swimmers with spinal cord injuries tend to be complete paraplegics with lesions below L4 to L5. When swimming, they are able to kick but limited use of their ankles means that their propulsion from kicking can be limited. They normally do diving starts from the platform but are not able to get full power because of limited use of their legs. They do leg turns but have limited propulsion power off the wall.
A study of was done comparing the performance of athletics competitors at the 1984 Summer Paralympics. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m freestyle. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 14 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 50 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 4 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100 m freestyle.
This is wheelchair sport classification that corresponds to the neurological level L2 - L5. Historically, this class has been known as Lower 4, Upper 5. People with lesions at L4 have issues with their lower back muscles, hip flexors and their quadriceps. People with lesions at the L4 to S2 who are complete paraplegics may have motor function issues in their gluts and hamstrings. Their quadriceps are likely to be unaffected. They may be absent sensation below the knees and in the groin area.
People in this class have good sitting balance. People with lesions at L4 have trunk stability, can lift a leg and can flex their hips. They can walk independently with the use of longer leg braces. They may use a wheelchair for the sake of convenience. Recommended sports include many standing related sports. People in this class have a total respiratory capacity of 88% compared to people without a disability.
S8 swimmers with spinal cord injuries tend to be complete paraplegics with lesions below L4 to L5. When swimming, they are able to kick but limited use of their ankles means that their propulsion from kicking can be limited. They normally do diving starts from the platform but are not able to get full power because of limited use of their legs. They do leg turns but have limited propulsion power off the wall.
A study of was done comparing the performance of athletics competitors at the 1984 Summer Paralympics. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m freestyle. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 14 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m backstroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 4 (SP5, SP6), 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100m breaststroke. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 2 (SP4), 3 (SP4, SP5) and 4 (SP5, SP6) in the 25 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between women in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 50 m butterfly. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 4 x 50 m individual medley. It found there was little significant difference in performance times between men in 5 (SP6, SP7) and 6 (SP7) in the 100 m freestyle.
F8

 F8 is standing wheelchair sport class. The level of spinal cord injury for this class involves people who have incomplete lesions at a slightly higher level. This means they can sometimes bear weight on their legs. In 2002, USA Track & Field defined this class as, "These are standing athletes with dynamic standing balance. Able to recover in standing when balance is challenged. Not more than 70 points in legs." In 2003, Disabled Sports USA defined this class as, "In a sitting class but not more than 70 points in the lower limbs. Are unable to recover balance in challenged standing position." In Australia, this class means combined lower plus upper limb functional problems. "Minimal disability." It can also mean in Australia that the athlete is "ambulant with moderately reduced function in one or both lower limbs." They have a normalized drag in the range of 0.6 to 0.7.
F8 is standing wheelchair sport class. The level of spinal cord injury for this class involves people who have incomplete lesions at a slightly higher level. This means they can sometimes bear weight on their legs. In 2002, USA Track & Field defined this class as, "These are standing athletes with dynamic standing balance. Able to recover in standing when balance is challenged. Not more than 70 points in legs." In 2003, Disabled Sports USA defined this class as, "In a sitting class but not more than 70 points in the lower limbs. Are unable to recover balance in challenged standing position." In Australia, this class means combined lower plus upper limb functional problems. "Minimal disability." It can also mean in Australia that the athlete is "ambulant with moderately reduced function in one or both lower limbs." They have a normalized drag in the range of 0.6 to 0.7.
History
The classification was created by theInternational Paralympic Committee
The International Paralympic Committee (IPC; german: Internationales Paralympisches Komitee) is an international non-profit organisation and the global governing body for the Paralympic Movement. The IPC organizes the Paralympic Games and fun ...
and has roots in a 2003 attempt to address "the overall objective to support and co-ordinate the ongoing development of accurate, reliable, consistent and credible sport focused classification systems and their implementation." In 1997, ''Against the odds : New Zealand Paralympians'' said this classification was graded along a gradient, with S1 being the most disabled and S10 being the least disabled.
At the Paralympic Games
For the2016 Summer Paralympics
)
, nations = 159
, athletes = 4,342
, opening = 7 September
, closing = 18 September
, opened_by = President Michel Temer
, cauldron = Clodoaldo Silva
, events = 528 in 22 sports
, stadium = Maracanã
, sum ...
in Rio, the International Paralympic Committee
The International Paralympic Committee (IPC; german: Internationales Paralympisches Komitee) is an international non-profit organisation and the global governing body for the Paralympic Movement. The IPC organizes the Paralympic Games and fun ...
had a zero classification at the Games policy. This policy was put into place in 2014, with the goal of avoiding last minute changes in classes that would negatively impact athlete training preparations. All competitors needed to be internationally classified with their classification status confirmed prior to the Games, with exceptions to this policy being dealt with on a case-by-case basis.
Competitions
For this classification, organisers of the Paralympic Games have the option of including the following events on the Paralympic programme: 50 m and 100 m Freestyle, 400 m Freestyle, 100 m Backstroke, 100 m Butterfly, 100 m Breaststroke, and 200 m Individual Medley events.Paralympic records
The table below records the fastest ever Paralympic record in this class for specific events.Records
In the S8 50 m Freestyle Long Course, the men's world record is held by China'sXiaofu Wang
Wang Xiaofu (born November 1988) is a Chinese retired Paralympic swimmer and multiple gold medalist.
At the age of six, Wang lost his right arm and has impaired muscle strength in his legs following an electrical accident. At the age of 13, he ...
with a time of 00:26.45 and the women's world record is held by China's Shengnan Jiang
Jiang Shengnan (born June 25, 1991) is a Chinese Paralympic swimmer.
Career
At the 2012 Summer Paralympics she won three bronze medals: at the Women's 50 metre freestyle S8 event, at the Women's 100 metre butterfly S8 event and at the Women's ...
with a time of 00:30.85. In the S8 100 m Freestyle Long Course, the men's world record is held by Australia's Peter Leek
Peter Alan Stuart Leek, OAM (born 27 September 1988) is an Australian former swimmer with ataxic cerebral palsy, who won eight medals at the 2008 Beijing Paralympics.
Early life
Leek was born in the Sydney suburb of Blacktown. He began swimmi ...
and the women's world record is held by Australia's Maddison Elliott
Maddison Gae Elliott, (born 3 November 1998) is an Australian swimmer. At the 2012 Summer Paralympics in London, she became the youngest Australian Paralympic medallist by winning bronze medals in the women's 400 m and 100 m freesty ...
.
Getting classified
Swimming classification generally has three components. The first is a bench press. The second is water test. The third is in competition observation. As part of the water test, swimmers are often required to demonstrate their swimming technique for all four strokes. They usually swim a distance of 25 meters for each stroke. They are also generally required to demonstrate how they enter the water and how they turn in the pool. Classification generally has four phases. The first stage of classification is a health examination. For amputees in this class, this is often done on site at a sports training facility or competition. The second stage is observation in practice, the third stage is observation in competition and the last stage is assigning the sportsperson to a relevant class. Sometimes the health examination may not be done on site for amputees in this class because the nature of the amputation could cause not physically visible alterations to the body. In Australia, to be classified in this category, athletes contact theAustralian Paralympic Committee
Paralympics Australia (PA) previously called the Australian Paralympic Committee (APC) (1998–2019) is the National Paralympic Committee in Australia for the Paralympic Games movement. It oversees the preparation and management of Australian tea ...
or their state swimming governing body. In the United States, classification is handled by the United States Paralympic Committee
The United States Olympic & Paralympic Committee (USOPC) is the National Olympic Committee and the National Paralympic Committee for the United States. It was founded in 1895 as the United States Olympic Committee, and is headquartered in C ...
on a national level. The classification test has three components: "a bench test, a water test, observation during competition." American swimmers are assessed by four people: a medical classified, two general classified and a technical classifier.
Competitors
Swimmers who have competed in this classification includeAmanda Everlove
Amanda Everlove (born 1988 or 1989) is an American Paralympic swimmer.
Early life and career
Everlove was born in Valencia, California, but upon finishing her freshman year of St. Mary’s High School in July 2005, she and her family moved to ...
, Sean Fraser, and Heather Frederiksen
Heather Frederiksen MBE (born 30 December 1985) is a retired British Paralympic swimmer. She is former world record holder in the women's S8 100 m backstroke, 50 m freestyle, 100 m freestyle, 200 m freestyle and 400 m fr ...
, who all won medals in their class at the 2008 Paralympics
The 2008 Summer Paralympic Games (), the 13th Summer Paralympic Games, took place in Beijing, China from September 6 to 17, 2008. As with the 2008 Summer Olympics, equestrian events were held in Hong Kong and sailing events in Qingdao. It wa ...
. World champion Robert Griswold
Robert Griswold (born November 27, 1996) is an American swimmer. He was a member of the 2016 and 2020 U.S. Paralympic Swimming Teams. He holds multiple American and world paralympic swimming records in freestyle, backstroke, butterfly, and in ...
is also in this class.
References
{{Wheelchair sport classification Swimming at the Summer Paralympics Parasports classifications